Submitted:
21 June 2023
Posted:
23 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical analysis and research hypothesis
3. Research design
3.1. Regression model
3.2. Variable description
3.2.1. Indicators of regional high-quality development level
| First Level Indicators | Second Level Indicators | Third Level Indicators | Specific Indicators |
|---|---|---|---|
| High-quality development level (hqd) | Innovation (Z1) | The vitality of technological innovation (Z11): | Total number of full-time R&D employees Z11 |
| Technology research and development capability (Z12): | Number of invention patents authorized Z12 | ||
| Technology transformation capability (Z13): | High-tech industry’s development degree (Main Business Income/GDP) Z13 | ||
| Coordination (Z2) | The coordination of regional industrial structure(Z21): | Industrial structure rationalization index Z21 | |
| The coordination between urban and rural areas(Z22): | The ratio of rural income to urban income Z22 | ||
| Greenness (Z3) | Basic environmental change degree (Z31-34): |
Population-weighted concentrations of PM2.5 Z31; The average value of GDP per unit of energy consumption Z32; Comprehensive utilization rate of industrial solid waste Z33; Regional sewage recycling rate Z34 |
|
| The level of green technology development (Z35): | The regional granted number of green invention patents Z35 | ||
| Openness (Z4) | External attractiveness (Z41): | The regional actual scale of foreign capital utilized Z41 | |
| Degree of marketization (Z42): | Marketization Index by region Z42 | ||
| The development of ICT(Z43): | Regional Internet penetration rate Z43 | ||
| Sharing (Z5) | People’s quality of life (Z51): | Consumption level of regional residents Z51 | |
| Social civilization level (Z52): | Number of college students per unit of population in the region Z52 | ||
| Life and health security (Z53-54): | Number of hospital beds per ten thousand people in the region Z53; Number of practicing (assistant) physicians per ten thousand people in the region Z54 |
||
| Basic social security (Z55-57): | Utilization rate of labor resources Z55; Percentage of medical insurance cover Z56; Percentage of unemployment insurance cover Z57 |
