Submitted:
04 July 2023
Posted:
05 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Stretching Platform
2.2. Motorized Stage and Controller
2.3. PDMS Container
2.4. Cell Culture, Maintenance, and Co-Culture Using the Cell Stretching Device
2.5. Operation of the Cell Stretching Device
2.6. Immunofluorescence Staining
2.7. Image Analysis of the Stretched Cells
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Performance of the Cell Stretcher
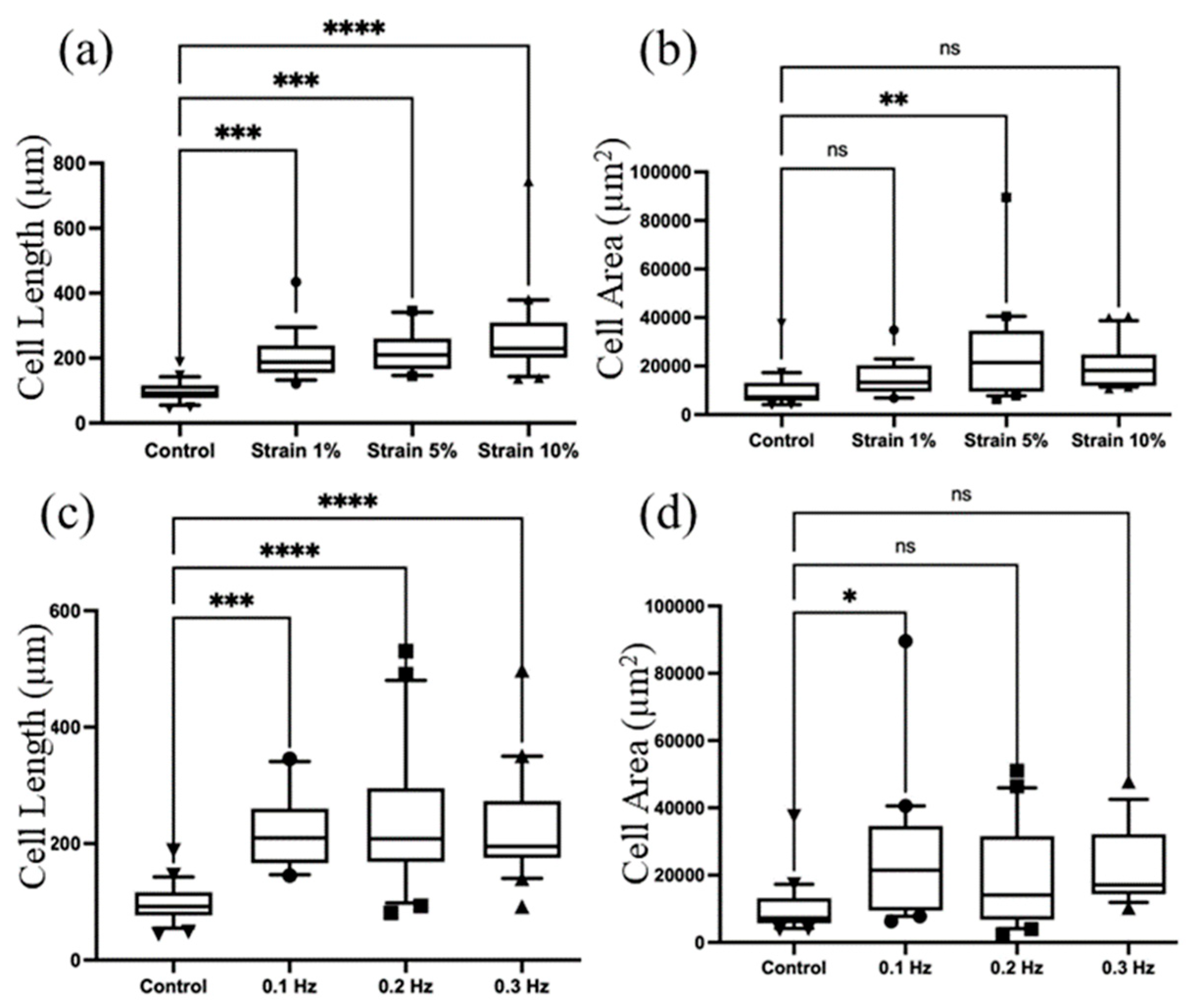
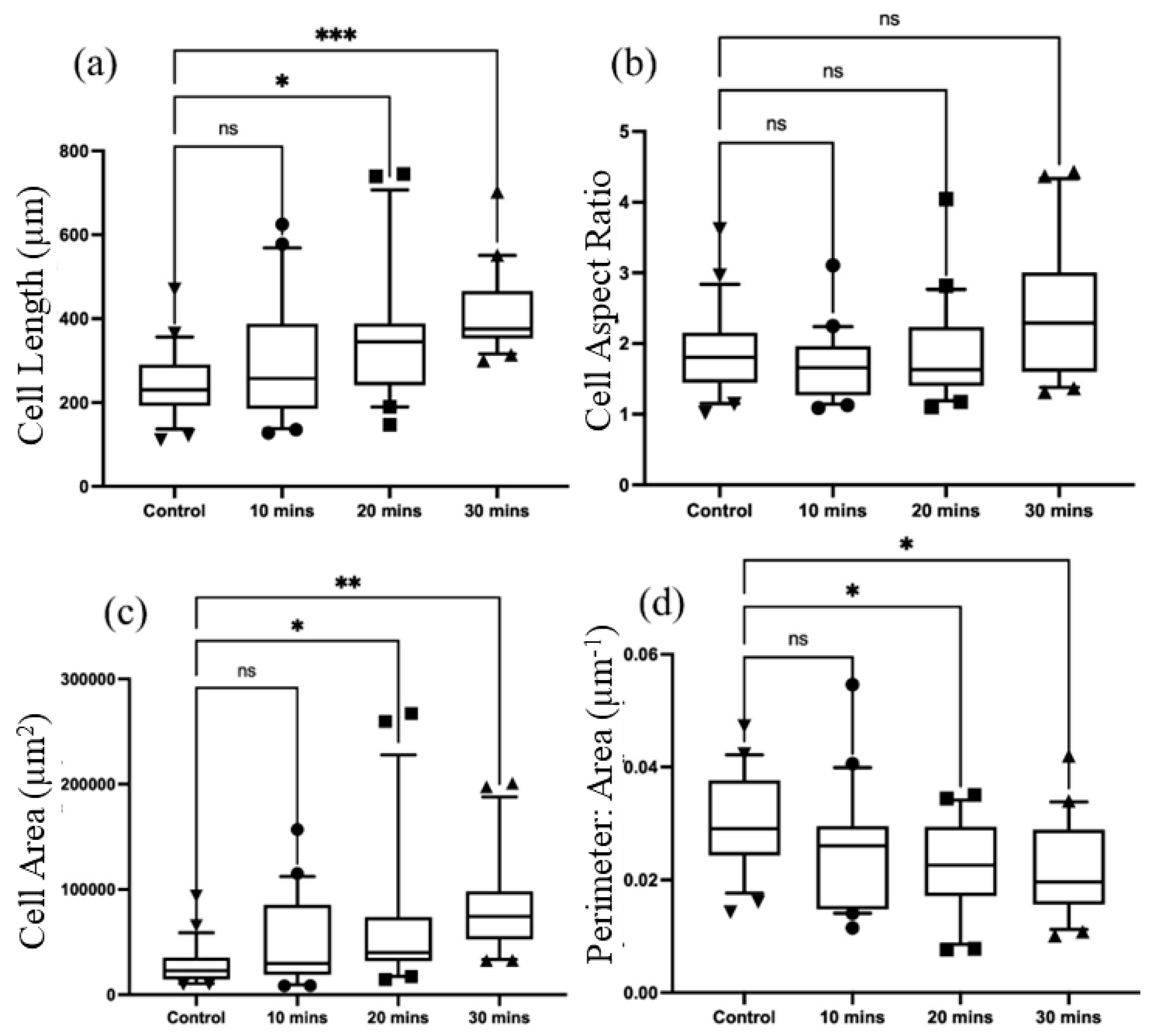
3.2. Parameter Optimization
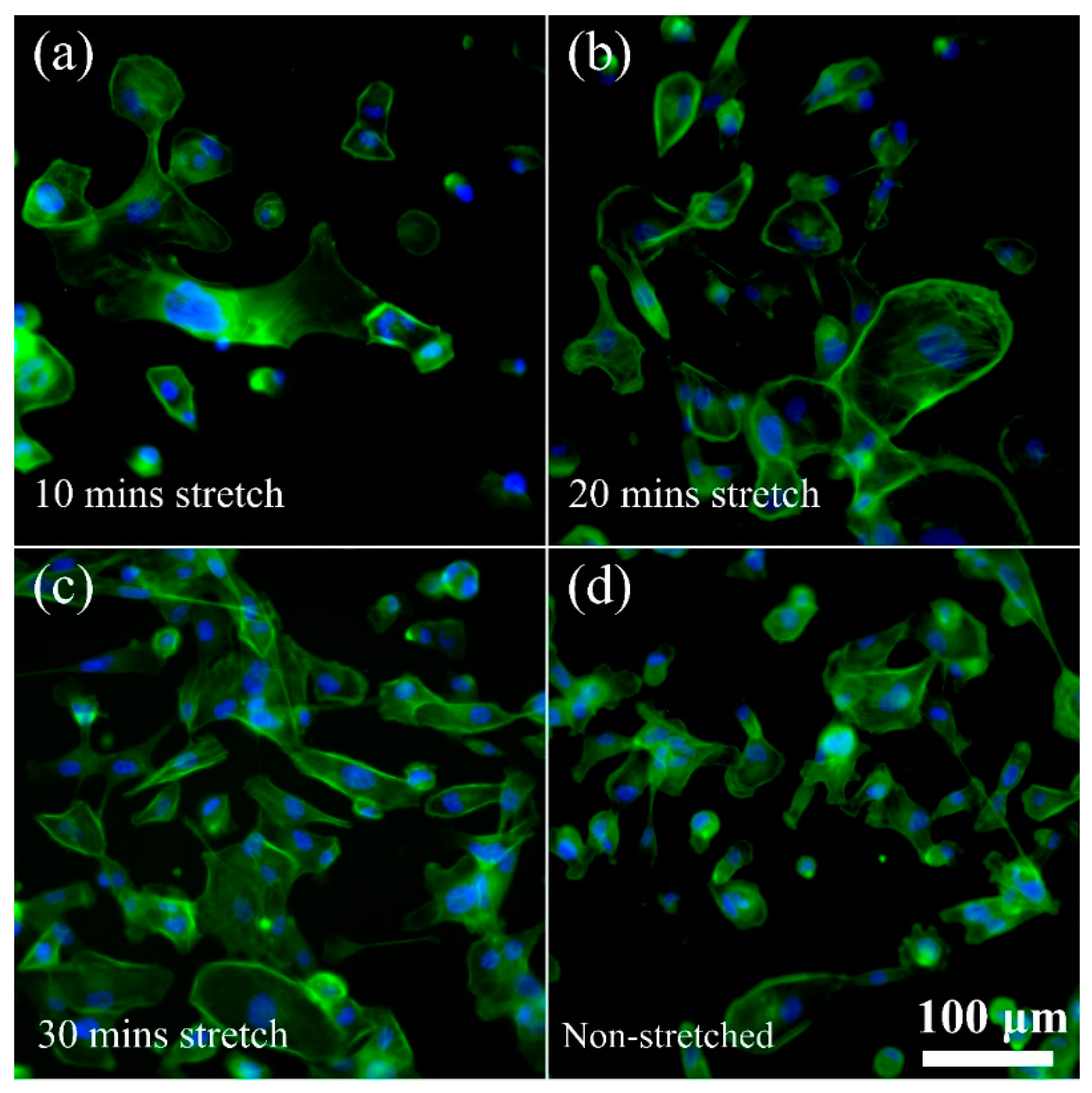
3.3. Cellular Rearrangement
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, C.S. Mechanotransduction–a field pulling together? Journal of cell science 2008, 121, 3285–3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orr, A.W.; Helmke, B.P.; Blackman, B.R.; Schwartz, M.A. Mechanisms of mechanotransduction. Developmental cell 2006, 10, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DuFort, C.C.; Paszek, M.J.; Weaver, V.M. Balancing forces: architectural control of mechanotransduction. Nature reviews Molecular cell biology 2011, 12, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, M.A. Integrins and extracellular matrix in mechanotransduction. Cold Spring Harbor perspectives in biology 2010, 2, a005066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller-Marschhausen, K.; Waschke, J.; Drenckhahn, D. Physiological hydrostatic pressure protects endothelial monolayer integrity. American Journal of Physiology-Cell Physiology 2008, 294, C324–C332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collinsworth, A.M.; Torgan, C.E.; Nagda, S.N.; Rajalingam, R.J.; Kraus, W.E.; Truskey, G.A. Orientation and length of mammalian skeletal myocytes in response to a unidirectional stretch. Cell and tissue research 2000, 302, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moghadas, H.; Saidi, M.S.; Kashaninejad, N.; Nguyen, N.