Submitted:
25 May 2023
Posted:
26 May 2023
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Methods
Results and Discussion
1. Pre-synaptic transmission of the impulse in sensory neurons
2. Synaptic Transmission of the Impulse
Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References
- Hodgkin A, Huxley, AF A. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952;117(4):500-544. [CrossRef]
- Hodgkin AL. Chance and design in electrophysiology: an informal account of certain experiments on nerve carried out between 1934 and 1952. J Physiol. 1976;263(1):1-21. [CrossRef]
- Augustine GJ, Santamaria F, Tanaka K. Local Calcium Signaling in Neurons. Neuron. 2003;40(2):331-346. [CrossRef]
- Neher E, Sakaba T. Multiple Roles of Calcium Ions in the Regulation of Neurotransmitter Release. Neuron. 2008;59(6):861-872. [CrossRef]
- Bagur R, Hajnóczky G. Intracellular Ca2+ Sensing: Its Role in Calcium Homeostasis and Signaling. Mol Cell. 2017;66(6):780-788. [CrossRef]
- Gruol D, Barker J, Huang L, McDonald J, Smith TJr. Hydrogen ions have multiple effects on the excitability of cultured mammalian neurons. Brain Res. 1980;183(1):247-252. [CrossRef]
- Krishtal O, Pidoplichko V. A receptor for protons in the nerve cell membrane. Neuroscience. 1980;5(12):2325-2327. [CrossRef]
- Bevan, S, Yeats, J. Protons activate a cation conductance in a sub-population of rat dorsal root ganglion neurones. J Physiol. 1991;433:145-161. [CrossRef]
- Swietach P, Youm JB, Saegusa N, Leem CH, Spitzer KW, Vaughan-Jones RD. Coupled Ca 2+ /H + transport by cytoplasmic buffers regulates local Ca 2+ and H + ion signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2013;110(22). [CrossRef]
- Deplazes E, White J, Murphy C, Cranfield CG, Garcia A. Competing for the same space: protons and alkali ions at the interface of phospholipid bilayers. Biophys Rev. 2019;11(3):483-490. [CrossRef]
- Molinari G, Nervo E. Role of protons in calcium signaling. Biochem J. 2021;478(4):895-910. [CrossRef]
- Zeng WZ, Xu TL. Proton production, regulation and pathophysiological roles in the mammalian brain. Neurosci Bull. 2012;28(1):1-13. [CrossRef]
- Soto E, Ortega-Ramírez A, Vega R. Protons as Messengers of Intercellular Communication in the Nervous System. Front Cell Neurosci. 2018;12:342. [CrossRef]
- OuYang, JB, Mellergård, P, Kristián, T, Kristiánova, V, Siesjö, BK. Influence of acid-base changes on the intracellular calcium concentration of neurons in primary culture. Exp Brain Res. 1994;101(2):265-271. [CrossRef]
- Garciarena CD, Malik A, Swietach P, Moreno AP, Vaughan-Jones RD. Distinct moieties underlie biphasic H + gating of connexin43 channels, producing a pH optimum for intercellular communication. FASEB J. 2018;32(4):1969-1981. [CrossRef]
- Nicholls DG, Chalmers S. The Integration of Mitochondrial Calcium Transport and Storage. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2004;36(4):277-281. [CrossRef]
- Sun GY, Xu J, Jensen MD, Simonyi A. Phospholipase A2 in the central nervous system. J Lipid Res. 2004;45(2):205-213. [CrossRef]
- Molinari G. Is hydrogen ion (H+) the real second messenger in calcium signalling? Cell Signal. 2015;27(7):1392-1397. [CrossRef]
- Cazzolli R, Shemon A, Fang M, Hughes W. Phospholipid signalling through phospholipase D and phosphatidic acid. IUBMB Life Int Union Biochem Mol Biol Life. 2006;58(8):457-461. [CrossRef]
- Majerus PW, York JD. Phosphoinositide phosphatases and disease. J Lipid Res. 2009;50:S249-S254. [CrossRef]
- Schmid F, Fliegert R, Westphal T, Bauche A, Guse AH. Nicotinic Acid Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate (NAADP) Degradation by Alkaline Phosphatase. J Biol Chem. 2012;287(39):32525-32534. [CrossRef]
- Wollny T, Wątek M, Durnaś B, et al. Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Metabolism and Its Role in the Development of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(4):741. [CrossRef]
