Submitted:
15 May 2023
Posted:
16 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ultra-high-frequency surface-acoustic-wave resonator biosensors
2.2. Functionalization and detection protocols
- cleaning of chips performed by sonication in acetone (ACE), isopropanol (IPA), and deionized- (DI-) water for 7 minutes each;
- drying of the chips with a stream of nitrogen;
- half-antibody functionalization incubated for 30 min with a solution made of 2 μl pAb (anti-GFAP polyclonal antibody, Synaptic System, 173-002), 4 μl DTT (DL-Dithothreitol 5g, by SIGMA ALDRICH) at a concentration of 1.5 mg/ml, 34 ul PBS 1X (phosphate buffer saline);
- wash in DI-water for 5 min;
- drying the chips with a stream of nitrogen and waiting 1 hour before use.
- recombinant GFAP (Synaptic Systems, 173-0P) 1000 nM in PBS, or clean PBS for the negative control, incubated for 30 min;
- wash in DI-water for 5 min;
- drying of the chips with a stream of nitrogen;
- pAb for 30 min;
- wash in DI-water for 5 min;
- drying of the chips with a stream of nitrogen;
2.3. Measurement setup and acquisition protocol
3. Results and Discussion
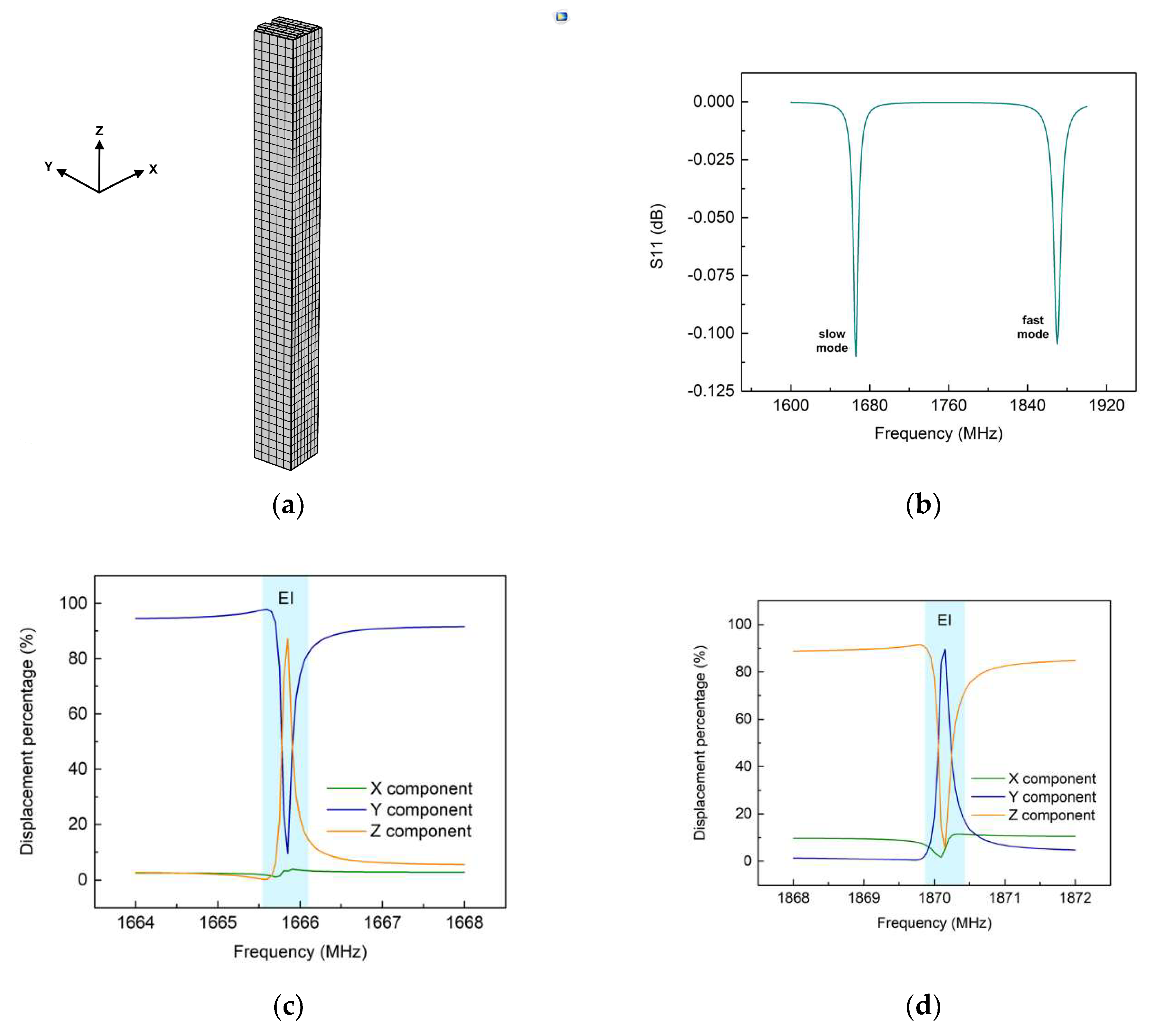
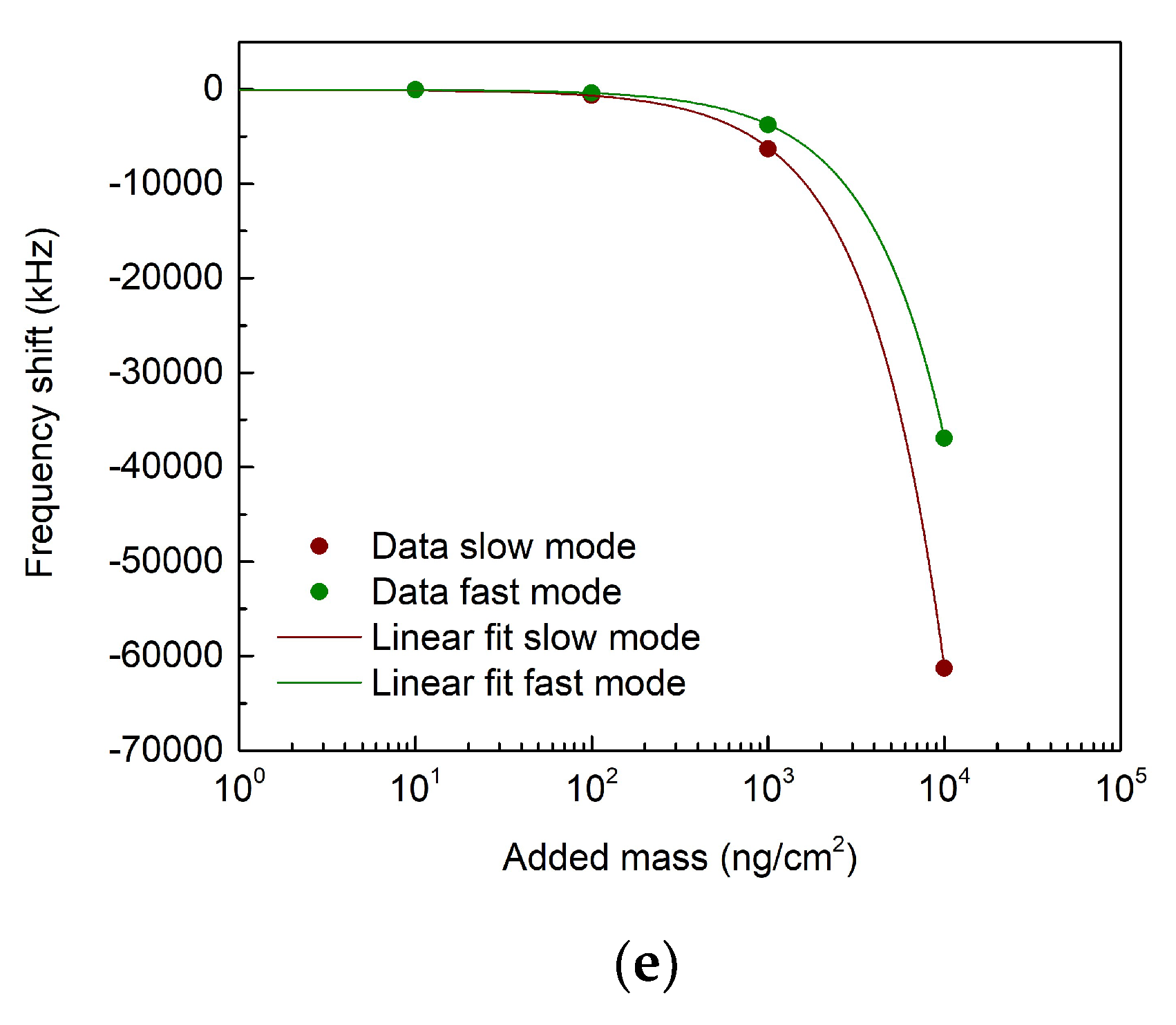
3.1. Finite-element-modelling simulations
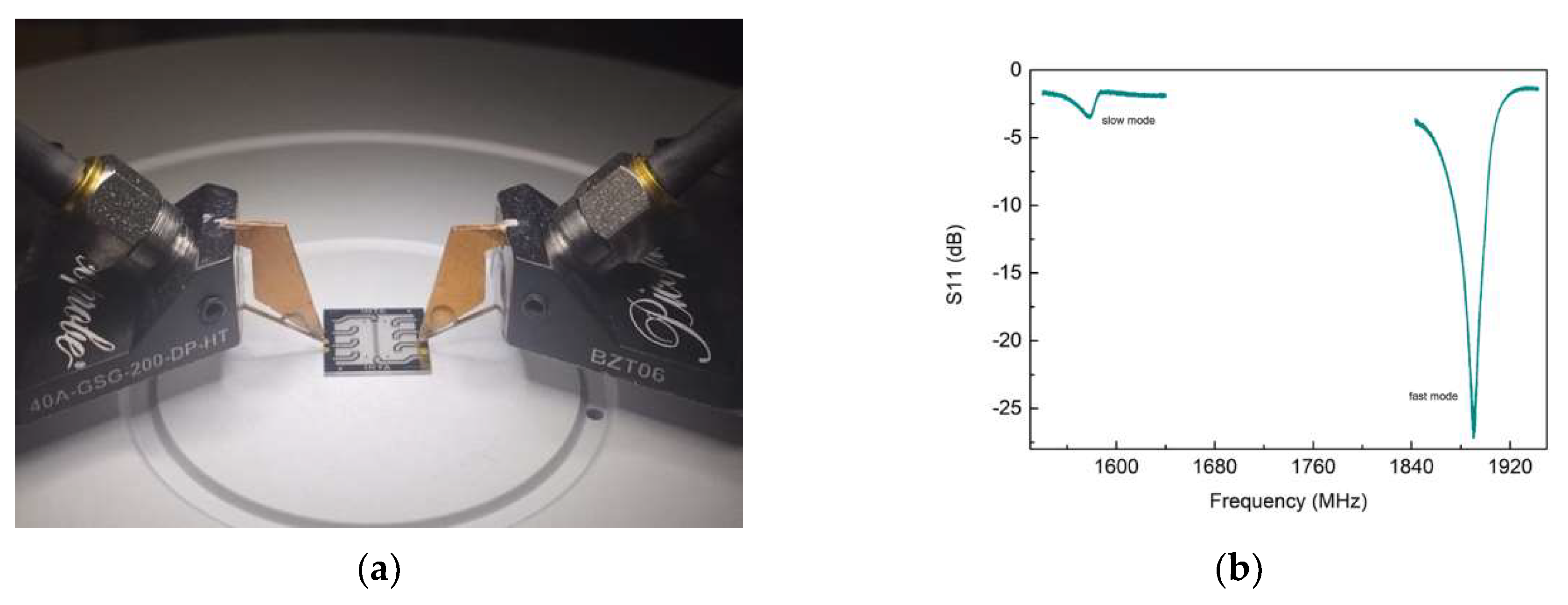
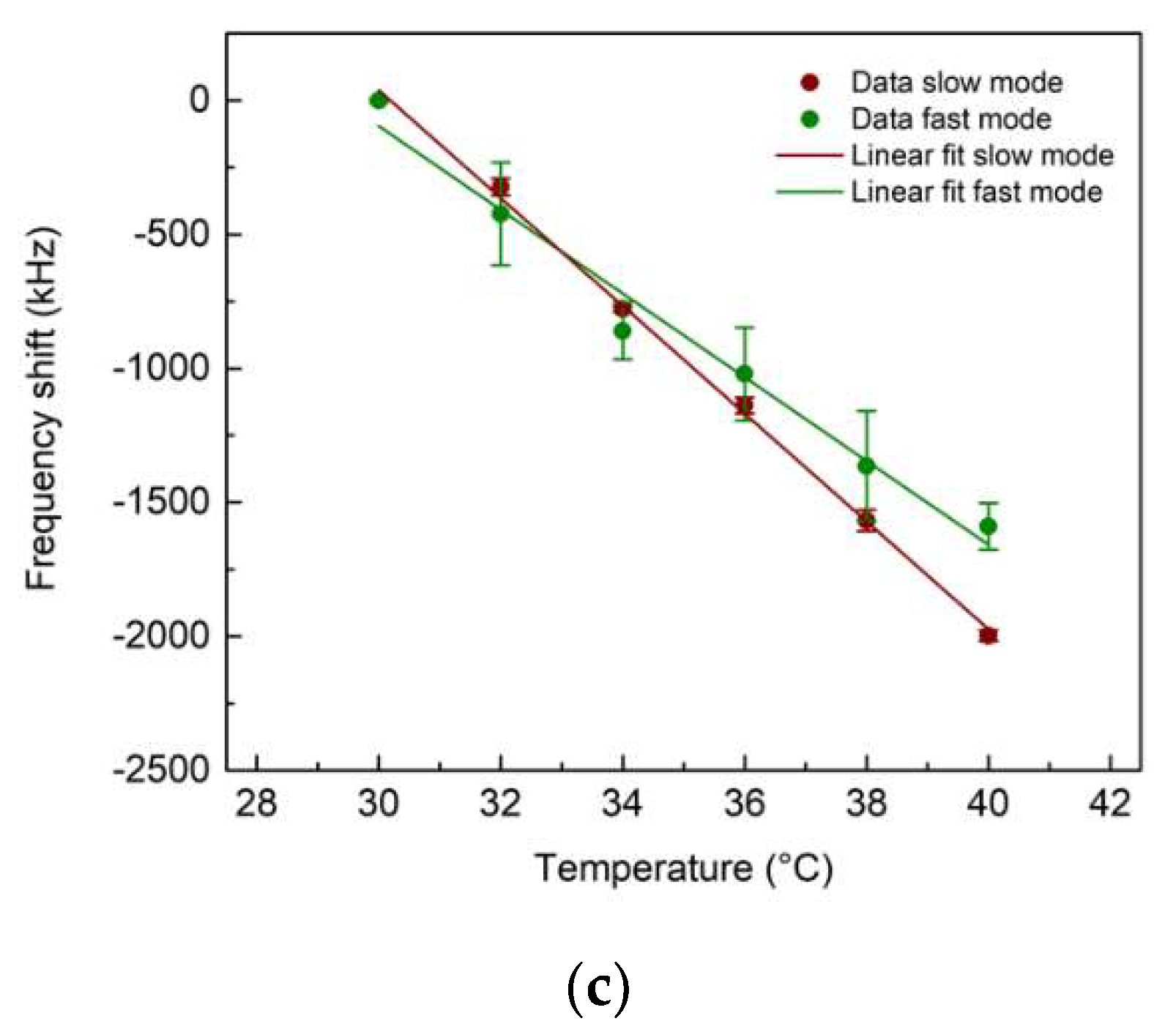
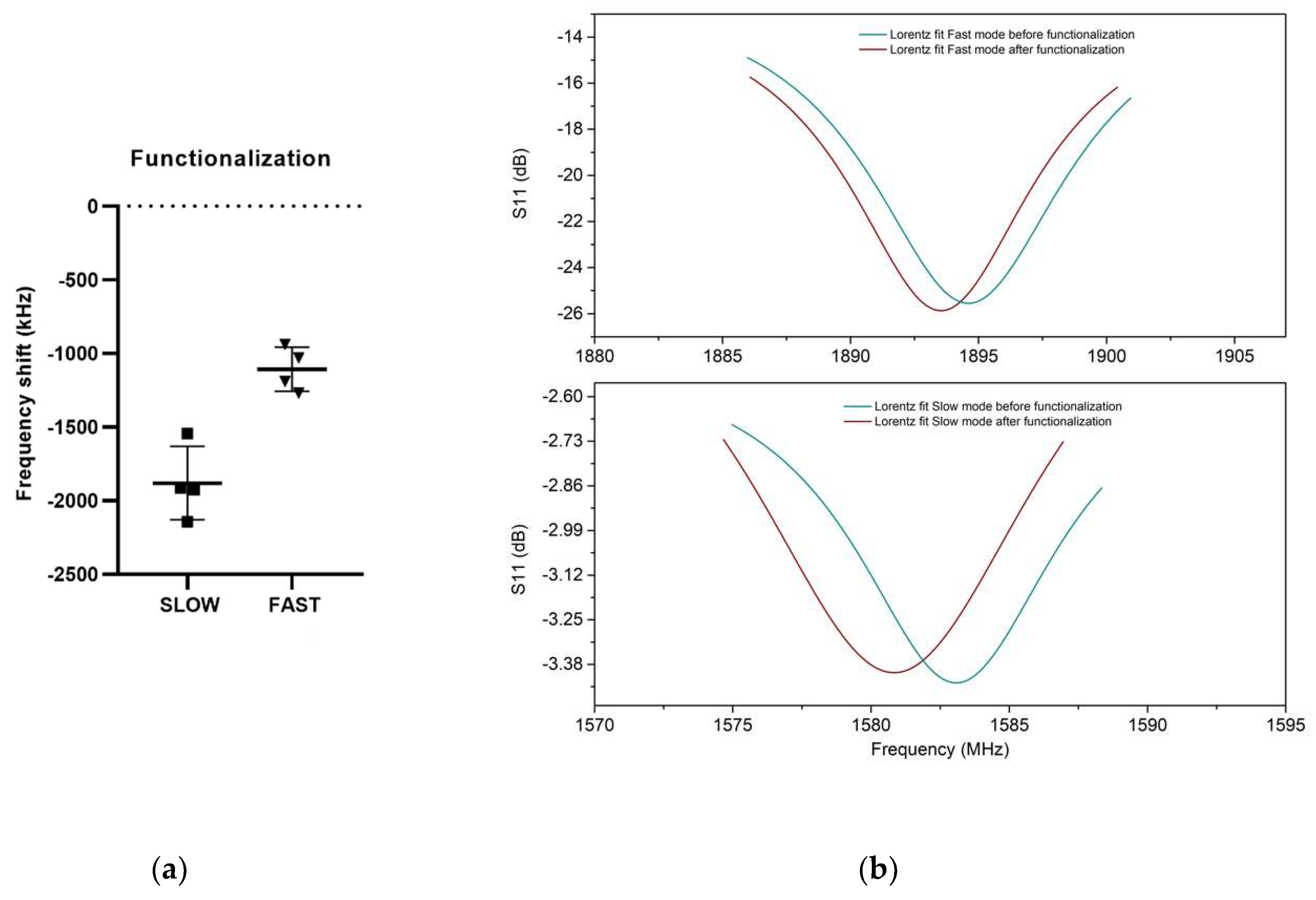
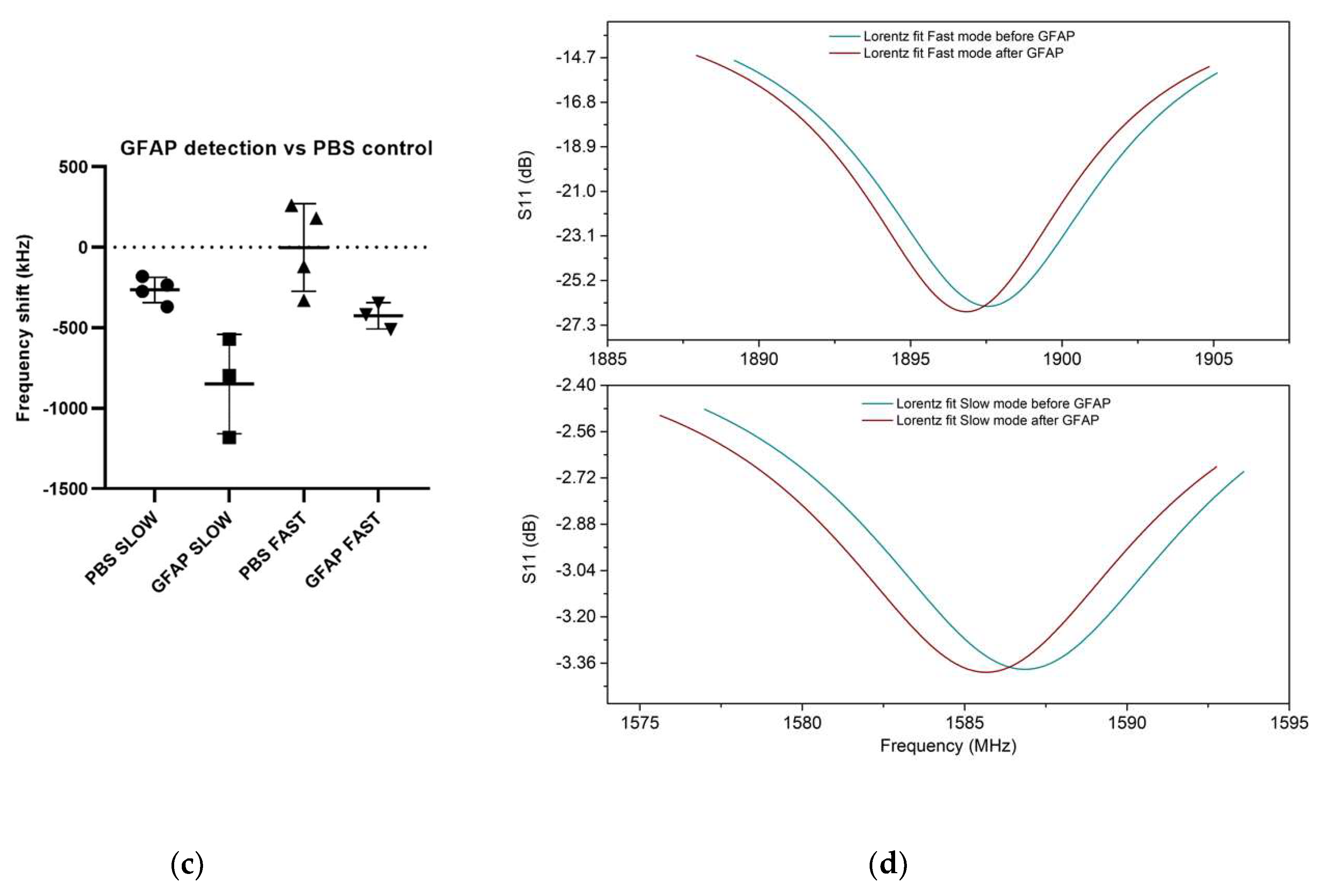
3.2. UHF-SAW biosensors
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bhalla, N.; Jolly, P.; Formisano, N.; Estrela, P. Introduction to biosensors. Essays in Biochemistry, 2016, 60, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner AP, F. Biosensors: Sense and sensibility. Chemical Society Reviews, 2013, 42, 3184–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naresh, V.; Lee, N. A review on biosensors