Submitted:
22 May 2023
Posted:
23 May 2023
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- a.
- The research method used was qualitative research with a descriptive approach using purposive sampling and snowball sampling techniques. The purposive sampling technique is to select research locations and stakeholders involved in forest management. While the snowball sampling technique is a sampling technique that is carried out by following a snowball pattern, starting with village leaders, then community leaders so that the information obtained is accurate regarding biophysical conditions, and forest damage and then the search for information will stop if the informant provides the same information as previous informants by the research objectives. The data was collected through in-depth interviews with informants and observing people's daily lives as well as forest damage and the causes of the damage.
- b.
- The data collected is in the form of primary data and secondary data. Primary data is in the form of interviews with informants about forest damage, secondary data includes village profiles and potential, and information retrieval from scientific journal references to complement primary data. Data collection techniques through interviews, observation and literature studies. Interviews, namely data collection techniques through question and answer with informants about forest damage, documentation, namely methods of collecting data by looking at the activities that cause damage and taking pictures of damaged areas and studying documents from the village office and at the FMU office
- c.
-
Spatial analysis
-
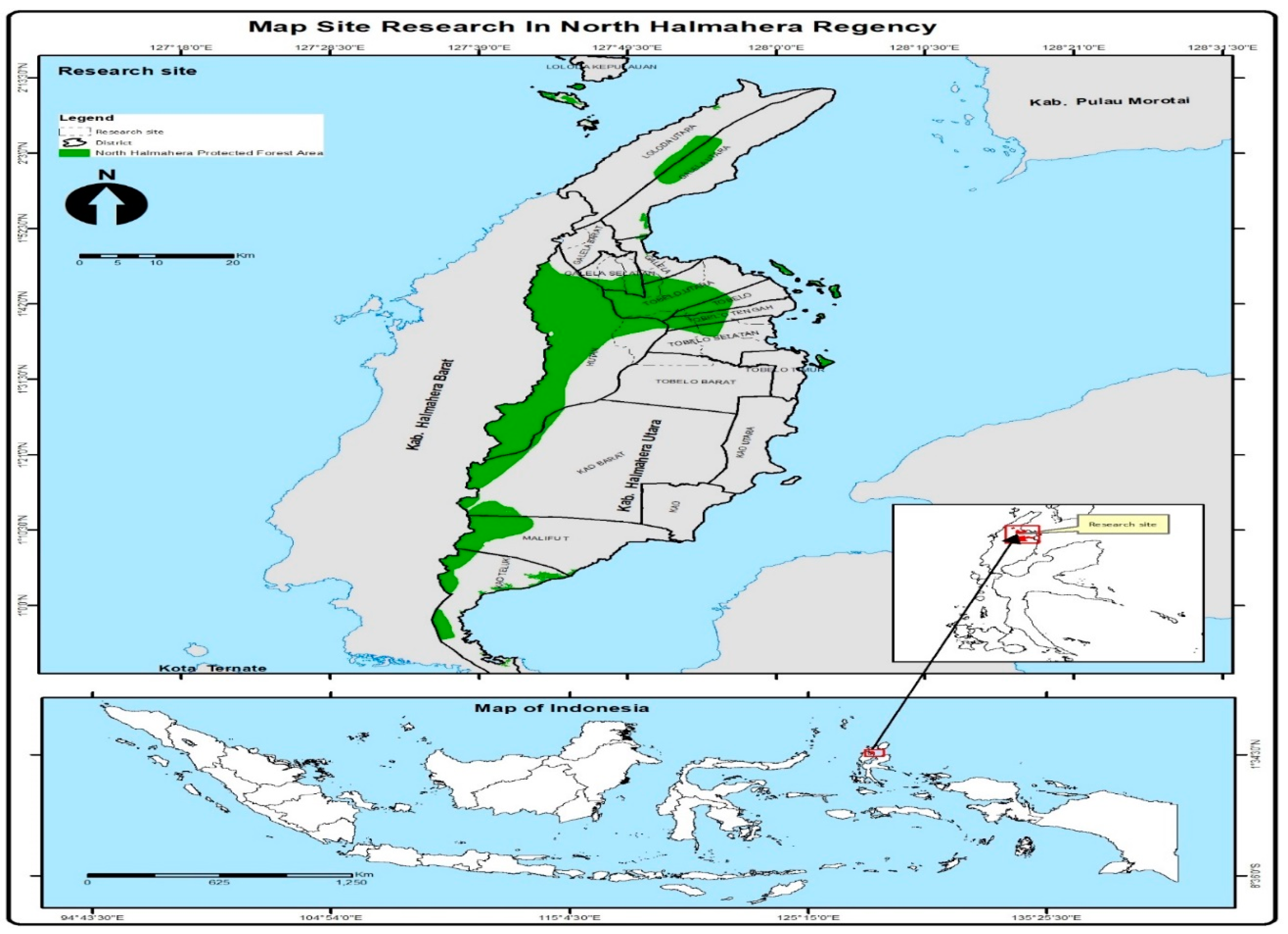
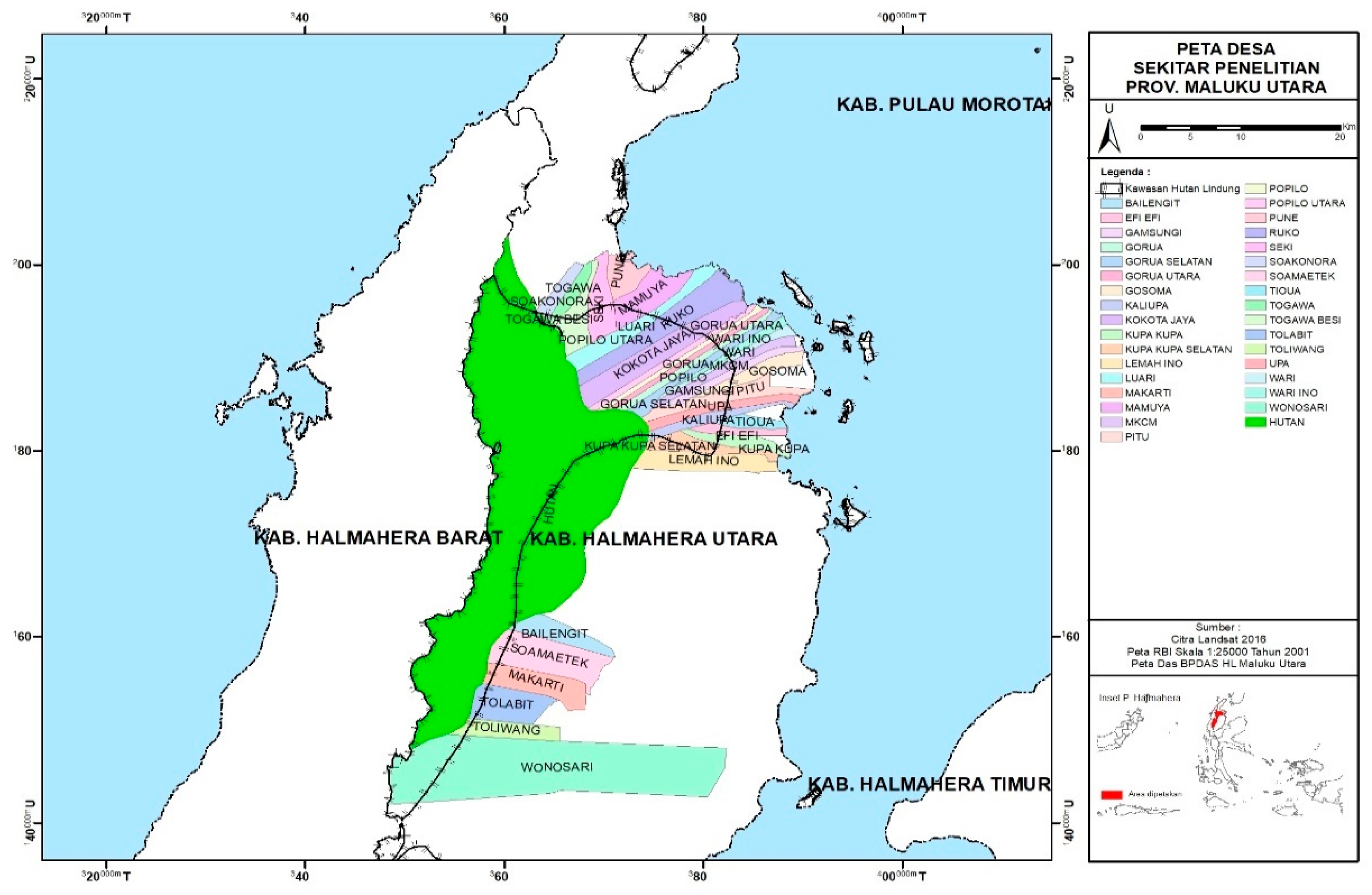
Changes in land coverTools and materials. The tools and materials used in this study were ArcGIS 10, series 10.4, a set of computer hardware, GPS, Landsat 7 ETM+ and Landsat 8 OLI satellite imagery of the forest area of Halmahera Island in 2006, 2011, 2016, 2021, a map of the North Halmahera area.
