Submitted:
23 May 2023
Posted:
24 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
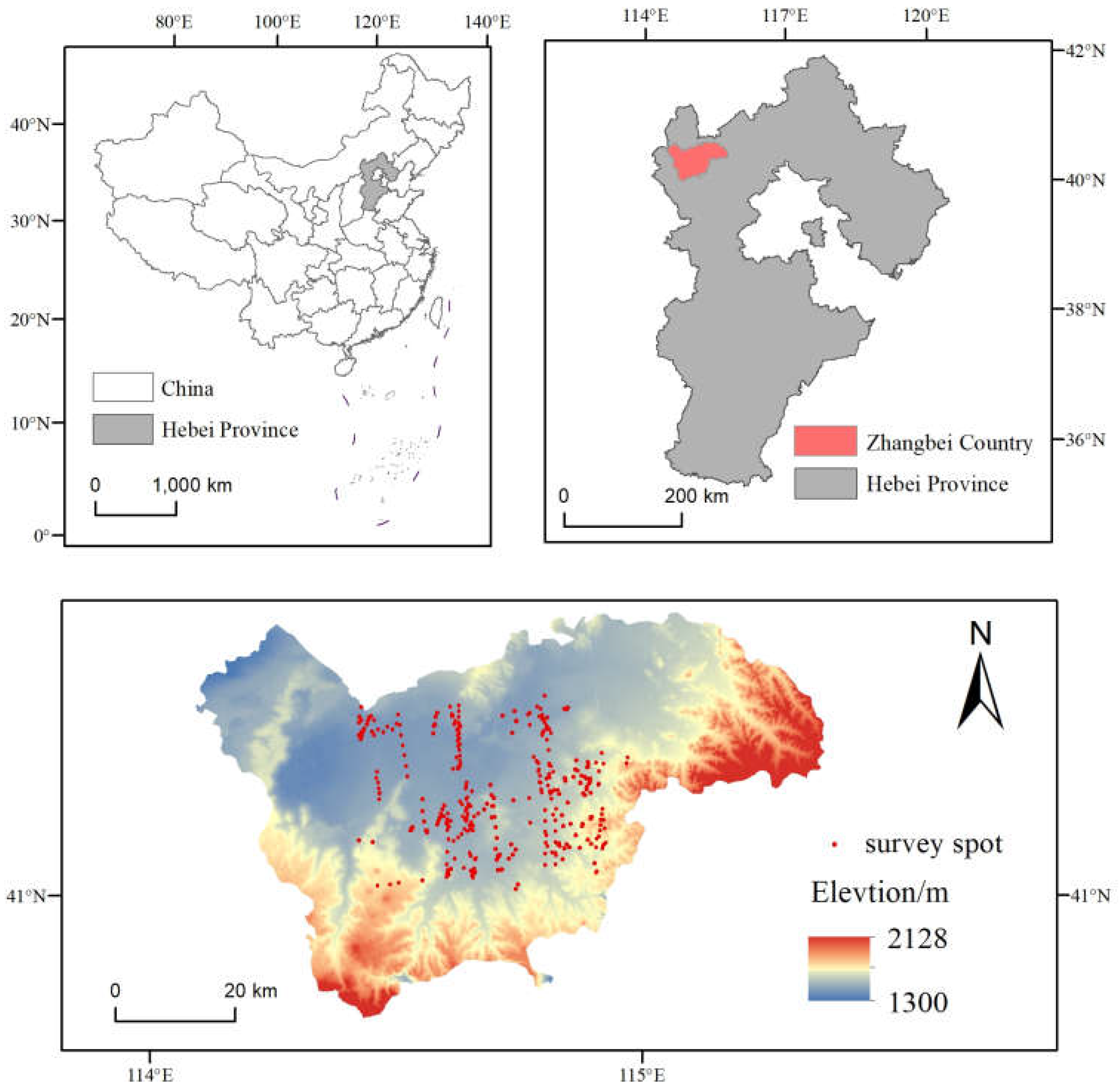
2.1. Study area
2.2. Data sources
2.3. Research methods
2.3.1. Classification of farm households by type
2.3.2. Measurement of livelihood diversity
2.3.3. Measurement of livelihood assets and well-being
2.3.4. Model of factors influencing the farm household welfare level
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of livelihood characteristics of farm households
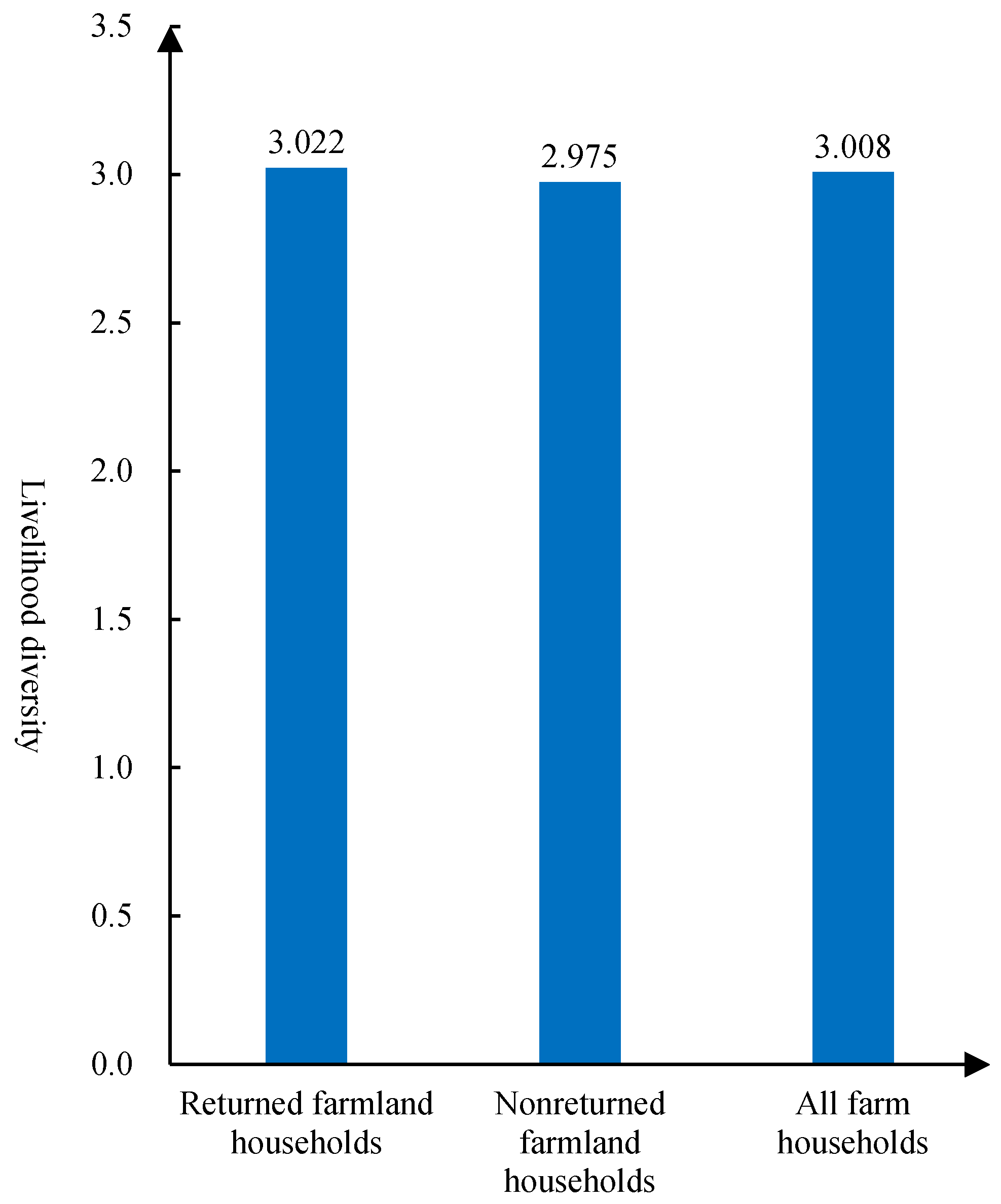
3.1.1. Farm households’ livelihood diversity characteristics
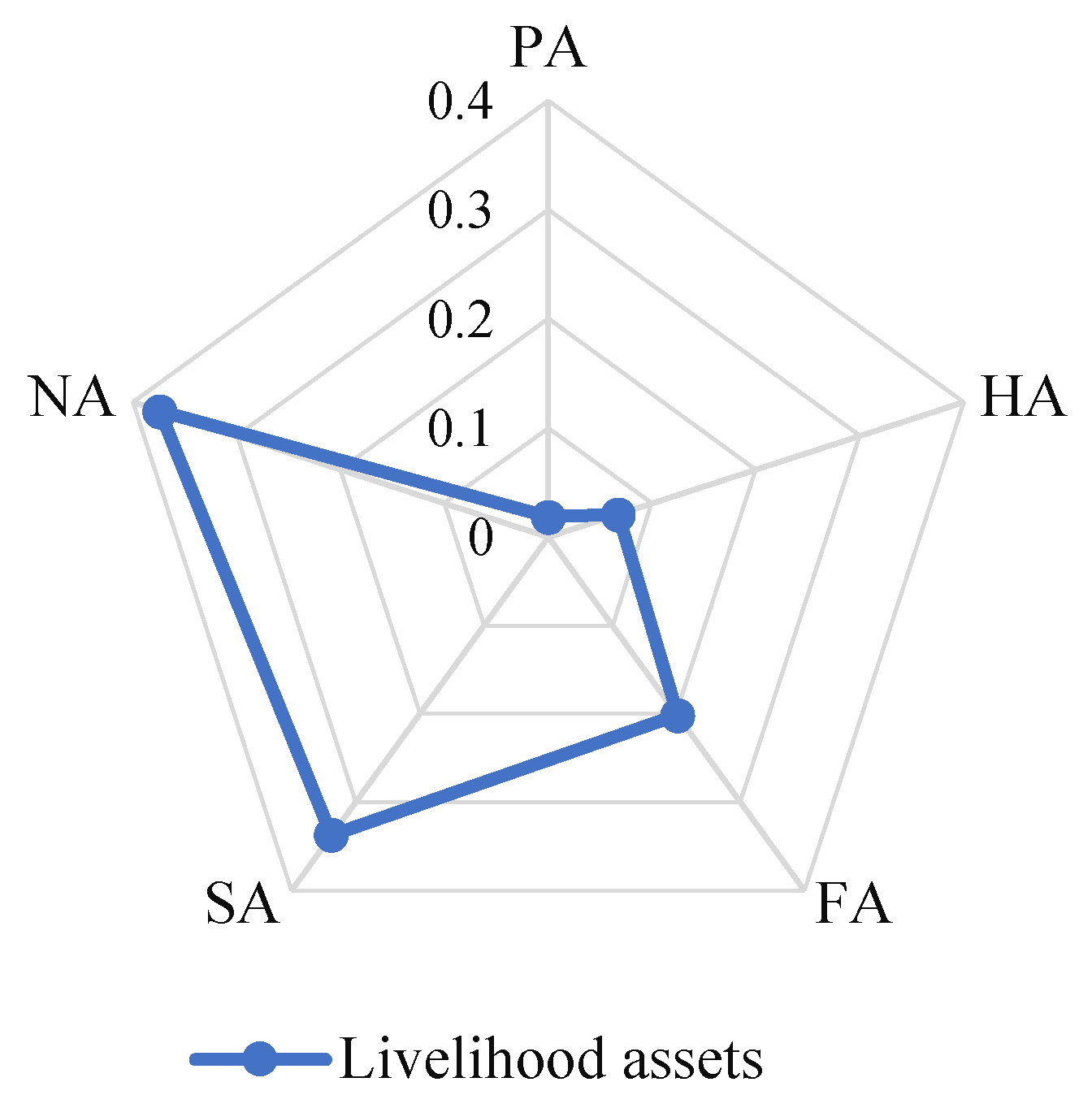
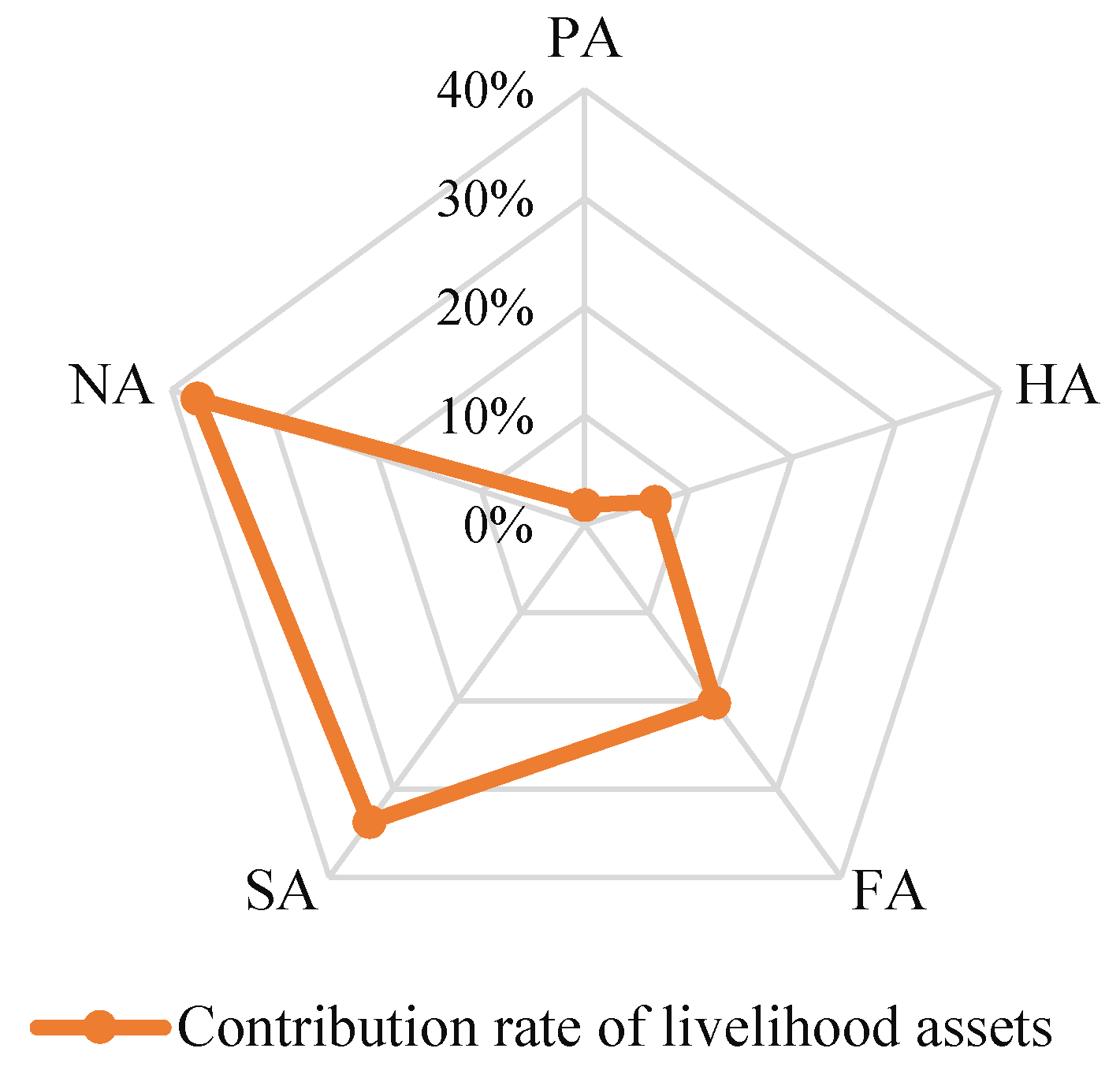
3.1.2. Farm households’ livelihood assets characteristics
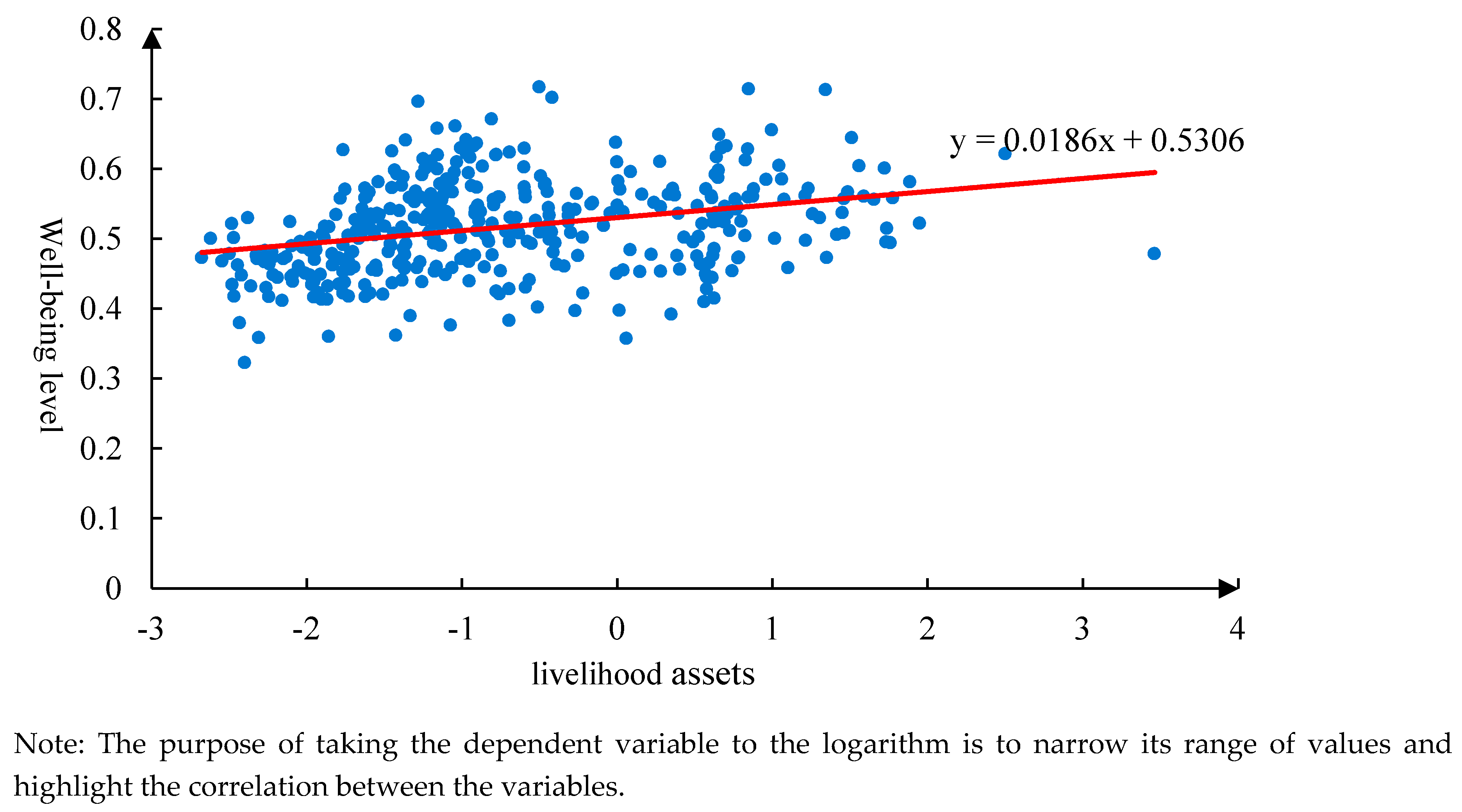
3.2. Analysis of the level of well-being of farm households
3.3. Analysis of the impact of farm household livelihoods on farm household well-being
3.3.1. Analysis of factors influencing farm household well-being for all farm households
3.3.2. Analysis of factors influencing farm household well-being for different types of farm households
4. Discussion
4.1. Geographical differences and similarities of farm household livelihoods
4.2. Grain for green policy impacts on farm households’ well-being
4.3. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shao, Q.Q.; Liu, S.C.; Ning, J.; Liu, G.B.; Yang, F.; Zhang, X.Y.; Niu, L.N.; Huang, H.B.; Fan, J.W.; Liu, J.Y. Assessment of ecological benefits of key national ecological projects in China in 2000-2019 using remote sensing. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2022, 77, 2133–2153. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.Q.; Zhao, X.Y.; Du, Y.X.; Ma, P.Y. Spatio-temporal changes of the coupling relationship between ecosystem services and residents’ well-being in Qinba Mountains Area. J. Nat. Resour. 2021, 36, 2522–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Wang, Y.K.; Xu, P.; Yan, K. A Review of Coupled Relationship of Rural Livelihoods and Ecosystem Services. Ecol. Econ. 2017, 33, 142–145+151. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, D.J.; Sun, L.L.; Zhou, L.L. Construction and Application of Coupling Model of Ecosystem Service and Farmers’ Livelihood in Three Gorges Reservoir Area. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2020, 27, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.C.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, W.; Wang, H.; Peng, W.J. Regional differences and the driving mechanism of relationships between rural household livelihood and ecosystem services: A case study in upstream watershed of Miyun Reservoir, China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2021, 32, 3872–3882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.N.; Zhang, T.; Yang, Y.J.; Niu, H.P.; Yang, D.G. Spatial flow of ecosystem services and impacts on human well-being in the Weigan River Basin. Resour. Sci. 2017, 39, 533–544. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.F.; Deng, W.; Zhu, C.L.; Zhao, Y.L. Spatial Relationship and Its Dynamic Features of Ecosystem Services and Human Wellbeing in the Upper Reaches of Minjiang River. J. Mount. Sci. 2017, 35, 388–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, R.; Xu, X.Y.; Gao, J.L.; Zhu, T.T.; Lu, B. Ecosystem Services’ Spatial Characteristics Patterns of Ecosystem Services and Their Relationships With Residents’ Well-being of Coal Resource-based Cities. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2020, 51, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.T.; Qiu, X.T.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, F.B.; Liu, Y.W. Spatial heterogeneity and dynamic features of the ecosystem services influence on human wellbeing in the West Sichuan Mountain Areas. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 7555–7567. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, D.B.; Chen, M.Q.; Liao, C.R.; Xie, X.X.; Liao, X.B.; Yao, D.L. Analysis of Subjective Well-being of Farmers with Land Transfer and Its Influencing Factors: From the Perspective of Livelihood Capitals. Chin. Land Sci. 2019, 33, 25–33. [Google Scholar]
- Costanza, R.; d’Arge, R.; De Groot, R.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.; Limburg, K.; Naeem, S.; O’Neill, R.V.; Paruelo, J.; Raskin, R.G.; Sutton, P.; Van Den Belt, M. The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Nature. 1997, 387, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Bei, Y.; Gu, H.; Zhang, P. Spatiotemporal Evolution of Ecosystem Services in the Wanhe Watershed Based on Cellular Automata (CA)-Markov and InVEST Models. Sustainability. 2022, 14, 13302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otoiu, A.; Titan, E.; Dumitrescu, R. Are the variables used in building composite indicators of well-being relevant? Validating composite indexes of well-being. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 46, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguado, M.; González, J.A.; López-Santiago, C.; Montes, C. Exploring subjective well-being and ecosystem services perception along a rural–urban gradient in the high Andes of Ecuador. Ecosyst. Serv. 2018, 34, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Y.; Luo, Y.T.; Han, Y.J.; Li, J. Regional difference and determinants of human well-being in China: Based on the analysis of human development index. Prog. Geogr. 2018, 37, 1150–1158. [Google Scholar]
