1. Introduction
Infections caused by
Staphylococcus aureus have emerged as one of the most significant global health problems. Various refractory infections are caused by
S. aureus, primarily due to its ability to develop resistance to many drugs and form biofilm. Methicillin-resistant
S. aureus (MRSA) is among the most dreadful clinical diseases. Every year, 20–50 new cases are diagnosed for every 100,000 people, resulting in a mortality rate of 40% [
1]. Antibiotic-resistant bacteria, as well as their ability to build biofilms, pose a serious challenge to current medicine [
2]. When the right antibiotic is identified in an effective time frame, thousands of lives could be saved, and drug-resistant bacteria would be slowed down [
3]. Hence, the search for antibiotic treatment for drug-resistant bacteria and the exploration of MRSA biofilm is crucial.
Biofilms are forms of microorganisms attached to extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) that provide a home to bacterial cells [
4]. Multi resistant strains develop into biofilms due to harsh environments, such as a lack of oxygen and insufficient nutrients. In this extreme condition, EPS gives stability and a niche to microorganisms. It is mainly composed of polysaccharides, proteins, lipids, and extracellular DNA [
5]. Biofilm formation involves complex developmental stages and usually follows three major phases: attachment, biofilm proliferation or maturation, and biofilm detachment or dispersal [
6,
7]. Biofilms emerge when planktonic cells permanently adhere to a surface and embed in an EPS. The sessile microbe proliferates and employs uses quorum sensing to grow into a stronger biofilm as the adhering bacterial cells are protected by EPS [
5]. Due to intense multicellular conglomerates, biofilms require up to 1000 times higher doses of antibiotics than planktonic bacteria [
8].
As biofilm infections are difficult to treat, rapid and easy diagnostic techniques are required to identify biofilm-forming multi resistant
S. aureus [
9]. Traditionally, biofilms are identified by applying crystal violet dye, and their optical density (OD) is measured to calculate the mass [
5,
6]. The structure of biofilms can be studied using various techniques, such as scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, atomic force microscopy, and confocal laser scanning microscopy [
8]. Nevertheless, every method requires an
in vitro cultivation of biofilms, which is time-consuming, costly, and labor-intensive [
10]. Moreover, there is limited information on interactions between strains and compounds in biofilms. Therefore, these methods cannot be applied in clinical diagnostics. Unlike other spectroscopies, Raman spectroscopy is label-free, quick, and contact-free. In this way, biomarker spectra can be obtained without invasive procedures. Bacteria can be identified using spectral information and statistical methods [
11].
Raman spectroscopy was used in several bacterial studies, as microscopic biochemical differences can be accurately characterized, discriminated, and identified at species and subspecies levels for bacteria, fungi, and yeasts [
3]. As all biologically associated molecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and lipids, exhibit unique spectral features, Raman spectroscopy is a powerful technique for identifying different organisms [
12,
13]. The Raman spectrum contains several peaks corresponding to bacteria, including DNA, amino acids, carbohydrates, and lipids [
14]. A chemometric approach was used to identify the correlation between Raman peaks and MRSA biofilm growth. To obtain a simple biological interpretation of the results, principal component analysis (PCA) is a powerful multivariate analysis tool for exploring and interpreting high dimensional data in many fields [
15,
16,
17,
18]. The algorithm was used to determine if minor differences among MRSA biofilm cell structures can be differentiated based on their individual spectra. An analysis of loading plots can efficiently understand the relative contributions of biofilm formation [
14,
19]. The optimal multi resistant biofilm formation time was determined based on the Raman spectrum.
Recently, as the advantages of Raman spectroscopy in microorganisms have been highlighted, the research on direct measurement of bacteria inoculated on a solid medium is increasing. Traditionally, liquid medium bacteria samples have weak Raman signals, which require costly and complex techniques such as SERS, and poor reproducibility. Alternatively, bacterial studies on solid media can be more traceable and durable, with less sample contamination and a stronger Raman spectrum. In 2022, Shen
et al. presented a new fiber probe-based Raman technique on an agar plate to obtain more reliable and stable data for microorganism identification [
20]. However, these studies focused only on planktonic bacteria and not biofilms. Here, the first direct observation of biofilm on a solid medium was performed.
Raman spectral data collected from MRSA biofilms were used to test the antibacterial efficacy of natural products. Since MRSA biofilms are resistant to antibiotics, searching for treatment from medicinal plants is important. Eugenol, an antimicrobial compound with natural properties, could help reduce antibiotic use. Various food products and cosmetics have used eugenol (4-allyl-2-methoxyphenol). In another research, eugenol is proven to be antimicrobial, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anticarminative, and antispasmodic [
21,
22,
23,
24,
25]. Herein, eugenol exhibits antimicrobial activity against MRSA biofilms. The effect of eugenol on MRSA biofilms at different timelines was analyzed by Raman spectroscopy. The efficacy of eugenol was tested on different biofilm phases, and the most potent time to apply antibiotics to the biofilms was similar to that based on colony forming units (CFUs) on antibiofilm tests.
In this study, the growth of multi resistant biofilm was monitored by in situ Raman. This study aimed to build a tool to directly monitor biofilms for hours, which allows the subsequent identification of the optimal time to eradicate growing biofilms with antimicrobial agents from natural product. We have developed a new technique for nondestructive monitoring of the growth of multi resistant biofilms and to detect the optimum condition for effective antimicrobial activity. Therefore, the tool offers a simple, rapid, and inexpensive analysis of life threatening clinical infections.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
MRSA USA 300 was obtained from Professor Chung (Chung don won) Dong duk women’s university in this study. All aqueous solutions were prepared using ultrapure water. Phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and dimethyl sulfoxide were purchased from Thermo Fisher Scientific. Tryptic soy broth (TSB; Difco, Becton Dickinson, and Company, USA), tryptic soy agar (TSA; Difco, Becton Dickinson, and Company, USA), and brain heart infusion agar (BHIA; Difco, Becton Dickinson, and Company, USA) were used to culture bacteria. Congo red dye (Daejung chemicals, Siheung-si, Korea) and saccharose (Sigma Aldrich; Seoul, Korea) were used for Congo red assay (CRA). Then, 3M Petrifilm staph express count plate (3M, MN, USA), plastic spreader, and phosphate-buffered dilution water were all purchased from 3M to calculate CFUs per mL. The reagents and media were sterilized in an autoclave at 121°C for 15 minutes before use. Vancomycin hydrochloride was purchased through Sigma Aldrich (Seoul, Korea). The antibiotic powders were dissolved in double distilled water to produce antibiotic stock solutions (10 mg/mL). Eugenol was purchased through Tokyo Chemical Industry (Tokyo, Japan).
2.2. Preparation of Agar Plates
It is necessary to differentiate staphylococci based on their biofilm phenotypes to clarify their impact on infection diagnosis [
26]. The phenotypic characterization of MRSA was done on a Congo red agar with 0.8 g of Congo red dye and 36 g of saccharose on 1.0 L of BHI agar [
27]. First, an MRSA strain was grown in TSB at 36°C for 24 h for activation. Then, 200 μL of sub-cultured microorganisms (OD600 = 1) was streaked on CRA and incubated at 37°C for 24 h. The red color of the former colonies indicated negative results, while a black color indicated positive results [
27].
