Submitted:
24 February 2025
Posted:
24 February 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
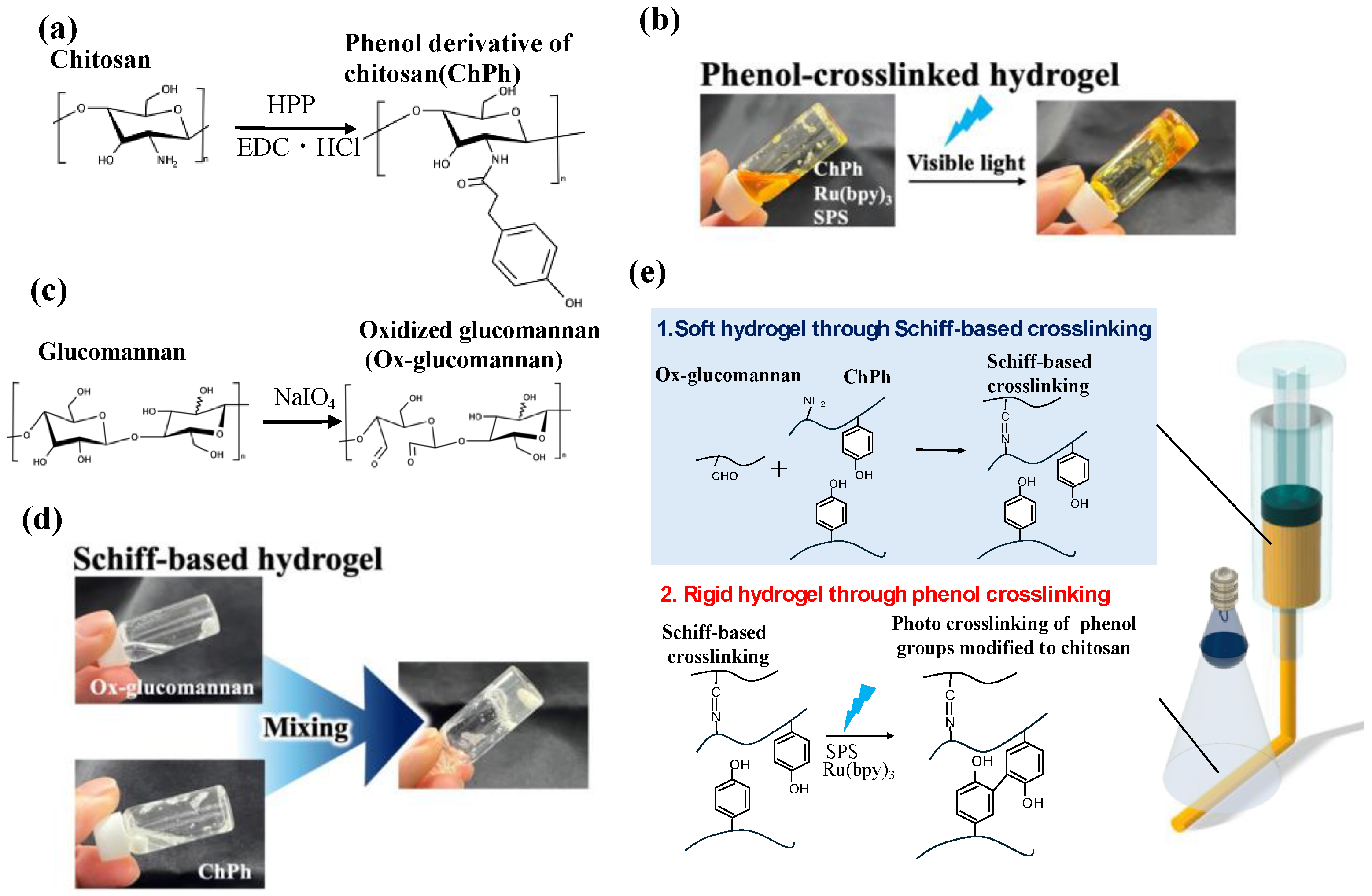
2.2. Synthesis of the Phenol Derivative of Chitosan (ChPh)
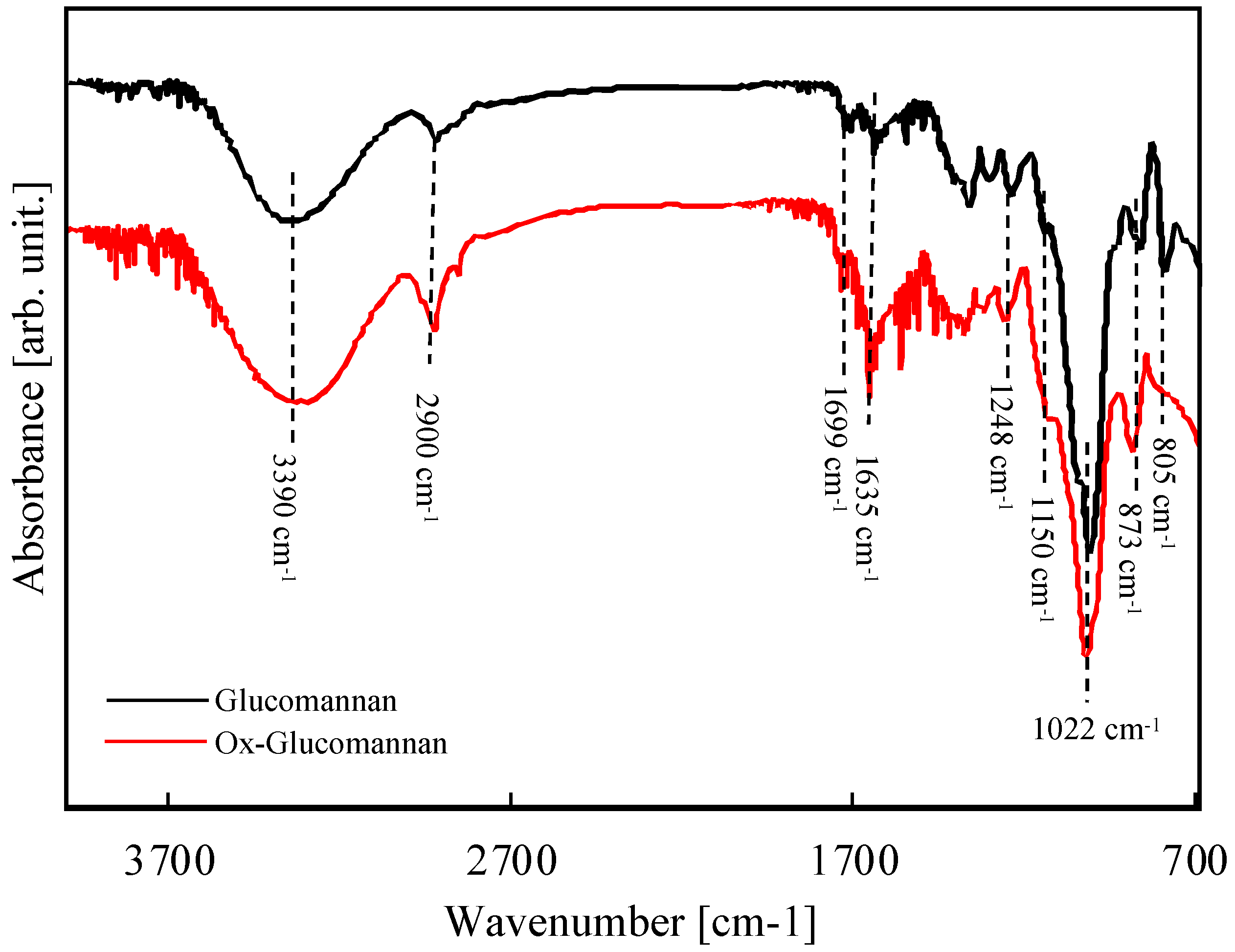
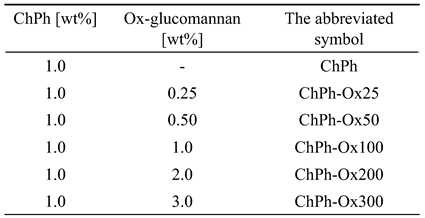
2.3. Synthesis of Oxidized Glucomannan (Ox-Glucomannan)
2.4. Fourier-Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy
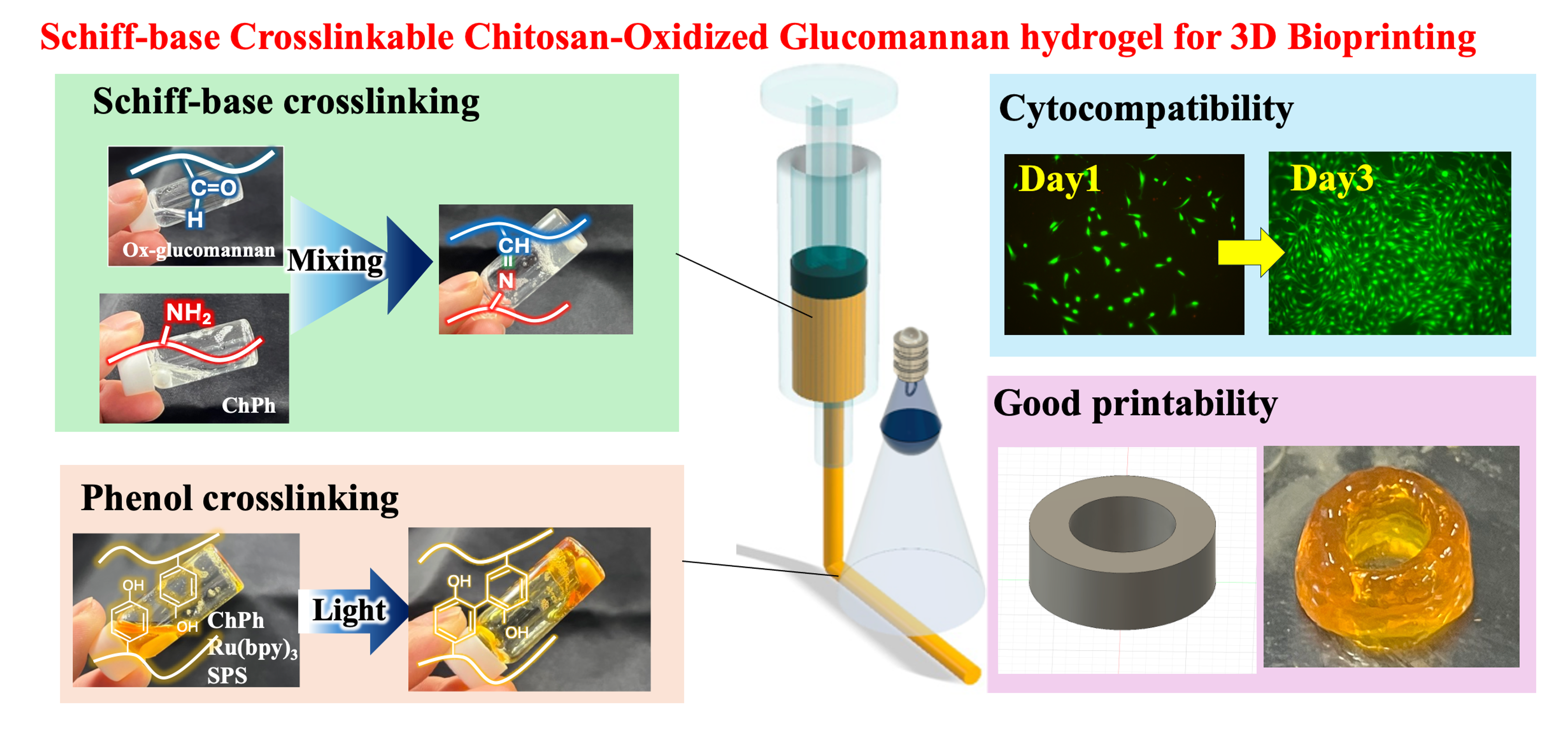
2.5. Preparation of Schiff Base Hydrogels
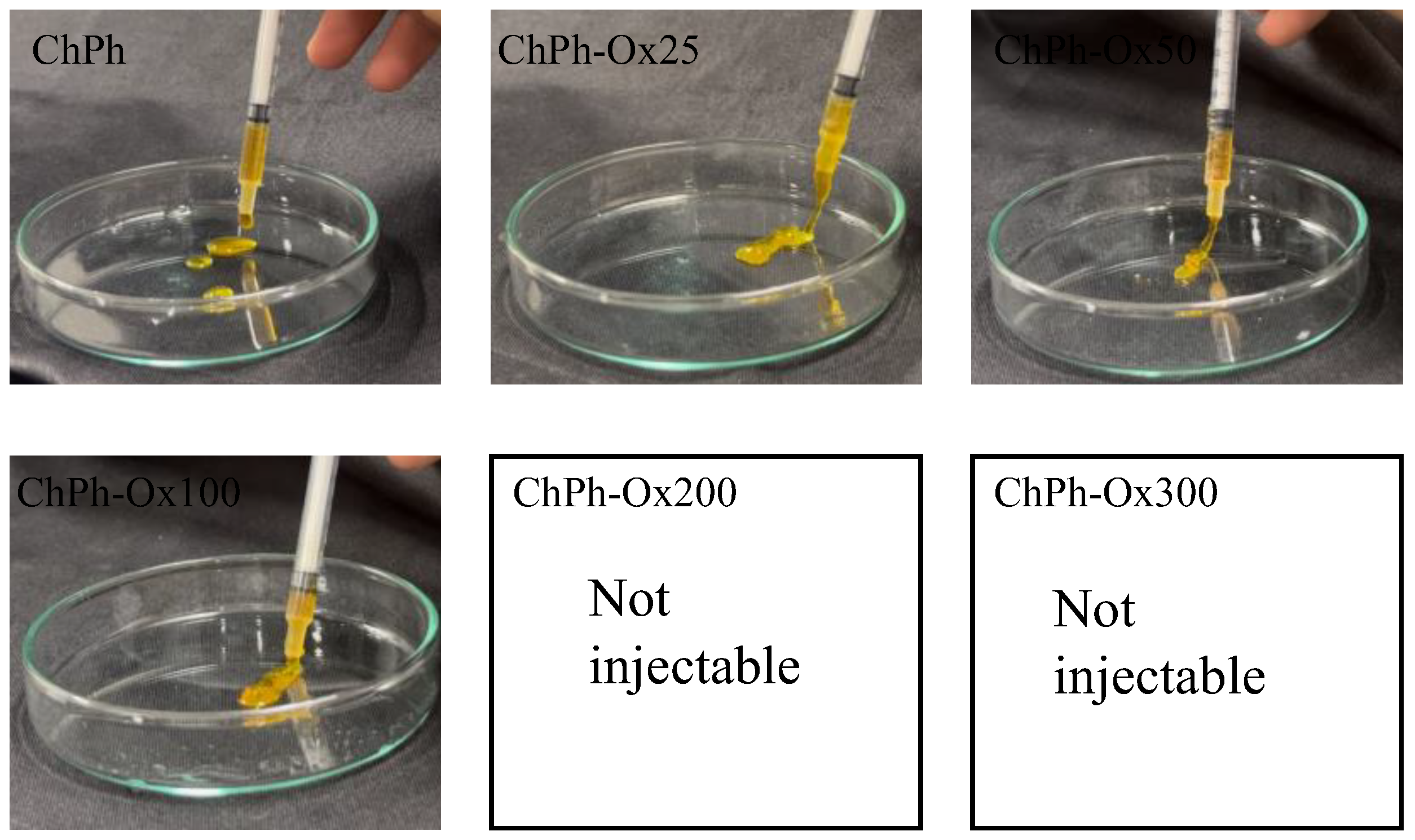
2.6. Extrudability
2.7. Rheological Properties
2.8. Swelling
2.9. Cell Viabilities
2.10. Antimicrobial Activities
2.11.3. D Printing
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. FTIR Spectra
3.2. Extrudability
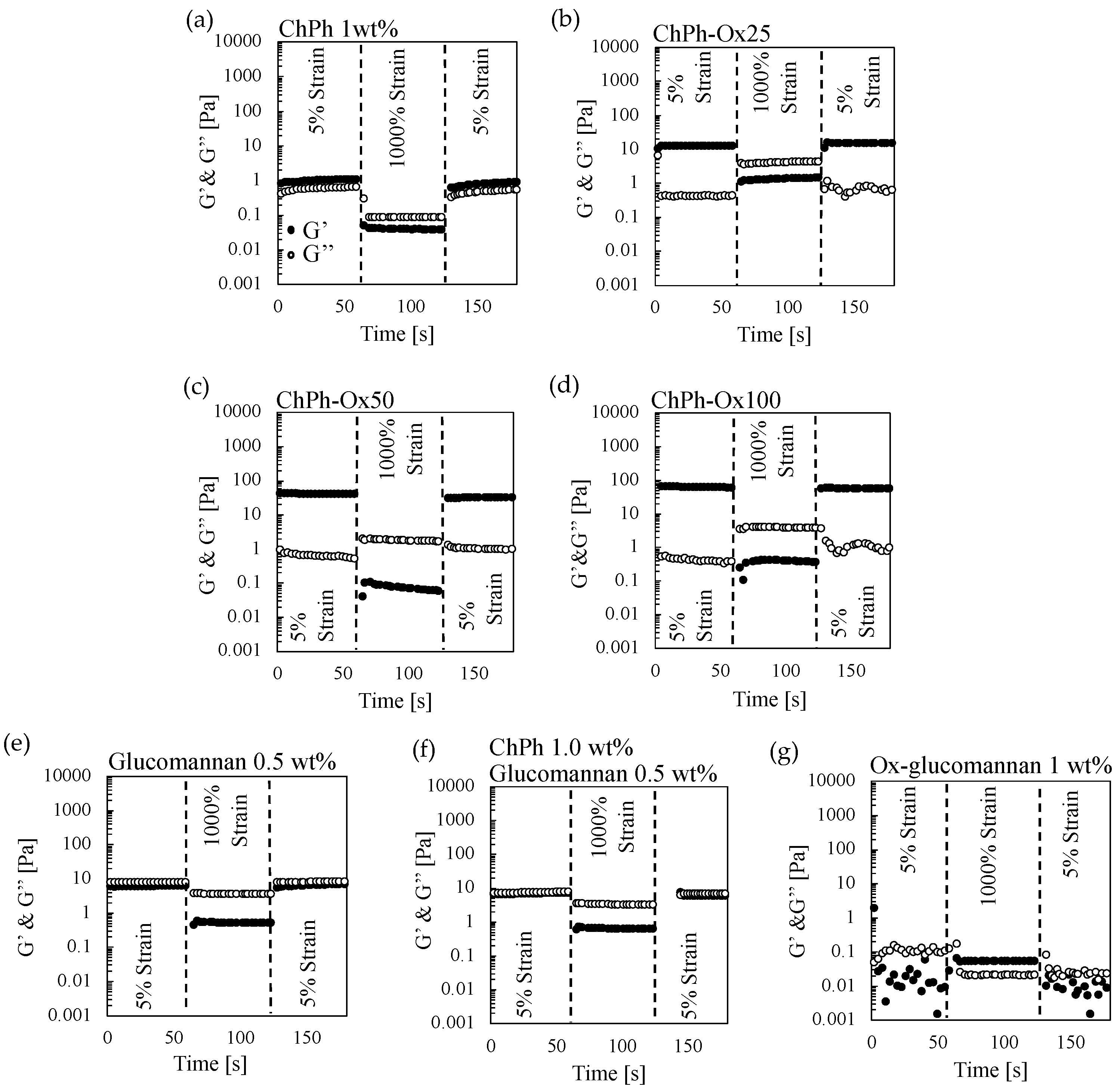
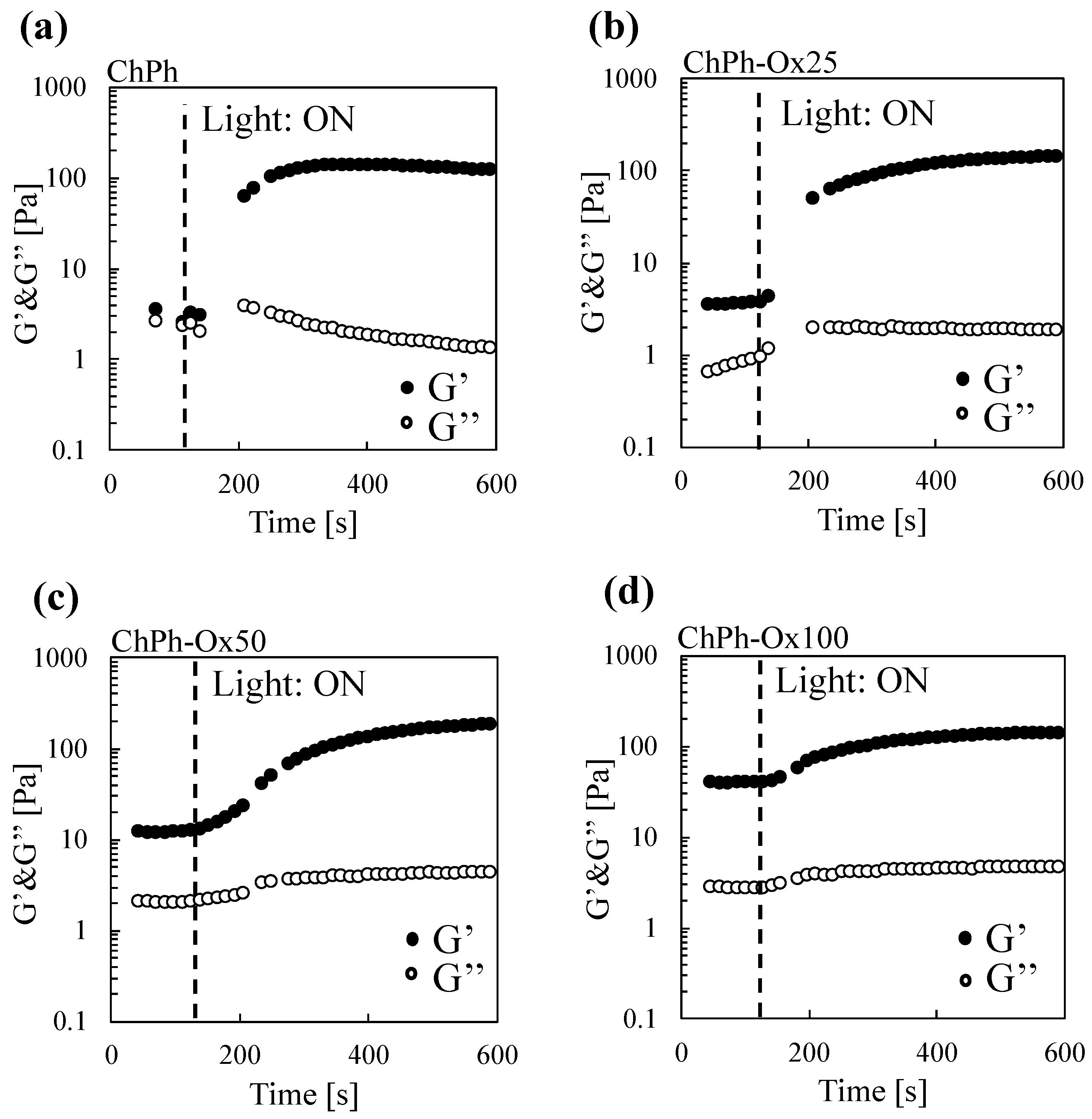
3.3. Rheological Properties of the Hydrogels with Schiff Base and Phenol Crosslinks
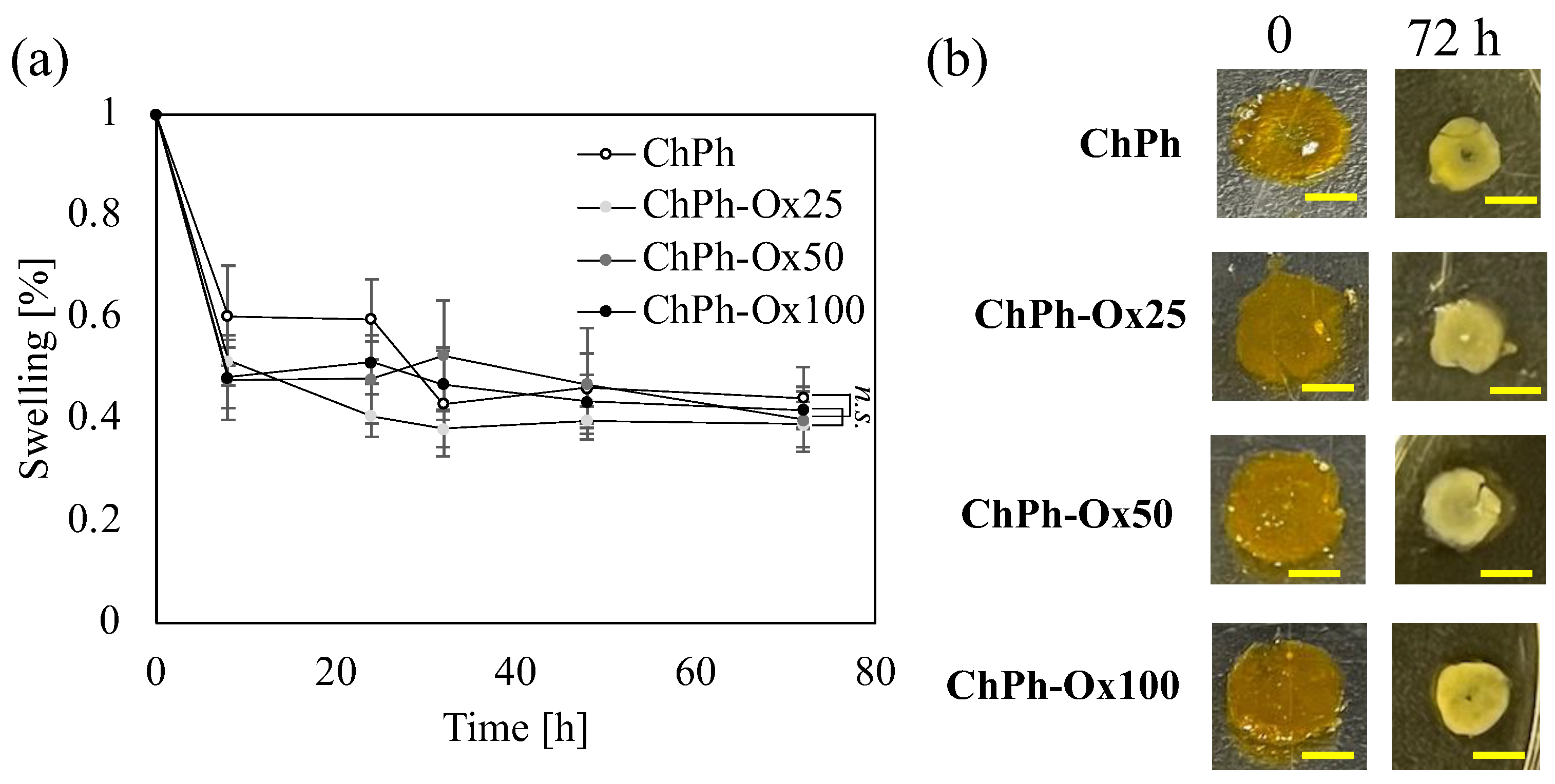
3.4. Swelling
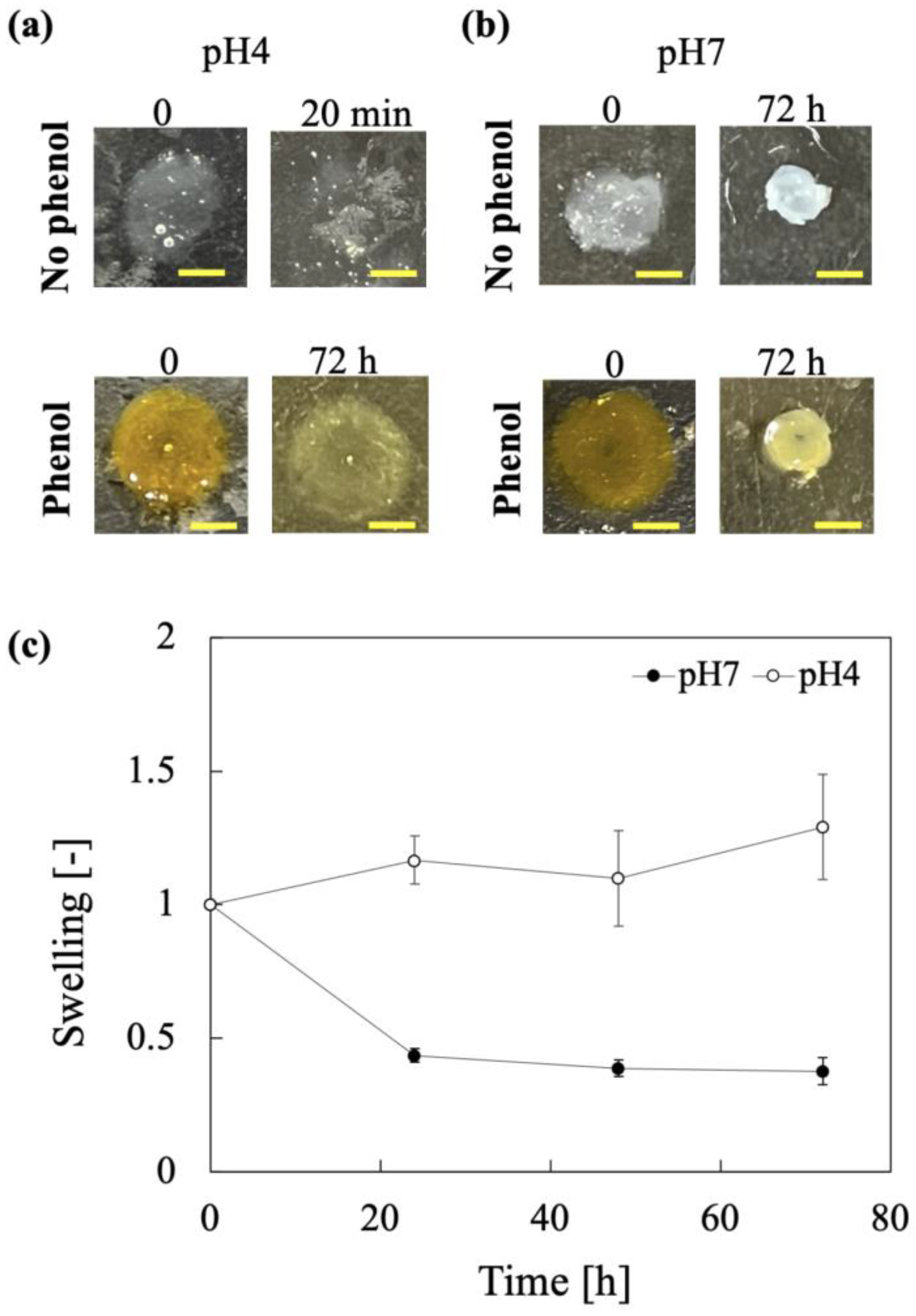
3.5. Effect of pH on Swelling and Stability
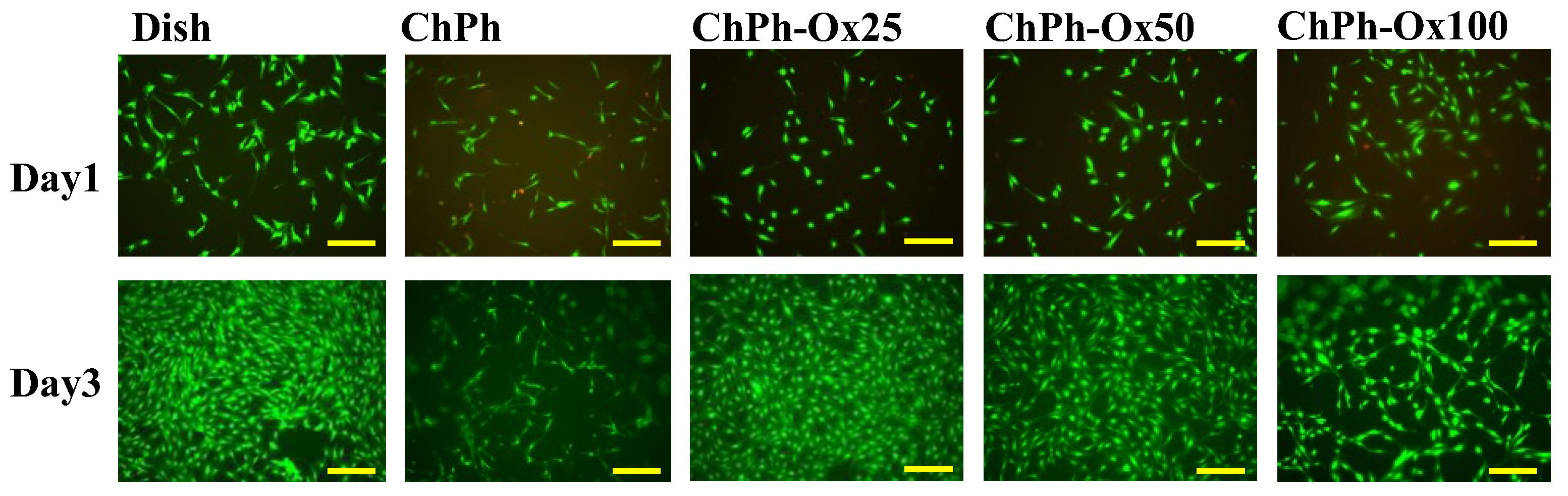
3.6. Cell Viabilities
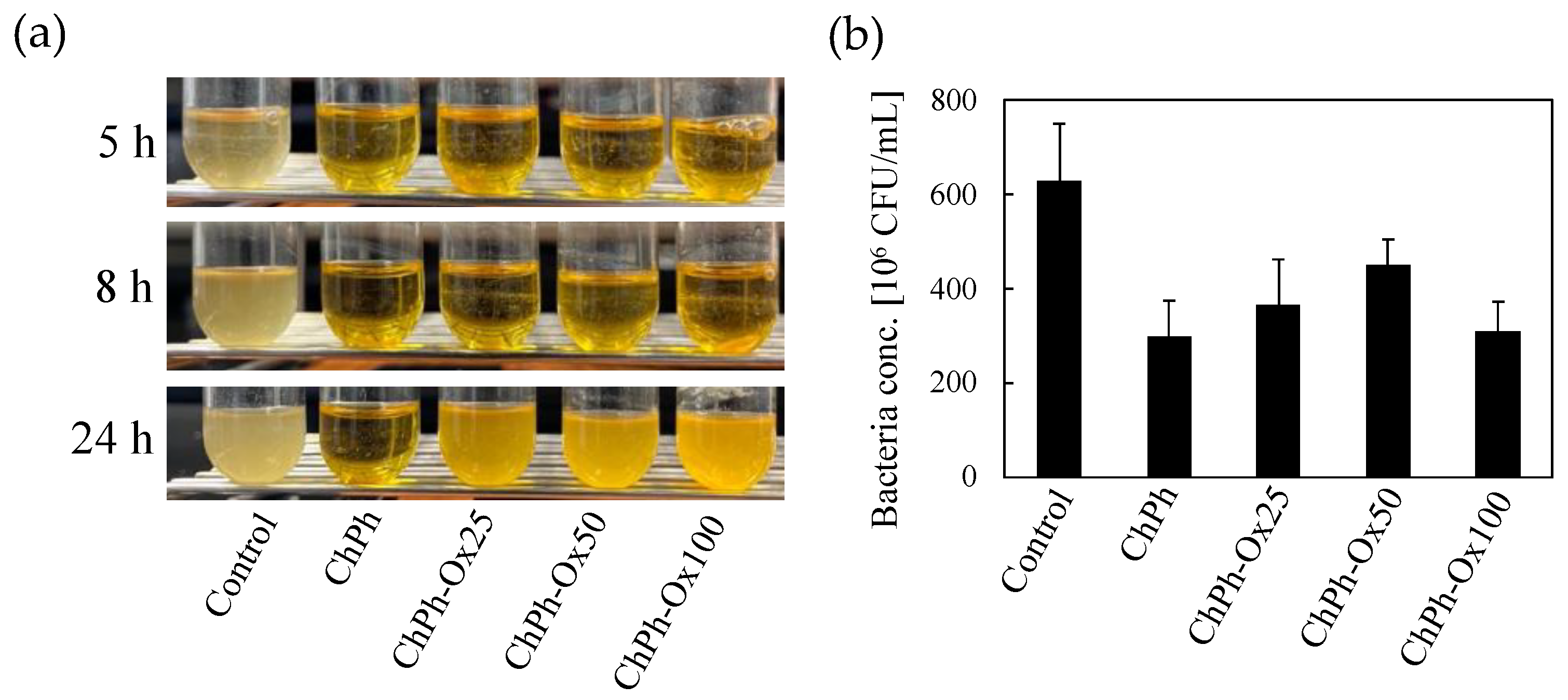
3.7. Antimicrobial Activities
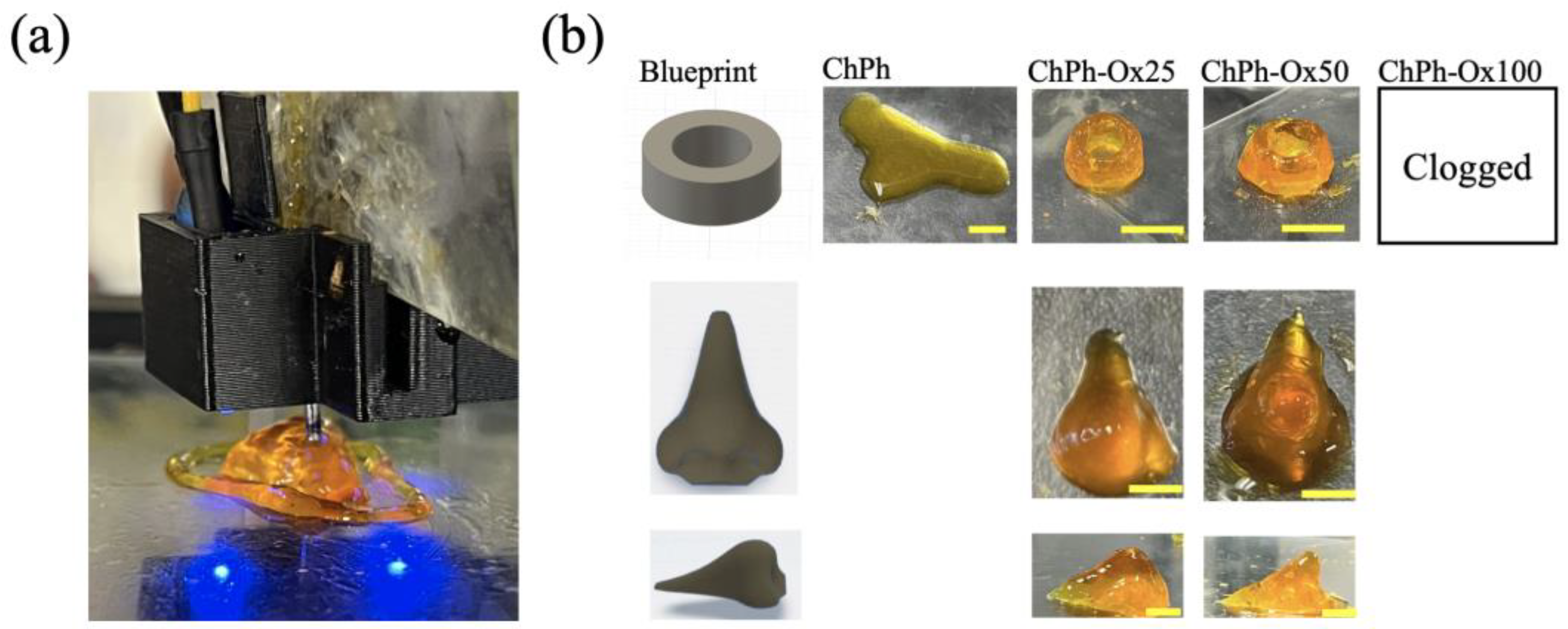
3.8. 3D Printing
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gungor-Ozkerim, P.S.; Inci, I.; Zhang, Y.S.; Khademhosseini, A.; Dokmeci, M.R., Bioinks for 3D Bioprinting: An Overview. Biomat Sci, 2018, 6, 915–946. [CrossRef]
- Pedroza-González, S.C.; Rodriguez-Salvador, M.; Pérez-Benítez, B.E.; Moisés Alvarez, M.; Santiago, G.T. De Bioinks for 3D Bioprinting: A Scientometric Analysis of Two Decades of Progress. Int J Bioprint, 2021, 7, 68–91. [CrossRef]
- Santoni, S.; Gugliandolo, S.G.; Sponchioni, M.; Moscatelli, D.; Colosimo, B.M. 3D Bioprinting: Current Status and Trends—a Guide to the Literature and Industrial Practice. Biodes Manuf, 2022, 5, 14–42. [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, B.; Pei, B.; Chen, J.; Zhou, D.; Peng, J.; Zhang, X.; Jia, W.; Xu, T. Inkjet Bioprinting of Biomaterials. Chem Rev, 2020, 120, 10793–10833. [CrossRef]
