Submitted:
08 June 2023
Posted:
09 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
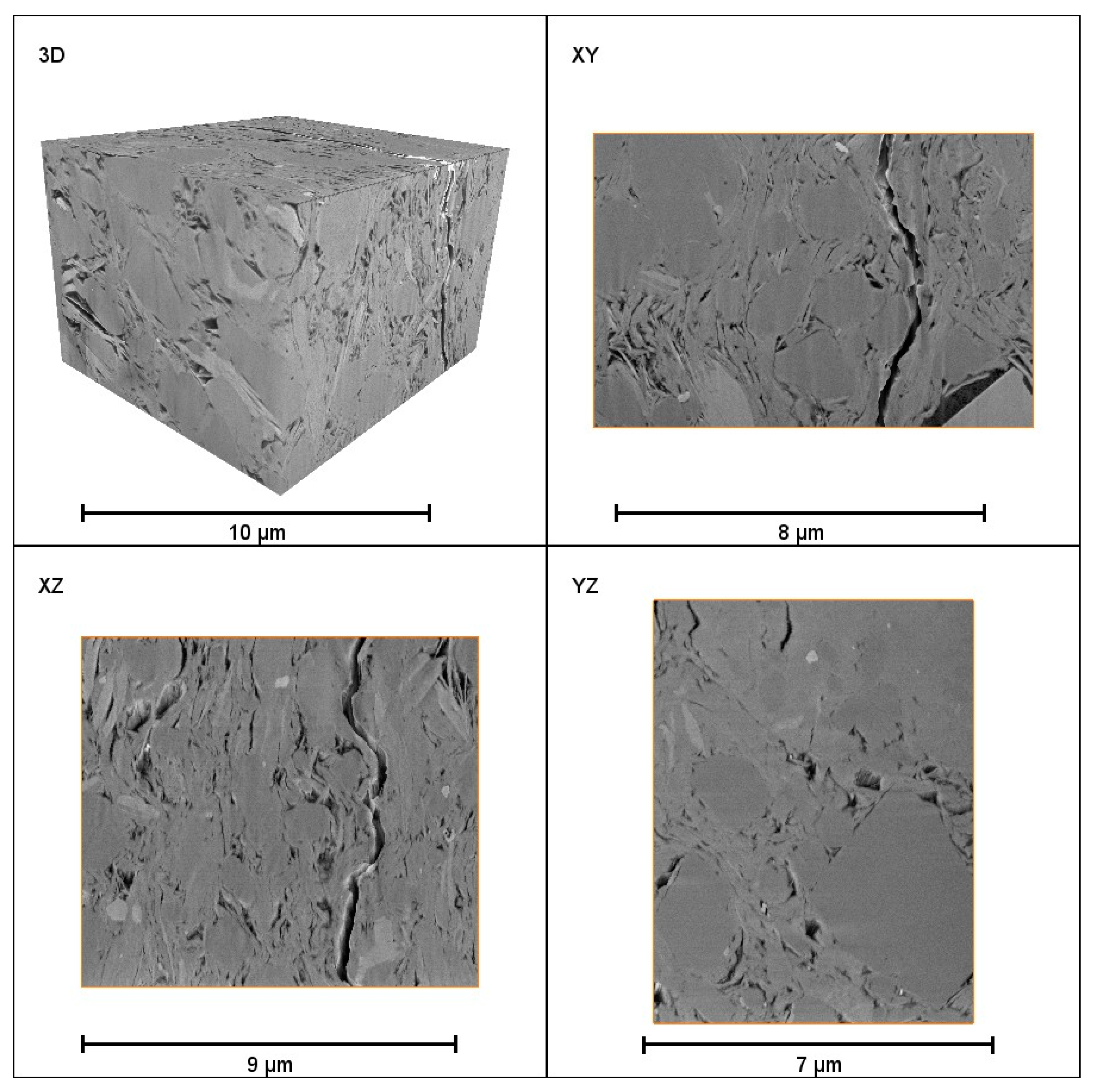
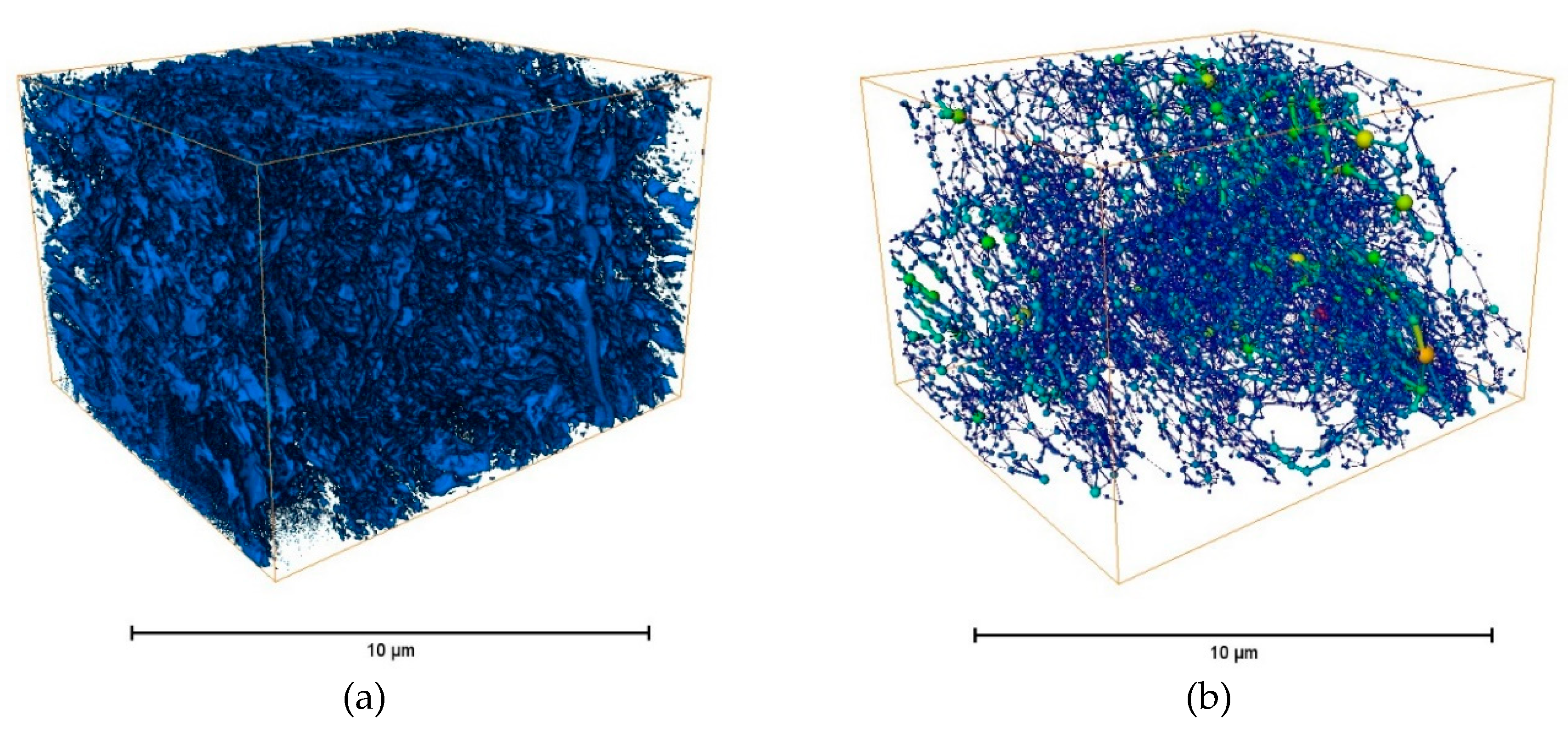
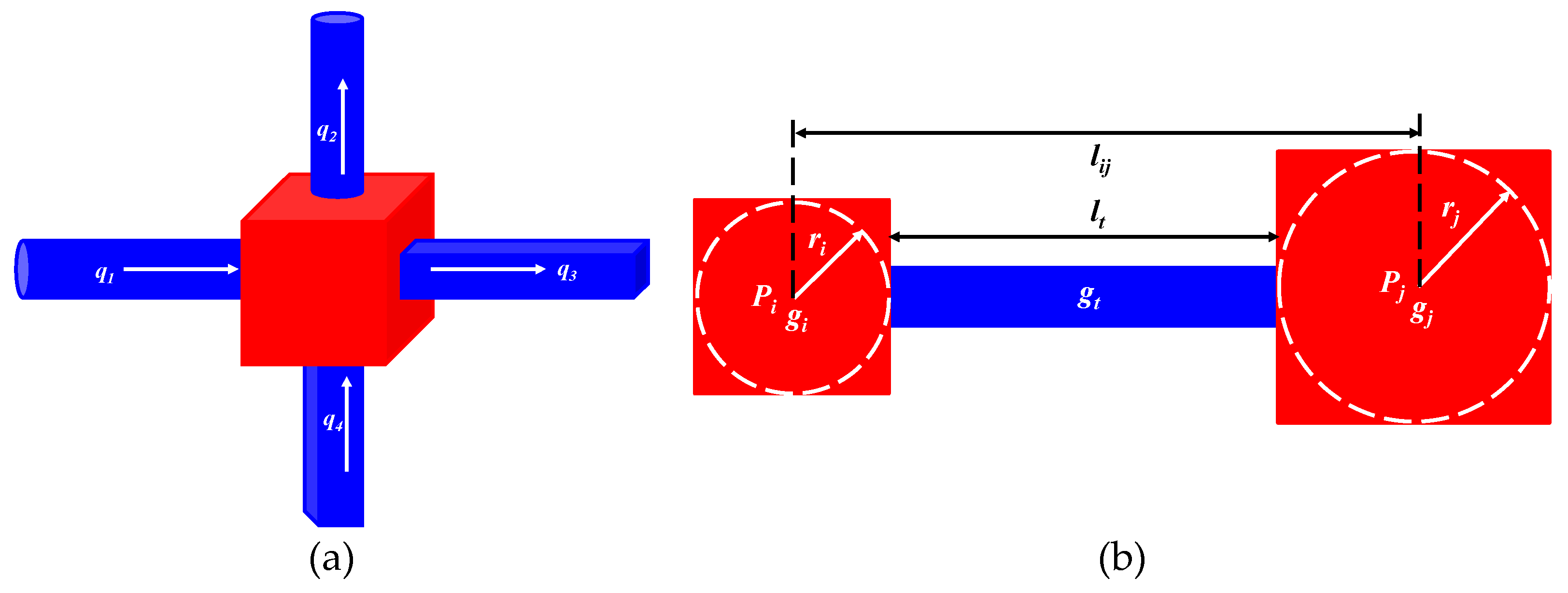
2.1. Establishment of pore network model based on FIB-SEM
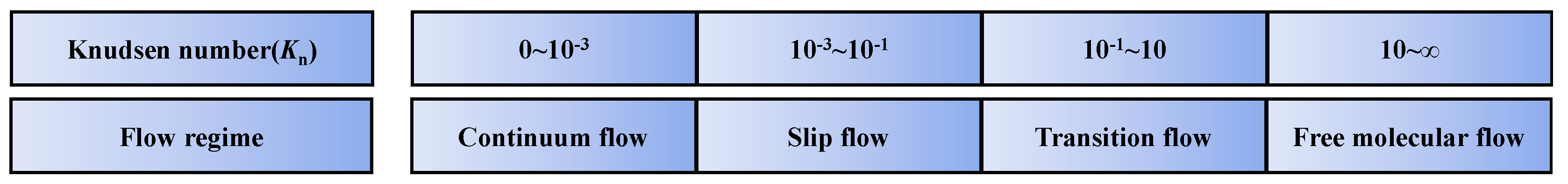
2.2. Quasi-static single-phase flow equations considering diffusion
2.3. Quasi-static two-phase flow equations
| Simulation parameter | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Pore number | / | 8717 |
| Throat number | / | 18494 |
| Oil density | g/cm3 | 0.7 |
| Water density | g/cm3 | 1 |
| Oil viscosity | mPa·s | 0.5 |
| Water viscosity | mPa·s | 1 |
| Oil-water contact angle | ° | 60 |
| Oil water interfacial tension | mN/m | 20 |
| Initial temperature | ℃ | 137 |
| Initial pressure | MPa | 37.5 |
3. Results and discussion
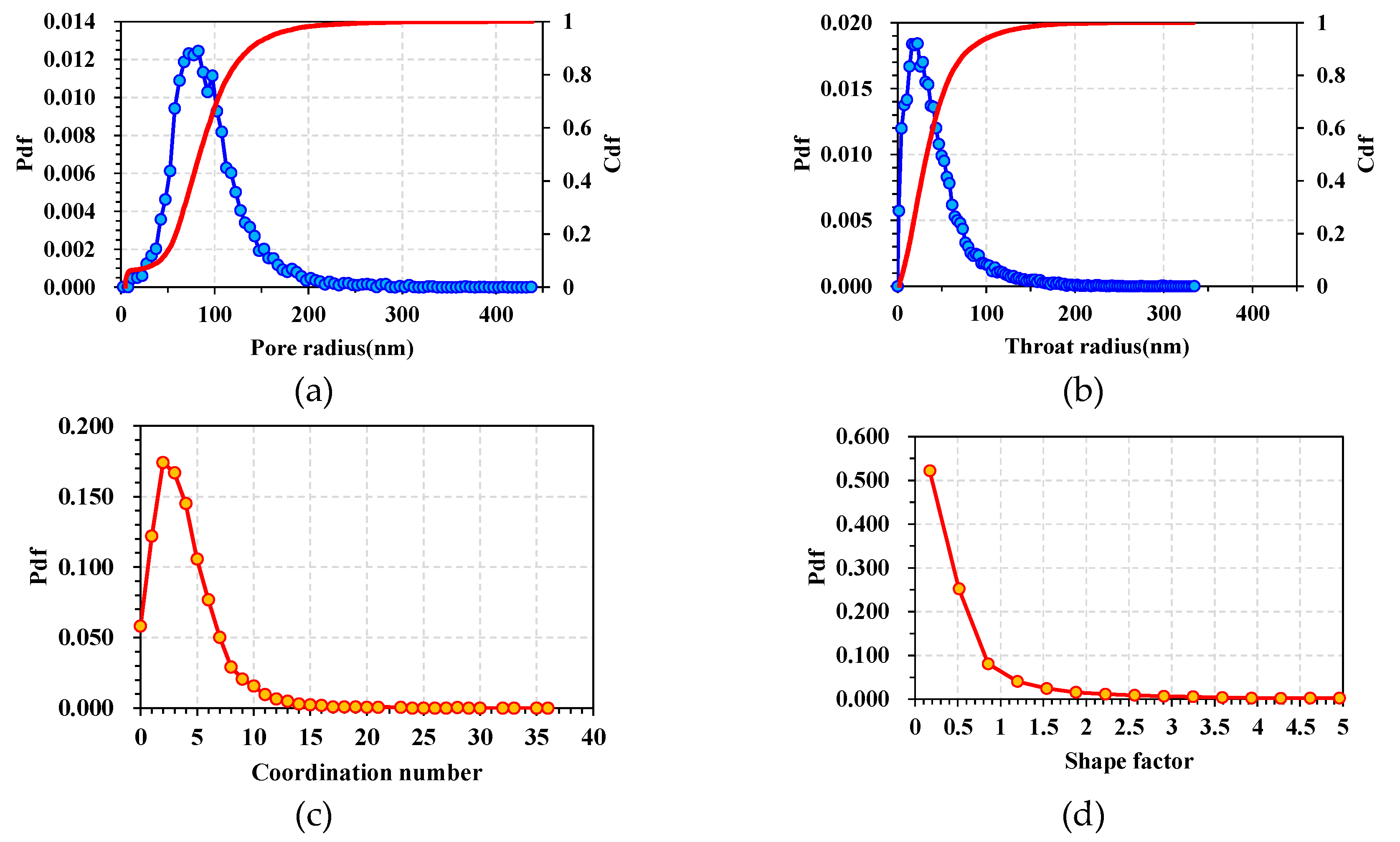
3.1. Pore-throat parameters characterization
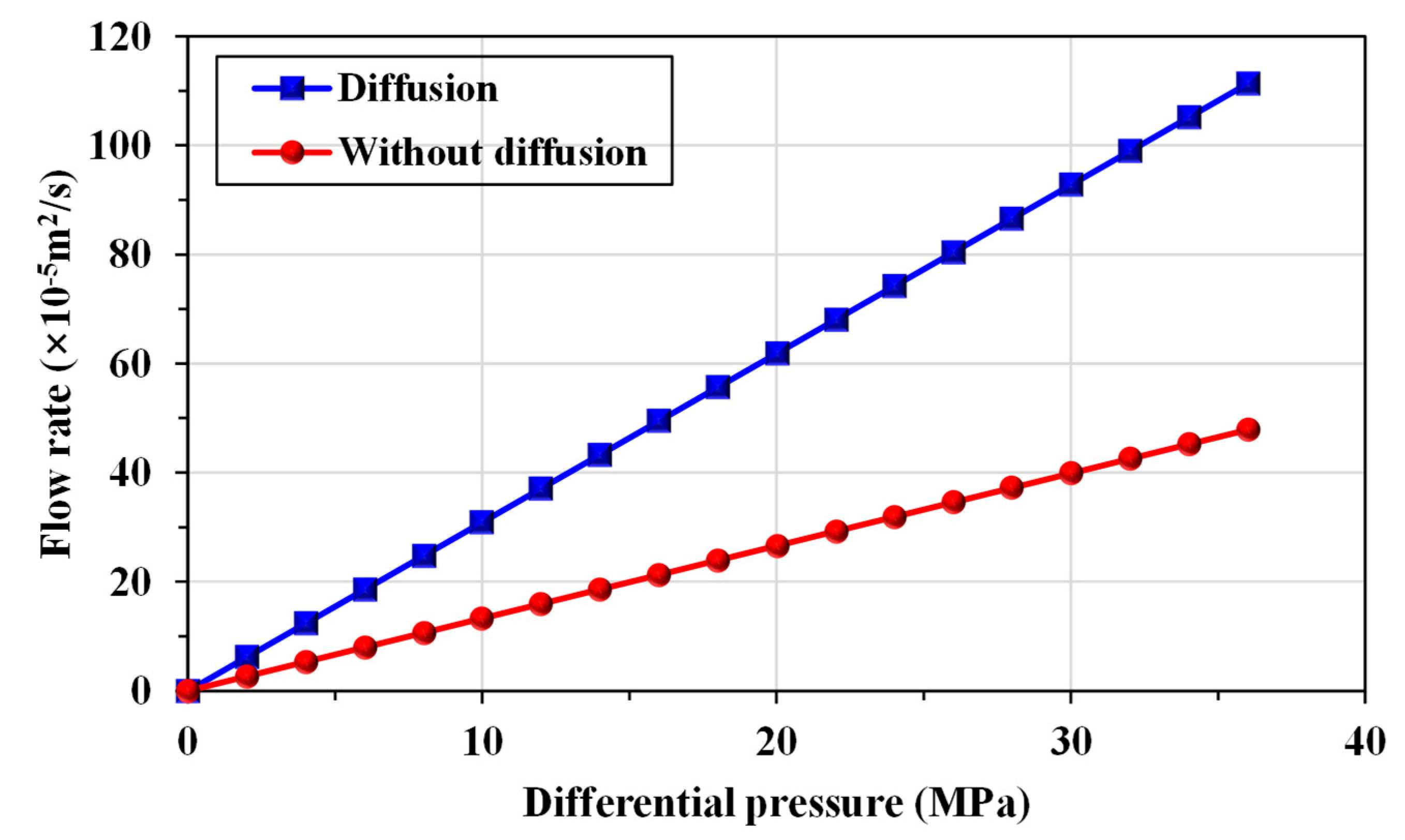
3.2. Apparent permeability characterization
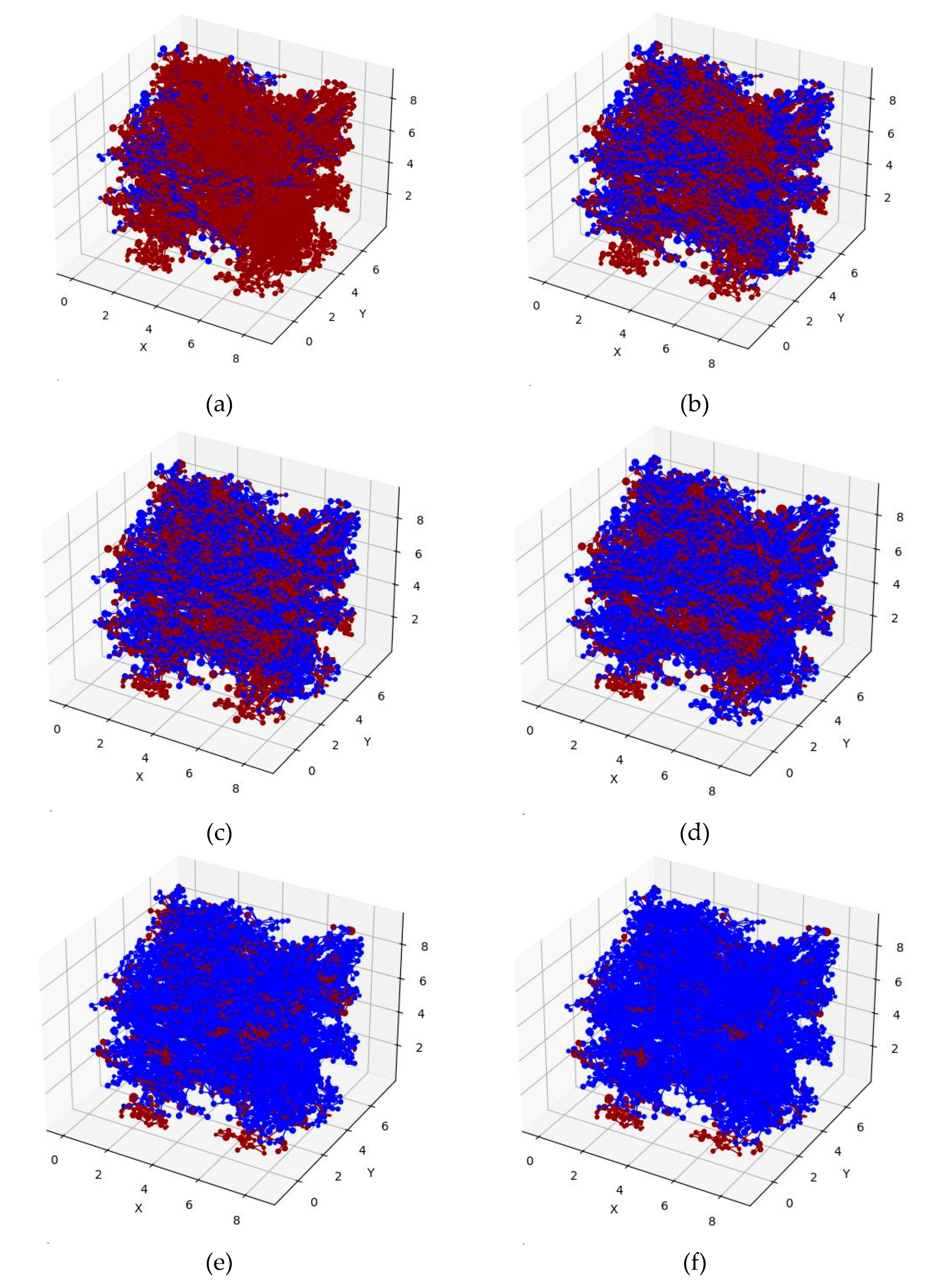
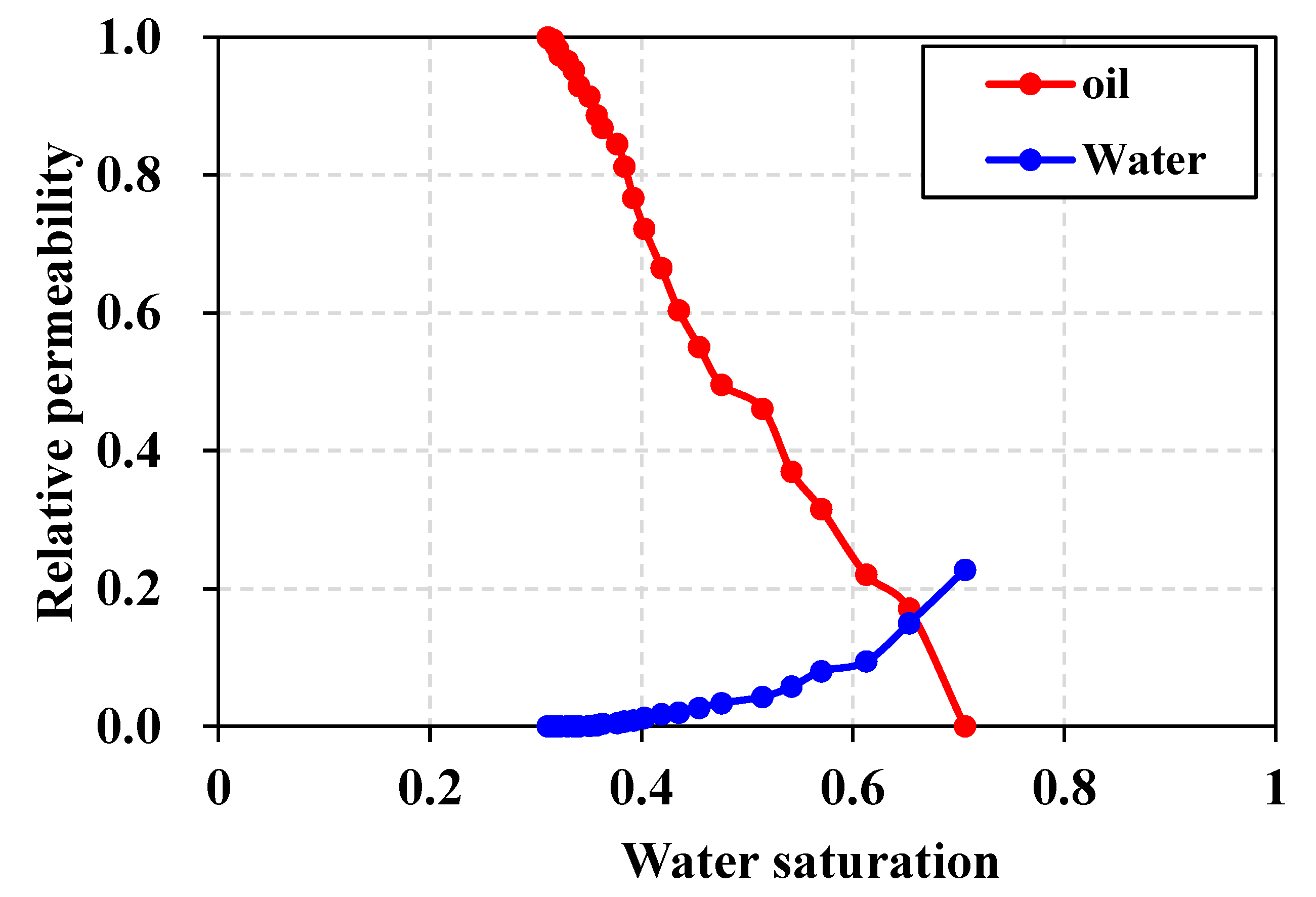
3.3. Relative permeability curves characterization
4. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| A | Cross-sectional area of the network model, m2 |
| DK | Knudsen diffusion coefficient, m2/s |
| DF | Fick diffusion coefficient, m2/s |
| DT | Transition diffusion coefficient, m2/s |
| d | Equivalent pore-throat diameter, m |
| gij | Conductivity |
| gp,ij | Effective conductivity of p phase |
| Kn | Knudsen number |
| kB | Boltzmann constant, 1.3806488×10-23 J/K |
| kabs | Absolute permeability, mD |
| kp | Effective permeability of p phase, mD |
| krp | Relative permeability of p phase |
| L | Length of pore network model, m |
| Lij | Distance between pore i and adjacent pore j |
| Ni | The number of pores connected to pore i |
| △p | The differential pressure at both ends of the network model, Pa |
| pi, pj | Pore pressure of numbered i, j |
| Pp,i, Pp,j | The pore i and p phase fluid pressure in j |
