1. Introduction
Tumor metastasis, primarily involves the lymphatic pathway and in this lymph nodes of regional lymphocenter plays a vital role. Both direct lymphography and indirect lymphography techniques can be used to visualize these lymphatic pathways and lymph nodes (Mayer et al.,2013; Brissot and Edery, 2016). Evaluation of a lymph node can be done clinically by using palpation, LN measurement (Beer et al.,2018; Fournier et al., 2018), FNAC (Fournier et al., 2018; Karakitsou et al., 2022), ultrasonography (Beer et al.,2018; Chiorean et al., 2016; Sahoo et al., 2021a), and histopathology (Sledge et al., 2016). Accurate assessment of the locoregional metastases is aided by the identification of initial draining LN or echelon nodes, or SLN in a regional lympho center (Morton et al., 1992; Skinner et al., 2017; Skinner et al., 2018, Sahoo et al., 2021b). Currently, several IL methods are used for assessing the lymphatic and lymph nodes draining the primary tumor mass. Those are vital blue dyes for visual detection (Mayer et al.,2013; Brissot and Edery, 2016), radiocolloid lymphoscintigraphy (Hlusko et al., 2020; Manfredi et al., 2021), radiographic lymphography (Mayer et al.,2013; Lee et al., 2018; Collivignarelli et al.,2021), computed tomography (CT), lymphography (Sarowitz et al., 2017; Grimes et al., 2017;Majeski et al., 2017; Rossi et al.,2018; Lapsley et al., 2020), fluorescent optical imaging or Near-infrared imaging (NIR)(Iida et al., 2913; Wan et al.,2021; Beer et al.,2022), contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS)(Gelb et al.,2010; Fournier et al., 2020), photoacoustic imaging(Garcia-Uribe et al., 2015), SPECT/PET CT(Beer et al., 2018; LeBlanc et al., 2013), Magnetic resonance (MR) lymphography (Turkbey et al., 2015), hybrid tracer (Nyberg et al., 2011), and nanocarriers (Jain et al., 2009). Manual detection of various types of cancerous tissues of canine patients is tedious process. Image processing and machine learning plays an important role for automatic detection of cancerous tissues. Automatic cancer detection system can be developed by applying image processing and machine learning techniques. Doctors can use automated system to take second opinion regarding this disease. Deep learning based VGGNet-16 along with support vector machine and random forest techniques are applied for classification of canine mammary tumor by using histopathological images (Kumar et al., 2020). Authors achieved highest 97% accuracy with VGGNet-16. Machine learning technique is applied to detect liver tumor of dogs by extracting texture features of CT-scan images (Shaker et al., 2021). They obtained 90%, 67%, and 100% accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity, respectively. The goal of present research is to validate the identification of tumor and lymph nodes with those analyzed through preliminary machine learning approach.
Indirect lymphography technique using three contrast agents viz. Iohexol, Lipiodol, and Methylene blue (MB) detects Sentinel lymph node (SLN) in canine solid tumors.
SLN detected in buttock sarcoma, cutaneous histiocytic sarcoma for the first time. Immunostaining of inguinal lymph node (LN) detects Lipiodol after one month, which clearly indicates its lymphotropic nature.
Lipiodol showed highest detection rate in skin tumors of forelimb, hind limb, and mammary gland whereas MB is very good in intraoperative SLN detection in mammary carcinoma.
Automatic cancer detection and classification system of canine patients is developed by applying image processing and supervised machine learning technique. Various statistical and texture-based features are extracted from X-Ray images and support vector machine with linear, polynomial, multilayer perceptron (MLP), and RBF kernel functions are applied for classification.
2. Material and Methods
The present study described 96 clinical cases of client-owned dogs with primary tumor masses referred to the department of Surgery, between October 2018 and February 2021.The study was approved by institutional animal ethical committee (IAEC). The various steps followed for this study is given in the following subsections.
2.1. Preclinical work up and clinical staging
Preclinical workup and clinical staging of all patients were done by physical examination, clinical symptoms, radiography, ultrasound scanning (GE Healthcare, Ireland), blood biochemistry, cytology (FNAC or impression smear), tissue biopsy or histopathology, CT scan of the tumor and lymph node.
2.2. Sentinel lymph node (SLN) Localization
Localization of SLN is performed through four types of IL technique:
indirect radiographic lymphography with Lipiodol Ultra-FluidTM (iodized ethyl-esters of the fatty acids of poppy seed oil, an oil-based nonionic iodine contrast agent, Guerbet, Aulnay-sous-bois, France; 480 mg iodine per ml).
IL with methylene blue (MB) dye (5mg/ml)
indirect radiographic lymphography with Omnipaque300 (Iohexol – a water-soluble nonionic iodine contrast agent (300mgI/ml), GE Healthcare, USA),
iohexol-based indirect CT lymphography. Brief description of each technique is given in next subsections.
-
(i)
Indirect radiographic lymphography with Lipiodol Ultra-Fluid
Indirect radiographic lymphography was performed with intradermal/submucosal injection of 2ml Lipiodol with a tiny gauge needle (24G needle or insulin syringe) in four-quadrant principle (at 12, 3, 6 and 9 o'clock position and dispersed in equal aliquot @ 0.5mL per site) at the peritumoral site, accomplished in a slow rate (at 2mL/min). Two orthogonal views (lateral and ventrodorsal views) of radiography images are recorded at intervals of 30 minutes, an hour, and 24hours following contrast injections to observe the uptake by first lymph node.
-
(ii)
Indirect lymphography with methylene blue dye
IL with MB dye (5mg/mL) is performed intradermally/subcutaneously and peritumorally in four-quadrant principle (equal aliquot of 0.5mL/site) using a 24G needle or insulin syringe, intraoperatively within 0.5 cm from primary tumor mass, and surgery began 10-15 min afterwards. The superficial lymphatic pathway from the injection site to the first draining LN was identified by dissecting skin flaps and monitoring the flow of dye. Visual evaluation of in vivo MB uptake indicated that nodes with dark blue coloring are acceptable, very pale blue coloration was fair, and absence of coloration or non-identification was unsatisfactory.
-
(iii)
Indirect radiographic lymphography with omnipaque-300 (iohexol)
Indirect radiographic lymphography with iohexol was performed in a similar four-quadrant concept (0.5mL per site) with a 22G 5mL syringe, with injections made intradermally and peritumorally at a distance of 0.5cm from the original lesion. To see how iohexol moved through the lymphatic system and into the first draining lymph node, digital radiography images were taken immediately after the injection (0 to 2 minute), then at 3, 5, 10, and 20 minutes.
-
(iv)
Indirect CT lymphography with iohexol
For indirect CT lymphography, patients were sedated on the CT table with injection Atropine sulphate (0.04 mg/Kg body weight) and injection Tiletamine, Zolazepam (Zoletil®, Virbac NZ) @ 10 mg/kg body weight). Precontrast CT study of the abdomen and pelvis was performed with 2.0 to 5.0-mm slices thickness in a 16- slice Siemen’s CT scanner. Technical settings were kept as 120-150 kV, mAs 60-200,512x 512 matrix, 250-500 mm field of view. Subsequently, Indirect CT lymphography is conducted via peritumoral injection (subcutaneous injection) of 2mL of iohexol in four-quadrant concept. CT scan was taken immediately after injection and then every 1, 3, 5, 10 min until the enhanced lymph nodes are visible. Medical image viewing software was used to measure images in DICOM format. A first-tier node, also referred to as an echelon node, is the node inside the regional lymphocenter that received the initial uptake of contrast material.
2.3. Automatic classification of cancerous and non-cancerous images using Machine learning technique
In this step, X-Ray images are used for automatic classification of cancerous and non- cancerous regions by applying machine learning techniques. The 300 regions are cropped from collected images which include 160 cancerous and 140 non-cancerous regions. Next, feature extraction is performed to characterize the cropped regions. Finally, support vector machine is used for classification of images as cancerous or non-cancerous. The description of extracted features and classifiers are given in next sub-sections.
2.4. Feature Extraction
Textural features play an important role to extract the meaningful information from the gray scale images. Texture features contain spatial relationship among pixels and gray value variations in the suspicious region. First order statistical and GLCM features are used to detect the cancerous regions in X-ray images.
2.5. First Order Statistical Features
Six first order statistical features namely mean, average contrast, skewness, kurtosis, energy and entropy are extracted from the suspicious ROI (Materka et al. 1973) For an image with probability density of intensity levels and maximum gray levels M, these features are expressed as:
Mean represents the average intensity value of image.
Average contrast gives intensity variation around the mean.
Skewness measures the histogram asymmetry around the mean.
Kurtosis represents the flatness of histogram.
Entropy indicates the randomness of intensity value of image.
The probability density of intensity levels
is calculated by
where
is total number of pixels with intensity value
and
is the total number of pixels in the image.
2.6. Gray Level Co-occurrences Matrix Features (GLCM)
GLCM gives the second-order features to generate texture attributes (Haralick
et al.1973
). GLCM represents distribution of intensities and the information about the relative positions of neighboring pixels of an image. The elements of GLCM represent the joint probabilities
of all pair wise combinations of gray level
and
. These pairs should be separated by a distance
in the given orientation
of a spatial window. The elements of GLCM can be represented as:
where, M denotes total number of gray levels,
represents number of occurrences of gray levels
and
within given spatial window in given pair
.
=
entry in marginal probability matrix obtained by summing the rows of
Assuming and
Fifteen GLCM features extracted from the segmented regions are represented as:
Energy, also known as uniformity or angular second moment, measures the textural uniformity, i.e., pixel pair repetitions.
Entropy measures the randomness of an image. It is large when the image is not texturally uniform.
Contrast measures the intensity difference between a pixel and its neighbor over the entire image.
Correlation measures how the pixel is correlated to its neighbors over the entire image.
where µ
x, µ
y, σ
x, and σ
y denote means and standard deviations of marginal probability matrix of g
x andg
y respectively.
Autocorrelation provide a measure of gray-tone dependencies in the image.
Maximum probability measures the strongest response of co-occurrence matrix.
Homogeneity, also known as inverse difference moments, measures the spatial closeness of the distribution of elements in co-occurrence matrix diagonally.
Variance measures image heterogeneity and is strongly correlated to standard deviation. It increases when the gray values differ from their mean.
The following features are secondary and defined in terms of the features discussed above:
Sum average is obtained from the pixel in consideration and the size of gray scale.
Sum Entropy is calculated as the logarithmic function of the image in consideration.
Sum Variance is calculated from the original image and the sum entropy (se).
Difference Entropy measures non-uniformity when difference measure obtained from the original image is considered.
Difference Variance is a variance measure between image intensities calculated as a function of the sum entropy (se).
Information Measure of Correlation1 (IMC1)
Information Measure of Correlation2 (IMC2)
2.7. Classification
SVM is used to discriminate cancerous and non-cancerous regions. It is a supervised machine learning technique which creates the hyper-plane to separate the objects of different classes (Cortes
et al. 1995). It creates support vectors to identify the boundaries between two classes. The optimal position of the hyper-plane is determined by the support vector. Suppose
represents a training set of
feature vectors in
dimensional feature space and
represents the class labels associated with
Normal and abnormal tissues are denoted by class label +1 and -1, respectively. Linear separable feature vector is accomplished by defining a hyper-plane as:
where
is normal to the hyper plane and
is threshold parameter. Generalized form of these equations can be expressed as:
Distance between two hyper planes is given as
. Better separation can be achieved between two classes for the optimized (maximum) value of the distance of two hyper planes. Maximum distance between two hyper planes is inversely proportional to
. Lagrangian function is used to obtain maximum distance and can be expressed as:
where
is a lagrangian multiplier of dual optimization problem that explains separating hyperplane
.
is classified as member of the positive class for all values of
otherwise it belongs to the negative class. The simplest way to separate two groups of data is with straight line (1-dimensional), flat-plane (2 dimensional) and N-dimensional hyper-plane. In many situations non-linear regions can separate the data more efficiently. SVM handles this situation by applying kernel function to map the data into different feature space where hyperplane is unable to group the data. SVM transform the data into higher dimensional feature space where linear separability is possible by applying kernel trick. SVM use various kernel functions such as linear, polynomial, RBF and MLP (Sigmoid) which are mathematically represented as:
| Kernel Function () |
Mathematical Description |
| Linear |
|
| Polynomial |
|
| RBF |
|
| MLP |
|
where,
is adjustable parameter,
is capacity constant,
is order of polynomial, and
, i.e., kernel function represents a dot product of data points mapped into higher dimensional feature space by transformation
3. Results
Four types of indirect lymphography (IL) technique was used for detection of sentinel lymph node in seven major cancer types: (i) oral and maxillofacial cancer in 14 subjects, (ii) anal sac tumors in 14 subjects, (iii) cancer of the skin and subcutis in 20 subjects, (iv) soft tissue sarcoma in 14 subjects, (v) lymphosarcoma in 6 subjects, (vi) cancer of male genital system in 5 subjects, and (vii) mammary carcinoma in 23 subjects. Four types of IL methods effectively detect SLNs in oral squamous cell carcinoma, fibromatous epulids, oral and maxillofacial osteosarcoma, ossifying epulids, and basal cell carcinoma.