- Ciftcioglu, G.C.; Ebedi, S.; Abak, K. Evaluation of the relationship between ornamental plants–based ecosystem services and human wellbeing: A case study from Lefke Region of North Cyprus. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 102, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Chen, H.; Zhang, H.; Shi, Q.Q.; Geng, T.W. The impact of ecosystem services on human well-being and its group differences in the loess hilly and gully region. Geogr Res. 2022, 41, 1298–1310. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, S.K.; Boundaogo, M.; DeClerck, F.A.; Estrada-Carmona, N.; Mirumachi, N.; Mulligan, M. Insights into the importance of ecosystem services to human well-being in reservoir landscapes. Ecosyst. Serv. 2019, 39, 100987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.F.; Wang, Y.Y.; Cao, Y.Q.; Wang, Y.H.; Hao, S.; Lv, L.T. Classification and spatiotemporal patterns of ecological well-being based on ecosystem services: Taking China’s prefecture-level and above cities for example. Resour. Sci. 2020, 42, 1110–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.M.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.F.; Zhang, A.L.; Yang, H.Z. Herdsman’s multidimensional well-being in response of natural resources protection in the source region of the Yellow River, China: Case study based on household investigation in Maduo County. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2014, 34, 6767–6777. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, W.T.; Qiao, D.; Ke, S.F.; Hou, Q.; Yan, R.H. How to Improve Ecological Compensation Mechanism from the Perspective of Resource Opportunity Cost? A Case Study Based on “Welfare Upside Down” of Forest Resources Compensation in State-owned Forest Area. Chin. Rural Surv. 2022, 2022, 59–78. [Google Scholar]
- Li, N.J.; Cao, G.Y.; He, B.H.; Luo, G.L. On the Relationship Between the Change in Farmer Wellbeing and Ecosystem Services—A Case Study of Wuling-Qinba Contiguous Destitute Areas in Chongqing. J. Southwest Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.). 2017, 39, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Hou, K.L.; Zheng, S.R.; Zhang, K.; Yang, T.H.; Zhao, D.D.; Sun, B.; Chen, L. Relationship between Farmer’s Well-Being and Ecosystem Services in Hilly and Mountainous Areas of South China Based on Structural Equation Model: A Case Study of Lechang in Guangdong Province. Trop. Geogr. 2020, 40, 843–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.H.; Yao, S.B. A comparative analysis of the impacts of the sloping land conversion program on the well-being of households in the Yellow and Yangtze river basins. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2017, 31, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.P.; He, M.Y.; Chen, S.Y. The impact of farmers’ livehood capital on the adoption of different preference technologies——An analysis based on the sustainable livelihood framework. Chin. J. Agriculture. Resour Region. Plan. 2022, 43, 197–205. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.G.; Ge, Y.X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.N. Impact of ecological compensation on sustainable livelihood capacity of farmers in water source area——Based on the improved DFID livelihood analysis framework. Chin. J. Agriculture. Resour Region. Plan. 2022, 43, 97–109. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Yu, Q.Q. Impact of Poverty Alleviation Resettlement on Rural Household Livelihood Resilience in Southern Shaanxi. Geogr. Geo-Info. Sci. 2023, 39, 105–110. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.S.; Le, Z. Livelihood capital, livelihood risk and farmers’ livelihood strategy. Issue. Agriculture. Econ. 2012, 33, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y. Poor Mountain Farmers Livelihood Capital Impact on Livelihoods Strategy Research: Based on the Survey Data Pingwu and Nanjiang County of Sichuan Province. Issue. Agriculture. Econ. 2016, 37, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.L.; Yang, X.J.; Yang, T. Exploring conditions, determinants and mechanisms of rural households’ adaptability to tourism development: A case study of Jinsixia in Qinling Mountains. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2013, 68, 1143–1156. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Q.J.; Li, W.; Zhu, Q.J.; Ma, X.M.; He, J.; Ma, X.J.; Luo, X. An analysis of the characteristics of water storage structure and the practice of groundwater exploration in the basalt area of Zhangbei County, Bashang, Hebei Province. Geol. Bul. Chin. 2020, 39, 1899–1907. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.L.; Li, W.P.; Sun, G.J.; Zhang, L.P. Analysis of Livelihood Capital and Its Coupling Coordination Degree of Farmers in Ecologically Vulnerable Alpine Areas —A Case of Xiahe County in Gannan Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2022, 29, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Chen, S.; Zhou, K.; Chen, X. Influence of Livelihood Capital of Rural Reservoir Resettled Households on the Choice of Livelihood Strategies in China. Water. 2022, 14, 4055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.G.; Wang, C.S. Project of Conversion of Cropland to Forest (Grass) Effect on Farmers’ Livelihood: A Case Study of Qinba Mountain Area in Gansu Province. Issue. Forest. Econ. 2017, 37, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.L.; Bai, X. The Performance and Mechanism of the Impact of the Sloping Land Conversion Program on Households’ Livelihood Strategies. Ecol. Econ. 2019, 35, 121–127. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.Q.; Zhang, J.X.; Gong, J.; Qian, C.Y. Spatial and Temporal Relations among Land-Use Intensity, Ecosystem Services and Human Well-Being in the Longzhong Loess Hilly Region: A Case Study of the Anding District, Gansu Province. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 637–648. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, J.Y.; Han, X.; Hou, Y.L.; Wen, Y.L. Subjective Well-Being of Households in Rural Poverty Regions in Xiangxi, Hunan Province. Ecol. Econ. 2014, 36, 2174–2182. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.M.; Yao, L.L.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, D.; Lin, Y.M. Estimate Well-Being of Urban and Rural Residents in the Yellow River Basin and Its Spatial-Temporal Evolution. Ecol. Econ. 2022, 38, 222–229. [Google Scholar]
