Submitted:
22 June 2023
Posted:
22 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
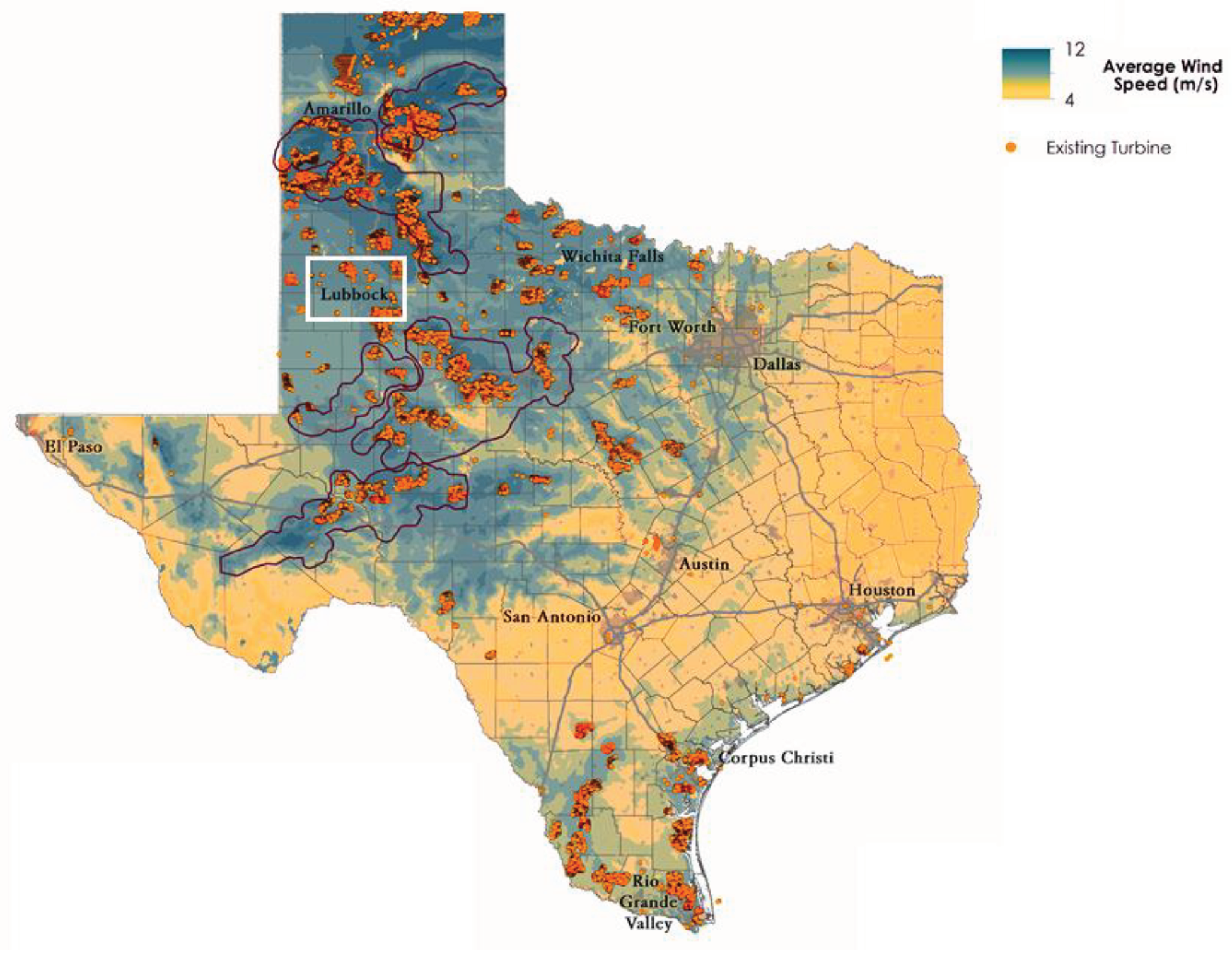
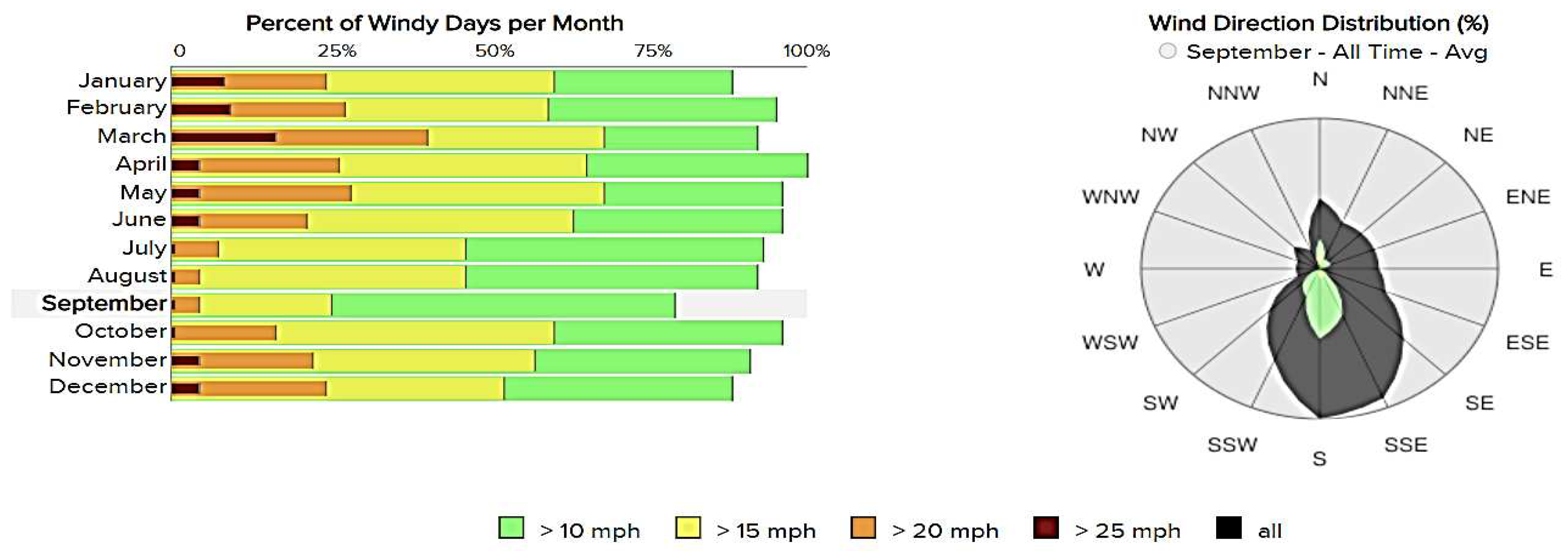
2. Wind scenarios in Lubbock
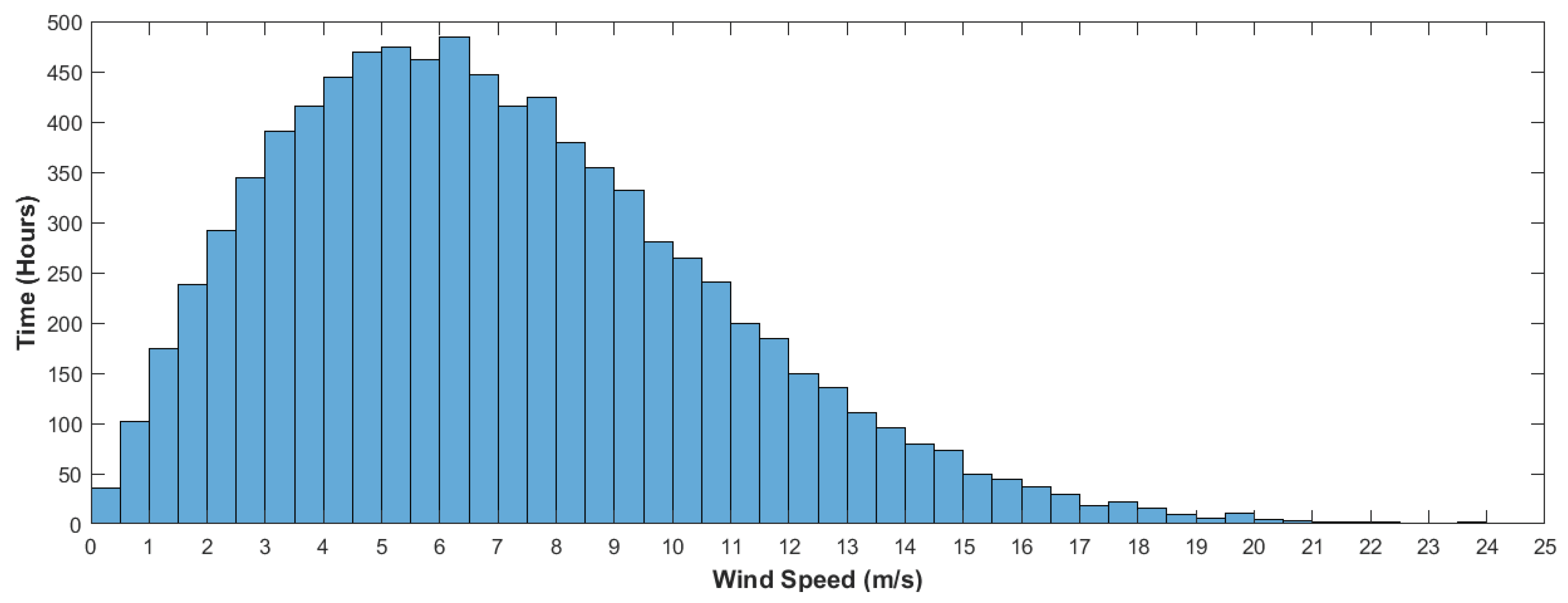
2.1. Data analysis
2.2. The optimum height for maximum wind velocity
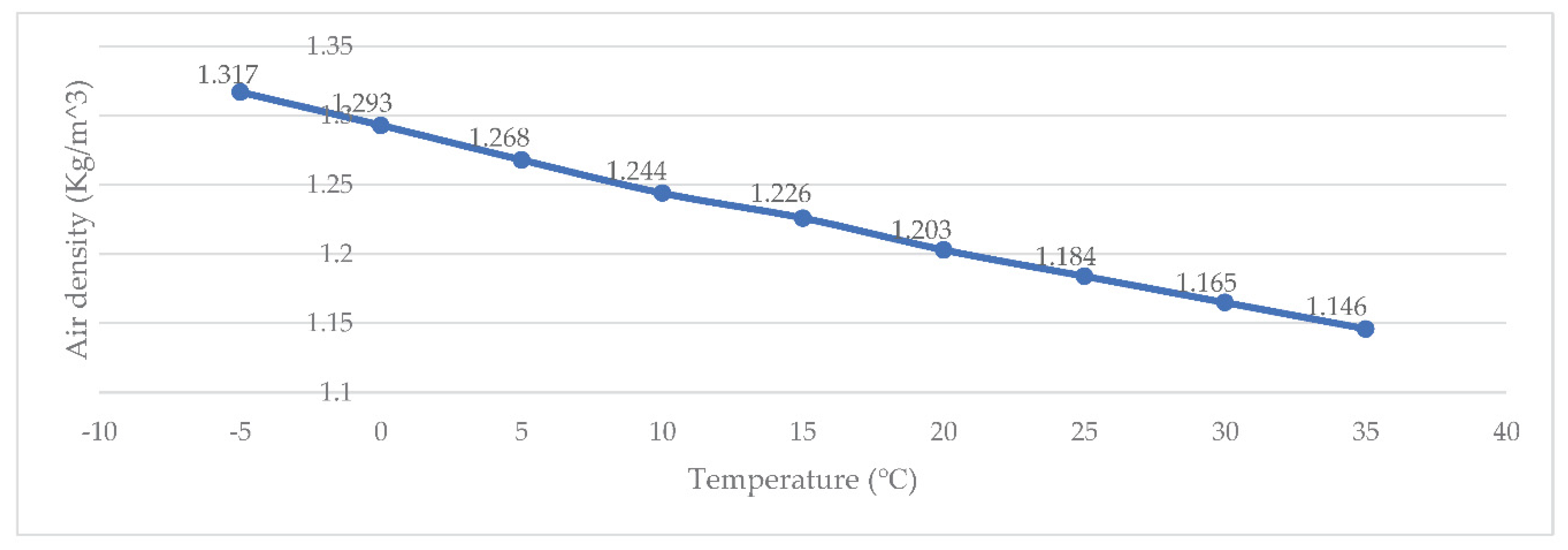
2.3. Air Density
2.4. Maximum Power Calculation
3. Design of 6 kW Wind Turbine
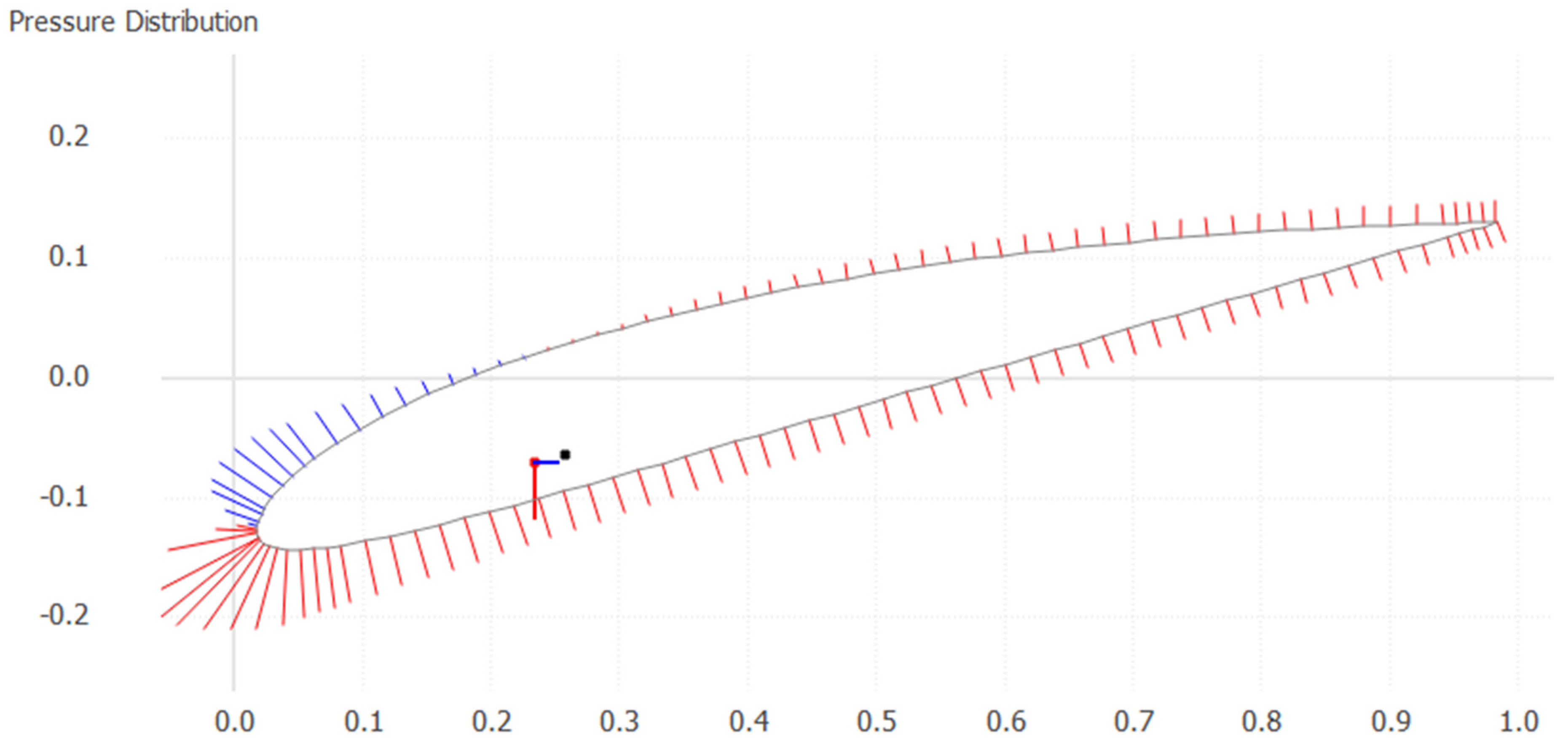
3.1. Blade design
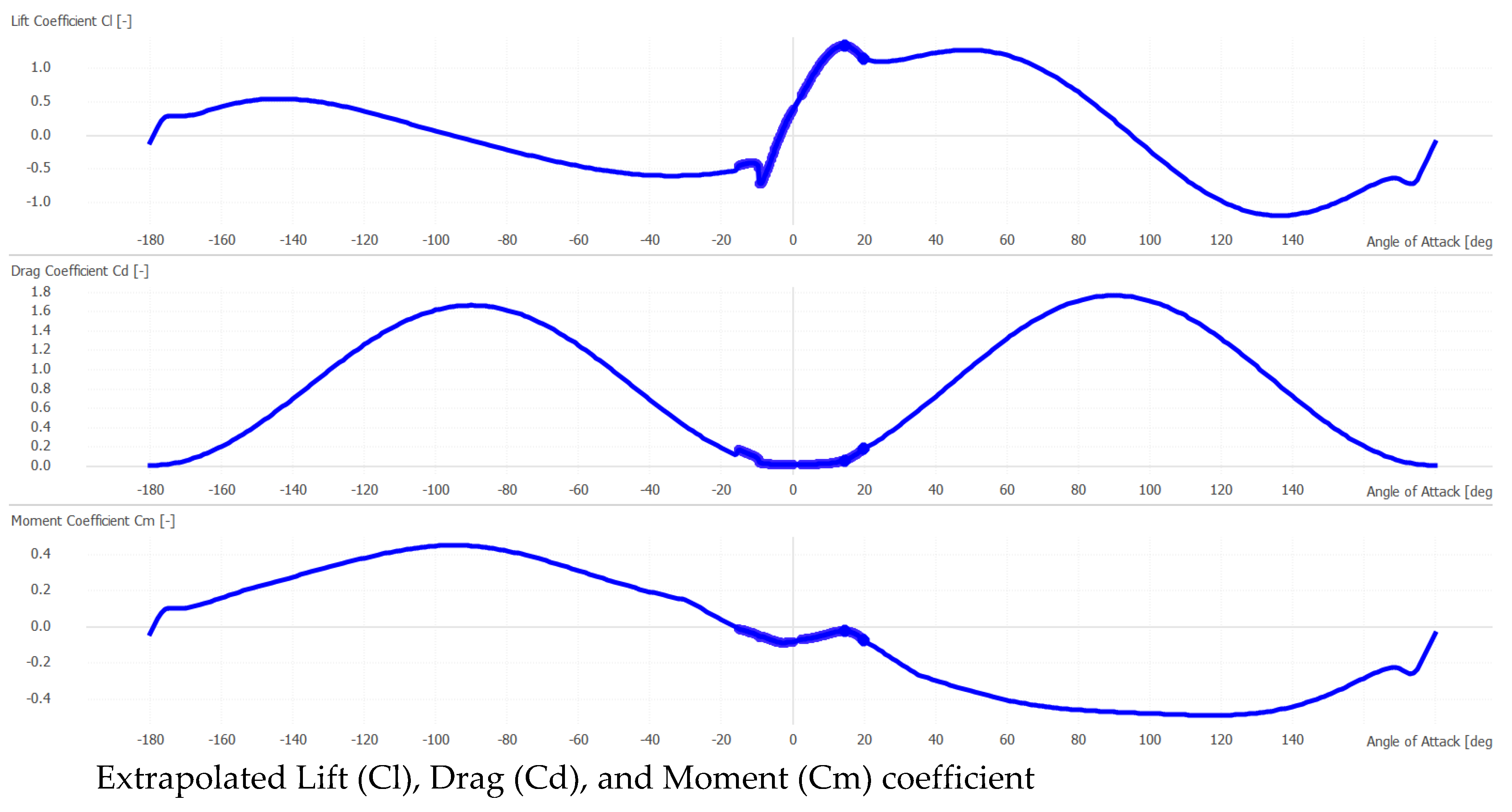
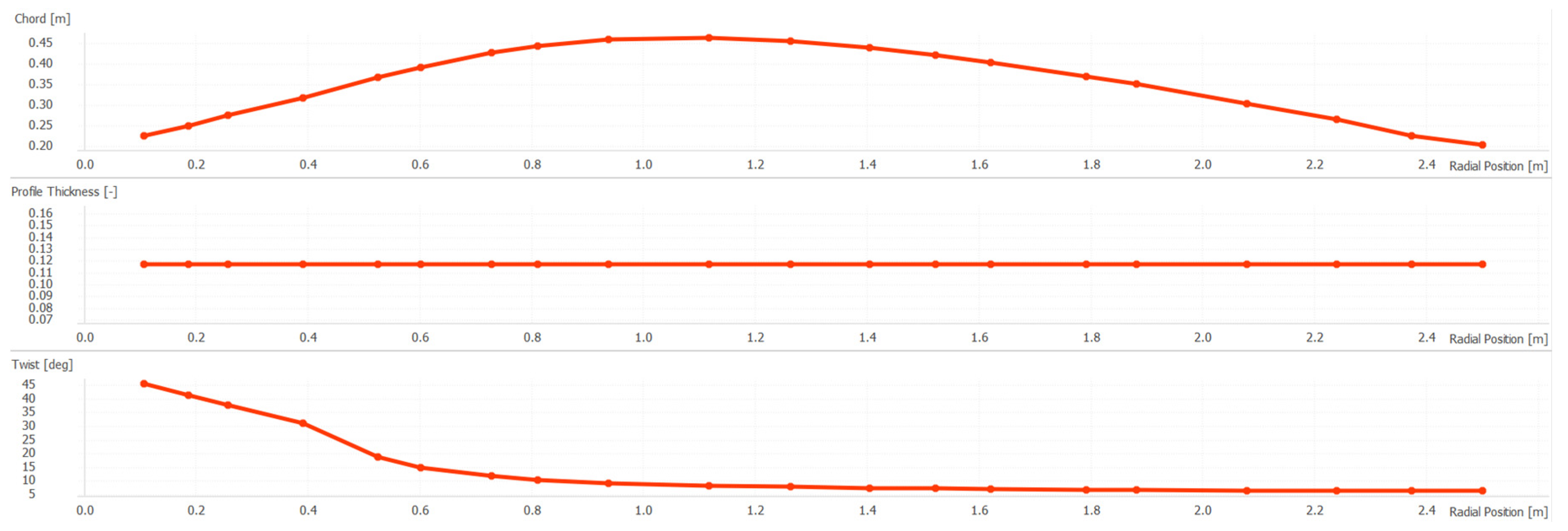
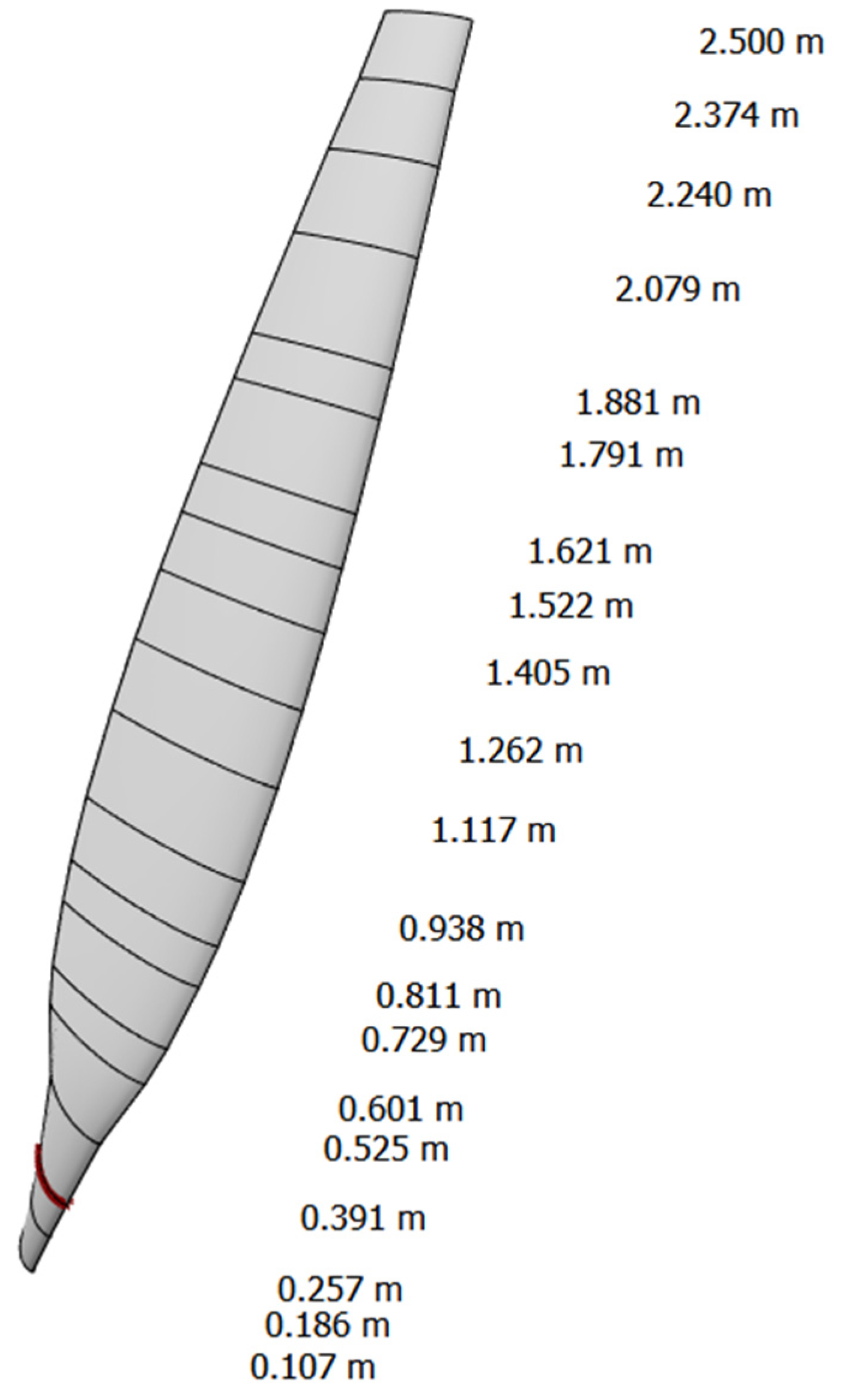
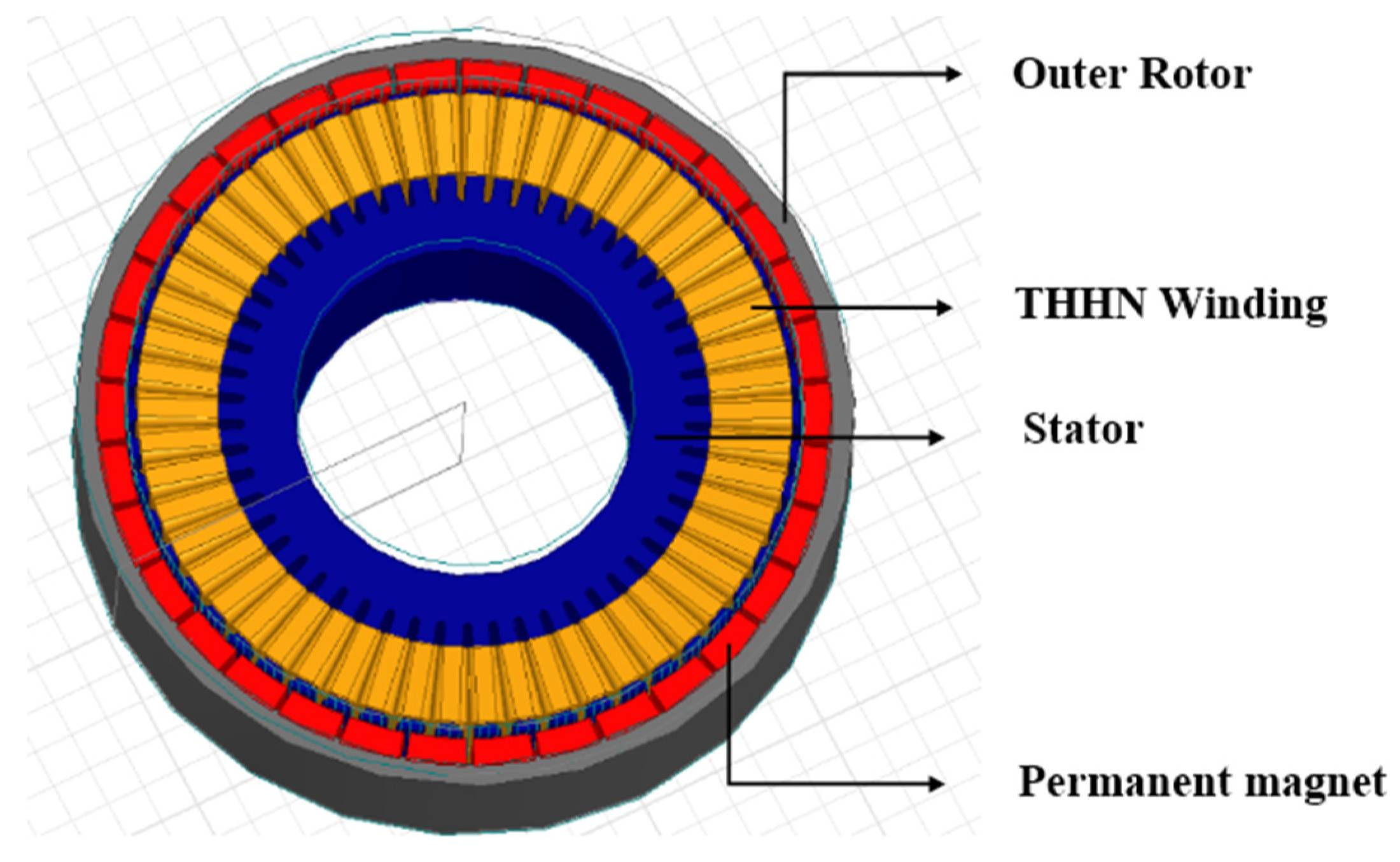
3.2. Permanent magnet alternator
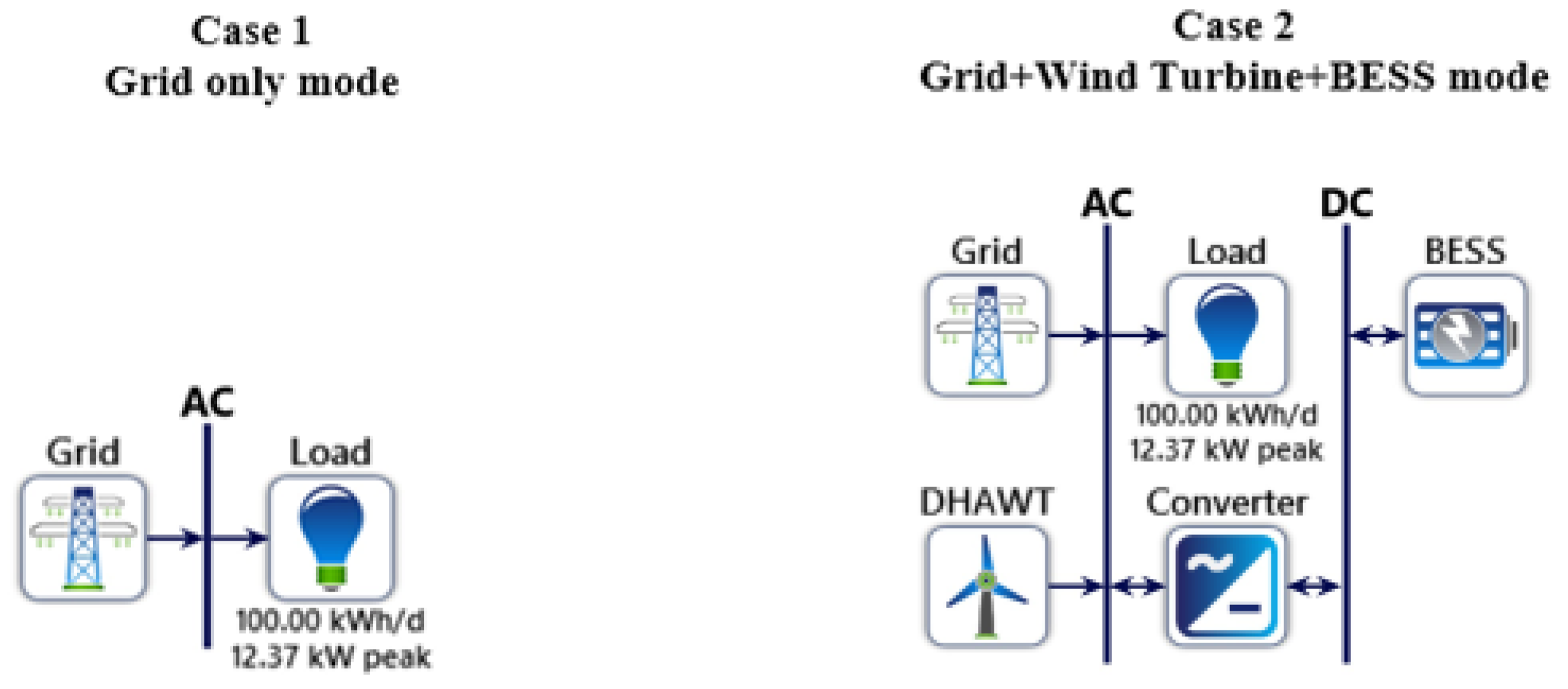
4. Result analysis
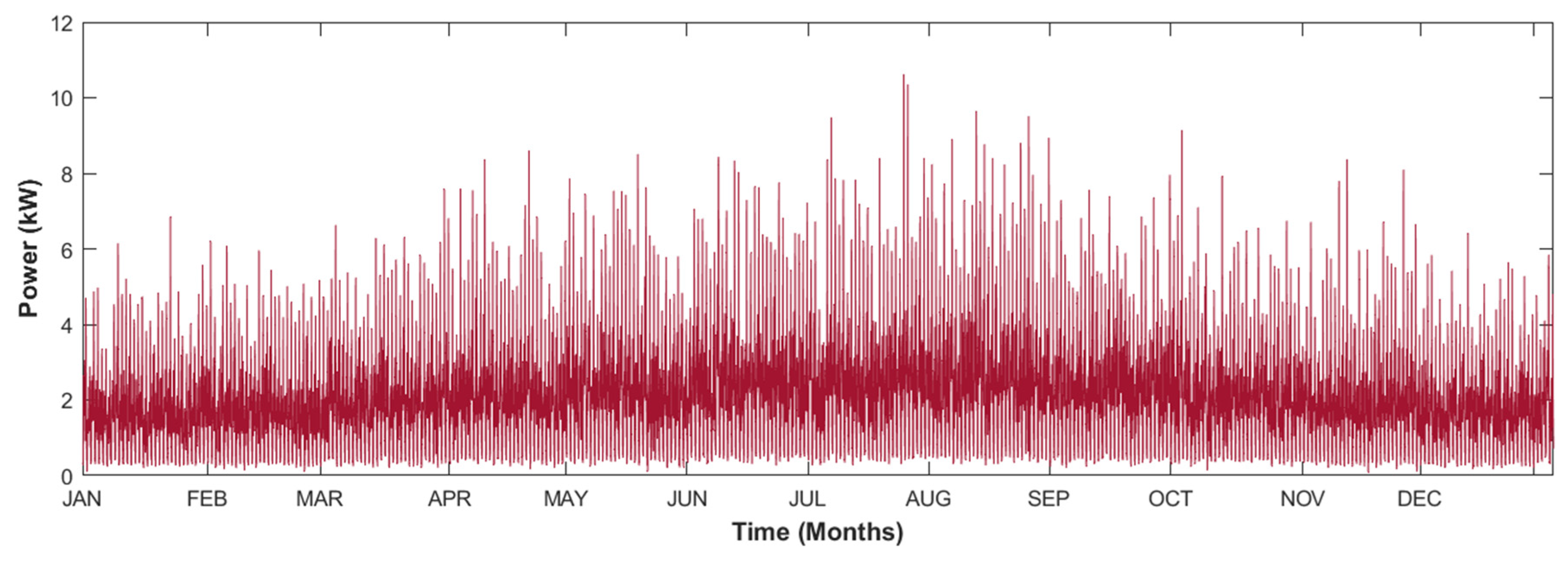
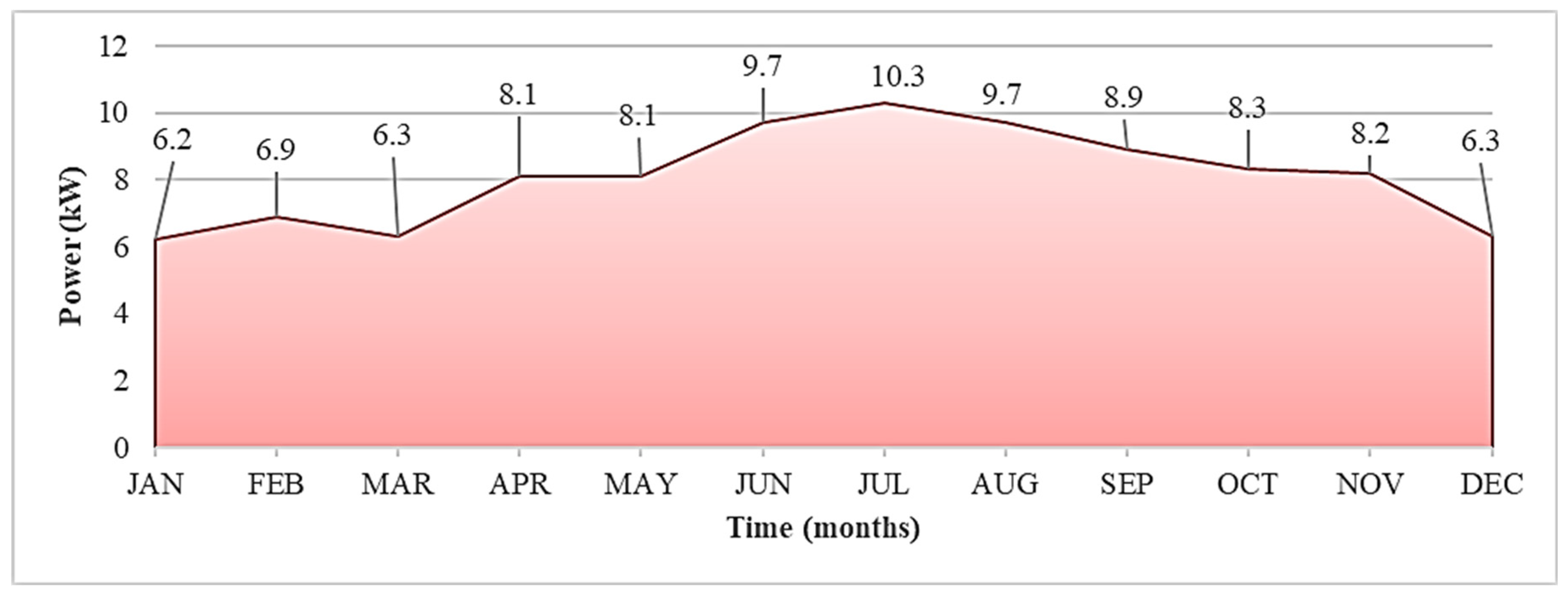
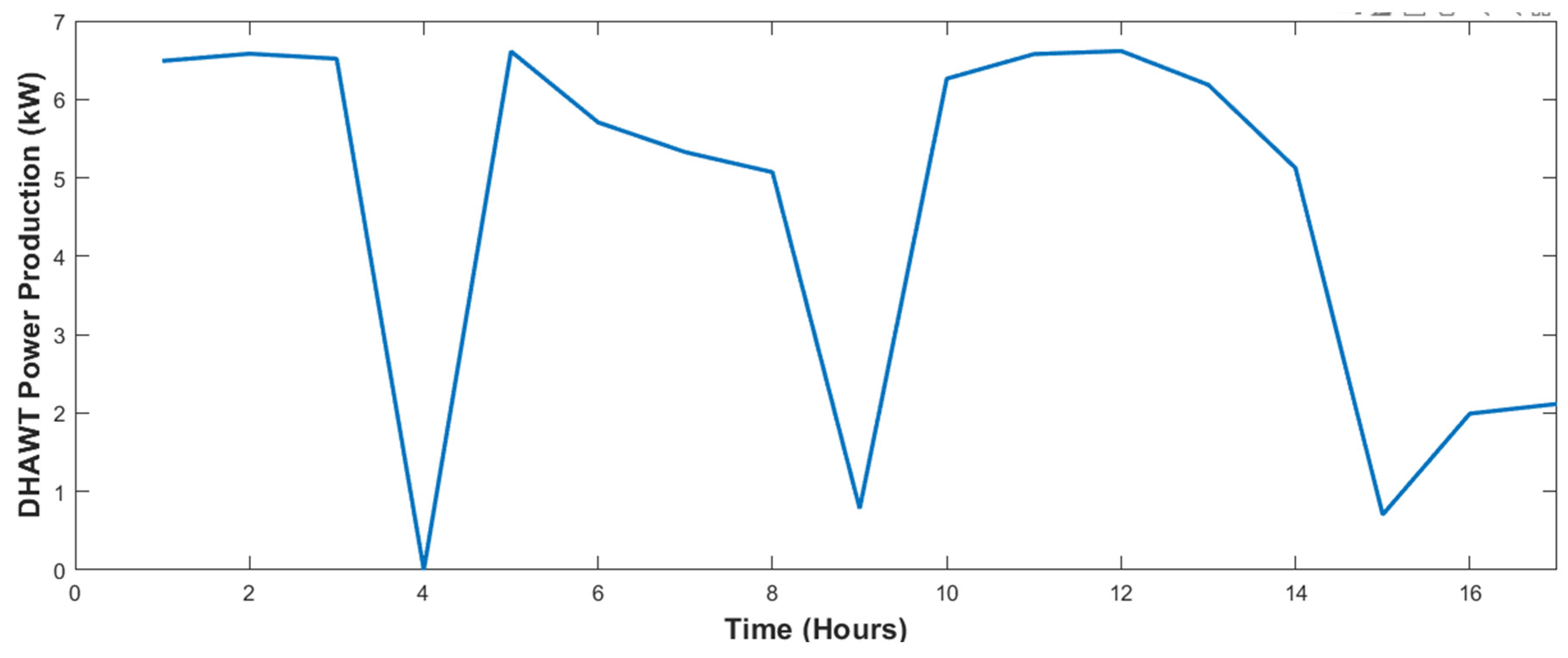
4.1. Power Generation
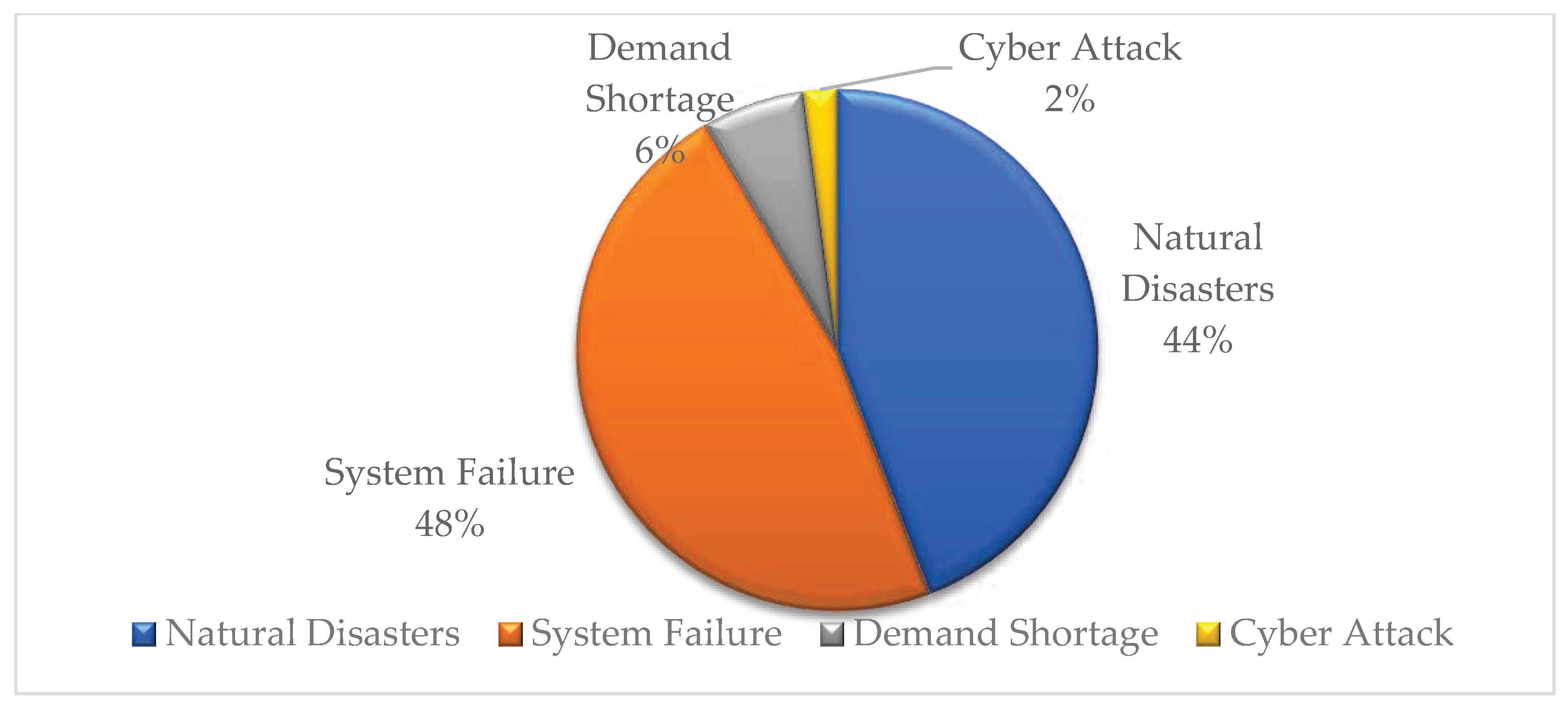
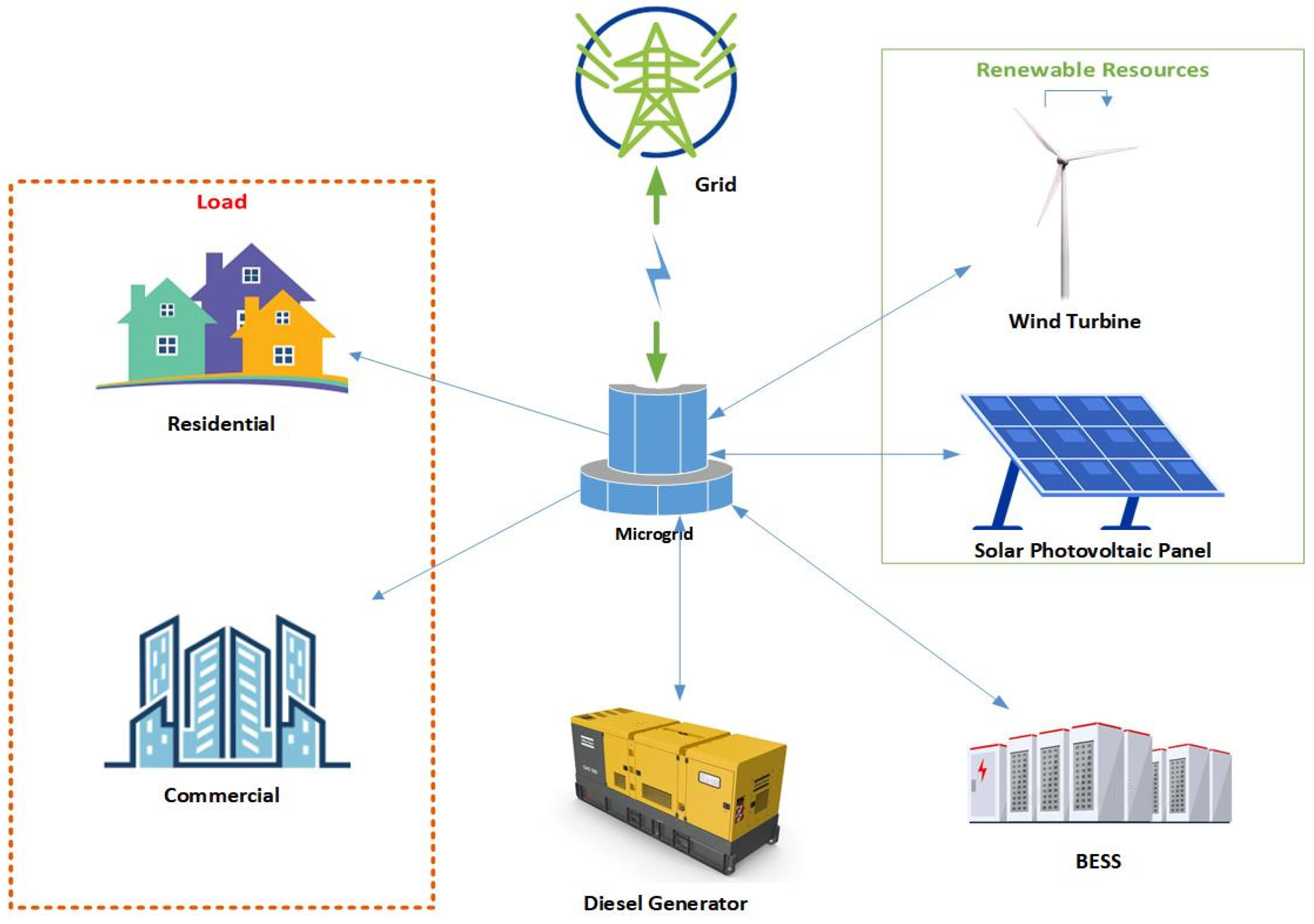
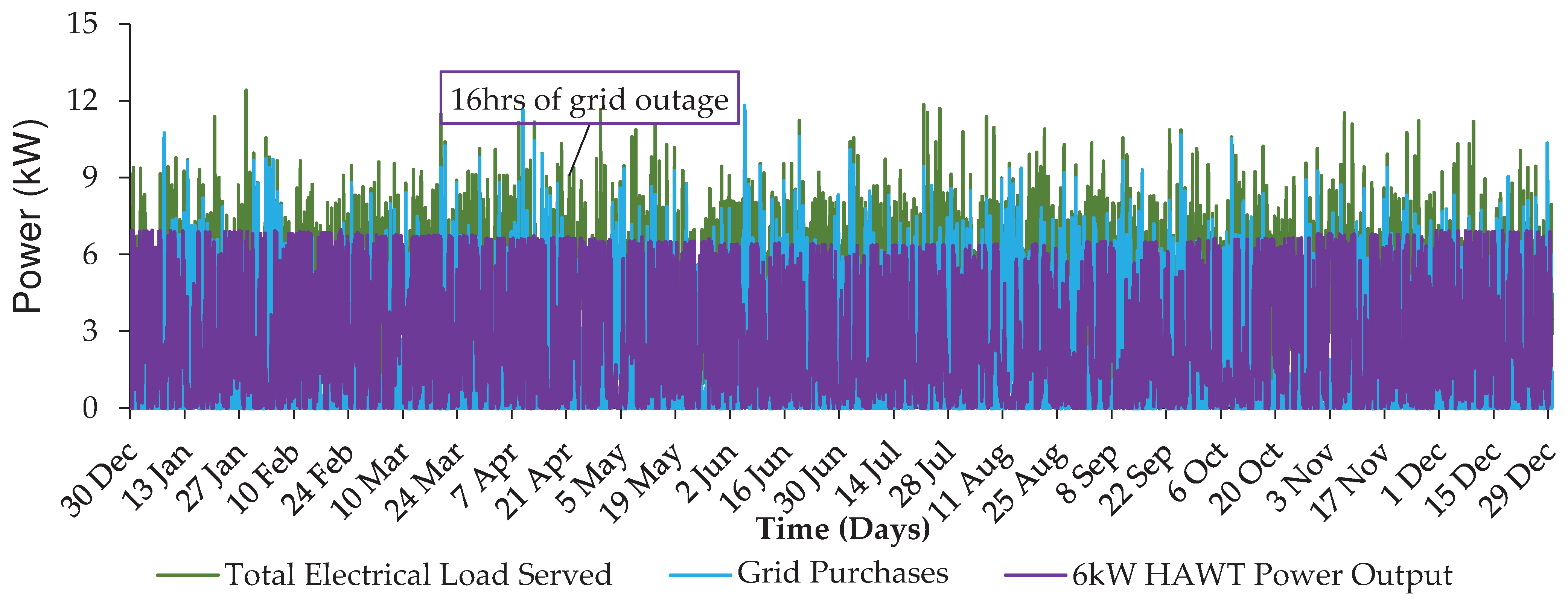
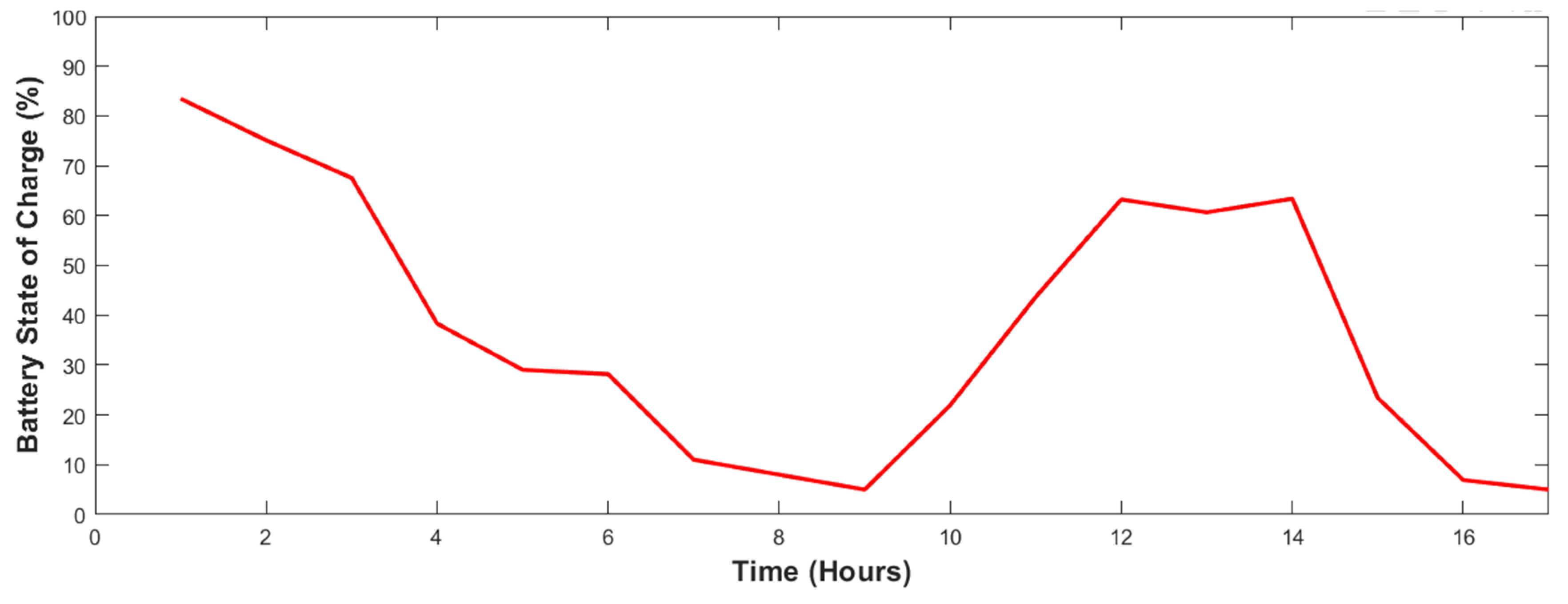
4.2. Resiliency analysis
4.3. Economic Benefits
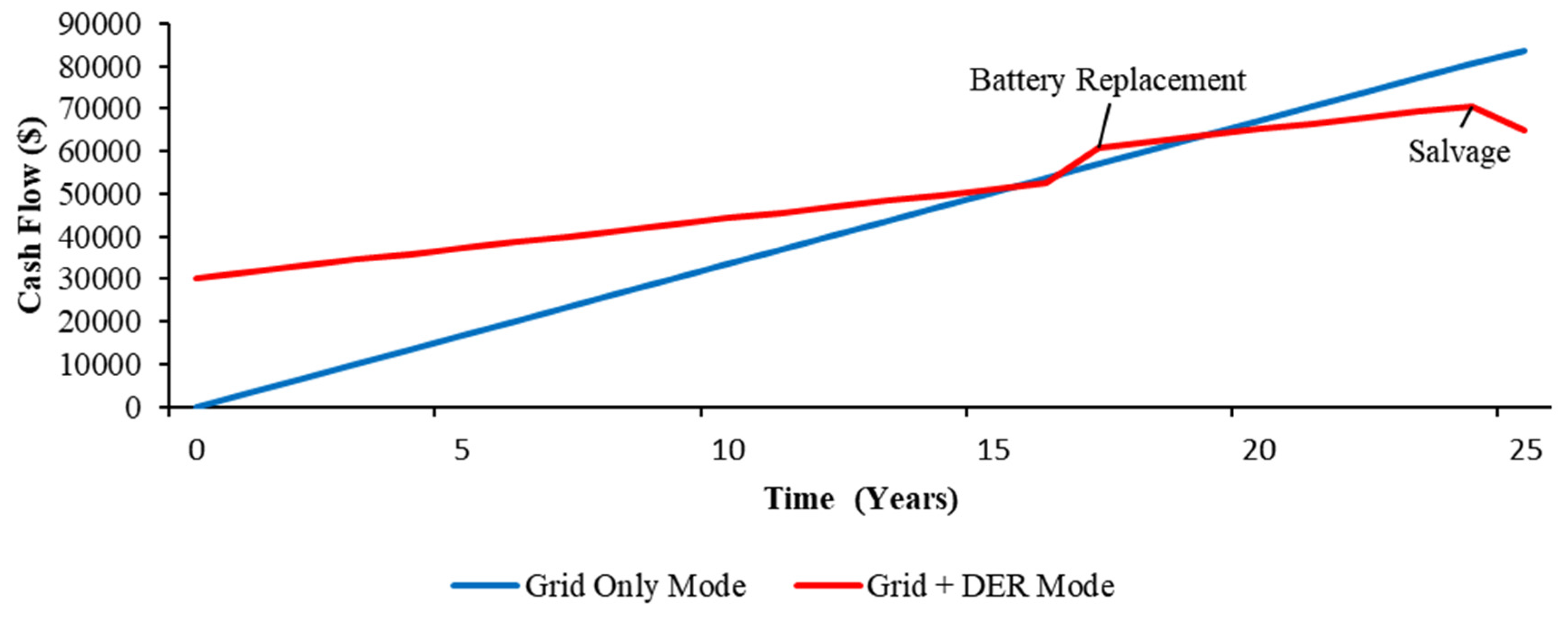
4.4. Environmental Benefits
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| NACA | National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics |
| NREL | National Renewable Energy Laboratory |