- Fillafer C, Koll YS, Schneider MF. Lipid Membrane State Change by Catalytic Protonation and the Implications for Synaptic Transmission. Membranes. 2021;12(1):5. [CrossRef]
- Bozdaganyan ME, Lokhmatikov AV, Voskoboynikova N, et al. Proton leakage across lipid bilayers: Oxygen atoms of phospholipid ester linkers align water molecules into transmembrane water wires. Biochim Biophys Acta BBA - Bioenerg. 2019;1860(6):439-451. [CrossRef]
- Volkov VI, Chernyak AV, Golubenko DV, et al. Hydration and Diffusion of H+, Li+, Na+, Cs+ Ions in Cation-Exchange Membranes Based on Polyethylene- and Sulfonated-Grafted Polystyrene Studied by NMR Technique and Ionic Conductivity Measurements. Membranes. 2020;10(10):272. [CrossRef]
- Brünig FN, Rammler M, Adams EM, Havenith M, Netz RR. Spectral signatures of excess-proton waiting and transfer-path dynamics in aqueous hydrochloric acid solutions. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):4210. [CrossRef]
- Agmon N, Bakker HJ, Campen RK, et al. Protons and Hydroxide Ions in Aqueous Systems. Chem Rev. 2016;116(13):7642-7672. [CrossRef]
- Silverstein TP. The Proton in Biochemistry: Impacts on Bioenergetics, Biophysical Chemistry, and Bioorganic Chemistry. Front Mol Biosci. 2021;8:764099. [CrossRef]
- King JR, Ullah A, Bak E, Jafri MS, Kabbani N. Ionotropic and Metabotropic Mechanisms of Allosteric Modulation of α 7 Nicotinic Receptor Intracellular Calcium. Mol Pharmacol. 2018;93(6):601-611. [CrossRef]
- Simms B, Zamponi G. Neuronal voltage-gated calcium channels: structure, function, and dysfunction. Neuron. 2014;82(1):24-45. [CrossRef]
- Sharma A, Rahman G, Gorelik J, Bhargava A. Voltage-Gated T-Type Calcium Channel Modulation by Kinases and Phosphatases: The Old Ones, the New Ones, and the Missing Ones. Cells. 2023;12(3):461. [CrossRef]
- Kraft R. STIM and ORAI proteins in the nervous system. Channels. 2015;9(5):245-252. [CrossRef]
- Guéguinou M, Chantôme A, Fromont G, Bougnoux P, Vandier C, Potier-Cartereau M. KCa and Ca2+ channels: The complex thought. Biochim Biophys Acta BBA - Mol Cell Res. 2014;1843(10):2322-2333. [CrossRef]
- Sancho M, Kyle BD. The Large-Conductance, Calcium-Activated Potassium Channel: A Big Key Regulator of Cell Physiology. Front Physiol. 2021;12:750615. [CrossRef]
- Hibino H, Inanobe A, Furutani K, Murakami S, Findlay I, Kurachi Y. Inwardly Rectifying Potassium Channels: Their Structure, Function, and Physiological Roles. Physiol Rev. 2010;90(1):291-366. [CrossRef]
- Ye W, Chang RB, Bushman JD, et al. The K + channel K IR 2.1 functions in tandem with proton influx to mediate sour taste transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2016;113(2). [CrossRef]
- DeCoursey TE. Voltage and pH sensing by the voltage-gated proton channel, H V 1. J R Soc Interface. 2018;15(141):20180108. [CrossRef]
- Zeng WZ, Liu DS, Liu L, She L, Wu LJ, Xu TL. Activation of acid-sensing ion channels by localized proton transient reveals their role in proton signaling. Sci Rep. 2015;5(1):14125. [CrossRef]
- Rook ML, Musgaard M, MacLean DM. Coupling structure with function in acid-sensing ion channels: challenges in pursuit of proton sensors. J Physiol. 2021;599(2):417-430. [CrossRef]
- Storozhuk M, Cherninskyi A, Maximyuk O, Isaev D, Krishtal O. Acid-Sensing Ion Channels: Focus on Physiological and Some Pathological Roles in the Brain. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2021;19(9):1570-1589. [CrossRef]
- Kweon HJ, Yu SY, Kim DI, Suh BC. Differential Regulation of Proton-Sensitive Ion Channels by Phospholipids: A Comparative Study between ASICs and TRPV1. Xu SZ, ed. PLOS ONE. 2015;10(3):e0122014. [CrossRef]
- Cao E. Structural mechanisms of transient receptor potential ion channels. J Gen Physiol. 2020;152(3):e201811998. [CrossRef]
- Sisignano M, Fischer MJM, Geisslinger G. Proton-Sensing GPCRs in Health and Disease. Cells. 2021;10(8):2050. [CrossRef]