- MA(Millennium Ecosystem Assessment). Ecosystems and human well-being; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, B.J.; Zhang, L.W. Land-use change and ecosystem services: Concepts, methods and progress. Prog. Geogr. 2014, 33, 441–446. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.Q.; Zhao, W.W.; Pereira, P.; Liu, Y.X. Socio-cultural valuation of rural and urban perception on ecosystem services and human well-being in Yanhe watershed of China. J. Environ. 2019, 251, 109615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.L.; Zhang, B.; Zheng, Q.R.; He, X.Q.; Zhang, T.F.; Jia, Y.Q.; Luo, Z.M. Impacts of Converting Farmland into Forests on Farmer Well-Being in the Earth-Rock Mountain Areas of the Loess Plateau. Resour. Sci. 2014, 36, 397–405. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.L.; Cao, H.; Jin, M. Influence Mechanism of Wetland Conservation on the Livelihood Outcomes of Farmers’: An Empirical Study Based on the Survey of Rural Households in Natural Reserves. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Asset type | Indicator | Symbol | Indicator meaning and value | Weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Human Assets (HA) |
Household size | H1 | Total household size | 0.010 |
| Educational attainment of household members | H2 | No formal education (little literacy) = 0; elementary school = 1; junior high school = 2; high school, junior college = 3; college, senior college = 4; university undergraduate and above = 5 | 0.042 | |
| Household labor capacity | H3 | Assigned according to age, where 6 and below = 0; 7−18 = 1; 18−25 = 2; 26−45 = 5; 46−60 = 4; 60 and above (including military/students aged 19−60) = 3 | 0.016 | |
| Natural Assets (NA) |
Area of arable land | N1 | Household arable land area | 0.045 |
| Area of watered land | N2 | Area of household watered land | 0.328 | |
| Area returned to farming | N3 | Area of land returned to farming by household | 0.001 | |
| Physical Assets (PA) |
Residential index | P1 | Residential index =αM+βC+γN, where M, C, and N denote the number of houses, house structure, and residential age, respectively; α, β, and γ are the weights of the three, respectively, using the entropy value method to calculate α=0.3949, β=0.4023, and γ=0.2028. where, house structure: civil structure = 1, brick structure = 2, brick and mixed structure = 4, others: such as brick = 3, relief = 0. If the house consists of different structures, the weighted summation is calculated in proportion to the number of rooms structure | 0.005 |