| BESS | Battery energy storage system |
| DHAWT | Distributed hotizontal axis wind turbine |
| SoC | State of Charge |
| Cl | Lift coefficient |
| Cd | Drag coefficient |
| Cm | Moment coefficient |
| AoA | Angle of attack |
| PMA | permanent magnet alternator |
| A | Swift area |
| h | Height |
| m | Mass of air, kg |
| v | Wind velocity, m/s |
| ρ | Air density, kg/m3 |
| C_P | Betz limit coefficient |
| α | Frictional coefficient |
| p | Static pressure, kPa |
| V | Volume of air, m3 |
| η | efficiency, % |
| N | rated speed |
| f | frequency |
| P | pole quantity |
| ϕ_g | magnetic flux |
| B_av | flux density |
| D= | stator diameter |
| L= | stator length. |
| T | Temperature, ℃ |
| IRR | Investment return rate |
References
- M Bilal, G Araya, Y Birkelund “Preliminary Assessment of Remote Wind Sites” 7th International Conference on Applied Energy–ICAE2015. [CrossRef]
- S. T. Tentzerakis, S. A. Papathanassiou “An Investigation of the Harmonic Emissions of Wind Turbines” IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion (Volume: 22, Issue: 1, March 2007). 20 March. [CrossRef]
- D. Hanselman, “Brushless permanent magnet motor design” Magna Physics Pub: Orono, ME, USA, 2003.
- Kazi Ahsanullah, Rukmi Dutta, John Fletcher, M.F. Rahman, “Design of an interior permanent magnet synchronous machine suitable for direct drive wind turbine” 2nd IET. In Renewable Power Generation Conference (RPG) 2013; pp. 1-4. [CrossRef]