-T. A high-performance polydimethylsiloxane electrospun membrane for cell culture in lab-on-a-chip. Biomicrofluidics 2018, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahyazadeh Shourabi, A.; Kashaninejad, N.; Saidi, M.S. An integrated microfluidic concentration gradient generator for mechanical stimulation and drug delivery. Journal of Science: Advanced Materials and Devices 2021, 6, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Møller, A.B.; Vendelbo, M.H.; Rahbek, S.K.; Clasen, B.F.; Schjerling, P.; Vissing, K.; Jessen, N. Resistance exercise, but not endurance exercise, induces IKKβ phosphorylation in human skeletal muscle of training-accustomed individuals. Pflügers Archiv-European Journal of Physiology 2013, 465, 1785–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Eyckmans, J.; Chen, C.S. Designer biomaterials for mechanobiology. Nature materials 2017, 16, 1164–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, M.; Epari, D.; Bieler, F.; Duda, G. In vitro models for bone mechanobiology: applications in bone regeneration and tissue engineering. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part H: Journal of Engineering in Medicine 2010, 224, 1533–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhuri, O.; Cooper-White, J.; Janmey, P.A.; Mooney, D.J.; Shenoy, V.B. Effects of extracellular matrix viscoelasticity on cellular behaviour. Nature 2020, 584, 535–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.H.; Li, B. Mechanics rules cell biology. BMC Sports Science, Medicine and Rehabilitation 2010, 2, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seriani, S.; Del Favero, G.; Mahaffey, J.; Marko, D.; Gallina, P.; Long, C.; Mestroni, L.; Sbaizero, O. The cell-stretcher: A novel device for the mechanical stimulation of cell populations. Review of