| Number of large production tools | P2 | Number of asset types owned by farm households | 0.013 | |
| Social Assets (SA) |
Number of public officials among relatives | S1 | Number of public officials among relatives | 0.290 |
| Number of channels for outworking | S2 | Number of types of channels for outworking | 0.024 | |
| Number of social contacts | S3 | Assigned according to the number of cell phone contacts, no cell phone = 0, 0–20 people = 1, 21–50 people = 2, 51–100 people = 3, 101 and above = 4 | 0.023 | |
| Financial Assets (FA) |
Total value of livestock | F1 | Total value of livestock = number of livestock × unit price of livestock (differentiate between young and adult livestock, unit price obtained from research data) | 0.138 |
| Annual household income | F2 | The sum of farm income, wage income, financial income (direct grain subsidy, old-age insurance, low-income insurance, social security), subsidies for retired farming and other income (medicine collection, etc.) in one year | 0.063 | |
| Annual household expenditure | F3 | Sum of children’s school fees, food consumption, gift expenditure, health expenditure, consumption of durable goods and consumption of daily necessities, etc. in one year | 0.001 |
| Well-being dimension | Indicator | Symbol | Indicator assignment | Weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labor Force Condition (FL) |
Household size | F1 | Number of farm household members | 0.052 |
| Household labor capacity | F2 | Assignment according to age, where 6 years and below = 0; 7–18 years = 1; 18–25 years = 2; 26–45 years = 5; 46–60 years = 4; 60 years and above (including military/students aged between 19–60) = 3 | 0.059 | |
| Educational attainment of labor force | F3 | No formal education (little literacy) = 0; elementary school = 1; junior high school = 2; high school, junior college = 3; college or senior college = 4; university undergraduate and above = 5 | 0.092 | |
| Number of people engaged in noncultivated agriculture | F4 | Assigned according to the nature of employment, where farming = 0; farming + other employment = 1; other employment = 2 | 0.112 | |
| Wealth Level (WL) |
Annual household income | T1 | Sum of agricultural income, wage income, financial income (direct food subsidy, old-age insurance, low-income insurance, social security), fallowing subsidy, and other income (medicine picking, etc.) in one year | 0.152 |
| Annual household expenditure | T2 | Sum of children’s school fees, food consumption, gift expenditure, health expenditure, consumption of durable goods, consumption of daily necessities, etc., in one year | 0.102 | |
| Arable land per capita | T3 | Arable land/total population | 0.109 | |
| Housing area per capita | T4 | Average housing area per capita | 0.028 | |
| Ecological Environment Quality (EQ) |