-
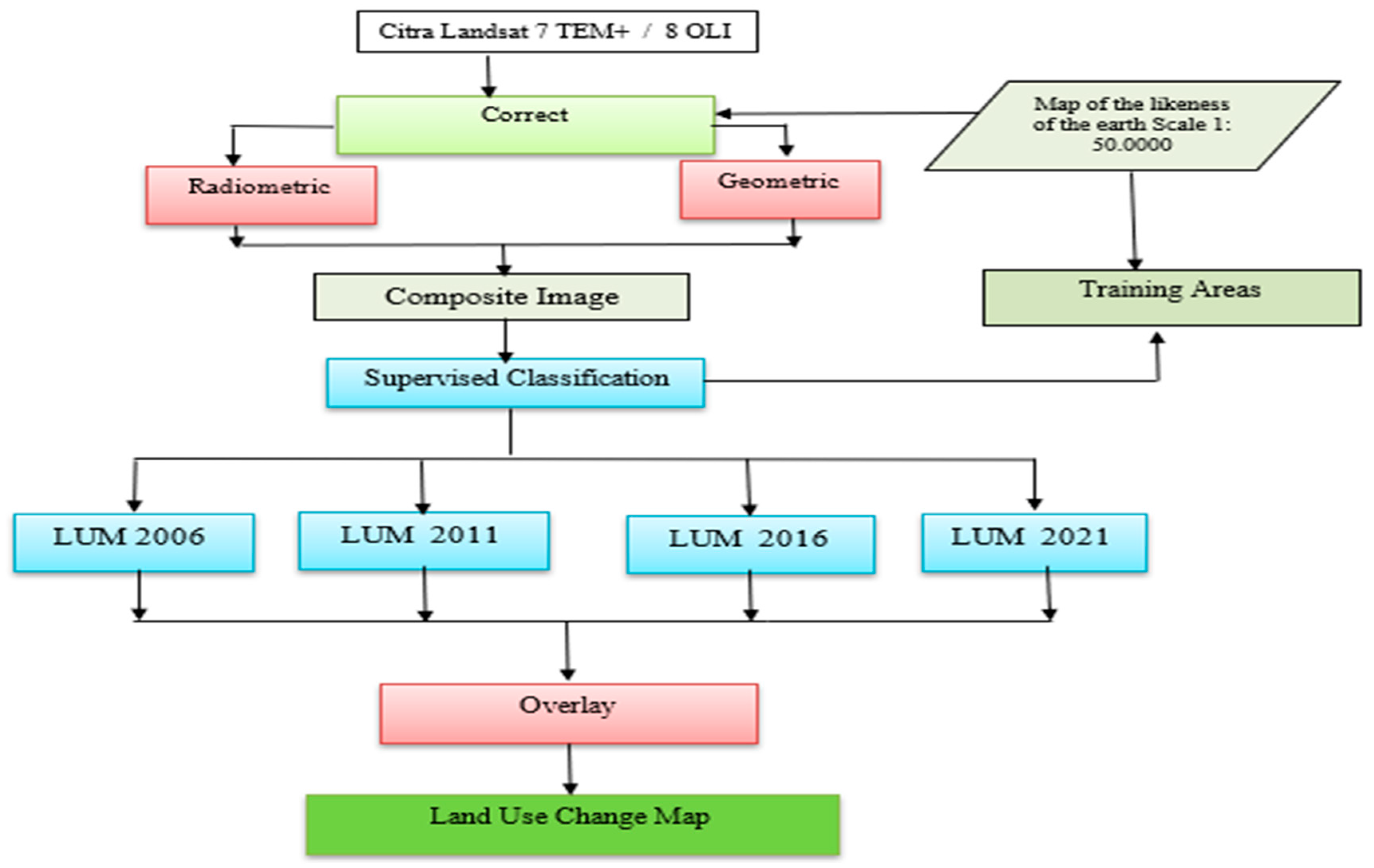
The procedure for making mapsAccording to [19] that the condition of land cover is very closely related to the pattern of land use that develops in an area. For processing land cover data obtained from the Ministry of Environment and Forestry of the Republic of Indonesia. Furthermore, using Landsat 7 ETM+ and 8 OLI imagery to calculate changes in forested land to non-forested land from 2006, 2011, 2016 and 2021. The method used is supervised classification with the maximum likelihood algorithm[15,16]. According to [20] the procedure for making a map is shown in Figure 2.
