Submitted:
07 June 2023
Posted:
08 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
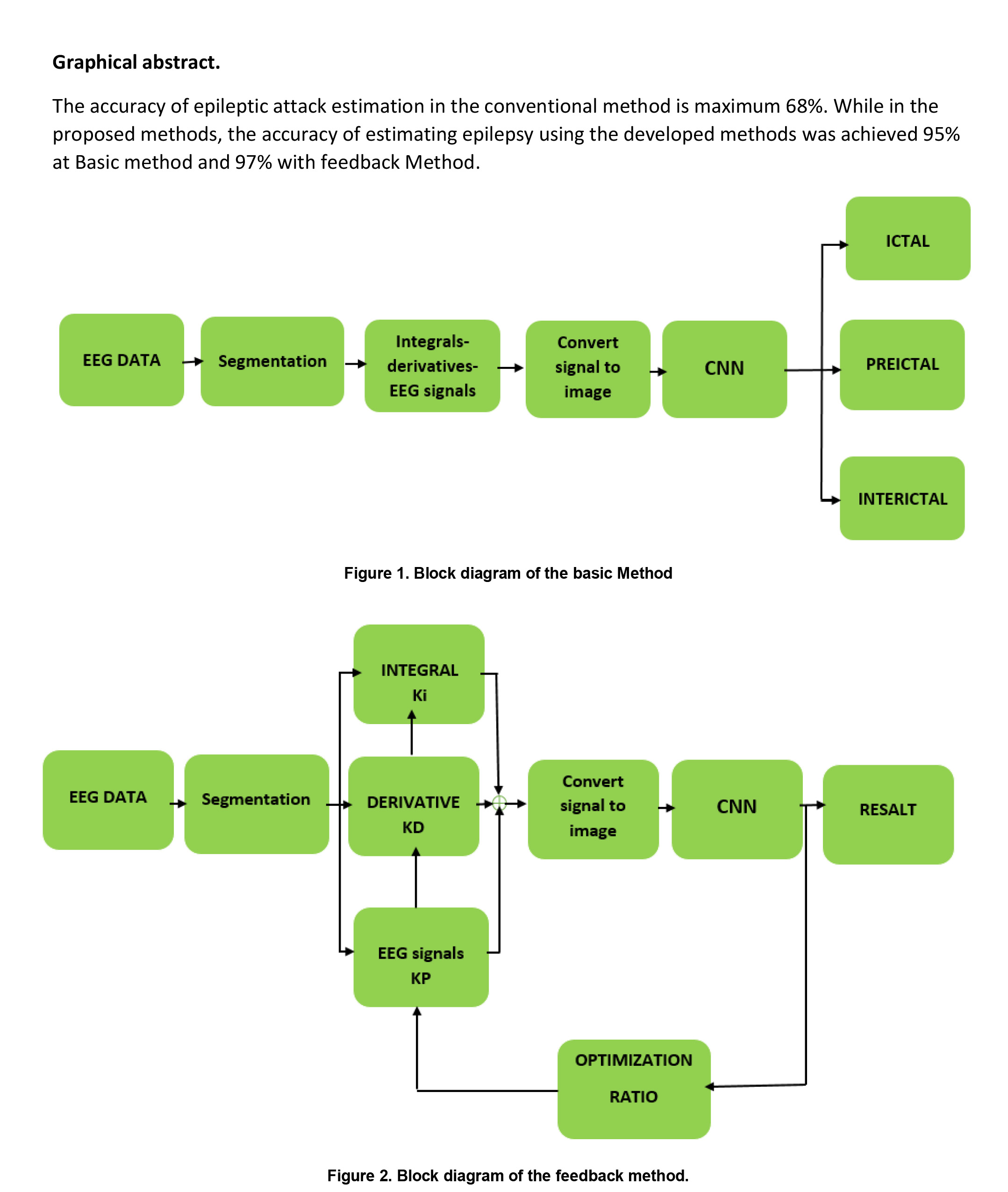
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. DATA
2.2. Convolutional neural network
2.2.1. Convolution Layer
2.2.2. Max Pooling Layer
2.2.3. Fully-connected Layer
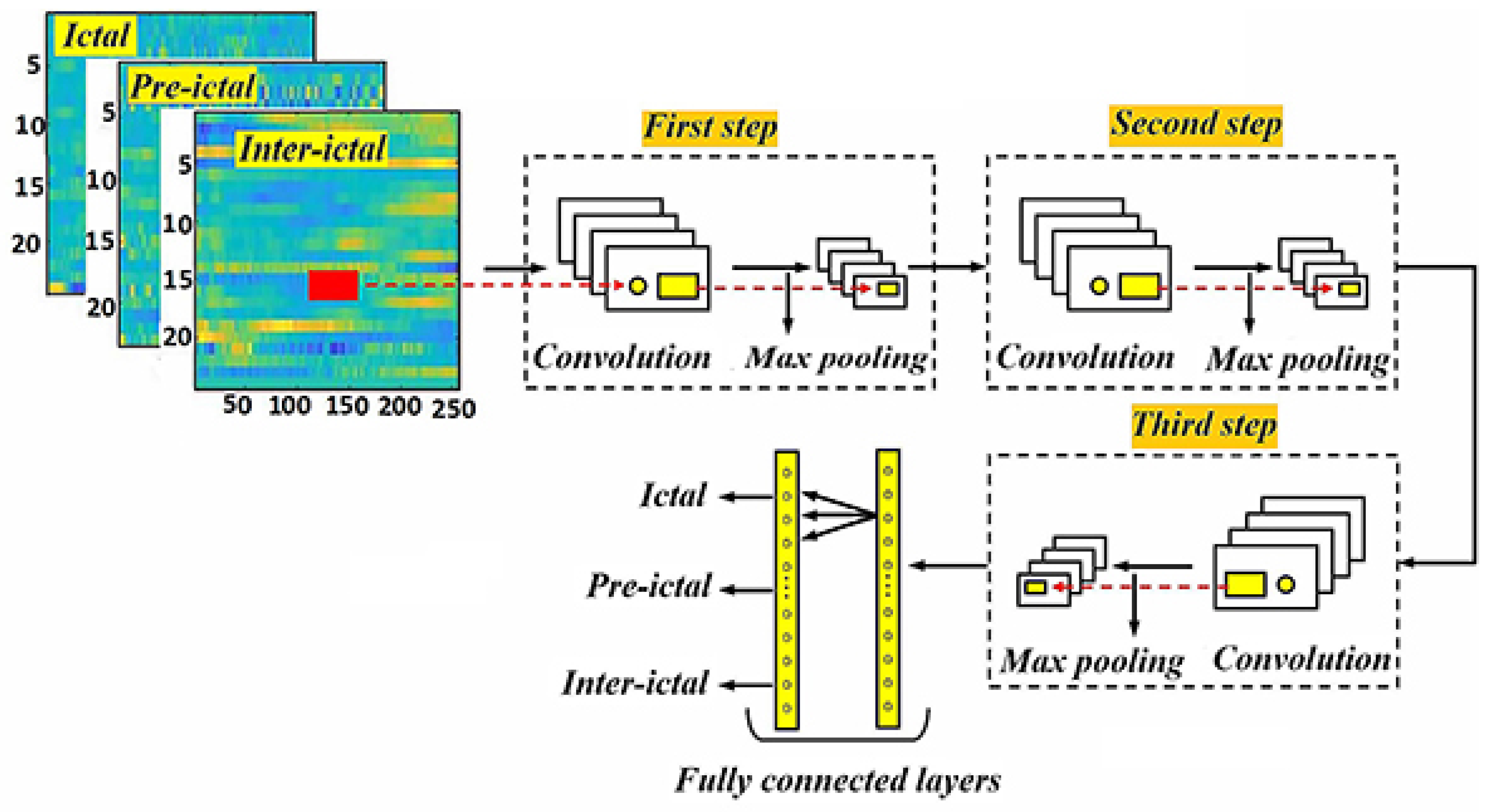
2.3. Proposed method
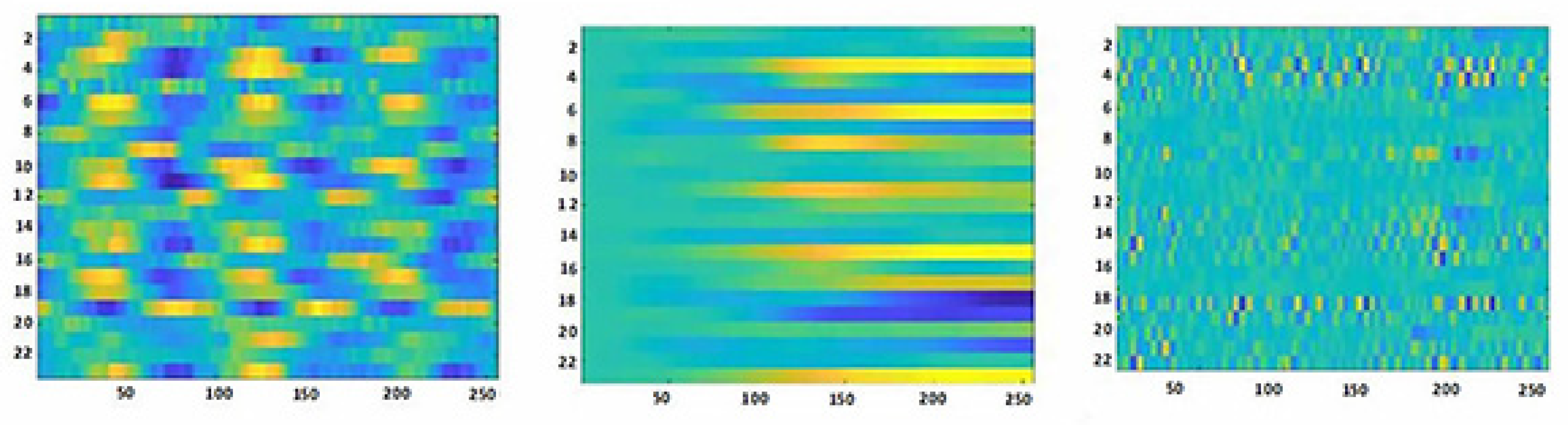
2.3.1. Data preprocessing
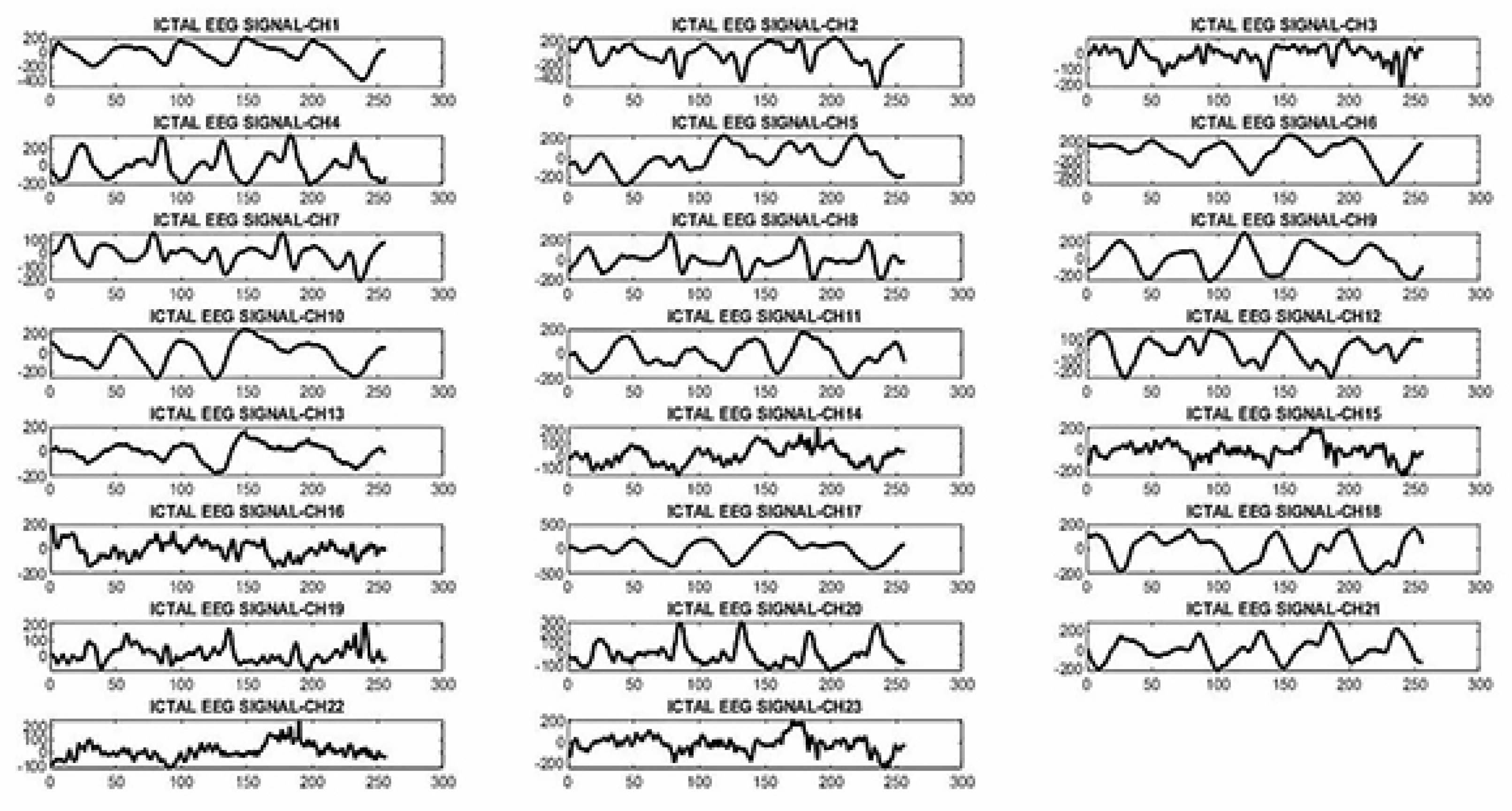
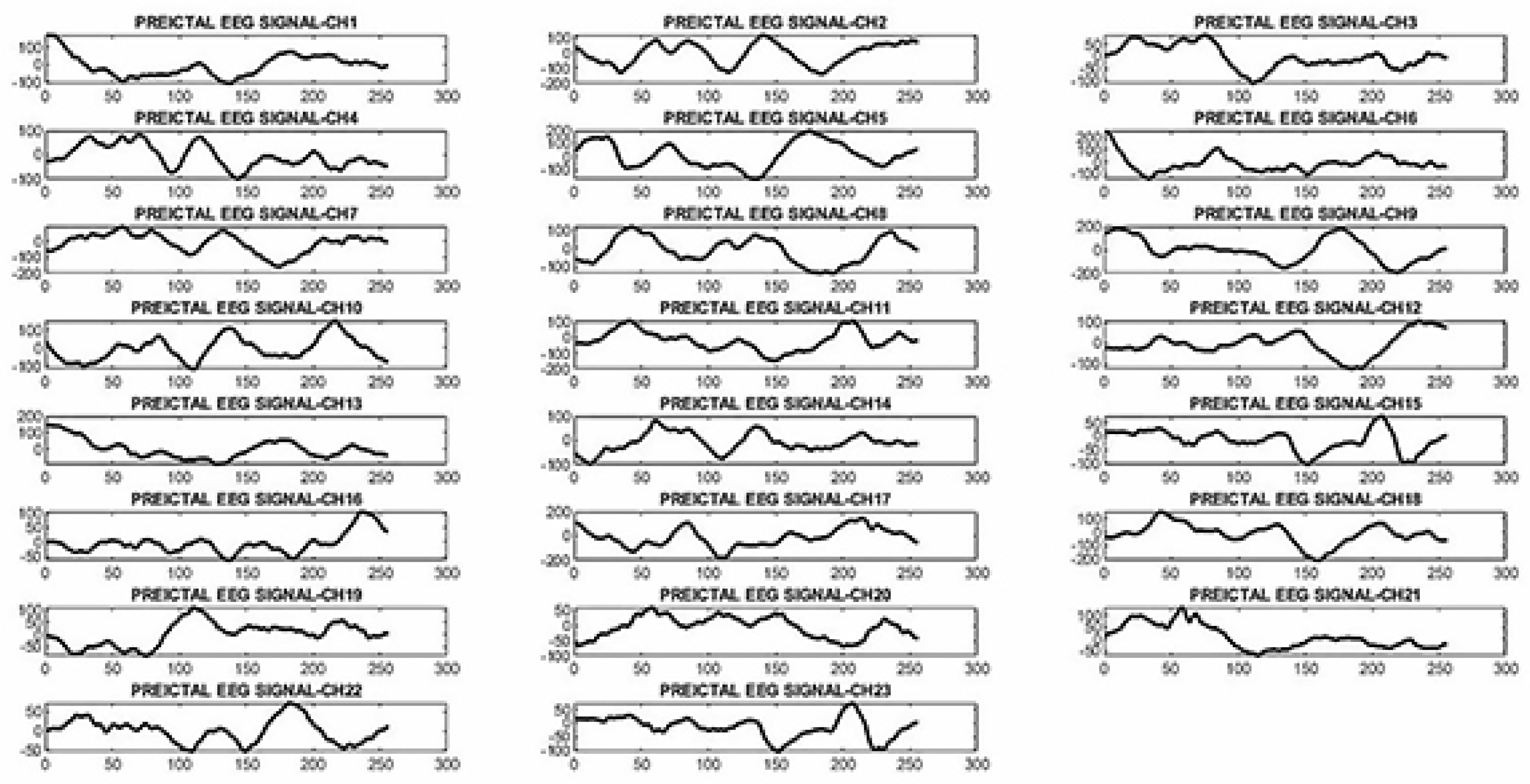
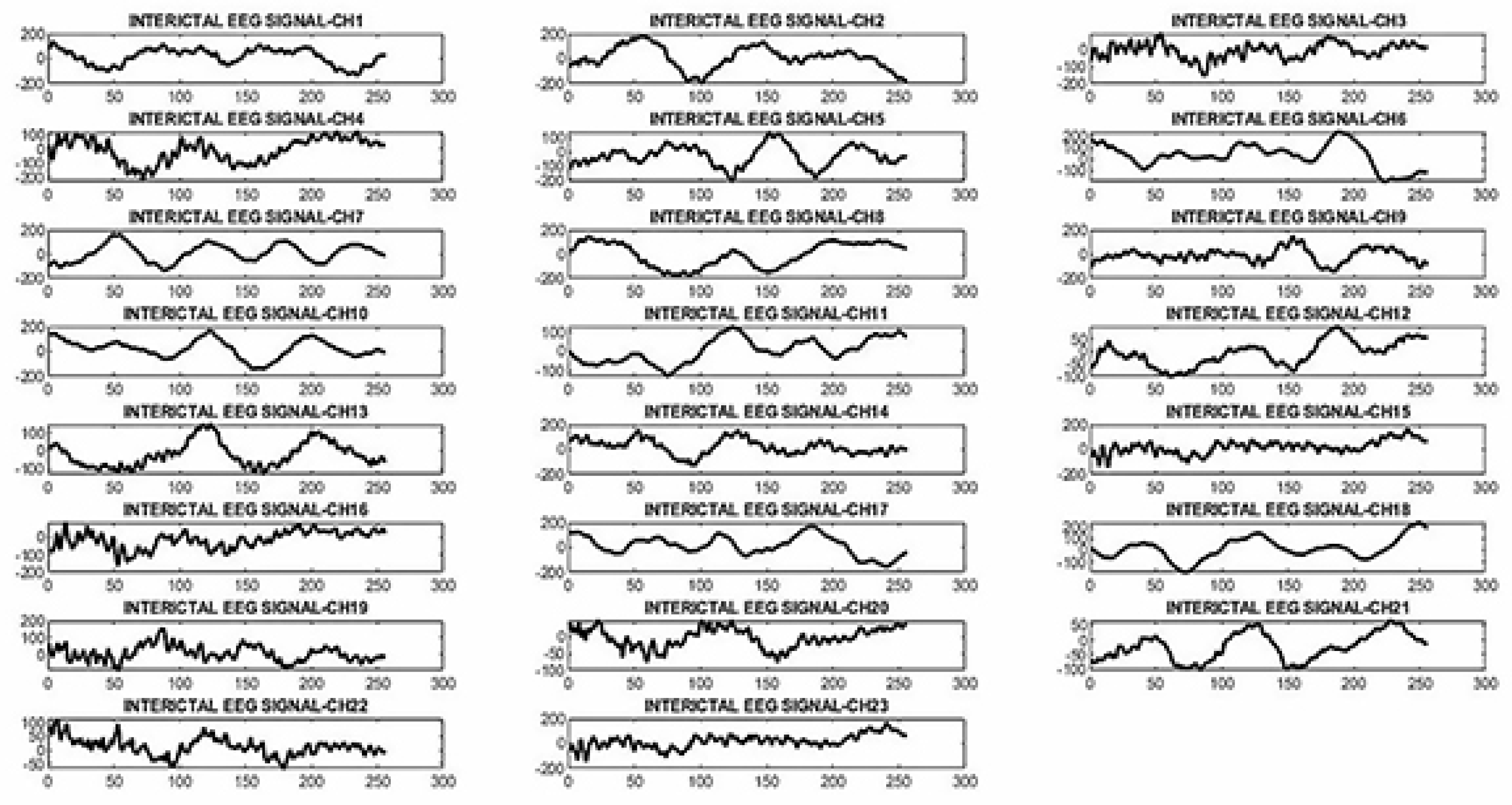
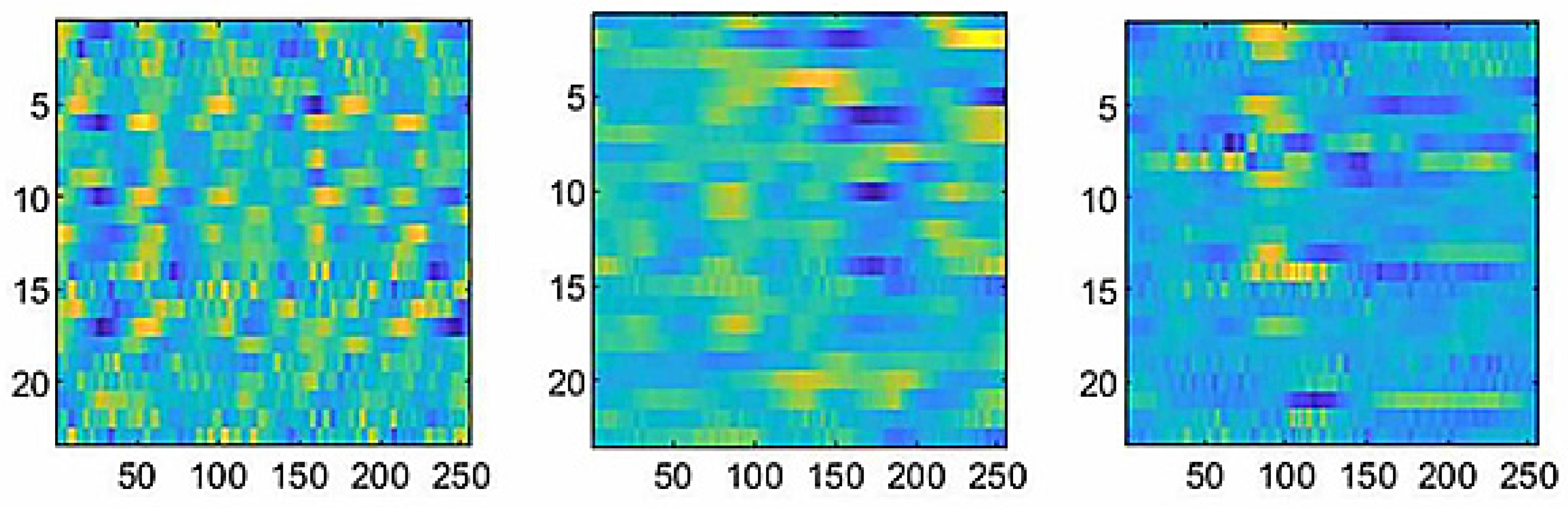
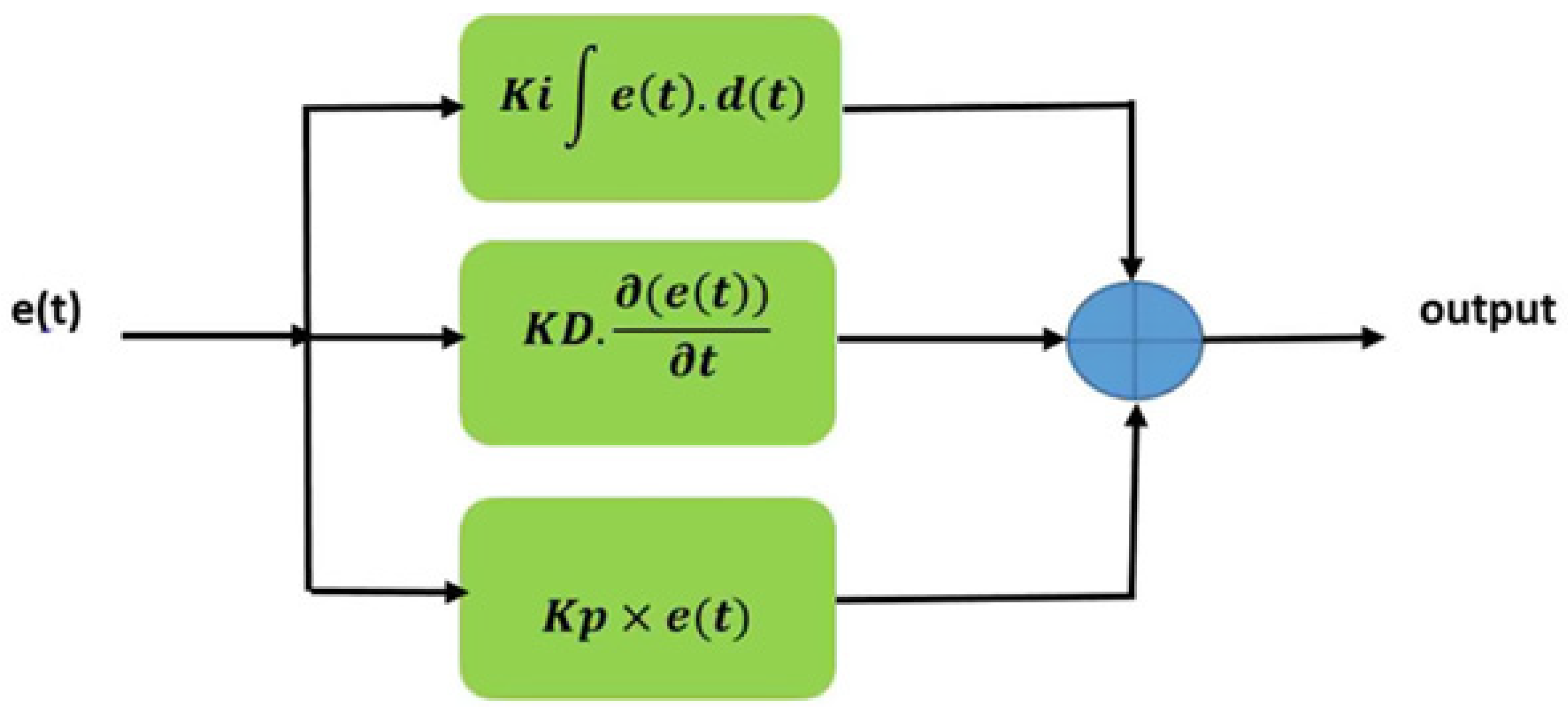
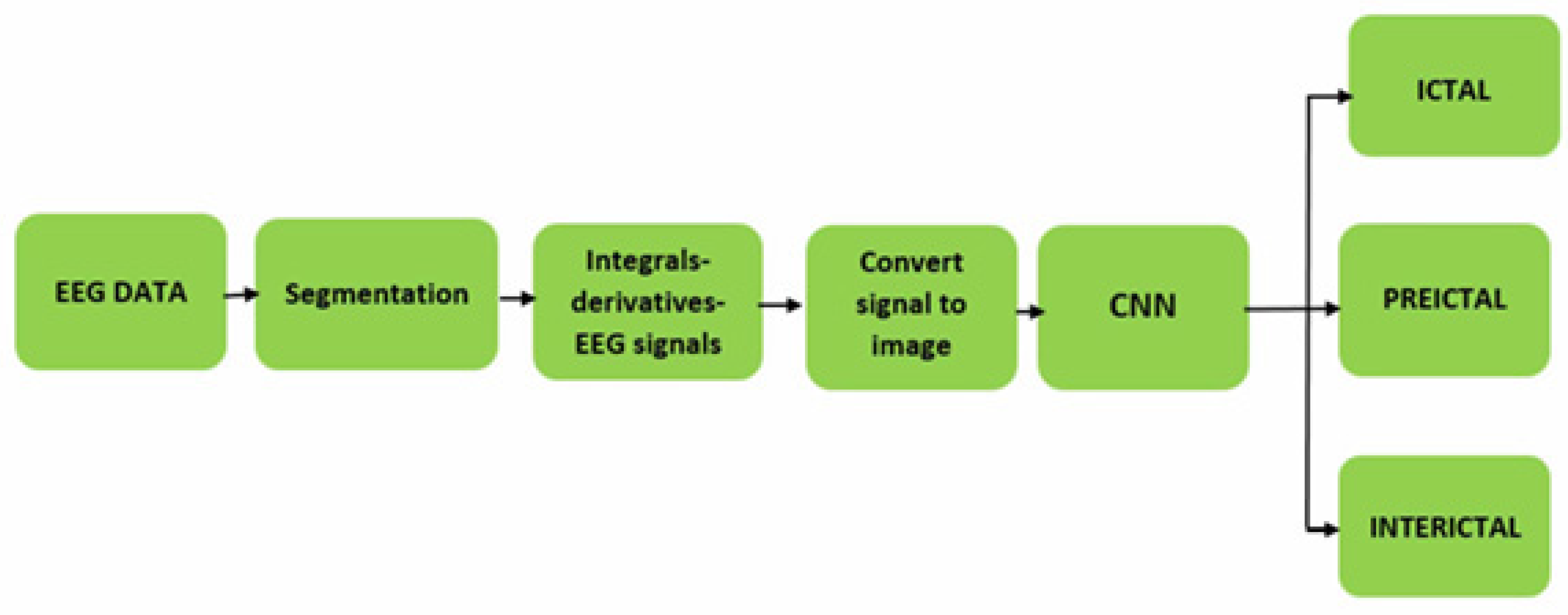
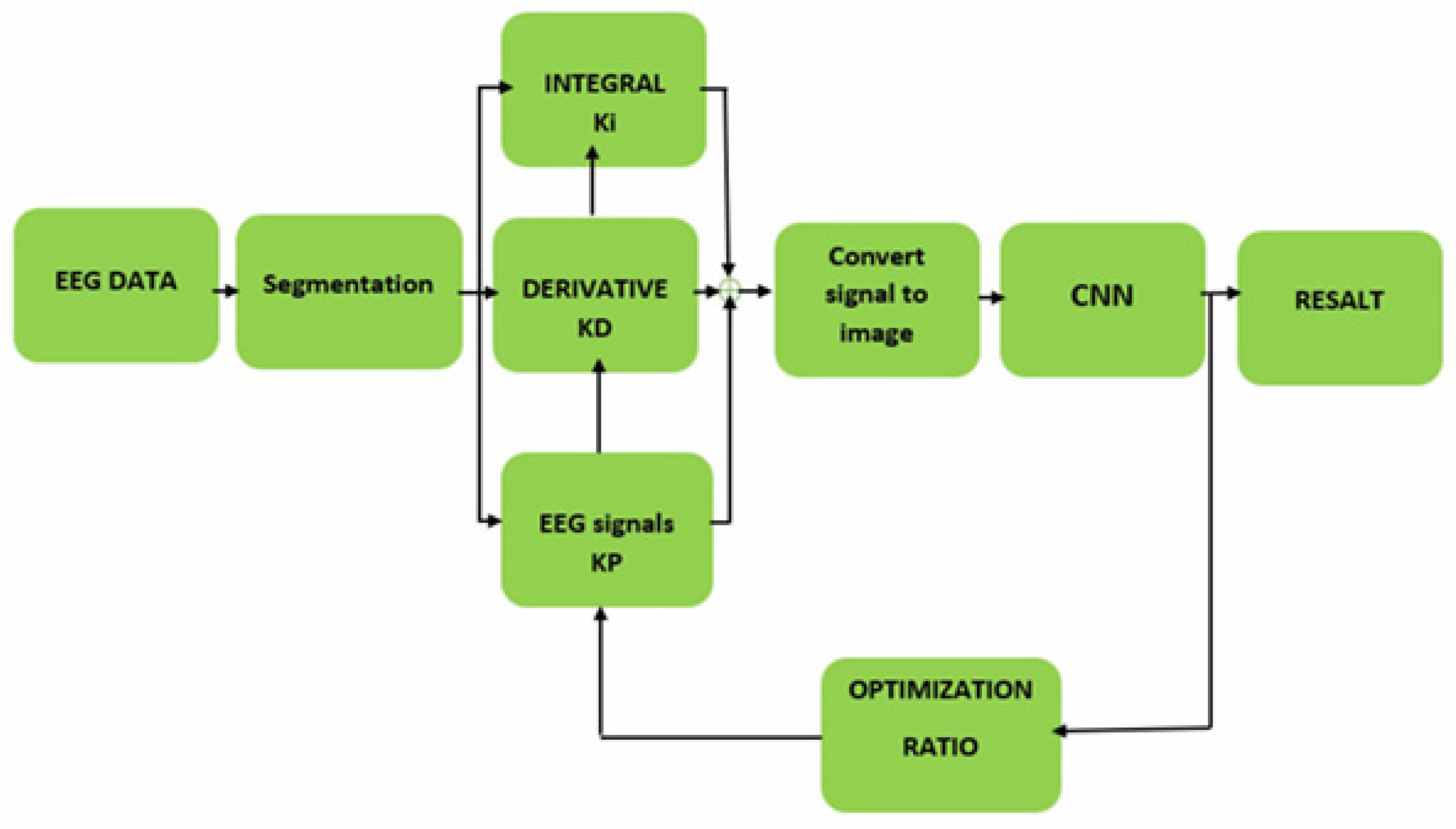
2.3.2. Proposed neural network architecture
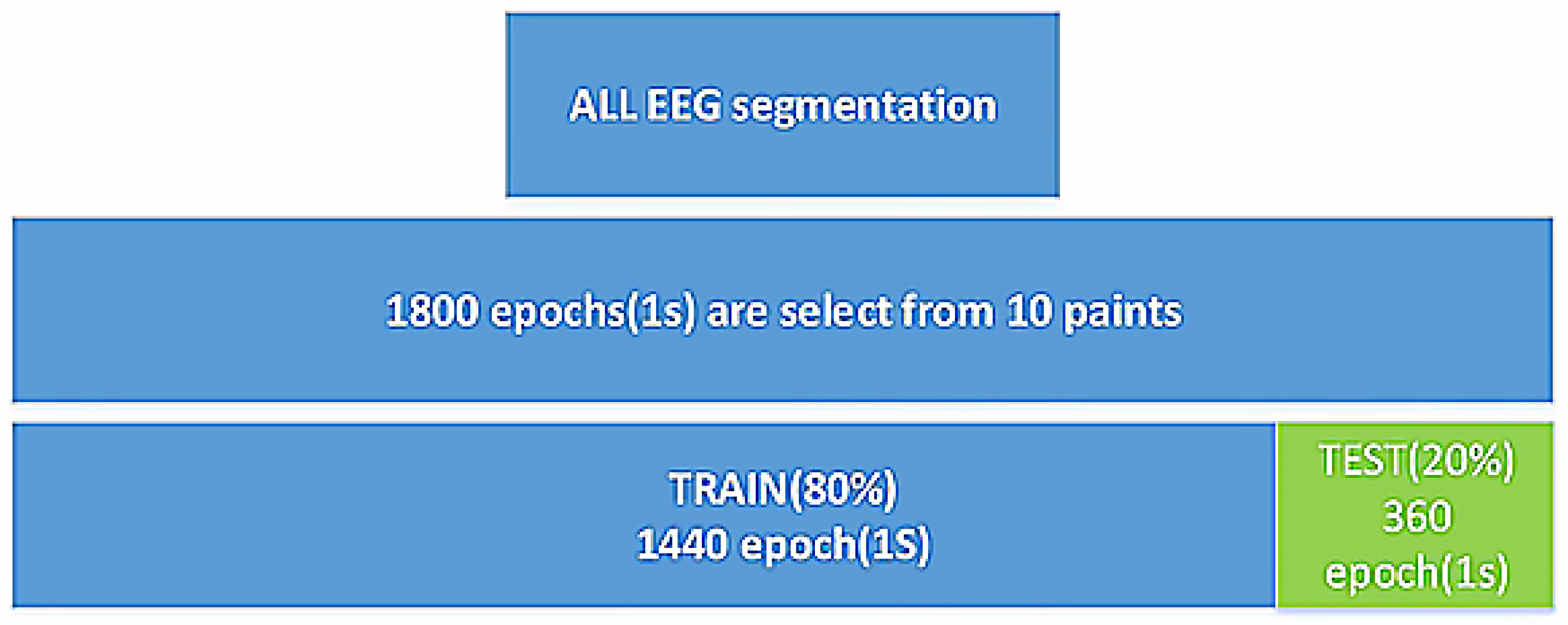
2.3.3. Data collection training and evaluation
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Subasi, A.; Gursoy, M.I. EEG signal classification using PCA, ICA, LDA and support vector machines. Expert Syst Appl. 2010, 37, 8659–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Geng, Y.; Wu, J.; Li, C. Interactions between multisensory inputs with voluntary spatial attention an fMRI study. Neuroreport. 2015, 26, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Hernández, E.; Bravo, J.; Solís, H. Epilepsia y antiepileptic’s de primera y segunda generación. Aspectos básicos útiles en la práctica clínica. Revista De La Facultad De Medicina. Epub ahead of print 2011. [Google Scholar]
- F. Mormann, R. G. Andrzejak et al. Seizure prediction the long and winding road. Brain 2006, 130, 314–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Zhao, S.; Uono, S.; Bi, X.; Tian, A.; Yoshimura, S. , et al. Target object moderation of attentional orienting by gazes or arrows. Attent. Percep. Psychophys. 2016, 78, 2373–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- P Kwan, M J Brodie (). Early identification of refractory epilepsy. The New England journal of medicine 2000, 342, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- J de Tisi, G, S Bell et al. The long-term outcome of adult epilepsy surgery, patterns of seizure remission, and relapse: a cohort study. Lancet (London, England) 2011, 378, 1388–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misulis, K, E Atlas of EEG. Seizure Semiology, and Management. New York, NY: Oxford University Press. 2013.