In addition, a new agar plate was developed to serve as a substrate for growing biofilms to be analyzed by Raman spectroscopy. A modified brain heart infusion sucrose (MBHI-sucrose) agar was established for Raman spectroscopy sample preparation. Initially, biofilm on CRA plates was measured directly, but the fluorescence peaks from the staining obscured the peak, making accurate measurements impossible. Hence, various agar plates were compared to develop a Raman-optimized biofilm medium. To induce biofilm on an agar plate, Freeman
et al. utilized 5% sucrose addition in BHI broth [
27]. As a result, the MBHI-sucrose agar plate included BHI broth, as well as 5% sucrose without Congo red dye. Next, 200 μL of MRSA was inoculated over MBHI-sucrose agar and incubated at 37°C. Raman spectroscopy was used to detect biofilm growth on MBHI-sucrose agar from 0 to 48 h.
2.3. Preparation of Microorganism Sample
MRSA strains were individually grown in TSB at 37°C for 24 h for activation. Then, 200 μL of sub-cultured microorganisms (OD 600 = 1) was inoculated on MBHI-sucrose agar. In order to monitor biofilm formation by Raman spectroscopy, the microorganisms were incubated on agar surfaces 0–48 h after inoculation. The incubation time refers to the duration the microorganisms were incubated on agar plates prior to Raman measurements. Bacterial isolates were cultivated overnight on agar plates using the medium and incubation conditions described above, and were adjusted to an OD of 0.15 prior to incubation. After 6 h, samples were cultured and adjusted to OD 0.1, 0.3, and 1.0 to see whether the bacterial density (CFU/mL) altered the Raman spectra. At each OD, a five-fold serial dilution in PBS was conducted, and colonies were enumerated at a dilution that yielded between 10 and 30 colonies per 10 μL. To see whether the time of growth had an effect on the Raman spectra, samples were cultured hourly and adjusted to an OD of 0.3 to ensure a consistent bacterial density across samples. Following incubation, 1 mL was centrifuged at 9000 rcf for 3 min, the bacterial pellet washed three times with PBS, and the supernatant was discarded. Dried drops were sonicated for 5 min. Each isolation was reproduced three times.
2.4. Antibiofilm Assay
To measure the efficacy of antibiotics against MRSA, minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) were determined. MIC is the lowest concentration of antibiotics that inhibits the visible growth of microbes overnight [
28]. The MICs of vancomycin and eugenol for MRSA were detected using the microdilution method. The minimum biofilm inhibition concentration (MBIC) is the lowest concentration of antibacterial agents that yields no colonies compared to the initial inoculum [
29].
Eugenol was evaluated in an antibiofilm assay. MRSA biofilms pre-formed over 24 h were treated in a conical tube with 416 µg/mL (MIC) and 1024 µg/mL (2×MIC) of eugenol. Biofilms prepared without eugenol were used as controls. To determine the CFU/mL of the biofilms, the biofilms were washed and counted [
29]. All determinations were done in triplicates.
The effect of eugenol on biofilms was tested after 5 h and 36 h by rinsing the biofilms in PBS to remove planktonic bacteria and exposing them to varying eugenol concentrations at 37°C. Then, the biofilms were again washed with PBS, sonicated, and dissolved in 200 μL of PBS. These diluted samples were plated and grown on MBHI-sucrose agar and viable CFUs per mL were determined. The Petrifilm was used to check the biomass of the biofilms at different hours. Tests were conducted in triplicates, and the result was expressed as activity in terms of μg of extract per mL. In parallel to Raman experiments, antibiotics on cell viability were tested in liquid broths with the same inoculum and reagents. The experiments were triplicated on different dates.
2.5. Quantification of Biofilm Cell Counts on Petrifilm
Petrifilm count plates were used to evaluate the antibacterial effect of different concentrations of eugenol and vancomycin against MRSA. Antibiotic samples were ultrasonicated for 15 min before use. Each sample had an initial concentration of 1.0 OD 600 nm prepared in a TSB medium. The MIC and MBIC of eugenol and vancomycin were added to the medium and incubated at 37°C for 4 h at 180 rpm [
30]. After incubation, Petrifilms were used to enumerate the efficacy of antibiotics [
31]. The samples were diluted 10 times, and 1 mL was inoculated on a 3M Petrifilm count plate and modified TSA and incubated at 37°C for 24 h.
According to 3M Petrifilm interpretation guidelines, bacterial colonies were counted after incubation. Red-violet colonies were counted as the total bacteria [
31]. The inoculated sample on agar plates was analyzed by Raman spectroscopy to evaluate the antibacterial effect of antibiotics.
2.6. Raman Instrumentation
The experiments were conducted using Raman spectroscopy (RAMANtouch, Nanophoton Co., Osaka, Japan) with a single-mode diode laser at 785 nm. An objective microscope lens (Nikon, Japan, 50x, numerical aperture 0.5, working distance 500 μm) was used for focusing the laser beam. The laser spot dimension was approximately 0.6 μm × 1.0 μm. Raman-dispersed light was collected through the same objective lens, passed through a 50-μm pinhole slit, and scattered via holographic grating (300 lines/mm) onto a thermoelectrically cooled (−70°C), deep-depleted, charge-coupled device (1340 × 400 pixels, Teledyne Princeton Instrument, Trenton, USA). Before and after experimental measurements, an internal silicon standard at 520 cm−1 was used to confirm system alignment and light throughput to the sample. A laser power of 30 mW and exposure time of 30 s were used for all Raman experiments.
2.7. Analyses and Characterizations
Analysis of variance was done to determine the antimicrobial efficacies of different concentrations of vancomycin and eugenol in the solutions. All data are presented as means of three replications. Procedures described by Association of Official Agricultural Chemists were used to calculate CFU/mL, which was converted to logarithms for statistical analysis [
31].
The acquired Raman spectra were baseline-corrected using multiple scatter correction before performing the multivariate analysis of PCA using commercial unscrambler software (Aspentech, Bedford, USA). The PCA scores of the first and second principal components were used to plot 3D charts, based on which the degree of similarity and difference of Raman spectra of biofilm grown at different times was analyzed.
PCA algorithms were used to develop models that allow the discrimination and classification of planktonic bacterial cells into biofilm clusters using the spectral characteristics of MRSA biofilms. SIMCA-P 17.0 (Umetrics, Umeå, Sweden) software was used to conduct PCA and PLS-DA data analysis. Graphs were created using Origin 8.0 (OriginLab Corp., Northampton, MA, USA). Origin 8.0 (OriginLab Corp., Northampton, MA, USA) was used to plot graphs.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Detection of the Biofilm Formation Phenotype by the CRA
The CRA developed by Freeman
et al. is the standard method to observing biofilm formation. The biofilm phenotype is tested on a Congo red agar, which identifies biofilm bacteria as black colonies and nonbiofilm bacteria as pink or red colonies [
32]. MRSA was grown on Congo red agar plate to confirm the biofilm formation. In supplementary
Figure S1, MRSA produced black colonies after 24 h of incubation. To observe the physical development of biofilms, the sample was carried out on Congo red agar. MRSA inoculated for 1 h showed red pigmentation, but it developed biofilm on CRA agar after 24 h of incubation, and black pigmentation was observed.