- W. Fei and P. C. K. Luk, “A new technique of cogging torque suppression in direct-drive permanent-magnet brushless machines,” IEEE International Electric Machines and Drives Conference 2009; 1332–1340. [CrossRef]
- Ting Liu, Shoudao Huang, Qiul ing Deng, Qingyun Pu, Keyuan Huang, “Effect of the number of slots per pole on the performance of permanent magnet generator direct-driven by wind turbine” IEEE International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS) 2011; 1-4. [CrossRef]
- C. Ocak, D. Uygun, Y. Cetinceviz, E. Demir, Y. Gungor, “Performance aspects and verifications of in-runner and out-runner permanent magnet synchronous generator designs of the same magnet structure for low-speed wind systems” 11th International Conference On Environment and Electrical Engineering (EEEIC) 2012. [CrossRef]
- T.W. Neumann, R.E. Tompkins, “Line start motor designed with NdFeB permanent magnet,” 8th International Workshop on Rare Earth Magnets and their Application, Dayton, Ohio, 1985, 77–89.
- P.J. Schubel and R.J. Crossley “Wind Turbine Blade Design Review” wind engineering 2012, 36, 365-388. 2012; 36, 365–388. [CrossRef]
- W. Wende, G. Jingcun, X. Gouliang, C. Yong, “High efficiency and energy-saving DC brushless motors” Electrical Energy Conference 1987, 499–502.