- Pachori, R.B.; Patidar, S. Epileptic seizure classification in EEG signals using second-order difference plot of intrinsic mode functions. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2014, 113, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litjens, G.; Kooi, T.; Bejnordi, B.E.; Aaa, S.; Ciompi, F.; Ghafoorian, M.; et al. A survey on deep learning in medical image analysis. Med Image Anal. 2017, 42, 60–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iasemidis, L.D.; Shiau, D.S.; Pardalos, P.M.; Chaovalitwongse, W.; Narayanan, K.; Prasad, A.; et al. Long-term prospective on-line real-time seizure prediction. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2005, 116, 532–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subasi, A.; Erçelebi, E. Classification of EEG signals using the neural network and logistic regression. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 2005, 78, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, T.; Wang, W.; Liu, T.; Chen, D.; Wang, C.; Li, Y.; et al. Increased local connectivity of brain functional networks during facial processing in schizophrenia: evidence from EEG data. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chengcheng Han. Highly Interactive Brain–Computer Interface Based on Flicker-Free Steady-State Motion Visual Evoked Potential. Scientific Reports 2018, 8, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- S. SHEYKHIVAND, T. YOUSEFI REZAII, Z.MOUSAVI, A. DELPAK. Automatic Identification of Epileptic Seizures from EEG Signals Using Sparse Representation-Based Classification. Published in IEEE Access Journal. 2020, 8, 138834–138845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.; Xu, Z.; Du, J.; Zhou, Q.; Yu, T.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y. Ictal High-Frequency Oscillation for Lateralizing Patients With Suspected Bitemporal Epilepsy Using Wavelet Transform and Granger Causality Analysis. Frontier in Neuroinformatice. 