1. Introduction
River basin is the basic geomorphic unit of surface runoff and sediment production, and river is an important channel for transporting water and sediment. The large rivers on the earth that eventually flow into the sea are the key links to provide water and sediment fluxes on land and sea. Therefore, the amount of water and sediment transported by the river and its changes will not only affect the environmental changes in the estuary area, but also reflect the changes in the conditions of water and sediment production in the basin. Generally, when the sedimentation in the lower reaches of a river basin or in the estuary area increases, the denudation in the sediment yield area of the basin also increases, and vice versa.
At least a century ago, most of the rivers in the world were basically in the stage of natural evolution. The water and sediment processes of these rivers were mainly affected by climate factors such as precipitation and evaporation. The water and sediment transported by the rivers mainly fluctuated with the fluctuation of climate, and their change trend was not obvious in decades time scale. In recent decades, the evolution of these rivers has superimposed more and more intense impacts of human activities, and the water and sediment changes of many rivers especially in arid and semi-arid regions of the world are mainly controlled by human activities (e.g., Li et al., 2007; Miao et al., 2010, 2011; Wang et al., 2012a, 2012b; Petts and Gurnell., 2013; Wang et al., 2015; Wang et al., 2016). Therefore, the river water and sediment tend to decrease in the last decades, while the global flux of fluvial sediment to the oceans has reduced significantly compared with the previous period (Walling, 2006, 2009). It is estimated that under the effect of human activities superimposed on climate change, the global land-sea fluvial sediment flux has decreased from about 19 billion tons per year (Milliman & Farnsworth, 2011) to about 1.3 billion tons per year, with a decrease of 30% (Liu et al., 2015, 2021).
Although fluvial sediment is mainly composed of suspended and bed loads, the suspended load transported by many rivers accounts for about 90% of the total sediment loads and occupies an absolute dominant position (e.g., Walling and Fang, 2003; Francke et al., 2008; Heng and Suetsugi, 2014; Shi et al., 2018). Therefore, the impact of human activities on river sediment is mainly reflected in the impact on its suspended sediment load. The Yellow River, once known for its extremely high sediment concentration and the largest carrier of fluvial sediment in the world, has experienced a dramatic reduction in its runoff and sediment transport in recent decades. (Yang et al., 1998; Wang et al., 2006a, 2006b; Liu et al., 2009; Zhang et al., 2009; Miao et al., 2010; Wang et al., 2012b; Yu et al., 2013; Wang et al., 2016; Wang et al., 2020). For instance, the annual suspended sediment transported by the Yellow River to the Bohai Sea decreased from 1.25 billion tons per year during the time period 1952–1968 to 132 million tons per year during the period 1997–2018 (Liu et al., 2021), with a decrease of up to 98.9%. Many research results show that this is mainly affected by the implementation of long-term comprehensive water and soil conservation and ecological protection measures in the Yellow River basin, of which vegetation restoration and water conservancy project construction play a pivotal role (e.g., Wang et al., 2012b; Wang et al., 2016; Liu et al., 2021).
Despite there have been many studies on the interannual and decadal changes of runoff and sediment in the Yellow River basin, there are still insufficient studies on the seasonal changes of water and sediment and the adjustment of water and sediment relationship. The purpose of this study is to: 1) Compare the annual and monthly variation trends and differences of runoff and suspended sediment transport in the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River; 2) Analyze the characteristics of monthly average sediment inflow coefficient, the change of relationship between monthly mean discharge and sediment concentration in different decades; and 3) Reveal the influence mechanism of environmental protection and dam construction in the Yellow River basin on the change of water and sediment volume and water and sediment relationship of the Yellow River. This work will help to further understand the change mechanism of water and sediment in the Yellow River, and provides reference for the effective protection of ecological environment in river basins including the Yellow River basin.
2. Study area and dataset
2.1. Study area
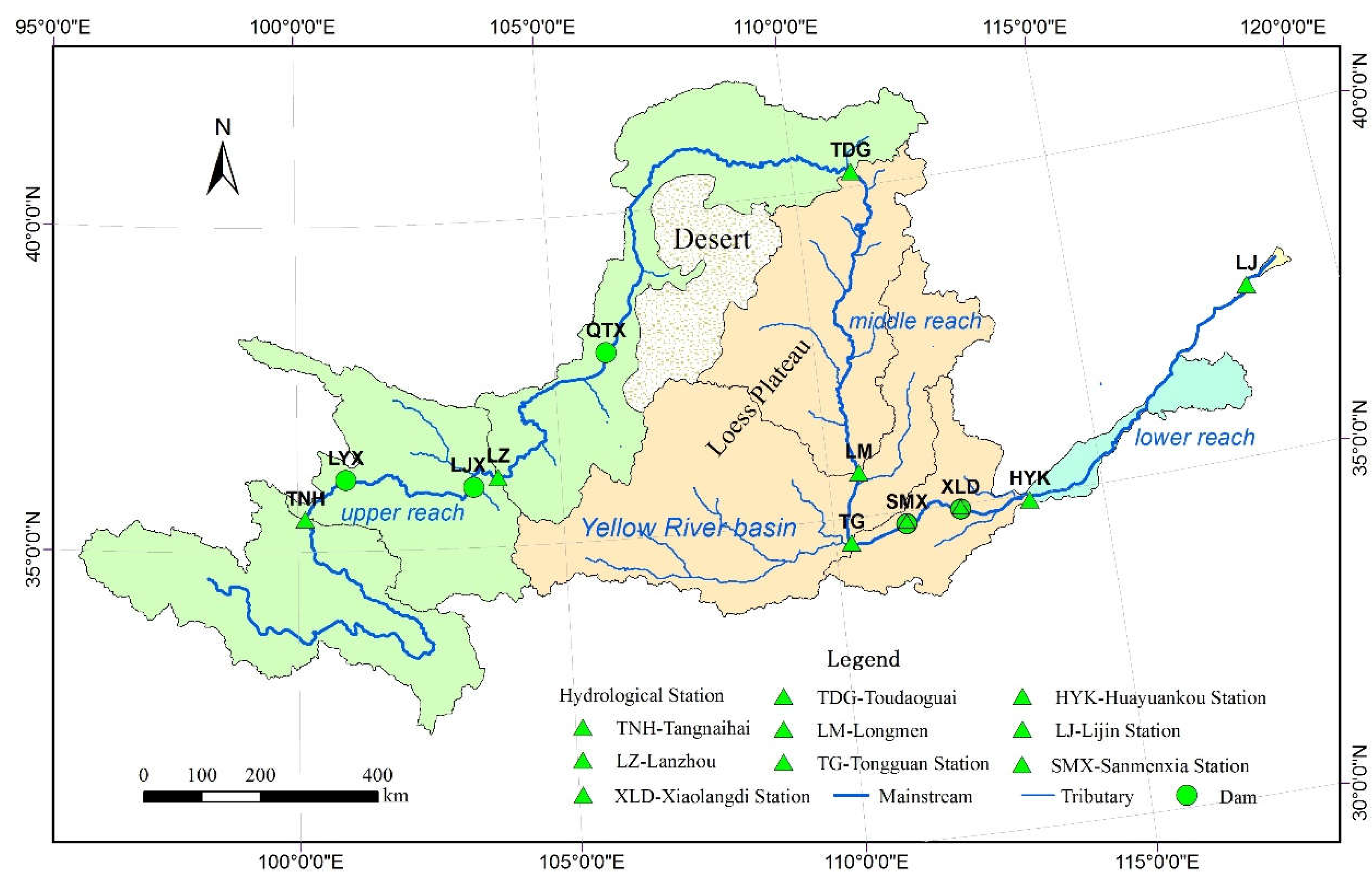
The Yellow River, which originates from the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau,traverses the Loess Plateau and the North China Plain, finally flows into the Bohai Sea (
Figure 1), has a total length of 5464 km and a total drainage area of 0.75 million km
2 (Wang et al., 2012a; Xia et al., 2016). The river basin is commonly divided into the upper (above Toudaoguai), middle (from Toudaoguai to Xiaolangdi), and lower (below Xiaolangdi) reaches with a channel length of 3472, 1206, and 786 km and a drainage area of 0.39, 0.34, and 0.02 million km
2, respectively (Qian et al., 1992; Wang et al., 2006a). The annual mean runoff produced in the three reaches is accounting for 54%, 36%, and 10% of the total runoff of the Yellow River basin, while the annual mean suspended sediment yield from the river reaches is accounting for 10%, 88%, and 2% of the total annual mean suspended sediment load.
The river catchment above Tangnaihai (TNH) hydrological station, commonly known as the source of the Yellow River (
Figure 1), is located on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, with a watershed area of 0.122 million km
2, annual mean runoff of 200.02 billion m
3, and annual mean SSL of 11.87 million tuns, which account for 16.3 %, 50.8%, and 1.1% of the total area, mean runoff and SSL of the entire river basin, respectively. The river reach from Tangnaihai to Xiaolangdi (XLD) hydrological stations is located on the Loess Plateau, with a watershed area of 0.57 million km
2, annual mean runoff of 302.21 billion m
3 and SSL of 960 million tuns, accounting for 70.0%, 39.2% and 88.9% of that for the total river basin, respectively.
Most areas of the Yellow River basin are located in arid and semi-arid climate regions with a mean annual temperature of 8–14 °C (Chen et al., 2005) and a mean annual precipitation of 478 mm (Wang et al., 2006a). Although the mean annual precipitation for the upper, middle, and lower reaches is 368, 530, and 670 mm, respectively (Wang et al., 2006b), the most runoff of the Yellow River originates from the upper reach, while the suspended sediment mainly yields from the middle reach (Xia et al., 2016). The Yellow River basin contains 12.6 million hectare of farmland and more than 40% of the farmland is irrigated using the water from the Yellow River (Xia et al., 2002).
2.2. Dataset and method
At the outlets of the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River, control hydrological gauging stations of Xiaolangdi and Lijin have been set up respectively, with a controlled drainage area of 0.6904 and 0.738 million km2, respectively. In addition to the two hydrological stations mentioned above, this study also involves the Tongguan and Sanmenxia gauging Stations in the middle reach and the Huayuankou gauging station in the lower reach of the Yellow River, which controlled a watershed area of 0.682, 0.688, and 0.730 million km2, respectively.
This paper uses the annual runoff and suspended sediment load (SSL) of the Tongguan, Sanmenxia, and Lijin hydrological stations gauged from 1950 to 2021 to investigate their interannual and interdecadal variation trends and analyze the differences among the stations (
Figure 2 and
Figure 3). Based on the daily observation data of Sanmenxia, Xiaolangdi, Huayuankou, and Lijin hydrological stations during 1960-2019, the focus of this article is to analyze the monthly variation of relevant hydrological parameters and their mean monthly variation in terms of decadal average. The monthly mean values of runoff, SSL, coefficient of sediment inflow, discharge, and suspended sediment concentration (SSC) for the four stations were calculated from the basic data. Based on the above calculation results, the decadal mean values of the corresponding parameters in each month for the hydrological gauging stations were also calculated. All of the daily original data and annual data were obtained from the Yellow River Water Conservancy Commission (1950-2021).