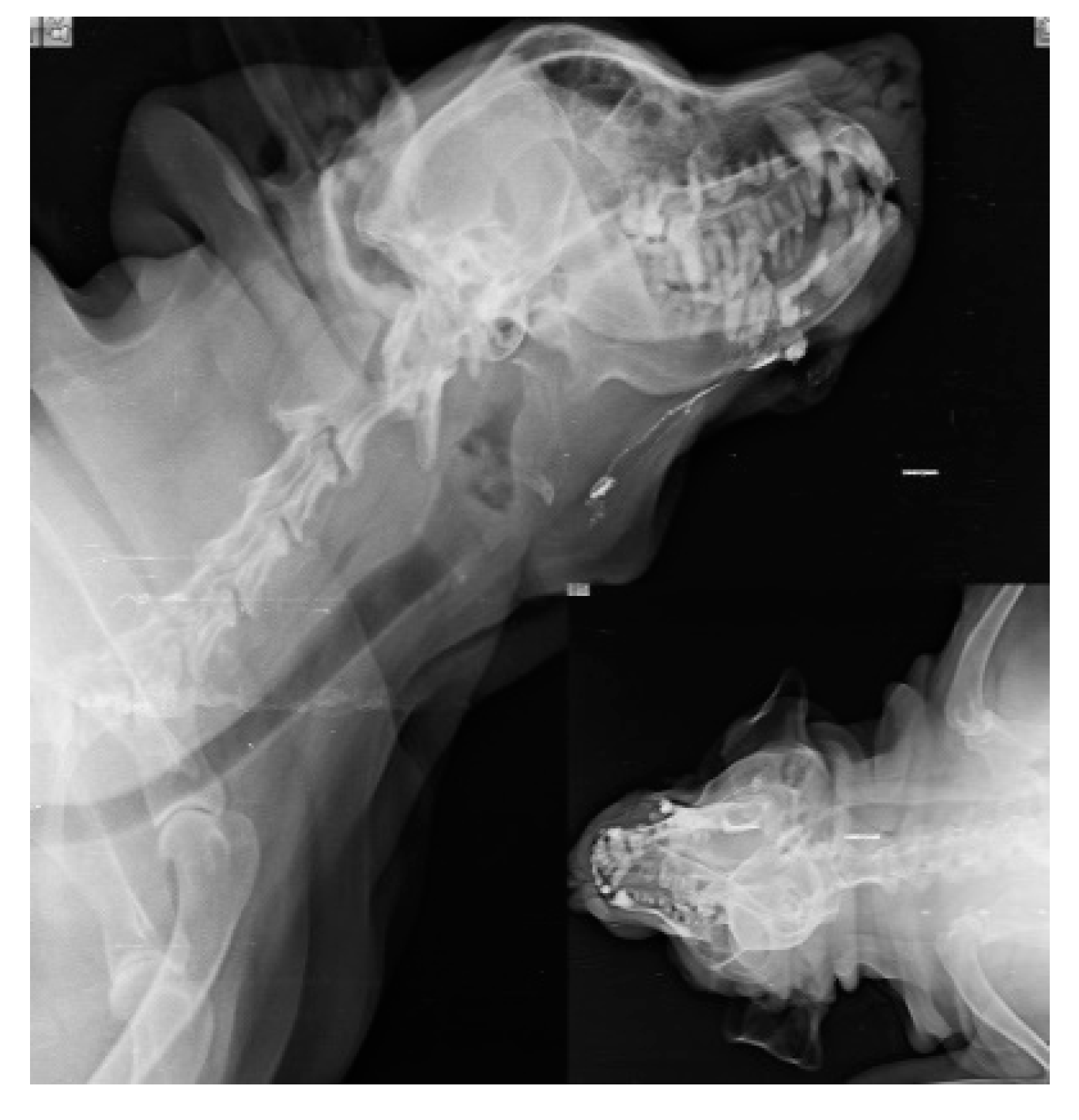
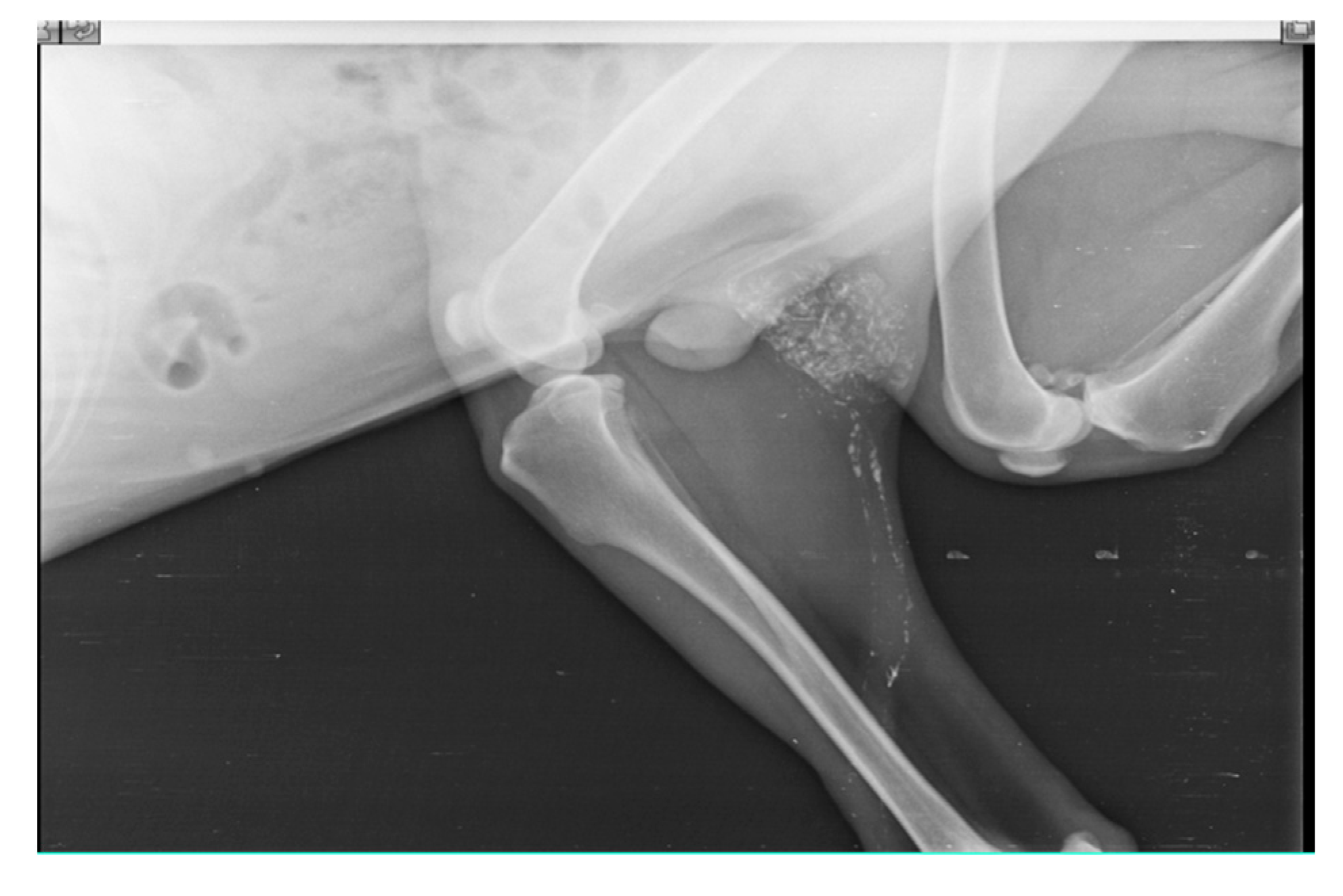
When injections are performed submucosally within 0.5cm from the tumor margin of oral SCC along with messaging in the direction of lymphatic flow, Lipiodol Ultrafluid successfully localize the mandibular lymph node in 6 subjects as SLN within 24 hours as shown in Fig.1. SLN (Mandibular LN) is discovered after 24 hours; when, the injection site is subcutaneous and more than 0.5cm from the underlying tumor (oral SCC). Out of 14 cases, SLN is identified in 10 cases, with 8 of them are found positive for metastases through biopsy, and 3 cases of SCC had a recurrence.
Figure 1.
lymphatic drainage pathway (white line) from oral squamous cell carcinoma (primary lesion) to Mandibular lymph node (Sentinel lymph node).
Figure 1.
lymphatic drainage pathway (white line) from oral squamous cell carcinoma (primary lesion) to Mandibular lymph node (Sentinel lymph node).
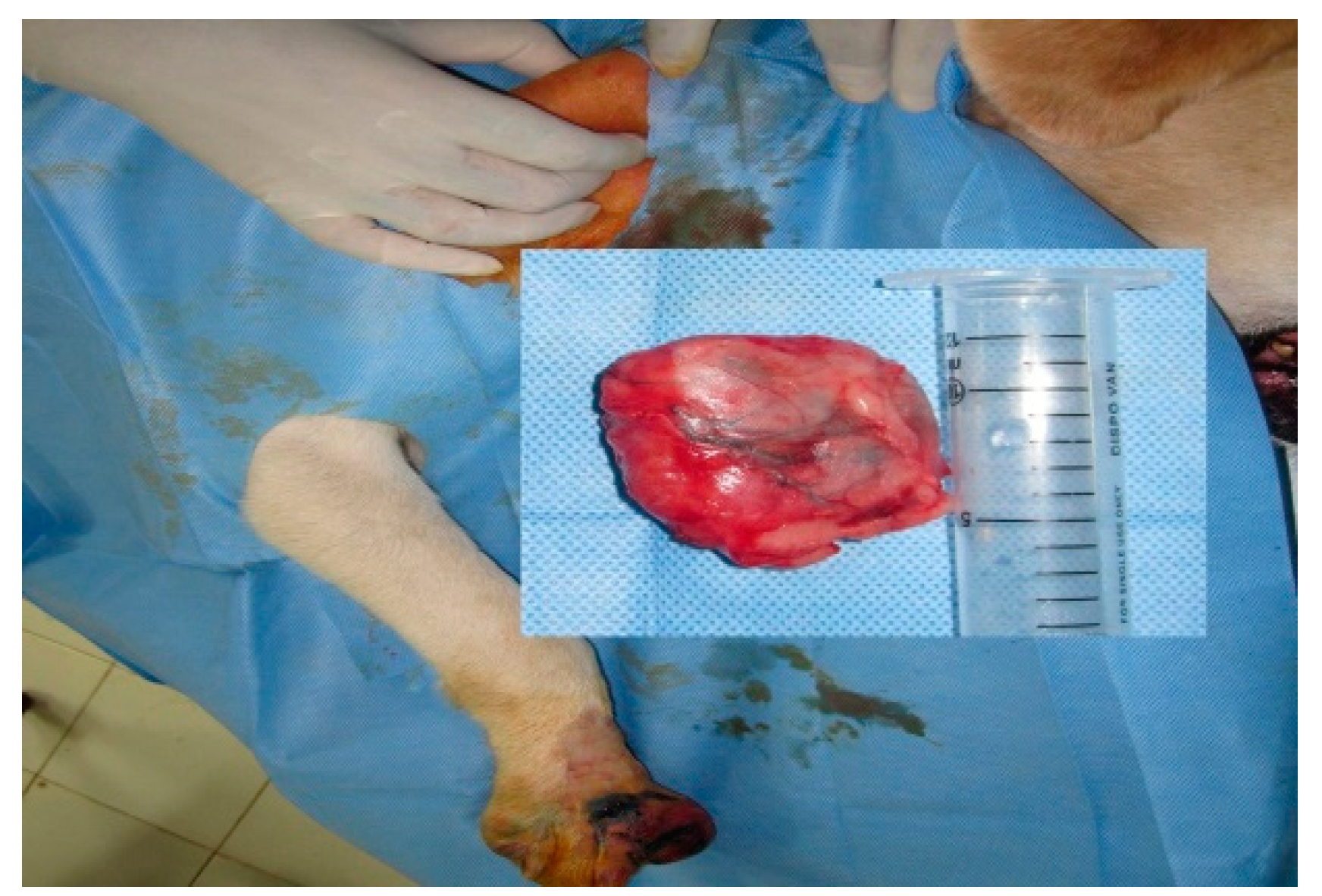
Out of 14 cases in perianal tumors (anal sac apocrine gland adenocarcinoma (ASAGAC) (n=11) and perianal gland adenocarcinoma (n=3), IL with MB is performed in 3 cases, IL with iohexol in 3 cases, and IL with Lipiodol in 8 cases. The medial iliac lymph node (n=4) is detected as the SLN for these cancers, when mapping is done with Lipiodol as shown in Fig. 2. Ultrasound-guided biopsy of miLN yields positive for metastases (n=2) which is a negative prognostic indicator. Closed anal sacculectomy and histopathology identify a solid type of ASAGAC (n=8).