3.2. Determination of MICs and MBICs to Test the Effectiveness of Antimicrobials against MRSA
For MRSA strain, MIC is the lowest antibiotic dose that inhibits bacteria from growing following overnight incubation [
33]. The MBIC is also known as the minimum biofilm inhibitory concentration [
34]. Microdilution was used to detect the MICs and MBICs of vancomycin and eugenol. In this study, the control was untreated biofilms to represent the growth of bacterial cells. The MIC and twice the MIC of vancomycin were used as negative controls. It is the most known lethal antibiotic treatment for MRSA. Natural compounds, such as eugenol, were chosen as potential conventional antibiotics capable of inhibiting the growth of planktonic and biofilm MRSA. The MIC and MBIC values of eugenol were determined to test the efficiency of the best antibiotics for the bacterium. As a result, the MIC of vancomycin for MRSA was 2 µg/mL. Eugenol exhibited MIC values of of 416–1024 µg/mL against MRSA, and its MBIC values were twice that of MIC [
28,
34].
3.3. Raman Spectral Signatures of MRSA Biofilms
Biofilm matrix components and their proportions are crucial to minimize and control biofilm formation. The matrix of biofilms typically consists of EPS, DNA, lipid, and extracellular vesicles [
7,
8].
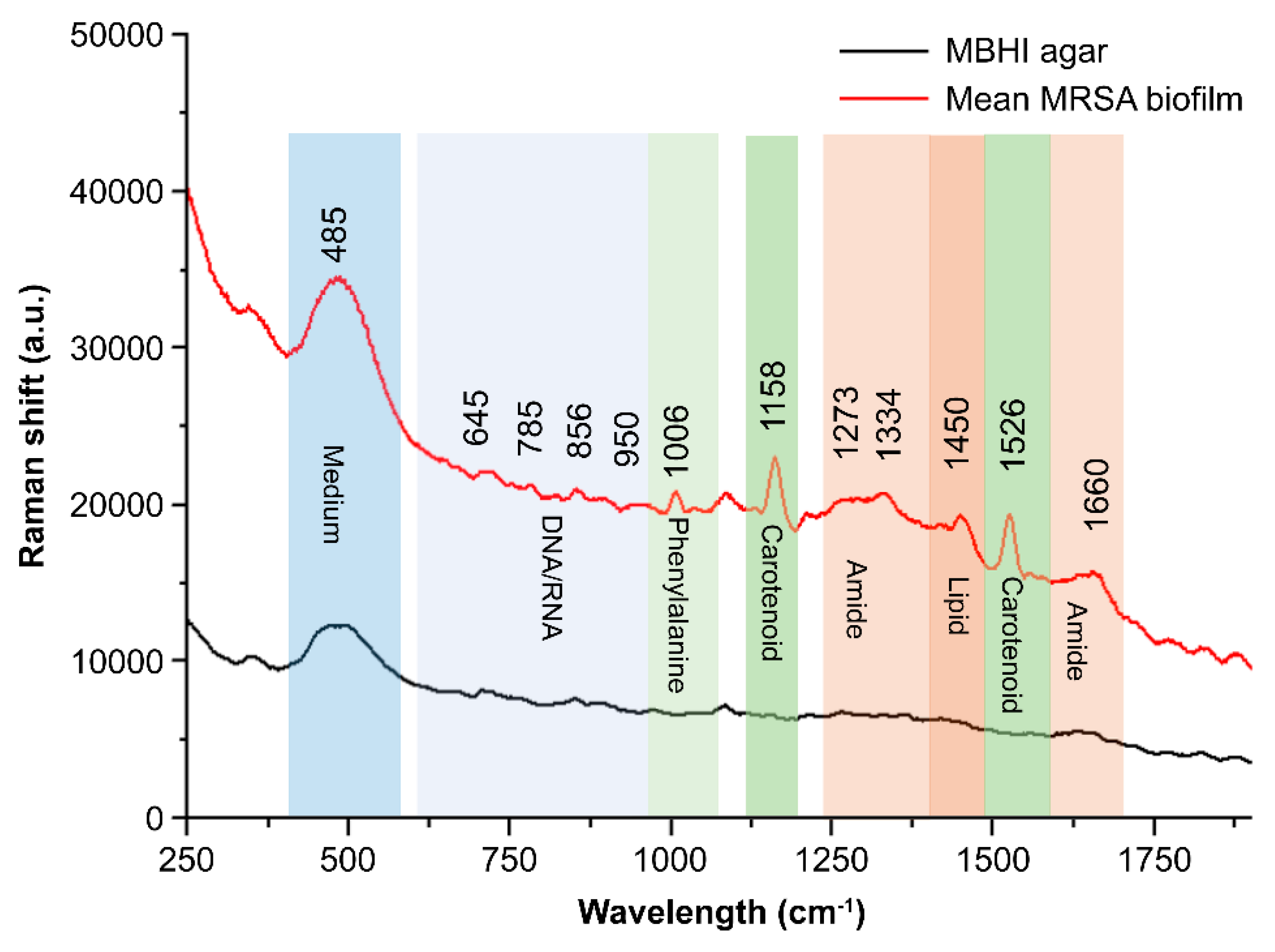
Figure 1 shows the prominent features observed in the Raman spectra of MRSA biofilms that were phenotypically confirmed. Bacterial samples were observed directly on MBHI-sucrose agar by Raman spectra. The Raman spectra of growth media were analyzed to identify a possible interference from the background. The Raman peak at 485 cm
−1 in
Figure 1 corresponded to monosaccharides, one of the ingredients in MBHI-sucrose agar, and did not overlap with the MRSA biofilm spectra [
35].
Spectrum studies on specific chemical structures were selected from previously published studies (
Table 1) [
35,
36,
37,
38,
39,
40,
41,
42,
43,
44].
Figure 1 illustrates a Raman spectrum of an average MRSA biofilm sample. The biofilm sample was at the beginning of the attachment on the agar plate, and Raman measurement was processed at 40 mW laser power and 50-s exposure time. This was repeated 10 times.
The characteristics of biofilm samples were less sharp spectral peaks than those of single-cell bacteria. Among the key peaks in biofilm samples were DNA/RNA-related peaks at 645 cm−1 assigned to the COO− deformation of guanine, 785 cm−1 assigned to A, T (ring in DNA/RNA bases).
Phenylalanine peak represents the existence of biofilms [
39]. Peaks that are related to proteins appear as biofilms mature. The band at 1006 cm
−1 represents the ring breathing of phenylalanine in a protein. The band at 856 cm
−1 is attributed to the carbohydrate of C–C stretching [
38]. The peaks at around 1273 and 1660 cm
−1 are mainly attributed to amide I, amide III vibrations, and carboxylic acid stretching [
36,
41,
42,
43]. Most peaks were found in bacterial Raman spectra of tryptophan at 1334 cm
−1, which was used for protein biosynthesis. Moreover, the CH
3CH
2 twisting mode of lipids can be found at 1450 cm
−1 [
36,
44].