- de la Roche J, Eberhardt MJ, Klinger AB, et al. The Molecular Basis for Species-specific Activation of Human TRPA1 Protein by Protons Involves Poorly Conserved Residues within Transmembrane Domains 5 and 6. J Biol Chem. 2013;288(28):20280-20292. [CrossRef]
- Almanza A, Mercado F, Vega R, Soto E. Extracellular pH modulates the voltage-dependent Ca2+ current and low threshold K+ current in hair cells. Neurochem Res. 2008;33(8):1435-1441. [CrossRef]
- Fluck EC, Yazici AT, Rohacs T, Moiseenkova-Bell VY. Structural basis of TRPV5 regulation by physiological and pathophysiological modulators. Cell Rep. 2022;39(4):110737. [CrossRef]
- Song MK, Namgung SD, Choi D, et al. Proton-enabled activation of peptide materials for biological bimodal memory. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):5896. [CrossRef]
- Yao X, Klyukin K, Lu W, et al. Protonic solid-state electrochemical synapse for physical neural networks. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):3134. [CrossRef]
- Davies NW, Lux HD, Morad M. Site and mechanism of activation of proton-induced sodium current in chick dorsal root ganglion neurones. J Physiol. 1988;400(1):159-187. [CrossRef]
- Traynelis SF, Cull-Candy SG. Pharmacological properties and H+ sensitivity of excitatory amino acid receptor channels in rat cerebellar granule neurones. J Physiol. 1991;433(1):727-763. [CrossRef]
- Ueno S, Nakaye T, Akaike N. Proton-induced sodium current in freshly dissociated hypothalamic neurones of the rat. J Physiol. 1992;447(1):309-327. [CrossRef]
- Tombaugh GC, Somjen GG. Effects of extracellular pH on voltage-gated Nae, K+ and Ca2+ currents in isolated rat CAI neurons. J Physiol. 1996;15(493 (Pt3)):719-732. [CrossRef]
- Willoughby D, Schwiening CJ. Electrically evoked dendritic pH transients in rat cerebellar Purkinje cells. J Physiol. 2002;544(2):487-499. [CrossRef]
- Beg AA, Ernstrom GG, Nix P, Davis MW, Jorgensen EM. Protons Act as a Transmitter for Muscle Contraction in C. elegans. Cell. 2008;132(1):149-160. [CrossRef]
- Huang J, Liu CH, Hughes SA, Postma M, Schwiening CJ, Hardie RC. Activation of TRP Channels by Protons and Phosphoinositide Depletion in Drosophila Photoreceptors. Curr Biol. 2010;20(3):189-197. [CrossRef]
- Ruffin VA, Salameh AI, Boron WF, Parker MD. Intracellular pH regulation by acid-base transporters in mammalian neurons. Front Physiol. 2014;5. [CrossRef]
- Kier L. Nerve Conduction Through Dendrites via Proton Hopping. Curr Comput Aided-Drug Des. 2017;13(1):57-59. [CrossRef]
- Uchitel OD, González Inchauspe C, Weissmann C. Synaptic signals mediated by protons and acid-sensing ion channels. Synapse. 2019;73(10). [CrossRef]
- Highstein SM, Holstein GR, Mann MA, Rabbitt RD. Evidence that protons act as neurotransmitters at vestibular hair cell–calyx afferent synapses. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2014;111(14):5421-5426. [CrossRef]
- Fillafer C, Schneider MF. On the excitation of action potentials by protons and its potential implications for cholinergic transmission. Protoplasma. 2016;253(2):357-365. [CrossRef]
- Du J, Reznikov LR, Price MP, et al. Protons are a neurotransmitter that regulates synaptic plasticity in the lateral amygdala. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2014;111(24):8961-8966. [CrossRef]
- González-Inchauspe C, Urbano FJ, Di Guilmi MN, Uchitel OD. Acid-Sensing Ion Channels Activated by Evoked Released Protons Modulate Synaptic Transmission at the Mouse Calyx of Held Synapse. J Neurosci. 2017;37(10):2589-2599. [CrossRef]
- Lee JW. Protonic conductor: better understanding neural resting and action potential. J Neurophysiol. 2020;124(4):1029-1044. [CrossRef]
- Malchow RP, Tchernookova BK, Choi J in V, Smith PJS, Kramer RH, Kreitzer MA. Review and Hypothesis: A Potential Common Link Between Glial Cells, Calcium Changes, Modulation of Synaptic Transmission, Spreading Depression, Migraine, and Epilepsy—H+. Front Cell Neurosci. 2021;15:693095. [CrossRef]
