Submitted:
15 June 2023
Posted:
19 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Hyper Z Construction
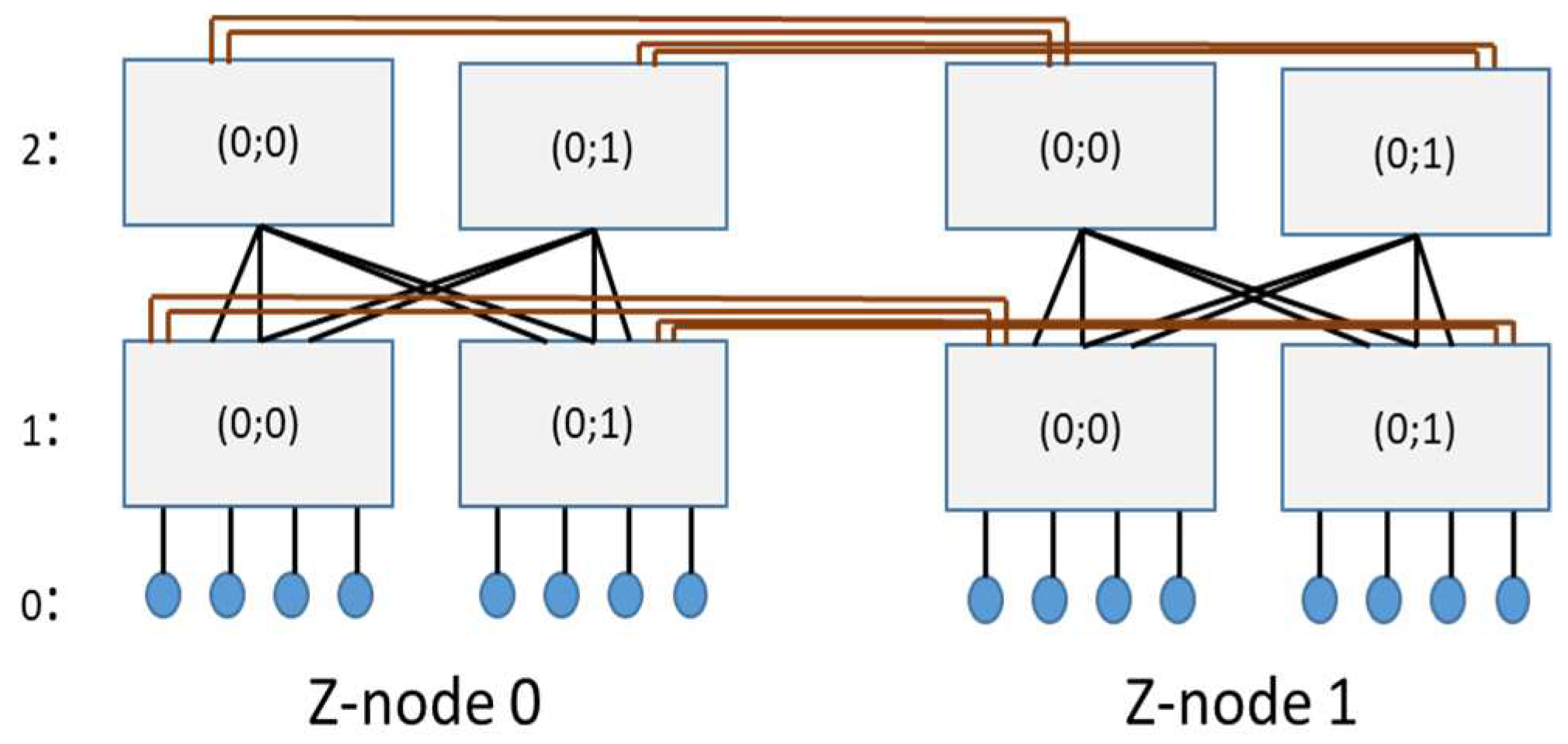
3.1.Hyper Z-Fat Tree Connectivity Rules
- They have the same flat address within their Z-nodes Xi =Yi ,
- The vector connectivity degree Qk = (q1k, q2k,…, qik …,qhk) in the kth-dimension has at least one element qik≠0,
- They differ in exactly one value in the kth dimension, ak ≠ bkfor all 1≤k≤d.