3. Results
3.1. Annual variations of runoff and SSL
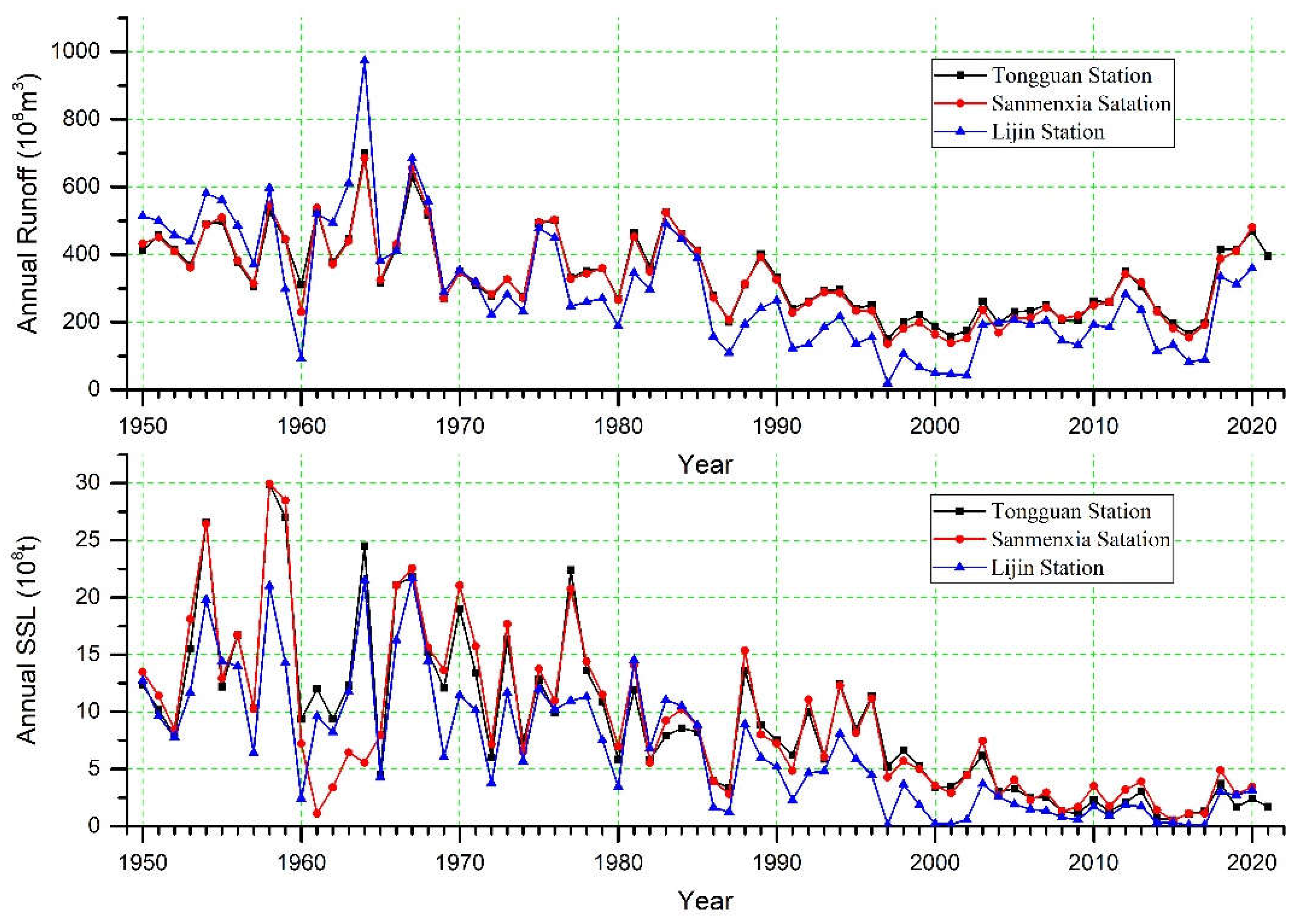
The annual runoff and SSL during the time period from 1950 to 2021 was examined at the Tongguan, Sanmenxia, and Lijin stations in the Yellow River (
Figure 2). The runoff fluctuated with a low amplitude and had no significant trend of change in the 1950s, while fluctuated greatly in the 1950s and its maximum value appeared in 1964. The runoff showed a trend of decreasing with minor fluctuations during 1964-1997 and an increasing trend in the time period 1997-2021. The annual SSL at the three stations presented an overall decreasing trend and their interannual fluctuations also decreased with time (
Figure 2). Compared with the three hydrological stations, the values and variation characteristics of the Tongguan and Sanmenxia Stations are very similar in terms of annual runoff and SSL.
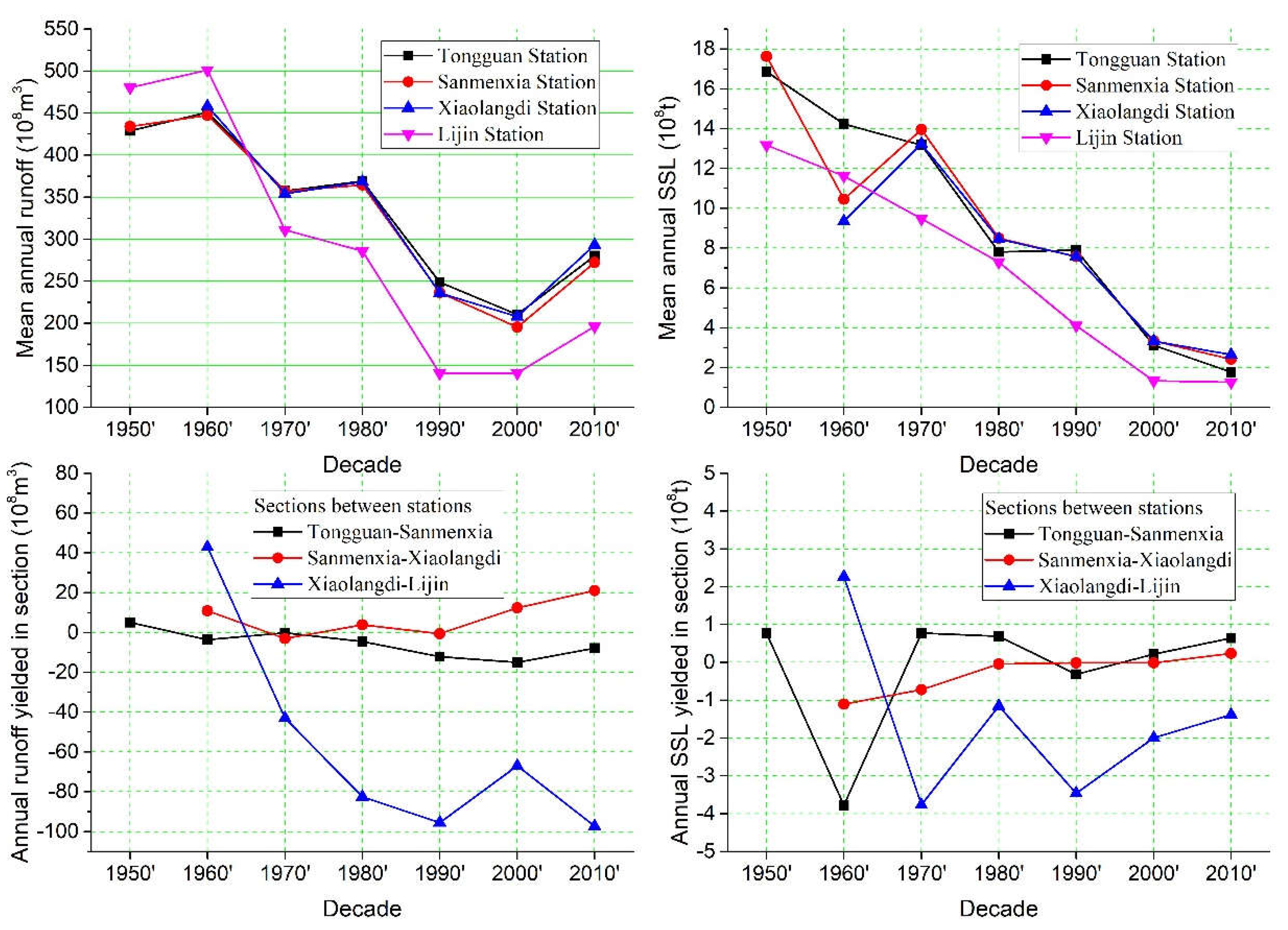
The mean annual runoff and SSL at four gauging stations (Tongguan, Sanmenxia, Xiaolangdi, and Ljin) as well as the net water and sediment yield in three sections (Tongguan-Sanmenxia, Sanmenxia-Xiaolangdi, and Xiaolangdi-Ljin) in different decades is showed in
Figure 3.
The variation trends in annual mean runoff of the four hydrological stations in different decades are generally similar, with Tongguan, Sanmenxia, and Xiaolangdi gauging stations having very similar trends. In comparison, the runoff difference between Lijin and other hydrological stations is relatively large, with the largest among all four hydrological stations in the 1950s and 1960s, and the smallest in subsequent decades (
Figure 3). For the 7 decades, the largest annual mean runoff occurred in the 1960′s, while the smallest occurred in the 2000′s (1990′s for the Lijin Station), with the latter accounting for only 46.7%, 43.7%, 45.4%, and 28,0% of the former.
The mean annual SSL of these four hydrological stations in the different decades has a monotonic decreasing trend with time changes (with the exception of Sanmenxia and Xiaolangdi in the 1960s) (
Figure 3). Except for Xiaolangdi, the minimum values of the other three hydrological stations appeared in the 2010′s and the maximum values in the 1950′s, with the former accounting for only 10.5%, 13.7%, and 9.6% of the latter. For all four hydrological stations, the sudden decrease in mean annual SSL mainly began in the 1970′s, with decreases of 86.5%, 82.7%, 80.0%, and 86.6% compared to that in the 2010′s.
Net yield in mean annual runoff for the section of Tongguan-Sanmenxia showed a slightly decreasing trend (from 0.5 billion m
3 yr
-1 in 1960′s to -15 billion m
3 yr
-1 in 2000′s, then it slightly increased to -7.9 billion m
3 yr
-1 in 2010′s) while net yield in mean annual suspended sediment in the section was only tens of millions of tons (46.3 million tons yr
-1 in average), except for -380 million tons yr
-1 in the 1970s (
Figure 3). The net yield in mean annual runoff for the section of Sanmenxia-Xiaolangdi fluctuated with small ranges in the 1960-1980s while increased slightly since the 1990′s. The net yield of mean annual SSL for the section showed a in creasing trend from -110 to 20 million tons yr
-1 in the decades from 1960′s to 2010′s. For the section of Xiaolangdi-Lijin, the net yield of mean annual runoff showed a decrease trend from 4.2 to -9.7 billion m
3 yr
-1 exception that in the 2000′s. The net yield of SSL for the section was 0.23 billion tons yr
-1 in the 1960′s, and then fluctuated in the range between -0.38 and -0.12 billion tons yr
-1.