| Q | The outlet or inlet flow of the network model, m3/s |
| q | Flow into or out of the pore |
| M | Molecular molar mass, g/mol |
| R | Ideal gas constant, 8.314462 J/(mol·K) |
| Sw | Water saturation of the pore network model |
| V | Volume of pore network model, m3 |
| λ | Mean free path, m |
| δ | Collision diameter of molecule, m |
References
- Dou, W.; Liu, L.; Jia, L. Pore structure, fractal characteristics and permeability prediction of tight sandstones: A case study from Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin, China. Marine and Petroleum Geology 2021, 123, 104737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Cheng, L.; Feng, H. Full composition numerical simulation of CO2 utilization process in shale reservoir using projection-based embedded discrete fracture model (pEDFM) considering nano-confinement effect. Gas Science and Engineering 2023, 111, 204932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noiriel, C.; Seigneur, N.; Le Guern, P. Geometry and mineral heterogeneity controls on precipitation in fractures: An X-ray micro-tomography and reactive transport modeling study. Advances in Water Resources 2021, 152, 103916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.; Wang, G.; Wang, Z. A review on pore structure characterization in tight sandstones. Earth-Science Reviews 2018, 177, 436–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasnan, H.K.; Sheppard, A.; Hassan, M.H. Digital core analysis: Characterizing reservoir quality through thin sandstone layers in heterolithic rocks. Journal of Applied Geophysics 2020, 182, 104178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasnan, H.K.; Sheppard, A.; Hassan, M.H. Digital core analysis: Improved connectivity and permeability characterization of thin sandstone layers in heterolithic rocks. Marine and Petroleum Geology 2020, 120, 104549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, W.; Chen, S.; Gao, Y. Evaluating seepage radius of tight oil reservoir using digital core modeling approach. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering 2019, 178, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ettemeyer, F.; Lechner, P.; Hofmann, T. Digital sand core physics: Predicting physical properties of sand cores by simulations on digital microstructures. International Journal of Solids and Structures 2020, 188–189, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatarangan, W. Investigating 3D geometry of porous media from high resolution images. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Part A: Solid Earth and Geodesy 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Su, M.; Liu, W. Digital core construction of fractured carbonate rocks and pore-scale analysis of acoustic properties. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering 2021, 196, 107771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Q.; Baychev, T.G.; Jivkov, A.P. Review of pore network modelling of porous media: Experimental characterisations, network constructions and applications to reactive transport. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology 2016, 192, 101–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Lin, M.; Jiang, W. Rapid multiscale pore network modeling for drainage in tight sandstone. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.; Hu, S.; Wu, S. Pore network extraction for shale gas flow in nanoporous media. Marine and Petroleum Geology 2021, 126, 104896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Sun, W.; Liu, Y. Effect of pore networks on the properties of movable fluids in tight sandstones from the perspective of multi-techniques. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering 2021, 201, 108449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Zehairy, A.A.; Nezhad, M.M.; Joekar-Niasar, V. Pore-network modelling of non-Darcy flow through heterogeneous porous media. Advances in Water Resources 2019, 131, 103378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F.; Talbi, M.; Prat, M. Non-local