3.2.2. The level of government expenditure on people’s livelihood
3.2.3. Indicators for measuring urbanization level
3.2.4. Description of control variables
3.3. Data sources
| VarName | Obs | Mean | Median | SD | Min | Max |
| hqd | 390 | 0.379 | 0.372 | 0.108 | 0.166 | 0.706 |
| Innovation | 390 | 0.162 | 0.108 | 0.159 | 0.005 | 0.958 |
| Coordination | 390 | 0.519 | 0.520 | 0.166 | 0.000 | 0.911 |
| Greenness | 390 | 0.449 | 0.448 | 0.092 | 0.249 | 0.815 |
| Openness | 390 | 0.385 | 0.356 | 0.159 | 0.106 | 0.805 |
| Sharing | 390 | 0.339 | 0.330 | 0.133 | 0.088 | 0.845 |
| ms | 390 | 6.667 | 6.787 | 0.774 | 4.098 | 8.351 |
| com | 390 | 1.207 | 1.023 | 0.708 | 0.380 | 4.250 |
| urb | 390 | 0.541 | 0.524 | 0.136 | 0.275 | 0.896 |
| cu | 390 | 0.365 | 0.365 | 0.062 | 0.218 | 0.542 |
| gdp | 390 | 0.133 | 0.121 | 0.063 | -0.040 | 0.298 |
| fdi | 390 | 0.109 | 0.072 | 0.132 | 0.000 | 0.851 |
| energy | 390 | 1.060 | 0.904 | 0.613 | 0.224 | 4.142 |
| rd | 390 | 2.164 | -0.192 | 7.604 | -0.946 | 66.562 |
| patent | 390 | 1.223 | 0.449 | 2.459 | 0.036 | 21.810 |
| upd | 390 | 0.280 | 0.258 | 0.122 | 0.060 | 0.631 |
4. Regression analysis
4.1. Evaluation of Indicator Measurements
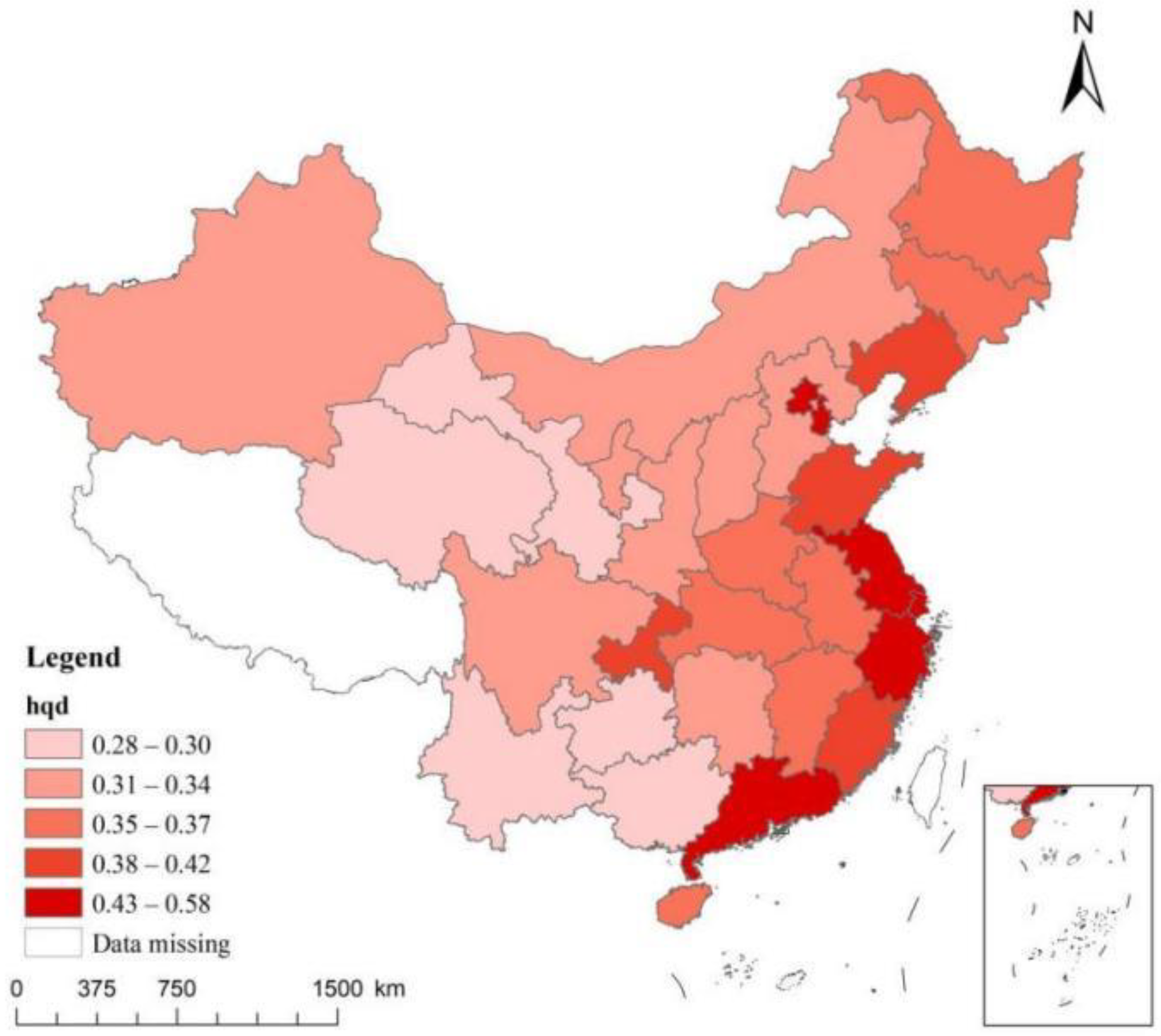
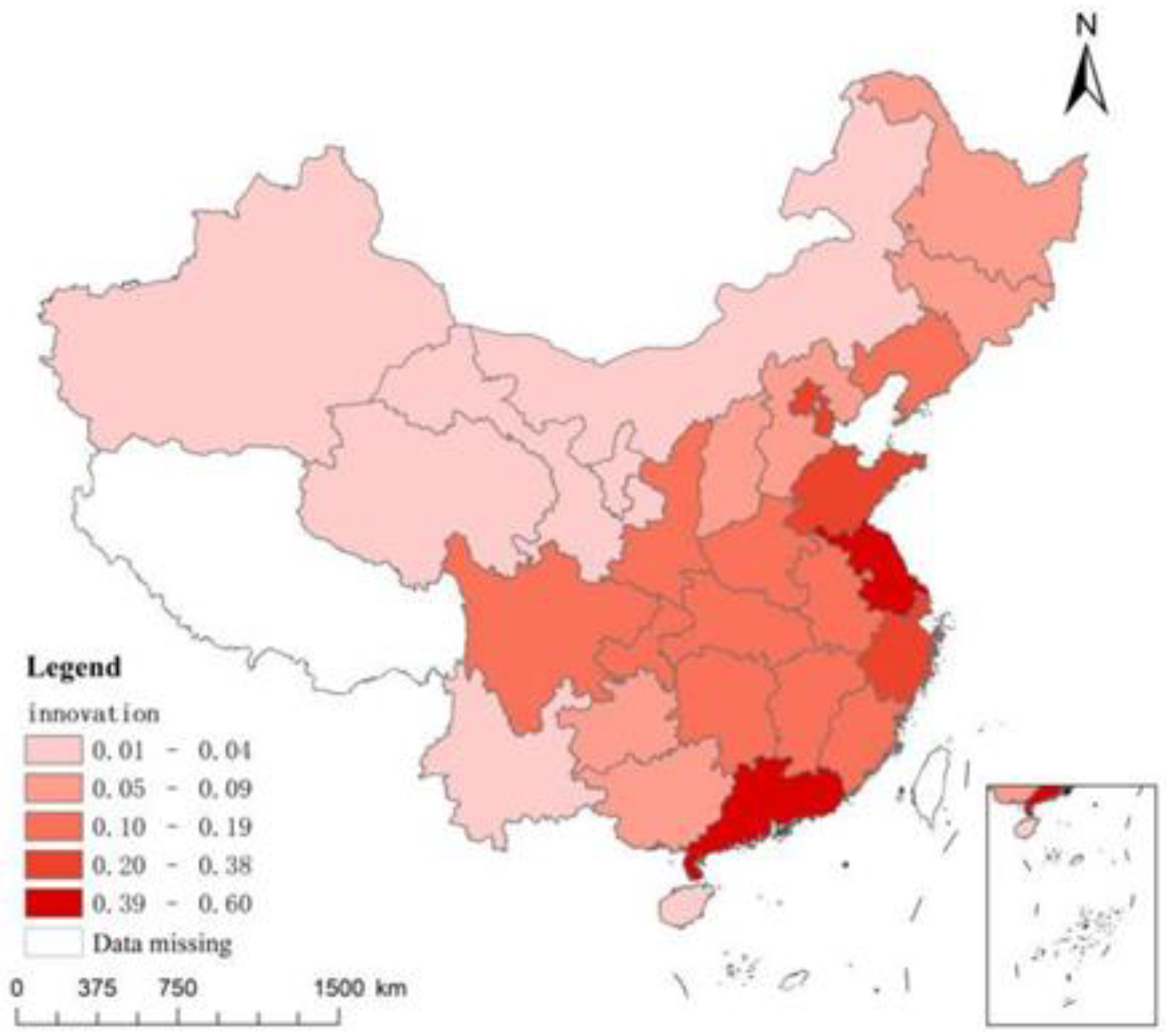
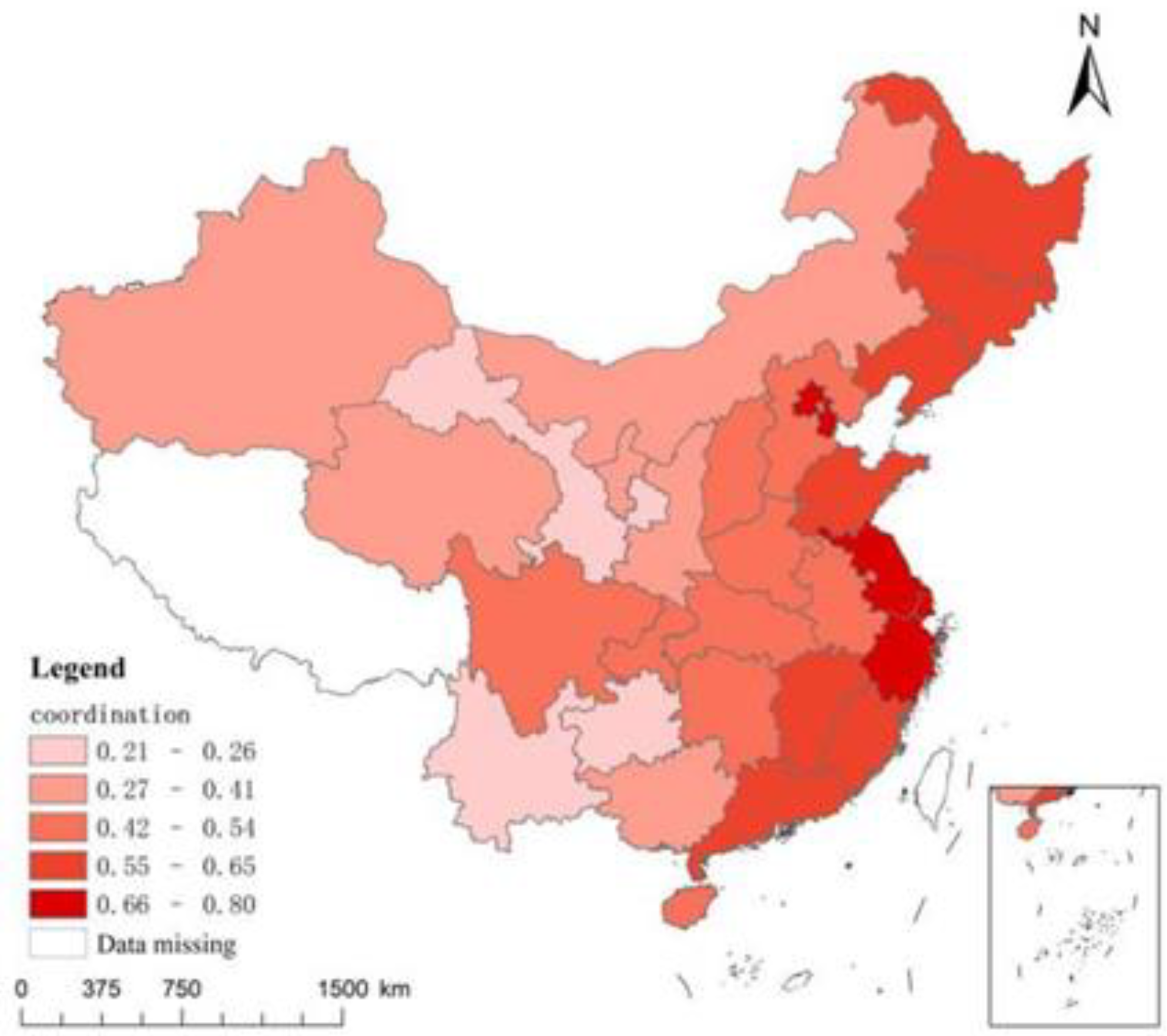
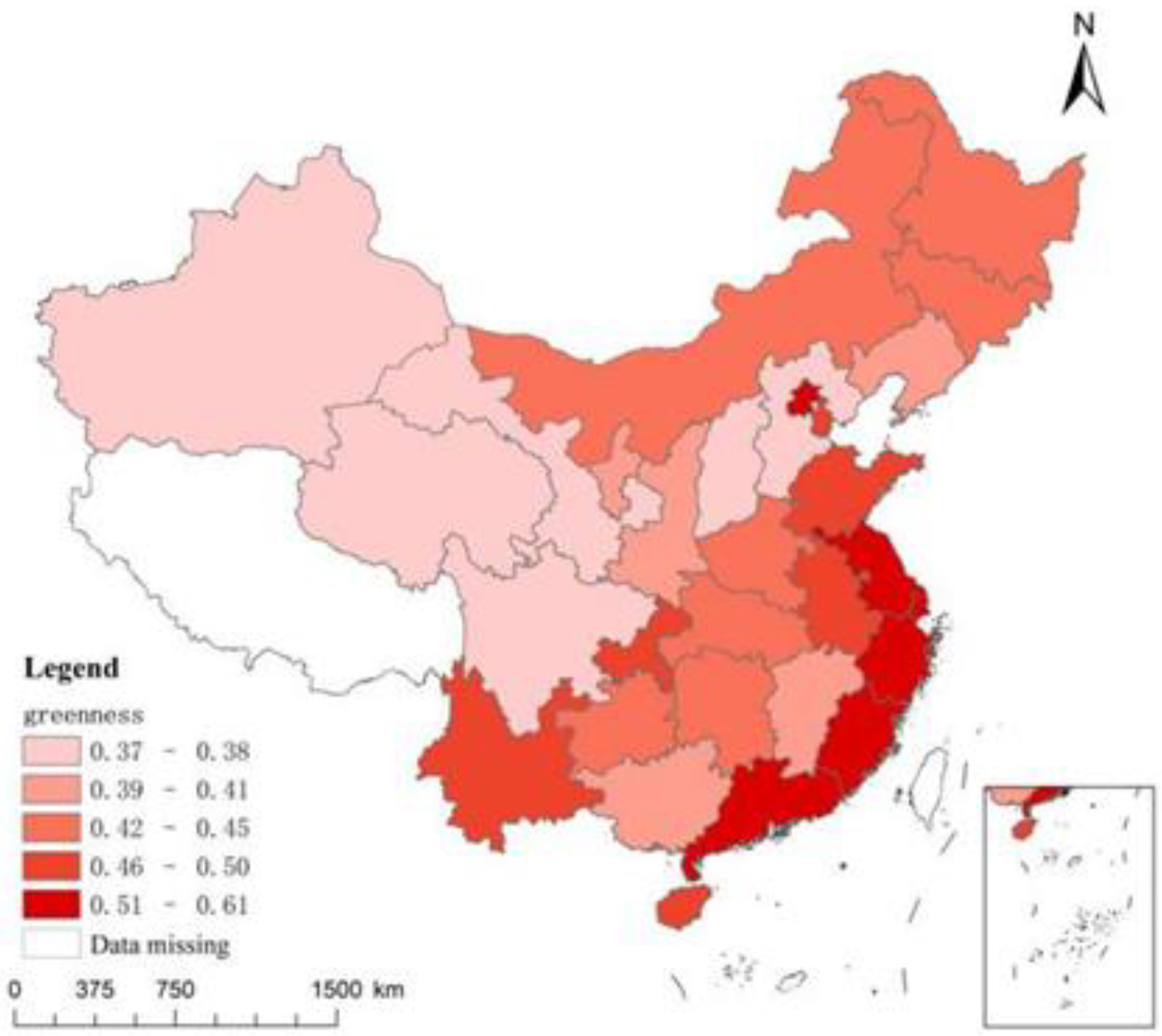
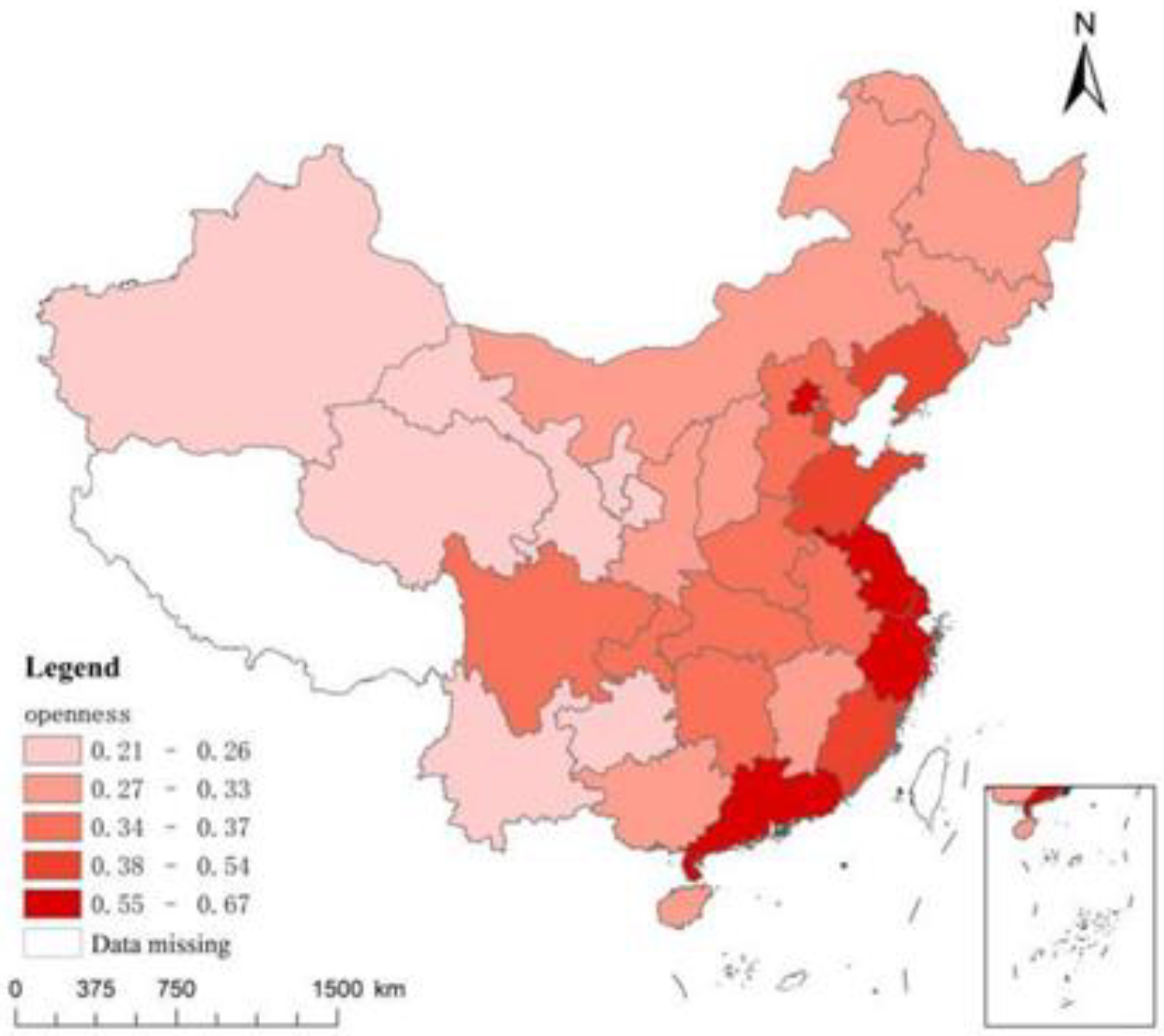
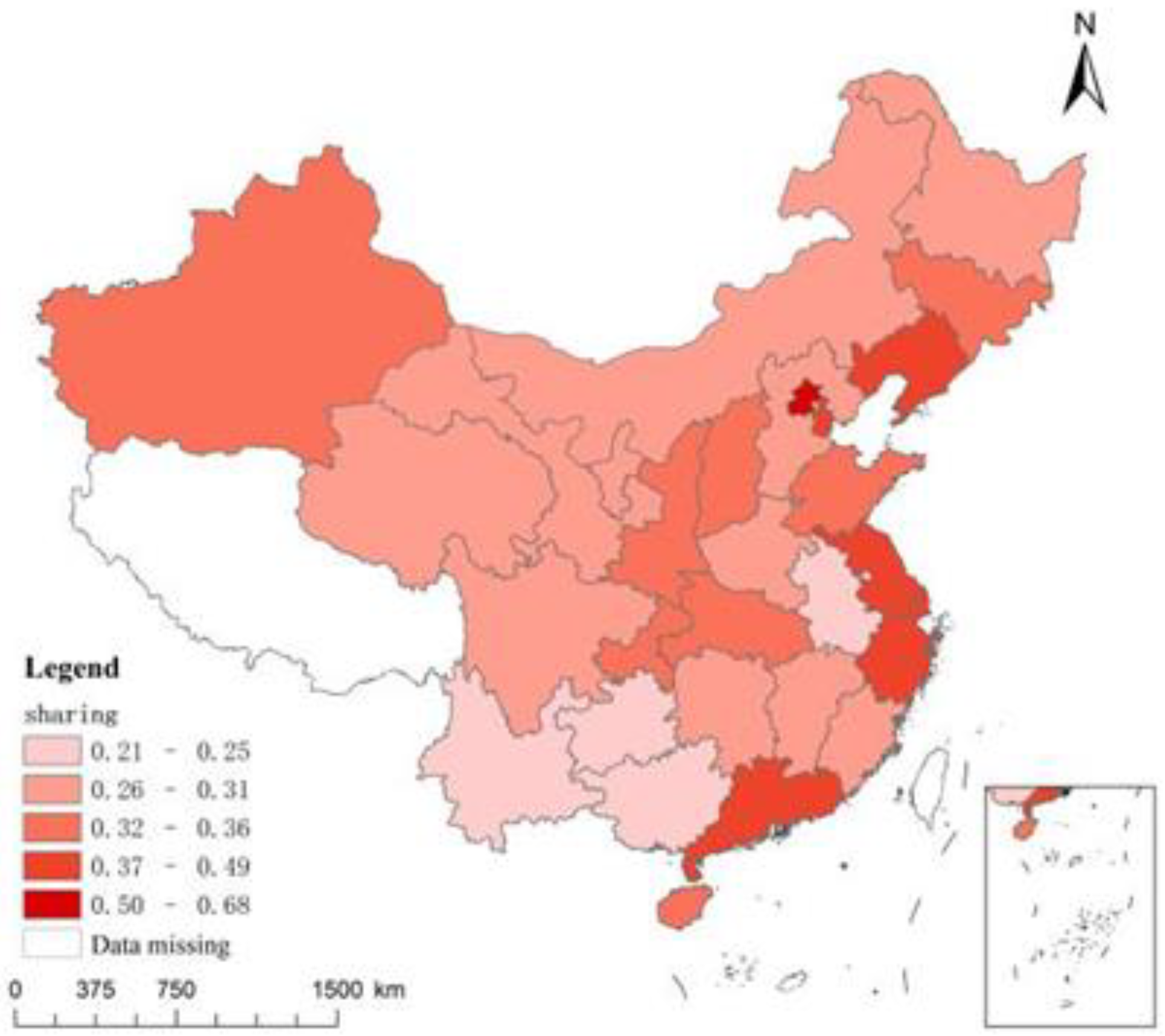
4.2. Baseline regression analysis
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | |
| hqd | hqd | hqd | hqd | hqd | |
| ms | 0.102*** | 0.095*** | 0.067*** | 0.107*** | 0.089*** |
| (0.005) | (0.005) | (0.009) | (0.005) | (0.011) | |
| gdp | -0.073*** | -0.089*** | -0.017 | -0.066*** | -0.012 |
| (0.024) | (0.026) | (0.036) | (0.024) | (0.034) | |
| energy | -0.016** | -0.023*** | -0.011* | -0.012 | -0.002 |
| (0.007) | (0.007) | (0.006) | (0.008) | (0.006) | |
| rd | 0.002*** | 0.002*** | 0.001*** | 0.002*** | 0.000 |
| (0.001) | (0.001) | (0.000) | (0.001) | (0.000) | |
| patent | 0.010*** | 0.011*** | 0.006*** | 0.010*** | 0.004*** |