- Jessop, Z.M.; Al-Sabah, A.; Gao, N.; Kyle, S.; Thomas, B.; Badiei, N.; Hawkins, K.; Whitaker, I.S. Printability of Pulp Derived Crystal, Fibril and Blend Nanocellulose-Alginate Bioinks for Extrusion 3D Bioprinting. Biofabrication, 2019, 11. [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wang, X. Synthetic Polymers for Organ 3D Printing. Polymers (Basel), 2020, 12., 1765. [CrossRef]
- Khoeini, R.; Nosrati, H.; Akbarzadeh, A.; Eftekhari, A.; Kavetskyy, T.; Khalilov, R.; Ahmadian, E.; Nasibova, A.; Datta, P.; Roshangar, L.; et al. Natural and Synthetic Bioinks for 3D Bioprinting. Adv Nanobiomed Res, 2021 1, 2000097. [CrossRef]
- Tai, C.; Bouissil, S.; Gantumur, E.; Carranza, M.S.; Yoshii, A.; Sakai, S.; Pierre, G.; Michaud, P.; Delattre, C. Use of Anionic Polysaccharides in the Development of 3D Bioprinting Technology. Appl Sci(Switzerland), 2019, 9, 2596. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Peng, J.; Xiao, H.; Xu, X.; Qian, Z. Polysaccharide Hydrogels: Functionalization, Construction and Served as Scaffold for Tissue Engineering. Carbohydr Polym, 2022, 278, 118952. [CrossRef]
- Shahidi, F.; Arachchi, J.K.V.; Jeon, Y.J. Food Applications of Chitin and Chitosans. Trends Food Sci Technol, 1999, 10, 37–51. [CrossRef]
- Ramirez Caballero, S.S.; Saiz, E.; Montembault, A.; Tadier, S.; Maire, E.; David, L.; Delair, T.; Grémillard, L. 3-D Printing of Chitosan-Calcium Phosphate Inks: Rheology, Interactions and Characterization. J Mater Sci Mater Med, 2019, 30, 6. [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.; Liu, Y. Chitosan-Based Biomaterials: From Discovery to Food Application. Polym Adv Technol, 2020, 31, 2408–2421. [CrossRef]
- Matica, M.A.; Aachmann, F.L.; Tøndervik, A.; Sletta, H.; Ostafe, V. Chitosan as a Wound Dressing Starting Material: Antimicrobial Properties and Mode of Action. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20, 5889. [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Ding, X.; Li, D.; Shen, C.; Xu, F.J. Dual-Crosslinked Amorphous Polysaccharide Hydrogels Based on Chitosan/Alginate for Wound Healing Applications. Macromol Rapid Commun, 2018, 39, 1–5. [CrossRef]