MRSA strains can produce a golden carotenoid pigment called staphyloxanthin, which can serve as a potential antivirulence target [
45]. The prominent two peaks at 1158 and 1526 cm
−1 correlate to carotenoid bands, which represent C−C stretching and C=C stretching, respectively [
39,
44].
3.4. MRSA Biofilm Growth Monitored for 48 h by Raman Spectroscopy and Microscope
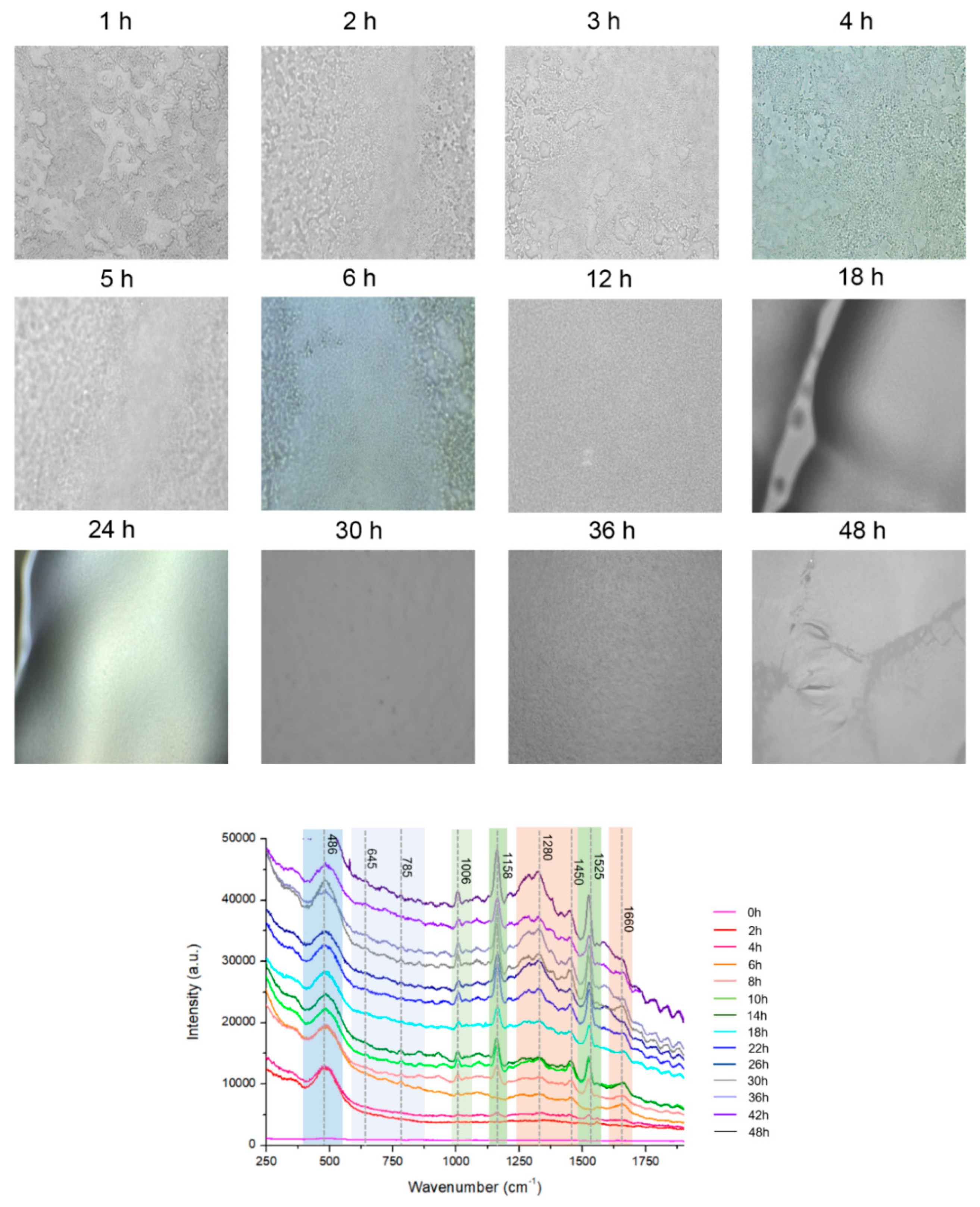
A microscope was used to examine the biofilm cells. At a high magnification, single cells and a clump of cells adhered to the surface were detected (
Figure 2A). The cells in the conglomerate generated yellowish slime, indicating the presence of EPS. CRA was to validate the establishment of the biofilm (
Figure S1). Microscopy images demonstrate that bacteria were primarily planktonic in the early stages of biofilm formation. The transformation of a three-dimensional biofilm occurs via reformation when the bacterial cells connect to the surface. Raman spectroscopy was applied to chemically characterize different multispecies biofilms using specific bands identified in reference materials.
Figure 2A shows representative microscopic images at different hours and the corresponding spectra of biofilms in
Figure 2B. Based on the signature peaks of MRSA biofilms, the growth was monitored with Raman spectroscopy from 0 to 48 h. The dataset consists of 174 spectra of MRSA biofilms over a range of 250 cm
−1–1900 cm
−1. Along with biofilm growth, microorganisms formed in different sizes and thicknesses. The Raman spectral data consist of different intensities and baselines due to chemical changes in biofilms over time. To correct this background spectral intensity at different hours, pre-processing was used to stabilize the baseline. The raw spectrum of biofilm growth was pre-processed using multiplicative scatter correction. Results showed that pre-processing can help in revealing the differences in the spectrum at different times.
The Raman spectrum of MRSA biofilms was acquired every 2 h for 48 h. In
Figure 2B, each spectrum was an average of 10 random points at indicated hours. At 0 h, there was no significant peak observed from MRSA biofilms. The spectra obtained at 2 h and 4 h were similar to each other, and the peak at 485 cm
−1 from monosaccharides in the culture medium was mainly observed in the spectrum. Starting from 4 h, very low-intensity carotenoid pigment peaks from MRSA strains started to appear at 1158 cm
−1 and 1526 cm
−1.
When the incubation time increased to 5 h, a different trend of the spectrum was observed. As the incubation time increased, the carotenoid and phenylalanine peaks increased. Especially at 6 h, peaks around 700–800 cm
−1 appeared in the spectrum, which represents the DNA/RNA fragments from MRSA strains. DNA/RNA-related peaks increased throughout the initial incubation period. Since the bands at 645 cm
−1 and 1525 cm
−1 were observed in the guanine spectrum, their intensity may reflect the changes in DNA or RNA concentrations of the biofilms [
37].
From 5 h of incubation, the band at 1006 cm
−1 from phenylalanine increased [
46,
47]. It was reported the phenylalanine bands could be used as the signature peak for biofilm formation [
48]. Therefore, the increase in the 1006 cm
−1 band suggests the formation of MRSA biofilm structure. Based on these changes, it can be speculated that an early biofilm maturation begins after 5 h, and planktonic bacterial cells existed until 5 h of inoculation, which is a more disruptive state of bacterial colonies.