Figure 2.
Medial iliac lymph node as SLN in Anal Sac apocrine gland adenocarcinoma.
Figure 2.
Medial iliac lymph node as SLN in Anal Sac apocrine gland adenocarcinoma.
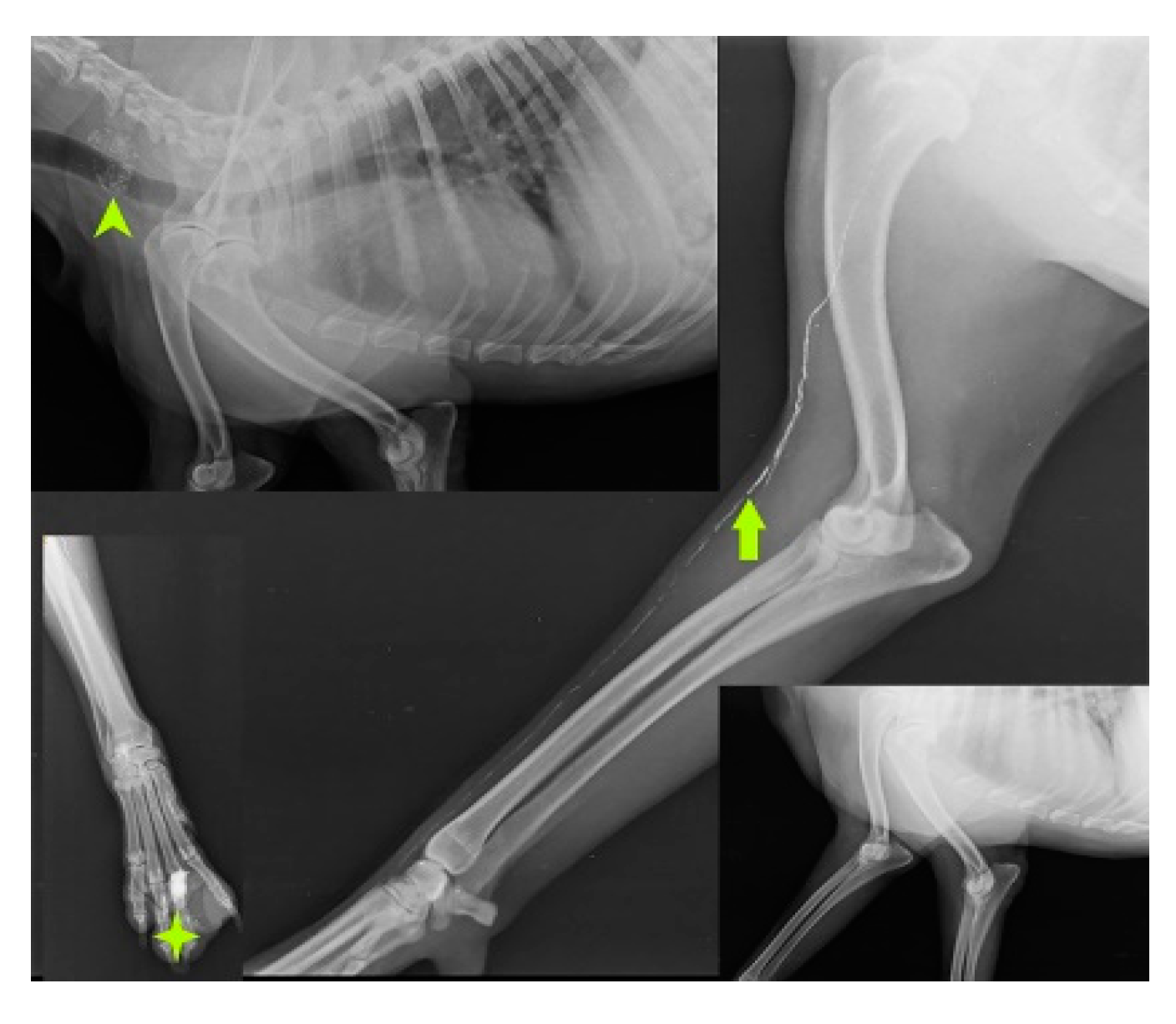
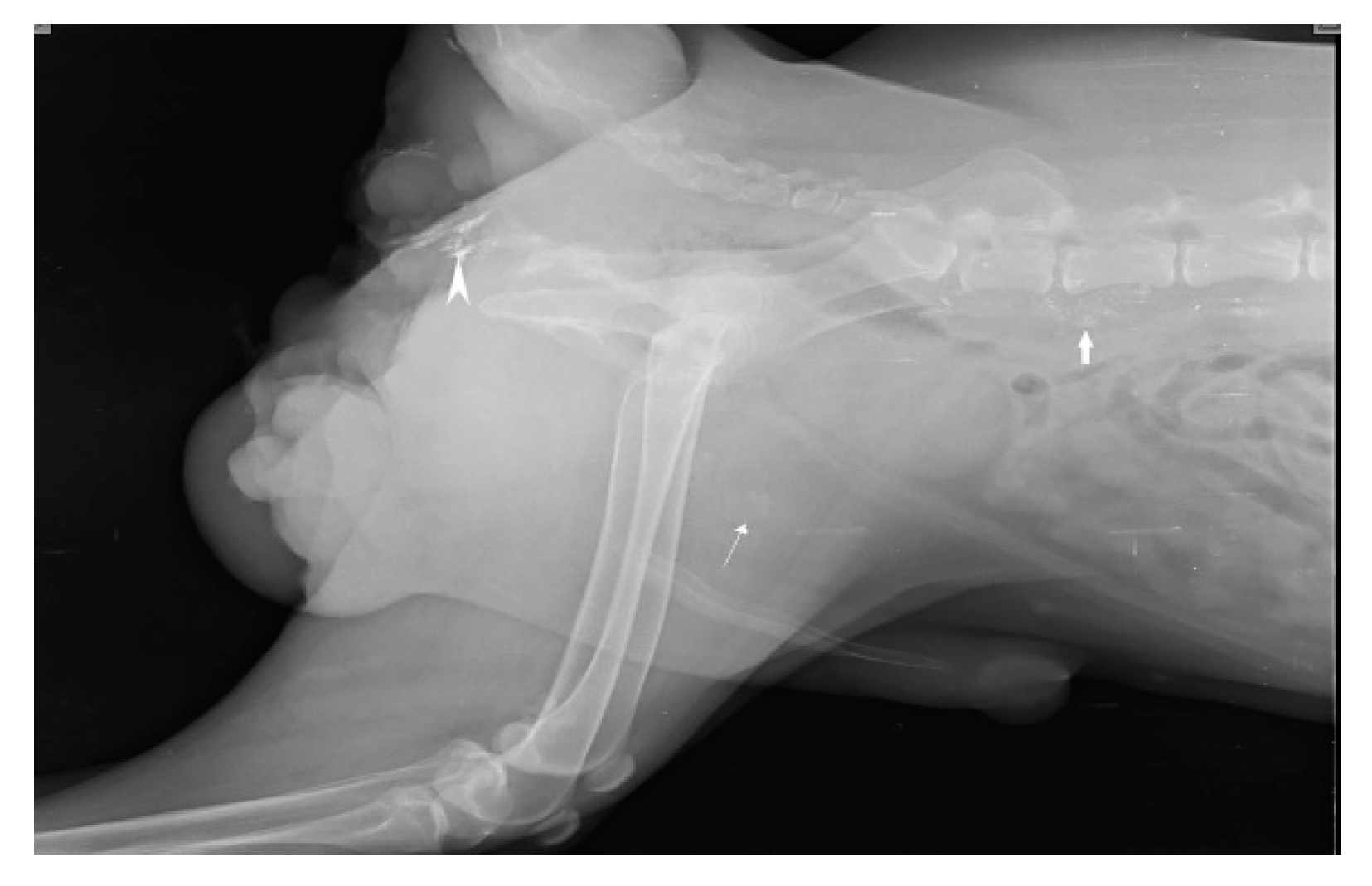
SLN mapping for 20 primary tumors (MCT-11, SCC-3, basal cell carcinoma-1, canine papillomatosis-3, cutaneous plasmocytoma-1, sebaceous gland adenocarcinoma-1) of skin and subcutaneous tissue is performed with four IL methods. MCT weighing 7.8 kg, 3kg, 1.9kg, 1.8kg, 300g, 250g, and lymph nodes weighing 3g, 5g, 10g, up to 90g are excised through en bloc surgical resection with a broad margin. According to the Patnaik grading system (Patnaik et al., 1984), the clinical staging of 11 MCT is Grade III (n=5), Grade II (n=3), and Grade I (n=3). In MCT(n=11), IL with Lipiodol results in 100% detection rate. SLN are detected within 24hr of injections along with gentle messaging in Lipiodol whereas 2 min of injection in iohexol(n=2). Six of the 15 SLN, discovered through cytology and biopsy are determined to be non-metastatic, whereas the other 9 are found to be positive for metastasis. IL was unable to detect any lymph node in rest 5 cases. The SLN for tumors in the front leg is the cervical lymph node as shown in Fig.3.
Figure 3.
Cervical lymph node (arrow head) as sentinel lymph node for mast cell tumor (solid star) of front leg.
Figure 3.
Cervical lymph node (arrow head) as sentinel lymph node for mast cell tumor (solid star) of front leg.