equilibrium continuum modeling of partially saturated drying porous media: Comparison with pore network simulations. Chemical Engineering Science 2020, 228, 115957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez de Castro, A.; Goyeau, B. A pore network modelling approach to investigate the interplay between local and Darcy viscosities during the flow of shear-thinning fluids in porous media. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 2021, 590, 446–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, X.; Zhang, J. An improved bounce-back scheme for complex boundary conditions in lattice Boltzmann method. Journal of Computational Physics 2012, 231, 4295–4303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuyama, T.; Abe, T.; Yamamoto, H. Lattice Boltzmann method study of Rayleigh instability of a charged droplet. Advanced Powder Technology 2007, 18, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pribec, I.; Hubman, A.; Urbic, T. A discrete reactive collision scheme for the lattice Boltzmann method. Journal of Molecular Liquids 2021, 332, 115871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilde, D.; Krämer, A.; Bedrunka, M. Cubature rules for weakly and fully compressible off-lattice Boltzmann methods. Journal of Computational Science 2021, 51, 101355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shams, M.; Raeini, A.Q.; Blunt, M.J. A numerical model of two-phase flow at the micro-scale using the volume-of-fluid method. Journal of Computational Physics 2018, 357, 159–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo, F.J.; Bourg, I.C.; Soulaine, C. Multiphase flow modeling in multiscale porous media: An open-source micro-continuum approach. Journal of Computational Physics: X 2020, 8, 100073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, A.; Adhikari, J. Fluid phase equilibria of triangle-well fluids confined inside slit pores: A transition matrix Monte Carlo simulation study. Journal of Molecular Liquids 2016, 221, 1184–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karki, S.; Chakraborty, S.N. A Monte Carlo simulation study of hydrogen adsorption in slit-shaped pores. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials 2021, 317, 110970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryazanov, A.V.; Dijke, M.I.; Sorbie, K.S. Two-Phase Pore-Network Modelling: Existence of Oil Layers During Water Invasion. Transport in Porous Media 2009, 80, 79–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Høiland, L.K.; Spildo, K.; Skauge, A. Fluid flow properties for different classes of intermediate wettability as studied by network modelling. Transport in Porous Media 2007, 70, 127–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piri, M.; Blunt, M.J. Three-dimensional mixed-wet random pore-scale network modeling of two- and three-phase flow in porous media. I. Model description. Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys 2005, 71 Pt 2, 026301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piri, M.; Blunt, M.J. Three-dimensional mixed-wet random pore-scale network modeling of two- and three-phase flow in porous media. II. Results. Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys 2005, 71 Pt 2, 026302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valvatne, P.H.; Blunt, M.J. Predictive pore-scale modeling of two-phase flow in mixed wet media. Water Resources Research 2004, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakke, S.; Øren, P.E. 3-D Pore-Scale Modelling of Sandstones and Flow Simulations in the Pore Networks. SPE Journal 1997, 2, 136–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, S.; Blunt, M. Prediction of relative permeability in simple porous media. Phys Rev A 1992, 46, 2004–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryazanov, A.; Dijke, M.V.; Sorbie, K. Pore-network Prediction of Residual Oil Saturation Based on Oil Layer Drainage in Mixed-wet Systems, SPE Improved Oil Recovery Symposium. 2010. [CrossRef]