- El-Araby, A.; Janati, W.; Ullah, R.; Ercisli, S.; Errachidi, F. Chitosan, Chitosan Derivatives, and Chitosan-Based Nanocomposites: Eco-Friendly Materials for Advanced Applications (a Review). Front Chem, 2023, 11, 1327426. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Cheng, F.; Islam, M.R.; Li, H. The Fabrication of the Chitosan-Based Bioink for in Vitro Tissue Repair and Regeneration: A Review. Int J Biol Macromol, 2024, 257, 128504. [CrossRef]
- Fatimi, A.; Okoro, O.V.; Podstawczyk, D.; Siminska-Stanny, J.; Shavandi, A. Natural Hydrogel-Based Bio-Inks for 3D Bioprinting in Tissue Engineering: A Review. Gels, 2022, 8, 179. [CrossRef]
- Fischetti, T.; Celikkin, N.; Contessi Negrini, N.; Farè, S.; Swieszkowski, W. Tripolyphosphate-Crosslinked Chitosan/Gelatin Biocomposite Ink for 3D Printing of Uniaxial Scaffolds. Front Bioeng Biotechnol, 2020, 8, 400. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Allardyce, B.J.; Rajkhowa, R.; Zhao, Y.; Dilley, R.J.; Redmond, S.L.; Wang, X.; Liu, X. 3D Printing of Silk Particle-Reinforced Chitosan Hydrogel Structures and Their Properties. ACS Biomater Sci Eng, 2018, 4, 3036–3046. [CrossRef]
- Hidaka, M.; Kojima, M.; Nakahata, M.; Sakai, S. Visible Light-Curable Chitosan Ink for Extrusion-Based and Vat Polymerization-Based 3d Bioprintings. Polymers (Basel), 2021, 13, 1382. [CrossRef]
- Hong, B.M.; Park, S.A.; Park, W.H. Effect of Photoinitiator on Chain Degradation of Hyaluronic Acid. Biomater Res, 2019, 23, 19–26. [CrossRef]
- Kurisawa, M.; Chung, J.E.; Yang, Y.Y.; Gao, S.J.; Uyama, H. Injectable Biodegradable Hydrogels Composed of Hyaluronic Acid-Tyramine Conjugates for Drug Delivery and Tissue Engineering. Chem Comm, 2005, 4312–4314. [CrossRef]
- Loebel, C.; Rodell, C.B.; Chen, M.H.; Burdick, J.A. Shear-Thinning and Self-Healing Hydrogels as Injectable Therapeutics and for 3D-Printing. Nat Protoc, 2017, 12, 1521–1541. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jing, X.; Zou, J.; Feng, P.; Wang, G.; Zeng, J.; Lin, L.; Liu, Y.; Mi, H.Y.; Nie, S. Mechanically Robust and Anti-Swelling Anisotropic Conductive Hydrogel with Fluorescence for Multifunctional Sensing. Adv Funct Mater, 2024. [CrossRef]
- Gogoi, D.; Kumar, M.; Singh, J. A Comprehensive Review on Hydrogel-Based Bio-Ink Development for Tissue Engineering Scaffolds Using 3D Printing. Ann 3D Print Med, 2024, 15,100159. [CrossRef]