-
3. Results
3.1. Anthropogenic Activity
3.2. Figures, Tables and Schemes
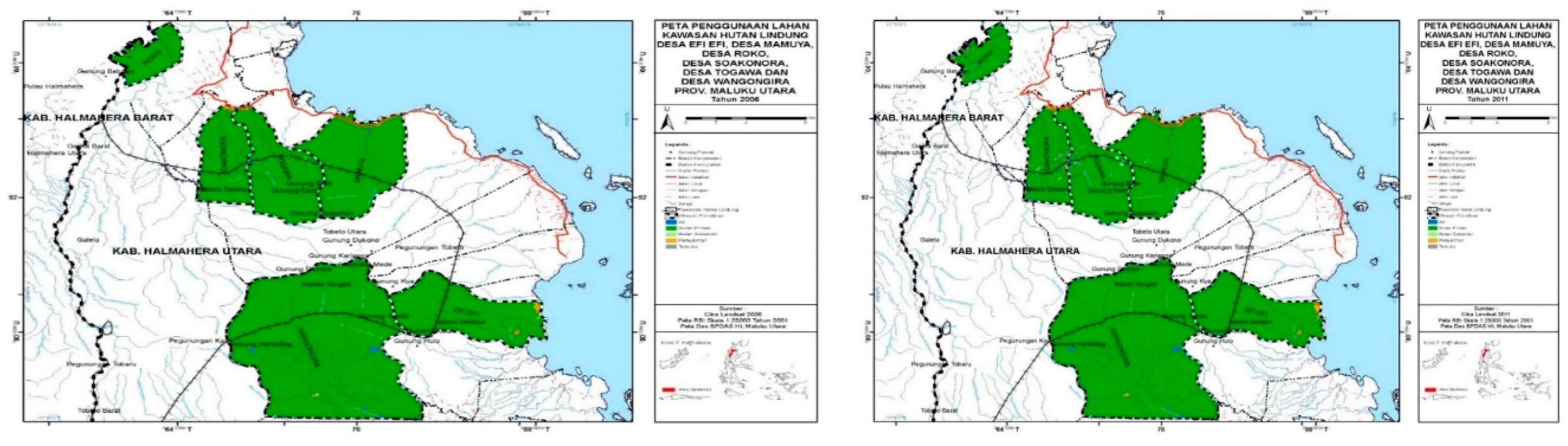
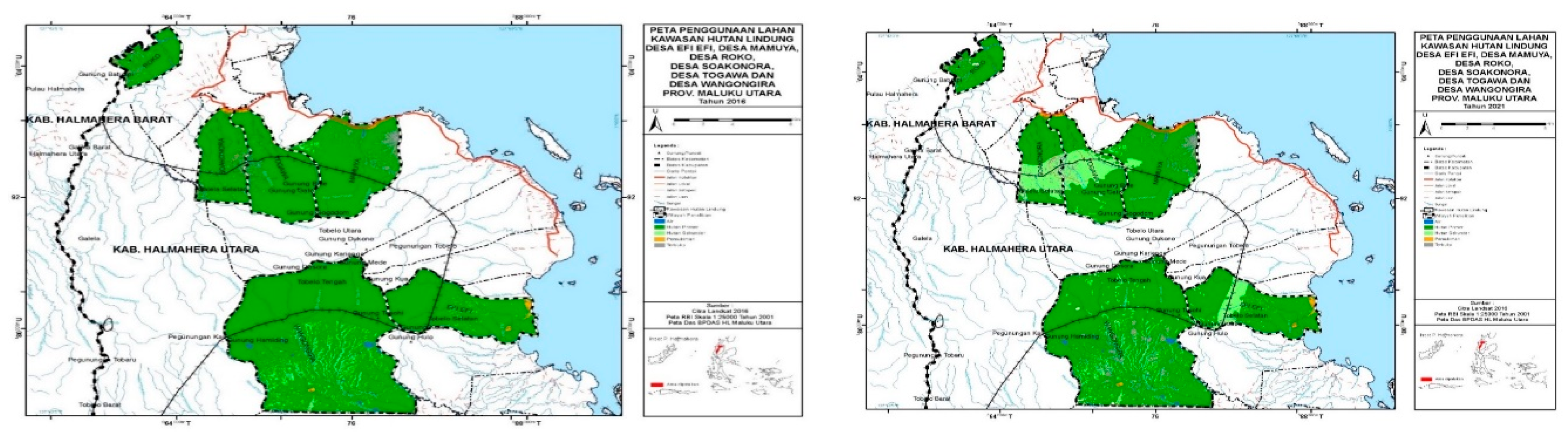
| Village name | 2006 | 2011 | Percentage | Fixed/Changed | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary | Secondary | Open | Ha | ||||
| Roko | Primary | Primary | 29.35 | 0.26 | Fixed | ||
| Roko | Primary | Open | 5.46 | 0.05 | Changed | ||
| Soakonora | Primary | Primary | 932.01 | 8.39 | Fixed | ||
| Soakonora | Primary | Secondary | 5,41 | 0.05 | Changed | ||
| Soakonora | Primary | Open | 72.64 | 0.65 | Changed | ||
| Soakonora | Secondary | Secondary | 2.69 | 0.02 | Fixed | ||
| Togawa | Primary | Primary | 2,472.58 | 22.26 | Fixed | ||
| Togawa | Primary | Secondary | 17.39 | 0.16 | Changed | ||
| Togawa | Primary | Open | 48.26 | 0.43 | Changed | ||
| Togawa | Secondary | Secondary | 6.31 | 0.06 | Fixed | ||
| Mamuya | Primary | Primary | 1,567.96 | 14.12 | Fixed | ||
| Efi-Efi | Primary | Primary | 1,501.04 | 13.51 | Fixed | ||
| Wangongira | Primary | Primary | 4,446.69 | 40.03 | Fixed | ||
| The total area of HMPF | 11,107.81 | 100 | |||||
| Changes in the area of protected forest | 76.81 | 0.69 | |||||
| Village name | 2011 | 2016 | Percentage | Fixed/Changed | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary | Secondary | Open | Ha | ||||
| Roko | Primary | Primary | 29.35 | 0.26 | Fixed | ||
| Roko | Open | Open | 5.46 | 0.05 | Fixed | ||
| Soakonora | Primary | Primary | 932.01 | 8.39 | Fixed | ||
| Soakonora | Secondary | Primary | 8.10 | 0.07 | Changed | ||
| Soakonora | Open | Open | 72.64 | 0.65 | Changed | ||
| Togawa | Primary | Primary | 2,472.58 | 22.26 | Fixed | ||
| Togawa | Secondary | Primary | 23.71 | 0.21 | Changed | ||
| Togawa | Open | Open | 48.26 | 0.43 | Fixed | ||
| Mamuya | Primary | Primary | 1,567.96 | 14.12 | Fixed | ||
| Efi Efi | Primary | Primary | 1,501.04 | 13.51 | Fixed | ||
| Wangongira | Primary | Primary | 4,446.69 | 40.03 | Fixed | ||
| The total area of HMPF | 11,107.81 | 100 | |||||
| Changes in the area of protected forest | 31.81 | 0.29 | |||||
| Village name | 2016 | 2021 | Percentage | Fixed/Changed | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary | Secondary | Open | Ha | ||||
| Roko | Primary | Primary | 29.35 | 0.26 | Fixed | ||
| Roko | Open | Open | 5.46 | 0.05 | Fixed | ||
| Soakonora | Primary | Primary | 344.37 | 3,10 | Fixed | ||
| Soakonora | Primary | Secondary | 595.74 | 5.36 | Changed | ||