2019, 13, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negin Moghim, David W. Predicting Epileptic Seizures in Advance. PLOS ONE. 2014, 10, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzieh Savadkoohi, Timothy Oladunni, Lara Thompson. A machine learning approach to epileptic seizure prediction using Electroencephalogram (EEG) Signal. The Journal of Biocybernetics and Biomedical Engineering 2020, 40, 1328–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Zhou, L.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, Y. Automatic seizure detection using three-dimensional CNN based on multi-channel EEG. BMC Medical Informatics and Decision Making. 2018, 18, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, M.; Pompili, D.; Elisevich, K.; Soltanian-Zadeh, H. Optimized Deep Learning for EEG Big Data and Seizure Prediction BCI via Internet of Things. IEEE Transactions on Big Data. 2017, 3, 392–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengni Zhou1, Cheng Tian1, Rui Cao2, Bin Wang1, Yan Niu1, Ting Hu1, Hao Guo1 and Jie Xiang1. Epileptic Seizure Detection Based on EEG Signals and CNN. Front. Neuroinform 2018, 12, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, W.; Xiao, Y.; Xiao, S.; Chen, S.; Xu, G.; Che, W. Cross-Subject Seizure Detection in EEGs Using Deep Transfer Learning. Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine. 2020, Article ID 7902072, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, S.M.; Khalid, S.; Aslam, M.H. Epileptic Seizures Prediction Using Deep Learning Techniques. Published in IEEE Access. 2020, 8, 39998–40007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilakiyaselvan, N.; Khan, A.N.; Shahina, A. Deep learning approach to detect seizure using reconstructed phase space images. The Journal of Biomedical Research 2020, 34, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Chen, D.; Ranjan, R.; et al. A lightweight solution to epileptic seizure prediction based on EEG synchronization measurement. The Journal of Supercomputing. 2020, 142, 1573–0484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Nie, W.; Zhou, W.; Xu, F.; Yuan, S.; Leng, Y.; Yuan, Q. . Epileptic seizure prediction based on local mean decomposition and deep convolutional neural network. The Journal of Supercomputing. Springer Science Business Media. 