- Saha, D.; Talukdar, D.; Pal, I.; Majumdar, S.; Lepcha, G.; Sadhu, S.; Yatirajula, S.K.; Das, G.; Dey, B. Mechanically Flexible Self-Healing Mg(II)-Metallogel: Approach of Triggering the ROS-Induced Apoptosis in Human Breast Cancer Cells. Langmuir, 2024, 40, 19816-19829. [CrossRef]
- Heinrich, M.A.; Liu, W.; Jimenez, A.; Yang, J.; Akpek, A.; Liu, X.; Pi, Q.; Mu, X.; Hu, N.; Schiffelers, R.M.; et al. 3D Bioprinting: From Benches to Translational Applications. Small, 2019, 15, 1–47. [CrossRef]
- Qin, D.; Zhang, A.; Wang, N.; Yao, Y.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y. Hydroxybutyl Chitosan/ Oxidized Glucomannan Self-Healing Hydrogels as BMSCs-Derived Exosomes Carriers for Advanced Stretchable Wounds. Appl Mater Today, 2022, 26, 101342. [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Xiong, G.; Hu, D.; Ren, K.; Yao, F.; Zhu, Y.; Gao, C.; Wan, Y. Characterization of TEMPO-Oxidized Bacterial Cellulose Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering Applications. Mater Chem Phys, 2013, 143, 373–379. [CrossRef]
- Heo, D.N.; Alioglu, M.A.; Wu, Y.; Ozbolat, V.; Ayan, B.; Dey, M.; Kang, Y.; Ozbolat, I.T. 3D Bioprinting of Carbohydrazide-Modified Gelatin into Microparticle-Suspended Oxidized Alginate for the Fabrication of Complex-Shaped Tissue Constructs. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2020, 12, 20295–20306. [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Hsu, S. hui. Hydrogels Based on Schiff Base Linkages for Biomedical Applications. Molecules, 2019, 24, 3005. [CrossRef]
- Korkiatithaweechai, S.; Umsarika, P.; Praphairaksit, N.; Muangsin, N. Controlled Release of Diclofenac from Matrix Polymer of Chitosan and Oxidized Konjac Glucomannan. Mar Drugs, 2011, 9, 1649–1663. [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; He, W.; Jin, X.; Song, X. Oxidized Konjac Glucomannan as a Paper Strength Agent. BioRes, 2015,10, 8089-8097. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xie, R.; Li, Q.; Dai, F.; Lan, G.; Shang, S.; Lu, F. A Self-Adapting Hydrogel Based on Chitosan/Oxidized Konjac Glucomannan/AgNPs for Repairing Irregular Wounds. Biomater Sci, 2020, 8, 1910–1922. [CrossRef]
