Submitted:
13 May 2023
Posted:
15 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
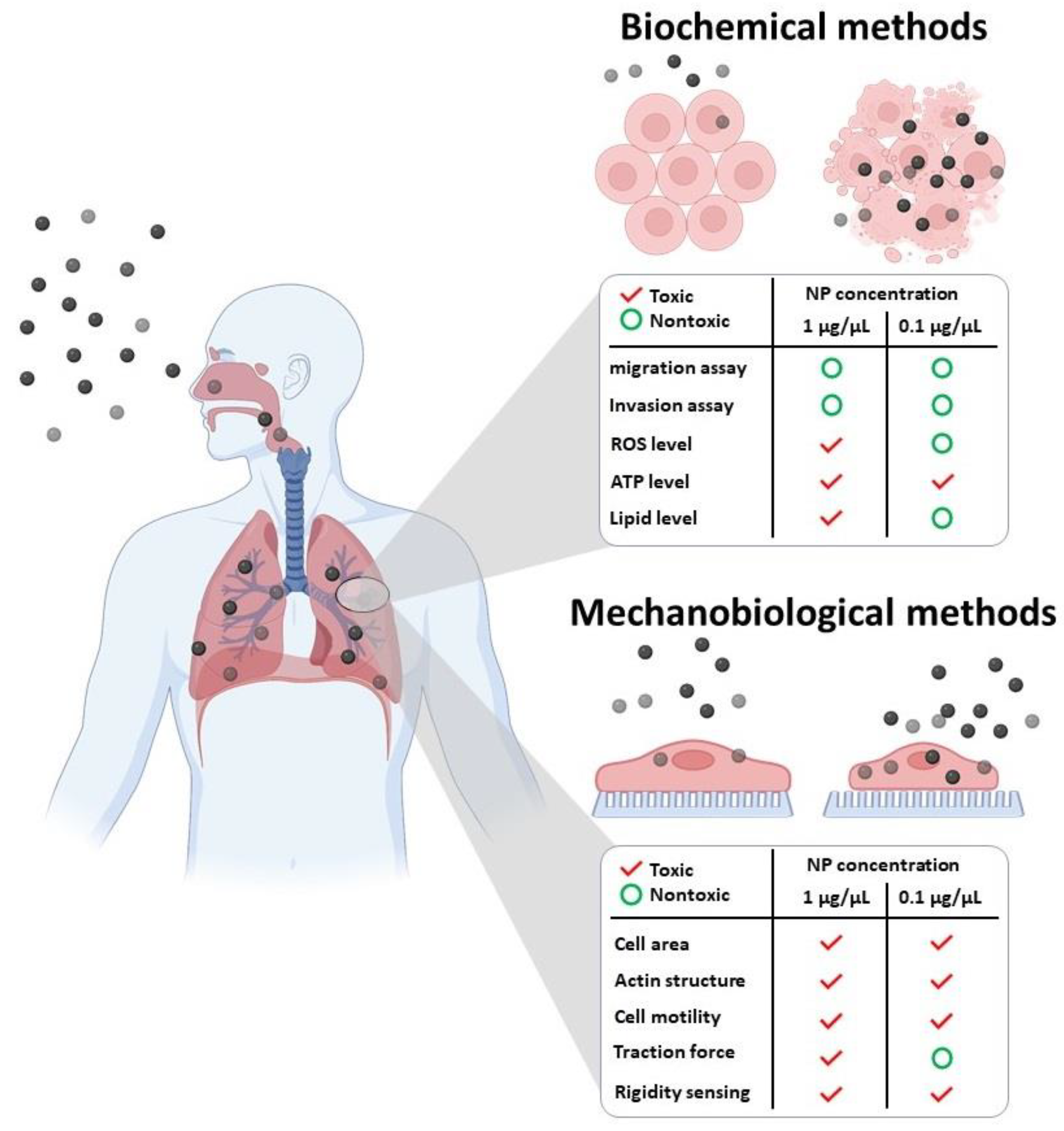
2. Interaction of NPs with the Cell Cytoskeleton
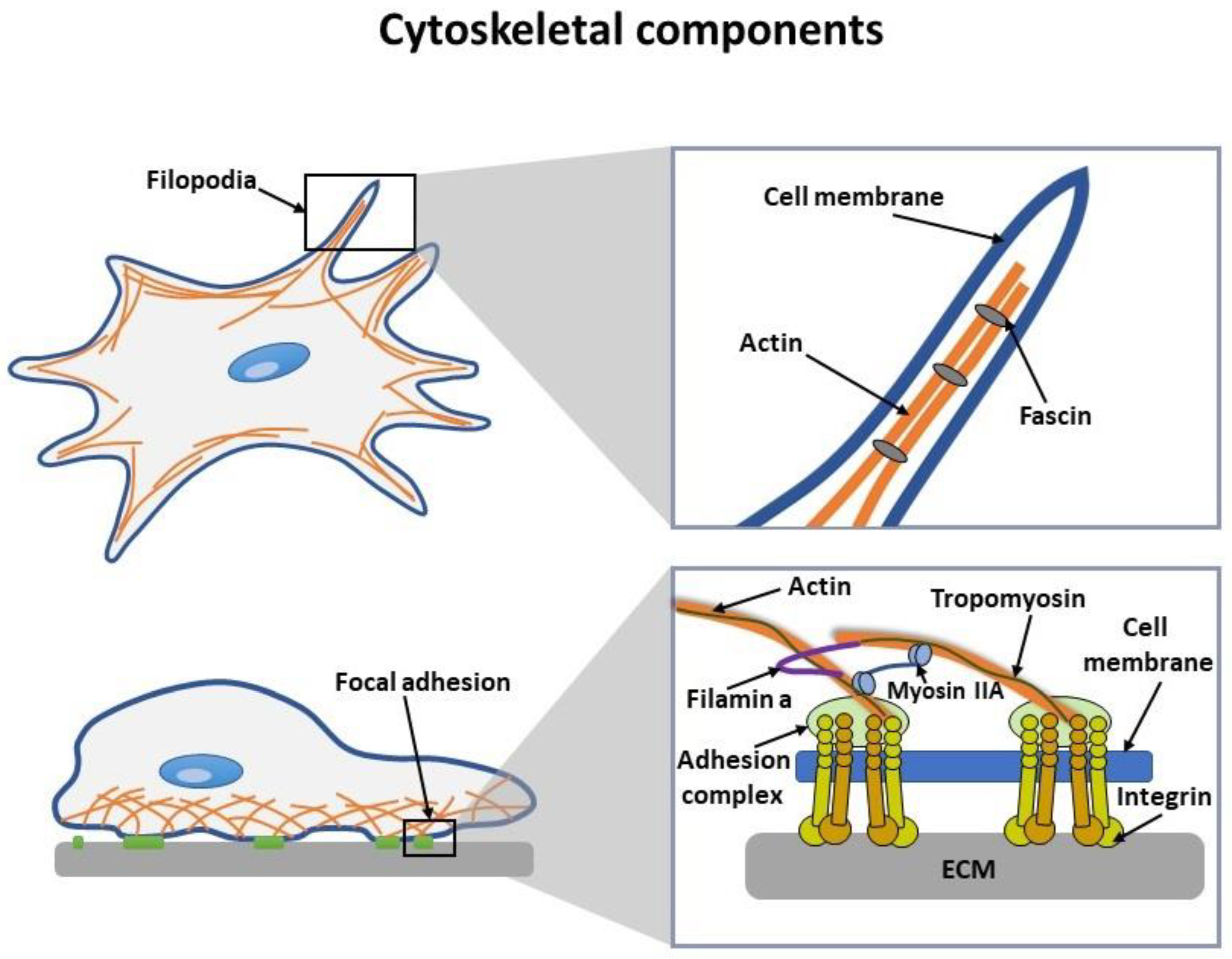
2.1. Direct Toxic Effect of NPs on Cell Cytoskeleton
2.2. Indirect Toxic Effect of NPs on Cell Cytoskeleton
3. Effects of NPs on Cell Mechanobiology
3.1. Cell Mechanobiology
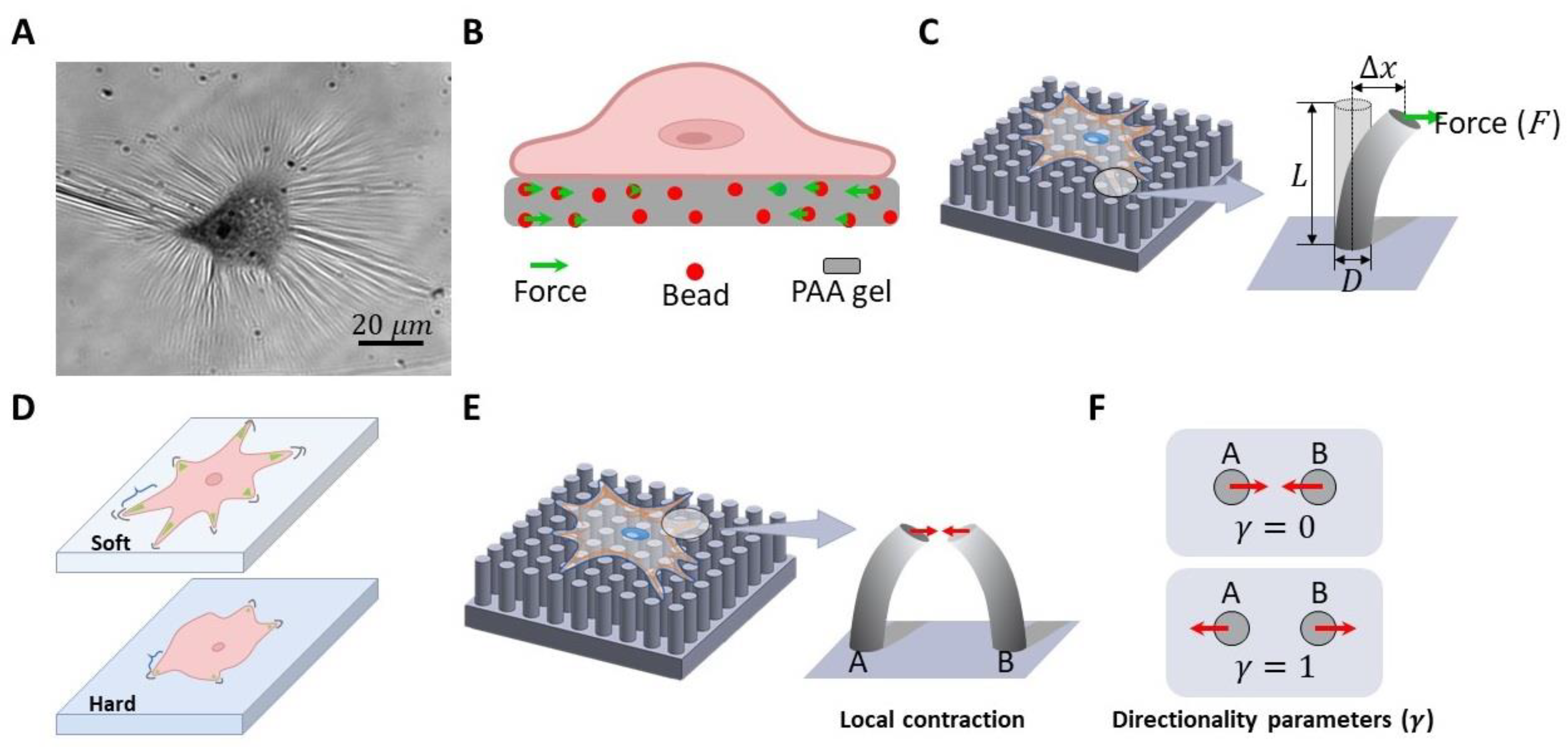
3.2. Methods to Investigate Cell Mechanobiology
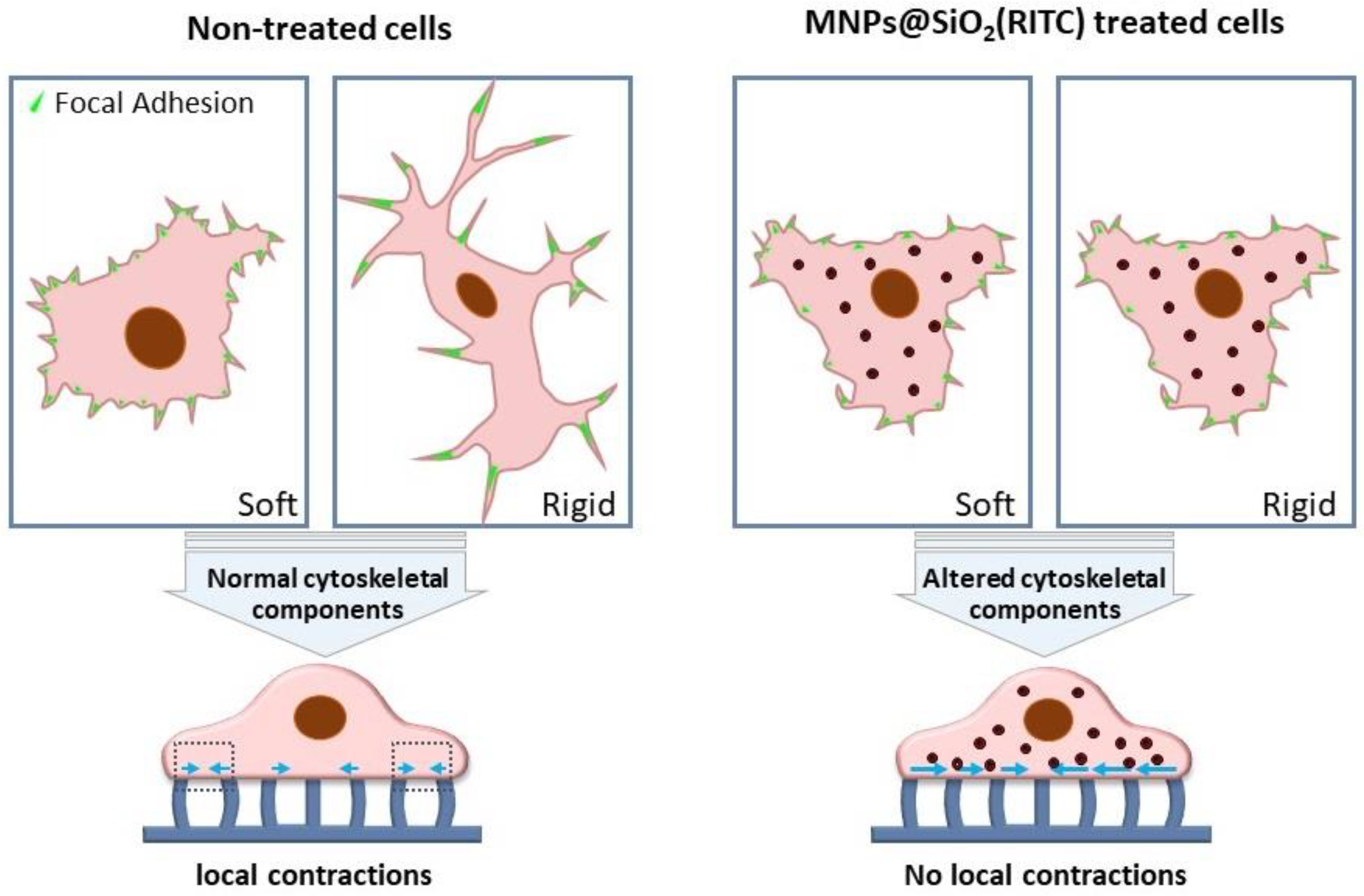
3.2.1. Cell traction force measurement.
3.2.2. Rigidity Sensing Measurement
4. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Availability of Data and Material
Competing Interests
References
- Stark, W.J. Nanoparticles in Biological Systems. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 1242–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouallegui, Y.; Ben Younes, R.; Turki, F.; Oueslati, R. Impact of Exposure Time, Particle Size and Uptake Pathway on Silver Nanoparticle Effects on Circulating Immune Cells in Mytilus Galloprovincialis. J. Immunotoxicol. 2017, 14, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzinger, M.; Le Goff, A.; Cosnier, S. Nanomaterials for Biosensing Applications: A Review. Front. Chem. 2014, 2, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, M.J.; Billingsley, M.M.; Haley, R.M.; Wechsler, M.E.; Peppas, N.A.; Langer, R. Engineering Precision Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 101–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delyagina, E.; Schade, A.; Scharfenberg, D.; Skorska, A.; Lux, C.; Li, W.; Steinhoff, G. Improved Transfection in Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Effective Intracellular Release of PDNA by Magnetic Polyplexes. Nanomedicine 2014, 9, 999–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulfer, S.K.; Ciccotto, S.L.; Gallo, J.M. Distribution of Small Magnetic Particles in Brain Tumor-Bearing Rats. J. Neurooncol. 1999, 41, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, A.; Scholz, R.; Wust, P.; Fähling, H.; Felix, R. Magnetic Fluid Hyperthermia (MFH): Cancer Treatment with AC Magnetic Field Induced Excitation of Biocompatible Superparamagnetic Nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1999, 201, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, T.J.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, B.G.; Yu, K.N.; Cho, M.H.; Lee, J.K. Multifunctional Nanoparticles Possessing a “Magnetic Motor Effect” for Drug or Gene Delivery. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 1068–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.S.; Tae, J.; Choi, B.; Kim, Y.S.; Moon, C.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.; Park, J.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, J.E.; Joh, J.-W.; Kim, S. Characterization, in Vitro Cytotoxicity Assessment, and in vivo Visualization of Multimodal, RITC-Labeled, Silica-Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles for Labeling Human Cord Blood-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Nanomedicine 2010, 6, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarzadeh, A.; Samiei, M.; Davaran, S. Magnetic Nanoparticles: Preparation, Physical Properties, and Applications in Biomedicine. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, B.A.; Haag, M.A.; Serkova, N.J.; Shroyer, K.R.; Stoldt, C.R. Controlled Aggregation of Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for the Development of Molecular Magnetic Resonance Imaging Probes. Nanotechnology 2008, 19, 265102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patitsa, M.; Karathanou, K.; Kanaki, Z.; Tzioga, L.; Pippa, N.; Demetzos, C.; Verganelakis, D.A.; Cournia, Z.; Klinakis, A. Magnetic Nanoparticles Coated with Polyarabic Acid Demonstrate Enhanced Drug Delivery and Imaging Properties for Cancer Theranostic Applications. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck Jr, G.R.; Ha, S.-W.; Camalier, C.E.; Yamaguchi, M.; Li, Y.; Lee, J.-K.; Weitzmann, M.N. Bioactive Silica-Based Nanoparticles Stimulate Bone-Forming Osteoblasts, Suppress Bone-Resorbing Osteoclasts, and Enhance Bone Mineral Density in vivo. Nanomedicine 2012, 8, 793–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobrovolskaia, M.A.; McNeil, S.E. Immunological Properties of Engineered Nanomaterials. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2007, 2, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, H.; Pan, D.; Castranova, V. Engineered Nanoparticle Exposure and Cardiovascular Effects: The Role of a Neuronal-Regulated Pathway. Inhal. Toxicol. 2018, 30, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Liu, H.H.; Ji, Z.; Chang, C.H.; Xia, T.; Nel, A.E.; Cohen, Y. Evaluation of Toxicity Ranking for Metal Oxide Nanoparticles via an in Vitro Dosimetry Model. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 9303–9313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xiong, L.; Tang, M. Toxicity of Inhaled Particulate Matter on the Central Nervous System: Neuroinflammation, Neuropsychological Effects and Neurodegenerative Disease. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2017, 37, 644–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Z.; Petukhova, A.; Kumacheva, E. Properties and Emerging Applications of Self-Assembled Structures Made from Inorganic Nanoparticles. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2010, 5, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Liu, T.; Li, Y.; Lau, J.; Yang, Z.; Fan, W.; Zhou, Z.; Shi, C.; Ke, C.; Bregadze, V.I. Fenton-Reaction-Acceleratable Magnetic Nanoparticles for Ferroptosis Therapy of Orthotopic Brain Tumors. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 11355–11365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarma, A.; Bania, R.; Devi, J.R.; Deka, S. Therapeutic Nanostructures and Nanotoxicity. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2021, 41, 1494–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brook, R.D.; Franklin, B.; Cascio, W.; Hong, Y.; Howard, G.; Lipsett, M.; Luepker, R.; Mittleman, M.; Samet, J.; Smith Jr, S.C. Air Pollution and Cardiovascular Disease: A Statement for Healthcare Professionals from the Expert Panel on Population and Prevention Science of the American Heart Association. Circulation 2004, 109, 