Water safety | Z1 | Assigned according to farmers’ perception of changes in water pollution after fallowing, strong = 0; constant = 1; diminished = 2 | 0.039 |
| Air safety | Z2 | Assigned according to farmers’ perception of whether air quality has improved after fallowing, worse = 0; no change = 1; better = 2 | 0.020 | |
| Soil and water conservation | Z3 | Assigning values according to whether farmers’ soil erosion has improved after fallowing, severe = 0; no change = 1; improved = 2 | 0.021 | |
| Soil safety | Z4 | Assigned according to whether the farmer is serious about soil contamination after fallowing, serious = 0; not serious = 1 | 0.011 | |
| Social Conditions (SC) |
Traffic accessibility | S1 | Distance of farm households from the nearest road | 0.141 |
| Resource accessibility | S2 | Distance of farm households to the nearest hospital or school | 0.054 | |
| Policy satisfaction | S3 | Assignment of values according to whether farmers are willing to participate in the grain for green policy, where indifferent = 0; very unwilling = 1; not very willing = 2; average = 3; very willing = 4 | 0.011 |
| Livelihood assets | Returned farmland households | Nonreturned farmland households | All farm households | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asset level | Contribution rate % | Asset level | Contribution rate % | Asset level | Contribution rate % | ||
| Human assets | Household size | 0.010 | 14.97 | 0.010 | 14.30 | 0.010 | 14.76 |
| Educational attainment of household members | 0.041 | 61.43 | 0.044 | 62.26 | 0.042 | 61.69 | |
| Household labor capacity | 0.016 | 23.60 | 0.017 | 23.43 | 0.016 | 23.55 | |
| Natural assets | Area of arable land | 0.044 | 13.38 | 0.046 | 9.61 | 0.045 | 11.92 |
| Area of watered land | 0.285 | 86.21 | 0.428 | 90.06 | 0.328 | 87.69 | |
| Area returned to farming | 0.001 | 0.41 | 0.002 | 0.34 | 0.001 | 0.38 | |
| Physical assets | Residential index | 0.005 | 26.54 | 0.005 | 28.11 | 0.005 | 27.04 |
| Number of large production tools | 0.013 | 73.46 | 0.014 | 71.90 | 0.013 | 72.96 | |
| Social assets | Number of public officials among relatives | 0.280 | 85.30 | 0.315 | 87.74 | 0.290 | 86.09 |
| Number of channels for outworking | 0.025 | 7.48 | 0.022 | 5.99 | 0.024 | 7.00 | |
| Number of social contacts | 0.024 | 7.22 | 0.023 | 6.27 | 0.023 | 6.91 | |
| Financial assets | Total value of livestock | 0.143 | 69.31 | 0.127 | 65.69 | 0.138 | 68.26 |
| Annual household income | 0.062 | 30.30 | 0.066 | 33.90 | 0.063 | 31.34 | |
| Annual household expenditure | 0.001 | 0.39 | 0.001 | 0.41 | 0.001 | 0.39 | |
| Indicator | Returned farmland households | Nonreturned farmland households | All farm households | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Well-being level | Contribution rate % | Well-being level | Contribution rate % | Well-being level | Contribution rate % | ||