| Soakonora | Open | Open | 72.64 | 0.65 | Fixed | ||
| Togawa | Primary | Primary | 1,687.55 | 15.19 | Fixed | ||
| Togawa | Primary | Secondary | 805.49 | 7.25 | Changed | ||
| Togawa | Primary | Grass | 3.25 | 0.03 | Changed | ||
| Togawa | Open | Open | 48.26 | 0.43 | Fixed | ||
| Mamuya | Primary | Primary | 1,559.52 | 14.04 | Fixed | ||
| Mamuya | Primary | Secondary | 8.44 | 0.08 | Changed | ||
| Efi Efi | Primary | Primary | 1,263.47 | 11.37 | Fixed | ||
| Efi Efi | Primary | Secondary | 237.57 | 2.13 | Changed | ||
| Wangongira | Primary | Primary | 4,300.65 | 38.72 | Fixed | ||
| Wangongira | Primary | Secondary | Secondary | 133.60 | 1.20 | Changed | |
| Wangongira | Primary | Grass | 12.44 | 0.11 | Changed | ||
| The total area of HMPF | 11,107.81 | 100 | |||||
| Changes in the area of protected forest | 1,796.54 | 16.17 | |||||
4. Discussion
4.1. Anthropogenic Damage
- a.
- Forest Encroachment
- b.
- Shifting Cultivation
- c.
- Illegal logging
- d.
- Herding and poaching
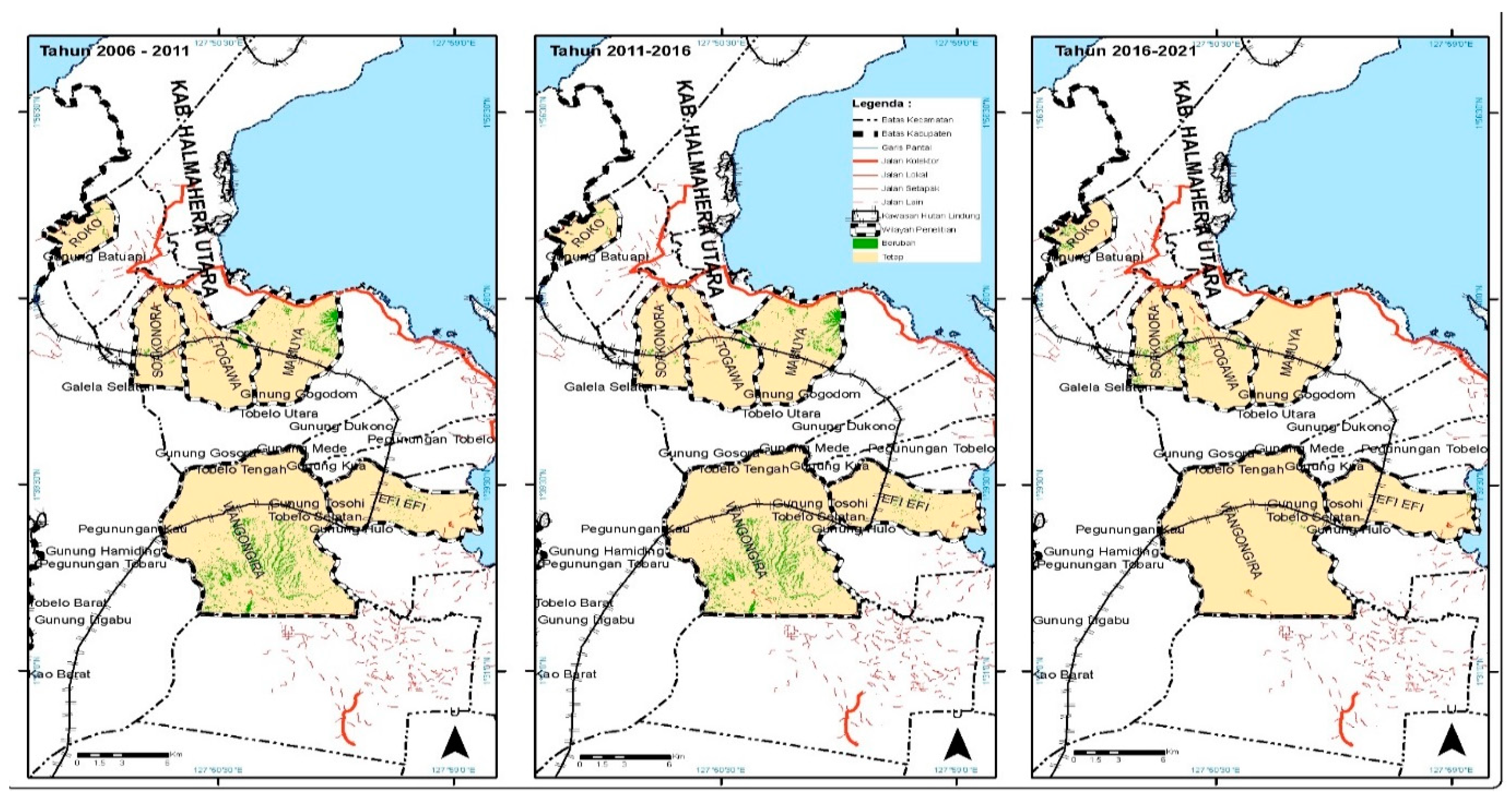
4.2. Land Cover Change
4.3. Mitigation of preventing HMPF damage with the Social Forestry Strategy in HMPF Management with the Community
- Increasing productivity in forest areas in the form of non-timber forest products and environmental services.
- Improving the standard of living and welfare of communities living around forest areas by involving community participation in forest management
- Realizing forest management while still paying attention to its main function as a regulator of water management, flood and erosion control through a forest ecosystem management (FEM) approach.
- Supporting regional development as an integral part of national development in the framework of the development of the Indonesian people as a whole and the development of all Indonesian people.
- Forest Engineering
- 2.
- Social Engineering
- Community Empowerment
- 2.
- Institutional Strengthening
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

References
- Cleary, D.F.R.; DeVantier, L. Indonesia: Threats to the Country’s Biodiversity; 2nd ed.; Elsevier Inc., 2019; ISBN 9780444639523.