2018, 76, 3462–3476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, R.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Das, S. Patient-Specific Seizure Prediction Using the convolutional Neural Network. The Journal of Intelligence Enabled Research. Advances in Intelligent Methods and Computing 2020, 1109, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, S.M.; Khalid, S.; Aslam, M.H. Epileptic Seizures Prediction Using Deep Learning Techniques. Published in IEEE Access 2020, 8, 39998–40007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulnasir Yildiza, Hasan Zanb, Sherif Said. Classification and analysis of epileptic EEG recordings using convolutional neural network and class activation mapping. Published in Biomedical Signal Processing and Control. 2021, 68, 102720 – 37504. [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Zou, J.; Zhang, J.; Xu, J. Automatic epileptic EEG detection using convolutional neural network with improve mention time-domain. Published in Biomedical Signal Processing and Control 2019, 53, 101551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- S Raghu, Natarajan Sriraam, Yasin Temel, Shyam Vasudeva Rao, Pieter L. Kubben. EEG based multi-class seizure type classification using convolutional neural network and transfer learning. Published in Neural Networks Elsevier 2020, 124, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- S, R Ashokkumar, S Anupallavi, M Premkumar, V Jeevanantham. Implementation of deep neural networks for classifying electroencephalogram signal using fractional S-transform for epileptic seizure detection. Published in The International Journal of Imaging Methods and Technology (IMA) 2021, 31, 895–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, J.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, R.; Han, G.; Jia, W.; Li, C. Pair-Wise Matching of EEG Signals for Epileptic Identification via Convolutional Neural Network. Published in in IEEE Access 2020, 8, 40008–40017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, Kunihiko,Neocognitron. A hierarchical neural network capable of visual pattern recognition. Neural networks1.2. 