Microcolony was observed around 20 h, as indicated by the expression of carbohydrates and proteins. Biofilm matrix formation depends on fibrillary proteins present in the biofilm maturation process [
48]. Microcolony formation, which was the attached bacteria beginning to replicate and encapsulate in EPS, was observed up until 24 h (
Figure 2B). Carbohydrate bands (856 and 1158 cm
−1) were found to be positively correlated with the
in vitro formation of biofilms. It is also interesting to note that 24 h biofilms exhibit a relative reduction in nucleic acid band intensities compared with 5 h biofilms [
46]. As illustrated in
Figure 2B, the spectra from different structures of EPS matrix are characterized by strong polysaccharides [
46,
49,
50] and lipopolysaccharides [
50,
51]. The initial formation of MRSA biofilms was in agreement with CRA and microbiological analysis.
After 26–48 h of incubation, the overall intensity of the spectrum increased. Protein- and lipid-related bands at 1280, 1450, and 1660 cm
−1 also increased significantly. However, the relative intensity of DNA/RNA fragment peaks decreased. The changes in the spectrum indicate that the metabolic activity of biofilms stopped, and the departure of bacteria started. Protein synthesis and lipid synthesis increase over time in response to environmental stress induced by nutrient depletion [
52]. Bacteria respond to stress by increasing their protein and lipid synthesis. During the late stationary phase, bacterial cell metabolism ceases, and thus, no DNA, protein, or lipid synthesis occurs [
53,
54].
MRSA biofilm time points were cross-checked through viable counts (CFU/mL) and CRA. Therefore, the monitoring of bacteria through the Raman spectrum, which is correlated to biomarkers in biofilms, can non-destructively analyze the entire biofilm life cycle. As the biofilm life cycle progresses, the intensity of bands changes, reflecting the changes in their concentration profiles. Biofilms are structures that surround bacterial cells and serve as a shell for living systems, limiting their interaction with the environment. This process continues until the completion of biofilms, and the process was in situ analyzed with Raman spectroscopy.
MRSA biofilm formation was confirmed using the Congo red agar assay and microbiological analysis. As shown in
Figure 2B, MRSA biofilm formation started after approximately 5 h, which represented the beginning of the maturation of the biofilms. Although it was not possible to observe any changes in the growth curve after approximately 12 h using OD and viable counts, Raman spectroscopy is sufficiently sensitive to detect changes in bacteria from 0 h to 48 h. Unlike traditional measurements that only involve the concentration of cells in a sample, Raman spectroscopy can provide a “fingerprint” of the DNA, RNA, protein, and lipid content of the cells, which can be used to monitor the physiological changes in the samples [
54].
3.5. PCA Plot to Classify Biofilm Growth Depending on Spectral Differences
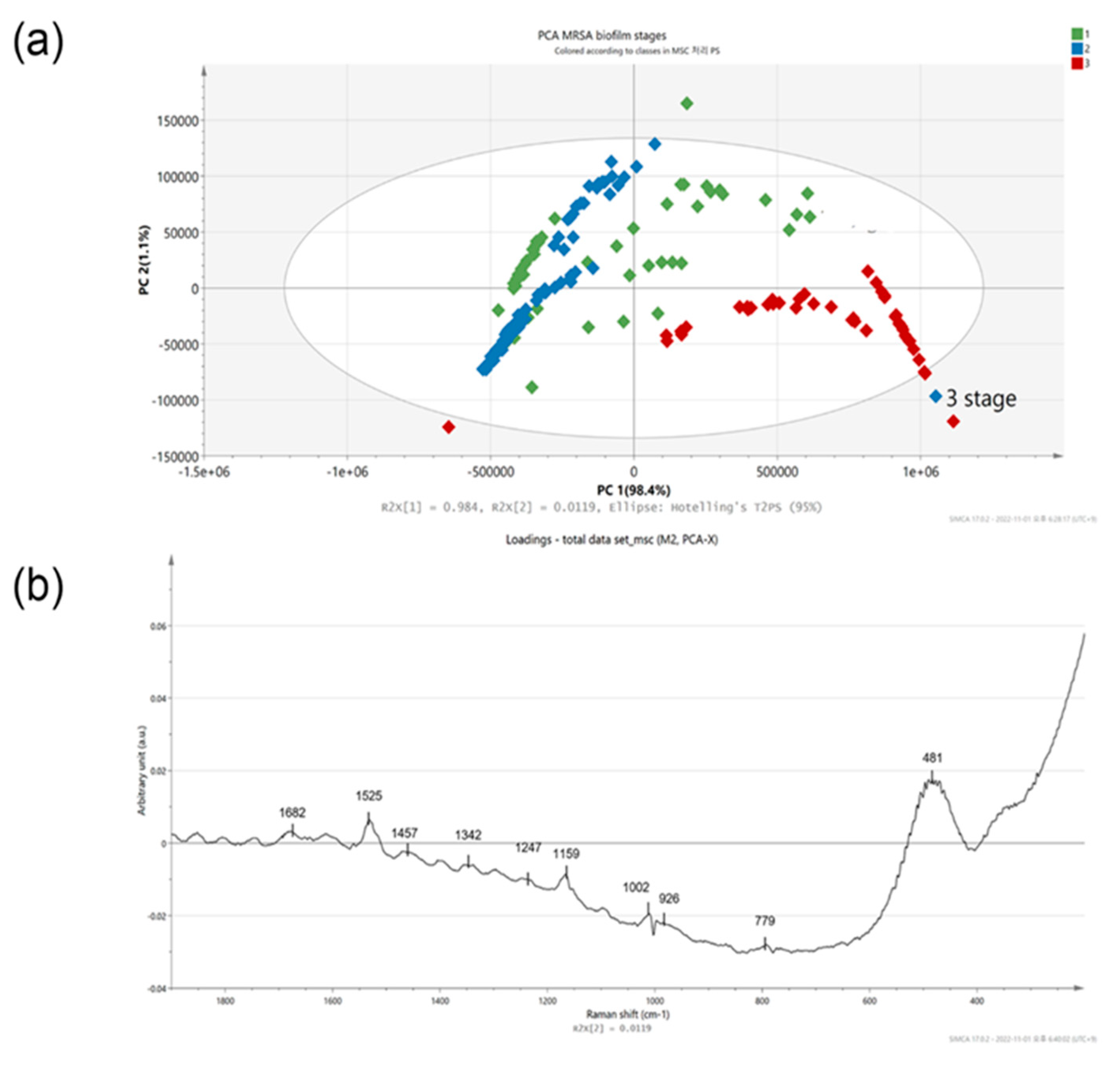
To track the evolution of a biofilm community from a single cell to a multicellular level, an analytical tool was used to track multiple cells and clusters regarding their growth dynamics, size, and shape [
55]. Biofilm growth was assessed using spectral shift over time, as shown in
Figure 2B. To confirm the prediction, PCA analysis was applied to the 171 spectral data. The Raman spectra of MRSA bacterial colonization and further growth of the colonizers on the surface, leading to structured microbial communities, could be more clearly identified and visualized by performing PCA on the Raman spectra, as shown in
Figure 3A. PCA modeling was used to determine biomarkers to identify the indicators for assessing planktonic bacteria’s transition to biofilm maturation and categorization [
56]. To acquire an initial overview of the dataset and to find patterns, a PCA analysis was performed. No samples fell outside of the 95% confidence ellipse, according to Hotelling T2 analysis. The findings of the analysis are supported by high levels of explained variation (R2X = 0.99) and predictive ability Q2 (cum) = 0.99. In the PCA, approximately 99% of data variance is explained by the first two Principal components: PC1, and PC2.