| (0.001) | (0.001) | (0.001) | (0.001) | (0.001) | |
| fdi | -0.008 | 0.020 | 0.050** | -0.023 | 0.022 |
| (0.023) | (0.024) | (0.019) | (0.023) | (0.019) | |
| upd | 0.034 | 0.021 | 0.003 | 0.040* | 0.019 |
| (0.023) | (0.024) | (0.019) | (0.024) | (0.019) | |
| constant | -0.303*** | -0.242*** | -0.093* | -0.337*** | -0.234*** |
| (0.044) | (0.043) | (0.053) | (0.044) | (0.063) | |
| Individual fixed | NO | NO | NO | YES | YES |
| Time fixed | NO | NO | YES | NO | YES |
| 0.067*** | |||||
| (0.009) | |||||
| 0.022*** | |||||
| (0.001) | |||||
| R2 | 0.946 | 0.911 | 0.948 | ||
| Wald Test | 3684.90*** | 3141.59*** | |||
| Observations | 390 | 390 | 390 | 390 | 390 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | |
| Innovation | Coordination | Greenness | Openness | Sharing | hqd | hqd | hqd | |
| ms | 0.142*** | 0.091*** | 0.087*** | 0.020 | 0.102*** | 0.031*** | 0.036*** | 0.089*** |
| (0.025) | (0.021) | (0.017) | (0.014) | (0.016) | (0.005) | (0.005) | (0.011) | |
| constant | -0.789*** | -0.131 | -0.127 | 0.090 | -0.328*** | 0.258*** | 0.218*** | -0.227*** |
| (0.147) | (0.122) | (0.100) | (0.084) | (0.094) | (0.041) | (0.042) | (0.065) | |
| control | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Individual fixed | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Time fixed | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Observations | 390 | 390 | 390 | 390 | 390 | 360 | 360 | 360 |
| R2 | 0.561 | 0.809 | 0.845 | 0.938 | 0.939 | 0.807 | 0.806 | 0.945 |
4.3. Heterogeneity analysis
| 2006-2012 | 2013-2018 | |
| hqd | hqd | |
| ms | 0.019* | 0.133*** |
| (0.010) | (0.024) | |
| constant | 0.153** | -0.477*** |
| (0.060) | (0.165) | |
| control | YES | YES |
| Individual fixed | YES | YES |
| Time fixed | YES | YES |
| R2 | 0.936 | 0.908 |
| Observations | 210 | 180 |
| (The Eastern) | (The Central) | (The Western) | |
| hqd | hqd | hqd | |
| ms | 0.093*** | 0.070** | 0.061*** |
| (0.023) | (0.027) | (0.014) | |
| constant | -0.257* | -0.134 | -0.044 |
| (0.132) | (0.150) | (0.075) | |
| control | YES | YES | YES |
| Individual fixed | YES | YES | YES |
| Time fixed | YES | YES | YES |
| R2 | 0.937 | 0.978 | 0.974 |