2655–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, P.P.; Xia, Q.; Hwang, H.M.; Ray, P.C.; Yu, H. Mechanisms of Nanotoxicity: Generation of Reactive Oxygen Species. J. Food Drug Anal. 2014, 22, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nel, A.; Xia, T.; Mädler, L.; Li, N. Toxic Potential of Materials at the Nanolevel. Science 2006, 311, 622–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phukan, G.; Shin, T.H.; Shim, J.S.; Paik, M.J.; Lee, J.K.; Choi, S.; Kim, Y.M.; Kang, S.H.; Kim, H.S.; Kang, Y.; Lee, S.H.; Mouradian, M.; Lee, G. Silica-Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles Impair Proteasome Activity and Increase the Formation of Cytoplasmic Inclusion Bodies in Vitro. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, T.H.; Lee, D.Y.; Ketebo, A.A.; Lee, S.; Manavalan, B.; Basith, S.; Ahn, C.; Kang, S.H.; Park, S.; Lee, G. Silica-Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles Decrease Human Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell Migratory Activity by Reducing Membrane Fluidity and Impairing Focal Adhesion. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, T.H.; Seo, C.; Lee, D.Y.; Ji, M.; Manavalan, B.; Basith, S.; Chakkarapani, S.K.; Kang, S.H.; Lee, G.; Paik, M.J. Silica-Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles Induce Glucose Metabolic Dysfunction in Vitro via the Generation of Reactive Oxygen Species. Arch. Toxicol. 2019, 93, 1201–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thai, S.-F.; Wallace, K.A.; Jones, C.P.; Ren, H.; Prasad, R.Y.; Ward, W.O.; Kohan, M.J.; Blackman, C.F. Signaling Pathways and MicroRNA Changes in Nano-TiO2 Treated Human Lung Epithelial (BEAS-2B) Cells. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2015, 15, 492–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, R.J.; Hussain, S.; Rice, A.B.; Garantziotis, S. Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes Induce Altered Morphology and Loss of Barrier Function in Human Bronchial Epithelium at Noncytotoxic Doses. Int. J. Nanomedicine 2014, 9, 4093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernodet, N.; Fang, X.; Sun, Y.; Bakhtina, A.; Ramakrishnan, A.; Sokolov, J.; Ulman, A.; Rafailovich, M. Adverse Effects of Citrate/Gold Nanoparticles on Human Dermal Fibroblasts. Small 2006, 2, 766–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.B.; Dembo, M.; Wang, Y.L. Substrate Flexibility Regulates Growth and Apoptosis of Normal but Not Transformed Cells. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2000, 279, C1345–C1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, T.H.; Ketebo, A.A.; Lee, S.; Kang, S.H.; Basith, S.; Manavalan, B.; Kwon, D.H.; Park, S.; Lee, G. Decrease in Membrane Fluidity and Traction Force Induced by Silica-Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles. J. Nanobiotechnology 2021, 19, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ketebo, A.A.; Shin, T.H.; Jun, M.; Lee, G.; Park, S. Effect of Silica-Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles on Rigidity Sensing of Human Embryonic Kidney Cells. J. Nanobiotechnology 2020, 18, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colin-York, H.; Shrestha, D.; Felce, J.H.; Waithe, D.; Moeendarbary, E.; Davis, S.J.; Eggeling, C.; Fritzsche, M. Super-Resolved Traction Force Microscopy (STFM). Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 2633–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, F.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, P.; Gao, J.; Wu, X. Regulation of Hippo Signaling by Mechanical Signals and the Cytoskeleton. DNA Cell Biol. 2020, 39, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, L.; Puzzonia, M.D.S.; Ricci, R.; Aureli, F.; Guarguaglini, G.; González-Bermúdez, B.; Guinea, G. V; Plaza, G.R. Advances in Micropipette Aspiration: Applications in Cell Biomechanics, Models, and Extended Studies. Biophys. J. 2019, 116, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bustamante, C.J.; Chemla, Y.R.; Liu, S.; Wang, M.D. Optical Tweezers in Single-Molecule Biophysics. Nat. Rev. Methods Prim. 2021, 1, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Schell, C.; Huber, T.B.; Şimşek, A.N.; Hersch, N.; Merkel, R.; Gompper, G.; Sabass, B. Traction Force Microscopy with Optimized Regularization and Automated Bayesian Parameter Selection for Comparing Cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruthamuthu, V.; Sabass, B.; Schwarz, U.S.; Gardel, M.L. Cell-ECM traction force modulates endogenous tension at cell-cell contacts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2011, 108, 4708–4713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.L.; Tien, J.; Pirone, D.M.; Gray, D.S.; Bhadriraju, K.; Chen, C.S. Cells Lying on a Bed of Microneedles: An Approach to Isolate Mechanical Force. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2003, 100, 1484–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- du Roure, O.; Saez, A.; Buguin, A.; Austin, R.H.; Chavrier, P.; Silberzan, P.; Ladoux, B. Force Mapping in Epithelial Cell Migration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2005, 102, 2390–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghassemi, S.; Biais, N.; Maniura, K.; Wind, S.J.; Sheetz, M.P.; Hone, J. Fabrication of Elastomer Pillar Arrays with Modulated Stiffness for Cellular Force Measurements. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B Microelectron. Nanom. Struct. Process. Meas. Phenom. 2008, 26, 2549–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Tofangchi, A.; Anand, S. V; Saif, T.A. A Novel Cell Traction Force Microscopy to Study Multi-Cellular System. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2014, 10, e1003631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamimura, M.; Sugawara, M.; Yamamoto, S.; Yamaguchi, K.; Nakanishi, J. Dynamic Control of Cell Adhesion on a Stiffness-Tunable Substrate for Analyzing the Mechanobiology of Collective Cell Migration. Biomater. Sci. 2016, 4, 933–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limbach, L.K.; Li, Y.; Grass, R.N.; Brunner, T.J.; Hintermann, M.A.; Muller, M.; Gunther, D.; Stark, W.J. Oxide Nanoparticle Uptake in Human Lung Fibroblasts: Effects of Particle Size, Agglomeration, and Diffusion at Low Concentrations. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 9370–9376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shim, W.; Paik, M.J.; Nguyen, D.T.; Lee, J.K.; Lee, Y.; Kim, J.H.; Shin, E.H.; Kang, J.S.; Jung, H.S.; Choi, S.; Park, S.; Shim, J.S.; Lee, G. Analysis of Changes in Gene Expression and Metabolic Profiles Induced by Silica-Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 7665–7680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Tiruppathi, C.; Minshall, R.D.; Malik, A.B. Size and Dynamics of Caveolae Studied Using Nanoparticles in Living Endothelial Cells. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 4110–4116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilar, R.C.; Wendland, B. Endocytosis of membrane receptors: two pathways are better than one. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2005, 102, 2679–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, N.; Han, L.; Pan, X.; Su, L.; Jiang, Z.; Lin, Z.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, B. Nano-Mg (OH) 2-Induced Proliferation Inhibition and Dysfunction of Human Umbilical Vein Vascular Endothelial Cells through Caveolin-1-Mediated Endocytosis. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2015, 31, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krug, H.F.; Wick, P. Nanotoxicology: An Interdisciplinary Challenge. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 1260–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuong, N.Q.; Goegan, P.; Mohottalage, S.; Breznan, D.; Ariganello, M.; Williams, A.; Elisma, F.; Karthikeyan, S.; Vincent, R.; Kumarathasan, P. Proteomic Changes in Human Lung Epithelial Cells (A549) in Response to Carbon Black and Titanium Dioxide Exposures. J. Proteomics 2016, 149, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.; Yang, S.; Li, Z.; Xia, T.; Chen, J.; Ji, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Lin, S.; Huang, C. Aspect Ratio Determines the Quantity of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticle Uptake by a Small GTPase-Dependent Macropinocytosis Mechanism. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 4434–4447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.; Dong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xia, L.; Gu, W.; Bai, X.; Chang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Chen, K.; Li, J. Fullerenol Nanoparticles with Structural Activity Induce Variable Intracellular Actin Filament Morphologies. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2016, 12, 1234–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.C.; Liu, Y.J.; Qin, P.; Liang, S.X.; Sercombe, T.B.; Zhang, L.C. Selective Laser Melting of Ti–35Nb Composite from Elemental Powder Mixture: Microstructure, Mechanical Behavior and Corrosion Behavior. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 760, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgantzopoulou, A.; Serchi, T.; Cambier, S.; Leclercq, C.C.; Renaut, J.; Shao, J.; Kruszewski, M.; Lentzen, E.; Grysan, P.; Eswara, S. Effects of Silver Nanoparticles and Ions on a Co-Culture Model for the Gastrointestinal Epithelium. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2015, 13, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Hu, T.; Zhou, L.; Wu, D.; Huang, X.; Ren, X.; Lv, Y.; Hong, W.; Huang, G.; Lin, Z. Nrf2 Protects against Oxidative Stress Induced by SiO2 Nanoparticles. Nanomedicine 2017, 12, 2303–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ispanixtlahuatl-Meráz, O.; Schins, R.P.F.; Chirino, Y.I. Cell Type Specific Cytoskeleton Disruption Induced by Engineered Nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Nano 2018, 5, 228–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudhakaran, S.; Athira, S.S.; Mohanan, P. V Zinc Oxide Nanoparticle Induced Neurotoxic Potential upon Interaction with Primary Astrocytes. Neurotoxicology 2019, 73, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Nyström, A.M. Endocytic Uptake and Intracellular Trafficking of Bis-MPA-Based Hyperbranched Copolymer Micelles in Breast Cancer Cells. Biomacromolecules 2012, 13, 3814–3822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruenraroengsak, P.; Florence, A.T. Biphasic Interactions between a Cationic Dendrimer and Actin. J. Drug Target. 2010, 18, 803–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Ta, H.T.; Nguyen, N. Mechanobiology in Cardiology: Micro-and Nanotechnologies to Probe Mechanosignaling. View 2021, 2, 20200080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özbek, S.; Balasubramanian, P.G.; Chiquet-Ehrismann, R.; Tucker, R.P.; Adams, J.C. The Evolution of Extracellular Matrix. Mol. Biol. Cell 2010, 21, 4300–4305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watt, F.M.; Huck, W.T.S. Role of the Extracellular Matrix in Regulating Stem Cell Fate. Nat. Rev. Mol. cell Biol. 2013, 14, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tymchenko, N.; Wallentin, J.; Petronis, S.; Bjursten, L.M.; Kasemo, B.; Gold, J. A Novel Cell Force Sensor for Quantification of Traction during Cell Spreading and Contact Guidance. Biophys. J. 2007, 93, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, C.M.; Wang, H.B.; Dembo, M.; Wang, Y.L. Cell Movement Is Guided by the Rigidity of the Substrate. Biophys. J. 2000, 79, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engler, A.J.; Sen, S.; Sweeney, H.L.; Discher, D.E. Matrix Elasticity Directs Stem Cell Lineage Specification. Cell 2006, 126, 677–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McBeath, R.; Pirone, D.M.; Nelson, C.M.; Bhadriraju, K.; Chen, C.S. Cell Shape, Cytoskeletal Tension, and RhoA Regulate Stem Cell Lineage Commitment. Dev. Cell 2004, 6, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich, T.A.; de Juan Pardo, E.M.; Kumar, S. The Mechanical Rigidity of the Extracellular Matrix Regulates the Structure, Motility, and Proliferation of Glioma Cells. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 4167–4174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Discher, D.E.; Janmey, P.; Wang, Y. Tissue Cells Feel and Respond to the Stiffness of Their Substrate. Science 2005, 310, 1139–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishwakarma, M.; Spatz, J.P.; Das, T. Mechanobiology of Leader–Follower Dynamics in Epithelial Cell Migration. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2020, 66, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carisey, A.; Tsang, R.; Greiner, A.M.; Nijenhuis, N.; Heath, N.; Nazgiewicz, A.; Kemkemer, R.; Derby, B.; Spatz, J.; Ballestrem, C. Vinculin Regulates the Recruitment and Release of Core Focal Adhesion Proteins in a Force-Dependent Manner. Curr. Biol. 2013, 23, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kater, S.B.; Davenport, R.W.; Guthrie, P.B. Filopodia as Detectors of Environmental Cues: Signal Integration through Changes in Growth Cone Calcium Levels. Prog. Brain Res. 1994, 102, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razinia, Z.; Mäkelä, T.; Ylänne, J.; Calderwood, D.A. Filamins in Mechanosensing and Signaling. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2012, 41, 227–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geiger, B.; Spatz, J.P.; Bershadsky, A.D. Environmental Sensing through Focal Adhesions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyckmans, J.; Boudou, T.; Yu, X.; Chen, C.S. A Hitchhiker’s Guide to Mechanobiology. Dev. Cell 2011, 21, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iskratsch, T.; Wolfenson, H.; Sheetz, M.P. Appreciating Force and Shape—the Rise of Mechanotransduction in Cell Biology. Nat. Rev. Mol. cell Biol. 2014, 15, 825–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphrey, J.D.; Dufresne, E.R.; Schwartz, M.A. Mechanotransduction and Extracellular Matrix Homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Mol. cell Biol. 2014, 15, 802–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beningo, K.A.; Dembo, M.; Kaverina, I.; Small, J.V.; Wang, Y.L. Nascent Focal Adhesions Are Responsible for the Generation of Strong Propulsive Forces in Migrating Fibroblasts. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 153, 881–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Wolfenson, H.; Chung, V.Y.; Nakazawa, N.; Liu, S.; Hu, J.; Huang, R.Y.-J.J.; Sheetz, M.P. Stopping Transformed Cancer Cell Growth by Rigidity Sensing. Nat. Mater. 2019, 19, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, C.; Denisin, A.K.; Pruitt, B.L.; Nelson, W.J. Changes in E-Cadherin Rigidity Sensing Regulate Cell Adhesion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2017, 114, E5835–E5844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfenson, H.; Meacci, G.; Liu, S.; Stachowiak, M.R.; Iskratsch, T.; Ghassemi, S.; Roca-Cusachs, P.; O’Shaughnessy, B.; Hone, J.; Sheetz, M.P. Tropomyosin Controls Sarcomere-like Contractions for Rigidity Sensing and Suppressing Growth on Soft Matrices. Nat. Cell Biol. 2016, 18, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plotnikov, S. V.; Pasapera, A.M.; Sabass, B.; Waterman, C.M. Force Fluctuations within Focal Adhesions Mediate ECM-Rigidity Sensing to Guide Directed Cell Migration. Cell 2012, 151, 1513–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, J.L.; Holle, A.W.; Spatz, J.P. Nanoscale and Mechanical Properties of the Physiological Cell–ECM Microenvironment. Exp. Cell Res. 2016, 343, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geiger, B.; Spatz, J. Application of Synthetic Biology Approaches for Understanding Encounters between Cells and Their Microenvironment. Cell Adh. Migr. 2016, 10, 447–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, A.K.; Wild, P.; Stopak, D. Silicone Rubber Substrata: A New Wrinkle in the Study of Cell Locomotion. Science 1980, 208, 177–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuda, S.P.; Matsui, T.S.; Ichikawa, T.; Furukawa, T.; Kioka, N.; Fukushima, S.; Deguchi, S. Cellular Force Assay Detects Altered Contractility Caused by a Nephritis-associated Mutation in Nonmuscle Myosin IIA. Dev. Growth Differ. 