Submitted:
24 June 2023
Posted:
25 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
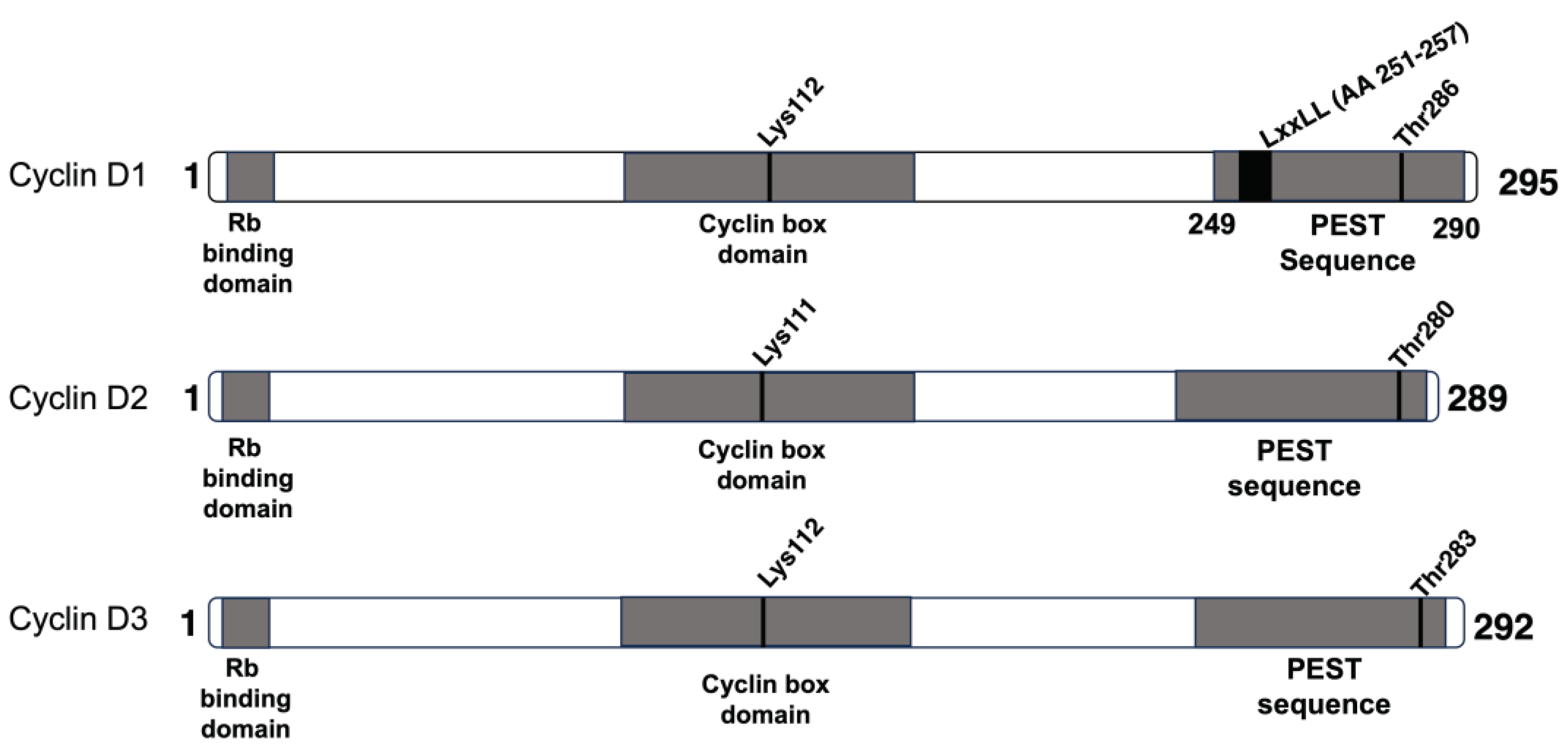
2. Cyclin D1
3. Cyclin D2
4. Cyclin D3
5. Current therapeutic strategies for D-type Cyclin disorders
6. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Malumbres, M.; Barbacid, M. To cycle or not to cycle: a critical decision in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2001, 1, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lolli, G.; Johnson, L.N. CAK-Cyclin-dependent Activating Kinase: a key kinase in cell cycle control and a target for drugs? Cell Cycle 2005, 4, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryadinata, R.; Sadowski, M.; Sarcevic, B. Control of cell cycle progression by phosphorylation of cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) substrates. Biosci Rep 2010, 30, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malumbres, M.; Pellicer, A. RAS pathways to cell cycle control and cell transformation. Front Biosci 1998, 3, d887–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobrinik, D. Pocket proteins and cell cycle control. Oncogene 2005, 24, 2796–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz, J.F.; Ruxmohan, S.; Khurana, M.; Hidalgo, J.; Alzamora, I.M.; Patel, A. Megalencephaly Polymicrogyria Polydactyly Hydrocephalus (MPPH): A Case Report and Review of Literature. Cureus 2021, 13, e16132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirzaa, G.; Parry, D.A.; Fry, A.E.; Giamanco, K.A.; Schwartzentruber, J.; Vanstone, M.; Logan, C.V.; Roberts, N.; Johnson, C.A.; Singh, S.; et al. De novo CCND2 mutations leading to stabilization of cyclin D2 cause megalencephaly-polymicrogyria-polydactyly-hydrocephalus syndrome. Nat Genet 2014, 46, 510–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colas, P. Cyclin-dependent kinases and rare developmental disorders. Orphanet J Rare Dis 2020, 15, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherr, C.J.; Roberts, J.M. CDK inhibitors: positive and negative regulators of G1-phase progression. Genes Dev 1999, 13, 1501–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuura, I.; Denissova, N.G.; Wang, G.; He, D.; Long, J.; Liu, F. Cyclin-dependent kinases regulate the antiproliferative function of Smads. Nature 2004, 430, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Leone, G.W.; Wang, H. Cyclin D-CDK4/6 functions in cancer. Adv Cancer Res 2020, 148, 147–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, L.; Ke, N.; Hydbring, P.; Choi, Y.J.; Widlund, H.R.; Chick, J.M.; Zhai, H.; Vidal, M.; Gygi, S.P.; Braun, P.; et al. A systematic screen for CDK4/6 substrates links FOXM1 phosphorylation to senescence suppression in cancer cells. Cancer Cell 2011, 20, 620–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inaba, T.; Matsushime, H.; Valentine, M.; Roussel, M.F.; Sherr, C.J.; Look, A.T. Genomic organization, chromosomal localization, and independent expression of human cyclin D genes. Genomics 1992, 13, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.; Menninger, J.; Beach, D.; Ward, D.C. Molecular cloning and chromosomal mapping of CCND genes encoding human D-type cyclins. Genomics 1992, 13, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciemerych, M.A.; Kenney, A.M.; Sicinska, E.; Kalaszczynska, I.; Bronson, R.T.; Rowitch, D.H.; Gardner, H.; Sicinski, P. Development of mice expressing a single D-type cyclin. Genes Dev 2002, 16, 3277–3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozar, K.; Ciemerych, M.A.; Rebel, V.I.; Shigematsu, H.; Zagozdzon, A.; Sicinska, E.; Geng, Y.; Yu, Q.; Bhattacharya, S.; Bronson, R.T.; et al. Mouse development and cell proliferation in the absence of D-cyclins. Cell 2004, 118, 477–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherr Charles, J. Cancer Cell Cycles. Science 1996, 274, 1672–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, K.A.; Xiong, Y.; Beach, D.; Gilman, M.Z. Growth-regulated expression of D-type cyclin genes in human diploid fibroblasts. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 1992, 89, 9910–9914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musgrove, E.A. Cyclins: Roles in mitogenic signaling and oncogenic transformation. Growth Factors 2006, 24, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicinski, P.; Donaher, J.L.; Parker, S.B.; Li, T.; Fazeli, A.; Gardner, H.; Haslam, S.Z.; Bronson, R.T.; Elledge, S.J.; Weinberg, R.A. Cyclin D1 provides a link between development and oncogenesis in the retina and breast. Cell 1995, 82, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alt, J.R.; Cleveland, J.L.; Hannink, M.; Diehl, J.A. Phosphorylation-dependent regulation of cyclin D1 nuclear export and cyclin D1-dependent cellular transformation. Genes & development 2000, 14, 3102–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaa, G.; Parry, D.A.; Fry, A.E.; Giamanco, K.A.; Schwartzentruber, J.; Vanstone, M.; Logan, C.V.; Roberts, N.; Johnson, C.A.; Singh, S.; et al. De novo CCND2 mutations leading to stabilization of cyclin D2 cause megalencephaly-polymicrogyria-polydactyly-hydrocephalus syndrome. Nature genetics 2014, 46, 510–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
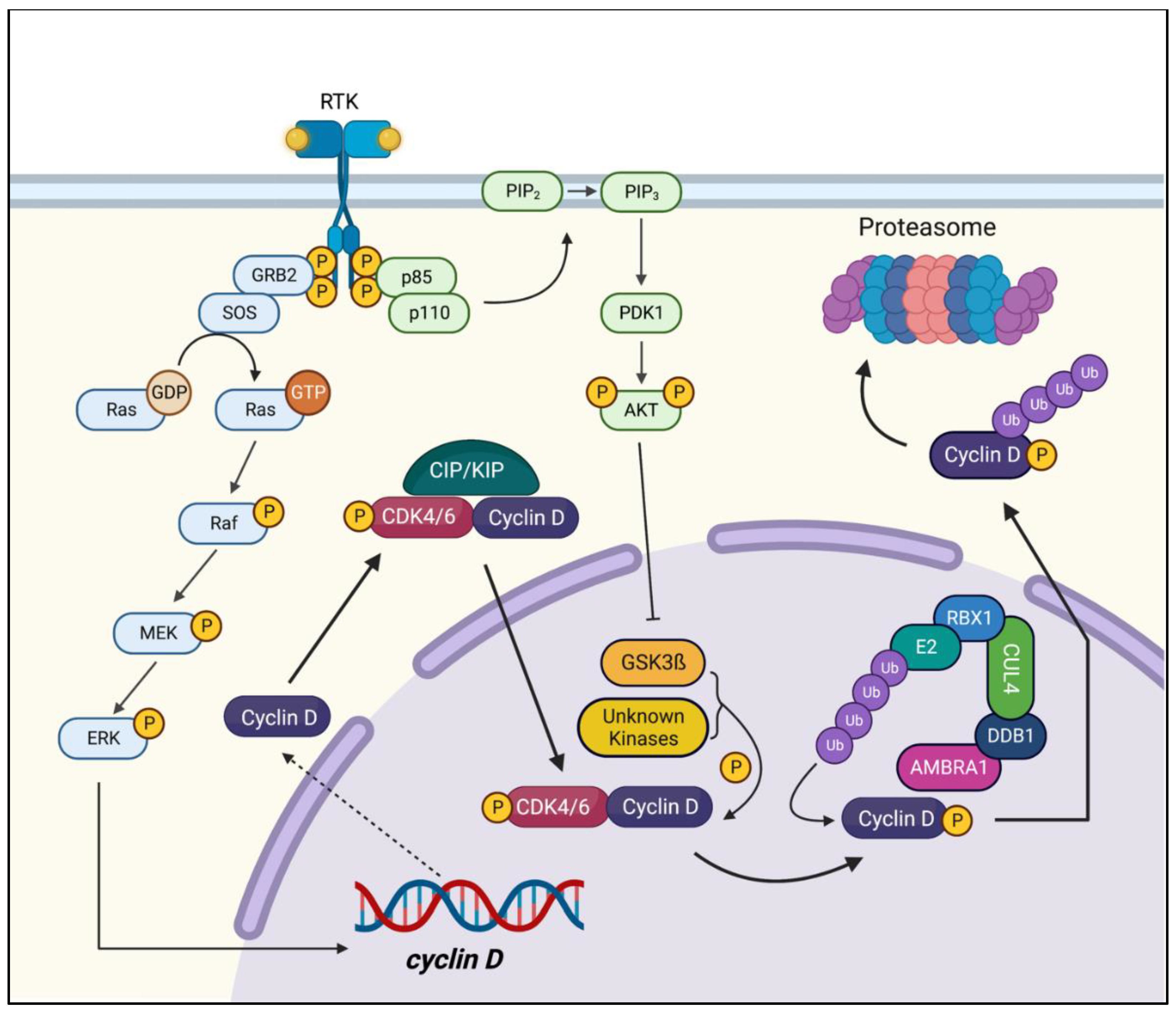
- Maiani, E.; Milletti, G.; Nazio, F.; Holdgaard, S.G.; Bartkova, J.; Rizza, S.; Cianfanelli, V.; Lorente, M.; Simoneschi, D.; Di Marco, M.; et al. AMBRA1 regulates cyclin D to guard S-phase entry and genomic integrity. Nature 2021, 592, 799–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaikovsky, A.C.; Li, C.; Jeng, E.E.; Loebell, S.; Lee, M.C.; Murray, C.W.; Cheng, R.; Demeter, J.; Swaney, D.L.; Chen, S.-H.; et al. The AMBRA1 E3 ligase adaptor regulates the stability of cyclin D. Nature 2021, 592, 794–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoneschi, D.; Rona, G.; Zhou, N.; Jeong, Y.-T.; Jiang, S.; Milletti, G.; Arbini, A.A.; O’Sullivan, A.; Wang, A.A.; Nithikasem, S.; et al. CRL4AMBRA1 is a master regulator of D-type cyclins. Nature 2021, 592, 789–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaikovsky, A.C.; Sage, J.; Pagano, M.; Simoneschi, D. The Long-Lost Ligase: CRL4(AMBRA1) Regulates the Stability of D-Type Cyclins. DNA and cell biology 2021, 40, 1457–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germain, D.; Russell, A.; Thompson, A.; Hendley, J. Ubiquitination of free cyclin D1 is independent of phosphorylation on threonine 286. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2000, 275, 12074–12079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alao, J.P. The regulation of cyclin D1 degradation: roles in cancer development and the potential for therapeutic invention. Molecular Cancer 2007, 6, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Jiao, X.; Wang, C.; Shirley, L.A.; Elsaleh, H.; Dahl, O.; Wang, M.; Soutoglou, E.; Knudsen, E.S.; Pestell, R.G. Alternative cyclin D1 splice forms differentially regulate the DNA damage response. Cancer Res 2010, 70, 8802–8811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudsen, K.E. The cyclin D1b splice variant: an old oncogene learns new tricks. Cell Div 2006, 1, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchakarska, G.; Sola, B. The double dealing of cyclin D1. Cell Cycle 2020, 19, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, F.; Gladden, A.B.; Diehl, J.A. An alternatively spliced cyclin D1 isoform, cyclin D1b, is a nuclear oncogene. Cancer Res 2003, 63, 7056–7061. [Google Scholar]