- Sutarno. Setyawan AD Biodiversitas Indonesia: Penurunan Dan Upaya Pengelolaan Untuk Menjamin Kemandirian Bangsa. Biodiversitas 2015, 1, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang; Kant, S. ; Liu, J. Principal-Agent Relationships in Rural Governance and Benefit Sharing in Community Forestry: Evidence from a Community Forest Enterprise in China. For. Policy Econ. 2019, 107, 101924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yang, W.; Zhang, L.; Hull, V.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, H.; Liu, J.; Polasky, S.; et al. Strengthening Protected Areas for Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services in China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2017, 114, 1601–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugroho, H.Y.S.H.; Nurfatriani, F.; Indrajaya, Y.; Yuwati, T.W.; Ekawati, S.; Salminah, M.; Gunawan, H.; Subarudi, S.; Sallata, M.K.; Allo, M.K.; et al. Mainstreaming Ecosystem Services from Indonesia’s Remaining Forests. Sustain. 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, F.; Adrian Bruijnzeel, L.; Meli, P.; Martin, P.A.; Zhang, J.; Nakagawa, S.; Miao, X.; Wang, W.; McEvoy, C.; Peña-Arancibia, J.L.; et al. The Biodiversity and Ecosystem Service Contributions and Trade-Offs of Forest Restoration Approaches. Science (80-. ). 2022, 376, 839–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudy, R.; Yonariza, Y.; Yanfika, H.; Rahmat, A.; Ramadhani, W.S.; Mutolib, D.A. Forest Cover Change and Legal Pluralism in Forest Management: A Review and Evidence from West Sumatra, Indonesia. Indonesia. J. Sci. Technol. 2021, 6, 299–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wade, C.M.; Austin, K.G.; Cajka, J.; Lapidus, D.; Everett, K.H.; Galperin, D.; Maynard, R.; Sobel, A. What Are Threatening Forests in Protected Areas? A Global Assessment of Deforestation in Protected Areas, 2001-2018. Forests 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waas, R.M.; Riry, W.A. Protection And Utilization Of Protected Forests In Ambon City Environmental Law Perspective. Balobe Law J. 2022, 2, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.; Jallat, H.; Hussain, E.; Saqib, N. u.; Saqib, Z.; Khokhar, M.F.; Khan, W.R. Quantitative Assessment of Deforestation and Forest Degradation in Margalla Hills National Park (MHNP): Employing Landsat Data and Socio-Economic Survey. Forests 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, N.; Furukawa, T.; Tsujino, R.; Kitamura, S.; Yumoto, T. Factors Affecting Forest Area Change in Southeast Asia during 1980-2010. PLoS One 2018, 13, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, Y.; He, C. Impact of Land Use Change on the Spatial and Temporal Evolution of Ecosystem Service Values in South China Karst Areas. 2023.