1988, 2, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sermanet, P.; Eigen, D.; Zhang, X.; Mathieu, M.; Fergus, R.; Lecun, Y. integrated recognition, localization and detection using convolutional networks. 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ullah, I.; Hussain, M.; Qazi EU, H.; Aboalsamh, H. An Automated Method for epilepsy detection using eeg brain signals based on deep learning approach. Exp. Syst. Appli. 2018, 107, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | Search Space | Optimal Value |
| Optimizer | RMSProp, Adam, Sgd, Adamax, Steplr, Cycliclr | Sgd |
| Cost function | MSE, Cross-entropy | Cross-entropy |
| Dropout rate | 0,0.2,0.3,0.4,0.5 | 0.2 |
| Batch Size | 4,8,10,16,32,64,100 | 4 |
| Learning rate | 0.01,0.001,0.0001 | 0.0001 |
| Momentum and Gamma Parameters | 0.6,0.7,0.8,0.9 | 0.9 |
| Decay Rate of the Weights | 2, 3, 4 , 5 , 6 | 5 |
| Activation function after the BN Layer | Leaky-Relu , Sigmoid , Relu , Linear | Relu |
| Activation function in the first FC Layer | Leaky-Relu , Sigmoid , Relu , Linear | Relu |
| Activation function in the Last Layer | Softmax, Sigmoid | Softmax |
| Convolutional network architecture | Filter dimensions | Input image dimensions | Dimensions of the output image of the convolutional floor | Dimensions of Max Pauling floor output image | Number and dimensions of the output image |
| First part | 3×3 | 64×64 | 64×64 | 32×32 | 8@(32×32) |
| second part | 3×3 | 32×32 | 32×32 | 16×16 | 16@(16×16) |
| third part | 3×3 | 16×16 | 8×8 | 8×8 | 32@(8×8) |
|
Patient ID |
conventional method | basic method KP=0.5,KI=0.5,KD=5 | basic method KP=0,KI=0,KD=5 | basic method KP=KD=0,KI=10 |
||||||||
| acc | sen | spe | acc | sen | spe | acc | sen | spe | acc | acc | acc | |
| 1 | 0.611 | 0.781 | 0.720 | 0.8650 | 0.7738 | 0.8539 | 0.5833 | 0.9184 | 0.2333 | 0.6465 | 0.8387 | 0.5581 |
| 2 | 0.682 | 0.697 | 0.690 | 0.8565 | 0.7674 | 0.8621 | 0.6204 | 0.8889 | 0.3929 | 0.6162 | 0.7143 | 0.5641 |
| 3 | 0.656 | 0.660 | 0.658 | 0.7037 | 0.6239 | 0.7596 | 0.5463 | 0.8333 | 0.1724 | 0.6667 | 0.6458 | 0.7500 |