- L.M.C. Mhango, “Benefits of Nd-Fe-B magnet in brushless DC motor design for aircraft applications,” 4th IET International Conference on Electrical Machines and Drives 1989, 76-79.
- M Murshed, M Y Arafat, M A Razzak “Analysis of Air Foils and Design of Blades for a Low-Speed 250W Vertical Axis Wind Turbine Suitable for Coastal Areas of Bangladesh” e 2019 5th International Conference on Advances in Electrical Engineering (ICAEE) 26-28 September. [CrossRef]
- Y. Arafat, M. Murshed, MA Razzak, “Design and Analysis of an In-Runner Permanent Magnet Alternator for Low-Speed Wind Turbine” 4th International Conference on the Developments in Renewable Energy Technology (ICDRET) 2016, 1-5. [CrossRef]
- General Cable, “Building Wire and Cable for Commercial and Residential Applications” USA, 2012.
- Gyeong-Chan Lee, Su-Min Kang, Tae-Uk Jung, “Permanent magnet structure design of outer rotor radial flux permanent magnet generator for reduction cogging torque with the design of experiment,” International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems 2013, 315–319. [CrossRef]
- M. Y. Arafat, M. Murshed, M. M. Hasan, M.bA. Razzak, “Impacts of Cogging Torque and Its Reduction for an External Rotor Permanent Magnet Alternator,” 5th IEEE International Conference on Informatics, Electronics, and Vision (ICIEV), 2016, 1-6. [CrossRef]