and recent development of nanostructured materials-enabled biosensors. Sensors 2021, 21, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grieshaber, D.; Mackenzie, R.; Vörös, J.; Reimhult, E. Electrochemical Biosensors-Sensor Principles and Architectures. Sensors, 2008, 8, 1400–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pashchenko, O. A Comparison of Optical, Electrochemical, Magnetic, and Colorimetric Point-of-Care Biosensors for Infectious Disease Diagnosis. ACS Infectious Diseases 2018, 4, 1162–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenzel, S.W.; White, R.M. Analytic comparison of the sensitivities of bulk-wave, surface-wave, and flexural plate-wave ultrasonic gravimetric sensors. Applied Physics Letters, 1989, 54, 1976–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostini, M.; Cecchini, M. Ultra-high-frequency (UHF) surface-acoustic-wave (SAW) microfluidics and biosensors. Nanotechnology 2021, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, D.; Banerjee, S. Surface AcousticWave (SAW) Sensors: Physics, Materials, and Applications. Sensors 2022, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Das, P. K.; Bhethanabotla, V. R. Surface acoustic waves in biosensing applications. Sensors and Actuators Reports 2021, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha-Gaso, M. I.; March-Iborra, C.; Montoya-Baides, Á.; Arnau-Vives, A. Surface Generated Acoustic Wave Biosensors for the Detection of Pathogens: A Review. Sensors 2009a, 9, 5740–5769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostini, M.; Greco, G.; Cecchini, M. Full-SAW Microfluidics-Based Lab-on-a-Chip for Biosensing. IEEE Access, 2019, 7, 70901–70909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiokawa, S.; Matsui, Y.; Ueda, T. Liquid streaming and droplet formation caused by leaky