Submitted:
11 June 2023
Posted:
12 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant materials and growth conditions
2.2. Extraction of total RNA, reverse-transcription, and extraction of genomic DNA
2.4. Measurement of fresh weight, soluble phosphate (Pi), and total P contents in soybean seedlings
2.5. Data analysis
3. Results
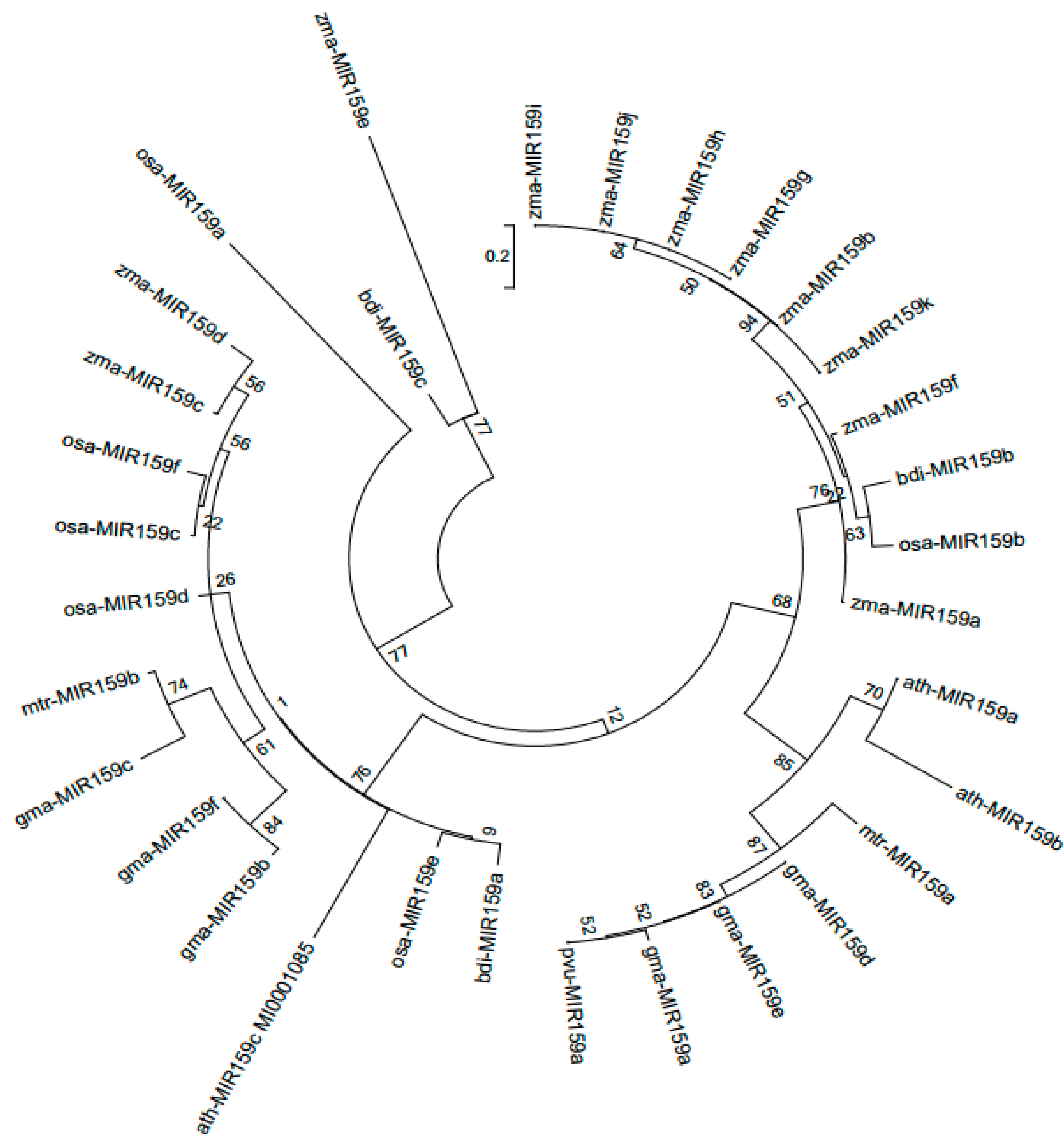
3.1. Identification of MIR159 gene family members in soybean
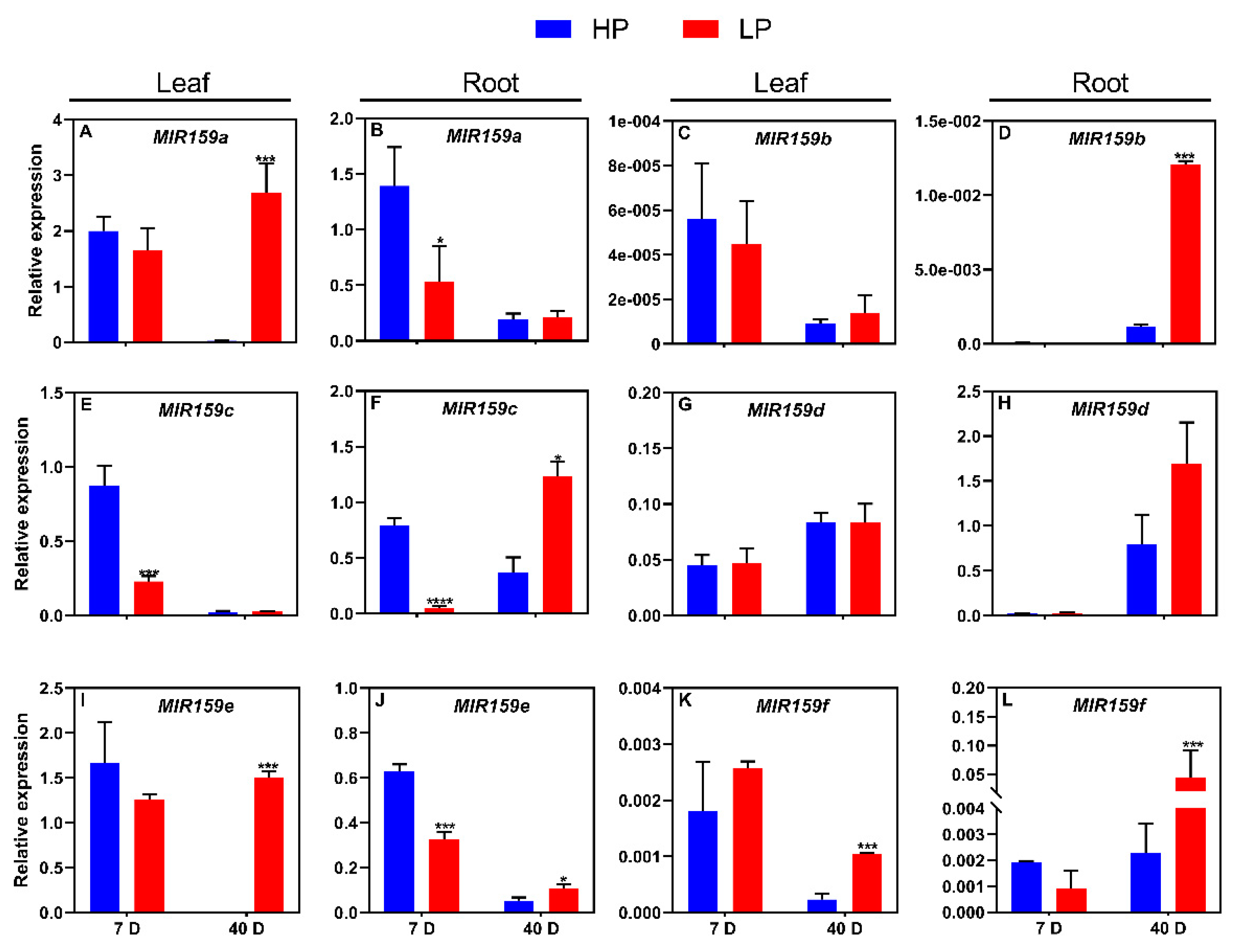
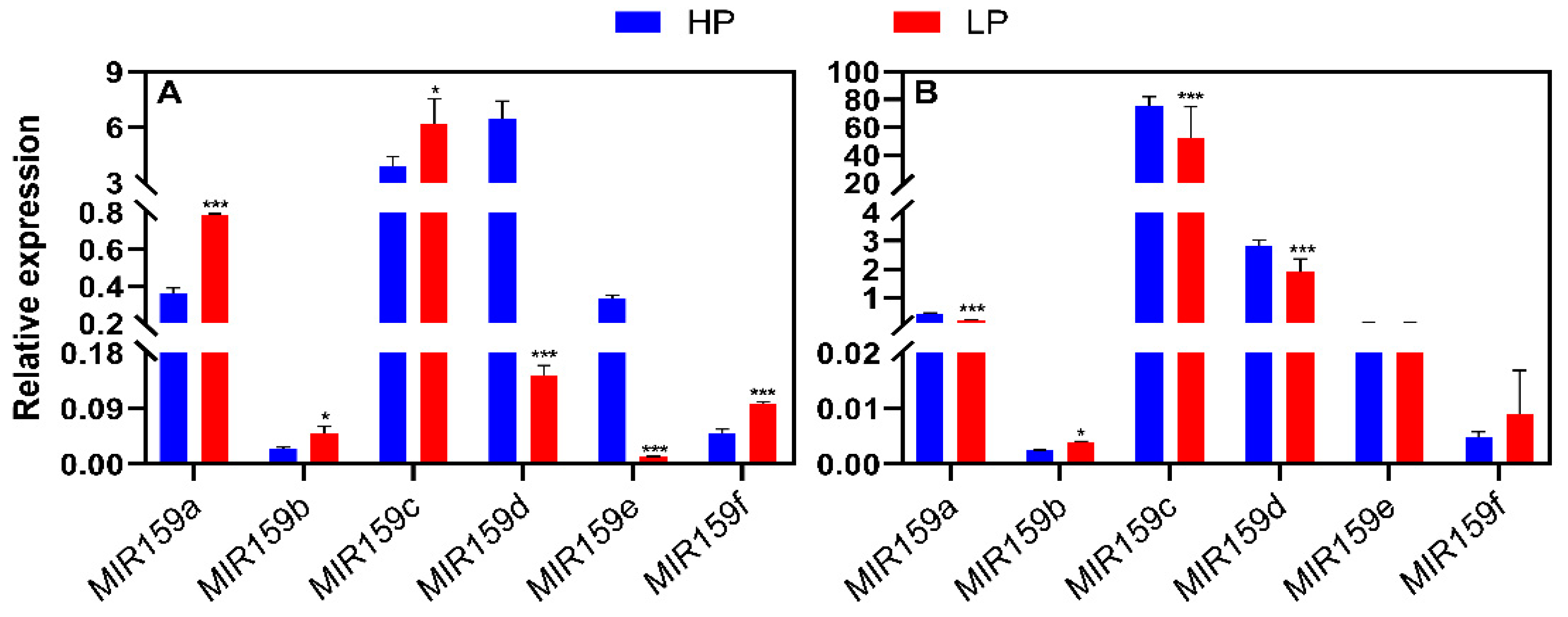
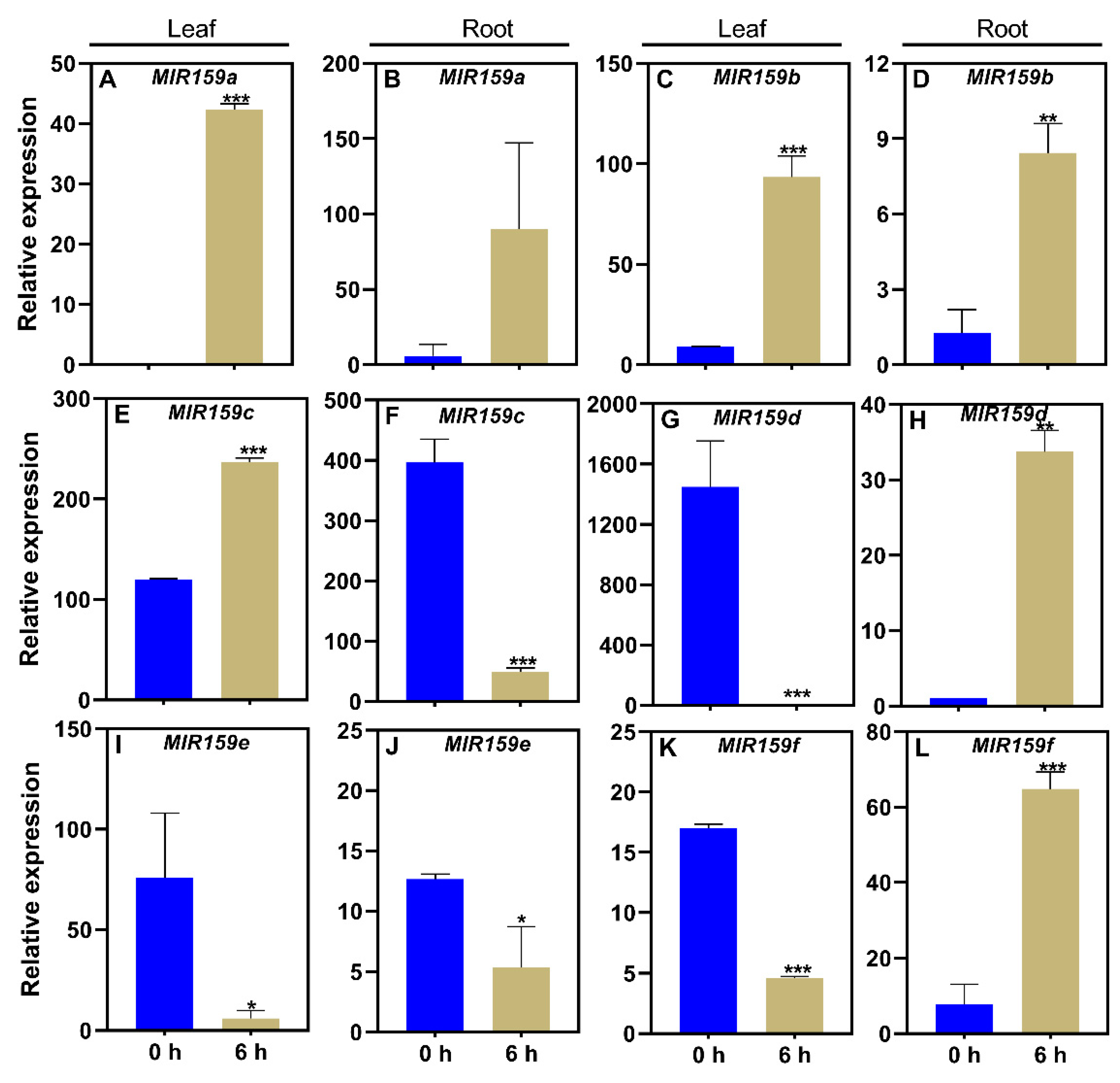
3.2. Responses of the soybean MIR159 gene family to low-P stress
3.3. Responses of the soybean MIR159 gene family to salt stress
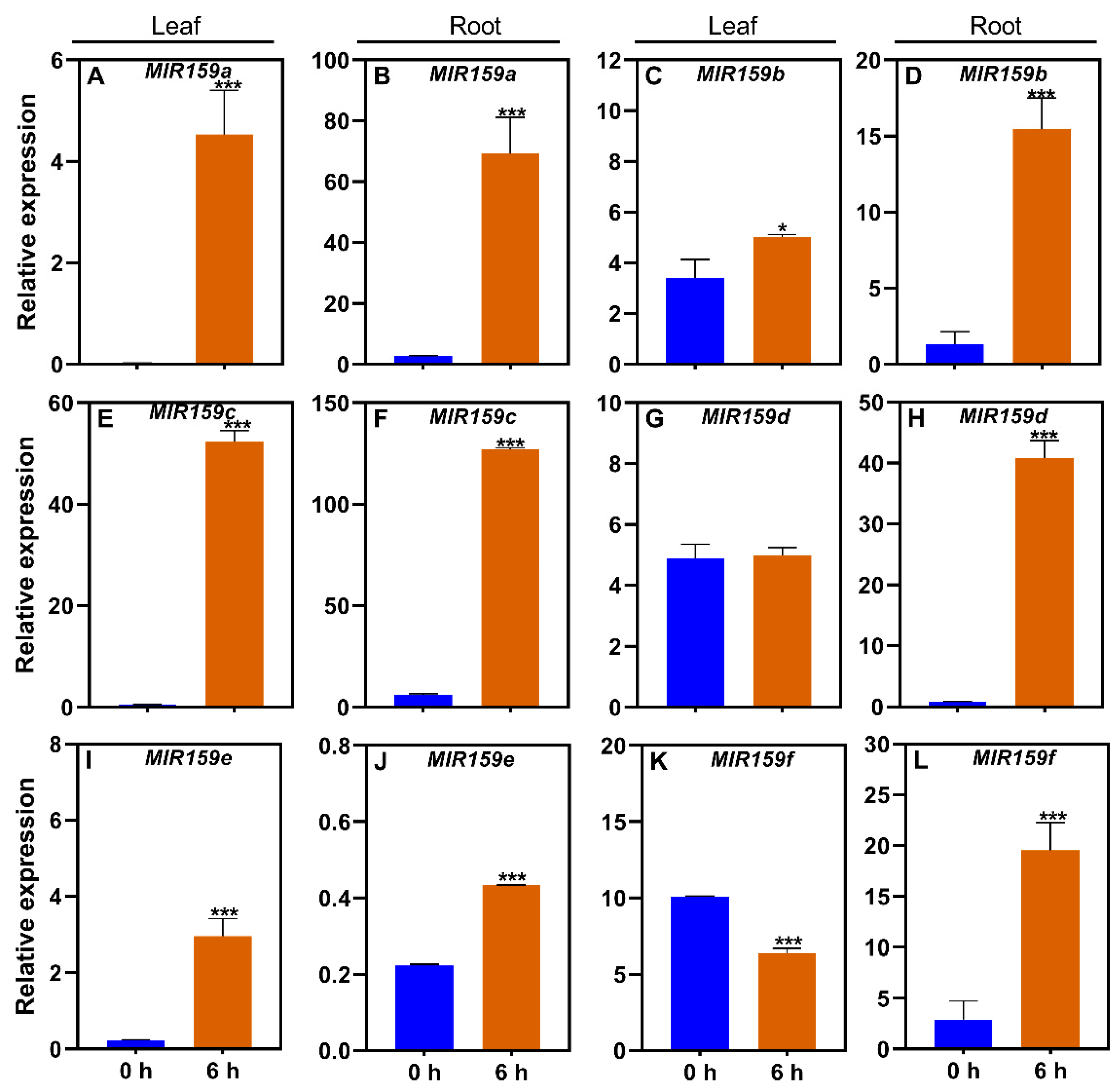
3.4. Responses of the soybean MIR159 gene family to ABA
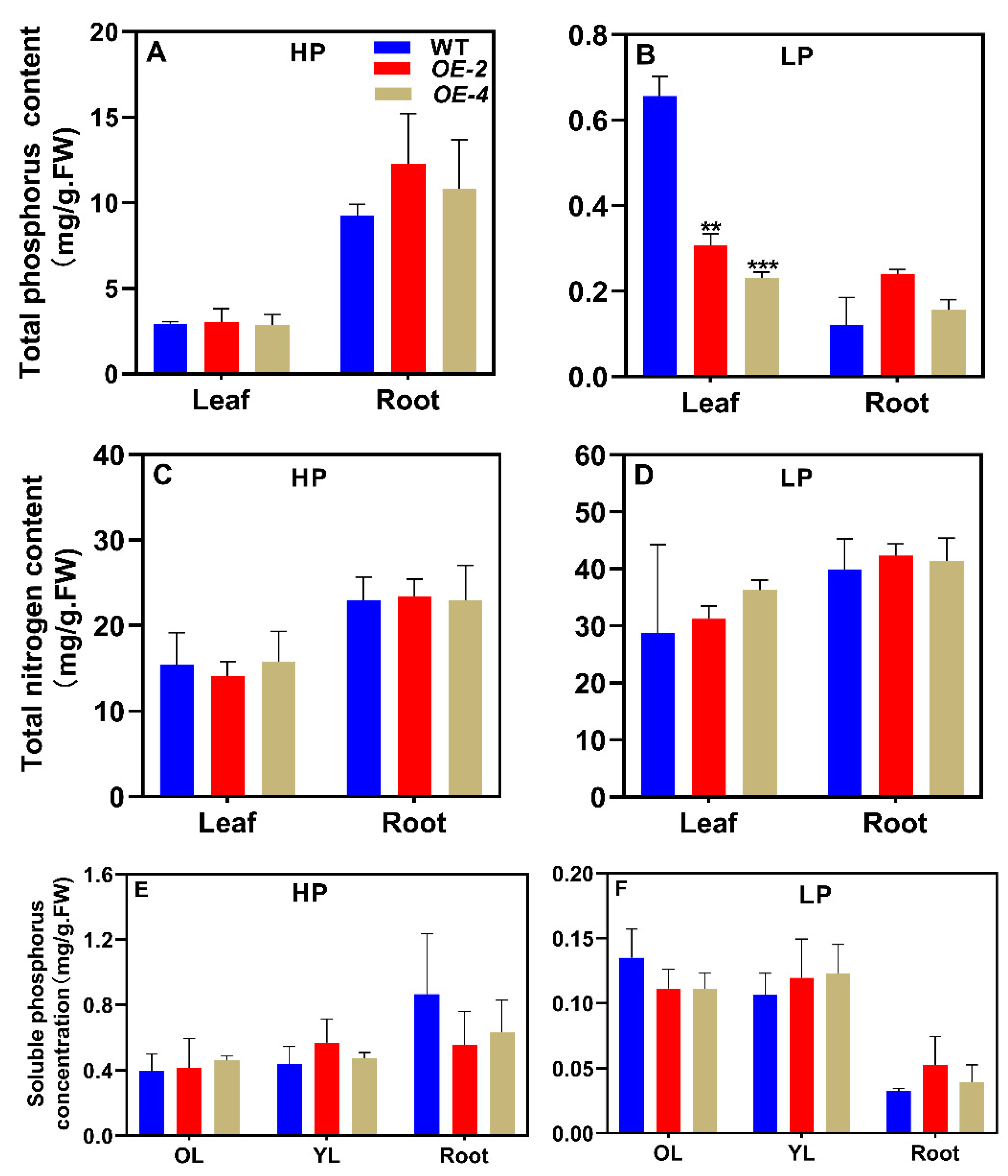
3.5. Overexpressing MIR159e decrease total phosphorus content in soybean leavea under LP conditions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
References
- Jonesrhoades, M.W.; Bartel, D.P.; Bartel, B. MicroRNAs and their Regulatory roles in Plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol 2006, 57, 19–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, K.; Chen, X. Biogenesis, turnover, and mode of action of plant microRNAs. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 2383–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.Q.; Zhu, Y.i.Y.; Huang, S.i.Q.; Yang, Z.M. Analysis of phosphorus-deficient responsive miRNAs and cis-elements from soybean (Glycine max L.). J Plant Physiol 2010, 167, 1289–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallory, A.C.; Vaucheret, H. Functions of microRNAs and related small RNAs in plants. Nat Genet 2006, 38, S31–S36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Xie, M.; Ren, G.; Yu, B. CDC5, a DNA binding protein, positively regulates posttranscriptional processing and/or transcription of primary microRNA transcripts. PNAS 2013, 110, 17588–17593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, M.N.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, Y. Response of salt-tolerant mirnas to high-salt habitats in mangrove companion plant hippocampal teeth. MPB 2017, 15, 1137–1142. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, C.; Fedoroff, N. A Mutation in the Arabidopsis HYL1 Gene Encoding a dsRNA Binding Protein Affects Responses to Abscisic Acid, Auxin, and Cytokinin. Plant Cell 2000, 12, 2351–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Molina, L.; Mongrand, S.; Mclachlin, D.T.; Mclachlin, B.T.; Chait, N.-H.C. ABI5 acts downstream of ABI3 to execute an ABA-dependent growth arrest during germination. Plant J 2002, 32, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.H.; Pan, X.P.; Wang, Q.L.; Cobb, G.P.; Anderson, T.A. Identification and characterization of new plant microRNAs using EST analysis. Cell Res 2005, 15, 336–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, H.; Urao, T.; Ito, T.; Seki, M.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. Arabidopsis AtMYC2 (bHLH) and AtMYB2 (MYB) Function as Transcriptional Activators in Abscisic Acid Signaling. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 63–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, H.; Chiou, T.J.; Lin, S.I.; Aung, K. A miRNA Involved in Phosphate-Starvation Response in Arabidopsis. Current Biology CB 2005, 15, 2038–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, W.G.; Li, B.D.; Kuang, J.B. Functional Characterization of the Steroid Reductase Genes GmDET2 and GmDET2b from Glycine max. Int J Mol Sci 2018, 19, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Jiao, F.; Wu, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; He, X.; Zhong, W.; Wu, P. OsPHR2 is involved in phosphate-starvation signaling and excessive phosphate accumulation in shoots of plants. Plant Physiol 2008, 146, 1673–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Tamura, K. MEGA-CC: Computing core of molecular evolutionary genetics analysis program for automated and iterative data analysis. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2685–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Zhao, P.X. psRNATarget: A plant small RNA target analysis server. Nucleic Acids Research 2011, 39, W155–W159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.; Liu, Q.; Chen, L.; Kuang, J.B.; Liao, H. Genome-wide identification of soybean microRNAs and their targets reveals their organ-specificity and responses to phosphate starvation. BMC Genomics 2013, 14, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.S.; Li, J.; Alonsoperal, M.M. MicroR159 regulation of most conserved targets in Arabidopsis has negligible phenotypic effects. Silence 2010, 1, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nord, E.A.; Lynch, J.P. Delayed reproduction in Arabidopsis thaliana improves fitness in soil with suboptimal phosphorus availability. Plant Cell & Environment 2008, 31, 1432–1441. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, F.; Wang, J.X. Research progress of MicroRNA regulating nutrient stress response of leguminous crops. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Journal 2016, 22, 236–244. [Google Scholar]
- Reyes, J.L.; Chua, N. ABA induction of miR159 controls transcript levels of two MYB factors during Arabidopsis seed germination. Plant Journal for Cell & Molecular Biology 2007, 49, 592–606. [Google Scholar]
- Khraiwesh, B.; Zhu, J.K.; Zhu, J. Role of miRNAs and siRNAs in biotic and abiotic stress responses of plants. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 2012, 1819, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millar, A.A.; Gubler, F. The Arabidopsis GAMYB-Like Genes, MYB33 and MYB65, Are MicroRNA-Regulated Genes That Redundantly Facilitate Anther Development. Plant Cell 2005, 17, 705–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.S.; Li, J.; Stahle, M.I. Genetic analysis reveals functional redundancy and the major target genes of the Arabidopsis miR159 family. PNAS 2007, 104, 16371–16376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Jin, Y.X. Evolution of MIR159/319 MicroRNA Genes and Their Post-transcriptional Regulatory Link to siRNA Pathways. BMC Evol Biol 2011, 11, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmutz, J.; Cannon, S.B.; Schlueter, J.; Ma, J.X.; Mitros, T.; Nelson, W.; Hyten, D. Genome sequence of the paleopolyploid soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merr.). Nature 2010, 463, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustos, R.; Castrillo, G.; Linhares, F.; Puga, M.I.; Rubio, V.; P’erez-Perez, J.; Solano, R.; Leyva, A.; Paz-Ares, J. A central