- TongGuang Wang, Long Wang, Wei Zhong, BoFeng Xu & Li Chen “Large-scale wind turbine blade design and aerodynamic analysis” Chinese Science Bulletin 2012, 57, 466–472. [CrossRef]
- TV Ramachandra, B.V. Shruti, “Wind energy potential mappings in Karnataka, India, using GIS” Energy Conversion and Management 2005, 46, 1561–1578. [CrossRef]
- M Murshed, Y Arafat, M. A Razzak “Design of blades for a low-speed 400W wind turbine suitable for coastal area of Bangladesh” 3rd International Conference on Green Energy and Technology (ICGET), 2015. [CrossRef]
- Md. Habib Ullah, Tamzi dul Hoque, Md Mus addaqul Hasib, “Current Status of Renewable Energy Sector in Bangladesh and a Proposed Grid-Connected Hybrid Renewable Energy System” International Journal of Advanced Renewable Energy Research 2012, 1, 618-627. 2012; 1, 618–627.
- Ajinkya Padate, “Tidal and wind energy and wind energy conversion duo,” International Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy 2013, 2, 163–166.
- M. L. Kubik, P. J. Coker, C. Hunt, “Using meteorological wind data to estimate turbine generation output: A sensitivity analysis” World Renewable Energy Congress Linkoping, Sweden, 2011.