- Solomon, D.A.; Wang, Y.; Fox, S.R.; Lambeck, T.C.; Giesting, S.; Lan, Z.; Senderowicz, A.M.; Conti, C.J.; Knudsen, E.S. Cyclin D1 splice variants. Differential effects on localization, RB phosphorylation, and cellular transformation. J Biol Chem 2003, 278, 30339–30347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosokawa, Y.; Gadd, M.; Smith, A.P.; Koerner, F.C.; Schmidt, E.V.; Arnold, A. Cyclin D1 (PRAD1) alternative transcript b: full-length cDNA cloning and expression in breast cancers. Cancer Lett 1997, 113, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burd, C.J.; Petre, C.E.; Morey, L.M.; Wang, Y.; Revelo, M.P.; Haiman, C.A.; Lu, S.; Fenoglio-Preiser, C.M.; Li, J.; Knudsen, E.S.; et al. Cyclin D1b variant influences prostate cancer growth through aberrant androgen receptor regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2006, 103, 2190–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosokawa, Y.; Joh, T.; Maeda, Y.; Arnold, A.; Seto, M. Cyclin D1/PRAD1/BCL-1 alternative transcript [B] protein product in B-lymphoid malignancies with t(11;14)(q13;q32) translocation. Int J Cancer 1999, 81, 616–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantl, V.; Stamp, G.; Andrews, A.; Rosewell, I.; Dickson, C. Mice lacking cyclin D1 are small and show defects in eye and mammary gland development. Genes Dev 1995, 9, 2364–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landis, M.W.; Pawlyk, B.S.; Li, T.; Sicinski, P.; Hinds, P.W. Cyclin D1-dependent kinase activity in murine development and mammary tumorigenesis. Cancer cell 2006, 9, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, S.; Amos, C.I.; Luthra, R.; Lynch, P.M.; Levin, B.; Frazier, M.L. Effects of cyclin D1 polymorphism on age of onset of hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer. Cancer Res 2000, 60, 249–252. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, S.; Wei, Q.; Amos, C.I.; Lynch, P.M.; Levin, B.; Zong, J.; Frazier, M.L. Cyclin D1 polymorphism and increased risk of colorectal cancer at young age. J Natl Cancer Inst 2001, 93, 1106–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Marchand, L.; Seifried, A.; Lum-Jones, A.; Donlon, T.; Wilkens, L.R. Association of the cyclin D1 A870G polymorphism with advanced colorectal cancer. JAMA 2003, 290, 2843–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinhold, N.; Johnson, D.C.; Chubb, D.; Chen, B.; Forsti, A.; Hosking, F.J.; Broderick, P.; Ma, Y.P.; Dobbins, S.E.; Hose, D.; et al. The CCND1 c.870G>A polymorphism is a risk factor for t(11;14)(q13;q32) multiple myeloma. Nat Genet 2013, 45, 522–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimura, T.; Ochiai, Y.; Noma, N.; Oikawa, T.; Sano, Y.; Fukumoto, M. Cyclin D1 overexpression perturbs DNA replication and induces replication-associated DNA double-strand breaks in acquired radioresistant cells. Cell Cycle 2013, 12, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casimiro, M.C.; Velasco-Velázquez, M.; Aguirre-Alvarado, C.; Pestell, R.G. Overview of cyclins D1 function in cancer and the CDK inhibitor landscape: past and present. Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs 2014, 23, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalides, R.; van Veelen, N.; Hart, A.; Loftus, B.; Wientjens, E.; Balm, A. Overexpression of cyclin D1 correlates with recurrence in a group of forty-seven operable squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck. Cancer Res 1995, 55, 975–978. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Navarro, A.; Beà, S.; Jares, P.; Campo, E. Molecular Pathogenesis of Mantle Cell Lymphoma. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am 2020, 34, 795–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capurso, G.; Festa, S.; Valente, R.; Piciucchi, M.; Panzuto, F.; Jensen, R.T.; Delle Fave, G. Molecular pathology and genetics of pancreatic endocrine tumours. Journal of molecular endocrinology 2012, 49, R37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sini, M.C.; Doneddu, V.; Paliogiannis, P.; Casula, M.; Colombino, M.; Manca, A.; Botti, G.; Ascierto, P.A.; Lissia, A.; Cossu, A. Genetic alterations in main candidate genes during melanoma progression. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 8531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautschi, O.; Ratschiller, D.; Gugger, M.; Betticher, D.C.; Heighway, J. Cyclin D1 in non-small cell lung cancer: a key driver of malignant transformation. Lung cancer 2007, 55, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, C.; Zhu, X.; Han, Y.; Song, C.; Liu, C.; Lu, S.; Zhang, M.; Yu, F.; Peng, Z.; Zhou, C. Elevated HOXA1 expression correlates with accelerated tumor cell proliferation and poor prognosis in gastric cancer partly via cyclin D1. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research 2016, 35, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Albasri, A.; Yosef, H.; Hussainy, A.S.; Sultan, S.A.; Alhujaily, A. Histopathological features of colorectal cancer in Al-Madinah region of Saudi Arabia: 8 years experience. Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention 2014, 15, 3133–3137. [Google Scholar]
- Yildirim, H.T.; Nergiz, D.; Sadullahoglu, C.; Akgunduz, Z.; Yildirim, S.; Dogan, S.; Sezer, C. The extent of cyclin D1 expression in endometrial pathologies and relevance of cyclin D1 with the clinicopathological features of endometrioid endometrial carcinoma. Indian Journal of Pathology and Microbiology 2020, 63, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartkova, J.; Lukas, J.; Müller, H.; Lützhøt, D.; Strauss, M.; Bartek, J. Cyclin D1 protein expression and function in human breast cancer. International Journal of Cancer 1994, 57, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiestner, A.; Tehrani, M.; Chiorazzi, M.; Wright, G.; Gibellini, F.; Nakayama, K.; Liu, H.; Rosenwald, A.; Muller-Hermelink, H.K.; Ott, G. Point mutations and genomic deletions in CCND1 create stable truncated cyclin D1 mRNAs that are associated with increased proliferation rate and shorter survival. Blood, The Journal of the American Society of Hematology 2007, 109, 4599–4606. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, Y.; Menninger, J.; Beach, D.; Ward, D.C. Molecular cloning and chromosomal mapping of CCND genes encoding human D-type cyclins. Genomics 1992, 13, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Leone, G.W.; Wang, H. Chapter Four - Cyclin D-CDK4/6 functions in cancer. In Advances in Cancer Research, Tew, K.D., Fisher, P.B., Eds.; Academic Press: 2020; Volume 148, pp. 147–169.
- Zwijsen, R.M.; Buckle, R.S.; Hijmans, E.M.; Loomans, C.J.; Bernards, R. Ligand-independent recruitment of steroid receptor coactivators to estrogen receptor by cyclin D1. Genes & development 1998, 12, 3488–3498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petre-Draviam, C.E.; Williams, E.B.; Burd, C.J.; Gladden, A.; Moghadam, H.; Meller, J.; Diehl, J.A.; Knudsen, K.E. A central domain of cyclin D1 mediates nuclear receptor corepressor activity. Oncogene 2005, 24, 431–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, C.; Suthiphongchai, T.; DiRenzo, J.; Ewen, M.E. P/CAF associates with cyclin D1 and potentiates its activation of the estrogen receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1999, 96, 5382–5387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalermrujinanant, C.; Michowski, W.; Sittithumcharee, G.; Esashi, F.; Jirawatnotai, S. Cyclin D1 promotes BRCA2-Rad51 interaction by restricting cyclin A/B-dependent BRCA2 phosphorylation. Oncogene 2016, 35, 2815–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Body, S.; Esteve-Arenys, A.; Miloudi, H.; Recasens-Zorzo, C.; Tchakarska, G.; Moros, A.; Bustany, S.; Vidal-Crespo, A.; Rodriguez, V.; Lavigne, R.; et al. Cytoplasmic cyclin D1 controls the migration and invasiveness of mantle lymphoma cells. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 13946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, C.; Jiao, X.; Lu, Y.; Fu, M.; Quong, A.A.; Dye, C.; Yang, J.; Dai, M.; Ju, X.; et al. Cyclin D1 regulates cellular migration through the inhibition of thrombospondin 1 and ROCK signaling. Mol Cell Biol 2006, 26, 4240–4256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pestell, R.G.; Li, Z. Antisense to cyclin D1 inhibits VEGF-stimulated growth of vascular endothelial cells: implication of tumor vascularization. Clin Cancer Res 2006, 12, 4459–4462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pontano, L.L.; Aggarwal, P.; Barbash, O.; Brown, E.J.; Bassing, C.H.; Diehl, J.A. Genotoxic stress-induced cyclin D1 phosphorylation and proteolysis are required for genomic stability. Molecular and cellular biology 2008, 28, 7245–7258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benzeno, S.; Lu, F.; Guo, M.; Barbash, O.; Zhang, F.; Herman, J.G.; Klein, P.S.; Rustgi, A.; Diehl, J.A. Identification of mutations that disrupt phosphorylation-dependent nuclear export of cyclin D1. Oncogene 2006, 25, 6291–6303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, J.Y.; Matsuoka, M.; Strom, D.K.; Sherr, C.J. Regulation of cyclin D-dependent kinase 4 (cdk4) by cdk4-activating kinase. Mol Cell Biol 1994, 14, 2713–2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, H.; An, X.; Wang, T.; Meng, A. Migratory localization of cyclin D2-Cdk4 complex suggests a spatial regulation of the G1-S transition. Cell Struct Funct 2008, 33, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, M.A.; Jakoi, L.; Nevins, J.R. A unique role for the Rb protein in controlling E2F accumulation during cell growth and differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1996, 93, 3215–3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, J.; Matsushime, H.; Hiebert, S.W.; Ewen, M.E.; Sherr, C.J. Direct binding of cyclin D to the retinoblastoma gene product (pRb) and pRb phosphorylation by the cyclin D-dependent kinase CDK4. Genes Dev 1993, 7, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, A.; Filipkowski, R.K.; Rylski, M.; Wilczynski, G.M.; Konopacki, F.A.; Jaworski, J.; Ciemerych, M.A.; Sicinski, P.; Kaczmarek, L. The critical role of cyclin D2 in adult neurogenesis. J Cell Biol 2004, 167, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platek, R.; Rogujski, P.; Mazuryk, J.; Wisniewska, M.B.; Kaczmarek, L.; Czupryn, A. Impaired Generation of Transit-Amplifying Progenitors in the Adult Subventricular Zone of Cyclin D2 Knockout Mice. Cells 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipkowski, R.K.; Kaczmarek, L. Severely impaired adult brain neurogenesis in cyclin D2 knock-out mice produces very limited phenotypic changes. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2018, 80, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, M.E.; Carter, M.L.; Lee, J.H. MN20, a D2 cyclin, is transiently expressed in selected neural populations during embryogenesis. J Neurosci 1996, 16, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindhurst, M.J.; Parker, V.E.; Payne, F.; Sapp, J.C.; Rudge, S.; Harris, J.; Witkowski, A.M.; Zhang, Q.; Groeneveld, M.P.; Scott, C.E.; et al. Mosaic overgrowth with fibroadipose hyperplasia is caused by somatic activating mutations in PIK3CA. Nat Genet 2012, 44, 928–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Huynh, M.; Silhavy, J.L.; Kim, S.; Dixon-Salazar, T.; Heiberg, A.; Scott, E.; Bafna, V.; Hill, K.J.; Collazo, A.; et al. De novo somatic mutations in components of the PI3K-AKT3-mTOR pathway cause hemimegalencephaly. Nat Genet 2012, 44, 