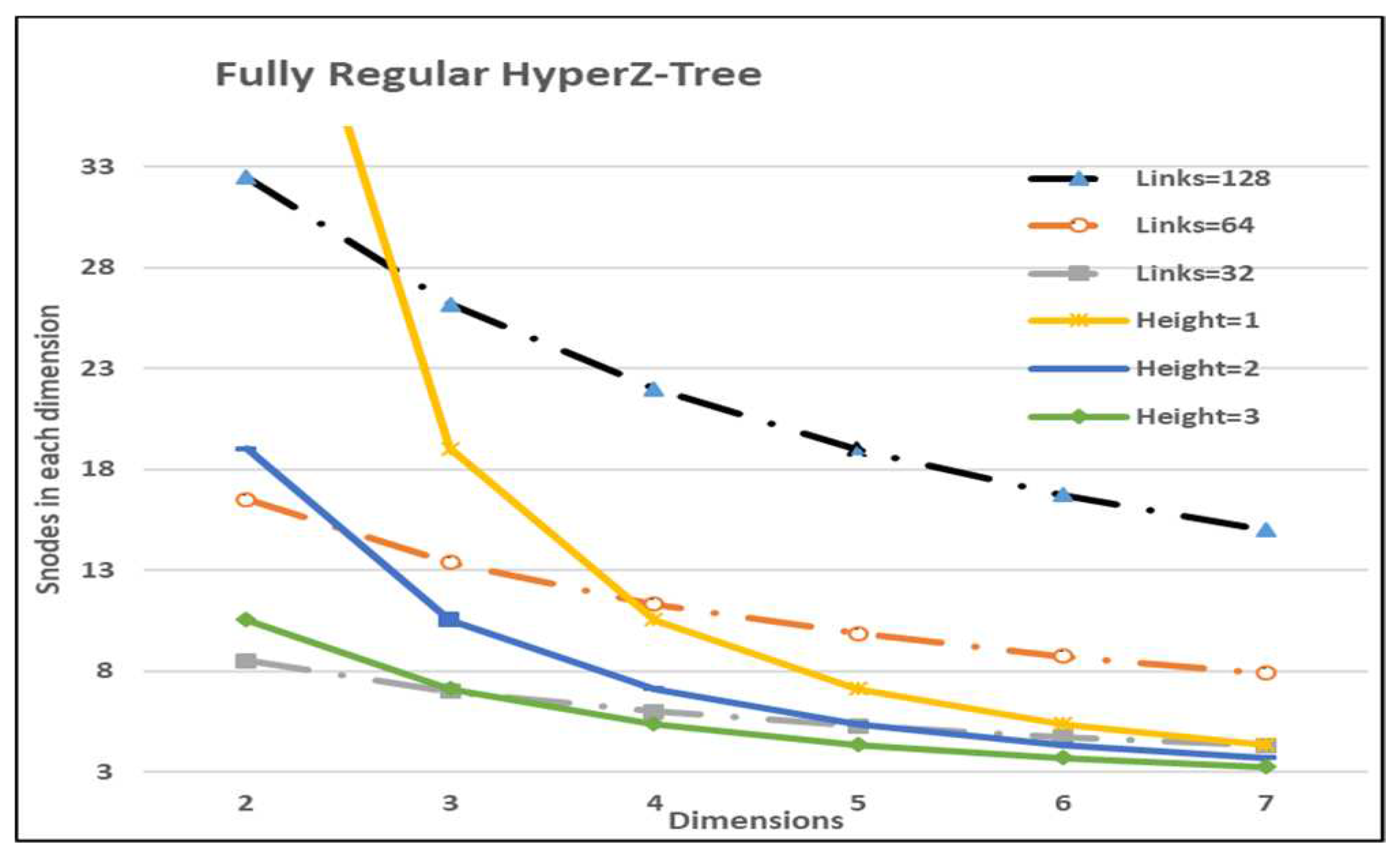
3.2. Topology Features
4. Adaptive Routing in HyperZ
 (d)=
{xk | xk = 1 if ak=bk ∨ xk
= 0 if ak≠bk,
∀ 1≤k≤d}.
(d)=
{xk | xk = 1 if ak=bk ∨ xk
= 0 if ak≠bk,
∀ 1≤k≤d}.
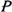 (3) = {1, 0, 1} meaning the
routes have to go through dimension 3 and then dimension 1, or dimension 1
followed by dimension 3. There is no route through dimension 2. This is a well-known
concept of GHC topology.
(3) = {1, 0, 1} meaning the
routes have to go through dimension 3 and then dimension 1, or dimension 1
followed by dimension 3. There is no route through dimension 2. This is a well-known
concept of GHC topology.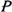 (d) where all the
elements are equal to 1 referring to routable or offset dimensions,
(d) where all the
elements are equal to 1 referring to routable or offset dimensions, 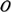 ⊆
⊆ 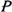 (d)= {xk≠0, ∀ 1≤k≤d}.
(d)= {xk≠0, ∀ 1≤k≤d}.
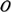 |, of the set,
|, of the set, 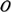 , determines the number of hops to reach the destination and the
factorial of the cardinality, |
, determines the number of hops to reach the destination and the
factorial of the cardinality, |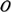 |!