- A Balal, M Murshed “Implementation and comparison of Perturb and Observe, and Fuzzy Logic Control on Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) for a Small Satellite” journal of soft computing and decision support systems ISSN: 2289-8603.
- H. Panofsky, J. Dutton, “Atmospheric Turbulence: Models and methods for engineering applications” Pennsylvania State University: John Wiley and Sons, 1984.
- John McCosker, “Design and Optimization of a Small Wind Turbine” An Engineering Project Submitted to the Graduate Faculty of Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute. http://www.ewp.rpi.edu/hartford/ ~ernesto/SPR/McCosker-FinalReport.pdf (Accessed 21 July 2022). Stevenson, R. Discourse, power, and energy conflicts: Understanding Welsh renewable energy planning policy. Environment and Planning C: Government and Policy 2009, 27, 512–26. [CrossRef]
- Swofford, J. and Slattery, M. Public attitudes of wind energy in Texas: Local communities in close proximity to wind farms and their effect on decision-making. Energy Policy 2010, 38, 2508–19. [CrossRef]
- Toke, D., Breukers, S. and Wolsink, M. Wind power deployment outcomes: How can we account for the differences. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2008, 12, 1129–1147. [CrossRef]
- Energy, U.S. Department of. 20% Increasing wind energy’s contribution to U.S. electricity supply, Washington, DC: Wind energy by 2030 DOE/GO-102008-2567 U.S. Department of Energy, 2008.