3.2. Monthly variation of runoff and SSL
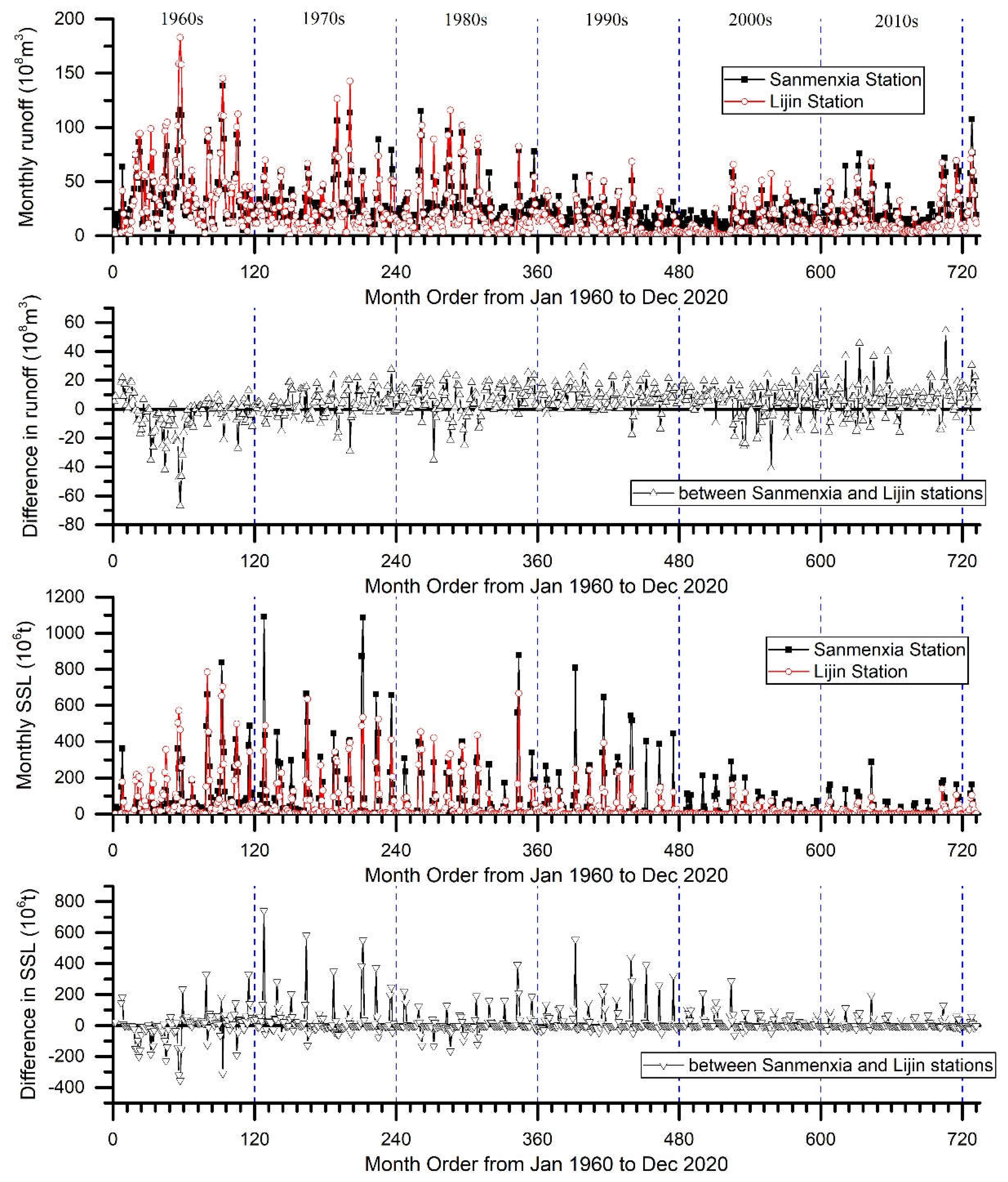
The variation of monthly runoff and SSL at the Sanmenxia and Lijin gauging stations and their net yield in the section between the stations of the Yellow River during the time period from Jan. of 1960 to Dec. of 2020 (the month order is from 1 to 732) are showed in
Figure 4. The maximum monthly runoff decreased in the decades from the 1960′s to the 1990′s and then increased in small ranges for the two stations. The minimum and maximum monthly net runoff yield in the section between Sanmenxia to Lijin was in the 1960′s and 2010′s, respectively. In comparison, the maximum monthly SSL per year increased in the 1960s, fluctuated significantly in the 1970s and 1980s, and decreased significantly since the 1990s. The monthly net suspended sediment yield in the section was generally the smallest and dominated by negative values (scouring) in the 1960s, and in the 1980s, positive and negative values alternated (scouring and silting). Since then, the maximum monthly net sediment yield in various decades has shown a downward trend.
3.3. Change of monthly runoff and SSL in decadal average
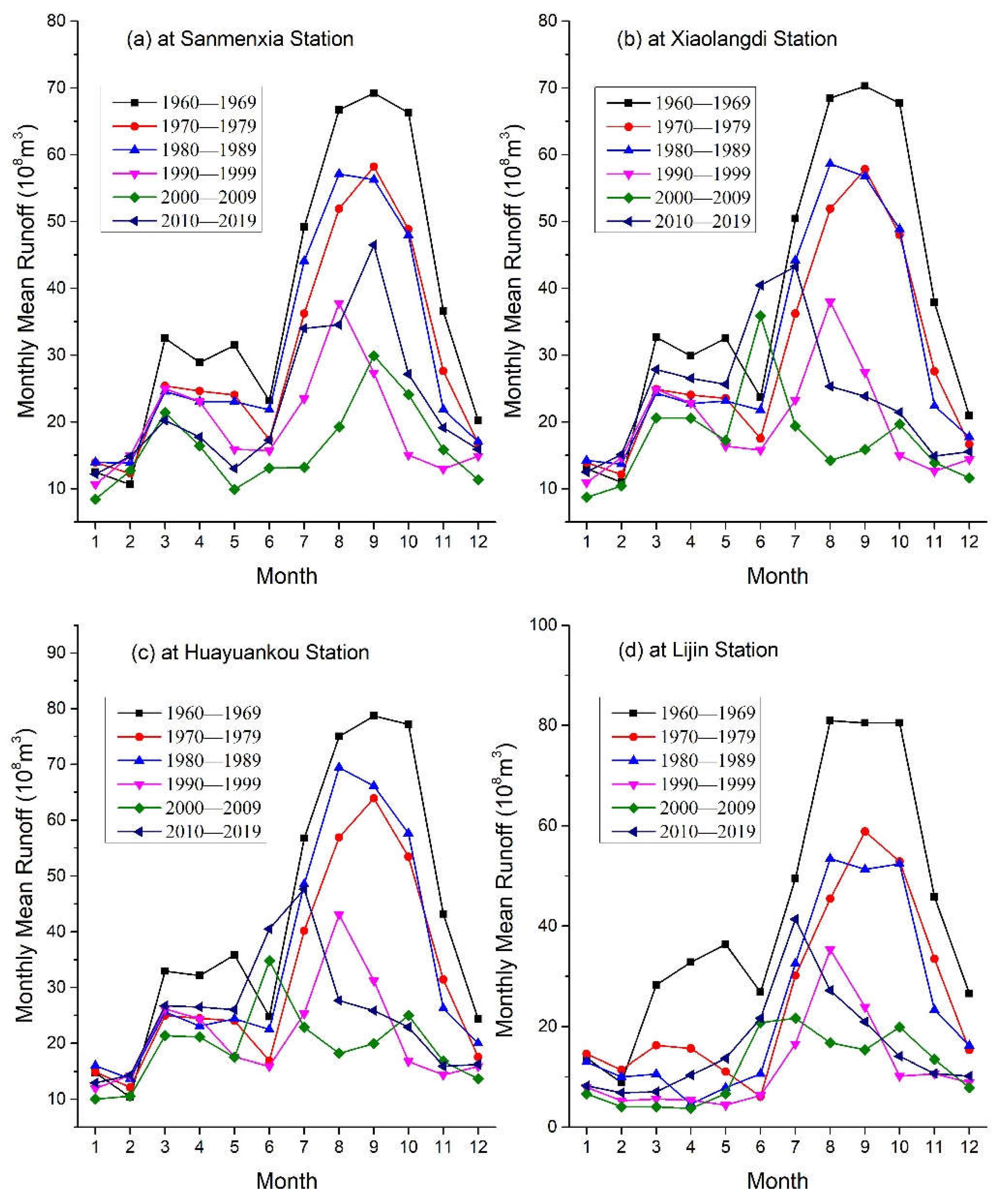
The changes of monthly runoff in decadal average at the Sanmenxia, Xiaolangdi, Huayuankou, and Lijin hydrological stations in the six decades from 1960 to 2019 are shown in
Figure 5. The monthly average runoff variation curve at Sanmenxia hydrological station (
Figure 5a) shows that in the decade before 1990, the three high values of the runoff occurred in the flood season (from July to October), while the three low values occurred in winter (January, February, and December). In the three decades from 1990, the mean monthly runoff in the flood season significantly decreased, and the monthly average runoff distribution curve in the flood season changed from a convex peak shape in previous decades to a peak shape, that is, the mean monthly runoff value in August or September was the maximum value in each decade, while the values in other months of the flood season significantly decreased compared to that of the previous decades. Especially in the 2000′s and 2010′s, the maximum mean monthly runoff during the flood season was less than half of that in each decade of the 20th century. The minimum and sub minimum of the mean monthly runoff occurred in January and May, that was 840 and 989 million m
3 in the 2000′s and 1.22 and 1.30 million m
3 in the 2010′s, respectively. The total runoff during the flood season is 8.64 billion m
3 and 14.22 billion m
3 respectively, accounting for only 34.4% and 56.6% of the total runoff during the flood season in the 1960s.
The distribution curve of the monthly runoff in decadal average at Xiaolangdi gauging station was very similar to that of Sanmenxia gauging station over the last four decades of the 20th century (
Figure 5b), while was a significant difference in the 2000′s and 2010′s, mainly manifested in the fact that the maximum or sub-maximum of the monthly runoff occurred in June (non-flood season). The total runoff during the flood season in the last two decades was 6.91 billion m
3 and 11.39 billion m
3, respectively, accounting for only 26.9% and 44.3% of that during the flood season in the 1960s.
The distribution curve of the monthly runoff in decadal average of Huayuankou gauging station (
Figure 5c) in the three decades before 1990 is also roughly similar to that at Sanmenxia and Xiaolangdi stations. In the 2000′s and 2010′s, the peak shape changed from a convex peak in the previous decades to a sharp peak, and the peak tip gradually shifted from the October to July, with the peak tip in the 2000′s even appearing in June which belong to the non-flood season. The total runoff in the flood season of the last two decades was 8.6 billion m
3 and 1.24 billion m
3, respectively, accounting for only 29.9% and 43.1% of that in the 1960′s.
The distribution curve of the monthly runoff in decadal average (
Figure 5c) at Lijin gauging station is roughly similar to the above three stations in the three decades before 1990. In the 2000′s, the peak shape in the flood season changed from a convex peak for the previous decades to a double peak, while in the 2010′s, it showed a sharp peak. The peak tip also gradually shifted from October to July, but they were all distributed in the flood season. The total runoff during the flood season in the last two decades was 7.36 billion m
3 and 10.36 billion m
3, respectively, accounting for only 25.3% and 35.5% of that for the 1960′s, that was the largest decline among the four gauging stations.