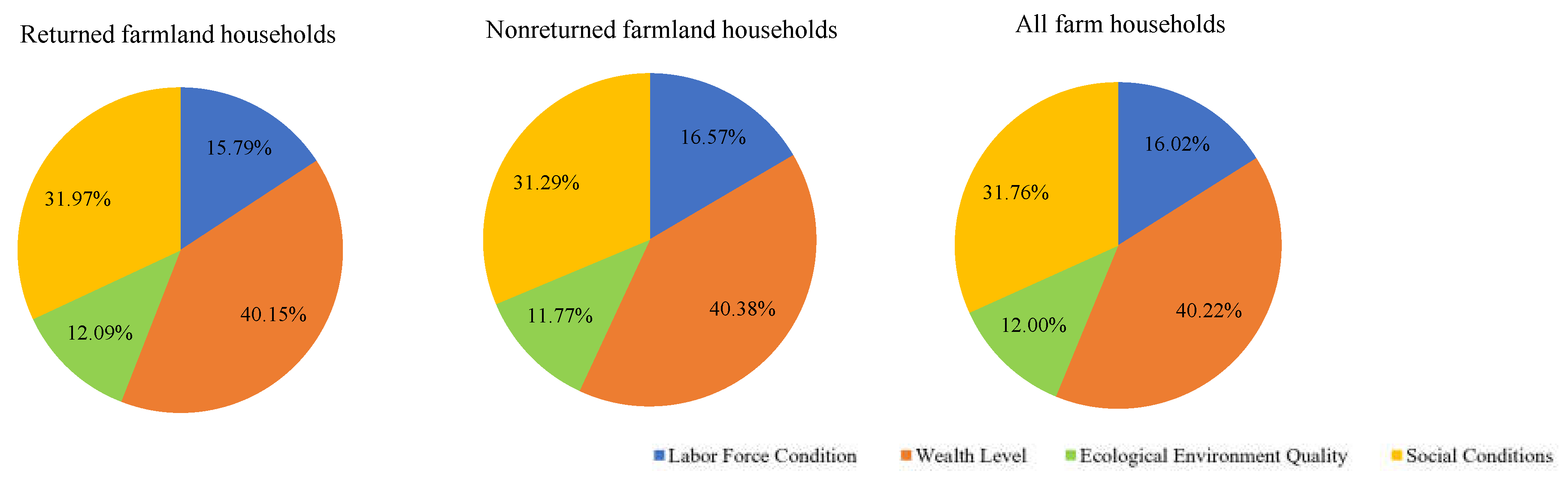
| Labor Force Condition | Household size | 0.014 | 17.51 | 0.016 | 18.36 | 0.015 | 17.78 |
| Household labor capacity | 0.017 | 20.78 | 0.018 | 21.49 | 0.017 | 21.00 | |
| Educational attainment of labor force | 0.023 | 27.61 | 0.024 | 28.11 | 0.023 | 27.76 | |
| Number of people engaged in noncultivated agriculture | 0.028 | 34.10 | 0.027 | 32.04 | 0.028 | 33.46 | |
| Wealth level | Annual household income | 0.008 | 3.62 | 0.007 | 3.55 | 0.008 | 3.60 |
| Annual household expenditure | 0.091 | 43.48 | 0.089 | 43.36 | 0.090 | 43.44 | |
| Arable land per capita | 0.102 | 48.78 | 0.100 | 48.36 | 0.101 | 48.65 | |
| Housing area per capita | 0.009 | 4.12 | 0.010 | 4.73 | 0.009 | 4.30 | |
| Ecological environment Quality | Water safety | 0.022 | 34.66 | 0.020 | 33.68 | 0.021 | 34.37 |
| Air safety | 0.018 | 28.28 | 0.017 | 27.87 | 0.018 | 28.16 | |
| Soil and water conservation | 0.013 | 20.01 | 0.013 | 20.73 | 0.013 | 20.22 | |
| Soil safety | 0.011 | 17.04 | 0.011 | 17.72 | 0.011 | 17.24 | |
| Social conditions | Traffic accessibility | 0.117 | 70.39 | 0.114 | 71.53 | 0.116 | 70.73 |
| Resource accessibility | 0.039 | 23.71 | 0.036 | 22.40 | 0.038 | 23.33 | |
| Policy satisfaction | 0.010 | 5.89 | 0.010 | 6.07 | 0.010 | 5.95 | |
| Impact factor | All farm households | Returned farmland households | Nonreturned farmland households | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard coefficient | Sig. | Standard coefficient | Sig. | Standard coefficient | Sig. | |
| Household size | 0.366*** | 0.000 | 0.345*** | 0.000 | 0.392*** | 0.000 |
| Educational attainment of household members | 0.323*** | 0.000 | 0.305*** | 0.000 | 0.415*** | 0.000 |
| Household labor capacity | 0.166*** | 0.010 | 0.203** | 0.015 | 0.156 | 0.128 |
| Area of arable land | −0.208*** | 0.000 | −0.19*** | 0.000 | −0.199*** | 0.000 |
| Area of watered land | 0.034 | 0.343 | 0.042 | 0.380 | −0.012 | 0.813 |
| Area returned to farming | −0.048 | 0.097 | −0.035 | 0.317 | — | — |
| Residential index | 0.015 | 0.603 | 0.053 | 0.145 | -0.044 | 0.379 |
| Number of large production tools | 0.086*** | 0.005 | 0.035 | 0.376 | 0.116** | 0.021 |
| Number of public officials among relatives | 0.026 | 0.395 | 0.017 | 0.659 | −0.008 | 0.867 |
| Number of channels for outworking | 0.009 | 0.767 | 0.014 | 0.688 | −0.030 | 0.540 |
| Number of social contacts | −0.005 | 0.862 | −0.056 | 0.146 | 0.067 | 0.180 |
| Total value of livestock | 0.064** | 0.034 | 0.076** | 0.034 | 0.081 | 0.106 |
| Annual household income | 0.055 | 0.091 | 0.081** | 0.034 | 0.056 | 0.344 |
| Annual household expenditure | 0.157*** | 0.000 | 0.222*** | 0.000 | 0.071 | 0.179 |
| Livelihood diversity | 0.107*** | 0.003 | 0.091** | 0.047 | 0.149*** | 0.009 |
| Constant | — | 0.000 | — | 0.000 | — | 0.000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