- Budiprakoso, B.; Ichwandi, I.; Rusdiana, O. Institutional Analysis of Protection Forest Area Land Use Pattern in the North Bandung Area, Bandung Regency. J. Pengelolaan Sumberd. Alam dan Lingkung. (Journal Nat. Resour. Environ. Manag. 2021, 11, 463–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacconi, L.; Rodrigues, R.J.; Maryudi, A. Law Enforcement and Deforestation: Lessons for Indonesia from Brazil. For. Policy Econ. 2019, 108, 101943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, G.M.; Adami, M.; Galbraith, D.; Nascimento, R.G.M.; Wang, Y.; Shimabukuro, Y.E.; Emmert, F. Spatial Distribution of Secondary Forests by Age Group and Biomass Accumulation in the Brazilian Amazon. 2023.
- Voigt, M.; Supriatna, J.; Deere, N.J.; Kastanya, A.; Mitchell, S.L.; Rosa, I.M.D.; Santika, T.; Siregar, R.; Tasirin, J.S.; Widyanto, A.; et al. Emerging Threats from Deforestation and Forest Fragmentation in the Wallacea Centre of Endemism. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rofita; Utami, S. N.H.; Maas, A.; Nurudin, M. Spatial Distribution of Soil Morphology and Physicochemical Properties to Assess Land Degradation under Different NDVI and TRI in North Halmahera, Indonesia. J. Degrad. Min. Lands Manag. 2021, 9, 3137–3154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buruso, F.H.; Adimassu, Z.; Sibali, L.L. Effects of Land Use/Land Cover Changes on Soil Properties in Rib Watershed, Ethiopia. Catena 2023, 224, 106977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahyu, E. Peluang Dan Tantangan Dalam Pengembangan Silvofishery Di Pulau Lombok. Seminar Nasional Agroforestri III.; 2012.
- Apriyanti, D.; Faqih, R.; Purnawan, B. Pembuatan Peta Penutup Lahan Menggunakan Klasifikasi Terbimbing Metode Maximum Likelilhood Pada Citra Landsat 8 ( Studi Kasus : Kabupaten Indramayu, Provinsi Jawa Barat ) Making Land Cover Map Using Supervised Classification Maximum Likelihood Method In. Semin. Nasioanl Penginderaan Jauh 2017, 8, 225–235. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Hai, Q.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, D.; Shao, Y.; Zhao, Y. Spatial and Temporal Changes in Vegetation Cover in the Three North Protection Forest Project Area Supported by GEE Cloud Platform. 2023.
- Fisher, R. Tropical Forest Monitoring, Combining Satellite and Social Data, to Inform Management and Livelihood Implications: Case Studies from Indonesian West Timor. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2012, 16, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq Shiek Marifatul, S.; Soares, E.; Rashid, I.; Khuroo, A.A. Trees, Forests and People Human-Driven Disturbances Change the Vegetation Characteristics of Temperate Forest Stands : A Case Study from Pir Panchal Mountain Range in Kashmir Himalaya ☆. Trees, For. People 2021, 6, 100134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomon, W.; Sikuzani, Y.U.; Kouakou, A.T.M.; Barima, S.S.; Theodat, J.M.; Bogaert, J. Monitoring of Anthropogenic Effects on Forest Ecosystems within the Municipality of Vallières in the Republic of Haiti from 1984 to 2019. Trees, For. People 2021, 6, 100135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfany Zelly, Markum, B.S. The Analysis of Factors That Cause The Encroachment Forest in The Production Forest Area Sub-. 2017.
- Fazriyas, F.; Tamin, R.P.; Irawan, D. Faktor Yang Berhubungan Dengan Perambahan Kawasan Hutan Lindung Gambut (Studi Kasus Desa Bram Itam Kanan Kecamatan Bram Itam Kabupaten Tanjung …. J. Silva Trop. 2018, 2, 6–10. [Google Scholar]
- Simanjuntak Radios, Sulistiyowati Eny, M.E. Pertanian Pala Sebagai Alternatif Mata Pencaharian Bagi Perambah Hutan Di Desa Wangongira Dan Di Desa Wateto, Kabupaten Halmahera Utara. ejournal.unkhair.ac.id 2018, 74–83.