regulatory system largely controls transcriptional activation and repression responses to phosphate starvation in Arabidopsis. PLOS Genet 2010, 6, e1001102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, X.Y.; Song, D.F.; Han, S.Y.; Wang, J.H.; Zhu, M.Y. Flowering time control in ornamental gloxinia (Sinningia speciosa) by manipulation of miR159 expression. Annals of Botany 2013, 111, 791–799. [Google Scholar]
- Csukasi, F.; Donaire, L.; Casañal, A.; Martínez-Priego, L.; Botella, M.A.; Medina-Escobar N,Llave, C.; Valpuesta, V. Two strawberry miR159 family members display developmental-specific expression patterns in the fruit receptacle and cooperatively regulate Fa-GAMYB. New Phytol 2012, 195, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivera, M.; Tejera, N.; Lribarne, C.; Ocaña, A.; Lluch, C. Growth, nitrogen fixation and ammonium assimilation in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris): Effect of phosphorus. Physiol Plantarum 2004, 121, 498–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, J.; Temple, G.; Temple, S.J.; Beschow, H.; Vance, C.P. Nitrogen fixation by white lupin under phosphorus deficiency. Annals of Botany 2006, 98, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucchero, J.C.; Caspi, M.; Dunn, K. ngl9: A third MADS box gene expressed in alfalfa root nodules. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 2001, 14, 1463–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.J.; Alonso-Peral, M.; Wong, G.; Wang, M.B.; Millar, A.A. Ubiquitous miR159 repression of MYB33/65 in Arabidopsis rosettes is robust and is not perturbed by a wide range of stresses. Bmc Plant Biology 2016, 16, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.T.; Yan, C.X.; Zhao, X.B.; Li, C.J.; Shi, C.R.; Yu, J.J.; Chan, S.H.; Li, R.G. Identification and functional characterization of salt tolerance related microRNAs in roots of peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Journal of Peanut Science 2016, 45, 36–42. [Google Scholar]
- Panda, S.K.; Sunkar, R. Nutrient- and other stress-responsive microRNAs in plants: Role for thiol-based redox signaling. Plant Signaling & Behavior 2015, 10, e1010916. [Google Scholar]
- Raghothama, K.G. Phosphate Acquisition. Annu Rev Plant Phys 1999, 274, 665–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinhart, B.J.; Weinstein, E.G.; Rhoades, M.W.; Bartel, B.; Bartel, D. MicroRNAs in plants. Genes & Development 2002, 16, 1616–1626. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.R.; Yan, X.L.; Liao, H. Genetic improvement for phosphorus efficiency in soybean: A radical approach. Ann Bot 2010, 106, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, X.; Liu, Z.; Dai, X.; Xiang, F. Primary root growth in Arabidopsis thaliana is inhibited by the miR159 mediated repression of MYB33, MYB65 and MYB101. Plant Sci 2017, 262, 182–189. [Google Scholar]
| Name | Mature miRNA sequence | Position on chromosome |
|---|---|---|
| MIR159a | GAGCUCCUUGAAGUCCAAUUG | Gm09: 40266722-40266935 + |
| MIR159b | GAGUUCCCUGCACUCCAAGUC | Gm07: 5424789-5424974 − |
| MIR159c | AUUGGAGUGAAGGGAGCUCCG | Gm16: 2830034-2830218 − |
| MIR159d | AGCUGCUUAGCUAUGGAUCCC | Gm09:40267077-40267097+ |
| MIR159e | GAGCUCCUUGAAGUCCAAUU | Gm07: 9561934-9562144 − |
| MIR159f | GAGUUCCCUGCACUCCAAGUC | Gm16: 2819636-2819815 − |
| Low-P Responsive Elements | NaCl-Responsive Elements | ABA-Responsive Elements | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TATA -Box | TATA -Box Like | W-Box | PHR1 Element | ABRE-like | ACGT Sequence | rd22 | AtMYB2 | MYC2 | ABRE | DPBF | RY Elements |
|
| MIR159a | 4 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| MIR159b | 4 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| MIR159c | 4 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | |||
| MIR159d | 4 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| MIR159e | 4 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| MIR159f | 4 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