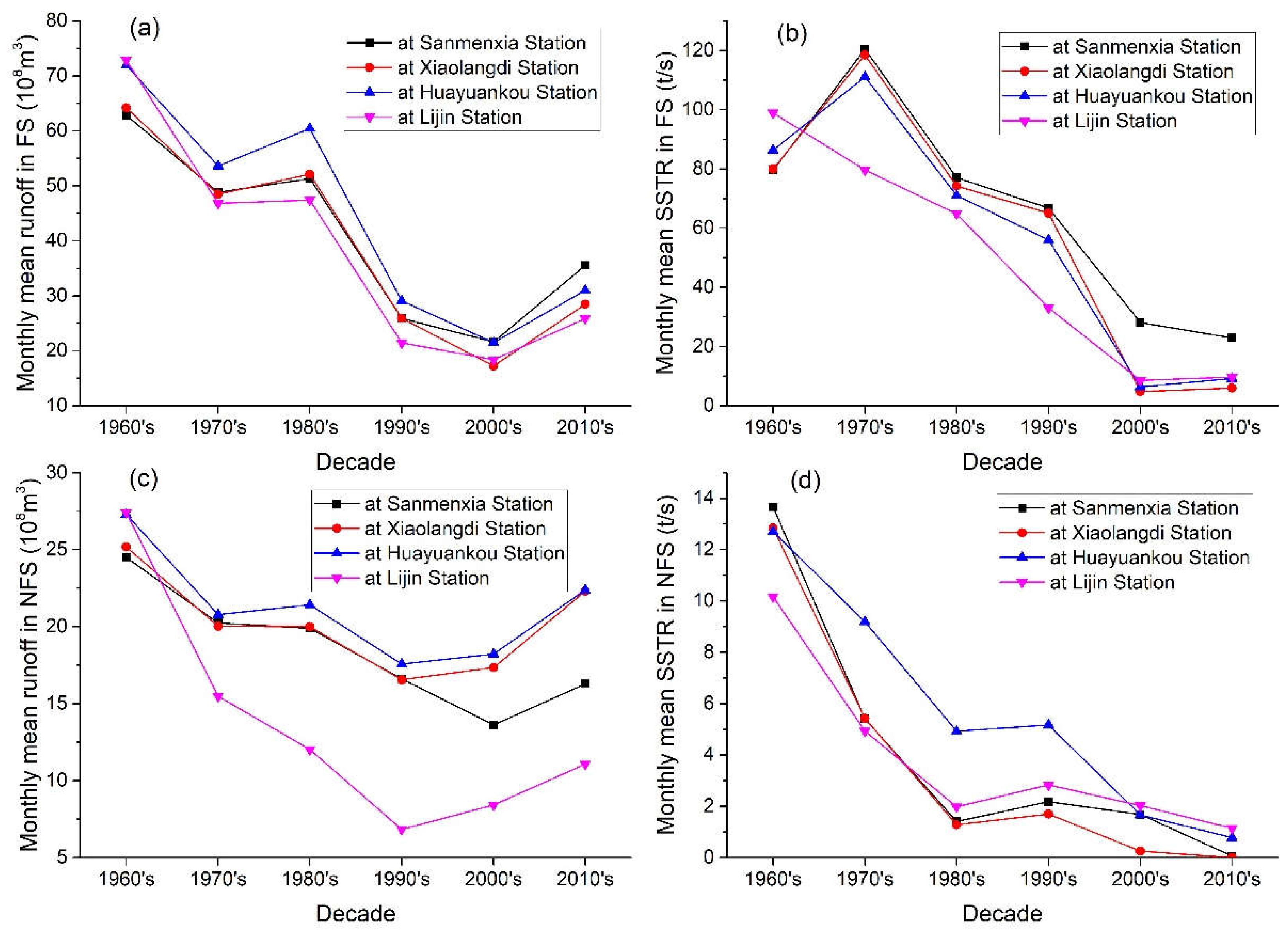
There are significant seasonal differences in water and sediment changes in the Yellow River basin (
Figure 6). During the flood seasons, the monthly mean runoff at the hydrological stations of the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River presented a synchronous significant decrease trend with the passage of time, and reached the minimum value in 2000′s, only increasing in the 1970′s and 2020′s compared to the previous period (
Figure 6a). The SSTR during the flood season has generally shown a significant decrease trend since the 1970′s. Except for the small decrease in 2010′s, the decrease in other time periods was significant (
Figure 6b). In comparison, the monthly mean runoff in non-flood seasons decreased generally in the last century, mainly increasing in this century (
Figure 6c), while the monthly mean SSTR in non-flood seasons showed a decreasing trend except in the 1990s, with a smaller extent compared to that of the flood seasons (
Figure 6d).
3.4. Change of monthly SSTR in decadal average
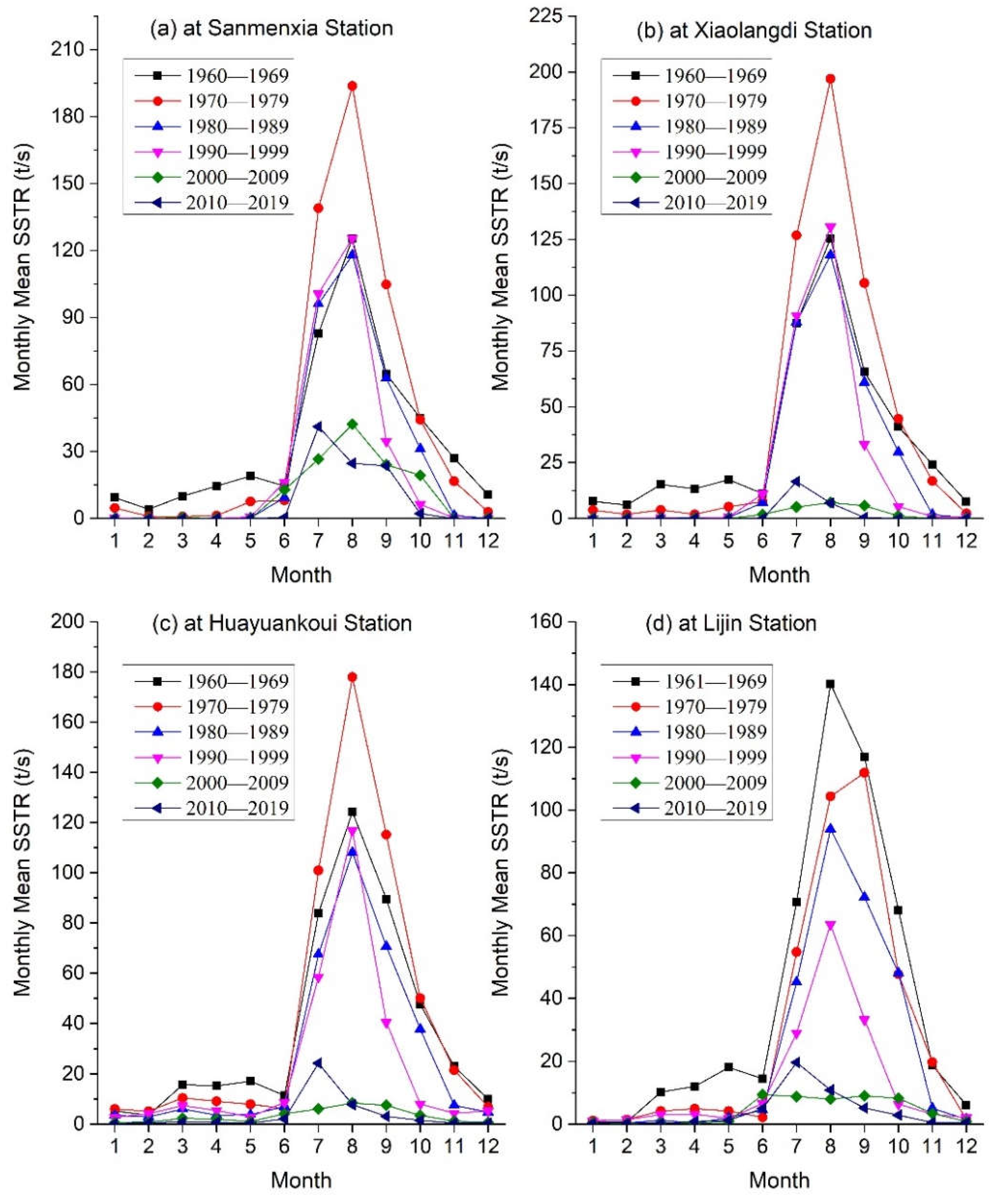
The change of the monthly suspended sediment transport rate (SSTR) in decadal average at the Sanmenxia, Xiaolangdi, Huayuankou, and Lijin hydrological stations during the six decades from 1960 to 2019 are shown in
Figure 7. The monthly variation curve of the SSTR at the Sanmenxia station (
Figure 7a) showed that in the four decades before 2000, the high values occurred in the three months from Jul. to Sep. (belong to the flood season), with the largest in the 1970′s and similar in the other three decades; The low values appeared in winter and early spring. In the 2000′s and 2010′s, the monthly mean SSTR during the flood season significantly decreased, and its distribution curve shape in the flood season changed from the previous high peak to a gentle peak. The mean SSTR during the flood season in the 2000′s and 2010′s only accounted for 35.3% and 28.8% of that in the 1960s.
For the Xiaolangdi hydrological station, the distribution curve of the monthly mean SSTR in the four decades of the 20th century (
Figure 7b) is almost the same as that of the Sanmenxia station during the same period, but in the 2000′s and 2010′s, it is quite different from that of the Sanmenxia station in the same period. The main differences are that the monthly mean SSTR during the flood season has significantly decreased, and there is no significant difference compared to other months. The mean SSTR during the flood season in these two decades only accounted for 6.0% and 7.5% of that during the same period in the 1960s.
The distribution curves of the monthly mean SSTR (
Figure 7c,d) at the Huayuankou and Lijin gauging stations are generally similar to those at Xiaolangdi station, with the difference that the monthly mean SSTR during the flood season gradually decreased over time, which was particularly evident at Lijin station. Therefore, the value for the two hydrological stations during the flood season in the 2000s were only 7.4% and 8.6% of those in the 1960s, while those in the 1990s were only 10.7% and 9.8%, respectively.
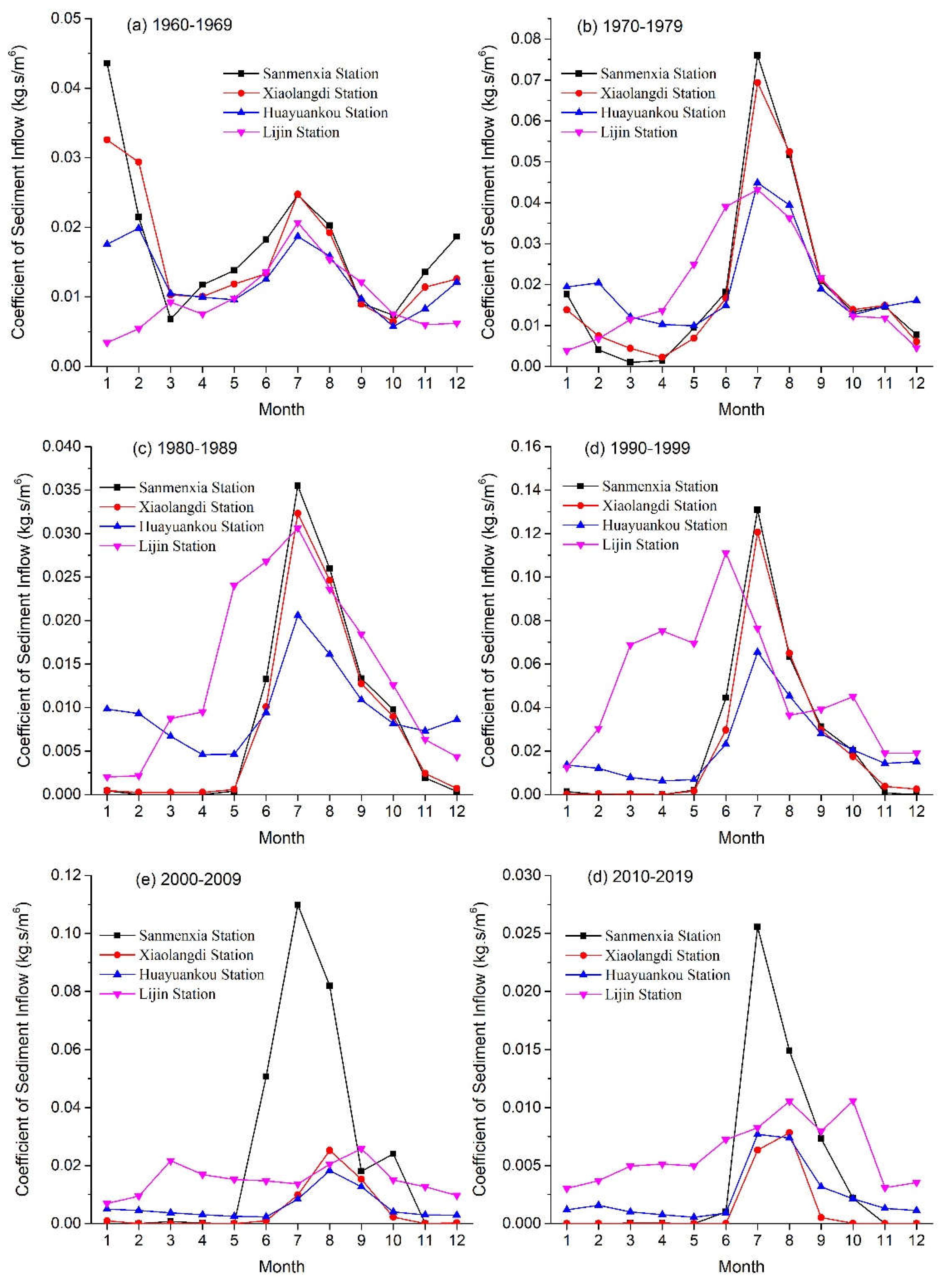
3.5. Change of monthly sediment inflow coefficient
The sediment inflow coefficient is defined as the ratio of sediment concentration to water discharge, and its unit is kg.s/m6. As pointed out by Wu and Shen (2008), it can indicate the sediment concentration per unit discharge or per unit flow power, implying the ratio of the sediment concentration that reflects the scouring and silting capacity of the river to the critical sediment concentration. The sediment inflow coefficient can be used as a judgment for river scouring and silting, and is also a key parameter in the formula in term of non-equilibrium transport of sediment. Therefore, analyzing the temporal and spatial changes of the sediment inflow coefficient is of great significance for understanding the changes in river flow and sediment, as well as the changes in riverbed erosion and deposition.