Figure 3A shows the score plot of PC1, and PC2 of the growing MRSA biofilm, each of which accounts for 98.4%, and 1.1% of the variance, respectively. The data at different time points was demonstrated in three other groups to show the classification of biofilm states.
Figure 3A shows the PCA of Raman spectra for MRSA biofilms with different cultivation times ranging from 0 to 48 h. The different groups represent the single cell to a multicellular level of biofilm and display significant changes in Raman peak intensities and peak ratios. MRSA biofilms at other metabolic states were clearly distinguished by the score plot. These classifications can be identified based on the following score plot: 0–5 h, which corresponds to the attachment of a single planktonic cell during biofilm formation (green); 6–24 h, which corresponds to biofilm proliferation during multicellular status (blue); and 26–48 h, which corresponds to the conglomerate of bacteria during biofilm dispersion (red). A separation of the groups was better between the second (6–24 h) and third time points (26–48 h) (
Figure 3A). Bacterial cells in the first two groups overlapped slightly with biofilm colonies at the multicellular level. A poor group separation in the latter group of cell growth between the first and second groups indicates that there was an increasingly heterogeneous population of colonies from 5 to 10 h, with some colonies reversibly and irreversibly attaching to surfaces. However, there is a significant separation between the second and third groups of biofilm levels because in the proliferative state, biofilm cells actively underwent metabolic modifications, while metabolic cells remained inert 24 h of biofilm development. Principal component (PC) loadings provide information on variables (wavenumber of the spectrum) that are important for group separation. By analyzing these plots, one can indicate the most important variables in the dataset. The loading values of PCA are plotted in
Figure 3B. Based on these plots, it is possible to distinguish microorganisms by their unique metabolic activities. The analysis of the loading plot leads to the differentiation of important factors attributed to biofilm biomarkers depending on time. Using correlation coefficients (loadings) of component scores, spectral features important for planktonic bacteria to biofilm growth were identified and their contributions to each variable were determined using PC. Instead, of examining a single wavenumber peak, a more chemically rich analysis is possible using regions of wavenumbers determined by correlation coefficients. It is more reliable to identify biomarkers important for discrimination when the selected spectral regions from loadings explain larger variances in data. As shown in the loading plot, no significant contribution from biofilm growth was observed in the peak at 481 cm
−1, which arises from monosaccharides in the medium. However, signature bands at 779, 926, 1002, 1159, 1247, 1342, 1457, 1525, and 1682 cm
−1 had high loading values. In particular, the hidden peak from 1682 cm
−1 (amide I) was observed with a relatively high loading value by PCA. A significant intensity increase appeared for the amide I band of proteins, at 1600 cm
−1, after biofilm growth for 26 h. The increases in protein and lipid peaks indicate the stress response to biofilm growth [
57]. An increase in the protein concentration over longer incubation times can be explained by the connection between protein expression and biofilm formation [
57]. Based on the PCA results, the Raman peaks demonstrate the most significant separation and absolute variances over time [
53]. The loading peaks in PCA are highly correlated with the activation of DNA/RNA formation at 600–800 cm
−1 [
37]. After 5 h of biofilm growth, the signature peaks of MRSA carotenoids and biofilm marker phenylalanine (at 1002 and 1159 cm
−1, respectively) are prominent [
39,
40]. Lastly, the peaks that are different after 24 h of biofilm growth are correlated with lipids and amides at 1400–1600 cm
−1, which are important EPS components of biofilms [
36,