- Warren TJ, Van Hook MJ, Supuran CT, Thoreson WB. Sources of protons and a role for bicarbonate in inhibitory feedback from horizontal cells to cones in Ambystoma tigrinum retina: Protons and bicarbonate in horizontal cell feedback to cones. J Physiol. 2016;594(22):6661-6677. [CrossRef]
- Country MW, Jonz MG. Calcium dynamics and regulation in horizontal cells of the vertebrate retina: lessons from teleosts. J Neurophysiol. 2017;117(2):523-536. [CrossRef]
- Deng B. Alternative Models to Hodgkin-Huxley Equations. Bull Math Biol. 2017;79(6):1390-1411. [CrossRef]
- Catterall WA, Lenaeus MJ, Gamal El-Din TM. Structure and Pharmacology of Voltage-Gated Sodium and Calcium Channels. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2020;60(1):133-154. [CrossRef]
- Catacuzzeno L, Franciolini F. The 70-year search for the voltage-sensing mechanism of ion channels. J Physiol. 2022;600(14):3227-3247. [CrossRef]
- Silbering AF, Benton R. Ionotropic and metabotropic mechanisms in chemoreception: “chance or design”? EMBO Rep. 2010;11(3):173-179. [CrossRef]
- Liman ER, Zhang YV, Montell C. Peripheral coding of taste. Neuron. 2014;81(5):984-1000. [CrossRef]
- Tu YH, Cooper AJ, Teng B, et al. An evolutionarily conserved gene family encodes proton-selective ion channels. Science. 2018;359(6379):1047-1050. [CrossRef]
- Chang RB, Waters H, Liman ER. A proton current drives action potentials in genetically identified sour taste cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2010;107(51):22320-22325. [CrossRef]
- Wang YY, Chang RB, Allgood SD, Silver WL, Liman ER. A TRPA1-dependent mechanism for the pungent sensation of weak acids. J Gen Physiol. 2011;137(6):493-505. [CrossRef]
- Huque T, Cowart BJ, Dankulich-Nagrudny L, et al. Sour Ageusia in Two Individuals Implicates Ion Channels of the ASIC and PKD Families in Human Sour Taste Perception at the Anterior Tongue. Matsunami H, ed. PLoS ONE. 2009;4(10):e7347. [CrossRef]
- Liman ER, Kinnamon SC. Sour taste: receptors, cells and circuits. Curr Opin Physiol. 2021;20:8-15. [CrossRef]
- Shah KR, Guan X, Yan J. Structural and Functional Coupling of Calcium-Activated BK Channels and Calcium-Permeable Channels Within Nanodomain Signaling Complexes. Front Physiol. 2022;12:796540. [CrossRef]
- Orfali R, Albanyan N. Ca2+-Sensitive Potassium Channels. Molecules. 2023;28(2):885. [CrossRef]
- Liccardo F, Luini A, Di Martino R. Endomembrane-Based Signaling by GPCRs and G-Proteins. Cells. 2022;11(3):528. [CrossRef]
- Imenez Silva PH, Wagner CA. Physiological relevance of proton-activated GPCRs. Pflüg Arch - Eur J Physiol. 2022;474(5):487-504. [CrossRef]
- Xue T, Do MTH, Riccio A, et al. Melanopsin signalling in mammalian iris and retina. Nature. 2011;479(7371):67-73. [CrossRef]
- Liu G, Badeau RM, Tanimura A, Talamo BR. Odorant receptors directly activate phospholipase C/inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate coupled to calcium influx in Odora cells. J Neurochem. 2006;96(6):1591-1605. [CrossRef]
- Szebenyi SA, Ogura T, Sathyanesan A, AlMatrouk AK, Chang J, Lin W. Increases in intracellular calcium via activation of potentially multiple phospholipase C isozymes in mouse olfactory neurons. Front Cell Neurosci. 2014;8. [CrossRef]
- Geppetti, P, Veldhuis, NA, Lieu, TM, Bunnett, NW. G Protein-Coupled Receptors: Dynamic Machines for Signaling Pain and Itch. Neuron. 2015;88(4):635-649. [CrossRef]
- Deshpande DA, Wang WCH, McIlmoyle EL, et al. Bitter taste receptors on airway smooth muscle bronchodilate by localized calcium signaling and reverse obstruction. Nat Med. 2010;16(11):1299-1304. [CrossRef]
- Lee A, Owyang C. Sugars, Sweet Taste Receptors, and Brain Responses. Nutrients. 2017;9(7):653. [CrossRef]
- Ahmad R, Dalziel JE. G Protein-Coupled Receptors in Taste Physiology and Pharmacology. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:587664. [CrossRef]