| 4 | 0.642 | 0.687 | 0.666 | 0.8608 | 0.8608 | 0.8132 | 0.5048 | 0.5345 | 0.4750 | 0.4921 | 0.4412 | 0.5625 |
| 5 | 0.600 | 0.645 | 0.623 | 0.8481 | 0.7778 | 0.8352 | 0.5714 | 0.6364 | 0.6389 | 0.5556 | 0.4999 | 0.7619 |
| 6 | 0.595 | 0.632 | 0.615 | 0.8312 | 0.7529 | 0.8242 | 0.5048 | 0.5345 | 0.4750 | 0.5873 | 0.4865 | 0.8542 |
| 7 | 0.620 | 0.666 | 0.643 | 0.8186 | 0.7294 | 0.7912 | 0.5349 | 0.7143 | 0.4717 | 0.5476 | 0.4881 | 0.8810 |
| 8 | 0.684 | 0.707 | 0.696 | 0.7829 | 0.7447 | 0.8077 | 0.5581 | 0.7547 | 0.4902 | 0.6984 | 0.5857 | 0.8667 |
| 9 | 0.642 | 0.625 | 0.633 | 0.8519 | 0.7660 | 0.9189 | 0.4806 | 0.7143 | 0.3922 | 0.6190 | 0.5181 | 0.8571 |
| 10 | 0.652 | 0.641 | 0.646 | 0.6952 | 0.5435 | 0.7500 | 0.5079 | 0.6418 | 0.5000 | 0.5079 | 0.6667 | 0.5714 |
| 11 | 0.657 | 0.649 | 0.653 | 0.8083 | 0.7334 | 0.8333 | 0.6566 | 0.7500 | 0.6154 | 0.6977 | 0.6744 | 0.6780 |
| 12 | 0.663 | 0.660 | 0.661 | 0.7847 | 0.7170 | 0.7963 | 0.7172 | 0.7381 | 0.6944 | 0.6883 | 0.5957 | 0.6939 |
| 13 | 0.645 | 0.628 | 0.636 | 0.8186 | 0.7619 | 0.7826 | 0.6162 | 0.7143 | 0.5641 | 0.7172 | 0.7381 | 0.6944 |
| 14 | 0.653 | 0.643 | 0.648 | 0.7132 | 0.8000 | 0.6905 | 0.7048 | 0.6739 | 0.7941 | 0.6667 | 0.6458 | 0.7500 |
| 15 | 0.636 | 0.615 | 0.625 | 0.7265 | 0.6465 | 0.7907 | 0.6970 | 0.7200 | 0.6452 | 0.7048 | 0.6739 | 0.7941 |
| 16 | 0.632 | 0.609 | 0.620 | 0.7847 | 0.7170 | 0.7963 | 0.4952 | 0.5818 | 0.5750 | 0.6286 | 0.5273 | 0.7317 |
| patient No. 08 | basic method KP=0.5,KI=0.2 | basic method KP=0.3,KI=0.3 | basic method KP=0.3,KI=0.5 | basic method KP=0.3,KI=0.6 | ||||||||
| %acc | %sen | %spe | %acc | %sen | %spe | %acc | %sen | %spe | %acc | %sen | %spe | |
| KD=0.1 | 0.8608 | 0.8235 | 0.8161 | 0.8734 | 0.7907 | 0.8824 | 0.8734 | 0.8118 | 0.8588 | 0.8945 | 0.8608 | 0.8506 |
| KD=0.2 | 0.8608 | 0.7952 | 0.8333 | 0.9072 | 0.8391 | 0.9136 | 0.8228 | 0.7556 | 0.8111 | 0.9156 | 0.8750 | 0.8851 |
| KD=0.3 | 0.8734 | 0.8000 | 0.8636 | 0.8861 | 0.8295 | 0.8941 | 0.8861 | 0.8391 | 0.8706 | 0.8523 | 0.7727 | 0.8636 |
| KD=0.4 | 0.8439 | 0.7294 | 0.8539 | 0.8861 | 0.8276 | 0.8824 | 0.8887 | 0.8395 | 0.8750 | 0.9072 | 0.8537 | 0.8953 |