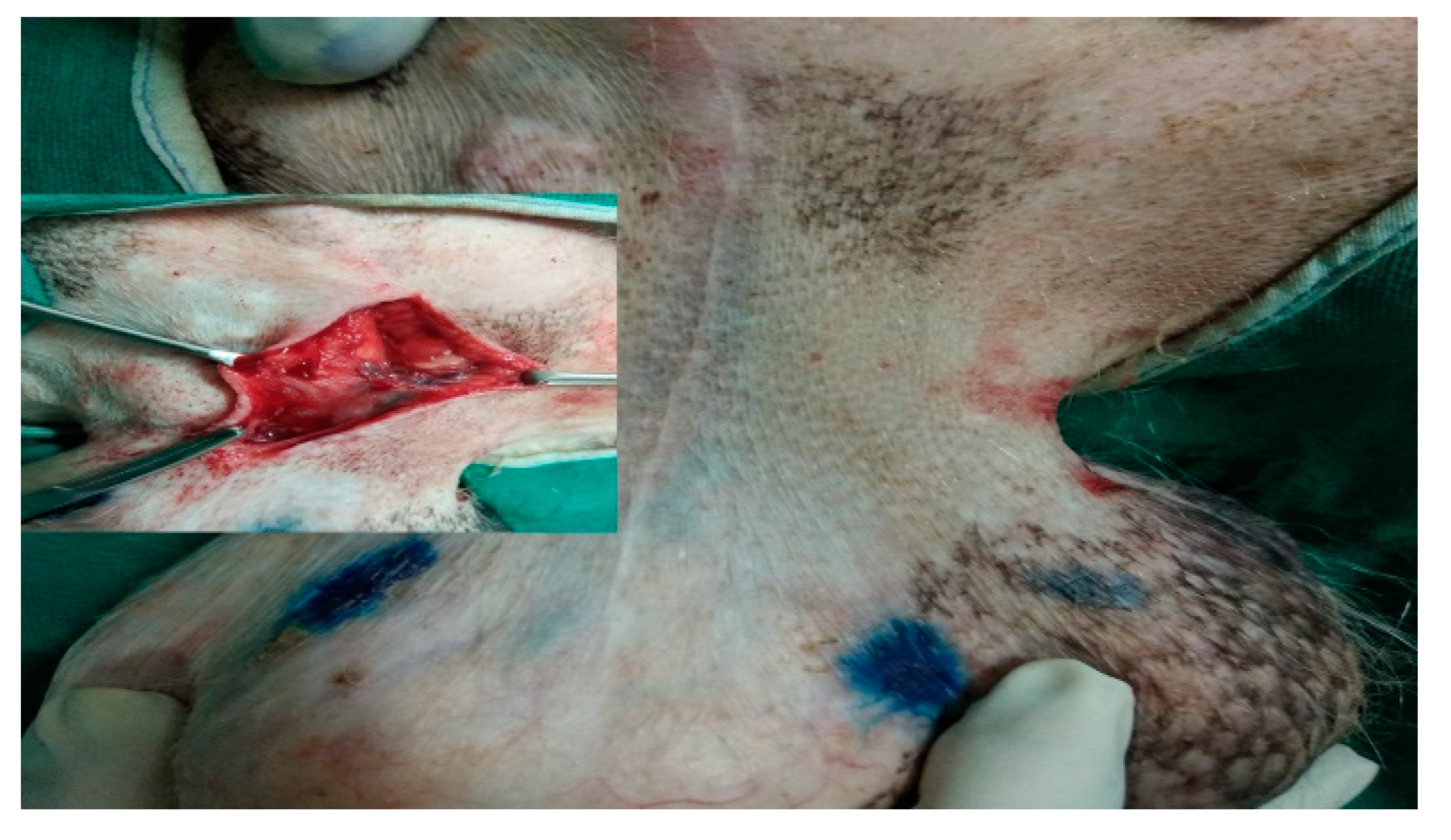
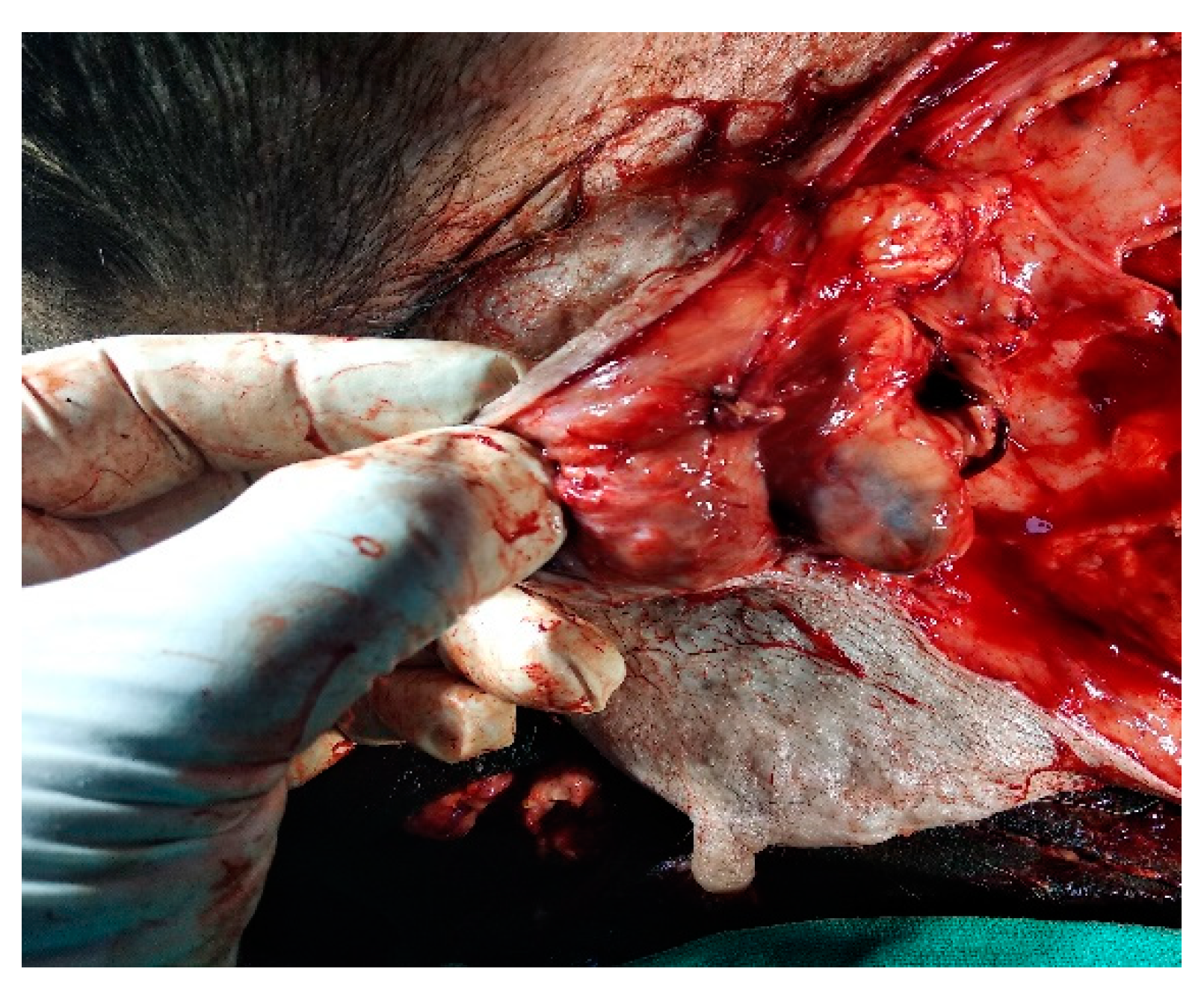
IL with MB employed in the second digit of the right front leg with recurrent MCT perioperatively and cervical lymph node stained blue within 10-15 min of injection as shown in Fig. 4.
Figure 4.
cervical LN (inset mass) as SLN detected using MB dye in front leg.
Figure 4.
cervical LN (inset mass) as SLN detected using MB dye in front leg.
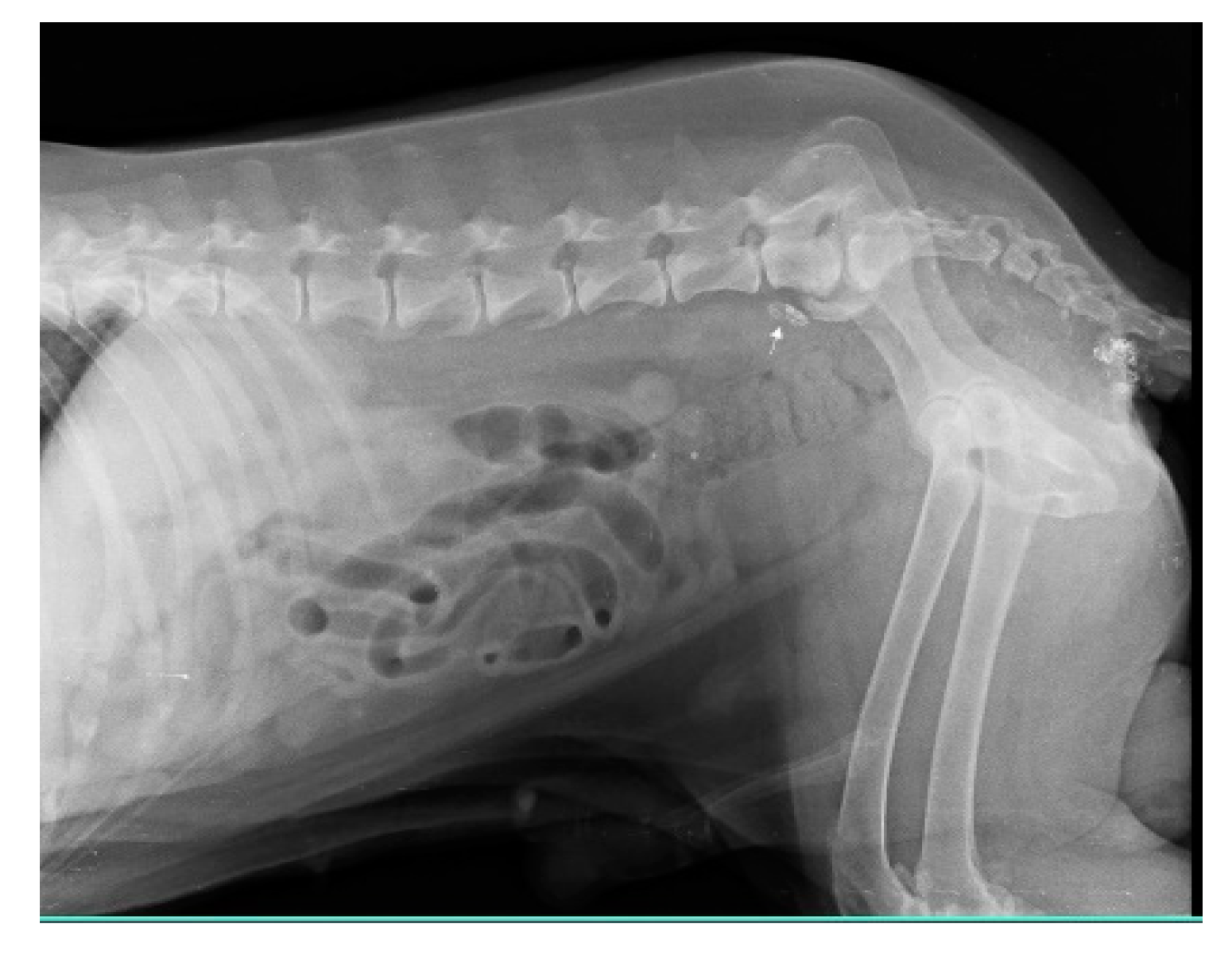
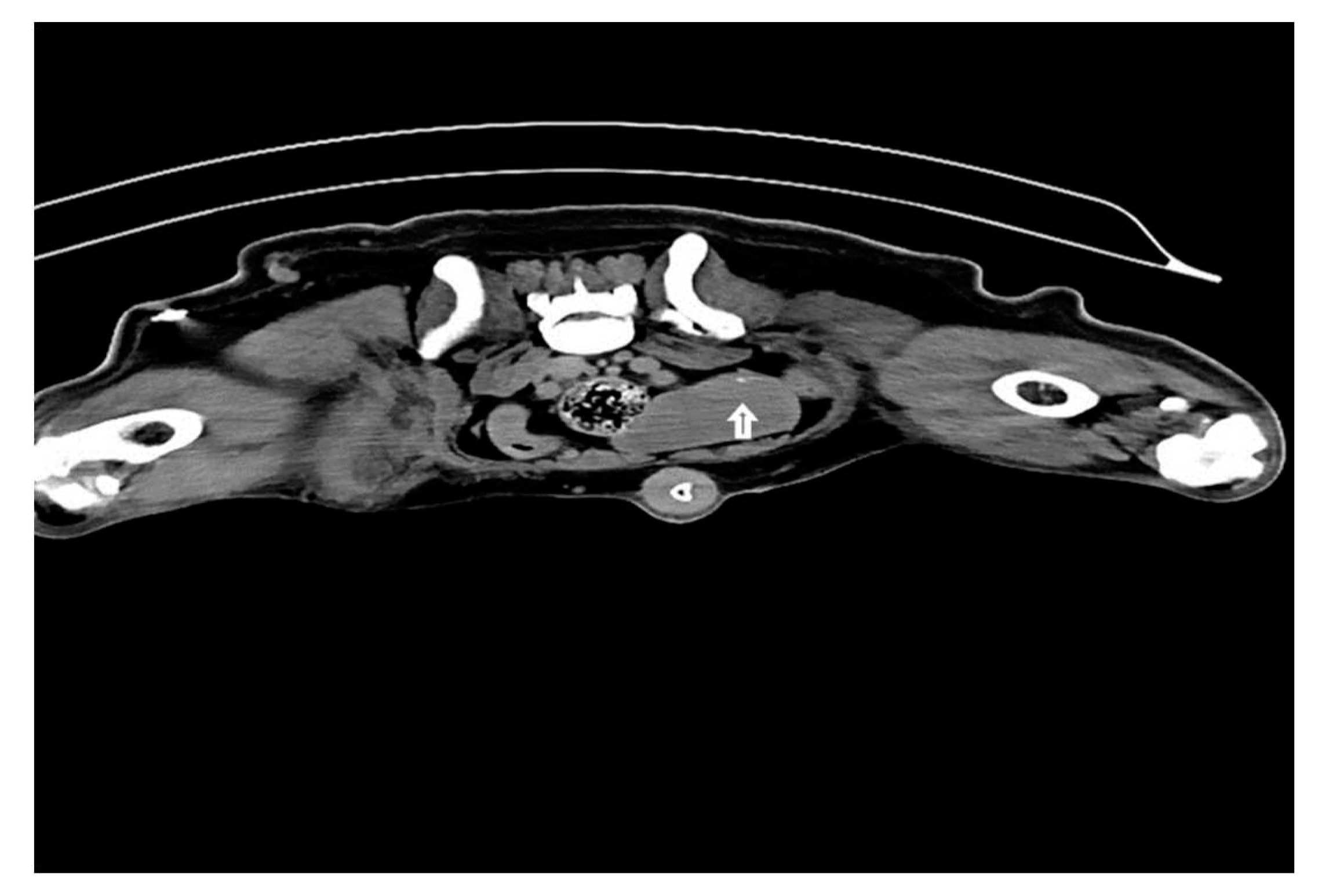
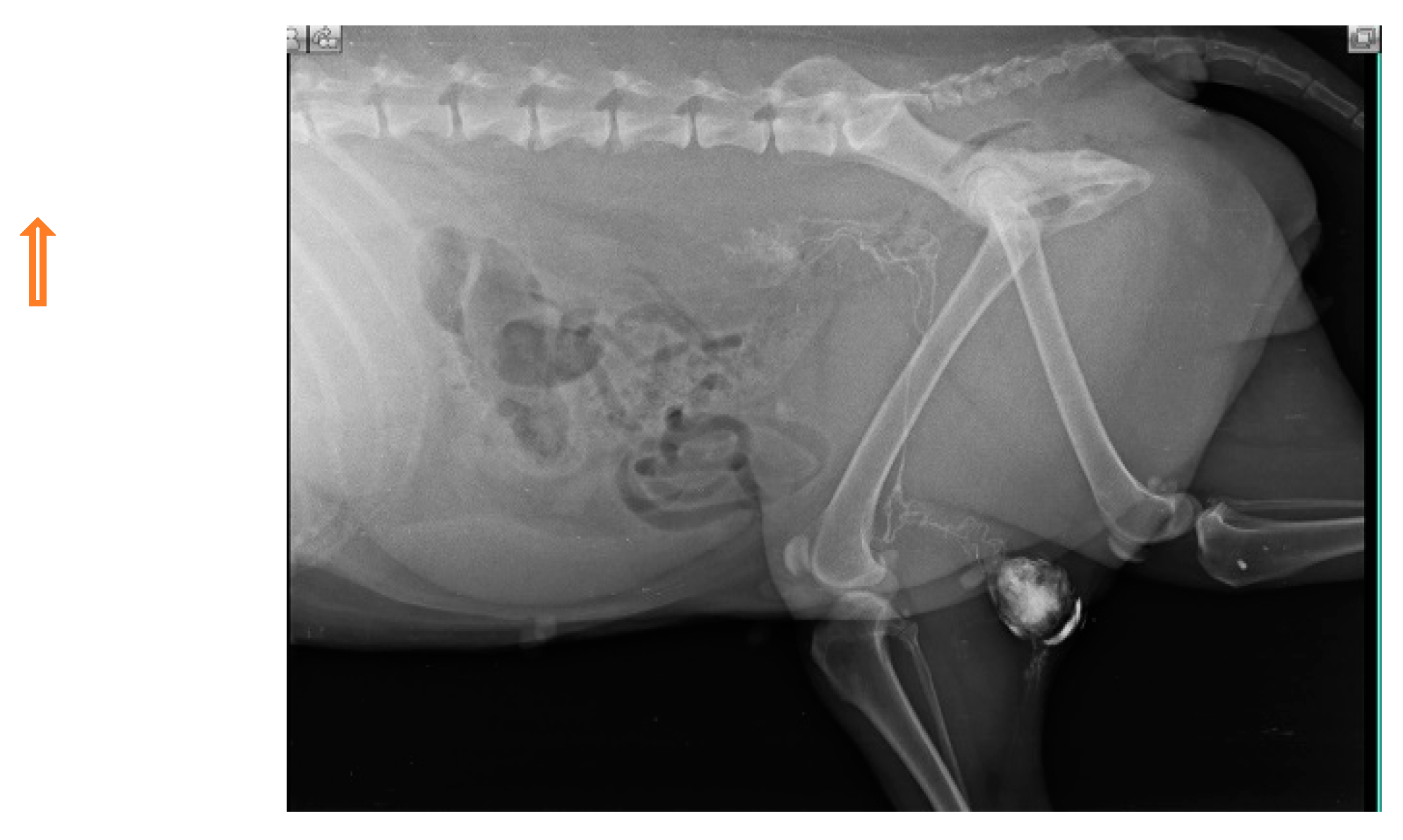
Injections of iohexol into the MCT of the hind leg immediately identify popliteal LN as SLN within 1-2 min. Indirect CT lymphography with iohexol in MCT of upper thigh detects inguinal LN as SLN and miLN as second-tier node in 2 min of intradermal and peritumoral injection in MCT of the hindleg as shown in Fig. 5.
Figure 5.
Inguinal LN (contrast enhanced pointing arrow) was detected as SLN in MCT of right upper thigh.
Figure 5.