- Sakai, S.; Yamada, Y.; Zenke, T.; Kawakami, K. Novel Chitosan Derivative Soluble at Neutral PH and In-Situ Gellable via Peroxidase-Catalyzed Enzymatic Reaction. J Mater Chem, 2009, 19, 230–235. [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.J.; Chu, Y.Z.; Chen, C.K.; Liao, Y.S.; Yeh, M.Y. Preparation of Conductive Self-Healing Hydrogelsviaan Interpenetrating Polymer Network Method. RSC Adv, 2021, 11, 6620–6627. [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Yoon, J.; Ahn, K.H.; Choi, S.H.; Char, K. Injectable Hydrogels with Improved Mechanical Property Based on Electrostatic Associations. Colloid Polym Sci, 2021, 299, 575–584. [CrossRef]
- Sakai, S.; Ohi, H.; Hotta, T.; Kamei, H.; Taya, M. Differentiation Potential of Human Adipose Stem Cells Bioprinted with Hyaluronic Acid/Gelatin-Based Bioink through Microextrusion and Visible Light-Initiated Crosslinking. Biopolymers, 2018, 109. [CrossRef]
- Wahid, M.H.; Eroglu, E.; LaVars, S.M.; Newton, K.; Gibson, C.T.; Stroeher, U.H.; Chen, X.; Boulos, R.A.; Raston, C.L.; Harmer, S.L. Microencapsulation of Bacterial Strains in Graphene Oxide Nano-Sheets Using Vortex Fluidics. RSC Adv, 2015, 5, 37424–37430. [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, L.; Mao, C.; Song, Z.; Li, X.; Liu, C. Preparation and Characterization of Konjac Glucomannan and Gum Arabic Composite Gel. Int J Biol Macromol, 2021, 183, 2121–2130. [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Wang, K.; Liu, M.; He, Z. In Vitro Evaluations of Konjac Glucomannan and Xanthan Gum Mixture as the Sustained Release Material of Matrix Tablet. Carbohydr Polym, 2008, 73, 241–247. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Reddy, C.K.; Huang, K.; Chen, L.; Xu, B. Hydrocolloidal Properties of Flaxseed Gum/Konjac Glucomannan Compound Gel. Int J Biol Macromol, 2019, 133, 1156–1163. [CrossRef]
- Chua, M.; Chan, K.; Hocking, T.J.; Williams, P.A.; Perry, C.J.; Baldwin, T.C. Methodologies for the Extraction and Analysis of Konjac Glucomannan from Corms of Amorphophallus Konjac K. Koch. Carbohydr Polym, 2012, 87, 2202–2210. [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, M.; Willems, C.; Rodríguez-fernández, J.; Gallego- Ferrer, G.; Groth, T. Synthesis and Characterization of