Submitted:
15 June 2023
Posted:
16 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
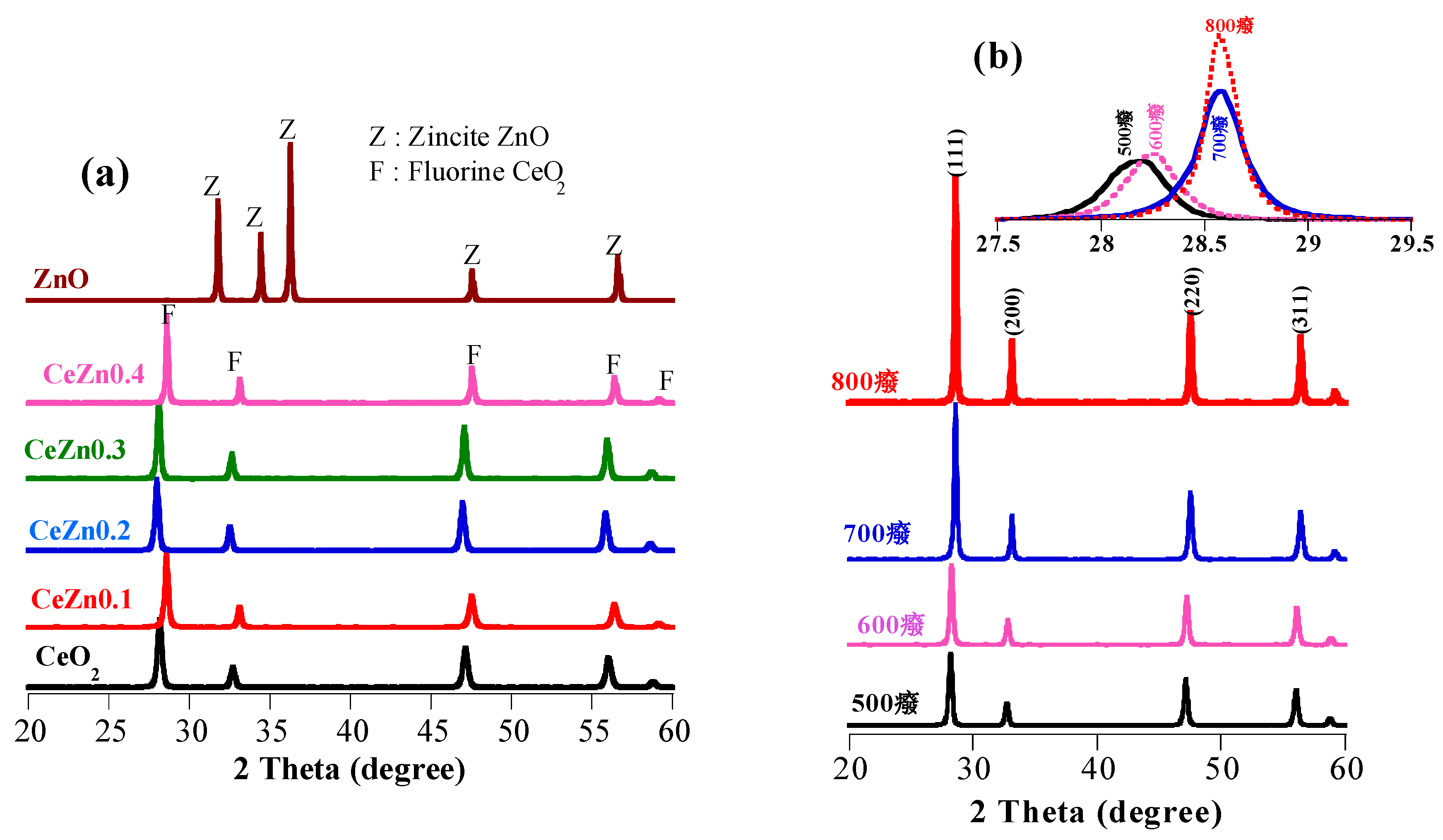
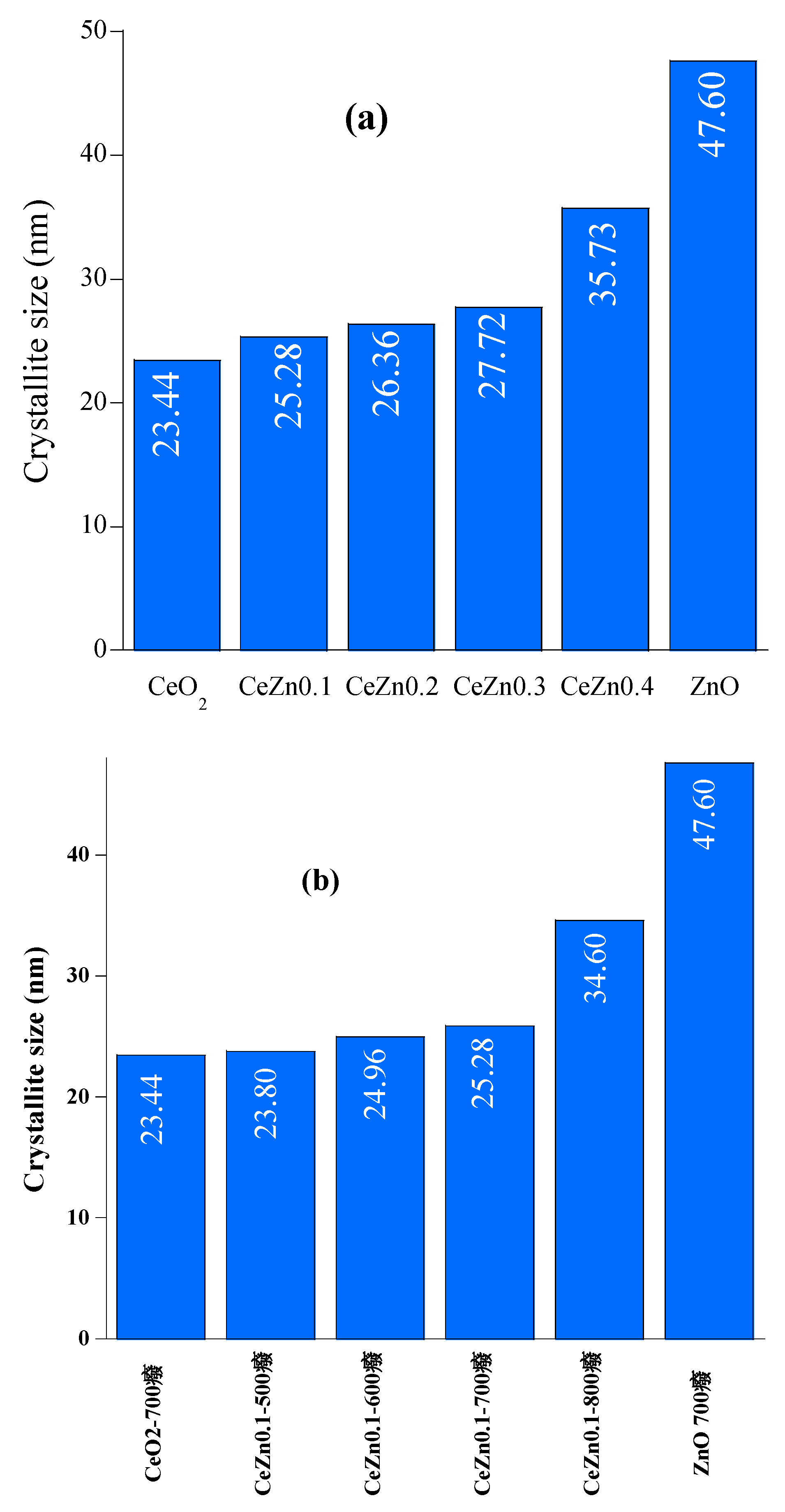
2.1. Structural Analysis
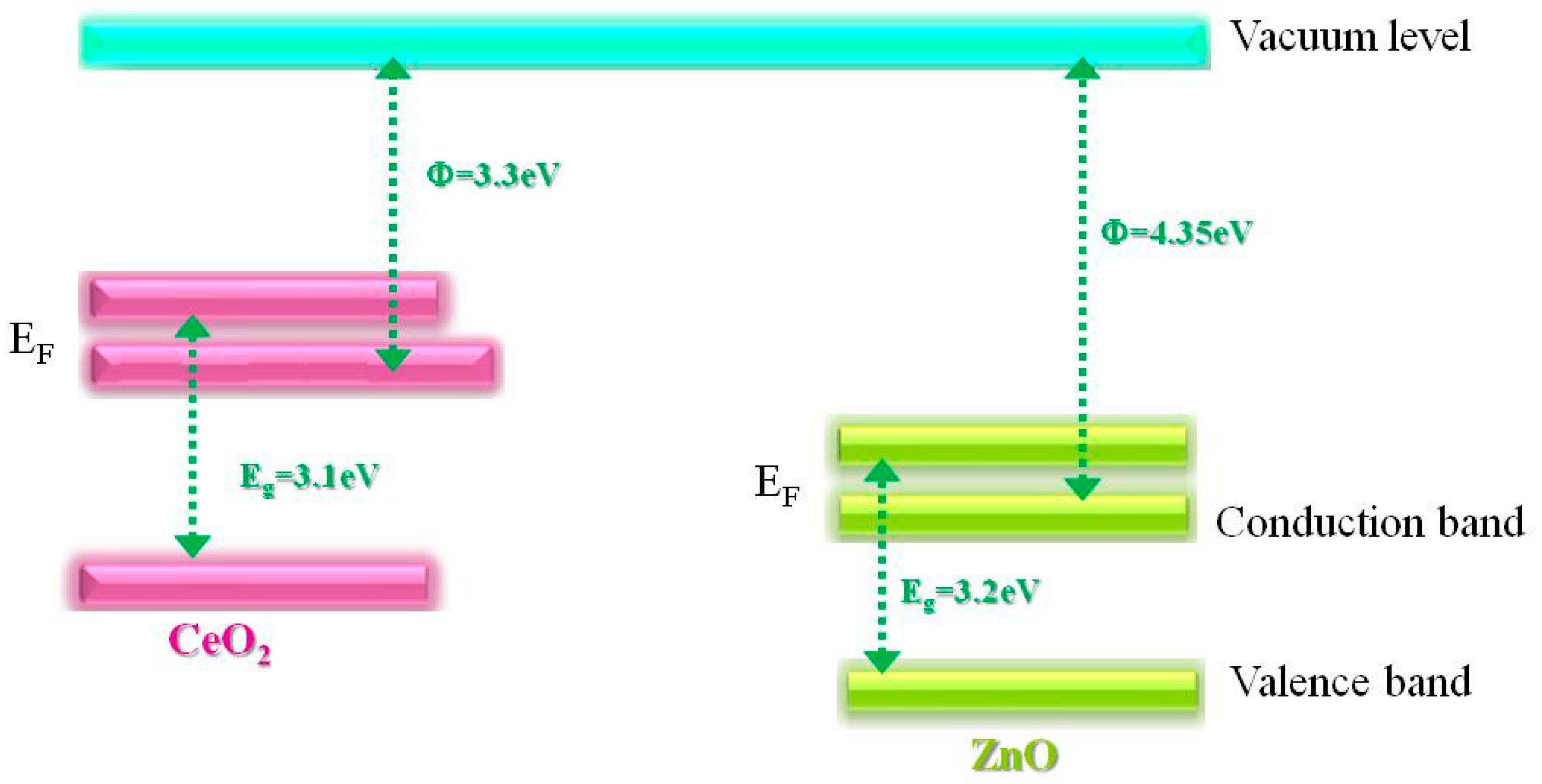
2.2. Optical properties
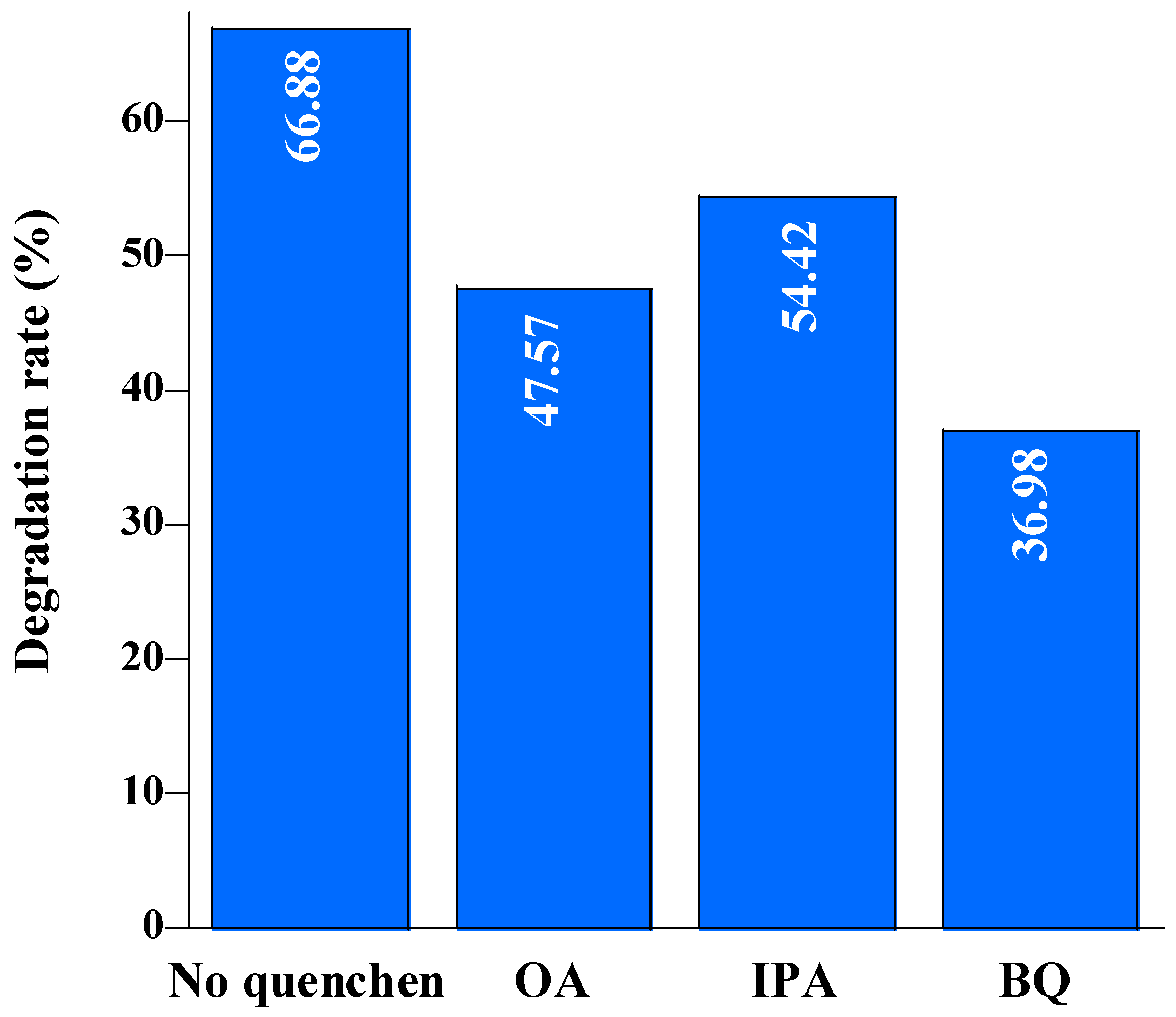
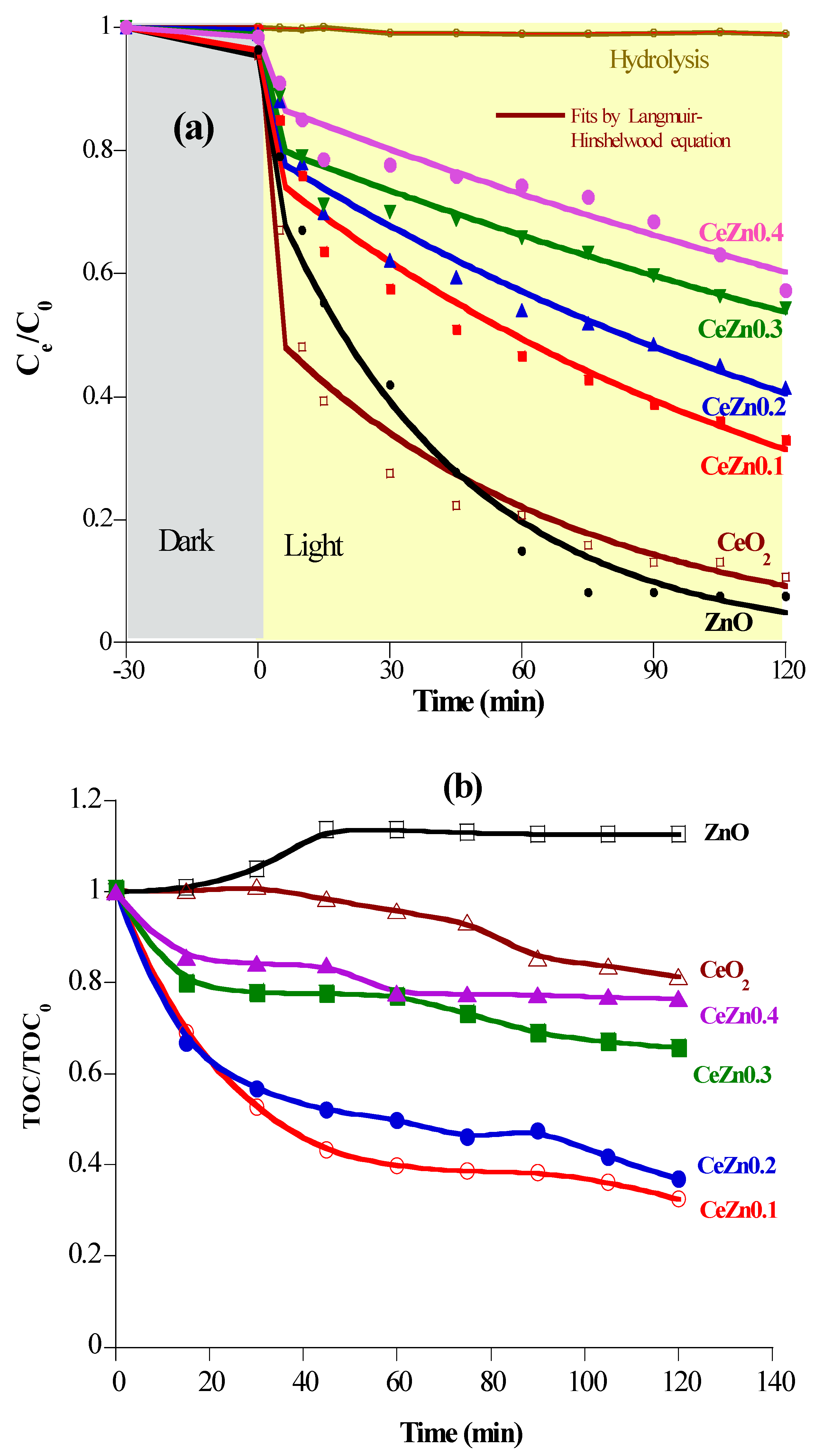
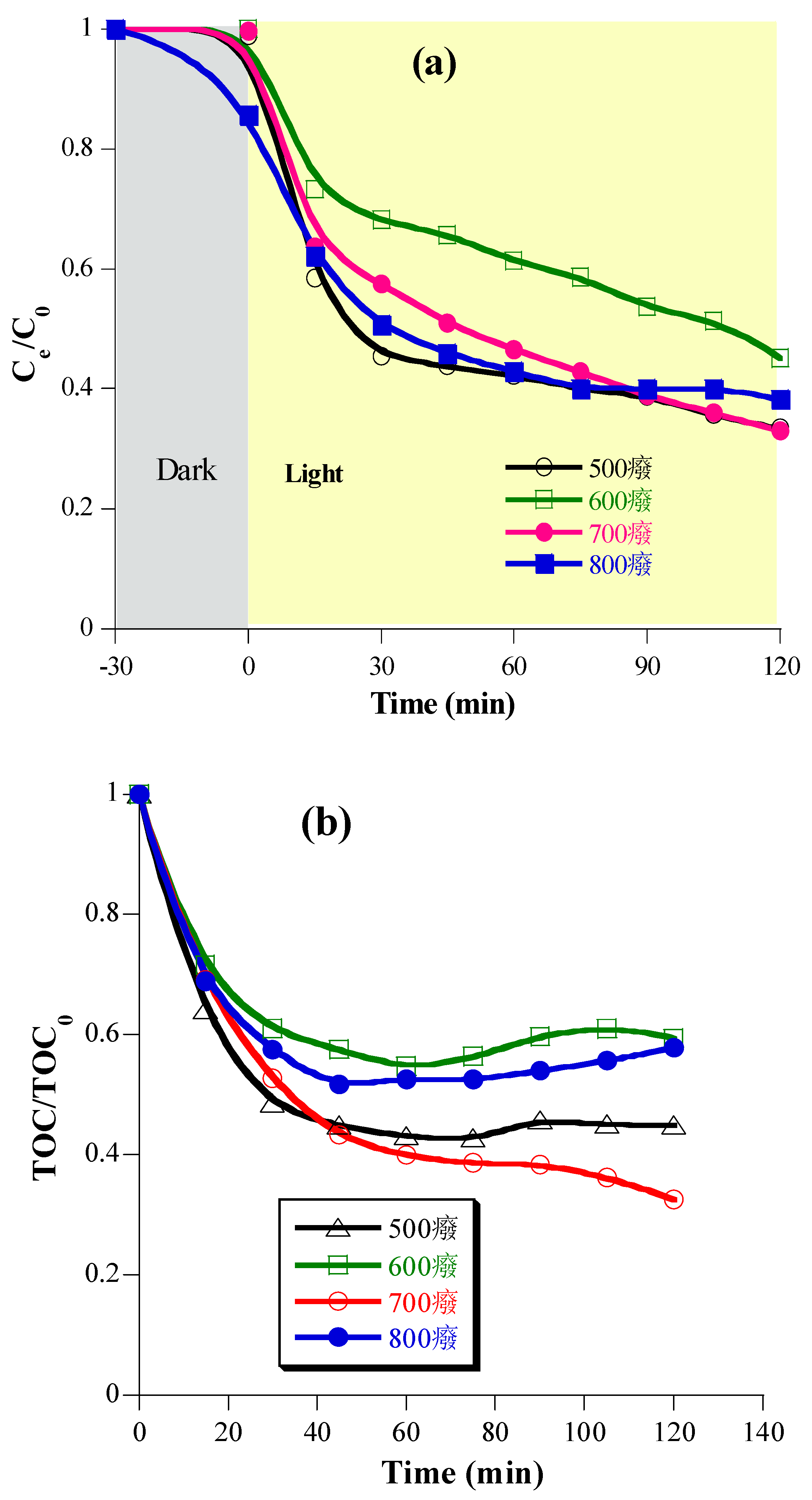
2.3. Photocatalytic mineralization of diclofenac
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Synthesis of ZnO, CeO2 and Ce1-xZnxO2-x solid solutions
3.3. Methods of characterization
3.4. Evaluation of photocatalytic performance
4. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Evgenidou, E.N.; Konstantinou, I.K.; Lambropoulou, D.A. Occurrence and removal of transformation products of PPCPs and illicit drugs in wastewaters: A review. Sci. Total. Environ. 2015, 505, 905–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakada, N.; Shinohara, H.; Murata, A.; Kiri, K.; Managaki, S.; Sato, N.; Takada, H. Removal of selected pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) and endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) during sand filtration and ozonation at a municipal sewage treatment plant. Water Res. 2007, 41, 