- Watimena, G. Indigenous Knowledge. In Proceedings of the Proceeding; 2011; pp. 343–368. [Google Scholar]
- Santoro, A.; Piras, F. Natural Forests or Cultural Forests ? Forest Changes within Italian Protected Areas in the Last 85 Years. 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Bentsi-Enchill, F.; Damptey, F.G.; Pappoe, A.N.M.; Ekumah, B.; Akotoye, H.K. Impact of Anthropogenic Disturbance on Tree Species Diversity, Vegetation Structure and Carbon Storage Potential in an Upland Evergreen Forest of Ghana, West Africa. Trees, For. People 2022, 8, 100238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulja, F.; Hermansyah, A. Penanggulangan Tindak Pidana Illegal Logging Di Kawasan Hutan Lindung Beutong. 2020, 4, 503–511. [Google Scholar]
- Kurniadi, R.; Purnomo, H.; Wijayanto, N.; Fuah, A.M. Model Pengelolaan Ternak Di Sekitar Hutan Gunung Mutis Dan Dampaknya Terhadap Kelestarian Hutan. J. Ilmu Kehutan. 2017, 11, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ziv, G.; Adami, M.; Almeida, C.A. de; Antunes, J.F.G.; Coutinho, A.C.; Esquerdo, J.C.D.M.; Gomes, A.R.; Galbraith, D. Upturn in Secondary Forest Clearing Buffers Primary Forest Loss in the Brazilian Amazon. Nat. Sustain. 2020, 3, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chazdon, R.L.; Broadbent, E.N.; Rozendaal, D.M.A.; Bongers, F.; Zambrano, A.M.A.; Aide, T.M.; Balvanera, P.; Becknell, J.M.; Boukili, V.; Brancalion, P.H.S.; et al. Carbon Sequestration Potential of Second-Growth Forest Regeneration in the Latin American Tropics. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molins, J. Masyarakat Hutan Dan Global Harus Bersatu Dalam Menangani Risiko Perburuan Satwa Liar. 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Dako, F.X. Pengelolaan Hutan Lindung Mutistimau Dengan Prinsip Kehutanan Social, UGM, Yogyakarta, 2020.
- Putraditama, A.; Kim, Y.S.; Sánchez Meador, A.J. Community Forest Management and Forest Cover Change in Lampung, Indonesia. For. Policy Econ. 2019, 106, 101976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Doyog, N.D. Challenges of Retrieving LULC Information in Rural-Forest Mosaic Landscapes Using Random Forest Technique. Forests 2023, 14, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annika, K.; Mikko, K.; Teppo, H.; Kyle, E.; Jyrki, K. Decision Support for Forest Management; Gadow, K. Von, Georg-August, Pukkala, T., Tome, M., Eds.; 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, 2015; ISBN 978-3-319-23521-9. [Google Scholar]
- Suryani, E.; Dariah, A. Peningkatan Produktivitas Tanah Melalui Sistem Agroforestri. J. Sumberd. Lahan 2012, 101–109. [Google Scholar]
- Rohandi, A. Karakteristik Agroekologi Dan Daya Aaptasi Tanaman Garut (Maranta Arundinaceae L) Pada Sistem Agroforestri Di Kabupaten Garut, UNversitas Gadjah Mada, 2018.
- Chavan, S.B.; Dhillon, R.S.; Sirohi, C.; Uthappa, A.R.; Jinger, D.; Jatav, H.S.; Chichaghare, A.R.; Kakade, V.; Paramesh, V.; Kumari, S.; et al. Carbon Sequestration Potential of Commercial Agroforestry Systems in Indo-Gangetic Plains of India: Poplar and Eucalyptus-Based Agroforestry Systems. Forests 2023, 14, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alimah Siti, Mudjiono, Susiati Heni, Hastuti Ristianan Dwi, Irawan Dimas, N. A. Jurnal Pengembangan Energi Nuklir Informasi Artikel Abstrak. J. Pengemb. Energi Nukl. 2019, 21, 63–70. [Google Scholar]
- Sanudin, S.A.A. Evaluasi Kehutanan Social: Tantangan Generasi 3, 2019.
- Sari, Novita, G. ; Toknok, B. Kelembagaan Kelompok Tani Hutan Program Pendampingan Scbfwm Disekitar Sub Daerah Aliran Sungai Miu ( Kasus Desa Pakuli Kecamatan Gumbasa Kabupaten Sigi ). War. Rimba 2013, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Kusnandar, K.; Padmaningrum, D.; Rahayu, W.; Wibowo, A. Rancang Bangun Model Kelembagaan Agribisnis Padi Organik Dalam Mendukung Ketahanan Pangan. J. Ekon. Palembang. Kaji. Masal. Ekon. dan Pembang. 2013, 14, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamzah, H.; Suharjito, D.; Istomo, I. Efektifitas Kelembagaan Lokal Dalam Pengelolaan Sumber Daya Hutan Pada Masyarakat Nagari Simanau, Kabupaten Solok. Rizal. Kebijak. Pertan. Dan Lingkung. Rumusan Kaji. Strategy. Bid. Pertan. dan Lingkung. 2016, 2, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awang, S.A.; Budi, W.E.; Suryanto, S. Unit Manajement Hutan Rakyat; Proses Konstruksi Pengetahuan, Lokal, Firman, F., Noor, R.Z., Eds.; Pertama.; Banyumili Art Network: Yogyakarta, 2007; ISBN 978-979-16380-0-5. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