| Observations | 143 | 104 | 143 |
4.4. Analysis of the mediating effect
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | |
| com | hqd | Innovation | Coordination | Greenness | Openness | Sharing | |
| ms | 0.472*** | 0.081*** | 0.088*** | 0.075*** | 0.094*** | 0.066*** | 0.098*** |
| (0.034) | (0.006) | (0.013) | (0.013) | (0.009) | (0.010) | (0.010) | |
| com | 0.055*** | 0.007 | 0.067*** | -0.010 | 0.107*** | 0.101*** | |
| (0.008) | (0.017) | (0.016) | (0.011) | (0.012) | (0.013) | ||
| constant | -2.163*** | -0.219*** | -0.524*** | -0.056 | -0.177*** | -0.206*** | -0.375*** |
| (0.275) | (0.044) | (0.093) | (0.088) | (0.060) | (0.067) | (0.070) | |
| control | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Individual fixed | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Time fixed | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| R2 | 0.897 | 0.922 | 0.529 | 0.713 | 0.841 | 0.886 | 0.901 |
| Observations | 390 | 390 | 390 | 390 | 390 | 390 | 390 |
| Sobel test | 0.026*** | 0.003 | 0.031*** | -0.005 | 0.050*** | 0.048*** | |
| (0.004) | (0.009) | (0.008) | (0.005) | (0.007) | (0.007) | ||
| Bootstrap test | 0.026*** | 0.003 | 0.031*** | -0.005 | 0.050*** | 0.048*** | |
| (0.004) | (0.011) | (0.007) | (0.006) | (0.009) | (0.005) |
4.5. Analysis of the moderating effect
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |
| hqd | hqd | hqd | hqd | |
| ms | 0.089*** | 0.046*** | 0.016 | 0.056*** |
| (0.011) | (0.011) | (0.013) | (0.011) | |
| urb | 0.540*** | 0.102 | 0.102 | |
| (0.063) | (0.118) | (0.118) | ||
| urb×ms | 0.074*** | |||
| (0.017) | ||||
| c_urb×ms | 0.074*** | |||
| (0.017) | ||||
| constant | -0.234*** | -0.268*** | -0.069 | -0.069 |
| (0.063) | (0.057) | (0.072) | (0.072) | |
| control | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Individual fixed | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Time fixed | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| R2 | 0.948 | 0.957 | 0.960 | 0.960 |
| Observations | 390 | 390 | 390 | 390 |
5. Conclusions and Implications
Funding
References