- Joekar-Niasar, V.; Prodanović, M.; Wildenschild, D. Network model investigation of interfacial area, capillary pressure and saturation relationships in granular porous media. Water Resources Research 2010, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, F.O.; Owens, W.W. A Laboratory Study of Low-Permeability Gas Sands. Journal of Petroleum Technology 1980, 32, 1631–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Cheng, L.; Cao, R. A new approach to calculate permeability stress sensitivity in tight sandstone oil reservoirs considering micro-pore-throat structure. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering 2015, 133, 576–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valvatne, P.H.; Piri, M.; Lopez, X. Predictive Pore-Scale Modeling of Single and Multiphase Flow. Transport in Porous Media 2005, 58, 23–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Reza, Z. Prediction of pore-scale transport properties in unconventional reservoirs using novel theoretical dendroidal pore-network model. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering 2018, 170, 712–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Daigle, H. Permeability prediction from a pore-scale network model constrained by low-pressure nitrogen sorption isotherms. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering 2018, 162, 554–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azarafza, A.; King, A.J.; Mead-Hunter, R. Prediction of residual saturation and pressure drop during coalescence filtration using dynamic pore network model. Separation and Purification Technology 2021, 254, 117588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merey, Ş. Prediction of transport properties for the Eastern Mediterranean Sea shallow sediments by pore network modelling. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering 2019, 176, 403–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakhelpour-Ghoveifel, J.; Shahverdi, H. Prediction of gas-oil capillary pressure of carbonate rock using pore network modeling. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering 2020, 195, 107861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Lin, M.; Jiang, W. Rapid multiscale pore network modeling for drainage in tight sandstone. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering 2021, 204, 108682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, M.M.; Wilkinson, D. Percolation with trapping. Journal of Physics A: Mathematical and General 1986, 19, 3131–3146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knackstedt, M.A.; Sahimi, M.; Sheppard, A.P. Invasion percolation with long-range correlations: First-order phase transition and nonuniversal scaling properties. Physical Review E 2000, 61, 4920–4934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, D.; Willemsen, J.F. Invasion percolation: a new form of percolation theory. Journal of Physics A: Mathematical and General 1983, 16, 3365–3376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broadbent, S.R.; Hammersley, J.M. Percolation processes: I. Crystals and mazes. Mathematical Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society 1957, 53, 629–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dullien, F.A.L. New network permeability model of porous media. Aiche Journal 1975, 21, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenormand, R.; Zarcone, C.; Sarr, A. Mechanisms of the displacement of one fluid by another in a network of capillary ducts. Journal of Fluid Mechanics 1983, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oak, M.J.; Baker, L.E.; Thomas, D.C. Three-Phase Relative Permeability of Berea Sandstone. Journal of Petroleum Technology 1990, 42, 1054–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Øren, P.E.; Pinczewski, W.V. Fluid distribution and pore-scale displacement mechanisms in drainage dominated three-phase flow. Transport in Porous Media 1995, 20, 105–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blunt, M.J. Effects of Heterogeneity and Wetting on Relative Permeability Using Pore Level Modeling. SPE Journal 1997, 2, 70–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blunt, M.J. Physically-based network modeling of multiphase flow in intermediate-wet porous media. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering 1998, 20, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Øren, P.; Bakke, S.; Arntzen, O.J. Extending Predictive Capabilities to Network Models. 1998, 3. 3. [CrossRef]
- VOGEL, J. H. Morphological determination of pore connectivity as a function of pore size using serial sections. European Journal of Soil Science 2008, 48, 365–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, H.J. A numerical experiment on pore size, pore connectivity, water retention, permeability, and solute transport using network models. European Journal of Soil Science 2000, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blunt, M.J.; Jackson, M.D.; Piri, M. Detailed physics, predictive capabilities and macroscopic consequences for pore-network models of multiphase flow. Advances in Water Resources 2002, 25, 1069–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piri, M.; Blunt, M.J. Three-dimensional mixed-wet random pore-scale network modeling of two- and three-phase flow in porous media. I. Model description. Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys 2005, 71 Pt 2, 026301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Cheng, L.; Wang, X. Pore network modelling of fluid flow in tight formations considering boundary layer effect and media deformation. Journal of Petroleum Science & Engineering 2019, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Cheng, L.; Zhou, J. Upscaling simulation method of fluid flow for fracturing-shut in-flowback-production process in tight oil reservoirs: Hysteresis effects of capillary pressure and relative permeability. Geoenergy Science and Engineering 2023, 226, 211792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