4373–4382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguela, C.B.D.; Manga, N.H.; Marchal, C.; Abega, A.V.; Nsami, N.J.; Robert, D. Effect of Biogenic Silica Behavior in the Incorporation of Mesoporous Anatase TiO2 for Excellent Photocatalytic Mineralization of Sodium Diclofenac. Catalysts 2022, 12, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, J.; Freier, U.; Wecks, M.; Hohmann, S. Degradation of diclofenac in water by heterogeneous catalytic oxidation with H2O2. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2007, 70, 447–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosales, E.; Diaz, S.; Pazos, M.; Sanromán, M.A. Comprehensive strategy for the degradation of anti-inflammatory drug diclofenac by different advanced oxidation processes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 208, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.; Zhou, Q. Degradation of some typical pharmaceuticals and personal care products with copper-plating iron doped Cu2O under visible light irradiation. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 24, 827–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daghrir, R.; Drogui, P.; Robert, D. Modified TiO2 For Environmental Photocatalytic Applications: A Review. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 3581–3599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruna, A.; Wu, Z.; Zapien, J.; Li, Y.; Ruotolo, A. Enhanced photocatalytic performance of ZnO nanostructures by electrochemical hybridization with graphene oxide. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 441, 936–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.; Jalil, A.; Triwahyono, S.; Ripin, A.; Aziz, F.; Fatah, N.; Jaafar, N.; Hitam, C.; Salleh, N.; Hassan, N. Strategies for introducing titania onto mesostructured silica nanoparticles targeting enhanced photocatalytic activity of visible-light-responsive Ti-MSN catalysts. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 143, 948–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, B.; Li, Z.; Wu, Z.; Zhu, K.; Zhuang, J.; Xi, Q.; Hou, Y.; Chen, J.; Cong, M.; et al. Photo-Fenton reaction and H2O2 enhanced photocatalytic activity of α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles obtained by a simple decomposition route. J. Alloy. Compd. 2018, 771, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, B. Zhu, B. Zhong, L. Zhang, B. Cheng, Direct Z-scheme TiO2/CdS hierarchical photocatalyst for enhanced photocatalytic H2-production activity, Applied Surface Science. 422 (2017) 518–527. [CrossRef]