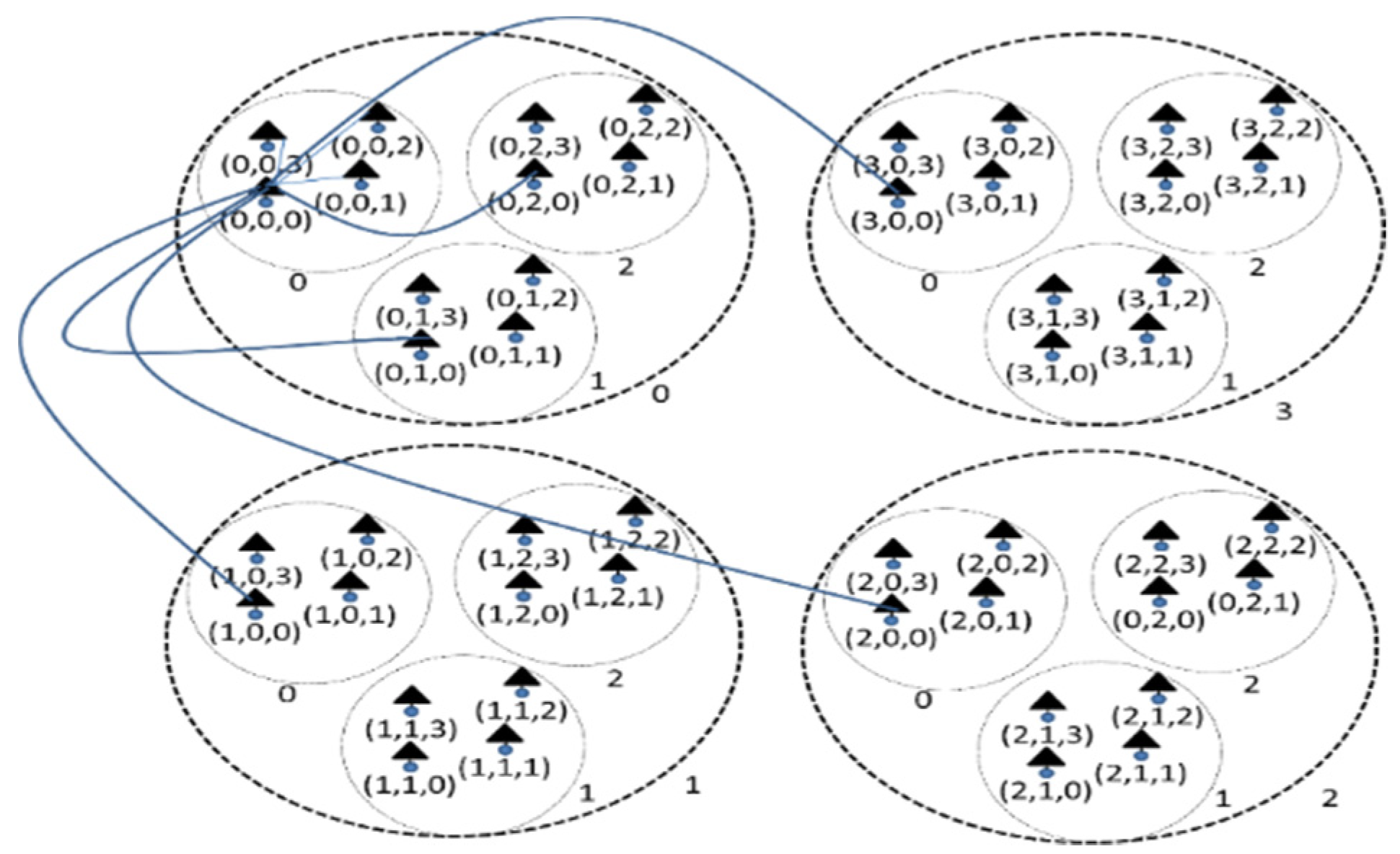
defines the number of possible shortest paths between two Z-nodes. Again in Figure 3, the ordered set of short paths
between the Z-nodes (0, 0, 0) and (3, 0, 1) is
|!
defines the number of possible shortest paths between two Z-nodes. Again in Figure 3, the ordered set of short paths
between the Z-nodes (0, 0, 0) and (3, 0, 1) is 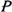 (3)= {1, 0, 1},
and the set,
(3)= {1, 0, 1},
and the set, 
 {1, 1}, |
{1, 1}, | |! = 2! = 2, indicates that
there are 2 shortest paths of 2 hops each.