Rayleigh waves. Ultrasonics Symposium Proceedings, 1989, 1, 643–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shilton, R.J.; Travagliati, M.; Beltram, F.; Cecchini, M. Nanoliter-droplet acoustic streaming via ultra high frequency surface acoustic waves. Advanced Materials, 2014, 26, 4941–4946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, G.; Agostini, M.; Tonazzini, I.; Sallemi, D.; Barone, S.; Cecchini, M. Surface-Acoustic-Wave (SAW)-Driven Device for Dynamic Cell Cultures. Analytical Chemistry, 2018, 90, 7450–7457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha-Gaso, M. I.; March-Iborra, C.; Montoya-Baides, Á.; Arnau-Vives, A. Surface Generated Acoustic Wave Biosensors for the Detection of Pathogens: A Review. Sensors 2009b, 9, 5740–5769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyder, A. A.; Wunderlich, C. A.; Puvanachandra, P.; Gururaj, G.; Kobusingye, O. C. The impact of traumatic brain injuries: A global perspective. In NeuroRehabilitation; IOS Press, 2007; Vol. 22. [Google Scholar]
- Okonkwo, D. O.; Yue, J. K.; Puccio, A. M.; Panczykowski, D. M.; Inoue, T.; McMahon, P. J.; Sorani, M. D.; Yuh, E. L.; Lingsma, H. F.; Maas, A. I. R.; et al. GFAP-BDP as an acute diagnostic marker in traumatic brain injury: Results from the prospective transforming research and clinical knowledge in traumatic brain injury study. Journal of Neurotrauma, 2013, 30, 1490–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhak, A.; Foschi, M.; Abu-Rumeileh, S.; Yue, J. K.; D’Anna, L.; Huss, A.; Oeckl, P.; Ludolph, A. C.; Kuhle, J.; Petzold, A.; et al. Blood GFAP as an emerging biomarker in brain and spinal cord disorders. Nature Reviews Neurology 2022, 18, 158–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostini, M.; Greco, G.; Cecchini, M. A Rayleigh Surface Acoustic Wave (R-SAW) Resonator Biosensor based on Positive and Negative Reflectors with Sub-Nanomolar Limit of Detection. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical 2017, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David Morgan. Surface Acoustic Wave Filters, 2007.
- Agostini, M.; Lunardelli, F.; Gagliardi, M.; Miranda, A.; Lamanna, L.; Luminare, A. G.; Gambineri, F.; Lai, M.; Pistello, M.; Cecchini, M. Surface-Acoustic-Wave (SAW) Induced Mixing Enhances the Detection of Viruses: Application to Measles Sensing in Whole Human Saliva with a SAW Lab-On-a-Chip. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2201958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, G.; Agostini, M.; Cecchini, M. Ultra-High-Frequency Love Surface Acoustic Wave Device for Real-Time Sensing Applications. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 112507–112514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