- Cheng, Cecilia, Wang,Hsin-yi, & Ebrahimi,Omid V. Adjustment to a “New Normal:” Coping Flexibility and Mental Health Issues During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Frontiers in Psychiatry 2021, 12. [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Qu, X. Export Trade, Absorptive Capacity, and High-Quality Economic Development in China. Systems 2023, 11, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakker V, Bakshi B R. Toward sustainable circular economies: A computational framework for assessment and design. Journal of Cleaner Production 2021, 295, 126353. [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, R. D., & Wu, J. J. The 2017 state new economy index. Ssrn Electronic Journal 2017. [CrossRef]
- P Bolcárová, & KolosTa, S. Assessment of sustainable development in the eu 27 using aggregated sd index. Ecological Indicators 2015, 48, 699–705. [CrossRef]
- Held, B., Rodenhaeuser, D., Diefenbacher, H., & Zieschank, R. The national and regional welfare index (nwi/rwi): redefining progress in germany. Ecological Economics 2018, 145, 391–400. [CrossRef]
- Pearce DW, Turner RK, Turner RK. Economics of natural resources and the environment. Johns Hopkins University Press; 1990.
- Jin Bei. Study on the “High-Quality Development” Economics. China Industrial Economics 2018, 5-18. Available online at: https://www.emerald.com/insight/content/doi/10.1108/CPE-10-2018-016/full/html?utm_source=TrendMD&utm_medium=cpc&utm_campaign=China_Political_Economy_TrendMD_1.
- M Mlachila, R Tapsoba, SJA Tapsoba. A Quality of Growth Index for Developing Countries: A Proposal. Social Indicators Research 2017, 134, 675–710. [CrossRef]
- Butkiewicz, J. L., & Yanikkaya, H. Institutional quality and economic growth: maintenance of the rule of law or democratic institutions, or both? Economic Modelling 2016, 23, 648–661. [CrossRef]
- Khalfaoui H, Derbali A. Quality of human capital accumulation, higher education graduates and economic growth: a comparative analysis between BRICS, Southeast Asian and MENA countries. Human Systems Management 2020, 40, 723–735. [CrossRef]