Oxidized Polysaccharides for in Situ Forming Hydrogels. Biomolecules, 2020, 10, 1–18. [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, J.; Li, K.; Xie, C.; Liu, J. Oxidized Konjac Glucomannan-Cassava Starch and Sucrose Esters as Novel Excipients for Sustained-Release Matrix Tablets. Int J Biol Macromol, 2020, 156, 1045–1052. [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Li, L.; Xing, J.; Cheng, C.; Hu, M.; Luo, Y.; Shi, S.; Liu, Y.; Cui, Z.; Yu, X. Cross-Linking Porcine Peritoneum by Oxidized Konjac Glucomannan: A Novel Method to Improve the Properties of Cardiovascular Substitute Material. Collagen and leather, 2023, 5, 5. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Liao, S.; Chu, Y.; Yuan, B.; Tao, X.; Hu, X.; Wang, Y. An Injectable Bioink with Rapid Prototyping in the Air and In-Situ Mild Polymerization for 3D Bioprinting. Biofabrication, 2021, 13. [CrossRef]
- Birman, T.; Seliktar, D. Injectability of Biosynthetic Hydrogels: Consideration for Minimally Invasive Surgical Procedures and 3D Bioprinting. Adv Funct Mater, 2021, 31, 29. [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Pei, M.; Wan, T.; Yang, H.; Gu, S.; Tao, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, W.; Xiao, P. Self-Healing Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogels Based on Dynamic Schiff Base Linkages as Biomaterials. Carbohydr Polym, 2020, 250, 116922. [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Bu, N.; Chen, J.; Chen, Y.; Sun, R.; Wu, C.; Pang, J. Construction of Konjac Glucomannan/Oxidized Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogels for Controlled Drug Release. Polymers (Basel), 2022, 14. [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Fei, F.; Li, X.; Nie, Z.; Zhou, D.; Liu, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Fei, Z.; Xu, T. A Facile, Versatile Hydrogel Bioink for 3D Bioprinting Benefits Long-Term Subaqueous Fidelity, Cell Viability and Proliferation. Regen Biomater, 2021, 8, rbab026. [CrossRef]
- Sakai, S.; Kamei, H.; Mori, T.; Hotta, T.; Ohi, H.; Nakahata, M.; Taya, M. Visible Light-Induced Hydrogelation of an Alginate Derivative and Application to Stereolithographic Bioprinting Using a Visible Light Projector and Acid Red. Biomacromolecules, 2018, 19, 672–679. [CrossRef]