- Warren, C. R. and Birnie, R. V. Re-powering Scotland: Wind farms and the “energy or environment” debate. Scottish Geographical Journal 2009, 125, 97–126. [CrossRef]
- Warren, C. R., Lumsden, C., O’Dowd, S. and Birnie, R. V. “Green on green”: Public perceptions of wind power in Scotland and Ireland. Journal of Environmental Planning and Management 2005, 48, 853–75. [CrossRef]
- Warren, C. R. and McFayden, M. Does community ownership affect public attitudes to wind energy? A case study from southwest Scotland. Land Use Policy 2010, 27, 204–13. [CrossRef]
- Wilson, E. J. and Stephens, J. C. Wind deployment in the United States: States, resources, policy, and discourse. Environmental Science and Technology 2009, 43, 9063–70. [CrossRef]
- Wolsink, M. Wind power and the NIMBY-myth: Institutional capacity and the limited significance of public support. Renewable Energy 2000, 21, 49–64. [CrossRef]
- M.H. Mohamed, A.M. Ali, A.A. Hafiz, “CFD analysis for H-rotor Darrieus turbine as a low-speed wind energy converter” International Journal of Engineering Science and Technology 2015, 18, 1-13. [CrossRef]
- Amshumaan Raghunatha, “Direct-drive permanent magnet synchronous generator design for hydrokinetic energy extraction,” Masters Theses Paper 7123, Missouri University of Science and Technology 2013, 19–60.