- Meng, JL. Economic Growth Effect of Public Health Investment and Its Impact on Living Environment. Journal of environmental and public health 2022, 2192255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Lingming, Wenzhong Ye, Congjia Huo, & Kieran James. Environmental Regulations, the Industrial Structure, and High-Quality Regional Economic Development: Evidence from China. Land 2020, 9, 517. [CrossRef]
- Liu, P., Zhao, Y., Zhu, J., and Yang, C. (2022). Technological industry agglomeration, green innovation efficiency, and development quality of city cluster. Green Finance 2013, 4, 411–435. [CrossRef]
- Yaya, Keho. The impact of trade openness on economic growth: The case of Cote d’Ivoire. Cogent Economics & Finance 2017, 5. [CrossRef]
- Bekhet, H. A., & Latif, N. The impact of technological innovation and governance institution quality on malaysia’s sustainable growth: evidence from a dynamic relationship. Technology in Society 2018, 54, 27–40. [CrossRef]
- Gangqiang Yang, Yongyu Xue. & Yuxi Ma. Social Organization Participation, Government Governance and the Equalization of Basic Public Services: Evidence from China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2019, 16, 2996. [CrossRef]
- Hari Nugroho, N. Haidy Ahmad Pasay, Arie Damayanti, Maddaremmeng A. Panennungi. Institutions as the Main Determinant in Economic Growth. Etikonomi 2019, 18, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sineviciene, L. , & Vasiliauskaite, A. Fiscal policy interaction with private investment: the case of the baltic states. Inzinerine Ekonomika Engineering Economics 2012, 23, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo S J, Jiang T Y. China’s "New Normal": from Social Control to Social Governance. Journal of Chinese Political Science 2017, 22, 327–340. [CrossRef]
- Liu, J. Y. Analysis of the synergistic impacts of public services expenditure on economic growth and social equity. International Conference on Management Science & Engineering. IEEE 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easterly W, Rebelo S T. Fiscal Policy and Economic Growth: An Empirical Investigation. Journal of Monetary Economics 1993, 32, 417–458. [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, C. . Is There a Trade-Off between Employment and Growth? Oxford Economic Papers-New Series 1997, 49, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellettini G, Ceroni C B. Social security expenditure and economic growth: an empirical assessment. Research in Economics 2000, 54, 249–275. [CrossRef]