- Gaohua, L.; Miao, X.; Dou, L. Crosstalk of Physiological PH and Chemical PKa under the Umbrella of Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Modeling of Drug Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, Excretion, and Toxicity. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol, 2021, 17, 1103–1124. [CrossRef]
- Szymańska, E.; Winnicka, K. Stability of Chitosan - A Challenge for Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Applications. Mar Drugs, 2015, 13, 1819–1846. [CrossRef]
- Filimonova, E.; Bergmann, T.; Zhao, S.; Dyatlov, V.A.; Malfait, W.J.; Wu, T. Effect of Polymer Concentration and Cross-Linking Density on the Microstructure and Properties of Polyimide Aerogels. J Solgel Sci Technol, 2024, 110, 747–759. [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, E.M. Hydrogel: Preparation, Characterization, and Applications: A Review. J Adv Res, 2015, 6, 105–121. [CrossRef]
- Rolannd, B; Agnese, M; Marco, C.; Swelling Behavior of Carboxymethylcellulose Hydrogels in Relation to Cross-Linking, pH, and Charge Density, Macromolucules, 2000, 33, 7454-7480. [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Matysiak, S. Effect of PH on Chitosan Hydrogel Polymer Network Structure. Chem Comm, 2017, 53, 7373–7376. [CrossRef]
- Hidaka, M.; Kojima, M.; Sakai, S. Characterization of Chitosan Hydrogels Obtained through Phenol and Tripolyphosphate Anionic Crosslinking, Polymers, 2024, 16, 1274. [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.R.; Covington, A.D.; Hancock, R.A. Structure-Activity Relationships in the Hydrophobic Interactions of Polyphenols with Cellulose and Collagen. Biopolymers, 2003, 70, 403–413. [CrossRef]
- Rumon, M.M.H.; Akib, A.A.; Sultana, F.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Niloy, M.S.; Shakil, M.S.; Roy, C.K. Self-Healing Hydrogels: Development, Biomedical Applications, and Challenges. Polymers (Basel), 2022, 14, 4539. [CrossRef]
- Schmid-Wendtner, M.H.; Korting, H.C. The PH of the Skin Surface and Its Impact on the Barrier Function. Skin Pharmacol Physiol, 2006, 19, 296–302. [CrossRef]