- W. Fei and P. C. K. Luk, “A new technique of cogging torque suppression in direct-drive permanent-magnet brushless machines” IEEE International Electric Machines and Drives Conference 2009, 1332–1340. [CrossRef]
- Ting Liu, Shoudao Huang, Qiul ing Deng, Qingyun Pu, Keyuan Huang, “Effect of the number of slots per pole on the performance of permanent magnet generator direct-driven by wind turbine” IEEE International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS) 2011, 1-4. [CrossRef]
- M Alaskari, O Abdullah, and M H. Majeed “Analysis of Wind Turbine Using QBlade Software” IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, Volume 518, Issue 3. [CrossRef]
- T.W. Neumann, R.E. T.W. Neumann, R.E. Tompkins, “Line start motor designed with NdFeB permanent magnet,” 8th International Workshop on Rare Earth Magnets and their Application, Dayton, Ohio, 1985, 77–89.
- Aguirre, B., R. R. Dynes, J. Kendra, and R. Connell. Institutional resilience and disaster planning for new hazards: Insights from hospitals. Journal of Homeland Security and Emergency Management 2005, 2, 1–17. [CrossRef]
- Allenby, B., and J. Fink. Toward inherently secure and resilient societies. Science 2005, 309, 1034–36. [CrossRef]
- Berke, P. R., and T. J. Campanella. Planning for post disaster resiliency. The Annals of the American Academy of Political and Social Science 2006, 604, 192–207. [CrossRef]
- Borg, I., and J. C. Lingoes. Multidimensional similarity structure analysis. New York, NY: Springer-Verlag, 1987.
- Bradley, D., and A. Grainger. Social resilience as a controlling influence on desertification in Senegal. Land Degradation and Development 2004, 15, 451–70. [CrossRef]
- Brooks, N., N. W. Adger, and M. P. Kelly. The determinants of vulnerability and adaptive capacity at the national level and the implications for adaptation. Global Environmental Change A 2005, 15, 733–52. [CrossRef]
- Bruneau, M., S. E. Chang, R. T. Eguchi, G. C. Lee, T. D. O’Rourke, A. M. Reinhorn, M. Shinozuka, K. T. Tierney, W. A. Wallace, and D. von Winterfeldt. A framework to quantitatively assess and enhance the seismic resilience of communities. Earthquake Spectra 2003, 19, 733–52. [CrossRef]
- Buckle, P. Assessing social resilience. In Disaster resilience: An integrated approach, ed. D. Paton and D. Johnston 2006, 88–103. Springfield, IL: Thomas.
- E. Alegria, T. Brown, E. Minear, R.H. Lasseter “CERTS microgrid demonstration with large-scale energy storage and renewable generation” IEEE Trans Smart Grid 2014, 5, 937-943. [CrossRef]
- R. Panora, J. Gehret, M. Furse, R.H. Lasseter “Real-world Performance of a CERTS microgrid in Manhattan” IEEE Trans Sustain Energy 2014, 5, 1356-1360. [CrossRef]
- S. Parhizi, H. Lotfi, A. Khodaei, S. Bahramirad “State of the art in research on microgrids: A review” IEEE Access 2015, 3, 890-925. [CrossRef]
- M.F. Akorede, H. Hizam, E. Pouresmaeil “Distributed energy resources and benefits to the environment” Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev 2010, 14, 724-734. [CrossRef]
- R. Bayindir, E. Hossain, E. Kabalci, R. Perez “A comprehensive study on microgrid technology” Int J Renew Energy Res 2014, 4, 1094-1107.
- T. M. I. Riayatsyah, T. A. Geumpana, I. M. Rizwanul Fattah and T. M. Indra Mahlia “Techno-Economic Analysis of Hybrid Diesel Generators and Renewable Energy for a Remote Island in the Indian Ocean Using HOMER Pro” Sustainability 2022, 14, 9846. [CrossRef]
- C W King, G Gülen, S M Cohen5, and V Nuñez-Lopez”The system-wide economics of a carbon dioxide capture, utilization, and storage network: Texas Gulf Coast with pure CO2-EOR flood” Environmental Research Letter 2013, 8, 034030. [CrossRef]
- Anitha Sarah Subburaj; Preethi Kondur; Stephen B. Bayne; Michael G. Giesselmann; Mark A. Harral “Analysis and Review of Grid Connected Battery in Wind Applications” 2014 Sixth Annual IEEE Green Technologies Conference, 3-4 April 2014. 4 April. [CrossRef]
- M Chamana, K E K Schmitt, R Bhatta, S Liyanage, I Osman, M Murshed, S Bayne, J Macfie “Buildings Participation in Resilience Enhancement of Community Microgrids: Synergy Between Microgrid and Building Management Systems” IEEE Access, Volume: 10. [CrossRef]
- L.M.C. Mhango, “Benefits of Nd-Fe-B magnet in brushless DC motor design for aircraft applications,” 4th IET International Conference on Electrical Machines and Drives 1989, 76-79.
- Y. Arafat, M. Murshed, MA Razzak, “Design and analysis of an outer rotor permanent magnet alternator for a low-speed wind turbine” 3rd International Conference on Green Energy and Technology (ICGET) 2015, 1-7. [CrossRef]
- Y. Arafat, M. Murshed, MA Razzak, “Design and Analysis of an In-Runner Permanent Magnet Alternator for Low-Speed Wind Turbine” 4th International Conference on the Developments in Renewable Energy Technology (ICDRET), 2016, 1-5. [CrossRef]
- J Marqusee, W Becker, S Ericson “Resilience and economics of microgrids with PV, battery storage, and networked diesel generators” Advances in Applied Energy, Volume 3, 25 August 2021. Gyeong-Chan Lee, Su-Min Kang, Tae-Uk Jung, “Permanent magnet structure design of outer rotor radial flux permanent magnet generator for reduction cogging torque with the design of experiment,” International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems, 2013, 315–319. 25 August.
- M L. Shaltout, Z Yan, D Palejiya, D Chen ‘Tradeoff analysis of energy harvesting and noise emission for distributed wind turbines Sustainable Energy Technologies and Assessments 2015, 10, 12-21. [CrossRef]
- R Bhatta, R. Shrestha, C Negri, K Schmitt, M Murshed, M Chamana, O Illham, S. Bayne “Feasibility of a Real-world Test Microgrid Facility to Provide Economic and Resiliency Benefits in Extreme Weather Conditions” 2022 IEEE Power & Energy Society Innovative Smart Grid Technologies Conference (ISGT), 24-28 April 2022. [CrossRef]
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Rated power (Pout) | 6500 W |
| Reference speed (N) | 100 rpm |
| Voltage (V) | 24 V |
| Permanent magnet depth (LPM) | 10.0 mm |
| Stator slots amount (Q) | 54 |
| Poles (P) | 34 |
| Air-gap (g) | 1.0 mm |
| Stator diameter (outer) (Sout) | 208 mm |
| Stator diameter (inner) (Sin) | 92 mm |
| Stator length (L) | 61 mm |
| Rotor diameter (outer) (Rout) | 292 mm |
| Rotor diameter (inner) (Rin) | 270 mm |
| Distributed Wind turbine | Battery | System Converter | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quantity | Value | Units | Quantity | Value | Units | Quantity | Value | Units | ||
| Total Rated Capacity | 6 | kW | Energy In | 2,965 | kWh/yr | Hours of Operation | 8,374 | hrs/yr | ||
| Mean Output | 2.83 | kW | Energy Out | 2,865 | kWh/yr | Energy Out | 23,848 | kWh/yr | ||
| Capacity Factor | 47.1 | % | Storage Depletion | 18.8 | kWh/yr | Energy In | 24,586 | kWh/yr | ||
| Total Production | 24,757 | kWh/yr | Losses | 119 | kWh/yr | Losses | 738 | kWh/yr | ||
| Wind Penetration | 67.8 | % | Annual Throughput | 2,924 | kWh/yr | Capacity | 8 | kW | ||
| Hours of Operation | 8,253 | hrs/yr | Autonomy | 4.63 | hr | Mean Output | 2.72 | kW | ||
| Levelized Cost | 0.035 | $/kWh | Expected Life | 17 | yr | Maximum Output | 8 | kW | ||
| Economics | Units | Grid only | Grid and DER |
|---|---|---|---|
| Discount Rate | % | 3% | 3% |
| Annual Inflation | % | 3% | 3% |
| Project Life Time | Years | 25 | 25 |
| Total Net Present Value | $ | $83,795.64 | $64,985.94 |
| Levelized Cost of Energy | $/kWh | $0.09 | $0.0667 |
| Cost of Energy reduction | % | 0 | 23.00% |
| Capital Investment | $ | 0 | $30,300 |
| Replacement | $ | 0 | $7,100 |
| Salvage | $ | 0 | $7,092 |
| Operation and Maintenance | $ | $83,795.64 | $34,678 |
| Emission Penalty Rate | $/ton | $12/ ton | $12/ton |
| Emission Penalty | $ | $276 | $114 |
| Capital return rate, CRR | % | 0 | 3.82% |
| Simple Payback Period | Years | 0 | 15.4 years |
| Elements | Value (Grid only) | Value (Grid+6kW DHAWT) | Units |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Dioxide | 23,068 | 9,543 | kg/yr |
| Sulfur Dioxide | 100 | 41.4 | kg/yr |
| Nitrogen Oxides | 48.9 | 20.2 | kg/yr |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