The variation trend of monthly sediment inflow coefficient in decadal average at the Sanmenxia, Xiaolangdi, Huayuankou, and Lijin hydrological stations in the six decades from 1960 to 2019 is shown in
Figure 8. Its monthly variation curve at the Sanmenxia station (
Figure 8a) shows that in the 1960s, the monthly fluctuation was relatively low, with high values occurring in winter with low flow and low sediment concentration and summer with high flow and high sediment concentration. Moreover, the curve crest in winter is significantly higher than that in autumn, which is mainly the result of a large amount of sediment interception during the flood season and sediment discharge during non-flood season of the Sanmenxia Reservoir.
Compared with that in the 1960′s, the sediment inflow coefficient at the station significantly increased in the summer and autumn in the 1970′s, while significantly decreased in the winter and spring, with a larger seasonal fluctuation range (
Figure 8b). This is mainly due to the fact that the sediment trap capacity of Sanmenxia Reservoir has almost disappeared and the storage capacity has also been greatly consumed by sediment deposition. In the 1980′s, the sediment inflow coefficient in each month was lower than that in the 1970′s, and in the non-flood season, it was also lower than that in the 1960′s (
Figure 8c). This was mainly due to the joint operation of the Liujiaxia Reservoir and the Longyangxia Reservoir located in the upper reach of the Yellow River to reduce the flood peak. The sediment inflow coefficient in the flood seasons of the 1990′s and 2000′s (
Figure 8d,e) was the highest and second highest among these decades. In the 2010′s (
Figure 8f), the sediment inflow coefficient at the Sanmenxia station was only slightly higher in July than in the same period of the 1960′s, while the other months were the smallest among all months in all decades. At the same time, their monthly variability was also the smallest.
The distribution curve of the monthly mean sediment inflow coefficient at the Xiaolangdi Station over the four decades of the 20th century (
Figure 8a–d) is basically the same as that of the Sanmenxia Station during the same period, but it is significantly different in the 2000′s and 2010′s, mainly manifested in the significant decrease in the sediment inflow coefficient during the flood season, especially in the 2000′s, where the decrease was very significant, while the inter monthly fluctuation range was very small (
Figure 8e, 78). In addition, the monthly mean sediment inflow coefficient of the Xiaolangdi Station in the 1990′s is similar to that of the 1960′s, except for January and February, where the curve shape is very similar.
The distribution curve of the sediment inflow coefficient at Huayuankou Station (
Figure 8) is generally similar to that at Xiaolangdi Station, with the difference that the sediment inflow coefficient during non-flood season has differentiated over time and generally shows a trend of decreasing.
For the Lijin Station, the distribution curve of the sediment inflow coefficient (
Figure 8) is significantly different from that of the above three hydrological stations, which is mainly manifested in the following aspects. First, the sediment inflow coefficient at the Lijin Station in each month of the 1990′s is the largest in all decades, and its monthly distribution curve presents a multi-peak pattern; Secondly, in the decade of 2010′s, there was a bimodal pattern of the main peak in September and the second peak in March, and at the same time, there was minimal volatility in each month in all the decades.
In summary, the sediment inflow coefficients of these hydrological stations during the flood season were the highest in the 1990′s and higher in the 1970′s. In the 2000′s after the completion of Xiaolangdi Dam, except for the Sanmenxia hydrological station, which was still very large, it sharply decreased at the Xiaolangdi, Huayuankou, and Lijin stations located downstream of Xiaolangdi Dam. This is the result of a large amount of sediment retention in the Xiaolangdi Reservoir.
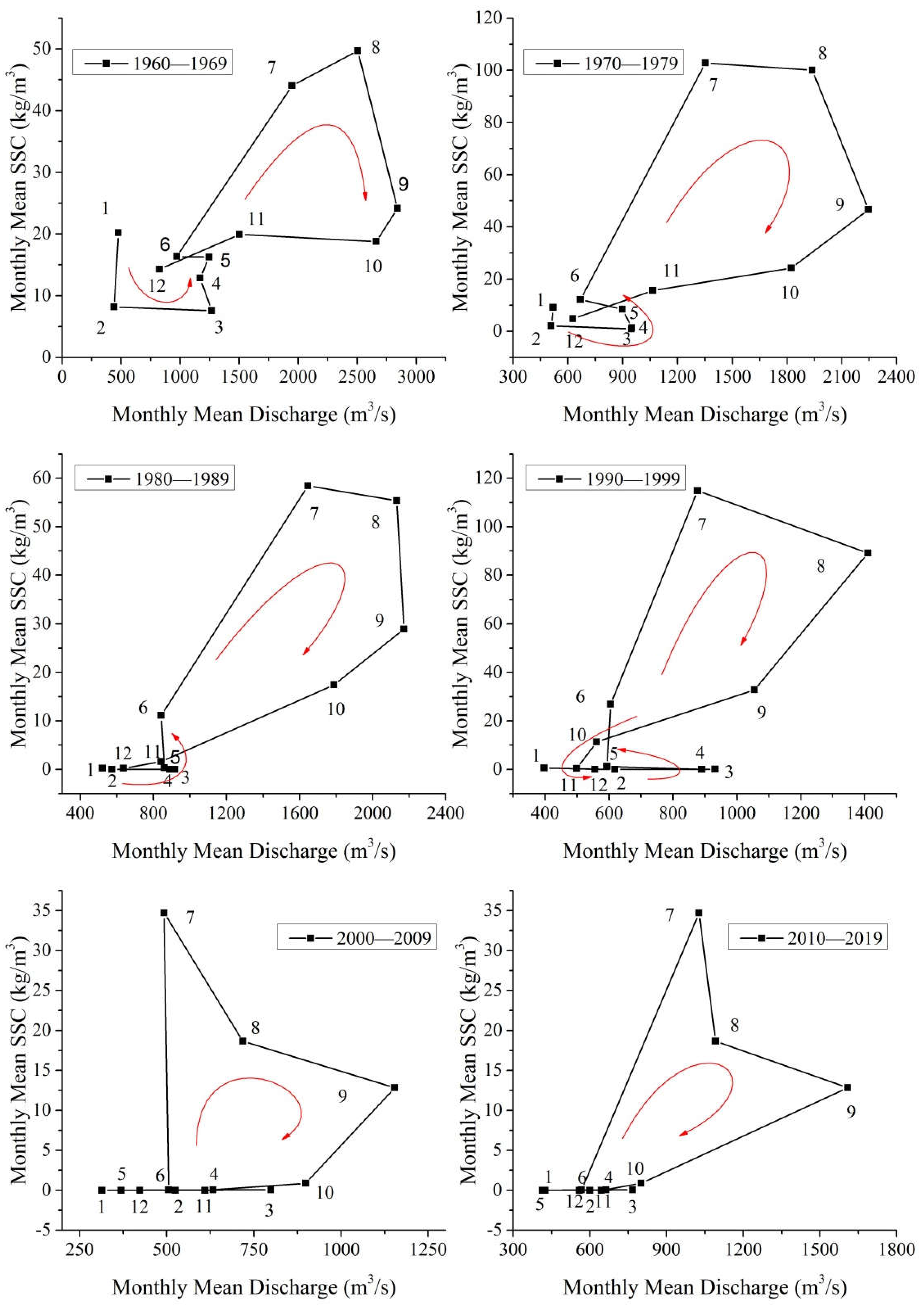
3.6. Monthly variation in hydrologic regime
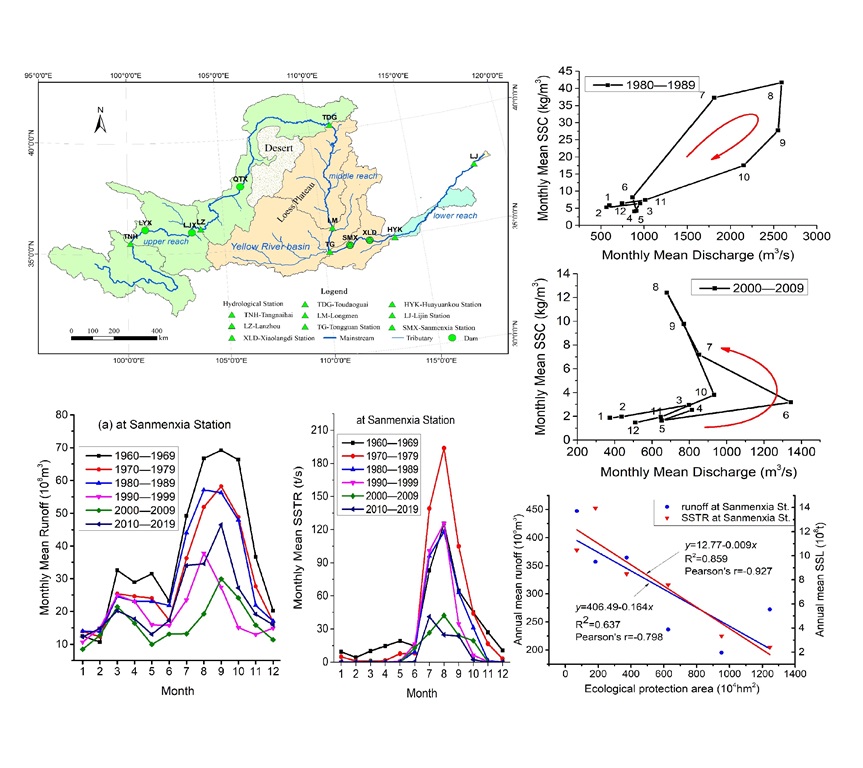
The monthly variation in hydrologic regime, in terms of relation between monthly mean discharge and sediment concentration, at the Sanmenxia Station shows that in the four decades of the twentieth century, there was an “8” shaped loop, which was composed of a counterclockwise loop for small flow stage and a clockwise loop for large flow stage (
Figure 9). In both decades of this century, there was a combination of clockwise loop and linear shape.
In the 1960′s, the counterclockwise loop of monthly variation in hydrologic regime at the Sanmenxia Station was significant at low flow stage (
Figure 9), indicating that the sediment concentration in the river flow relatively small at the beginning of the water level rise, and the sediment inflow was significantly lagging behind the inflow from the basin. At the end of the water level decline, it is significantly larger than the former, and also exhibits a sediment lag phenomenon. Therefore, the counterclockwise loop at low flow stage indicates that the sediment inflow coefficient at the beginning of rising water level is greater than that at the end of falling water level (
ξr<
ξf). In the following decades, this type of anticlockwise loop at small flow stage gradually became insignificant, and since 2000′s, it has disappeared, basically becoming a linear shape with a sediment concentration equal to zero at small flow stage.