| KD=0.5 | 0.9072 | 0.8571 | 0.8929 | 0.9072 | 0.8675 | 0.8824 | 0.8903 | 0.8452 | 0.8706 | 0.8861 | 0.8395 | 0.8506 |
| KD=0.6 | 0.8903 | 0.8140 | 0.8996 | 0.8439 | 0.7447 | 0.8721 | 0.8439 | 0.7391 | 0.8721 | 0.8819 | 0.8421 | 0.8352 |
| KD=0.7 | 0.8481 | 0.7831 | 0.8222 | 0.8734 | 0.8049 | 0.8539 | 0.8891 | 0.7791 | 0.9176 | 0.8692 | 0.8353 | 0.8576 |
| KD=0.8 | 0.8987 | 0.8022 | 0.9286 | 0.8861 | 0.8395 | 0.8506 | 0.8945 | 0.8214 | 0.8941 | 0.8945 | 0.8434 | 0.8736 |
| KD=0.9 | 0.8776 | 0.8415 | 0.8409 | 0.8734 | 0.7955 | 0.8824 | 0.8819 | 0.8375 | 0.8409 | 0.8987 | 0.8391 | 0.8902 |
| KD=1.00 | 0.8945 | 0.8642 | 0.8506 | 0.8819 | 0.8313 | 0.8506 | 0.8776 | 0.8313 | 0.8636 | 0.8819 | 0.8333 | 0.8953 |
| patient No. 08 | basic method KP=0.4,KD=0.9 | basic method KP=0.5,KD=0.9 | basic method KP=0.6,KD=0.9 | basic method KP=0.7,KD=0.9 |
||||||||
| %acc | %sen | %spe | %acc | %sen | %spe | %acc | %sen | %spe | %acc | %sen | %spe | |
| Ki=0.1 | 0.8565 | 0.8721 | 0.8172 | 0.8608 | 0.8608 | 0.8132 | 0.8608 | 0.7955 | 0.8571 | 0.8987 | 0.8919 | 0.8352 |
| Ki=0.2 | 0.8776 | 0.8642 | 0.8391 | 0.9114 | 0.8690 | 0.9059 | 0.8565 | 0.7792 | 0.8211 | 0.8734 | 0.8424 | 0.8523 |
| Ki=0.3 | 0.8565 | 0.8101 | 0.8111 | 0.8603 | 0.8118 | 0.8363 | 0.8692 | 0.8272 | 0.8352 | 0.9030 | 0.8452 | 0.9048 |
| Ki=0.4 | 0.8903 | 0.8500 | 0.8636 | 0.8481 | 0.7778 | 0.8352 | 0.8143 | 0.7284 | 0.7872 | 0.8650 | 0.8272 | 0.8409 |
| Ki=0.5 | 0.8312 | 0.7529 | 0.8242 | 0.8565 | 0.8023 | 0.8427 | 0.8776 | 0.8125 | 0.8556 | 0.8650 | 0.7976 | 0.8506 |
| Ki=0.6 | 0.8397 | 0.8705 | 0.8043 | 0.8565 | 0.8272 | 0.8111 | 0.8776 | 0.7976 | 0.8636 | 0.8903 | 0.8519 | 0.8523 |
| Ki=0.7 | 0.8397 | 0.7412 | 0.8352 | 0.8776 | 0.8333 | 0.8444 | 0.8776 | 0.8072 | 0.8652 | 0.8650 | 0.8140 | 0.8588 |
| Ki=0.8 | 0.8945 | 0.8353 | 0.9059 | 0.8692 | 0.8493 | 0.8105 | 0.8819 | 0.8500 | 0.8523 | 0.8945 | 0.8659 | 0.8605 |
| Ki=0.9 | 0.8565 | 0.8068 | 0.8488 | 0.8481 | 0.7412 | 0.8539 | 0.8734 | 0.8171 | 0.8427 | 0.8987 | 0.8235 | 0.8953 |
| Ki=1.00 | 0.8186 | 0.7294 | 0.7912 | 0.8945 | 0.8395 | 0.8652 | 0.8608 | 0.7619 | 0.8556 | 0.8945 | 0.8642 | 0.8506 |
|
KP, Ki and KD coefficients |
Results of identical integration tests |