Inguinal LN (contrast enhanced pointing arrow) was detected as SLN in MCT of right upper thigh.
To prevent any sort of allergic reaction and mast cell activation in the case of multiple MCT, only IL with iohexol was used. In SCC of hindleg, Popliteal LN (PoLN, Patchy contrast uptake) was localized as SLN within 24 hours of Lipiodol injection as shown in Fig. 6 and PoLN was also found positive for metastases on biopsy.
Figure 6.
Popliteal LN (PoLN, Patchy contrast enhanced) as SLN in hindleg SCC.
Figure 6.
Popliteal LN (PoLN, Patchy contrast enhanced) as SLN in hindleg SCC.
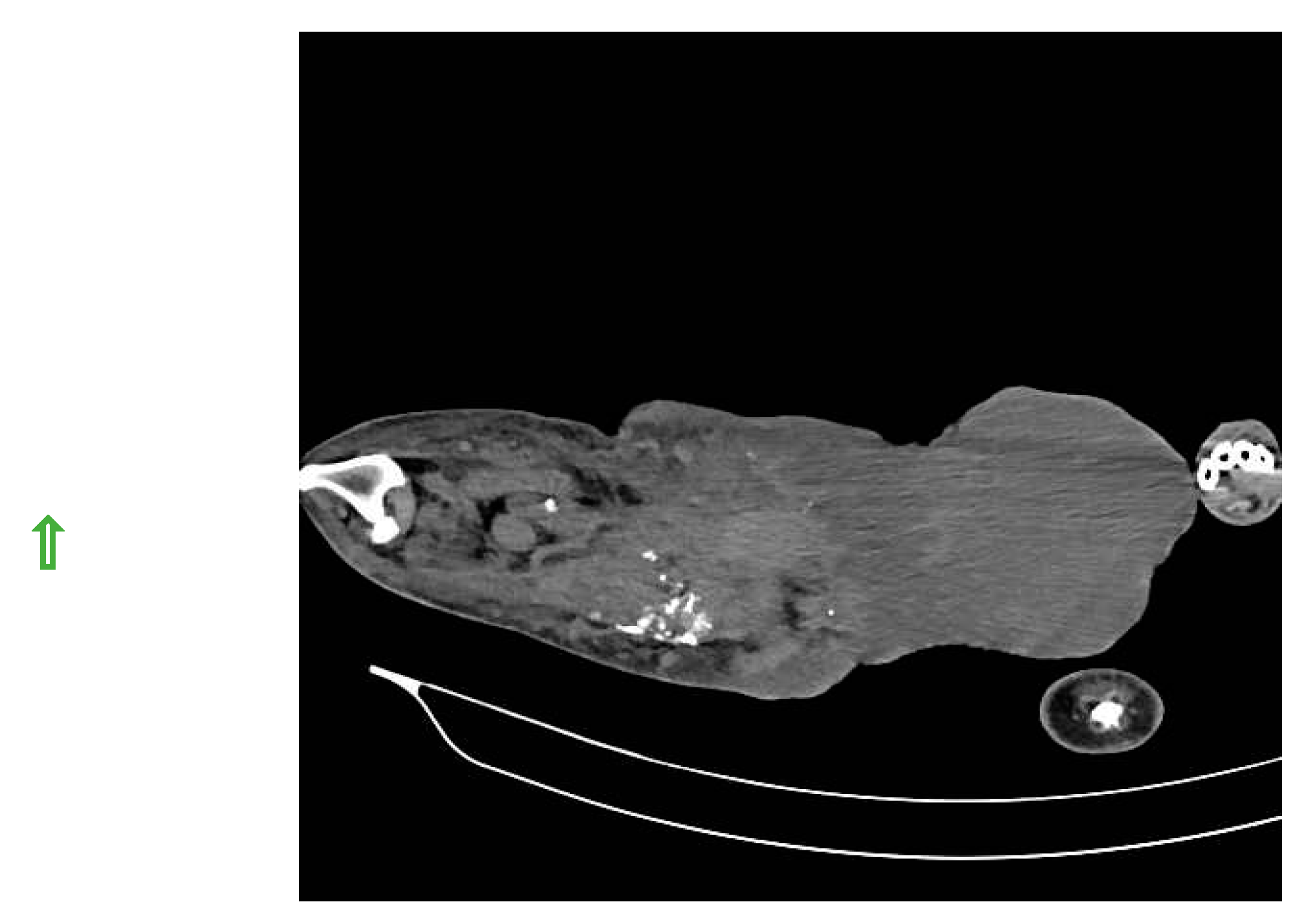
SLN was detected in histiocytic sarcoma (n=4) and buttock sarcoma (n=3) only, and not localized in other soft tissue sarcoma (n=7) (lipoma, liposarcoma, infiltrative lipoma, cavernous hemangioma and cutaneous fibrosarcoma). Indirect CT lymphography with iohexol injection in histiocytic sarcoma detects inguinal LN as SLN (
Figure 7) and miLN as a second-tier node within 2 min, and the inguinal node is found metastasis-free on cytology and biopsy.