The clockwise loop at the Sanmenxia Station played a leading role during the six decades when the flow was in high stage (
Figure 9). Its characteristic is that the sediment concentration (sediment inflow coefficient) during the rising process of the water level is greater than that at the same water discharge during the falling process of the water level, that is
ξr>
ξf. It is shown that the sediment supply from the basin surface plays a controlling role in the increasing process of water discharge and sediment concentration. During the decreasing process, the proportion of sediment concentration decrease relative to that of water discharge is greater, which is the joint result of the reduction of sediment from the basin surface and the deposition of some suspended sediment in the Sanmenxia Reservoir.
In addition, from the shape of the clockwise loop, it can be seen that in the four decades of the last century, there was a polygonal ring with convex curve connecting points, while in the two decades of this century, there was an irregular polygonal loop with a concave individual connecting point (such as the point in August), indicating that with the decrease of river flow or water discharge, the rate of relatively increasing sediment concentration in the water flow has a phased characteristic under the influence of reservoir operation measures.
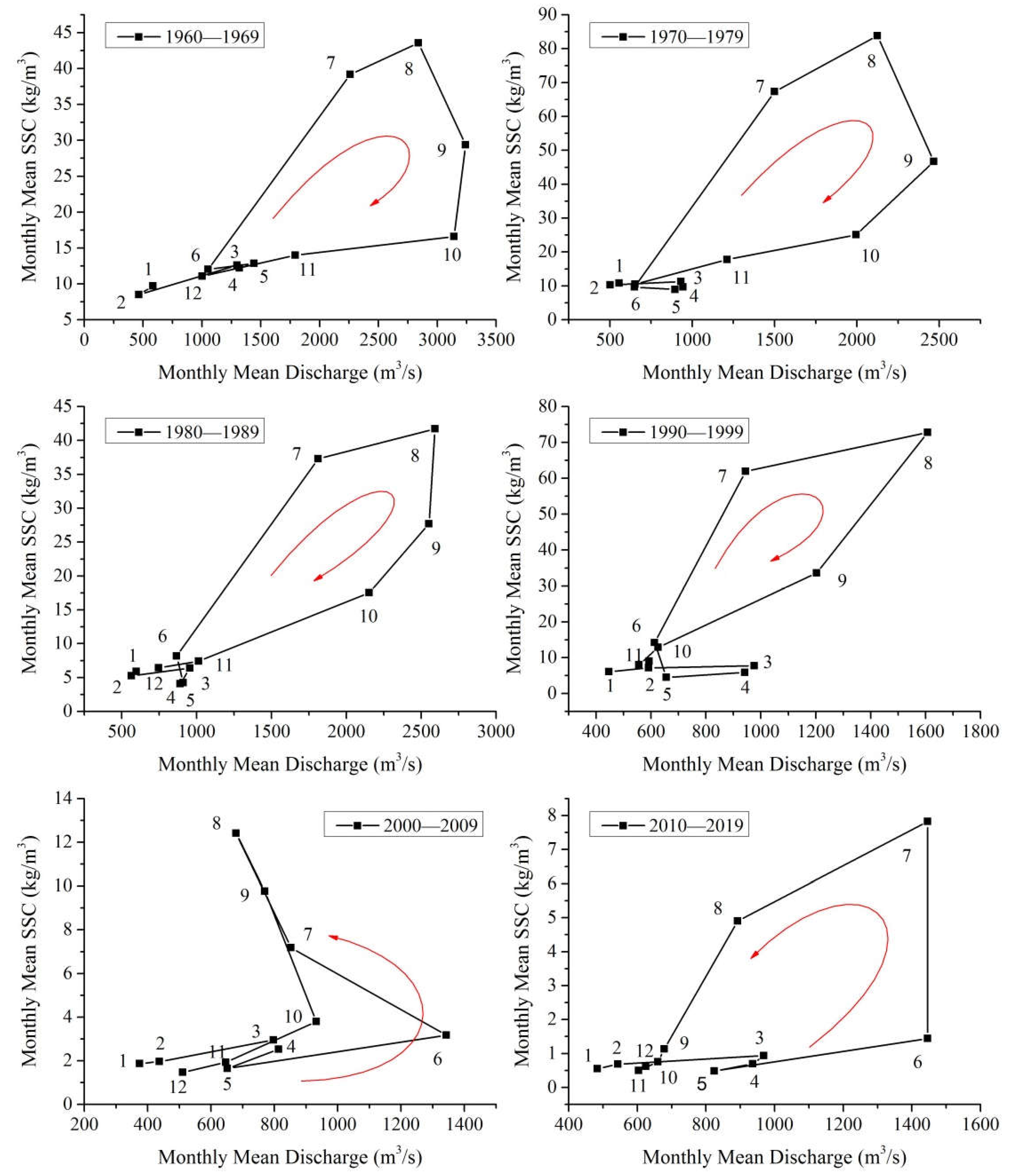
The monthly variation in hydrologic regime at the Huayuankou Station located at the beginning of the lower reach of the Yellow River in the different decades is shown in
Figure 10. The rating curve of the hydrologic regime at this station is significantly different from that of the upstream Sanmenxia and Xiaolangdi stations. In the four decades of the last century, the rating curve at the Huayuankou Station generally presented an obvious clockwise loop, which included almost all the variation intervals of monthly average flow, and only when the flow was extremely small, there was a negligible linear part (
Figure 10a–d). In addition, this type of convex polygon clockwise loop changed into a quadrangular loop in the 1990′s, indicating that the sediment concentration is decreasing in the months when the water discharge changes significantly, and is basically concentrated in the three months from July to September. The sediment inflow situation of the basin represented by these clockwise loops is similar to that of the Sanmenxia Station, except that the river channel where the Huayuankou section is located in an alluvial reach, and the significant decrease in sediment concentration during the water level reduction indicates that partial sedimentation of sediment has occurred in the river reach.
In the 2000′s, the rating curve of water discharge and sediment concentration at the station showed a combination of concave triangles and linear shapes, and the triangles belonged to a counterclockwise loop (
Figure 10e). This indicates that during the period from May to June, the monthly mean sediment concentration of the station increased at a low speed with the increase of the monthly mean water discharge. During the period from June to July, the water discharge was decreasing, while the sediment concentration was increasing at a low speed. For the period from July to August, the water discharge was decreasing while the sediment concentration was rapidly increasing. In the period from August to October, the water discharge increased slightly, while the sediment concentration decreased significantly. It can be seen that the monthly variation of the water sediment relationship presented more complex and diverse characteristics.
In the 2010′s, there was a counterclockwise loop characterized by a convex quadrilateral shape (
Figure 10f). The changes in the water sediment relationship mainly occurred in July and August, indicating that during the period from June to July, the monthly mean water discharge increased at a low speed, while the monthly mean sediment concentration increased at a high speed. During the two periods from July to August and August to September, the water discharge is decreasing, while the sediment concentration is decreasing at lower and higher rates, respectively. In other months, the monthly mean sediment concentration does not change significantly with the monthly mean discharge.
4. Discussion
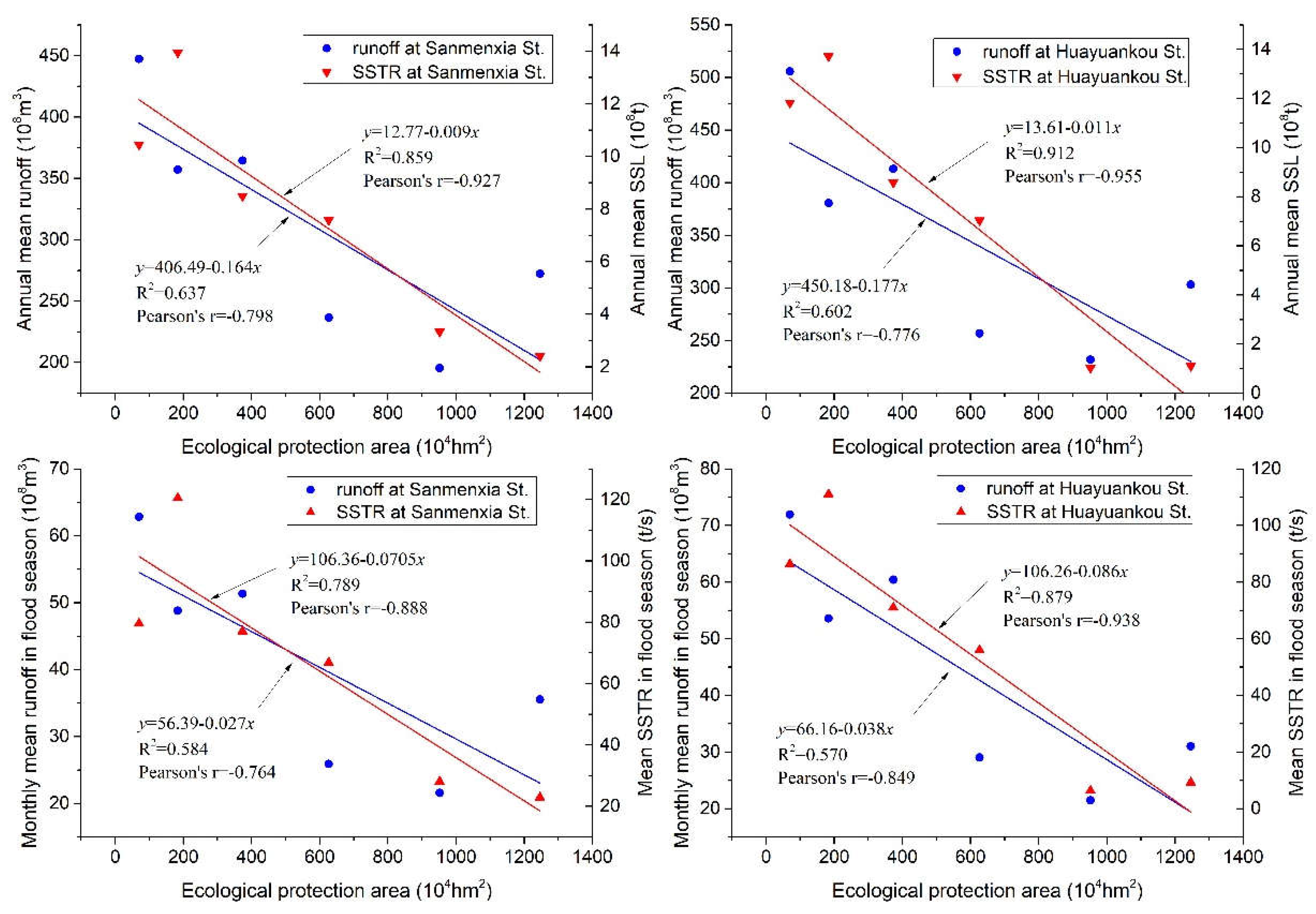
4.1. Ecological protection and its water conservation and sediment reduction
The annual and monthly variations of runoff and sediment discharge in the Yellow River basin have shown a significant decrease, which is mainly affected by various human activities in the basin, while the impact of climate change is relatively limited (e.g., Li et al., 2009; Wang et al., 2012b; Lu et al., 2013; Li et al., 2018; Gao et al., 2019; Liu et al., 2021; Chen et al., 2022). These human activities are mainly the continuous implementation of diversified and integrated ecological protection measures, as well as the constructions of large-scale water conservancy projects based on electricity production and water diversion that contribute to ecological improvement.
As shown above, the runoff of the Yellow River basin mainly comes from its source area (above Tangnaihai Station,
Figure 1), where the impact of human activities is relatively limited. Except for the interannual adjustment changes in runoff caused by the construction of the Longyangxia Reservoir, there is no obviously trend change in runoff. The vast majority about 97% of the suspended sediment transported by the Yellow River comes from the Loess Plateau (Hu & Zhang, 2020), which occupies all of the middle reach and most of the upper reach of the Yellow River basin and with loose surface material that is prone to erosion by precipitation and stream flow. Therefore, interpreting the progress of ecological protection measures in the Loess Plateau region is helpful to understand the mechanism of runoff and sediment discharge changes especially in the reach above Xiaolangdi Station.