- Baxter, J.B.; Schmuttenmaer, C.A. Conductivity of ZnO Nanowires, Nanoparticles, and Thin Films Using Time-Resolved Terahertz Spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 25229–25239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meulenkamp, E.A. Electron Transport in Nanoparticulate ZnO Films. J. Phys. Chem. B 1999, 103, 7831–7838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.M.; Lai, C.W.; Ngai, K.S.; Juan, J.C. Recent developments of zinc oxide based photocatalyst in water treatment technology: A review. Water Res. 2016, 88, 428–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yusoff, N.; Ho, L.-N.; Ong, S.-A.; Wong, Y.-S.; Khalik, W. Photocatalytic activity of zinc oxide (ZnO) synthesized through different methods. Desalination Water Treat. 2015, 57, 12496–12507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kositzi, M.; Poulios, I.; Samara, K.; Tsatsaroni, E.; Darakas, E. Photocatalytic oxidation of Cibacron Yellow LS-R. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 146, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fang, H.-B.; Zheng, Y.-Z.; Ye, R.; Tao, X.; Chen, J.-F. Controllable assembly of well-defined monodisperse Au nanoparticles on hierarchical ZnO microspheres for enhanced visible-light-driven photocatalytic and antibacterial activity. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 19118–19128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- W. Yu, D. Xu, T. Peng, Enhanced photocatalytic activity of gC 3 N 4 for selective CO2 reduction to CH 3 OH via facile coupling of ZnO: a direct Z-scheme mechanism, Journal of Materials Chemistry A. 3 (2015) 19936–19947. [CrossRef]
- R. Zha, R. R. Zha, R. Nadimicherla, X. Guo, Ultraviolet photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange by nanostructured TiO2/ZnO heterojunctions, Journal of Materials Chemistry A. 3 (2015) 6565–6574. [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, M.; Samadi, M.; Yousefzadeh, S.; Soltani, M.; Rahimi, A.; Chou, T.-C.; Chen, L.-C.; Chen, K.-H.; Moshfegh, A.Z. Improved Solar-Driven Photocatalytic Activity of Hybrid Graphene Quantum Dots/ZnO Nanowires: A Direct Z-Scheme Mechanism. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 5, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Bian, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, A.; Wu, H.; Cui, H.; Chu, D.; Pan, J. Construction of Z-Scheme System for Enhanced Photocatalytic H2 Evolution Based on CdS Quantum Dots/CeO2 Nanorods Heterojunction. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 2552–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M. Haneda, T. M. Haneda, T. Kaneko, N. Kamiuchi, M. Ozawa, Improved three-way catalytic activity of bimetallic Ir–Rh catalysts supported on CeO2/ZrO2, Catalysis Science & Technology. 