941–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riviere, J.B.; Mirzaa, G.M.; O'Roak, B.J.; Beddaoui, M.; Alcantara, D.; Conway, R.L.; St-Onge, J.; Schwartzentruber, J.A.; Gripp, K.W.; Nikkel, S.M.; et al. De novo germline and postzygotic mutations in AKT3, PIK3R2 and PIK3CA cause a spectrum of related megalencephaly syndromes. Nat Genet 2012, 44, 934–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zega, K.; Jovanovic, V.M.; Vitic, Z.; Niedzielska, M.; Knaapi, L.; Jukic, M.M.; Partanen, J.; Friedel, R.H.; Lang, R.; Brodski, C. Dusp16 Deficiency Causes Congenital Obstructive Hydrocephalus and Brain Overgrowth by Expansion of the Neural Progenitor Pool. Front Mol Neurosci 2017, 10, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirozzi, F.; Lee, B.; Horsley, N.; Burkardt, D.D.; Dobyns, W.B.; Graham, J.M., Jr.; Dentici, M.L.; Cesario, C.; Schallner, J.; Porrmann, J.; et al. Proximal variants in CCND2 associated with microcephaly, short stature, and developmental delay: A case series and review of inverse brain growth phenotypes. Am J Med Genet A 2021, 185, 2719–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glickstein, S.B.; Moore, H.; Slowinska, B.; Racchumi, J.; Suh, M.; Chuhma, N.; Ross, M.E. Selective cortical interneuron and GABA deficits in cyclin D2-null mice. Development 2007, 134, 4083–4093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garthe, A.; Huang, Z.; Kaczmarek, L.; Filipkowski, R.K.; Kempermann, G. Not all water mazes are created equal: cyclin D2 knockout mice with constitutively suppressed adult hippocampal neurogenesis do show specific spatial learning deficits. Genes Brain Behav 2014, 13, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huard, J.M.; Forster, C.C.; Carter, M.L.; Sicinski, P.; Ross, M.E. Cerebellar histogenesis is disturbed in mice lacking cyclin D2. Development 1999, 126, 1927–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Towers, M.; Mahood, R.; Yin, Y.; Tickle, C. Integration of growth and specification in chick wing digit-patterning. Nature 2008, 452, 882–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnaiya, K.; Tickle, C.; Towers, M. Sonic hedgehog-expressing cells in the developing limb measure time by an intrinsic cell cycle clock. Nat Commun 2014, 5, 4230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDermott, J.H.; Hickson, N.; Banerjee, I.; Murray, P.G.; Ram, D.; Metcalfe, K.; Clayton-Smith, J.; Douzgou, S. Hypoglycaemia represents a clinically significant manifestation of PIK3CA- and CCND2-associated segmental overgrowth. Clin Genet 2018, 93, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stutterd, C.; McGillivray, G.; Stark, Z.; Messazos, B.; Cameron, F.; White, S.; Melbourne Genomics Health, A.; Mirzaa, G.; Leventer, R. Polymicrogyria in association with hypoglycemia points to mutation in the mTOR pathway. Eur J Med Genet 2018, 61, 738–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salpeter, S.J.; Klochendler, A.; Weinberg-Corem, N.; Porat, S.; Granot, Z.; Shapiro, A.M.; Magnuson, M.A.; Eden, A.; Grimsby, J.; Glaser, B.; et al. Glucose regulates cyclin D2 expression in quiescent and replicating pancreatic beta-cells through glycolysis and calcium channels. Endocrinology 2011, 152, 2589–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faber, Z.J.; Chen, X.; Gedman, A.L.; Boggs, K.; Cheng, J.; Ma, J.; Radtke, I.; Chao, J.R.; Walsh, M.P.; Song, G.; et al. The genomic landscape of core-binding factor acute myeloid leukemias. Nat Genet 2016, 48, 1551–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisfeld, A.K.; Kohlschmidt, J.; Schwind, S.; Nicolet, D.; Blachly, J.S.; Orwick, S.; Shah, C.; Bainazar, M.; Kroll, K.W.; Walker, C.J.; et al. Mutations in the CCND1 and CCND2 genes are frequent events in adult patients with t(8;21)(q22;q22) acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2017, 