As we all know, the Yellow River is the world’s largest sediment carrying river, and it is also a region with a very fragile ecological environment. Until the end of the last century, the water and soil loss in the middle reach is extremely serious, not only threatening the production and living activities of local people, but also causing severe siltation of the riverbed in the lower reach due to its large sediment production, which has brought great potential risks to the flood control of the vast areas on both sides of the lower reach. In order to alleviate water and sediment disasters, the Chinese government and relevant management departments have issued a number of ecological protection policies, and specialized departments have formulated various targeted ecological protection measures. Local people have actively participated in the implementation of relevant ecological protection measures.
The ecological protection work with soil and water conservation as the main purpose in the Loess Plateau has gone through the several typical stages (
e.g., Gao et al., 2019; Hu & Zhang, 2020). The different governance stages are outlined below: small regional experiment and demonstration stage in the 1950′s, comprehensive planning stage in the 1960′s, comprehensive treatment stage in the 1970′s, key governance stage in the 1980′s, strengthen engineering project promotion stage in the 1990′s and 2000′s, stage combining ecological naturally restoration and water and soil conservation engineering in the 2010′s. Accordingly, the total area of ecological protection such as terrace construction, grass planting, artificial forest land, closed managed land, and flat land formed by the construction of dams for sediment retention in the Loess Plateau continues to increase. The area of land that has been fully ecologically protected increased from 698000 hectares in the 1960′s to 1.838 million hectares in the 1970′s, 3.733 million hectares in the 1980′s, 6.263 million hectares in the 1990′s, 9.518 million hectares in the 2000′s, and over 12.459 million hectares in the 2010′s. The ecological protection work in soil and water loss areas on the Loess Plateau has a very good promoting effect on water conservation and sediment reduction in the basin, and the effect is obvious (
Figure 11). This has become a key factor in regulating runoff and significantly reducing suspended sediment in the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River basin, and has also become a good example of environmental protection in river basin management.
The Yellow River flows through the Loess Plateau with a total area of 640000 square kilometers, including 454000 square kilometers of soil erosion. By 2020, the Yellow River Basin has completed preliminary control of 244000 square kilometers of water and soil loss, which means that more than half of the water and soil loss area has been preliminarily controlled, resulted in mean annual intercepted suspended sediment of 435 million tons for the last six decades while of 800 million tons for the last two decades (Yellow River Conservancy Commission, 2020-2021).
4.2. Construction of dams and its impact on water and sediment processes
As mentioned above, the ecological protection in the Yellow River basin, especially the Loess Plateau, has played an extremely important role in water conservation and sediment reduction on the surface of the river basin. Construction of check dams, as an important engineering measure of ecological protection on the Loess Plateau, has been developed for decades. The check dams are one of the key factors for sediment reduction in the Yellow River. The gully areas in the Loess Plateau are the main sediment producing regions of the Yellow River. More than 90% of the sediment of the Yellow River comes from these regions. Since the 1950s, more than 59000 check dams have been constructed in these regions (Hu & Zhang, 2020). These engineering measures have intercepted a large amount of sediment transported by the tributaries of the Yellow River (Wang et al., 2012b; Liu et al., 2021). Generally, these check dams undergo continuous sediment deposition and will form a series of dam lands in about 20 years, which will become fertile and leveled land in the gully region of the Loess Plateau. In addition, these dam areas have sufficient water resources, which will become a good growth base for crops, forests, and other vegetation, making an indelible contribution to water storage, sediment reduction, and ecological protection in the tributaries of the Yellow River basin.
Most areas of the Yellow River basin are located in an arid to semi-arid climate region, with precipitation mainly occurring during the flood season from July to October, showing uneven annual and interannual distribution. Vegetation in non-flood seasons is difficult to thrive due to a lack of water resources. Therefore, the construction of large reservoirs in the main stream of the Yellow River has become a beneficial artificial water resource regulation measure for rational allocation of water resources, and can also provide clean energy (hydropower production). This not only strengthens regional ecological protection, but also reduces the consumption of non-renewable fossil energy. The large reservoirs built on the main stream of the Yellow River not only have the function of depositing sediment and accumulating water, but also significantly change the flow and sediment processes of the river.
The large reservoirs have bult on the main stream are downstream the Longyangxia, Liujiaxia, Sanmenxia, and Xiaolangdi which have constructed in 1986, 1968, 1961, and 2001, respectively. The Longyangxia and Liujiaxia reservoirs are located in the upper reach and have limited impact on the water and sediment processes in the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River. The construction and operation of the Sanmenxia and Xiaolangdi reservoirs, located in the end of middle reach of the Yellow River, have greatly reduced the runoff and SSL in the lower Yellow River (
Figure 2,
Figure 3,
Figure 4,
Figure 5 and
Figure 6). The annual or monthly runoff decline was mainly due to industrial and agricultural water use, while the SSL decrease in the mainstream was sediment deposition in the large reservoirs (Liu et al., 2021). This is consistent with other research works on the impact of reservoir construction on sediment budget of rivers in the world (
e.g., Williams & Wolman, 1984; Magilligan & Nislow, 2006; Zahar et al., 2008; Walling, 2012; Su et al., 2015; Smith et al., 2016; Wang et al., 2016; Li et al., 2018; Kong et al., 2020; Li, et al., 2020; Liu et al., 2021). Although the total storage capacity of Sanmenxia Reservoir is 16.2 billion m
3, the total siltation in the reservoir amounted to 7.7 Gt during the year 1960–1973 due to a large amount of incoming sediment (Wang et al., 2007). Therefore, the sediment holding capacity of the reservoir has been greatly reduced since the 1970s.
As the most downstream reservoir on the Yellow River, the Xiaolangdi Reservoir has a water area of 272 km
2, storage capacity of 12.65 billion m
3, sediment storage capacity of 7.55 billion m
3, water and sediment regulation storage capacity of 1.05 billion m
3, and long-term effective storage capacity of 5.1 billion m
3. Its construction and operation not only have changed the distribution of the monthly mean SSTR (
Figure 7) and sediment inflow coefficient (
Figure 8), but also have changed the monthly variation pattern of discharge and sediment concentration, that is, from a clockwise loop to a counterclockwise loop (
Figure 10). In the last two decades, with the implementation of measures to increase the discharge of clean water from the Xiaolangdi Reservoir before flood season in order to scour the riverbed of the lower Yellow River, annual SSL in the lower reaches of the Yellow River has increased slightly, which is also a result of changes in the reservoir operation mode. At the same time, in order to ensure sufficient ecological water demand in the lower main stream of the Yellow River, the water consumption in the middle and upper reaches of the Yellow River has also been moderately limited, resulting in an increase in the runoff in the lower reach of the Yellow River. In any case, the adjustment of water and sediment processes caused by the construction of large reservoirs is long-term and difficult to reverse.
5. Conclusions
Based on the daily measured water and sediment data from typical hydrological stations in the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River during the period from 1960 to 2019, the variation trends of annual and monthly runoff and SSL were analyzed, at the same time, the monthly runoff, SSTR, sediment inflow coefficient, and hydrological regime curves in decadal average at typical hydrological stations were revealed. The main conclusions are as follows:
1) The interannual or monthly variation of runoff and SSL in the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River has a significant decreasing trend in the four decades of the last century, which is mainly in response to the gradual implementation of ecological protection measures such as afforestation, grass planting, terrace construction, closure and conservation of wasteland, and check dam construction in the Yellow River basin, especially in the Loess Plateau region. In the last two decades, the runoff of the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River has increased, while the SSL has fluctuated and increased slightly. This is a response to the implementation of new river management measures such as ensuring the ecological water demand of the lower reaches and scouring the riverbed by manually regulated clear water discharged from the Xiaolangdi Reservoir.
2) During the flood season (from July to October) in the last four decades of the last century, the monthly mean runoff and SSTR, in decadal average also showed a significant trend of decreasing, especially in the 2000′s and 2010′s. The maximum value of the monthly mean sediment inflow coefficient in decadal average was in the 1990′s while the sub-maximum was in the 1970′s for the typical hydrological stations, but the minimum and sub-minimum was in the 2000′s and 2010′s, respectively, except for Sanmenxia Station. That vas a comprehensive response to the environmental protection measures in the Yellow River basin, in which the construction and operation of the Xiaolangdi Reservoir played a key role.
3) The construction and operation of the Xiaolangdi Reservoir has changed the downstream hydrological regime in terms of the process curve of the monthly mean discharge and sediment concentration, mainly manifested in the change of curve shape of the process curve from a clockwise loop before the construction of the reservoir to a counterclockwise loop after its construction. Because the Sanmenxia Reservoir lost its sediment retention capacity early due to a large amount of sediment deposition in a few short years after its completion, so its later operation will not change the water sediment relationship of downstream river.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.W.; Formal Analysis, S.W and X.W.; Draft Preparation, X.W.; Review & Editing, S.W.
Acknowledgments
The author thanks the Yellow River Water Conservancy Committee, for permission to access the hydrological gauging data. Financial support for this research is from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41971004) and National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2022YFC3203903).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Francke T, López-Tarazón JA, Schröder, B. 2008. Estimation of suspended sediment concentration and yield using linear models, random forests and quantile regression forests. Hydrological Processes, 22(25): 4892–4904. [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.L.,Gao, Y.,Ma, H.B.,Dang, T.M., 2019. Study on characteristics of soil and water loss control in Loess Plateau in recent 70 Years. Yellow River, 41(11): 65-69.
- Heng S, Suetsugi, T. 2014. Development of a regional model for catchment-scale suspended sediment yield estimation in ungauged rivers of the Lower Mekong Basin. Geoderma, 235–236: 334–346. [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.H., Zhang, X.M., 2020. Loess Plateau soil erosion governance and runoff-sediment variation of Yellow River. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering, 51(1): 1–11.
- Kong, D., Latrubesse, E.M., Miao, C., Zhou, R., 2020. Morphological response of the Lower Yellow River to the operation of Xiaolangdi Dam, China. Geomorphology 350, 106931. [CrossRef]
- Li, S., Li, Y., Yuan, J., Zhang, W., Chai, Y., Ren, J., 2018. The impacts of the Three Gorges Dam upon dynamic adjustment mode alterations in the Jingjiang reach of the Yangtze River, China. Geomorphology 318, 230–239. [CrossRef]
- Li, L., Xia, J., Zhou, M., Deng, S., 2020. Riverbed armoring and sediment exchange process in a sand–gravel bed reach after the Three Gorges Project operation. Acta Geophys. 68, 243–252.
- Li, C., Zheng X., Yang Z., Pang A., Shen N., 2009. Trends of annual natural runoff in the Yellow River basin. Journal of Beijing Normal University (Natural Science), 45(1): 80-85 (in Chinese).
- Li, L.J., Zhang, L., Wang, H., Wang, J., Yang, J.W., Jiang, D.J., Li, J.Y., Qin, D.Y., 2007. Assessing the impact of climate variability and human activities on streamflow from the Wuding River basin in China. Hydrological Processes, 21, 3485–3491. [CrossRef]
- Liu C, He Y, Li Z, Chen J, Li Z, 2021. Key drivers of changes in the sediment loads of Chinese rivers discharging to the oceans. International Journal of Sediment Research 36 (2021) 747–755. [CrossRef]
- Liu, C., He, Y., Chen, J.G., Shi, H.L., 2015. Review of estimation of global fluvial sediment discharge to oceans. Advances in Science and Technology of Water Resources, 35(5), 47–51. (In Chinese).