5 (2015) 1792–1800. [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Yabe, S.; Yamashita, M.; Momose, S.; Yoshida, S.; Yin, S.; Sato, T. UV-shielding properties of zinc oxide-doped ceria fine powders derived via soft solution chemical routes. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2002, 75, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.; Lei, Z.; Xu, Z.; Chen, X.; Gong, B.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, C. Flame spray pyrolysis synthesized ZnO/CeO 2 nanocomposites for enhanced CO 2 photocatalytic reduction under UV–Vis light irradiation. J. CO2 Util. 2017, 18, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Li, H.; Xia, P.; Liu, Z.; Xiong, D. Hierarchical ZnO Decorated with CeO2 Nanoparticles as the Direct Z-Scheme Heterojunction for Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 39679–39687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- I.-Tsan Liu, Min-Hsiung Hon, L. G. Teoh, The preparation, characterization and photocatalyticactivity of radical-shaped CeO2/ZnO microstructures Ceramics International 40 (2014) 4019-4024. [CrossRef]
- Cerrato, E.; Gonçalves, N.P.F.; Calza, P.; Paganini, M.C. Comparison of the Photocatalytic Activity of ZnO/CeO2 and ZnO/Yb2O3 Mixed Systems in the Phenol Removal from Water: A Mechanicistic Approach. Catalysts 2020, 10, 1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- P. Caregnato, K.R. Espinosa Jimenez, P.I. Villabrille, Ce-doped ZnO as photocatalyst for carbamazepine degradation, Catal. Today. (2020). [CrossRef]
- Al Abri, R.; Al Marzouqi, F.; Kuvarega, A.T.; Meetani, M.A.; Al Kindy, S.M.; Karthikeyan, S.; Kim, Y.; Selvaraj, R. Nanostructured cerium-doped ZnO for photocatalytic degradation of pharmaceuticals in aqueous solution. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A: Chem. 2019, 384, 112065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- L. Wolski, K. L. Wolski, K. Grzelak, M. Muńko, M. Frankowski, T. Grzyb, G. Nowaczyk, Insight into photocatalytic degradation of ciprofloxacin over CeO2/ZnO nanocomposites: Unravelling the synergy between the metal oxides and analysis of reaction pathways, Applied Surface Science 563 (2021) 150338. [CrossRef]
- Q. Zhang, X. Q. Zhang, X. Zhao, L. Duan, H. Shen, R. Liu, Controlling oxygen vacancies and enhanced visible light photocatalysis of CeO2/ZnO nanocomposites, Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry 392 (2020) 112156. [CrossRef]