31, 1278–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, C.S.; Wang, S.C.; Yen, Y.T.; Lee, T.H.; Wen, W.C.; Lin, R.K. Hypermethylation of CCND2 in Lung and Breast Cancer Is a Potential Biomarker and Drug Target. Int J Mol Sci 2018, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evron, E.; Umbricht, C.B.; Korz, D.; Raman, V.; Loeb, D.M.; Niranjan, B.; Buluwela, L.; Weitzman, S.A.; Marks, J.; Sukumar, S. Loss of cyclin D2 expression in the majority of breast cancers is associated with promoter hypermethylation. Cancer Res 2001, 61, 2782–2787. [Google Scholar]
- Akone, S.H.; Ntie-Kang, F.; Stuhldreier, F.; Ewonkem, M.B.; Noah, A.M.; Mouelle, S.E.M.; Muller, R. Natural Products Impacting DNA Methyltransferases and Histone Deacetylases. Front Pharmacol 2020, 11, 992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Leung, W.K.; Ebert, M.P.; Leong, R.W.; Tse, P.C.; Chan, M.W.; Bai, A.H.; To, K.F.; Malfertheiner, P.; Sung, J.J. Absence of cyclin D2 expression is associated with promoter hypermethylation in gastric cancer. Br J Cancer 2003, 88, 1560–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshimo, Y.; Nakayama, H.; Ito, R.; Kitadai, Y.; Yoshida, K.; Chayama, K.; Yasui, W. Promoter methylation of cyclin D2 gene in gastric carcinoma. Int J Oncol 2003, 23, 1663–1670. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Uhlen, M.; Fagerberg, L.; Hallstrom, B.M.; Lindskog, C.; Oksvold, P.; Mardinoglu, A.; Sivertsson, A.; Kampf, C.; Sjostedt, E.; Asplund, A.; et al. Proteomics. Tissue-based map of the human proteome. Science 2015, 347, 1260419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartkova, J.; Lukas, J.; Strauss, M.; Bartek, J. Cyclin D3: requirement for G1/S transition and high abundance in quiescent tissues suggest a dual role in proliferation and differentiation. Oncogene 1998, 17, 1027–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Wang, G.L.; Salisbury, E.; Timchenko, L.; Timchenko, N.A. GSK3beta-cyclin D3-CUGBP1-eIF2 pathway in aging and in myotonic dystrophy. Cell Cycle 2009, 8, 2356–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athar, F.; Parnaik, V.K. Potential gene regulatory role for cyclin D3 in muscle cells. J Biosci 2015, 40, 497–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peled, J.U.; Yu, J.J.; Venkatesh, J.; Bi, E.; Ding, B.B.; Krupski-Downs, M.; Shaknovich, R.; Sicinski, P.; Diamond, B.; Scharff, M.D.; et al. Requirement for cyclin D3 in germinal center formation and function. Cell Res 2010, 20, 631–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicinska, E.; Aifantis, I.; Le Cam, L.; Swat, W.; Borowski, C.; Yu, Q.; Ferrando, A.A.; Levin, S.D.; Geng, Y.; von Boehmer, H.; et al. Requirement for cyclin D3 in lymphocyte development and T cell leukemias. Cancer Cell 2003, 4, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sicinska, E.; Lee, Y.M.; Gits, J.; Shigematsu, H.; Yu, Q.; Rebel, V.I.; Geng, Y.; Marshall, C.J.; Akashi, K.; Dorfman, D.M.; et al. Essential role for cyclin D3 in granulocyte colony-stimulating factor-driven expansion of neutrophil granulocytes. Mol Cell Biol 2006, 26, 8052–8060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, A.B.; Sawai, C.M.; Sicinska, E.; Powers, S.E.; Sicinski, P.; Clark, M.R.; Aifantis, I. A unique function for cyclin D3 in early B cell development. Nat Immunol 2006, 7, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketzer, F.; Abdelrasoul, H.; Vogel, M.; Marienfeld, R.; Muschen, M.; Jumaa, H.; Wirth, T.; Ushmorov, A. CCND3 is indispensable for the maintenance of B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Oncogenesis 2022, 11, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cato, M.H.; Chintalapati, S.K.; Yau, I.W.; Omori, S.A.; Rickert, R.C. Cyclin D3 is selectively required for proliferative expansion of germinal