- Lambers, H.; Piessens, S.; Bloem, A.; Pronk, H.; Finkel, P. Natural Skin Surface PH Is on Average below 5, Which Is Beneficial for Its Resident Flora. Int J Cosmet Sci, 2006, 28, 359–370. [CrossRef]
- Mansur, H.S.; de S. Costa Jr., E.; Mansur, A.A.P.; Barbosa-Stancioli, E.F. Cytocompatibility Evaluation in Cell-Culture Systems of Chemically Crosslinked Chitosan/PVA Hydrogels. Mater Sci Eng C, 2009, 29, 1574–1583. [CrossRef]
- Dettin, M.; Zamuner, A.; Roso, M.; Iucci, G.; Samouillan, V.; Danesin, R.; Modesti, M.; Conconi, M.T. Facile and Selective Covalent Grafting of an RGD-Peptide to Electrospun Scaffolds Improves HUVEC Adhesion. J Pept Sci, 2015, 21, 786–795. [CrossRef]
- Sivaraman, K.; Muthukumar, K.; Shanthi, C. Adhesion and Proliferation Properties of Type I Collagen-Derived Peptide for Possible Use in Skin Tissue Engineering Application. Cell Biol Int, 2022, 46, 391–402. [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.; Khademhosseini, A.; Dehghani, F. Enhancing Cell Penetration and Proliferation in Chitosan Hydrogels for Tissue Engineering Applications. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 9719–9729. [CrossRef]
- Ke, C.L.; Deng, F.S.; Chuang, C.Y.; Lin, C.H. Antimicrobial Actions and Applications of Chitosan. Polymers (Basel), 2021, 13, 904. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Xiao, S.; Li, W.; Wang, W.; Chen, H.; Yang, F.; Qin, C. Chitosan-Acorn Starch-Eugenol Edible Film: Physico-Chemical, Barrier, Antimicrobial, Antioxidant and Structural Properties. Int J Biol Macromol, 2019, 135, 344–352. [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.P.; Kumari, P.; Reddy, C.R.K. Antimicrobial Compounds from Seaweeds-Associated Bacteria and Fungi. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol, 2015, 99, 1571–1586. [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, R.R.; Ullah, M.W.; Pei, E.; Yang, G. Antimicrobial Inks: The Anti-Infective Applications of Bioprinted Bacterial Polysaccharides. Trends Biotechnol, 2019, 37, 1155–1159. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, M.; Bhandari, B.; Wang, Y. 3D Printing: Printing Precision and Application in Food Sector. Trends Food Sci Technol, 2017, 69, 83–94. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