- Weernink O, Han L, Jakobs, KH, Schmidt, M. Dynamic phospholipid signaling by G protein-coupled receptors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007;1768(4):888-900. [CrossRef]
- Balla T. Putting G protein–coupled receptor-mediated activation of phospholipase C in the limelight. J Gen Physiol. 2010;135(2):77-80. [CrossRef]
- Banno Y, Nozawa Y. Characterization of partially purified phospholipase C from human platelet membranes. Biochem J. 1987;248(1):95-101. [CrossRef]
- Roy G, Villar LM, Lazaro I, Gonzalez M, Bootello A, Gonzalez-Porque P. Purification and properties of membrane and cytosolic phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipases C from human spleen. J Biol Chem. 1991;266(18):11495-11501. [CrossRef]
- Nakamura Y, Fukami K. Regulation and physiological functions of mammalian phospholipase C. J Biochem (Tokyo). 2017;161(4):mvw094. [CrossRef]
- Chen W, Chen C, Yang K, et al. Arachidonic acid-induced H + and Ca 2+ increases in both the cytoplasm and nucleoplasm of rat cerebellar granule cells. J Physiol. 2001;537(2):497-510. [CrossRef]
- Križaj D, Mercer AJ, Thoreson WB, Barabas P. Intracellular pH modulates inner segment calcium homeostasis in vertebrate photoreceptors. Am J Physiol-Cell Physiol. 2011;300(1):C187-C197. [CrossRef]
- Caldwell L, Harries P, Sydlik S, Schwiening CJ. Presynaptic pH and vesicle fusion in Drosophila larvae neurones. Synapse. 2013;67(11):729-740. [CrossRef]
- Rossano AJ, Chouhan AK, Macleod GT. Genetically encoded pH-indicators reveal activity-dependent cytosolic acidification of Drosophila motor nerve termini in vivo: Genetic pH-indicators in motor nerve termini. J Physiol. 2013;591(7):1691-1706. [CrossRef]
- Zhang L, Bellve K, Fogarty K, Kobertz WR. Fluorescent Visualization of Cellular Proton Fluxes. Cell Chem Biol. 2016;23(12):1449-1457. [CrossRef]
- Wei D, Mei Y, Xia J, Hu H. Orai1 and Orai3 Mediate Store-Operated Calcium Entry Contributing to Neuronal Excitability in Dorsal Root Ganglion Neurons. Front Cell Neurosci. 2017;11:400. [CrossRef]
- Tombaugh GC, Somjen GG. Differential Sensitivity to Intracellular pH Among High- and Low-Threshold Ca 2+ Currents in Isolated Rat CA1 Neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1997;77(2):639-653. [CrossRef]
- Dolphin AC. Functions of Presynaptic Voltage-gated Calcium Channels. Function. 2020;2(1):zqaa027. [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran S, Rodgriguez S, Potcoava M, Alford S. Single Calcium Channel Nanodomains Drive Presynaptic Calcium Entry at Lamprey Reticulospinal Presynaptic Terminals. J Neurosci. 2022;42(12):2385-2403. [CrossRef]
- Harding EK, Zamponi GW. Central and peripheral contributions of T-type calcium channels in pain. Mol Brain. 2022;15(1):39. [CrossRef]
- Henrich M, Buckler KJ. Acid-evoked Ca2+ signalling in rat sensory neurones: effects of anoxia and aglycaemia. Pflüg Arch - Eur J Physiol. 2009;459(1):159-181. [CrossRef]
- Liu CH, Chen Z, Oliva MK, et al. Rapid Release of Ca 2+ from Endoplasmic Reticulum Mediated by Na + /Ca 2+ Exchange. J Neurosci. 2020;40(16):3152-3164. [CrossRef]
- Hu F, Song X, Long D. Transient receptor potential ankyrin 1 and calcium: Interactions and association with disease (Review). Exp Ther Med. 2021;22(6):1462. [CrossRef]
- Catterall WA, Goldin AL, Waxman SG. International Union of Pharmacology. XLVII. Nomenclature and Structure-Function Relationships of Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels. Pharmacol Rev. 2005;57(4):397-409. [CrossRef]
- Wu LG, Hamid E, Shin W, Chiang HC. Exocytosis and Endocytosis: Modes, Functions, and Coupling Mechanisms. Annu Rev Physiol. 2014;76(1):301-331. [CrossRef]
- Ge L, Shin W, Arpino G, et al. Sequential compound fusion and kiss-and-run mediate exo- and endocytosis in excitable cells. Sci Adv. 2022;8(24):eabm6049. [CrossRef]
- Grider MH, Jessu R, Kabir R. Physiology, Action Potential. Vol In: StatPearls [internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538143/.