- Z. Wang, P.Zhao, Y.Cheng, L. Liao, S. Li, Y.Luo , Z. Peng , P.Lin, D. He, Cerium oxide immobilized reduced graphene oxide hybrids with excellent microwave absorbing performance. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 14155–14165. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Li, F.; Liu, Y.; Li, P.; Chen, L.; Li, B.; Qian, T.; Liu, W. Degradation of diclofenac in a photosensitization-like photocatalysis process using palladium quantum dots deposited graphite carbon nitride under solar light. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
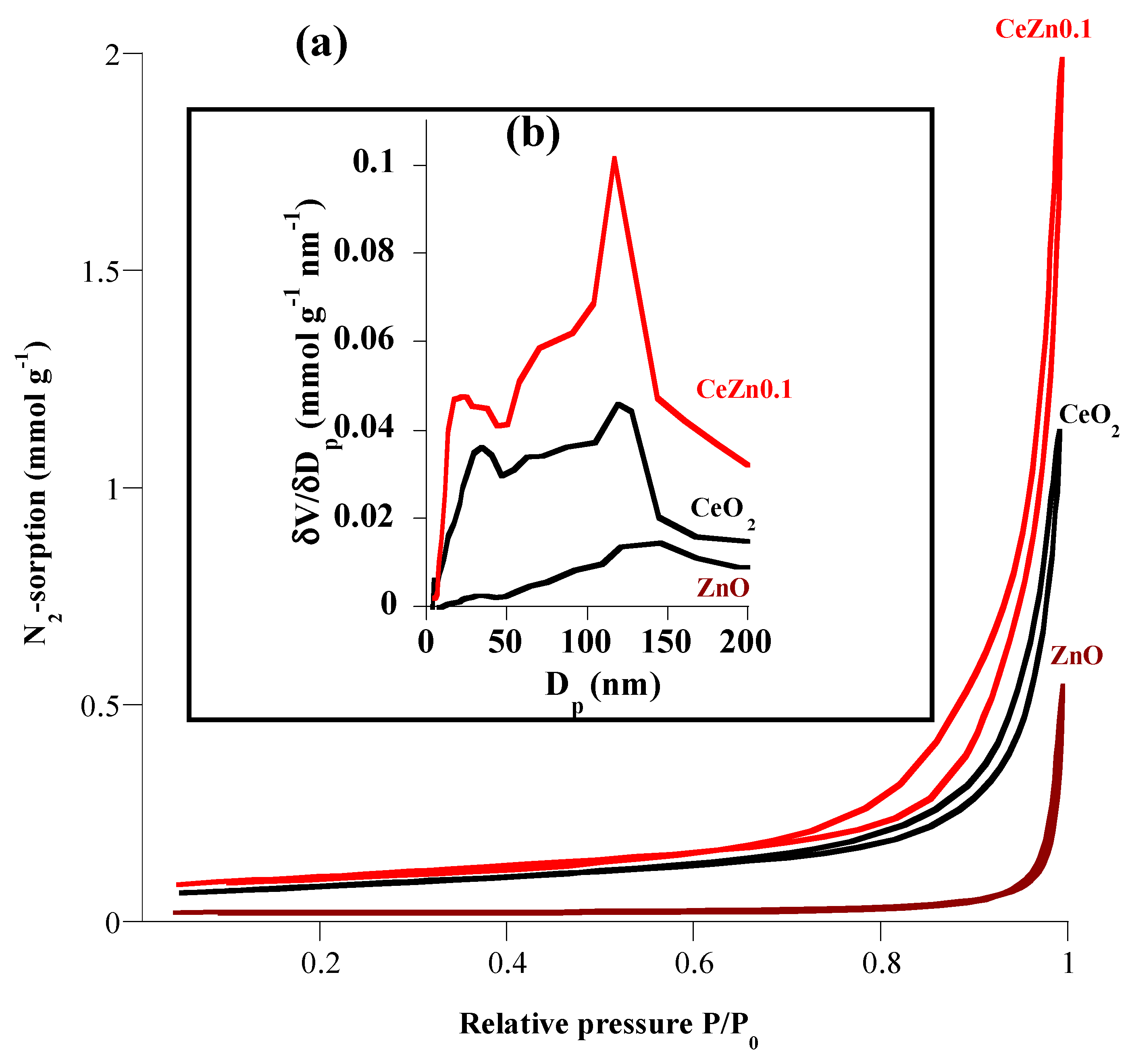
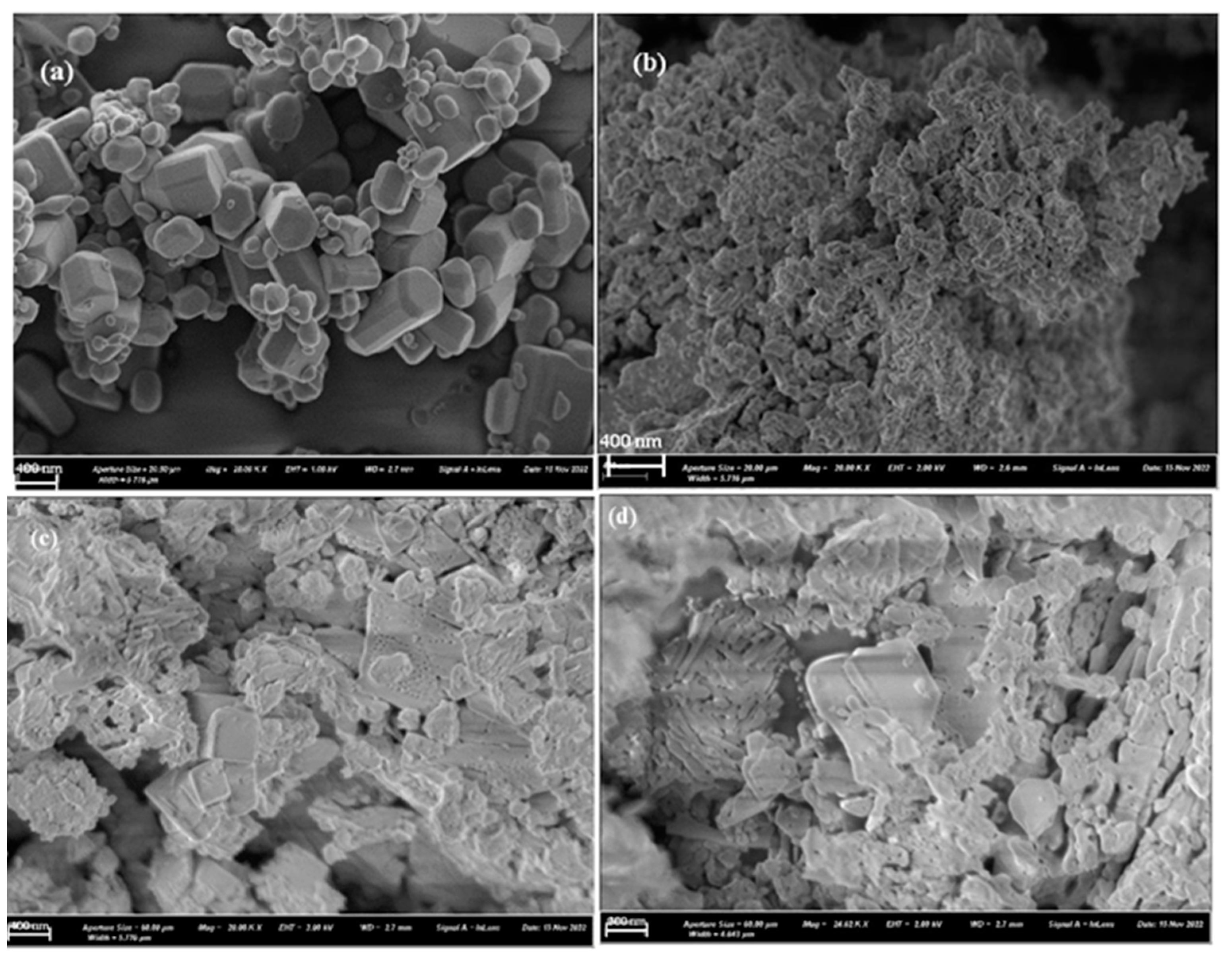
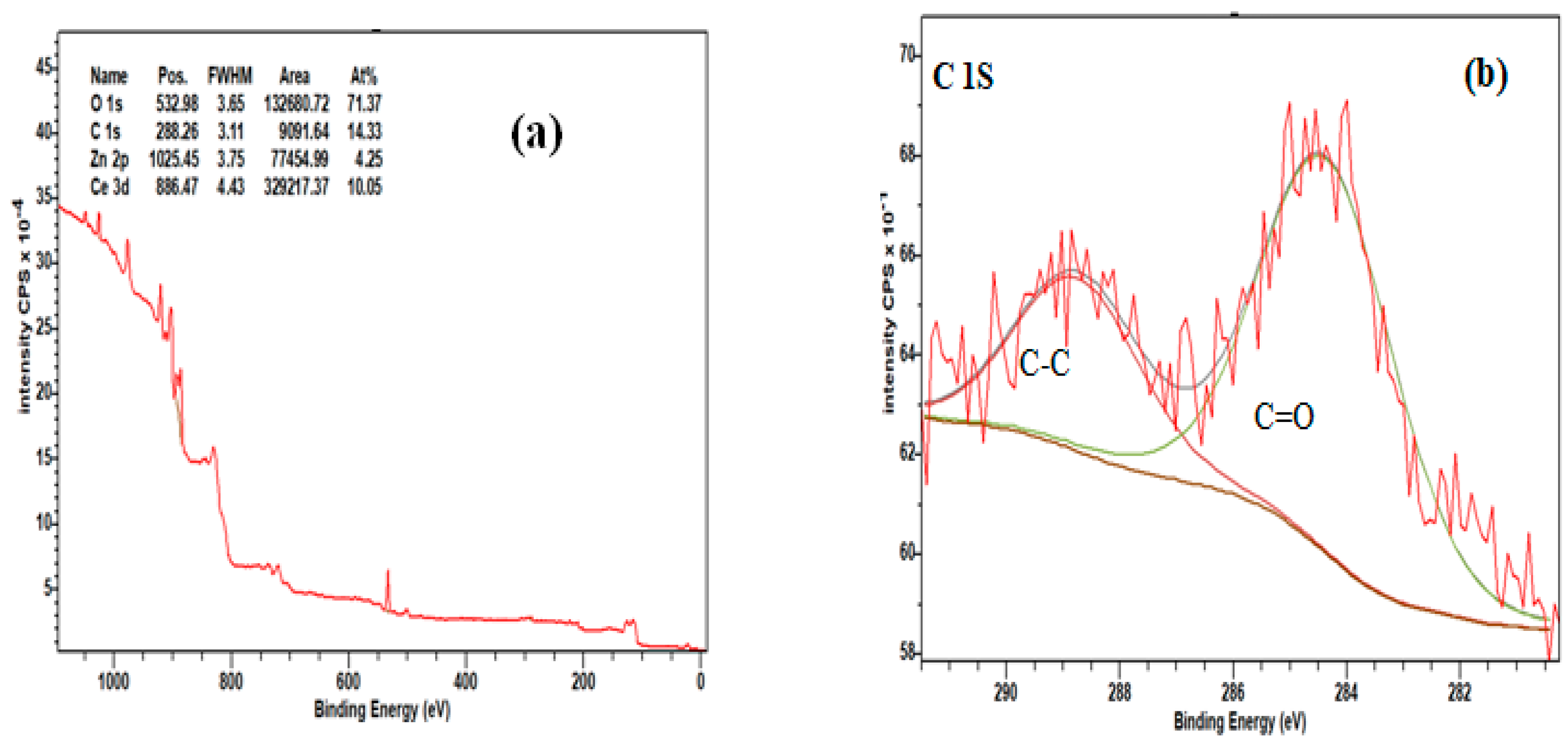
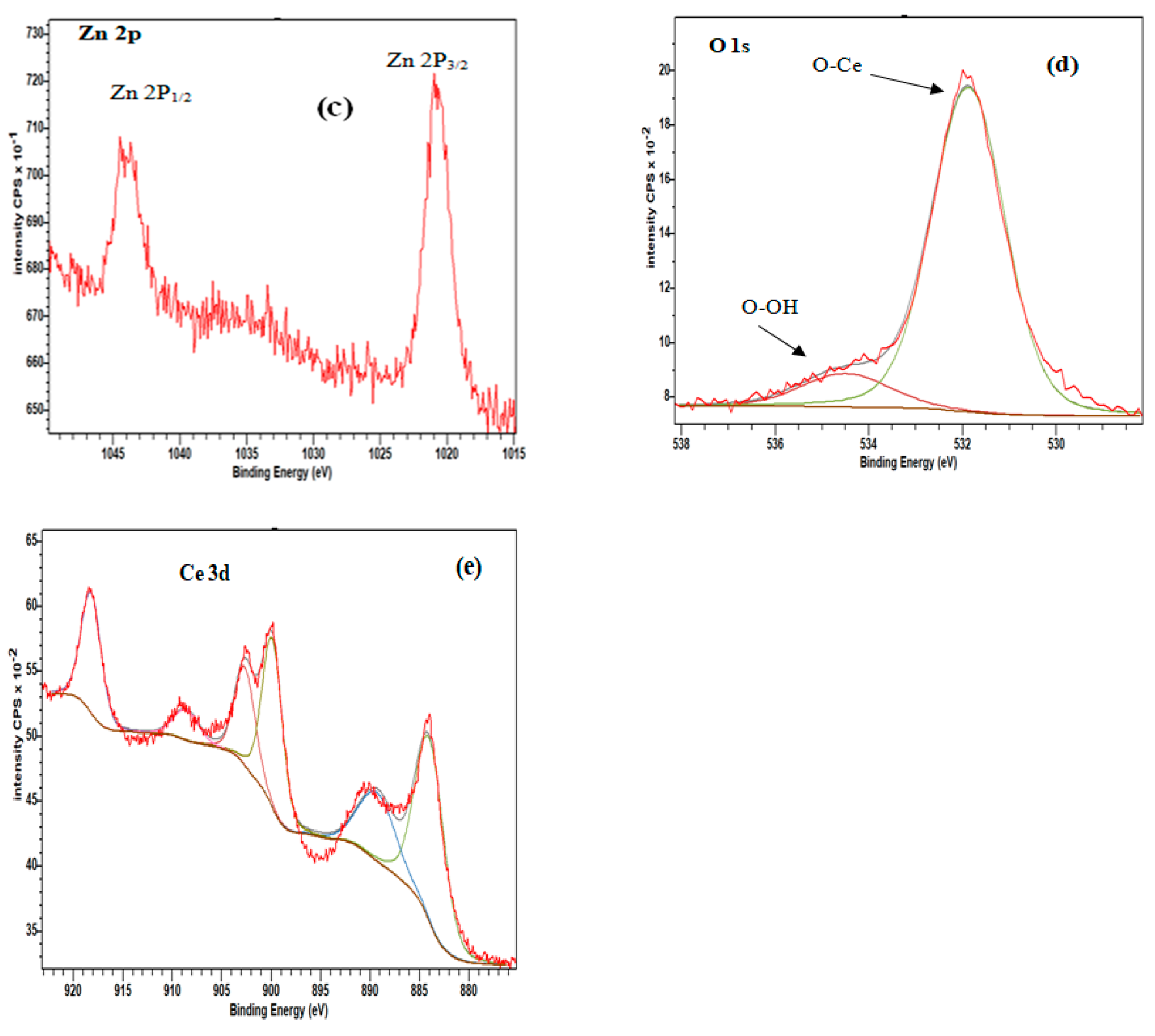

| 2θ (degree) | Microstrain (ε) | Dislocation density (δ) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CeO2 Ce1-xZnxO2-x |
28.16 | 0.617 | 1.820 | |
| 0.1 | 28.58 | 0.589 | 1.505 | |
| 0.2 | 27.98 | 0.544 | 1.439 | |
| 0.3 | 28.10 | 0.518 | 1.301 | |
| 0.4 | 28.61 | 0.438 | 0.783 | |
| ZnO | 36.17 | 0.236 | 0,441 |
| ZnO | CeO2 | CeZn0.1 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| SBET (m2 g-1) | 0.65 | 6.44 | 8.05 |
| Vp (cm3 g-1) | 0.006 | 0.039 | 0.069 |
| Dp (nm) | 70.25 | 29.62 | 40.89 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