2017, 59, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, U.S.; Soiné, J.R.D. Traction Force Microscopy on Soft Elastic Substrates: A Guide to Recent Computational Advances. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Molecular Cell Res. 2015, 1853, 3095–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghassemi, S.; Meacci, G.; Liu, S.; Gondarenko, A.A.; Mathur, A.; Roca-Cusachs, P.; Sheetz, M.P.; Hone, J. Cells Test Substrate Rigidity by Local Contractions on Submicrometer Pillars. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2012, 109, 5328–5333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trichet, L.; Le Digabel, J.; Hawkins, R.J.; Vedula, S.R.K.; Gupta, M.; Ribrault, C.; Hersen, P.; Voituriez, R.; Ladoux, B. Evidence of a Large-Scale Mechanosensing Mechanism for Cellular Adaptation to Substrate Stiffness. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2012, 109, 6933–6938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prager-Khoutorsky, M.; Lichtenstein, A.; Krishnan, R.; Rajendran, K.; Mayo, A.; Kam, Z.; Geiger, B.; Bershadsky, A.D. Fibroblast Polarization Is a Matrix-Rigidity-Dependent Process Controlled by Focal Adhesion Mechanosensing. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 1457–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, L.; Puzzonia, M.D.S.; Ricci, R.; Aureli, F.; Guarguaglini, G. Amorphous Silica Nanoparticles Alter Microtubule Dynamics and Cell Migration. Nanotoxicology 2014, 448, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Hevia, L.; Valiente, R.; Martín-Rodríguez, R.; Renero-Lecuna, C.; González, J.; Rodríguez-Fernández, L.; Aguado, F.; Villegas, J.C.; Fanarraga, M.L. Nano-ZnO Leads to Tubulin Macrotube Assembly and Actin Bundling, Triggering Cytoskeletal Catastrophe and Cell Necrosis. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 10963–10973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.; Gao, H.; Sui, J.; Duan, H.; Chen, W.N.; Ching, C.B. Cytotoxicity Evaluation of Oxidized Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes and Graphene Oxide on Human Hepatoma HepG2 Cells: An ITRAQ-Coupled 2D LC-MS/MS Proteome Analysis. Toxicol. Sci. 2012, 126, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shams, H.; Holt, B.D.; Mahboobi, S.H.; Jahed, Z.; Islam, M.F.; Dahl, K.N.; Mofrad, M.R.K. Actin Reorganization through Dynamic Interactions with Single-Wall Carbon Nanotubes. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.R.; Raftis, J.B.; Langrish, J.P.; McLean, S.G.; Samutrtai, P.; Connell, S.P.; Wilson, S.; Vesey, A.T.; Fokkens, P.H.B.; Boere, A.J.F. Correction to “Inhaled Nanoparticles Accumulate at Sites of Vascular Disease. ” ACS Nano 2017, 11, 10623–10624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