- Kariev AM, Green ME. Protons in Gating the Kv1.2 Channel: A Calculated Set of Protonation States in Response to Polarization/Depolarization of the Channel, with the Complete Proposed Proton Path from Voltage Sensing Domain to Gate. Membranes. 2022;12(7):718. [CrossRef]
- Han S, Peng S, Vance J, et al. Structural dynamics determine voltage and pH gating in human voltage-gated proton channel. eLife. 2022;11:e73093. [CrossRef]
- Koch KW, Dell’Orco D. Protein and Signaling Networks in Vertebrate Photoreceptor Cells. Front Mol Neurosci. 2015;8. [CrossRef]
- Marchetta P, Rüttiger L, Hobbs AJ, Singer W, Knipper M. The role of cGMP signalling in auditory processing in health and disease. Br J Pharmacol. 2022;179(11):2378-2393. [CrossRef]
- Douguet D, Honoré E. Mammalian Mechanoelectrical Transduction: Structure and Function of Force-Gated Ion Channels. Cell. 2019;179(2):340-354. [CrossRef]
- Bavi N, Nikolaev YA, Bavi O, et al. Principles of Mechanosensing at the Membrane Interface. In: Epand RM, Ruysschaert JM, eds. The Biophysics of Cell Membranes. Vol 19. Springer Series in Biophysics. Springer Singapore; 2017:85-119. [CrossRef]
- Cheng YR, Jiang BY, Chen CC. Acid-sensing ion channels: dual function proteins for chemo-sensing and mechano-sensing. J Biomed Sci. 2018;25(1):46. [CrossRef]
- Lin HH, Ng KF, Chen TC, Tseng WY. Ligands and Beyond: Mechanosensitive Adhesion GPCRs. Pharmaceuticals. 2022;15(2):219. [CrossRef]
- Wei WC, Bianchi F, Wang YK, Tang MJ, Ye H, Glitsch MD. Coincidence Detection of Membrane Stretch and Extracellular pH by the Proton-Sensing Receptor OGR1 (GPR68). Curr Biol. 2018;28(23):3815-3823.e4. [CrossRef]
- Iliff, AJ, Xu, XZS. A Mechanosensitive GPCR that Detects the Bloody Force. Cell. 2018;173(3):542-544. [CrossRef]
- Feng, PX. The Mechanism of Hydrolysis Reaction of Adenosine Triphosphate Molecules for the Generation of Bio-Energy and its Properties in the Living Systems. Int J Pharm Anal Acta. 2017;1(1):001-008.
- Barbosa ML de C, Fumian MM, Miranda ALP de, Barreiro EJ, Lima LM. Therapeutic approaches for tumor necrosis factor inhibition. Braz J Pharm Sci. 2011;47(3):427-446. [CrossRef]
- Rybalkin SD, Hinds TR, Beavo JA. Enzyme Assays for cGMP Hydrolyzing Phosphodiesterases. In: Krieg T, Lukowski R, eds. Guanylate Cyclase and Cyclic GMP. Vol 1020. Methods in Molecular Biology. Humana Press; 2013:51-62. [CrossRef]
- Michaelson, DM, Angel, I. Determination of ΔpH in cholinergic synaptic vesicle. Life Sci. 1980;27(1):39-44. [CrossRef]
- Fuldner, HH, Stadler, H. 31P-NMR Analysis of Synaptic Vesicles. Eur J Biochem. 1982;121:519-524.