Scientific Instruments 2016, 87, 084301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhuri, O.; Parekh, S.H.; Lam, W.A.; Fletcher, D.A. Combined atomic force microscopy and side-view optical imaging for mechanical studies of cells. Nature methods 2009, 6, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamble, H.; Barton, M.J.; Jun, M.; Park, S.; Nguyen, N.-T. Cell stretching devices as research tools: engineering and biological considerations. Lab on a Chip 2016, 16, 3193–3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Maslamani, N.A.; Khilan, A.A.; Horn, H.F. Design of a 3D printed, motorized, uniaxial cell stretcher for microscopic and biochemical analysis of mechanotransduction. Biology open 2021, 10, bio057778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulter, E.; Tissot, F.S.; Dilly, J.; Pisano, S.; Féral, C.C. Cyclic uniaxial mechanical stretching of cells using a LEGO® parts-based mechanical stretcher system. Journal of cell science 2020, 133, jcs234666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonakdar, N. Cell mechanics in response to large forces and deformations. Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg (FAU), 2014.
- Matsugaki, A.; Fujiwara, N.; Nakano, T. Conditions for Osteoblast Arrangement Induced under Long-Term Cyclic Stretching. Materials Transactions 2013, 54, 1195–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Nguyen, N.-T. A polymeric cell stretching device for real-time imaging with optical microscopy. Biomedical microdevices 2013, 15, 1043–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yost, M.J.; Simpson, D.; Wrona, K.; Ridley, S.; Ploehn, H.J.; Borg, T.K.; Terracio, L. Design and construction of a uniaxial cell stretcher. American Journal of Physiology-Heart and Circulatory Physiology 2000, 279, H3124–H3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Davis, S.P.; Yang, F.; Paulsen, K.S.; Kumar, M.; Sinnott