|! = 2! = 2, indicates that
there are 2 shortest paths of 2 hops each.
4.1 CLIOD and ALIOD Algorithms
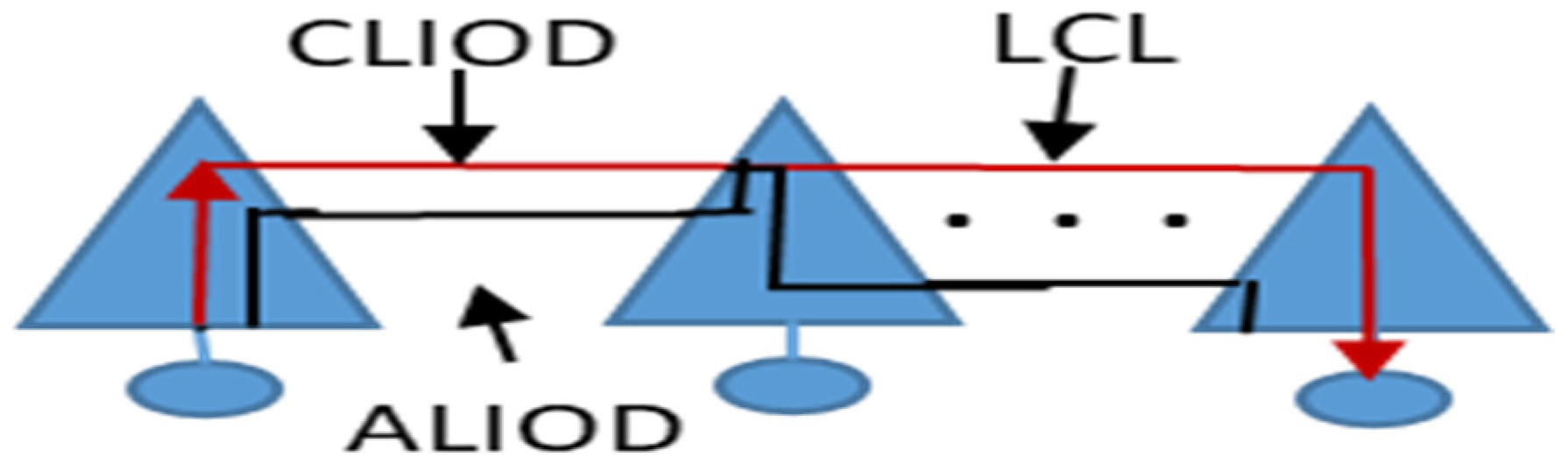
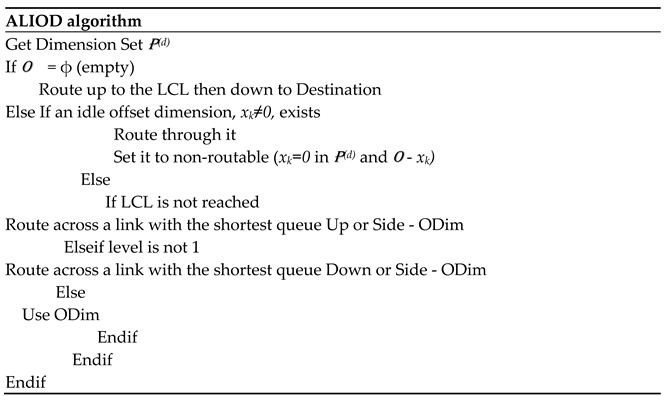
5. Performance Evaluation
5.1. Simulation Model
5.2 Results of the simulation
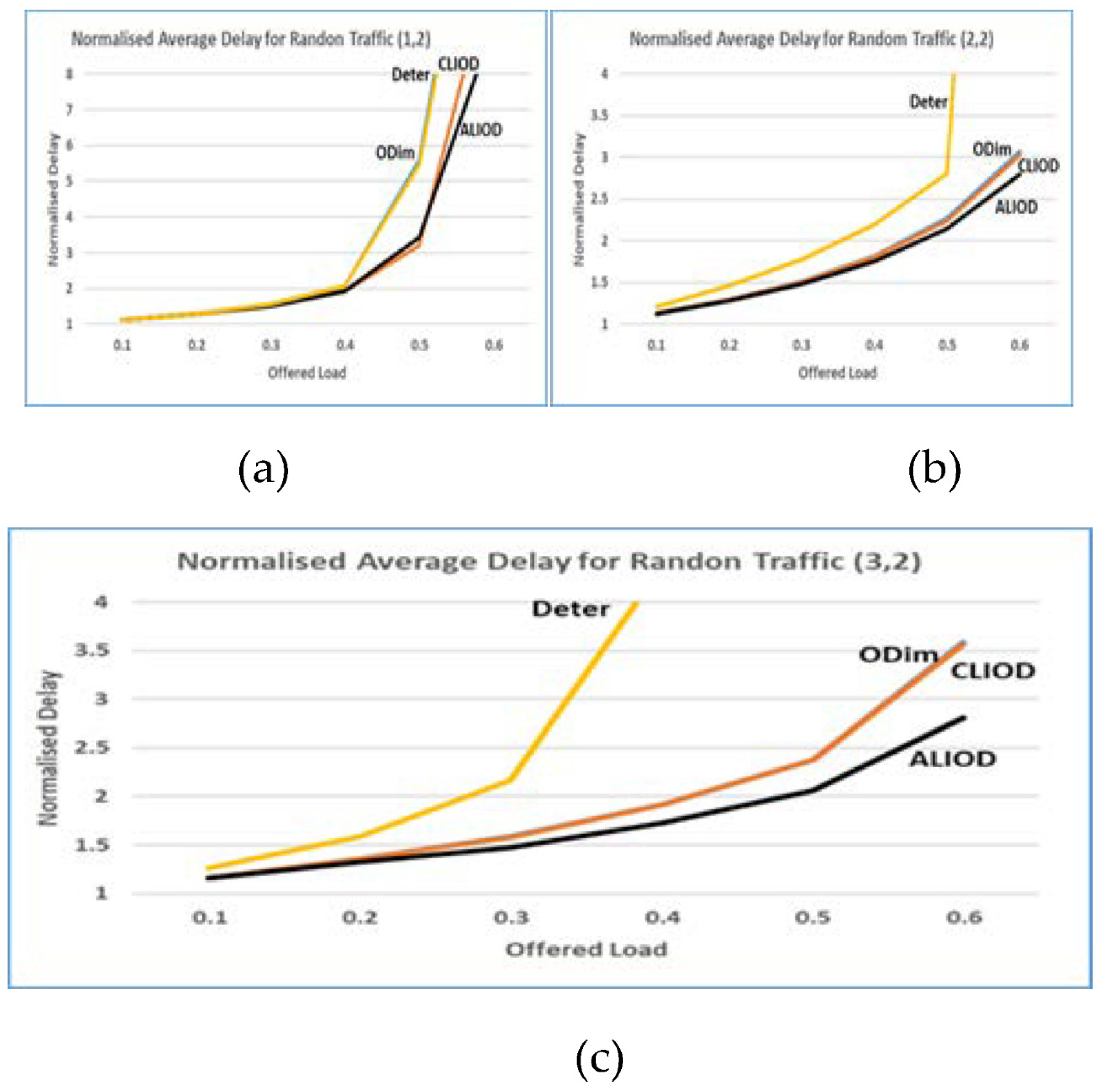
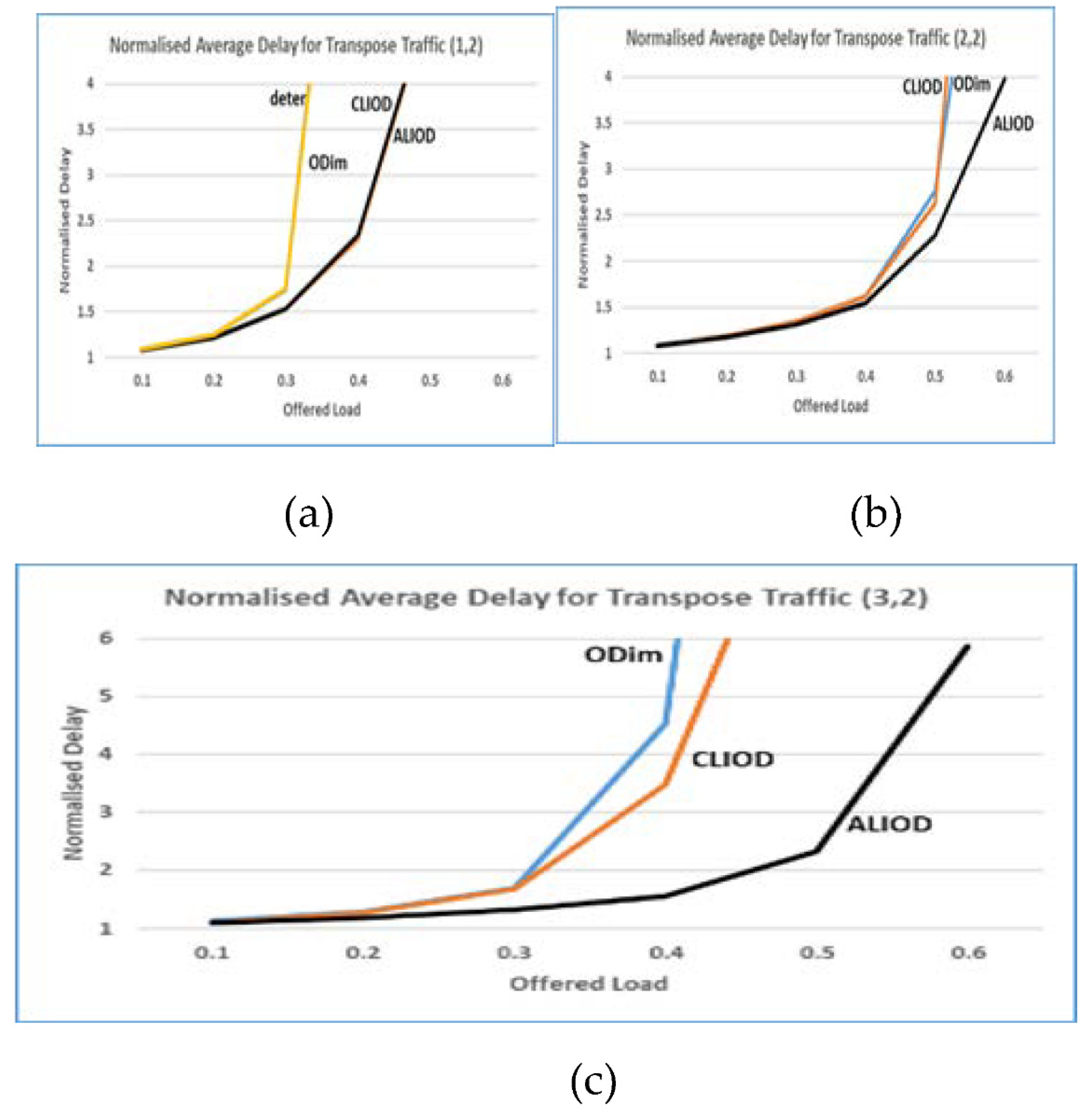
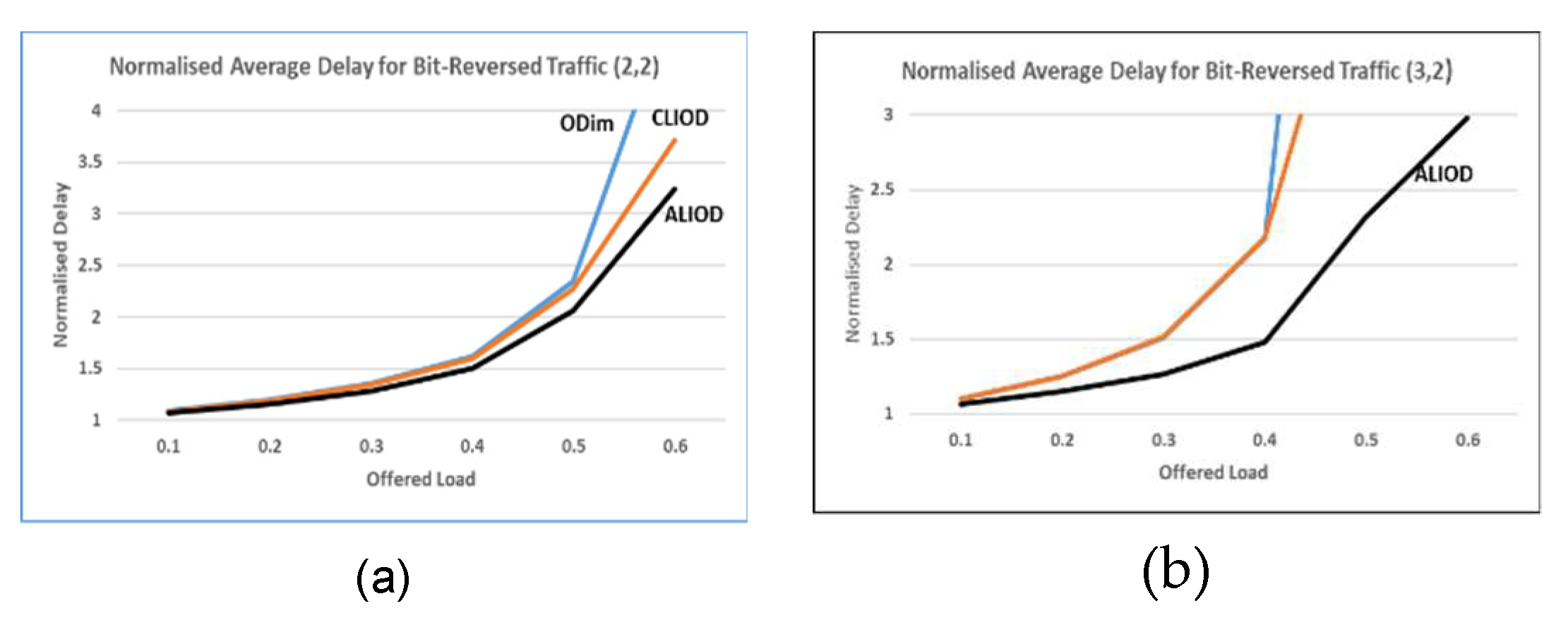
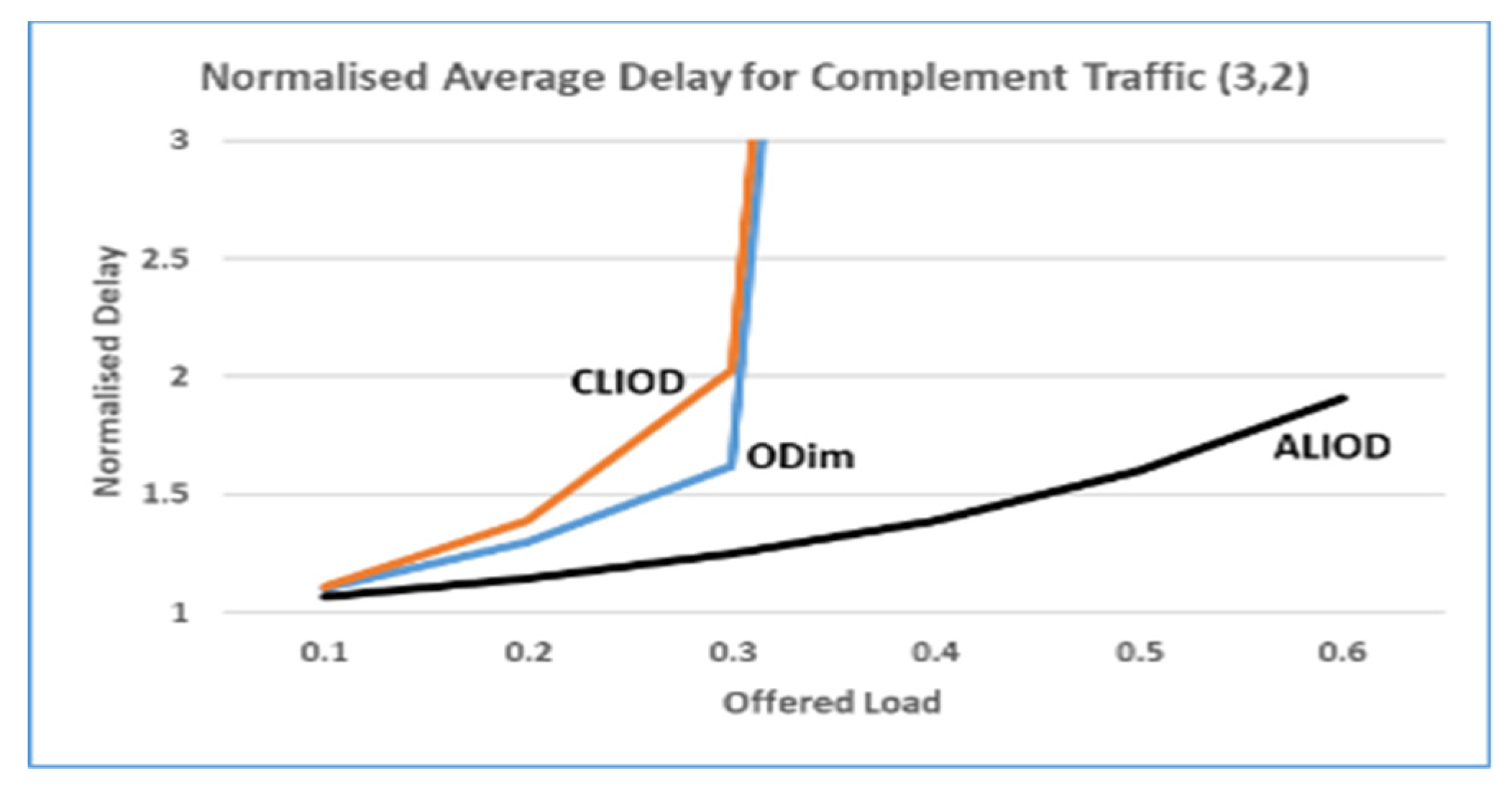
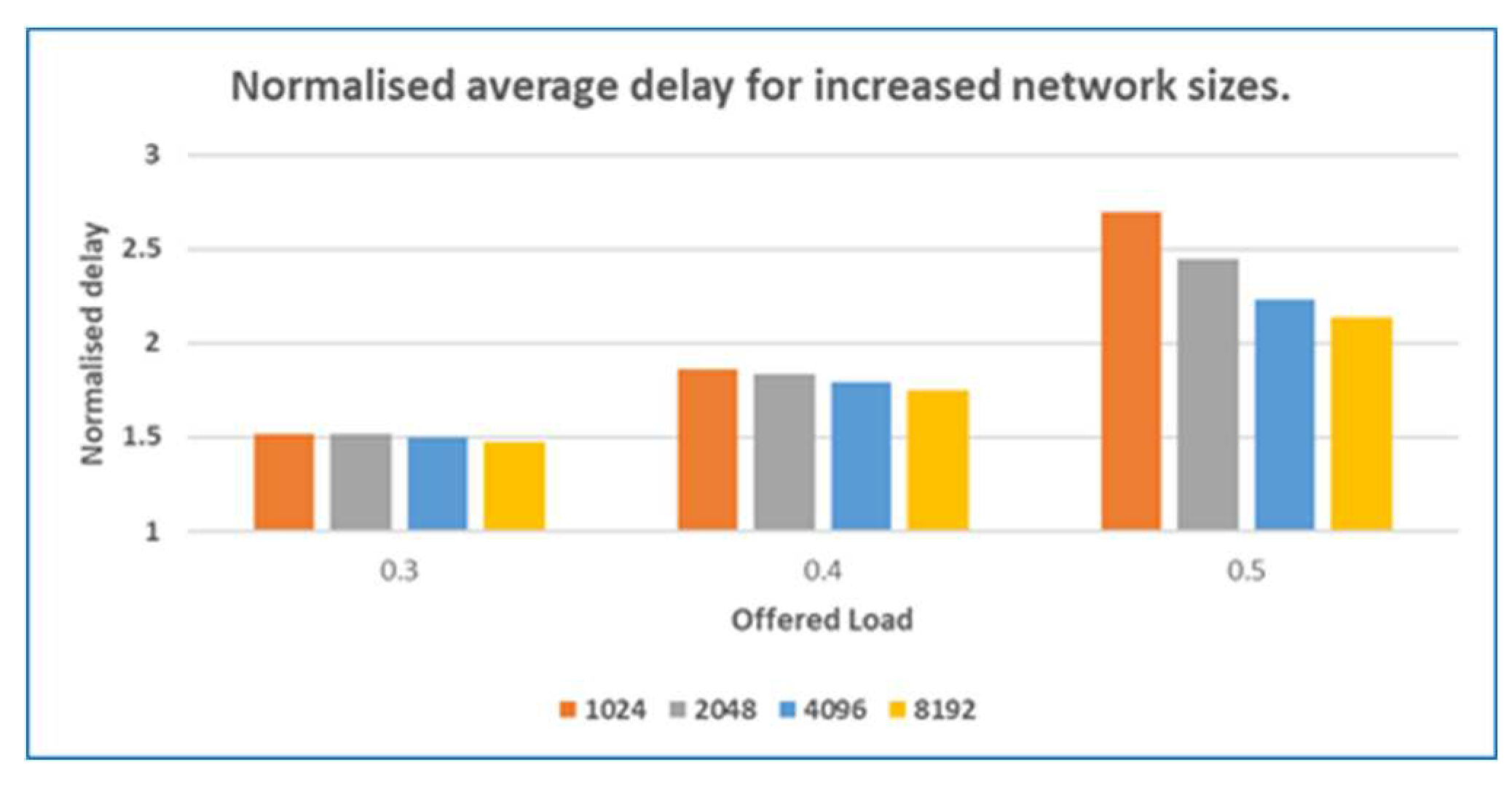
5.3. Scalability
5.4. Fault Tolerance
6. Conclusions
References