44]. In
Figure 3B, the most significant changes in spectral peaks during bacterial growth are presented. Raman analysis of these peaks can also be used to determine the metabolic state of unknown bacteria [
52].
The results indicate that the PCA-based Raman technique can potentially identify and classify growing biofilm samples. The PCA method performed well in analyzing the Raman spectrum of the evolution of biofilm, and this analysis should be applicable in time-dependent antibiotic analysis. To resolve metabolic variations, a supervised analysis was performed in the overlapping 0–5 h and 6–24 h biofilm statuses. To categorize the MRSA biofilm cellular levels, the PLS-DA model was used (
Figure S2). A receiver operating characteristic curve and permutation testing were used to verify the model (
Figure S3).
3.6. Morphological Characterization of MRSA Biofilm via Microscope and Biofilm Growth Assay Monitored in Time
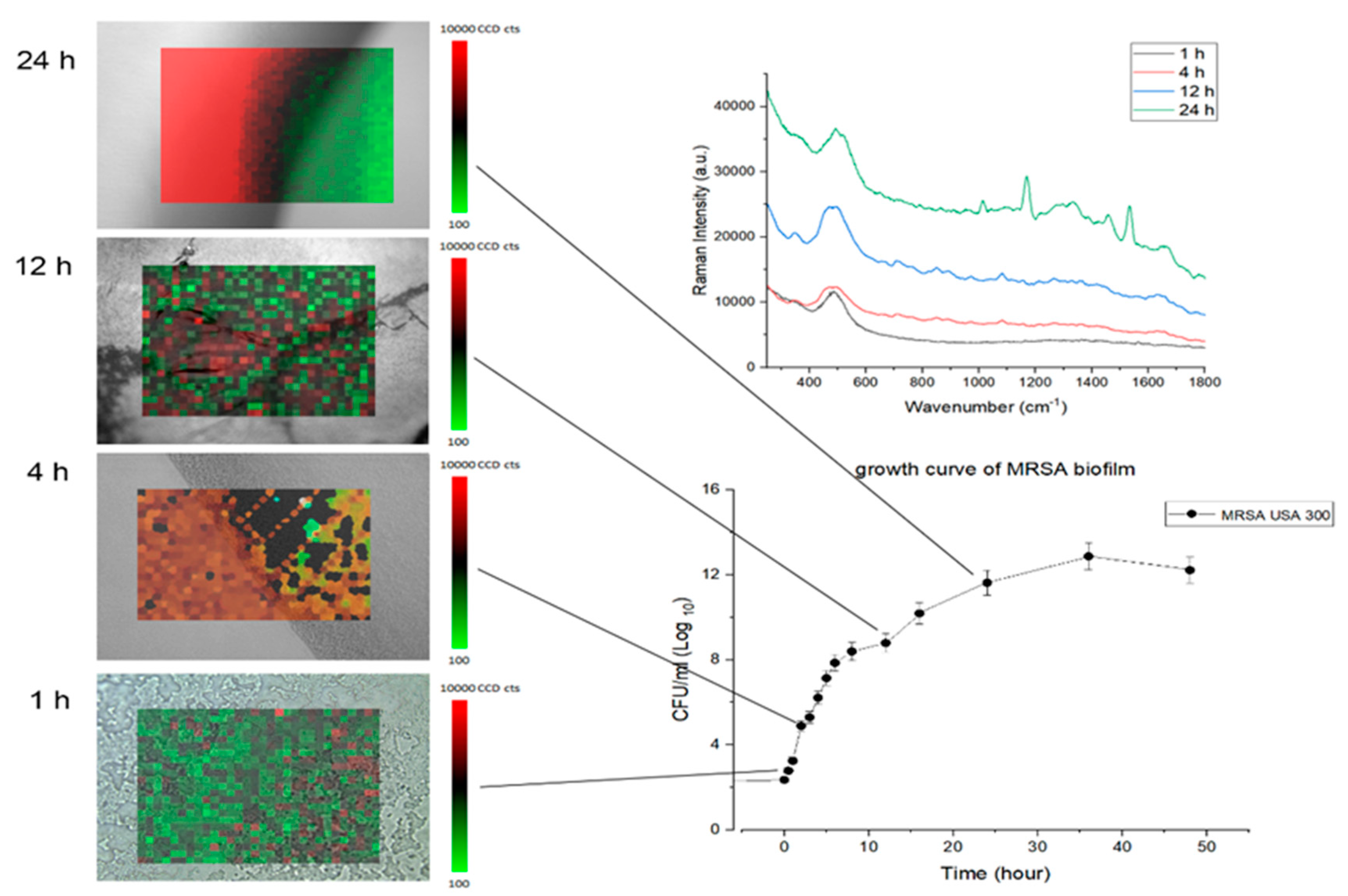
In
Figure 4A, accumulated biomass of biofilm growth over time was calculated simultaneously with the
xy mapping of Raman spectra to characterize the morphological change. The microscopy image and the Raman map show representative bacterial accumulation on the BHIA agar surface at the time points (scale bars are 20 μm). Average MRSA biofilm Raman spectra corresponding to each time point was compared in
Figure 4B.
Parallel to the Raman monitoring, biofilm development from the MBHI-sucrose agar was measured hourly for 48 h to evaluate the early attachment of the bacteria, with three independent assessments done on different days. The biofilm growth curve computed the time-dependent buildup of biofilm biomass based on
xy mapping images of the MRSA biofilm grown on a solid medium (
Figure 4C). The MRSA biofilm growth curve showed a comparable growth angle to the typical bacterial growth curve. The slope grew slowly during the first 4 h, then exponentially from 5 to 24 h. The biofilm mass grew rapidly and displayed a high growth angle, perhaps owing to the attachment of bacteria to the surface as opposed to planktonic bacteria. Finally, the slope slowed down from 25 to 48 h. The three distinct growth rates in
Figure 2 were closely associated with the PCA analysis. The
xy mapping of Raman spectra was used to characterize the morphological change during the biofilm growth. The Raman results showed spatial changes owing to the attachment of planktonic bacteria and the chemical alteration of biofilm at different time periods. Exemplary Raman images shows a planktonic bacterial cell (1 h), initial biofilm cell attachment (4 h), biofilm colony maturation (12 h), and conglomerate growth of biofilms on the agar surface (24 h). The morphological data and biofilm development curve show that
in situ Raman spectroscopy can properly monitor biofilm progression.
3.7. Antimicrobial Activity of Eugenol against MRSA Biofilm Growth by Raman Spectroscopy and Biomass
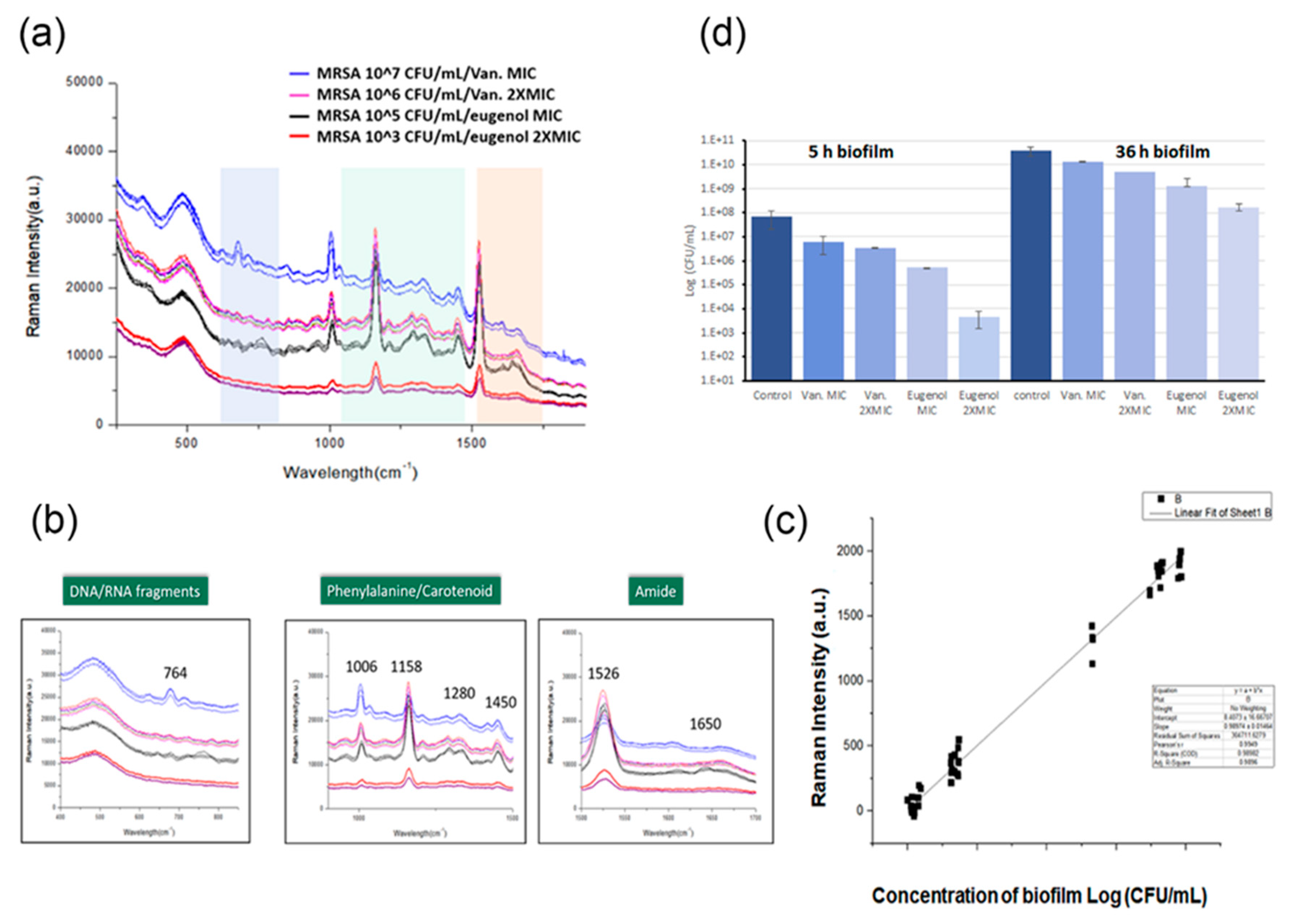
In this research, the growth of MRSA biofilm was analyzed by PCA, and the beginning of the maturation process starts after 5 h of incubation. The optimal time to eradicate biofilm is during the planktonic bacterial cells at attachment status (0–5 h), and this was validated through the characterization of eugenol-MRSA biofilm interaction using microbiological methods. Since eugenol is known to demonstrate strong antibiofilm properties against both MRSA and Methicillin-Sensitive Staphylococcus. aureus (MSSA) clinical strains, it was selected as a natural biofilm agent for rapid antibiofilm tests [
26]. In
Figure 5A and B, antibiofilm assay was performed to determine the antibacterial activity of eugenol on MRSA within the biofilms. Biofilms exposed to 2 × MIC displayed strong bactericidal effects against MRSA [
25]. After the treatment on 5 h grown biofilm, counts of viable bacterial cells were decreased by more than 2-log
10 and 4-log
10. This observation suggests that the strong antimicrobial activity of eugenol on MRSA within biofilms reaches maximal effect toward 0–5 h grown biofilm. The result is in agreement with the prediction.
In parallel to the antibiofilm assay, antibiotics on cell viability were tested in MBHI-sucrose agar plate with the same inoculum and reagents for Raman experiments.
To figure out when spectral changes occur, each time point was compared individually by Raman spectroscopy. Eugenol at MIC was applied to monitor its killing effect on biofilms at different time points. In
Figure 5A, 5-h-grown MRSA biofilm was treated with eugenol, and changes in the Raman spectrum were observed. The bands at 764, 1280, 1334, 1450, 1526, and 1650 cm
−1 significantly decreased after the antibiotic treatment. The peaks were correlated to DNA/RNA fragments, tryptophan, lipid, carotenoid, and amide of MRSA biofilms. The Raman spectra of MRSA biofilm cultured within the first 5 h were observed with eugenol and vancomycin in different concentrations. When MRSA was treated with vancomycin at MIC, the spectra decreased in intensity; however, the signature peaks did not decrease. Vancomycin was affected by the higher dosage, but it did not eradicate the biofilm. When treated with eugenol at the MBIC concentration, the peaks identified as 764, 1280, 1334, 1450, 1526, and 1650 cm
−1 were significantly reduced in intensity and disappeared. The spectral change indicates that eugenol had an eradicating effect of the MBIC concentration. In addition, the results showed that with the decrease in bacterial concentration, the intensity of the Raman spectrum decreased. In
Figure 5C, the linear correlation between biomass of the biofilm and the Raman intensity is shown. Consequently, Raman spectroscopy could measure the antimicrobial activity against MRSA biofilms by observing the spectral changes in the Raman spectrum of bacterial cells.
A biofilm is a dominant form of microbial life, and it is difficult to eliminate it completely. It provides protection to residing bacteria, so it is critical to find the best antibiotics in the most effective time frame. Therefore, the best time to apply eugenol was examined by Raman spectroscopy (
Figure 5A). According to CFU calculations in
Figure 5, the number of biofilms counted was in agreement with the above results.
Eugenol demonstrated antibiofilm properties against clinical MRSA strains, especially in the early phase of biofilm formation. The biomasses of established biofilms were significantly decreased by eugenol treatment. Similarly, the number of viable bacteria was significantly decreased in eugenol-treated biofilms. Biofilm biomass was significantly decreased by 50% when eugenol was applied at MIC [
25]. A decrease of 4-log
10 in the number of viable cells was observed in biofilms treated with eugenol at 2×MIC. The MBIC of eugenol against MRSA biofilms was found to be twice its MIC value [
30].
The antibacterial activities of eugenol were investigated against MRSA. Eugenol was evaluated for bactericidal activity by counting viable cells, providing a quantitative estimate of its efficacy. The inhibitory activities of eugenol and vancomycin are shown in
Figure 5D. The samples were enumerated for bacterial viability at 24 h of exposure to the antibiotics. The proliferation abilities of bacterial cells after treatment with the selected antibiotics at one and two times the MIC on biofilms at different hours are shown in
Figure 5D. When MRSA biofilms grown for 36 h were exposed to eugenol at MIC, no significant difference was observed in the proliferation ability of MRSA. At two times the MIC, 7.3 logs CFU/mL bacterial cells could proliferate, and at MIC, 8.5 logs CFU/mL bacterial cells survived. However, the proliferation ability of MRSA biofilms decreased sharply when only grown for less than 5 h and treated with eugenol. After the antibiotic treatment on 5h grown MRSA, biofilms showed 4.3 logs CFU/mL cells at two times the MIC and 5.7 logs CFU/mL cells at MIC. Similarly, 6.8 logs CFU/mL was observed for vancomycin treatments (
Figure 5A). Based on these findings, the treatment with eugenol at an early stage of biofilm formation may enhance its bactericidal effects.
To evaluate the influence of antibiotics on the biofilm, the CFUs in MRSA biofilms were measured. The colony forming units/mL values in the presence of different antibiotics after different periods of biofilm growth are presented in the data. In the early stages, the antimicrobial activity of MIC eugenol was approximately 15% higher than that of vancomycin at the MIC. At double concentration, the MBIC value, eugenol caused inhibition of more than 50% of the control before 5 h. However, the efficacy of eugenol on biofilms grown for 26 h was reduced only by 10% at the MBIC concentration.
Within an hour, our antibiofilm test was able to immediately detect the most efficient time for biofilm to apply an antibiofilm agent. This shows that eugenol is most potent during the attachment phase, as determined by Raman and CFU calculations. These recently identified natural antibiofilm compounds are interesting prospects for innovative biofilm-associated infection treatments.
4. Conclusion
In this study, a novel approach was presented using Raman spectroscopy to identify new, safe, and effective agents to combat the increasing number of multi resistant strains of bacteria. As the MRSA forms biofilm, the resistance against antibiotics increases and the natural compound eugenol was tested to inhibit the bacteria. Raman spectroscopy can predict the initial biofilm adhesion to the surface and the optimal antibiotic administration time to avoid resistance caused by biofilm formation. Biofilm formation was examined by measuring the changes in the Raman spectrum of biofilms and primary matrix materials, such as DNA, RNA, protein, lipid, and EPS. When analyzing the measured Raman spectra, PCA was used to predict the early stage of biofilm. The result showed that the planktonic bacteria attached to the surface to form biofilm at approximately 5 h. To confirm the optimal antibiotic administration times, eugenol was treated at 5 h, 24 h, and 36 h. The most effective biofilm growth could be inhibited when treated before 5 h, and this result was consistent with the results based on CFU/mL. Based on this study, Raman spectroscopy could be used as an antimicrobial drug discovery tool to rapidly measure real-time biofilm formation without staining and suggest the optimal time for antibiotic administration to prevent biofilm formation.