- Sugata, Ghosh, Udayan, et al. Fiscal policy, long-run growth, and welfare in a stock-flow model of public goods. Canadian Journal of Economics/Revue Canadienne Déconomique 2004, 27, 742–756. [CrossRef]
- Bosi, S., & Laurent, T. Health, growth and welfare: a theoretical appraisal of the long-run impact of medical R&D. Asia-Pacific Journal of Accounting & Economics 2011, 18. [CrossRef]
- Railaite, R., Ciutiene, R. The Impact of Public Health Expenditure on Health Component of Human Capital. Inzinerine Ekonomika Engineering Economics 2020, 31, 371–379. [CrossRef]
- Li Zhuangyuan. The Role of Public Services in China’s Economic Growth: Based on Population Structure and Population Aggregation. Population Research Available online at: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&dbname=CJFDLAST2020&filename=RKYZ202005007&uniplatform=NZKPT&v=5iSLgmb6sLgl6EkycTE5UZlYR2Gc-54CifEIFOxat3FEMEyAXvIBcOGpPTrj7nEX. 2020, 44, 92–107.
- Musgrave, R.A. The Theory of Public Finance; McGraw-Hill Book Company: New York, 1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modigliani F, Shi L C. The Chinese Saving Puzzle and the Life-Cycle Hypothesis. Journal of economic literature 2004, 42, 145–170. [CrossRef]
- Chao, C., C., Laffargue, J., & P., et al. The chinese saving puzzle and the life-cycle hypothesis: a revaluation. China Economic Review 2011, 22, 108–120. [CrossRef]
- Kassiola, J.J. Coordinated Rural–Urban Development in China: a New Social Spatial Reorganization Plan for Urbanization, Migration, and Rural Development. Journal of Chinese Political Science 2017, 22, 77–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siuskaite, D., Pilinkiene, V., Zvirdauskas, D. The Conceptualization of the Sharing Economy as a Business Model. Inzinerine Ekonomika Engineering Economics 2019, 30, 373–381. [CrossRef]