- C. Bekas, “Breaking the power wall in Exascale Computing, what is Exascale computing”, Scientific colloquium, of Steinbach Centre for Computing of Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, [Online] Available: http://www.scc.kit.edu/downloads/oko/SCC_Kolloquium_20131114_exascale_computing.pdf 2013.
- D. A. Reed, J. Dongarra, “Exascale Computing and Big Data”, Communications of the ACM, Vol. 58, No. 7, pp. 56-68, July 2015. [CrossRef]
- P. M. Reed, D. Hadka, “Evolving Many-Objective Water Management to Exploit Exascale Computing”, AGU Publications, 0 Oct 2014. [CrossRef]
- J. Torrelas, “Architectures for Extreme-Scale computing”, Computer, IEEE Computer Society, pp. 28-35, Nov 2009.
- J. A. Ang, et all., “Abstract Machine Models and Proxy Architectures for Exascale Computing”, Co-HPC '14 Proceedings of the 1st International Workshop on Hardware-Software Co-Design for High Performance Computing, pp. 25-32, 2014.
- F. Cappelo, et all., “Toward Exascale Resilience”, The International Journal of High Performance Computing Applications, Volume 23, No. 4, pp. 374–388, 2009.
- C. Leiserson, "Fat-trees: Universal networks for hardware-efficient supercomputing", IEEE Transactions on Computers, Vol. 34, No. 10, pp. 892-901, 1985. [CrossRef]
- B. Arimilli, et all., “The PERCS high-performance interconnect,” in Proc. 18th Annu. Symp. High-Perform. Interconnects, pp. 75–82, 2010. [CrossRef]
- Cray Inc., "Cray XK Series Supercomputers | Cray", Cray.com, 2013.[Online].Available:http://www.cray.com/Products/Computing/XK7.aspx. [Accessed: 02- Apr- 2013].
- IBM Bluewaters. “Blue Waters”, NCSA University of Illinois. [Online] Available: https://bluewaters.ncsa.illinois.edu/ [Accessed: 2 Apr 2013].