- Anderson RG, Orci L. A view of acidic intracellular compartments. J Cell Biol. 1988;106(3):539-543. [CrossRef]
- Miesenbock, G, De Angelis, DA. Visualizing secretion and synaptic transmission with pH-sensitive green fluorescent proteins. Nature. 1998;394(6689):192-195. [CrossRef]
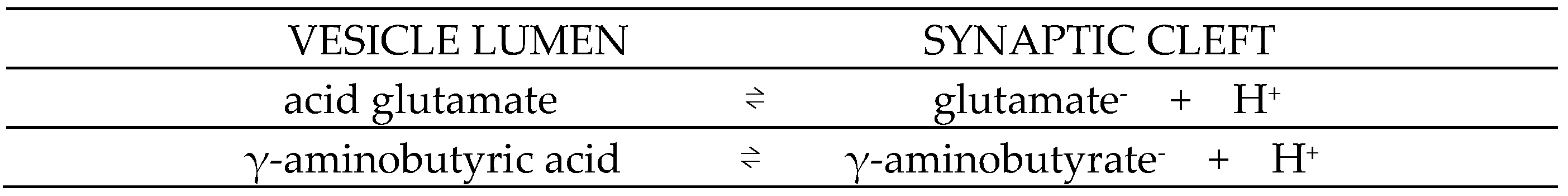
- Egashira Y, Takase M, Watanabe S, et al. Unique pH dynamics in GABAergic synaptic vesicles illuminates the mechanism and kinetics of GABA loading. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2016;113(38):10702-10707. [CrossRef]
- DeVries SH. Exocytosed Protons Feedback to Suppress the Ca2+ Current in Mammalian Cone Photoreceptors. Neuron. 2001;32(6):1107-1117. [CrossRef]
- Palmer MJ, Hull C, Vigh J, von Gersdorff H. Synaptic Cleft Acidification and Modulation of Short-Term Depression by Exocytosed Protons in Retinal Bipolar Cells. J Neurosci. 2003;23(36):11332-11341. [CrossRef]
- Ahdut-Hacohen R, Duridanova D, Meiri H, Rahamimoff R. Hydrogen ions control synaptic vesicle ion channel activity in Torpedo electromotor neurones: H + dependence of synaptic vesicle ion channels. J Physiol. 2004;556(2):347-352. [CrossRef]
- Kolen B, Borghans B, Kortzak D, et al. Vesicular glutamate transporters are H+-anion exchangers that operate at variable stoichiometry. Nat Commun. 2023;14(1):2723. [CrossRef]
- Marx MC, Billups D, Billups B. Maintaining the presynaptic glutamate supply for excitatory neurotransmission: Glutamate Recycling and Replenishment. J Neurosci Res. 2015;93(7):1031-1044. [CrossRef]
- Pathak D, Shields LY, Mendelsohn BA, et al. The Role of Mitochondrially Derived ATP in Synaptic Vesicle Recycling. J Biol Chem. 2015;290(37):22325-22336. [CrossRef]
- Eriksen J, Chang R, McGregor M, Silm K, Suzuki T, Edwards RH. Protons Regulate Vesicular Glutamate Transporters through an Allosteric Mechanism. Neuron. 2016;90(4):768-780. [CrossRef]
- Pulido, C, Ryan, TA. Synaptic vesicle pools are a major hidden resting metabolic burden of nerve terminals. Sci Adv. 2021;7(49):eabi9027. [CrossRef]
- Malik KU. Potentiation by Anticholinesterases of the Response of Rat Mesenteric Arteries to Sympathetic Postganglionic Nerve Stimulation. Circ Res. 1970;27(5):647-655. [CrossRef]
- Mike, A, Castro, NG, Albuquerque, EX. Choline and acetylcholine have similar kinetic properties of activation and desensitization on the alpha7 nicotinic receptors in rat hippocampal neurons. Brain Res. 2000;882(1-2):155-168. [CrossRef]
- Holzer P. Acid sensing by visceral afferent neurones: Acid sensing by visceral afferent neurones. Acta Physiol. 2011;201(1):63-75. [CrossRef]
- Leffler, A, Mönter, B, Koltzenburg, M. The role of the capsaicin receptor TRPV1 and acid-sensing ion channels (ASICS) in proton sensitivity of subpopulations of primary nociceptive neurons in rats and mice. Neuroscience. 2006;139(2):699-709. [CrossRef]
- Semtner M, Schaefer M, Pinkenburg O, Plant TD. Potentiation of TRPC5 by Protons. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(46):33868-33878. [CrossRef]
- Ryu S, Liu B, Yao J, Fu Q, Qin F. Uncoupling Proton Activation of Vanilloid Receptor TRPV1. J Neurosci. 2007;27(47):12797-12807. [CrossRef]
- Lipkin AM, Cunniff MM, Spratt PWE, Lemke SM, Bender KJ. Functional Microstructure of Ca V -Mediated Calcium Signaling in the Axon Initial Segment. J Neurosci. 2021;41(17):3764-3776. [CrossRef]