Figure 7.
Inguinal LN as SLN in histiocytic sarcoma detected through indirect CT lymphography with iohexol.
Figure 7.
Inguinal LN as SLN in histiocytic sarcoma detected through indirect CT lymphography with iohexol.
IL with Lipiodol in recurrent buttock sarcoma (operated six times) detects lymphatic flow to right inguinal LN only after 24 hours and to miLN after 48 hours as shown in Fig. 8. The opacity was noticeable upto 28 days of injection.
Figure 8.
Inguinal LN (plain arrow) as SLN for buttock sarcoma detected through IL with Lipiodol and miLN (solid arrow) is the second-tier node.
Figure 8.
Inguinal LN (plain arrow) as SLN for buttock sarcoma detected through IL with Lipiodol and miLN (solid arrow) is the second-tier node.
In multicentric lymphosarcoma (n=6), within minutes of peritumoral and intradermal injection of iohexol in popliteal LN, deep inguinal LN and miLN were discovered as SLN as shown in Fig. 9.
Figure 9.
Lymphatic channel from popliteal lymph node to inguinal lymph node and then to medial iliac lymph node (solid white arrow) in multicentric lymphosarcoma.
Figure 9.
Lymphatic channel from popliteal lymph node to inguinal lymph node and then to medial iliac lymph node (solid white arrow) in multicentric lymphosarcoma.
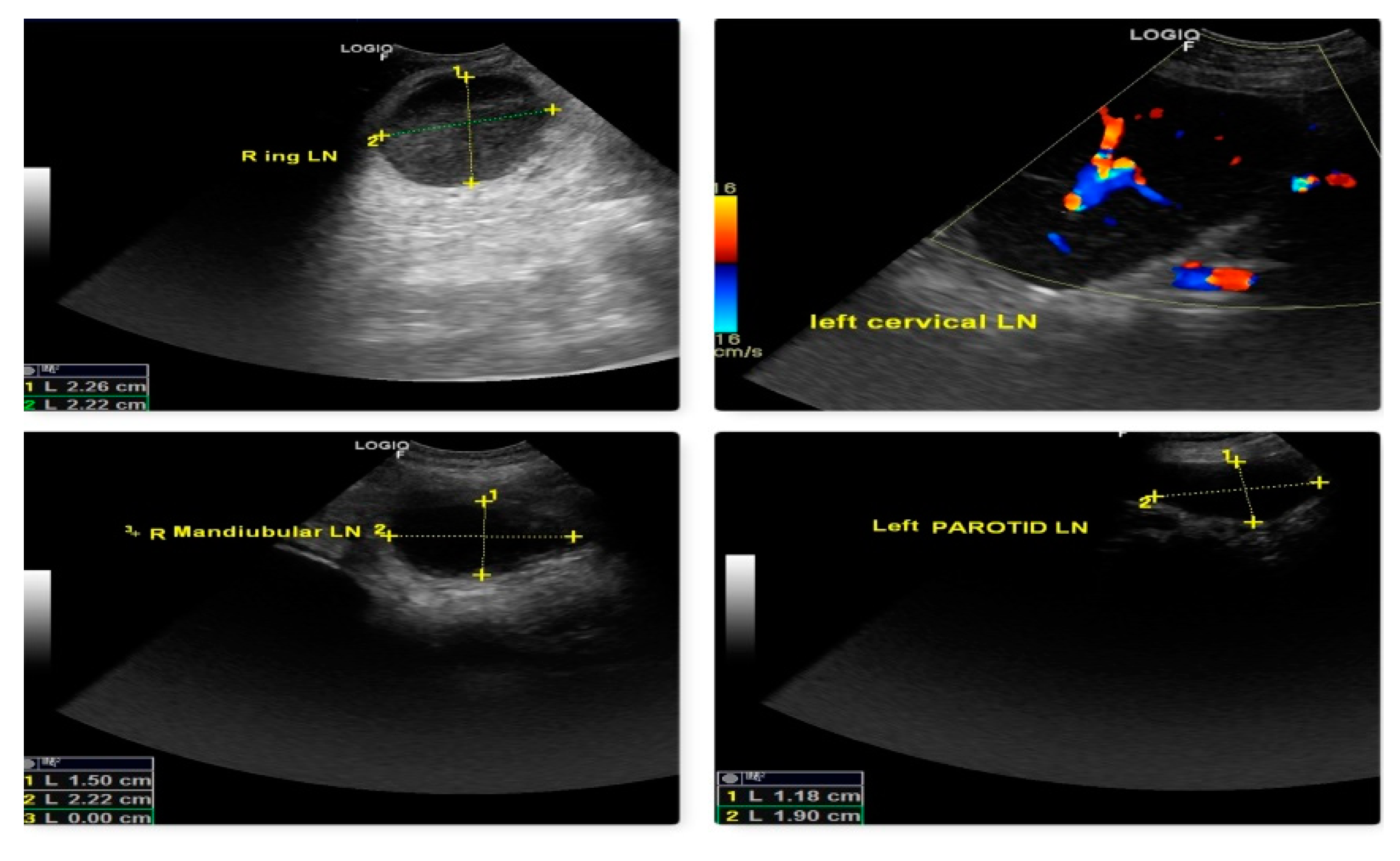
The malignancy criteria of the peripheral LN (submandibular, parotid, cervical, axillary, inguinal, and popliteal LN) were clearly described by ultrasonography. These criteria include oval form with S/L ratio 1, peripheral and central vascularization, and hypoechoic nodes as shown in Fig. 10, which are confirmed by cytology and biopsy. In the case of a primary tumor mass (lymphoma at 3rd molar) in the mouth cavity, mandibular LN were recognized as SLN within 2 minutes of indirect CT lymphography with iohexol. All superficial LN were found to have metastasized in lymphosarcoma which was a poor predictor of survival time.
Figure 10.
Malignant changes observed through B-mode USG and color Doppler as generalized lymphedema (hypoechoic texture with S/L ratio ≤ 1, peripheral and central vascularization) in lymphosarcoma (ocular form).
Figure 10.
Malignant changes observed through B-mode USG and color Doppler as generalized lymphedema (hypoechoic texture with S/L ratio ≤ 1, peripheral and central vascularization) in lymphosarcoma (ocular form).
The SLN for cancers of the male genital system (n=5) was the inguinal LN (TVT, mixed germ cell-stromal cell tumor). Within 10 minutes of intradermal and peritumoral MB dye injection, progression of the blue-stained lymphatic channel from the primary tumor mass (testicular tumor, mixed germ cell-stromal cell tumor) to the inguinal LN (enlarged, hard, fixed, and bilateral) is seen as in Fig. 11. Metastasis was detected in the excised inguinal LN by cytology. In TVT (n=2), within 2 minutes of injection, IL with iohexol detects inguinal LN as SLN in two cases, however those cases have not shown evidence of metastasis.
Figure 11.
Flow of MB dye through blue stained lymphatic from testicular tumor to inguinal LN (SLN).
Figure 11.
Flow of MB dye through blue stained lymphatic from testicular tumor to inguinal LN (SLN).
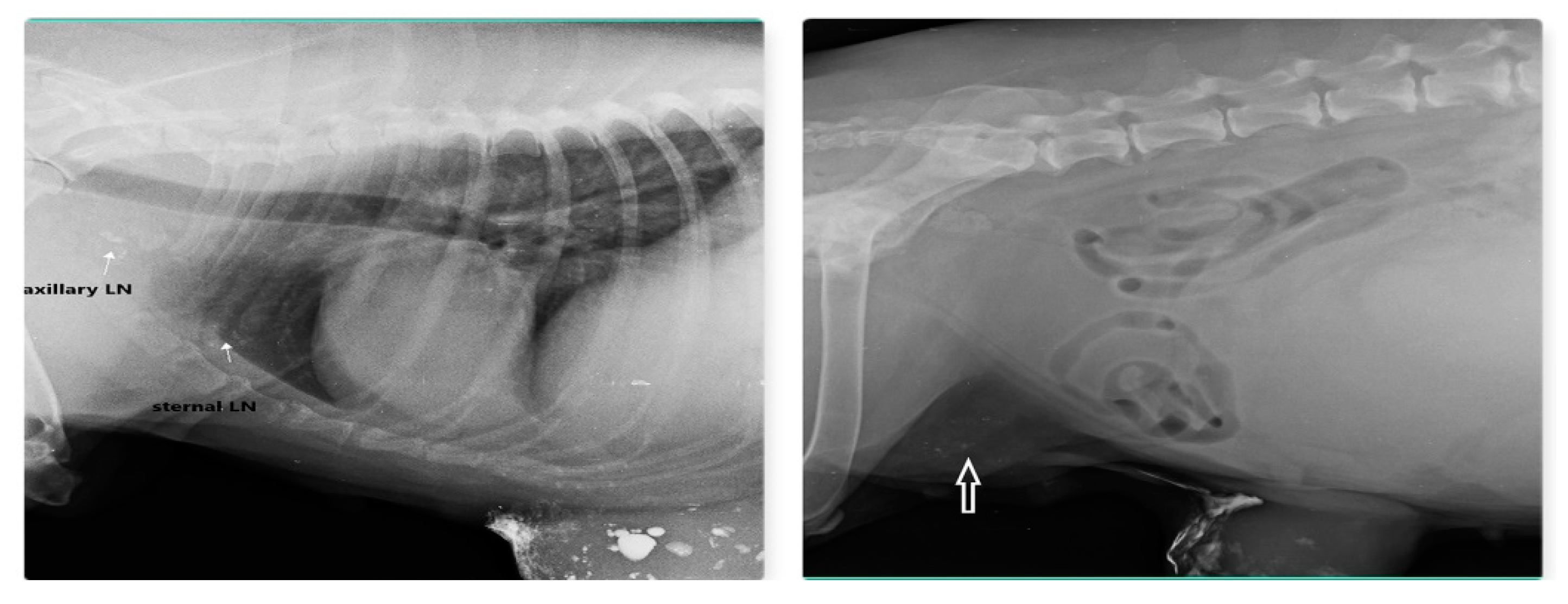
Out of 23 cases of mammary carcinoma, IL with MB dye procedure detects 12 SLN, IL with Lipiodol detects 9 SLN and IL with iohexol is able to detect SLN in 2 cases. Carcinoma was found in both sides from 2nd to 5th mammary gland (MG) but not in 1st MG. Preoperative IL with Lipiodol injection was performed in 9 primary mammary carcinomas via intradermal and subcutaneous routes, led to localization of nine SLN (lymphoid plexus of thigh –two, inguinal-four, axillary –two, and sternal-one). IL with Lipiodol in mammary carcinoma of 2nd MG and subsequent radiograph after 24hour detected sternal lymph node as SLN and axillary LN as second tier node after 48hour is shown in Fig. 12. Post injection radiographs are monitored in 5 patients up to 21 days with similar LN visibility
Figure 12.
Sternal LN as SLN for carcinoma of 2nd and 3rd MG (left) and inguinal LN (arrow) as SLN for carcinoma of 4th and 5th MG (right) detected through indirect radiographic lymphography with Lipiodol.
Figure 12.
Sternal LN as SLN for carcinoma of 2nd and 3rd MG (left) and inguinal LN (arrow) as SLN for carcinoma of 4th and 5th MG (right) detected through indirect radiographic lymphography with Lipiodol.
Perioperative IL with MB dye was conducted under sedation within the operating room at the start of the surgery (radical mastectomy or lumpectomy), and blue stained inguinal lymph node (SLN for mammary carcinoma of 5th MG) was visible within 10-15 min as shown in Fig. 13.
Figure 13.
IL with MB dye detect inguinal lymph node as SLN (stained blue) in mammary carcinoma of 5th mammary gland.
Figure 13.
IL with MB dye detect inguinal lymph node as SLN (stained blue) in mammary carcinoma of 5th mammary gland.
MB was employed in 12 procedures with the identification of 12 SLN (9 inguinal LN and three axillary LN). The lymph from the 2nd and 3rd mammary glands drains to the axillary and sternal LN, whereas the lymph from the 3rd, 4th, and 5th mammary glands flows to the inguinal lymph node and hind limb lymphoid plexus. Iohexol in indirect radiographic lymphography also detect SLN (inguinal LN) in 2 cases. Based on the cytology or histology of the excised LN, six nodes are found to be positive for metastases, while the remaining 17 echelon nodes are non-metastatic or non-malignant.
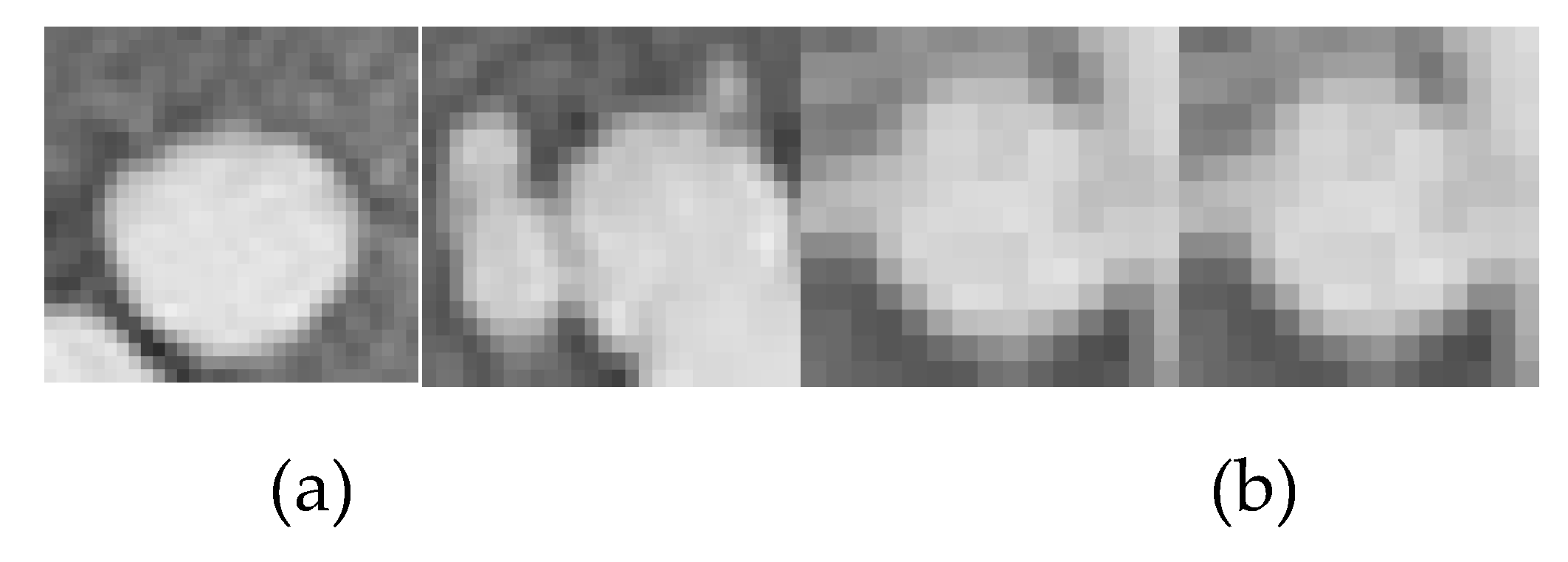
3.1. Automated Classification of Results and Analysis
Proposed automatic classification system is implemented on MATLAB® 2020a with 3.2GHz processor with 8GB RAM. The sample images of cropped regions are shown in Fig.14. Total six first-order statistical and fifteen GLCM features are extracted from all cropped regions and created feature set. Whole feature set is divided into 70% training and 30% testing set. SVM classifier with four kernel function namely, linear, polynomial, RBF, and MLP (Sigmoid) are used for classification. The various initial parameter values of SVM kernel functions taken for experiment are shown in
Table 1.
Figure 14.
Cropped regions from X-ray images (a) Cancerous (b) Non-Cancerous.
Figure 14.
Cropped regions from X-ray images (a) Cancerous (b) Non-Cancerous.
The performance of SVM classifier is evaluated by computing accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity which are mathematically defined as:
Sensitivity, also called True Positive Rate (TPR), is defined as the ratio of the actual positive which are correctly classified as cancerous. It is also known as the true positive fraction (TPF).
Specificity, also called False Positive Rate (FPR), is defined as the ratio of the actual negative which are correctly classified as non- cancerous. It is also known as the false positive fraction (FPF).
Accuracy is defined as the ratio of the correct classification to the total number of test cases.
4. Discussion
Four types of IL approaches used in the current research methodology successfully detected 74 SLN in 82 diversified canine malignancies of epithelial origin (carcinomas) i.e. accounting for 90% of the cases, and simultaneously localize 7 SLN out of 14 tumors of mesenchymal origin (sarcomas) (7/14) i.e. 50%. Since the potential use of these dyes and contrast agents in soft tissue sarcoma cases is limited, the viability of the IL method in these cases is examined using MB dye, iohexol, and lipiodol. B-mode grayscale ultrasonography, and strain elastography are powerful tools in the detection of nodes (metastatic/non-metastatic) in these malignancies, which are confirmed by cytology, FNAC, or biopsy of the targeted nodes. Machine learning approach is also used to detect the carcinoma and spread of these cancerous tissue in multilevel extraction method.
IL approaches (Indirect CT lymphography with iohexol and IL with Lipiodol) can detect SLN for the first time in histiocytic sarcoma and buttock sarcoma, despite the fact that the majority of STS spread hematogenously and locally. This is consistent with earlier reports of Blazer et al. (2003), that regional LN metastasis is valuable only in 3-4 percent of STS as in rhabdomyosarcoma, epithelioid sarcoma, clear cell sarcoma, synovial sarcoma, and vascular sarcomas. The prognosis of buttock sarcoma cases is poor due to detection of malignant nodes (SLN) whereas ultrasound guided biopsy of the anatomical lymph node in other STS reveals non-metastatic LN with favorable outcome.
Ipsilateral and Contralateral lymph node metastases are a common finding in the current investigation of canine oral and maxillofacial cancer (Grimes et al., 2017; Skinner et al., 2018; Randal et al., 2020). Patients with oral SCC showed identification of two lymphatic pathways from primary tumor masses at rostral mandible draining into two-echelon mandibular nodes (SLN), and cytology also revealed positive for metastasis. We have not observed that lymphadenectomy of the nodes positive for metastasis improve the OST in patient with oral SCC although it has modified clinical treatment and therapeutic intervention, comparable to findings by Skinner et al. 2017. Of the four IL techniques employed for SLN detection in our study, the Lipiodol-based IL methods has given better results than iohexol and MB as per the earlier report of Patsikas et al.2006, Mayer et al. 2013, and Brissot and Edery,2016. IL with MB is performed in two cases of ocular SCC where parotid lymphocentrum is identified as SLN in one case, which is confirmed to be metastatic, and have also tumor recurrence.
Lipiodol has a 100% detection rate when employed in 11 of 11 different neoplasms in the skin and subcutis. Cervical and popliteal LN is the first-tier node (SLN) for the forelimb and hind limb detected with both the IL techniques (Lipiodol and MB dye) respectively. The progress of Lipiodol through lymphatic and subsequent opacification of nodes take 24hours, compared to 2 minutes with iohexol, and 10-15 minute with MB dye.
Lipiodol has primarily used in our study for SLN mapping of ASAGAC and the medial iliac lymph node has recognized as SLN within 24h of injection and substantial contrast opacification is evident after 24h. The detection time and contrast enhancement are in line with other studies by earlier workers Majeski et al.2017, Liptak and Boston, 2019. Lymphadenomegaly was observed as mild in 4 cases, moderate in 1 case, and enlarged in 1 case. The size of the primary tumor mass (ASAGAC) is very large, measuring more than 2.5cm-10cm in length and 3-4cm diameter, and many of them showed lymphadenomegaly of at least one iliosacral LN (Sahoo et al., 2021b).
Lymphomas involving multiple nodes are involved in four cases, while popliteal LN and mediastinal mass are enlarged in one case each. All lymphomas shared the characteristic ultrasonography finding of rounded hypoechoic nodes with a S/L axis ratio 1. Cytology of the nodes is an essential criterion for the diagnostic of malignant lymphoma. Iohexol, both in radiography and CT, shows a 100 % detection rate (6 SLN in 5 cases), and lymphatic along with nodal opacification occurred within 2 minutes of injection. As most cases are multicentric involving several nodes and organs, the onset of the lesion may be traced to one site (for example- last molars in oral cavity and hyperemia of the eye in one case) based on clinical presentation and patient history. Sacral and iliac lymph nodes were identified as SLN in multicentric lymphoma with ocular involvement. The prognosis and OST in multicentric lymphoma are very poor, with less than three months of OST as observed by Falk, 2018. Canine lymphoma is similar in its clinical representation to human Non-Hodkinson's lymphoma. Further studies with a greater population of dogs will add to the therapeutic regimen in the human patient. IL with iohexol and MB was used for detection of SLN in TVT and mixed germ cell-stromal tumor. MB effectively localizes the lymphatic route draining from primary tumor mass to the superficial and deep inguinal LN (SLN), which was found positive for metastases. In TVT, inguinal LN is the SLN which is non-malignant on cytology.
The lymph drainage pattern and SLN found in the mammary carcinoma detected through Lipiodol ultra-fluid and MB are congruent with earlier reports (Chioreanet al., 2016; Lee et al., 2018; Manfredi et al., 2021). Timing of radiograph are zero (0),2, 5,30,60 min and 2, 24 and, 72 hours interval same as in Patsikas et al.2006 but further drainage to second-tier nodes as in Collivignarelli et al.2021 is because captured images at 24h interval with the subcutaneous route. Lymphatic drainage of Lipiodol through the intradermal route is found faster than the subcutaneous route, indicating lymph flow faster through the intradermal route than the subcutaneous route. Thoracic metastasis was observed in mammary carcinoma of 4th MG, where inguinal LN is detected as the SLN with Lipiodol. Therefore, the reason for pulmonary metastasis in this patient might be lymphatic flow from inguinal LN to iliosacral lymphocenter and from there to cisterna chyli, next to thoracic lymphatic ducts and finally drains to the thorax producing metastasis. The detection rate of SLN with Lipiodol and MB was 100% (21/21), confirming the sensitivity and specificity of these two dyes in clinical cases of breast cancer both in companion animals and human beings. The reason for the 100 % detection rate of Lipiodol in these cases and also other IL techniques employed in our study is that this lymphotropic agent stayed in the lymph node for a longer period, and because of its oil base, it did not disperse into the interstitial space quickly or flow into the excretory system. Contrary to iohexol, which is excreted through the kidney, Lipiodol is mainly metabolized in the liver and stays in the liver for many days. In the present study, the proportion of metastatic to non-metastatic nodes was found to be 36/38 (94%) in a population of 96 patients indicates importance of the IL procedure in identification of exact nodes that may harbor the malignant cells. The chances of survival are higher in patients in which non-metastatic LN are biopsied or removed than the canine patients in which metastatic LN are detected and removed. This indicates metastatic SLN is a poorer prognostic indicator in any neoplasm in agreement with Liptak and Boston, 2019.
4.1. Performance assessment of machine learning classifier model
The outcome obtained with SVM classifier with four different kernel function namely, linear, MLP, Polynomial, and RBF are shown in
Table 2
The highest 95.53% sensitivity, 94.64% specificity, 93.05% accuracy are observed with RBF kernel function. Performance of the SVM classifier with RBF kernel function is better as compared to linear, polynomial, and MLP functions. Highest obtained testing accuracy is 93.05% shows that performance of SVM classifier is reliable. It is concluded from the result that trained machine learning model is robust for automatic detection of cancerous and non-cancerous regions of animal’s images.
5. Conclusions
The patient's survival time is less in groups where metastatic SLN has removed; it might be due to lymphatic spread of the tumor or metastasis had already occurred before the procedure is employed. The authors recommend the inclusion of a SLN detection procedure in all types of malignancies for better prognosis and survival outcomes of the disease. Machine learning technique is also applied for automatic classification of cancerous tissues. Automatic detection system will helpful for the doctors to take second thoughts. In future, more robust and QoS based machine learning model will be developed with extended number of images.
Conflict of Interest
There is no conflict of interest
Ethical Statement
The retrospective cases were approved in Institutional Animal Ethical Committee (IAEC), College of Veterinary Science and AH, OUAT. All the procedure was performed through written consent from patient owner and postoperative of the animals were taken care of at owner’s residence. The excised samples collected and lymphography technique followed were as per the established protocol from cited literature.
References
- Beer, P.; Pozzi, A.; Bley, C.R.; Bacon, N.; Pfammatter, N.S.; Venzin, C. The role of sentinel lymph node mapping in small animal veterinary medicine: A comparison with current approaches in human medicine. Veter- Comp. Oncol. 2017, 16, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beer, P.; Rohrer-Bley, C.; Nolff, M.C. Near-infrared fluorescent image-guided lymph node dissection compared with locoregional lymphadenectomies in dogs with mast cell tumours. J. Small Anim. Pr. 2022, 63, 670–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blazer, D.G.; Sabel, M.S.; Sondak, V.K. Is there a role for sentinel lymph node biopsy in the management of sarcoma? Surgical Oncology 2003, 12, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brissot, H.N.; Edery, E.G. Use of indirect lymphography to identify sentinel lymph node in dogs: a pilot study in 30 tumors. Veterinary Comparative Oncology 2016, 15, 740–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiorean, L.; Cui, X.W.; Klein, S.A.; Budjan, J.; Sparchez, Z.; Radzina, M.; Jenssen, C.; Dong, Y.; Dietrich, C.F. Clinical value of imaging for lymph nodes evaluation with particular emphasis on ultrasonography. Z Gastroenterology 2016, 54, 774–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collivignarelli, F.; Tamburro, R.; Aste, G.; Falerno, I.; Del Signore, F.; Simeoni, F.; Patsikas, M.; Gianfelici, J.; Terragni, R.; Attorri, V.; et al. Lymphatic Drainage Mapping with Indirect Lymphography for Canine Mammary Tumors. Animals 2021, 11, 1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V. Support-vector networks. Machine learning 1995, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliker, K.R.; A Sommerville, B.; Broom, D.M.; E Neal, D.; Armstrong, S.; Williams, H.C. Key considerations for the experimental training and evaluation of cancer odour detection dogs: lessons learnt from a double-blind, controlled trial of prostate cancer detection. BMC Urol. 2014, 14, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falk Elin. Prognosis of malignant lymphoma in dogs and correlation to thymidine kinase (TK1) : a retrospective study. Second cycle, A2E. Uppsala: SLU, Dept. of Clinical Sciences, 2018; 1-39.
- Fournier, Q.; Cazzini, P.; Bavcar, S.; Pecceu, E.; Ballber, C.; Elders, R. Investigation of the utility of lymph node fine-needle aspiration cytology for the staging of malignant solid tumors in dogs. Veter- Clin. Pathol. 2018, 47, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, Q.; Thierry, F.; Longo, M. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound for sentinel lymph node mapping in the routine staging of canine mast cell tumors: A feasibility study. Veterinary Comparative Oncology 2020, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Uribe, A.; Erpelding, T.N.; Krumholz, A.; Ke, H.; Maslov, K.; Appleton, C.; Margenthaler, J.A.; Wang, L.V. Dual-Modality Photoacoustic and Ultrasound Imaging System for Noninvasive Sentinel Lymph Node Detection in Patients with Breast Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15748–15748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelb, H.R.; Freeman, L.J.; Rohleder, J.J.; Snyder, P.W. Feasibility of contrast enhanced ultrasoundguided biopsy of sentinel lymph nodes in dogs. Veter- Radiol. Ultrasound 2010, 51, 628–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimes, J.A.; Secrest, S.A.; Northrup, N.C.; Saba, C.F.; Schmiedt, C.W. Indirect computed tomography lymphangiography with aqueous contrast for evaluation of sentinel lymph nodes in dogs with tumors of the head. Veter- Radiol. Ultrasound 2017, 58, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hlusko, K.C.; Cole, R.; Tillson, D.M.; Boothe, H.W.; Almond, G.; Coggeshall, W.S.; Matz, B.M. Sentinel lymph node detection differs when comparing lymphoscintigraphy to lymphography using water soluble iodinated contrast medium and digital radiography in dogs. Veter- Radiol. Ultrasound 2020, 61, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haralick, R.M.; Shanmugam, K.; Dinstein, I.H. Textural Features for Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1973, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iida, G.; Asano, K.; Seki, M.; Ishigaki, K.; Teshima, K.; Yoshida, O.; Edamura, K. and Kagawa, Y. Intraoperative identification of canine hepatocellular carcinoma with indocyanine green fluorescent imaging. Journal of Small Animal Practice 2013, 54, 594–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.; Dandekar, P.; Patravale, V. Diagnostic nanocarriers for sentinel lymph node imaging. J. Control. Release 2009, 138, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karakitsou, V.; Christopher, M.M.; Meletis, E.; Kostoulas, P.; Pardali, D.; Koutinas, C.K.; Mylonakis, M.E. A comparison of cytologic quality in fine-needle specimens obtained with and without aspiration from superficial lymph nodes in the dog. J. Small Anim. Pr. 2021, 63, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Singh, S. K.; Saxena, S.; Lakshmanan, K.; Sangaiah, A. K.; Chauhan, H.; Singh, R. K. Deep feature learning for histopathological image classification of canine mammary tumors and human breast cancer. Information Sciences 2020, 508, 405–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapsley, J.; Hayes, G.M.; Janvier, V.; et al. Influence of locoregional lymph node aspiration cytology vs sentinel lymph node mapping and biopsy on disease stage assignment in dogs with integumentary mast cell tumors. Veterinary Surgery 2020, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBlanc, A.K.; Peremans, K. PET and SPECT Imaging in Veterinary Medicine. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2014, 44, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.E.; Matz, B.M.; Cole, R.C.; Boothe, H.W.; Tillson, D.M. Radiographic evaluation of subcutaneously injected, water-soluble, iodinated contrast for lymphography in dogs. 2018. 1-19. [CrossRef]
- Liptak, J.M.; Boston, S.E. Nonselective Lymph Node Dissection and Sentinel Lymph Node Mapping and Biopsy. Veterinary Clinics of North America: Small Animal Practice. 2019, 49, 793–807. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Majeski, S.A.; Steffey, M.A.; Fuller, M.; Hunt, G.B.; Mayhew, P.D.; Pollard, R.E. Indirect computed tomographic lymphography for iliosacral lymphatic mapping in a cohort of dogs with anal sac gland adenocarcinoma: technique description. Veter- Radiol. Ultrasound 2017, 58, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manfredi, M.; De Zani, D.; Chiti, L.E.; Ferrari, R.; Stefanello, D.; Giudice, C.; Pettinato, V.; Longo, M.; Di Giancamillo, M.; Zani, D.D. Preoperative planar lymphoscintigraphy allows for sentinel lymph node detection in 51 dogs improving staging accuracy: Feasibility and pitfalls. Veter- Radiol. Ultrasound 2021, 62, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Materka, A, Strzelecki, M. Texture analysis methods–a review, Technical University of Lodz, Institute Of Electronics, COST B11 report, Brussels, 1998, pp. 9-11.
- Morton, D.L.; Wen, D.-R.; Wong, J.H.; Economou, J.S.; Cagle, L.A.; Storm, F.K.; Foshag, L.J.; Cochran, A.J. Technical Details of Intraoperative Lymphatic Mapping for Early Stage Melanoma. Arch. Surg. 1992, 127, 392–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyberg, R.H.; Korkola, P.; Maenpaa, J. Ovarian sentinel node: is it feasible? International journal of Gynaecology and Cancer 2011, 21,568–72.
- Patnaik, A.K.; Ehler, W.J.; MacEwen, E.G. Canine Cutaneous Mast Cell Tumor: Morphologic Grading and Survival Time in 83 Dogs. Veter- Pathol. 1984, 21, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patsikas, M.N.; Karayannopoulou, M.; Kaldrymidoy, E.; Papazoglou, L.G.; Papadopoulou, P.L.; Tzegas, S.I.; Tziris, N.E.; Kaitzis, D.G.; Dimitriadis, A.S.; Dessiris, A.K. The Lymph Drainage of the Neoplastic Mammary Glands in the Bitch: A Lymphographic Study. Anat. Histol. Embryol. 2006, 35, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randall, E.K.; Jones, M.D.; Kraft, S.L.; Worley, D.R. The development of an indirect computed tomography lymphography protocol for sentinel lymph node detection in head and neck cancer and comparison to other sentinel lymph node mapping techniques. Veter- Comp. Oncol. 2020, 18, 634–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, F.; Körner, M.; Suárez, J.; Carozzi, G.; Meier, V.S.; Roos, M.; Bley, C.R. Computed tomographic-lymphography as a complementary technique for lymph node staging in dogs with malignant tumors of various sites. Veter- Radiol. Ultrasound 2017, 59, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, A.; Nath, I.; Senapati, S.; Panda, S.; Das, M.; Patra, B. Comparative Evaluation of Nutraceuticals (Curcuma longa L.; Syzygium aromaticum L. and Olea europaea) with Single-agent Carboplatin in the Management of Canine Appendicular Osteosarcoma. Indian J. Anim. Res. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, A.; Nath, I.; Senapati, S.; Panda, S.; Das, M.; Patra, B. Apocrine Gland Anal Sac Adenocarcinoma in Dogs: 22 Cases (2015-2020). Indian J. Anim. Res. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarowitz, B.N.; Davis, G.J.; Kim, S. Outcome and prognostic factors following curative-intent surgery for oral tumours in dogs: 234 cases (2004 to 2014). J. Small Anim. Pr. 2017, 58, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaker, R.; Wilke, C.; Ober, C.; Lawrence, J. Machine learning model development for quantitative analysis of CT heterogeneity in canine hepatic masses may predict histologic malignancy. Veter- Radiol. Ultrasound 2021, 62, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skinner, O.T.; Boston, S.E.; Souza, C.H.d.M. Patterns of lymph node metastasis identified following bilateral mandibular and medial retropharyngeal lymphadenectomy in 31 dogs with malignancies of the head. Veter- Comp. Oncol. 2016, 15, 881–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skinner, O.T.; Boston, S.E.; Giglio, R.F.; Whitley, E.M.; Colee, J.C.; Porter, E.G. Diagnostic accuracy of contrast-enhanced computed tomography for assessment of mandibular and medial retropharyngeal lymph node metastasis in dogs with oral and nasal cancer. Veter- Comp. Oncol. 2018, 16, 562–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sledge, D.G.; Webster, J.; Kiupel, M. Canine cutaneous mast cell tumors: A combined clinical and pathologic approach to diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment selection. Veter- J. 2016, 215, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkbey, B.; Hoyt, R.F.; Jr Agarwal, H.K.; et al. 2015. Magnetic resonance sentinel lymph node imaging of the prostate with gadofosveset trisodium-albumin: preliminary results in a canine model. Academic radiology22, 646–652.
- Wan, J.; Oblak, M.L.; Ram, A.; Singh, A.; Nykamp, S. Determining agreement between preoperative computed tomography lymphography and indocyanine green near infrared fluorescence intraoperative imaging for sentinel lymph node mapping in dogs with oral tumours. Veter- Comp. Oncol. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).