DeVaux, R.; Wang, X.; Conklin, D.S.; Oberai, A.; Herschkowitz, J.I. Inertial microfluidic cell stretcher (iMCS): fully automated, high-throughput, and near real-time cell mechanotyping. Small 2017, 13, 1700705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamble, H.; Vadivelu, R.; Barton, M.; Boriachek, K.; Munaz, A.; Park, S.; Shiddiky, M.J.; Nguyen, N.-T. An electromagnetically actuated double-sided cell-stretching device for mechanobiology research. Micromachines 2017, 8, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamotani, Y.; Bersano-Begey, T.; Kato, N.; Tung, Y.-C.; Huh, D.; Song, J.W.; Takayama, S. Individually programmable cell stretching microwell arrays actuated by a Braille display. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 2646–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Nguyen, N.-T.; Lok, K.S.; Lee, P.P.F.; Su, M.; Wu, M.; Kocgozlu, L.; Ladoux, B. Multiarray cell stretching platform for high-magnification real-time imaging. Nanomedicine 2013, 8, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremblay, D.; Chagnon-Lessard, S.; Mirzaei, M.; Pelling, A.E.; Godin, M. A microscale anisotropic biaxial cell stretching device for applications in mechanobiology. Biotechnology letters 2014, 36, 657–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atcha, H.; Davis, C.T.; Sullivan, N.R.; Smith, T.D.; Anis, S.; Dahbour, W.Z.; Robinson, Z.R.; Grosberg, A.; Liu, W.F. A low-cost mechanical stretching device for uniaxial strain of cells: a platform for pedagogy in mechanobiology. Journal of biomechanical engineering 2018, 140, 081005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, S.; Vadivelu, R.; Ahmed, M.; Barton, M.; Nguyen, N.-T. Stretching cells–An approach for early cancer diagnosis. Experimental Cell Research 2019, 378, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Barton, M.; