Submitted:
26 May 2023
Posted:
29 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
3D printed scaffold preparation and characterization
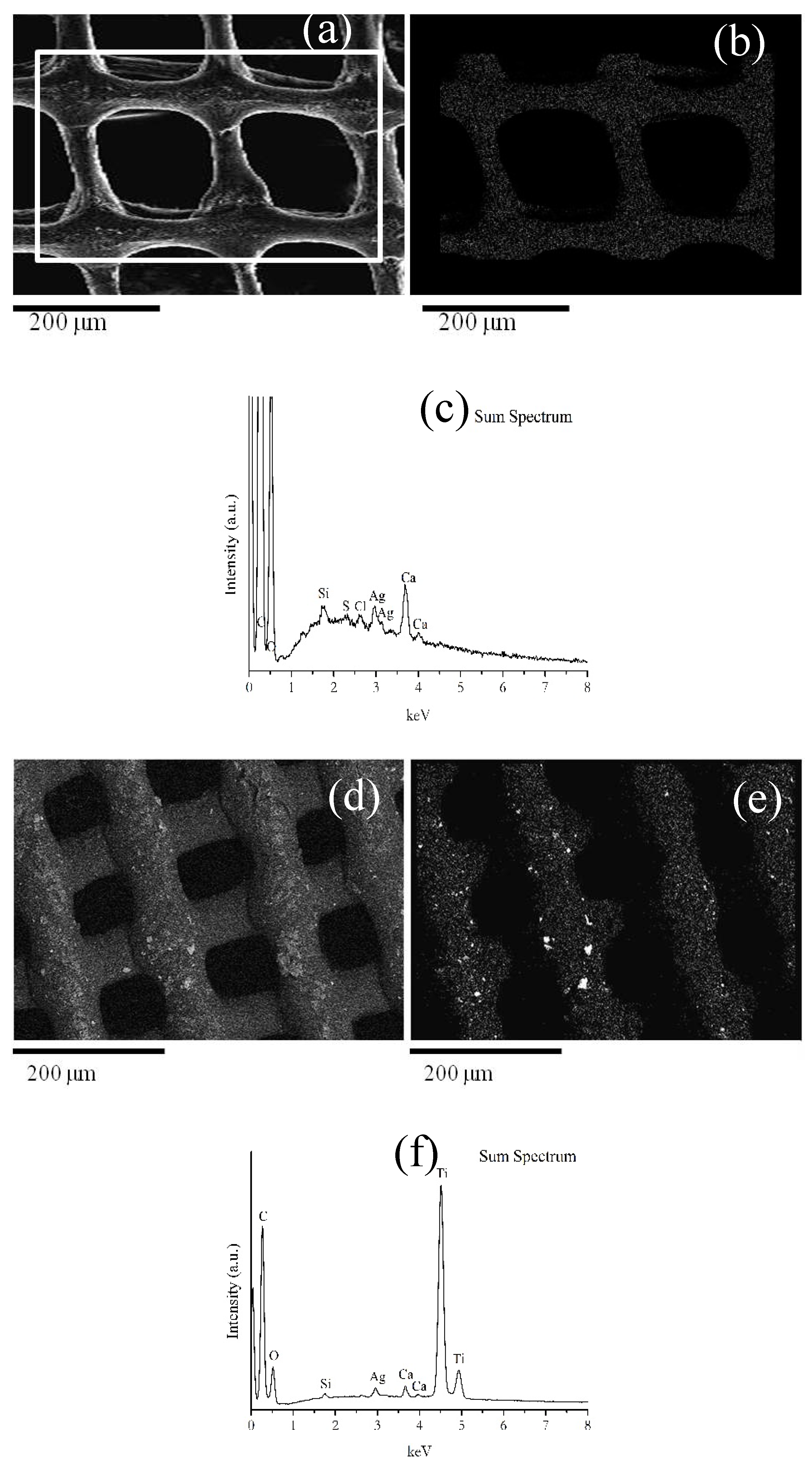
Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Energy-Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (EDS)
Antimicrobial Activity Assay
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
Materials
Methods
Ink preparation for 3D printing
3D printing and scaffold production
Scaffold characterization
SEM and SEM-EDS analysis
Antimicrobial activity tests
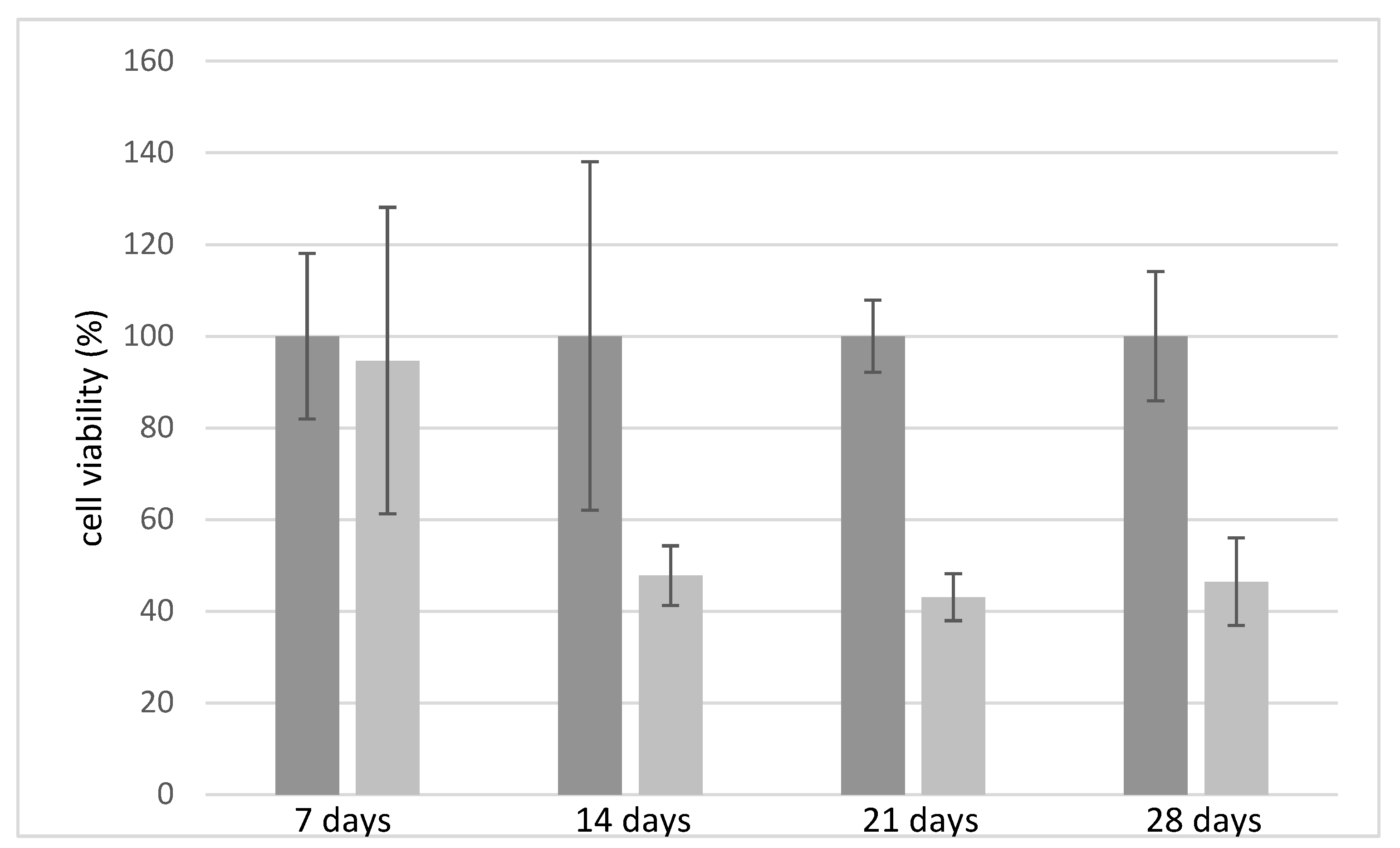
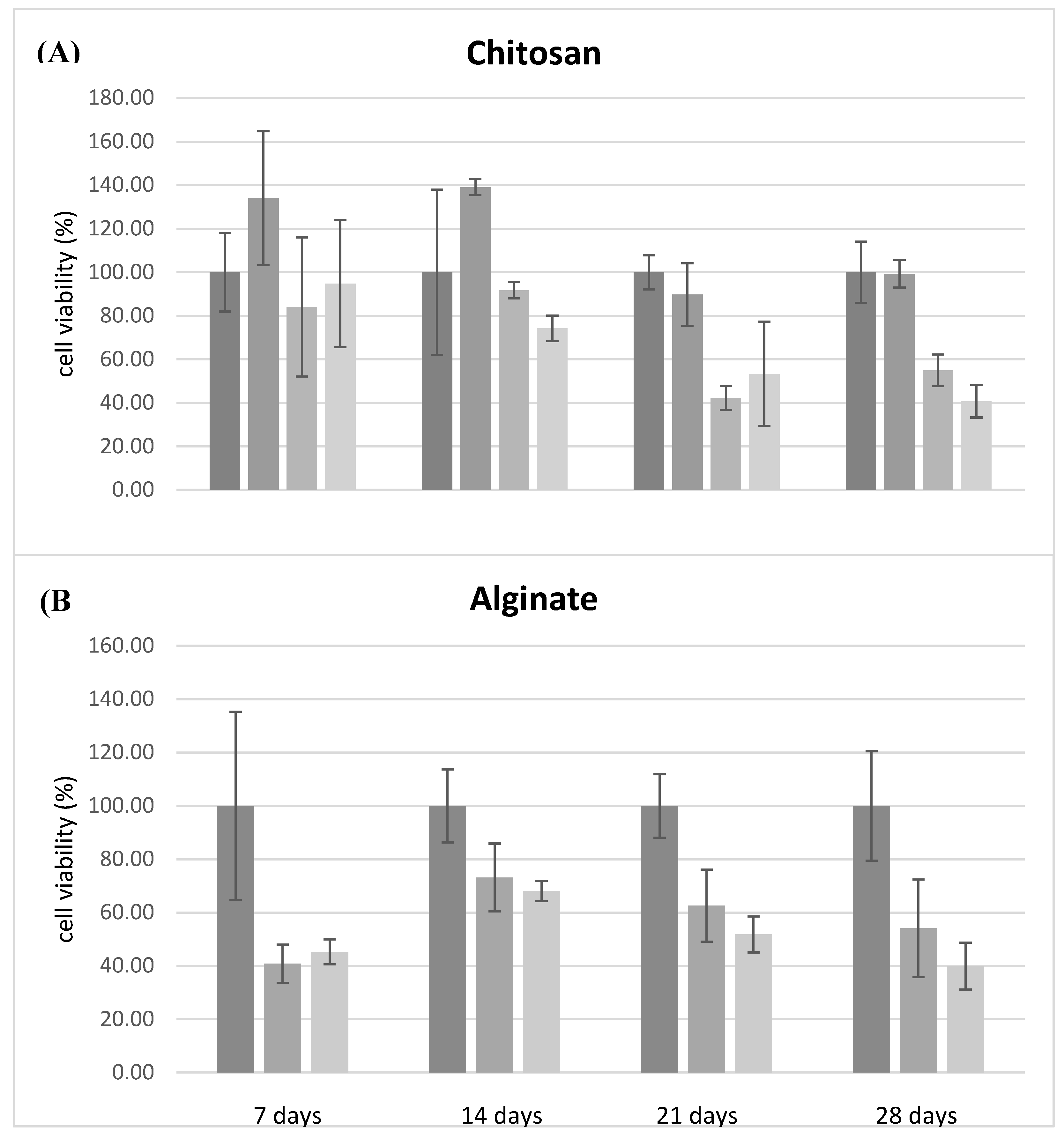
Cell viability test
Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heyer, K.; Herberger, K.; Protz, K.; Glaeske, G.; Augustin, M. Epidemiology of Chronic Wounds in Germany: Analysis of Statutory Health Insurance Data. Wound Repair Regen 2016, 24, 434–442. [CrossRef]
- Guest, J.F.; Ayoub, N.; McIlwraith, T.; Uchegbu, I.; Gerrish, A.; Weidlich, D.; Vowden, K.; Vowden, P. Health Economic Burden That Wounds Impose on the National Health Service in the UK. BMJ Open 2015, 5, e009283. [CrossRef]
- Salgado, A.J.; Oliveira, J.M.; Martins, A.; Teixeira, F.G.; Silva, N.A.; Neves, N.M.; Sousa, N.; Reis, R.L. Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine. In International Review of Neurobiology; Elsevier, 2013; Vol. 108, pp. 1–33 ISBN 978-0-12-410499-0.
- Church, D.; Elsayed, S.; Reid, O.; Winston, B.; Lindsay, R. Burn Wound Infections. Clin Microbiol Rev 2006, 19, 403–434. [CrossRef]
- Bergonzi, C.; Remaggi, G.; Graiff, C.; Bergamonti, L.; Potenza, M.; Ossiprandi, M.C.; Zanotti, I.; Bernini, F.; Bettini, R.; Elviri, L. Three-Dimensional (3D) Printed Silver Nanoparticles/Alginate/Nanocrystalline Cellulose Hydrogels: Study of the Antimicrobial and Cytotoxicity Efficacy. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 844. [CrossRef]
- Percival, S.L.; Bowler, P.G.; Dolman, J. Antimicrobial Activity of Silver-Containing Dressings on Wound Microorganisms Using an in Vitro Biofilm Model. Int Wound Journal 2007, 4, 186–191. [CrossRef]
- Gun’ko, V.; Savina, I.; Mikhalovsky, S. Properties of Water Bound in Hydrogels. Gels 2017, 3, 37. [CrossRef]
- Seal, B. Polymeric Biomaterials for Tissue and Organ Regeneration. Materials Science and Engineering: R: Reports 2001, 34, 147–230. [CrossRef]
- Jodar, K.S.P.; Balcao, V.M.; Chaud, M.V.; Tubino, M.; Yoshida, V.M.H.; Oliveira, J.M.; Vila, M.M.D.C. Development and Characterization of a Hydrogel Containing Silver Sulfadiazine for Antimicrobial Topical Applications. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 2015, 104, 2241–2254. [CrossRef]
- Cheung, H.-Y.; Lau, K.-T.; Lu, T.-P.; Hui, D. A Critical Review on Polymer-Based Bio-Engineered Materials for Scaffold Development. Composites Part B: Engineering 2007, 38, 291–300. [CrossRef]
- Goy, R.C.; Britto, D. de; Assis, O.B.G. A Review of the Antimicrobial Activity of Chitosan. Polímeros 2009, 19, 241–247. [CrossRef]
- Fajardo, A.R.; Lopes, L.C.; Caleare, A.O.; Britta, E.A.; Nakamura, C.V.; Rubira, A.F.; Muniz, E.C. Silver Sulfadiazine Loaded Chitosan/Chondroitin Sulfate Films for a Potential Wound Dressing Application. Materials Science and Engineering: C 2013, 33, 588–595. [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Gao, J.; He, Q.; Wu, J.; Liang, D.; Yang, H.; Chen, R. Enhanced Antibacterial and Wound Healing Activities of Microporous Chitosan-Ag/ZnO Composite Dressing. Carbohydrate Polymers 2017, 156, 460–469. [CrossRef]
- Woo, C.H.; Choi, Y.C.; Choi, J.S.; Lee, H.Y.; Cho, Y.W. A Bilayer Composite Composed of TiO 2 -Incorporated Electrospun Chitosan Membrane and Human Extracellular Matrix Sheet as a Wound Dressing. Journal of Biomaterials Science, Polymer Edition 2015, 26, 841–854. [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wang, J.; Wang, R.; Yuan, P.; Fan, Z.; Yang, S. Preparation and Properties of ZnO/Sodium Alginate Bi-Layered Hydrogel Films as Novel Wound Dressings. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 8684–8693. [CrossRef]
- Aderibigbe, B.; Buyana, B. Alginate in Wound Dressings. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 42. [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Vázquez, M.; Vega-Ruiz, B.; Ramos-Zúñiga, R.; Saldaña-Koppel, D.A.; Quiñones-Olvera, L.F. Chitosan and Its Potential Use as a Scaffold for Tissue Engineering in Regenerative Medicine. BioMed Research International 2015, 2015, 1–15. [CrossRef]
- Pereira, R.; Carvalho, A.; Vaz, D.C.; Gil, M.H.; Mendes, A.; Bártolo, P. Development of Novel Alginate Based Hydrogel Films for Wound Healing Applications. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 2013, 52, 221–230. [CrossRef]
- Jayakumar, R.; Ramachandran, R.; Sudheesh Kumar, P.T.; Divyarani, V.V.; Srinivasan, S.; Chennazhi, K.P.; Tamura, H.; Nair, S.V. Fabrication of Chitin–Chitosan/Nano ZrO2 Composite Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering Applications. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 2011, 49, 274–280. [CrossRef]
- Seo, S.Y.; Lee, G.H.; Lee, S.G.; Jung, S.Y.; Lim, J.O.; Choi, J.H. Alginate-Based Composite Sponge Containing Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized in Situ. Carbohydrate Polymers 2012, 90, 109–115. [CrossRef]
- Boateng, J.; Burgos-Amador, R.; Okeke, O.; Pawar, H. Composite Alginate and Gelatin Based Bio-Polymeric Wafers Containing Silver Sulfadiazine for Wound Healing. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 2015, 79, 63–71. [CrossRef]
- Chernousova, S.; Epple, M. Silver as Antibacterial Agent: Ion, Nanoparticle, and Metal. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 1636–1653. [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, C.; Li, C.; Qin, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, F.; Li, Z.; Wang, J. A Functional Chitosan-Based Hydrogel as a Wound Dressing and Drug Delivery System in the Treatment of Wound Healing. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 7533–7549. [CrossRef]
- Foster, H.A.; Ditta, I.B.; Varghese, S.; Steele, A. Photocatalytic Disinfection Using Titanium Dioxide: Spectrum and Mechanism of Antimicrobial Activity. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 2011, 90, 1847–1868. [CrossRef]
- Bui, V.; Park, D.; Lee, Y.-C. Chitosan Combined with ZnO, TiO2 and Ag Nanoparticles for Antimicrobial Wound Healing Applications: A Mini Review of the Research Trends. Polymers 2017, 9, 21. [CrossRef]
- Kambala, V.S.R.; Naidu, R. Disinfection Studies on TiO<SUB>2</SUB> Thin Films Prepared Bya Sol–Gel Method. Journal of Biomedical Nanotechnology 2009, 5, 121–129. [CrossRef]
- Maness, P.-C.; Smolinski, S.; Blake, D.M.; Huang, Z.; Wolfrum, E.J.; Jacoby, W.A. Bactericidal Activity of Photocatalytic TiO 2 Reaction: Toward an Understanding of Its Killing Mechanism. Appl Environ Microbiol 1999, 65, 4094–4098. [CrossRef]
- Seisenbaeva, G.A.; Fromell, K.; Vinogradov, V.V.; Terekhov, A.N.; Pakhomov, A.V.; Nilsson, B.; Ekdahl, K.N.; Vinogradov, V.V.; Kessler, V.G. Dispersion of TiO2 Nanoparticles Improves Burn Wound Healing and Tissue Regeneration through Specific Interaction with Blood Serum Proteins. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 15448. [CrossRef]
- Behera, S.S.; Das, U.; Kumar, A.; Bissoyi, A.; Singh, A.K. Chitosan/TiO 2 Composite Membrane Improves Proliferation and Survival of L929 Fibroblast Cells: Application in Wound Dressing and Skin Regeneration. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 2017, 98, 329–340. [CrossRef]
- Bergonzi, C.; Di Natale, A.; Zimetti, F.; Marchi, C.; Bianchera, A.; Bernini, F.; Silvestri, M.; Bettini, R.; Elviri, L. Study of 3D-Printed Chitosan Scaffold Features after Different Post-Printing Gelation Processes. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 362. [CrossRef]
- Intini, C.; Elviri, L.; Cabral, J.; Mros, S.; Bergonzi, C.; Bianchera, A.; Flammini, L.; Govoni, P.; Barocelli, E.; Bettini, R.; et al. 3D-Printed Chitosan-Based Scaffolds: An in Vitro Study of Human Skin Cell Growth and an in-Vivo Wound Healing Evaluation in Experimental Diabetes in Rats. Carbohydrate Polymers 2018, 199, 593–602. [CrossRef]
- Gorham, J.M.; MacCuspie, R.I.; Klein, K.L.; Fairbrother, D.H.; Holbrook, R.D. UV-Induced Photochemical Transformations of Citrate-Capped Silver Nanoparticle Suspensions. J Nanopart Res 2012, 14, 1139. [CrossRef]
- Elviri, L.; Foresti, R.; Bergonzi, C.; Zimetti, F.; Marchi, C.; Bianchera, A.; Bernini, F.; Silvestri, M.; Bettini, R. Highly Defined 3D Printed Chitosan Scaffolds Featuring Improved Cell Growth. Biomed. Mater. 2017, 12, 045009. [CrossRef]
- Nanomaterials in Drug Delivery, Imaging, and Tissue Engineering, 2013.
- Jayakumar, R.; Prabaharan, M.; Sudheesh Kumar, P.T.; Nair, S.V.; Tamura, H. Biomaterials Based on Chitin and Chitosan in Wound Dressing Applications. Biotechnology Advances 2011, 29, 322–337. [CrossRef]
- Bin Ahmad, M.; Lim, J.J.; Shameli, K.; Ibrahim, N.A.; Tay, M.Y. Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles in Chitosan, Gelatin and Chitosan/Gelatin Bionanocomposites by a Chemical Reducing Agent and Their Characterization. Molecules 2011, 16, 7237–7248. [CrossRef]
- Howling, G.I.; Dettmar, P.W.; Goddard, P.A.; Hampson, F.C.; Dornish, M.; Wood, E.J. The Effect of Chitin and Chitosan on the Proliferation of Human Skin Fibroblasts and Keratinocytes in Vitro. Biomaterials 2001, 22, 2959–2966. [CrossRef]
- Majima, T.; Funakosi, T.; Iwasaki, N.; Yamane, S.-T.; Harada, K.; Nonaka, S.; Minami, A.; Nishimura, S.-I. Alginate and Chitosan Polyion Complex Hybrid Fibers for Scaffolds in Ligament and Tendon Tissue Engineering. Journal of Orthopaedic Science 2005, 10, 302–307. [CrossRef]
- Bergamonti, L.; Bergonzi, C.; Graiff, C.; Lottici, P.P.; Bettini, R.; Elviri, L. 3D Printed Chitosan Scaffolds: A New TiO2 Support for the Photocatalytic Degradation of Amoxicillin in Water. Water Research 2019, 163, 114841. [CrossRef]
- Norahan, M.H.; Pedroza-González, S.C.; Sánchez-Salazar, M.G.; Álvarez, M.M.; Trujillo de Santiago, G. Structural and Biological Engineering of 3D Hydrogels for Wound Healing. Bioactive Materials 2023, 24, 197–235. [CrossRef]
- Basile, R.; Bergamonti, L.; Fernandez, F.; Graiff, C.; Haghighi, A.; Isca, C.; Lottici, P.P.; Pizzo, B.; Predieri, G. Bio-Inspired Consolidants Derived from Crystalline Nanocellulose for Decayed Wood. Carbohydrate Polymers 2018, 202, 164–171. [CrossRef]
- Bergonzi, C.; Bianchera, A.; Remaggi, G.; Ossiprandi, M.C.; Bettini, R.; Elviri, L. 3D Printed Chitosan/Alginate Hydrogels for the Controlled Release of Silver Sulfadiazine in Wound Healing Applications: Design, Characterization and Antimicrobial Activity. Micromachines 2023, 14, 137. [CrossRef]
- Godebo, G.; Kibru, G.; Tassew, H. Multidrug-Resistant Bacterial Isolates in Infected Wounds at Jimma University Specialized Hospital, Ethiopia. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob 2013, 12, 17. [CrossRef]
- Biemer, J.J. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing by the Kirby-Bauer Disc Diffusion Method. Ann Clin Lab Sci (1971) 1973, 3, 135–140.
- Stanley, B.A.; Neverova, I.; Brown, H.A.; Van Eyk, J.E. Optimizing Protein Solubility for Two-Dimensional Gel Electrophoresis Analysis of Human Myocardium. Proteomics 2003, 3, 815–820. [CrossRef]
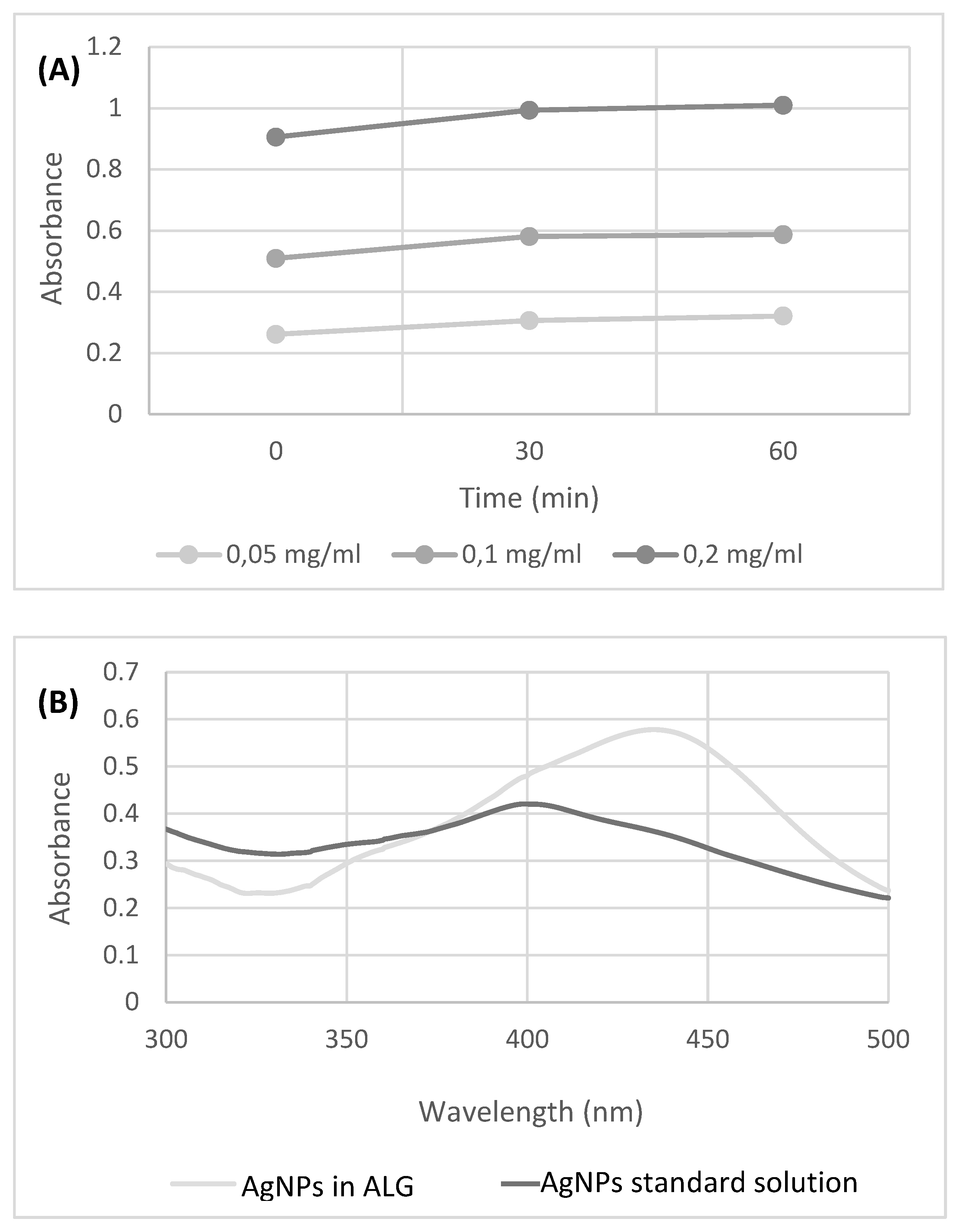
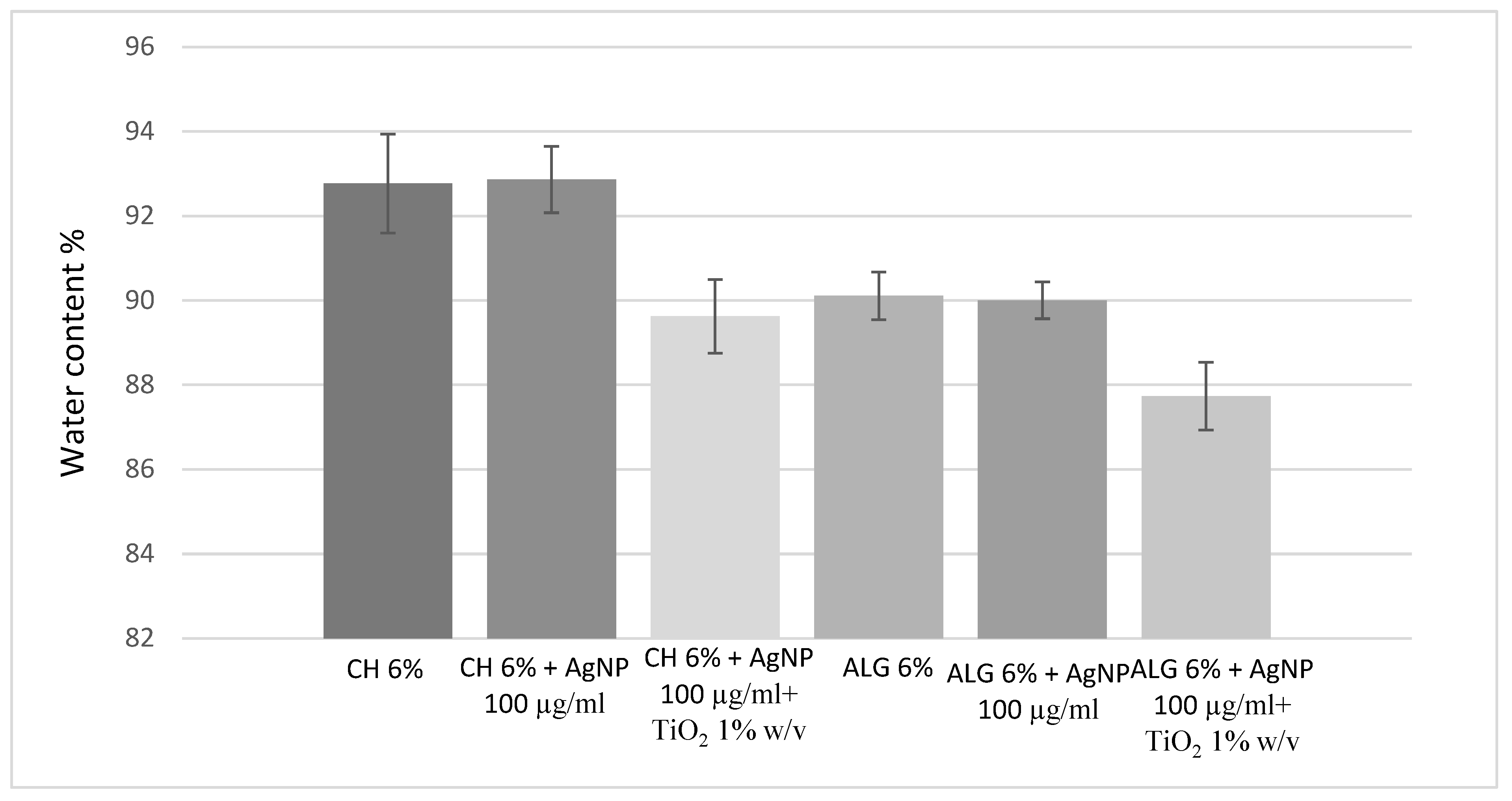
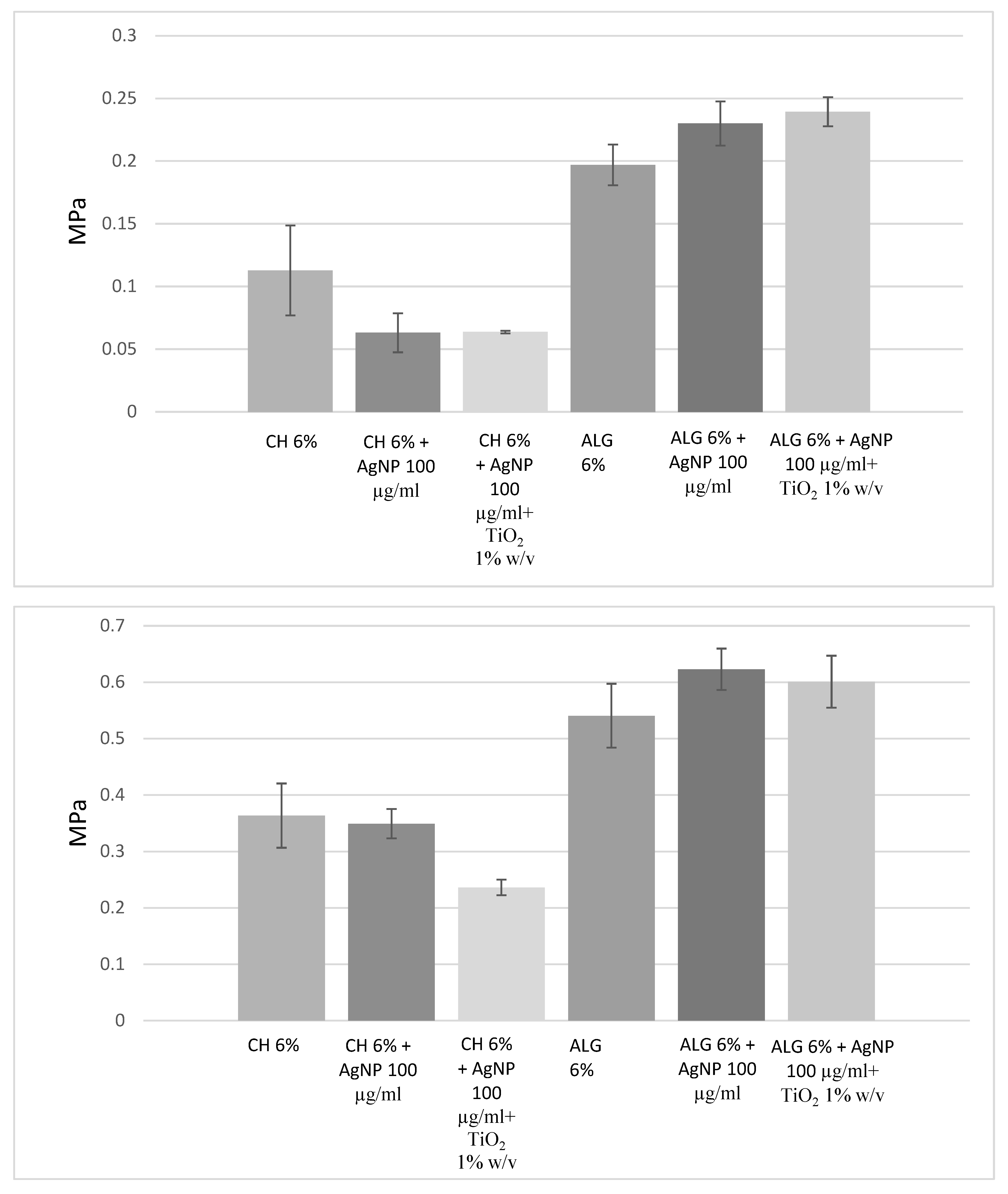
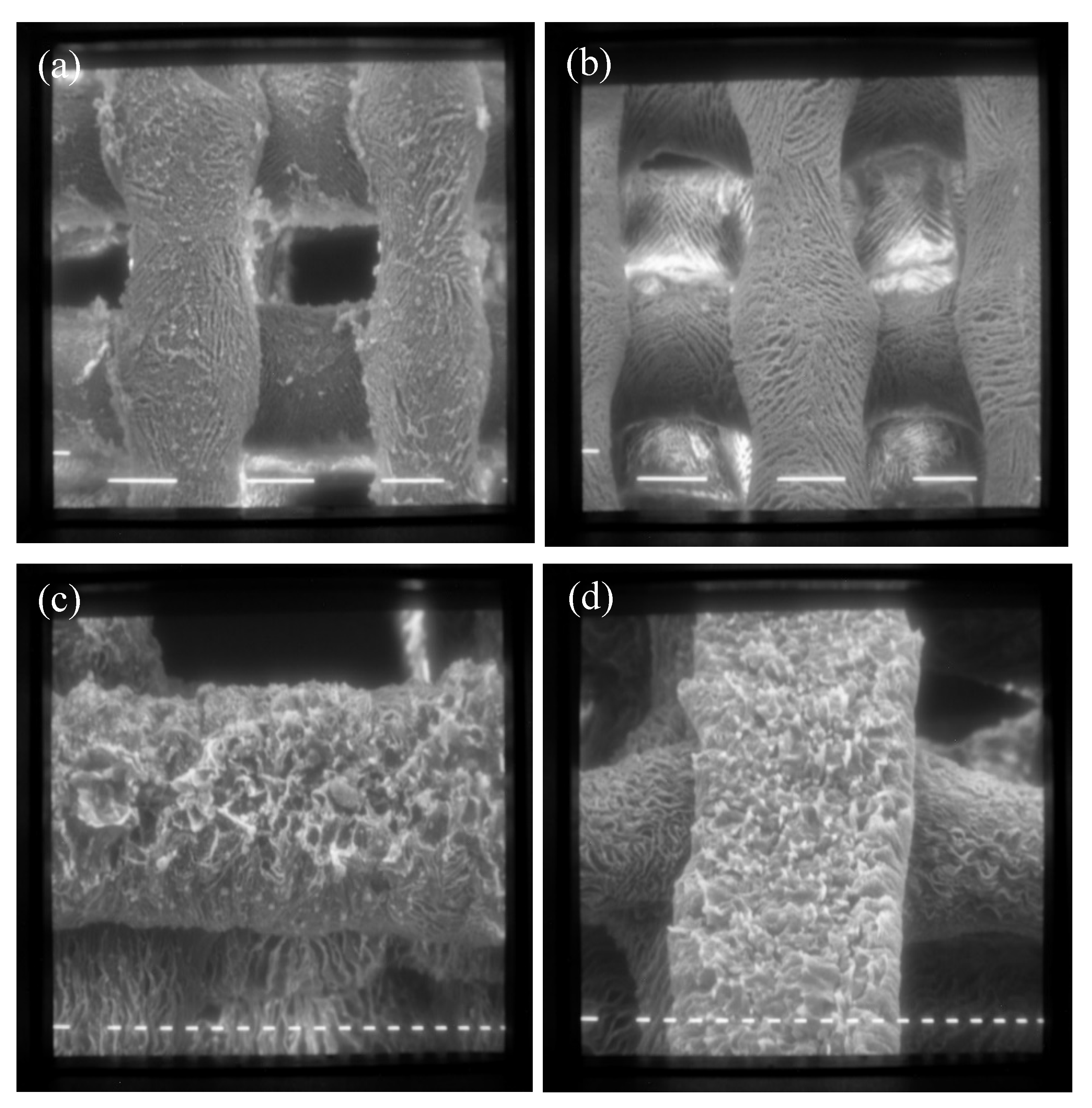
| SCAFFOLD (Ø 6 mm) | Staphylococcus aureus | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | ||
| Ø Inhibition Diameter (mm) | ||||
| CH 6% w/v | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| CH 6% w/v +AgNP 10 μg/ml | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 |
| CH 6% w/v + AgNP 100 μg/ml | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| CH 6% w/v + AgNP 100 μg/ml + TiO2 1% w/v | 8 | 8 | 6 | 6 |
| CH 6% w/v + TiO2 1% w/v | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| ALG 6% w/v | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| ALG 6% w/v + AgNP 100 μg/ml | 6 | 6 | 8 | 8 |
| ALG 6% w/v + AgNP 10 μg/ml | 6 | 6 | 8 | 8 |
| ALG 6% w/v + AgNP 5 μg/ml | 0 | 0 | 6 | 6 |
| ALG 6% w/v + AgNP 1 μg/ml | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| ALG 6% w/v + AgNP 100 μg/ml + TiO2 1% w/v | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| ALG 6% w/v + TiO2 1% w/v | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| Ink | Polysaccharide (w/v) | AgNPs (μg/ml) | TiO2 (w/v) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Chitosan 6% (ctrl) | - | - |
| 2 | Chitosan 6% | 10 | - |
| 3 | Chitosan 6% | 100 | - |
| 4 | Chitosan 6% | 100 | 1% |
| 5 | Chitosan 6% | - | 1% |
| 6 | Alginate 6% (ctrl) | - | - |
| 7 | Alginate 6% | 1 | - |
| 8 | Alginate 6% | 5 | - |
| 9 | Alginate 6% | 10 | - |
| 10 | Alginate 6% | 100 | - |
| 11 | Alginate 6% | 100 | 1% |
| 12 | Alginate 6% | - | 1% |
| Ink | Polysaccharide (w/v) | AgNPs (μg/ml) | TiO2 (w/v) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Chitosan 6% (ctrl) | - | - |
| 2 | Chitosan 6% | 10 | - |
| 3 | Chitosan 6% | 100 | - |
| 4 | Chitosan 6% | 100 | 1% |
| 5 | Chitosan 6% | - | 1% |
| 6 | Alginate 6% (ctrl) | - | - |
| 10 | Alginate 6% | 100 | - |
| 11 | Alginate 6% | 100 | 1% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