- R. A. Haring, et all., “The IBM Blue Gene/Q Computer Chip”, IEEE Micro, Vol. 32, No. 2, pp. 48-60, Mar/Apr 2012. [CrossRef]
- IBM Blue Gene team, "Design of the IBM Blue Gene/Q Compute Chip," IBM Journal of Research and Development, Issue 1/2, Jan-Mar 2013. [CrossRef]
- D. Chen, et all. "Looking under the hood of the IBM Blue Gene/Q network", 2012 International Conference for High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage and Analysis, 2012.
- N. Jain, et all. “ Maximizing Throughput on a Dragonfly Network”, SC '14: Proceedings of the International Conference for High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage and Analysis, 16-21 Nov 2014.
- M. Garcia, et all., , “On-the-fly adaptive routing in high-radix hierarchical networks,” in 41st International Conference on Parallel Processing (ICPP), pp. 279–288, 2012. [CrossRef]
- X. ZHU, "Xmesh: A Mesh-Like Topology for Network on Chip", Journal of Software, vol. 18, no. 9, p. 2194, 2007. [CrossRef]
- M. Rahman, Y. Inoguchi, F. Faisal and M. Kundu, "Symmetric and Folded Tori Connected Torus Network", Journal of Networks, vol. 6, no. 1, 2011. [CrossRef]
- M. Nikdast, J. Xu, X. Wu, Z. Wang, X. Wang and Z. Wang, "Fat-tree-based optical interconnection networks under crosstalk noise constraint", IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. Syst., vol. 23, no. 1, pp. 156-169, 2015. [CrossRef]
- H. Gu, S. Wang, Y. Yang and J. Xu, "Design of Butterfly-Fat-Tree Optical Network-on-Chip", Optical Engineering, 2010. [CrossRef]
- Amir Mansoor Kamali Sarvestani, PHD THESIS "Evaluating Techniques for Wireless Interconnected 3D Processor Arrays", York: University of York, 2013.
- M. Adda, A. Peratikou, “Routing and Fault Tolerance in Z-Fat Tree", IEEE Transaction on Parallel and Distributed Systems, Vol. 28, No. 8, 2017.
- D. Agrawal, “Generalized Hypercube and Hyperbus Structures for a computer”, IEEE Transactions on Computers Vol. 33, No.3, pp. 323-33, 1984.
- J. H. Ahn, N. L. Binkert, R. Schreider “HyperX: Topology, Routing, and Packaging of Efficient Large-Scale Networks”, Proceedings of the ACM/IEEE Conference on High Performance Computing, SC 2009, Nov 14-20, 2009.
- S. Azizi, F. Safaei, N. Hashemi, “On the Topology Properties of HyperX”, the Journal of Supercomputing, Vol. 66, No. 1, pp. 572-593, 2013.
- Mu, Y. & Li, K. (2011). “Extended Folded Cube: A Improved Hierarchical Interconnection Network”. Fourth International Symposium On Parallel Architectures, pp. 77-81. [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M., Inoguchi, Y., Faisal, F. A. & Kundu, M. K. (2011). « Symmetric and Folded Tori Connected Torus Network”. Journal of Networks, 6 (1). [CrossRef]
- N. Kini, M. Kumar and H. Mruthyunjaya, "Torus Embedded Hypercube Interconnection Network: A Comparative Study", International Journal of Computer Applications, vol. 1, no. 4, pp. 32-35, 2010. [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M. H., Jiang, X., Masud, M. & Horiguchi, S. (2009), “Network performance of pruned hierarchical torus network”, Sixth IFIP International Conference On Network and Parallel Computing, Oct 2009.Gold Coast: pp. 9--15.
- Khosravi, A., Khors, I, S. & Akbari, M. K. (2011). “Hyper node torus: A new interconnection network for high speed packet processors”. International Symposium On Computer Networks and Distributed Systems (CNDS, pp. 106--110. [CrossRef]
- Arimilli, B., Arimilli, R., Chung, V., Clark, S., Denzel, W., Drerup, B., Hoefler, T., Joyner, J., Lewis, J., Li, J. & Others (2010). “The PERCS high-performance interconnect”. 18Th IEEE Symposium On High Performance Interconnects., pp. 75--82.
- Faanes G, et Al (2012), “Cray cascade: a scalable HPC system based on dragonfly network”, Proceedings of the International Conference on Computing, Networking, Storage & Analysis. [CrossRef]
- L. G. Valiant (1982), “A scheme for fast parallel communication “, SIAM Journal on Computing, 11(2): 350-361. [CrossRef]
- J. Kim, W. J. Dally, S. Scott & D. Abts (2008), “Technology-Driven, Highly-Scalable Dragonfly Topology”, International Symposium on Computer Architecture.
- A. Peratikou, “An optimised and generalised node for fat tree classes” PhD thesis, School of Computing, University of Portsmouth, Portsmouth, 2014.
- OPNET Technologies “Opnet modeller accelerating network R&D”– Network Simulator | Riverbed", Riverbed, 2016. [Online].
 |
Mo Adda received his PhD degree in parallel and distributed systems from Surrey University, United Kingdom. He is currently a principal lecturer and MSc course leader for cyber security and digital forensics at Portsmouth University and Cambridge (EG). He has also worked for many years, as a senior consultant in the industry for simulation and modeling, where he developed many discreet event simulation tools for shipments and business process modelling. His current research includes parallel architectures, big data analytics, embedded systems, intelligent agents, network management, forensic information technology, network security and IoT forensics and cyber security. He is a member of the IEEE. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