Results of non-identical integration tests | |||||
| %acc | %sen | %spe | %acc | %sen | %spe | ||
| 1 | basic method KP=0.3,Ki=0.1,KD=0.8 |
0.6694 | 0.7329 | 0.6620 | 0.5048 | 0.5345 | 0.4750 |
| 2 | basic method KP=0.3,Ki=0.8,KD=0.5 |
0.6148 | 0.7288 | 0.6000 | 0.5048 | 0.5345 | 0.4750 |
| 3 | basic method KP=0.3,Ki=0.8,KD=0.2 |
0.6889 | 0.6942 | 0.7500 | 0.5048 | 0.5345 | 0.4750 |
| 4 | basic method KP=0.3,Ki=0.4,KD=1 |
0.7037 | 0.6239 | 0.7596 | 0.5714 | 0.6364 | 0.6389 |
| 5 | basic method KP=0.2,Ki=0.8,KD=0.2 |
0.6704 | 0.6466 | 0.7027 | 0.4762 | 0.4800 | 0.5217 |
| 6 | basic method KP=0.3,Ki=0.8,KD=0.5 |
0.7000 | 0.6917 | 0.7624 | 0.5048 | 0.5345 | 0.4750 |
| 7 | basic method KP=0.2,Ki=0.7,KD=2 |
0.7037 | 0.6581 | 0.7670 | 0.5714 | 0.6364 | 0.6389 |
| 8 | basic method KP=0.7,Ki=0.2,KD=2 |
0.6926 | 0.6789 | 0.7156 | 0.8945 |
0.8642 |
0.9059 |
| 9 | basic method KP=Ki=0.1,KD=5 |
0.7000 | 0.6695 | 0.7596 | 0.5079 | 0.6418 | 0.5000 |
| 10 | basic method KP=Ki=0.1,KD=2 |
0.9114 | 0.8690 | 0.8506 |
0.5079 | 0.6418 | 0.5000 |
| Accuracy% | Accuracy% | ||
| case | method | non-uniform integration method | uniform integration method |
| 1 | conventional method | 47% | 50% |
| 2 | basic method | 89% | 91% |
| 3 | feedback method | 93% | 95% |
| Case | Authors | Dataset | Accuracy% | Sensitivity% | Specificity% |
| 1 | Xiaoyan Wei et al, 2018.[19] | Department of Neurology-Xinjiang Medical University | 90 | 88.9 | 93.78 |
| 2 | M. Hosseini et al , 2017.[20] | the Center for Epilepsy | 93 | 94 | 94 |
| 3 | Mengni Zhou1 et al, 2018.[21] | The CHB-MIT | 91.1 | 83.6 | 85.1 |
| 4 | Zhang, S. et al , 2020.[25] | The CHB-MIT | 89.98 | 92.9 | 87.04 |
| 5 | Zuyi Yu · Weiwei Nie, 2018.[26] | the Center for Epilepsy at Freiburg University Hospital in Germany | - | 87.7 | - |
| 6 | Jana R., 2020.[27] | The CHB-MIT | 94.33 | 96 | 94.39 |
| 7 | S. Muhammad Usman, 2020.[28] | The CHB-MIT | - | 92.7 | 90.8 |
| 8 | Zuochen Wei, 2019.[30] | The CHB-MIT | 81.49 | 70.68 | 92.30 |
| 9 | S. Raghu 2020.[31] | The Temple University Hospital (TUH) | 88.3 | 88.4 | 84.1 |
| 10 | proposed method | The CHB-MIT | 97.1 | 97.5 | 96.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