- Liu W, Wang S, Sang Y, Ran L, Ma Y. 2021. Effects of large upstream reservoir operations on cross-sectional changes in the channel of the lower Yellow River reach. Geomorphology, 387: 107768. [CrossRef]
- Li, T., Wang, S., Liu, Y.X., Fu, B.J., & Zhao, W.W., 2018. Driving forces and their contribution to the recent decrease in sediment flux to ocean of major rivers in China. The Science of the Total Environment, 634, 534–541. [CrossRef]
- Liu, W., Wang, S., Sang, Y., Ran, L, Ma, Y., 2021. Effects of large upstream reservoir operations on cross-sectional changes in the channel of the lower Yellow River reach. Geomorphology, 387: 107768. [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.X., Ran, L.S., Liu, S., Jiang, T., Zhang, S.R., & Wang, J.J. (2013). Sediment loads response to climate change: A preliminary study of eight large Chinese rivers. International Journal of Sediment Research, 28(1), 1–14. [CrossRef]
- Chen L, Hou B, Zhan T, Ge L, Qin Y, Zhong W, 2022. Water-sediment-energy joint operation model of large-scale reservoir group for sediment-laden rivers. Journal of Cleaner Production 370: 133271. [CrossRef]
- Magilligan, F.J. and Nislow, K.H., 2006. Changes in hydraulic regime by dams. Geomorphology, 71(1~2): 61–78.
- Miao, C.Y., Ni, J.R., Borthwick, A.G.L., 2010. Recent changes of water discharge and sediment load in the Yellow River basin, China. Progress in Physical Geography, 34 (4), 541–561. [CrossRef]
- Miao C., Ni J., Borthwick A.G.L., Yang L., 2011. A preliminary estimate of human and natural contributions to the changes in water discharge and sediment load in the Yellow River. Global and Planetary Change, 76, 196–205.
- Milliman, J.D., & Farnsworth, K.L., 2011. River discharge to the coastal ocean: A global synthesis. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Petts, G., Gurnell., A., 2013. Hydrogeomorphic effects of reservoirs, dams and diversions. In: Shroder, J. (Editor in chief), James, L.A., Harden, C.P., Clague, J.J. (Eds.), Treatise on Geomorphology. Academic Press, San Diego, CA, vol. 13, Geomorphology of Human Disturbances, Climate Change, and Natural Hazards, pp. 96–114.
- Qian, Y., Ye, Q., Zhou, W., 1992. Water and Sediment Variation and River Bed Change in the Trunk Channel of the Yellow River. China Architecture Material Industry Press, Beijing (in Chinese).
- Shi X N, Zhang F, Lu X X, Wang Z Y, Gong T L, Wang G X, Zhang H B. 2018. Spatiotemporal variations of suspended sediment transport in the upstream and midstream of the Yarlung Tsangpo River (the upper Brahmaputra), China. Earth Surf. Process. Landforms, 43, 432–443 (2018).
- Smith, N.D., Morozova, G.S., Pérez-Arlucea, M., Gibling, M.R., 2016. Dam-induced and natural channel changes in the Saskatchewan River below the E.B. Campbell Dam, Canada. Geomorphology 269, 186–202. [CrossRef]
- Su, T., Wang, S., Mei, Y., 2015. Impact of joint operation of reservoirs on the change ratio of downstream cross-sectional geometry parameters: a case study of the Inner Mongolian reach of the Yellow River. Acta Geograph. Sin. 70, 918–925.
- Walling D E, Fang D., 2003. Recent trends in the suspended sediment loads of the world’s rivers. Global Planetaty Changes, 39(1–2): 111–126.
- Walling, D.E., 2006. Human impact on land-ocean sediment transfer by the world’s rivers. Geomorphology, 79(3–4), 192–216. [CrossRef]
- Walling, D.E., 2009. The impact of global change on erosion and sediment transport by rivers: Current progress and future challenges. Paris: UNESCO.
- Walling, D.E., 2012. The role of dams in the global sediment budget. In A. L. Collins, V. Golosov, A.J. Horowitz, X. Lu, M. Stone, D.E. Walling, & X. Zhang (Eds.), Erosion and sediment yields in the changing environment (pp. 3–11). Wallingford: International Association of Hydrological Science. IAHS Publication, NO. 356.
- Wang, H., Yang, Z., Saito, Y., Liu, P., Sun, X., Wang, Y., 2007. Stepwise decreases of the Huanghe (Yellow River) sediment load (1950–2005): impacts of climate change and human activities. Glob. Planet. Chang. 57, 331–354. [CrossRef]
- Wang S, Fu B, Piao S, Lü Y, Ciais P, Feng X, Wang Y., 2016. Reduced sediment transport in the Yellow River due to anthropogenic changes. Nature Geoscience 9, 38–41. [CrossRef]
- Wang S., Liu W., Yan M., He L., 2020. Stepped changes in suspended sediment transport efficiency and discharge ratio and the main causes in the lower reach of the Yellow River. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 27(2): 104–111. (in Chinese).
- Wang S., Yan Y., Yan M., Zhao X., 2012a, Quantitative estimation of the impact of precipitation and human activities on runoff change of the Huangfuchuan River basin. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 22(5), 906–918.
- Wang S, Yan M, Yan Y, Shi C, He L, 2012b, Contributions of climate change and human activities to the changes in runoff increment in different sections of the Yellow River. Quaternary International, 282: 66–77. [CrossRef]
- Wang S, Wang Y, Ran L, Su T, 2015, Climatic and anthropogenic impacts on runoff changes in the Songhua River basin over the last 56 years (1955-2010), Northeastern China. Catena, 127: 258–269.
- Wang S., Hassan M. A., Xie X., 2006a. Relationship between suspended sediment load, channel geometry and land area increment in the Yellow River delta. Catena 65(3), 302–314.
- Wang, H., Yang, S., Saito, Y, Liu, J., Sun, X., 2006b. Interannual and seasonal variation of the Huanghe (Yellow River) water discharge over the past 50 years: Connections to impacts from ENSO events and dams. Global and Planetary Change 50, 212–225. [CrossRef]
- Williams, G.P., Wolman, M.G., 1984. Effects of dams and reservoirs on surface-water hydrology; changes in rivers downstream from dams. U.S. Geological Survey Professional, 1286: 1-83.
- Zahar, Y., Ghorbel, A., Albergel, J., 2008, Impacts of large dams on downstream flow conditions of rivers: Aggradation and reduction of the Medjerda channel capacity downstream of the Sidi Salem dam (Tunisia). Journal of Hydrology, 351(3-4): 318-330. [CrossRef]
- Wu, B. S, Shen, G.Q., 2008. Discussion on the physical significance of sediment inflow coefficient. Yellow River, 30(4): 15~16. (in Chinese).
- Xia, X.H., Dong, J.W., Wang M. H., et al., 2016. Effect of water-sediment regulation of the Xiaolangdi reservoir on the concentrations, characteristics, and fluxes of suspended sediment and organic carbon in the Yellow River. Science of the Total Environment, 571: 487–497. [CrossRef]
- Xia, X., Zhou, J., Yang, Z., 2002. Nitrogen contamination in the Yellow River basin of China. Journal of Environmental Quality 31, 917–925.
- Yu, Y., Wang H, Shi X, Ran X, Cui T, Qiao S, Liu Y. 2013. New discharge regime of the Huanghe (Yellow River): Causes and implications. Continental Shelf Research, 69: 62–72 (2013).
- Yang Z., Milliman J. D., Galler J., Liu J., Sun X., 1998.Yellow River’s water and sediment discharge decreasing steadily. EOS 79, 589-592.
- Yellow River Conservancy Committee, 1950–2021. Annual Report of Yellow Water and Sediment (Interior Report, in Chinese).
- Yellow River Conservancy Commission, 2020-2021. Soil and water conservation bulletin in Yellow River basin.
- Zhang J., Wang G., He R. et al., 2009. Variation trends of runoffs in the middle Yellow River basin and its response to climate change. Advances in Water Science, 20(02): 153–158 (in Chinese).
Figure 1.
The watershed and locations of major hydrological stations and large reservoirs of the Yellow River.
Figure 1.
The watershed and locations of major hydrological stations and large reservoirs of the Yellow River.
Figure 2.
Annual variations of runoff and suspended sediment load (SSL) at the Tongguan, Sanmenxia, and Lijin gauging stations of the Yellow River.
Figure 2.
Annual variations of runoff and suspended sediment load (SSL) at the Tongguan, Sanmenxia, and Lijin gauging stations of the Yellow River.
Figure 3.
Annual mean runoff and suspended sediment load (SSL) in decadal average at the Tongguan, Sanmenxia, Xiaolangdi, and Lijin gauging stations and their net yield in the different sections of the Yellow River during the last decades.
Figure 3.
Annual mean runoff and suspended sediment load (SSL) in decadal average at the Tongguan, Sanmenxia, Xiaolangdi, and Lijin gauging stations and their net yield in the different sections of the Yellow River during the last decades.
Figure 4.
Variation of monthly runoff and SSL at the Sanmenxia and Lijin gauging stations and their net yield in the section between the two stations of the Yellow River during the time period from Jan. of 1960 to Dec. of 2020 (the serial number of months is from 1 to 732).
Figure 4.
Variation of monthly runoff and SSL at the Sanmenxia and Lijin gauging stations and their net yield in the section between the two stations of the Yellow River during the time period from Jan. of 1960 to Dec. of 2020 (the serial number of months is from 1 to 732).
Figure 5.
Distribution curves of the monthly runoff in decadal average at the Sanmenxia, Xiaolangdi, Huayunakou, and Lijin gauging stations of the Yellow River.
Figure 5.
Distribution curves of the monthly runoff in decadal average at the Sanmenxia, Xiaolangdi, Huayunakou, and Lijin gauging stations of the Yellow River.
Figure 6.
Changes of the monthly mean runoff and SSTR in decadal average in flood season (FS) and non-flood season (NFL) at the Sanmenxia, Xiaolangdi, Huayunakou, and Lijin gauging stations of the Yellow River.
Figure 6.
Changes of the monthly mean runoff and SSTR in decadal average in flood season (FS) and non-flood season (NFL) at the Sanmenxia, Xiaolangdi, Huayunakou, and Lijin gauging stations of the Yellow River.
Figure 7.
Monthly mean suspended sediment transport rate (SSTR) in decadal average at the Sanmenxia, Xiaolangdi, Huayunakou, and Lijin stations of the Yellow River.
Figure 7.
Monthly mean suspended sediment transport rate (SSTR) in decadal average at the Sanmenxia, Xiaolangdi, Huayunakou, and Lijin stations of the Yellow River.
Figure 8.
Spatial variation of the monthly mean coefficient of sediment inflow in decadal average at the Sanmenxia, Xiaolangdi, Huayunakou, and Lijin stations of the Yellow River during the last decades.
Figure 8.
Spatial variation of the monthly mean coefficient of sediment inflow in decadal average at the Sanmenxia, Xiaolangdi, Huayunakou, and Lijin stations of the Yellow River during the last decades.
Figure 9.
Variation in hydrologic regime in terms of process curve of monthly mean discharge and sediment concentration at the Sanmenxia gauging station in the last decades.
Figure 9.
Variation in hydrologic regime in terms of process curve of monthly mean discharge and sediment concentration at the Sanmenxia gauging station in the last decades.
Figure 10.
Variation in hydrologic regime in terms of process curve of monthly mean discharge and sediment concentration at the Huayuankou gauging station in the last decades.
Figure 10.
Variation in hydrologic regime in terms of process curve of monthly mean discharge and sediment concentration at the Huayuankou gauging station in the last decades.
Figure 11.
Relationships between annual and monthly mean runoff and SSTR in decadal average and the ecological protection area in the Yellow River basin.
Figure 11.
Relationships between annual and monthly mean runoff and SSTR in decadal average and the ecological protection area in the Yellow River basin.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).