center B cells. Mol Cell Biol 2011, 31, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Luca, G.; Ferretti, R.; Bruschi, M.; Mezzaroma, E.; Caruso, M. Cyclin D3 critically regulates the balance between self-renewal and differentiation in skeletal muscle stem cells. Stem Cells 2013, 31, 2478–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Beato, M.; Sanchez-Aguilera, A.; Piris, M.A. Cell cycle deregulation in B-cell lymphomas. Blood 2003, 101, 1220–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Beato, M.; Camacho, F.I.; Martinez-Montero, J.C.; Saez, A.I.; Villuendas, R.; Sanchez-Verde, L.; Garcia, J.F.; Piris, M.A. Anomalous high p27/KIP1 expression in a subset of aggressive B-cell lymphomas is associated with cyclin D3 overexpression. p27/KIP1-cyclin D3 colocalization in tumor cells. Blood 1999, 94, 765–772. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, X.; Maglione, P.J.; Wehr, C.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Abolhassani, H.; Deripapa, E.; Liu, D.; Borte, S.; Du, L.; et al. Genomic characterization of lymphomas in patients with inborn errors of immunity. Blood Adv 2022, 6, 5403–5414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipits, M.; Jaeger, U.; Pohl, G.; Stranzl, T.; Simonitsch, I.; Kaider, A.; Skrabs, C.; Pirker, R. Cyclin D3 is a predictive and prognostic factor in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res 2002, 8, 729–733. [Google Scholar]
- Carrillo-Tornel, S.; Chen-Liang, T.H.; Zurdo, M.; Puiggros, A.; Gomez-Llonin, A.; Garcia-Malo, M.D.; Cuenca-Zamora, E.J.; Ortuno, F.J.; Lopez, A.M.H.; Espinet, B.; et al. NOTCH1 mutation in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia is associated with an enhanced cell cycle G1/S transition and specific cyclin overexpression: Preclinical ground for targeted inhibition. Br J Haematol 2023, 201, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, I.; Minter, L.M.; Telfer, J.; Demarest, R.M.; Capobianco, A.J.; Aster, J.C.; Sicinski, P.; Fauq, A.; Golde, T.E.; Osborne, B.A. Notch signaling mediates G1/S cell-cycle progression in T cells via cyclin D3 and its dependent kinases. Blood 2009, 113, 1689–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Bian, Y.; Li, H.; Yin, J.; Tian, L.; Jiang, R.; Zeng, Z.; Shi, X.; Lei, Z.; Hou, C.; et al. A Comprehensive Understanding of the Genomic Bone Tumor Landscape: A Multicenter Prospective Study. Front Oncol 2022, 12, 835004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Annala, M.; Ji, P.; Wang, G.; Zheng, H.; Codgell, D.; Du, X.; Fang, Z.; Sun, B.; Nykter, M.; et al. Recurrent LRP1-SNRNP25 and KCNMB4-CCND3 fusion genes promote tumor cell motility in human osteosarcoma. J Hematol Oncol 2014, 7, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gounder, M.M.; Agaram, N.P.; Trabucco, S.E.; Robinson, V.; Ferraro, R.A.; Millis, S.Z.; Krishnan, A.; Lee, J.; Attia, S.; Abida, W.; et al. Clinical genomic profiling in the management of patients with soft tissue and bone sarcoma. Nat Commun 2022, 13, 3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, B.; Wang, E.S.; Donovan, K.A.; Liang, Y.; Fischer, E.S.; Zhang, T.; Gray, N.S. Development of Dual and Selective Degraders of Cyclin-Dependent Kinases 4 and 6. Angewandte Chemie (International ed. in English) 2019, 58, 6321–6326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pack, L.R.; Daigh, L.H.; Chung, M.; Meyer, T. Clinical CDK4/6 inhibitors induce selective and immediate dissociation of p21 from cyclin D-CDK4 to inhibit CDK2. Nature Communications 2021, 12, 3356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musgrove, E.A.; Caldon, C.E.; Barraclough, J.; Stone, A.; Sutherland, R.L. Cyclin D as a therapeutic target in cancer. Nature Reviews Cancer 2011, 11, 558–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