- Fan X, Lu Y, Du G, Liu J. Advances in the Understanding of Two-Pore Domain TASK Potassium Channels and Their Potential as Therapeutic Targets. Molecules. 2022;27(23):8296. [CrossRef]
- Boillat, A, Alijevic, O, Kellenberger, S. Calcium entry via TRPV1 but not ASICs induces neuropeptide release from sensory neurons. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2014;61:13-22. [CrossRef]
- Burke KJ, Bender KJ. Modulation of Ion Channels in the Axon: Mechanisms and Function. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019;13:221. [CrossRef]
- Negri S, Scolari F, Vismara M, et al. GABAA and GABAB Receptors Mediate GABA-Induced Intracellular Ca2+ Signals in Human Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells. Cells. 2022;11(23):3860. [CrossRef]
- Papke, RI, Lindstrom, JM. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors: Conventional and unconventional ligands and signaling. Neuropharmacology. 2020;15(168):108021. [CrossRef]
- Brown DA. Acetylcholine and cholinergic receptors. Brain Neurosci Adv. 2019;3:239821281882050. [CrossRef]
- Sam C, Bordoni B. Physiology, Acetylcholine. Vol In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL). StatPearls Publishing; 2022. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32491757/.
- Nicholson MW, Sweeney A, Pekle E, et al. Diazepam-induced loss of inhibitory synapses mediated by PLCδ/ Ca2+/calcineurin signalling downstream of GABAA receptors. Mol Psychiatry. 2018;23(9):1851-1867. [CrossRef]
- Ihle, Eva C., Patneau, Doris K. Modulation of α-Amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic Acid Receptor Desensitization by Extracellular Protons. Mol Pharmacol. 2000;58(6):1204-1212. [CrossRef]
- Mott DD, Washburn MS, Zhang S, Dingledine RJ. Subunit-Dependent Modulation of Kainate Receptors by Extracellular Protons and Polyamines. J Neurosci. 2003;23(4):1179-1188. [CrossRef]
- Zhang JB, Chang S, Xu P, et al. Structural Basis of the Proton Sensitivity of Human GluN1-GluN2A NMDA Receptors. Cell Rep. 2018;25(13):3582-3590.e4. [CrossRef]
- Dravid SM, Erreger K, Yuan H, et al. Subunit-specific mechanisms and proton sensitivity of NMDA receptor channel block: Proton sensitivity of NMDA receptor channel blockers. J Physiol. 2007;581(1):107-128. [CrossRef]
- Svensson E, Apergis-Schoute J, Burnstock G, Nusbaum MP, Parker D, Schiöth HB. General Principles of Neuronal Co-transmission: Insights From Multiple Model Systems. Front Neural Circuits. 2019;12:117. [CrossRef]
- Hunt PJ, Kochukov M, Pekarek BT, et al. Co-transmitting neurons in the lateral septal nucleus exhibit features of neurotransmitter switching. IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2022;12:390-398. [CrossRef]
| enzyme | substrate | acid product | reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| phospholipase A2 | phosphatidylcholine | arachidonic acid | Sun17 |
| phospholipase C | phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate | acid IP3 | Molinari, Fig.1A18 |
| phospholipase D | phosphatidylcholine | phosphatidic acid | Cazzolli19 |
| inositol 5-phosphatase | inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) | phosphoric acid | Majerus20 |
| alkaline phosphatase | NAADP | phosphoric acid | Schmid21 |
| S1P phosphatase | sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) | phosphoric acid | Wollny22 |
| acetylcholinesterase | acetylcholine | acetic acid | Fillafer23 |
 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