- Ha Minh N, Le Dang N. The relationship between urbanization and economic growth: An empirical study on ASEAN countries. International Journal of Social Economics 2018, 45, 00–00. [CrossRef]
- Bertinelli, L., & Black, D. Urbanization and growth. Journal of Urban Economics 2004, 56, 80–96. [CrossRef]
- Lin B, Zhu J. Energy and carbon intensity in China during the urbanization and industrialization process: A panel VAR approach. Journal of Cleaner Production 2017, 168, 780–790. [CrossRef]
- Bakirtas, Tahsin, Akpolat, Ahmet, & Gokce. The relationship between energy consumption, urbanization, and economic growth in new emerging-market countries. Energy Oxford 2018, 147, 110–121. [CrossRef]
- Zhang Y J, Liu Z, Zhang H, et al. The impact of economic growth, industrial structure and urbanization on carbon emission intensity in China. Natural Hazards 2014, 73, 579–595. [CrossRef]
- Zhou H L, and Li X S. Tobit model estimation method and application. Economic Perspectives 2012, 615, 105–119.
- Baron, R. M. & Kenny, D. A. The Moderator-mediator Variable Distinction in Social Psychological Research: Conceptual. Strategic and Statistical Considerations. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 1986, 51, 1173–1182. [CrossRef]
- Wen Z L, Zhang L, Hou J T, et al. Testing and application of the mediating effects. Acta Psychologica Sinica 2004, 614–620.
- Zhang Junkuo, Hou Yongzhi, Liu Peilin, et al. The Target Requirement and Strategic Path of High Quality Development. Management World Available online at: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&dbname=CJFDLAST2019&filename=GLSJ201907003&uniplatform=NZKPT&v=tI3YudqOkuK3SuOTUvsMh1 sPa8aTSsGIf1eIxkOC5L6Fgp0f3gytenlbQuF9okyZ. 2019, 35, 1–7.
- Ding, Lin, et al. A Comprehensive Evaluation of Urban Sustainable Development in China Based on the Topsis-Entropy Method. Sustainability 2016, 8, 746. [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y., Jia, S., Liao, J., and Yang, X. Evaluation of Urban High quality Development Level Based on Entropy Weight-TOPSIS Two step Method. Journal of Economic Analysis 2022, 1, 50–65.
| 1 | The specific method is given by following formula: |
| 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





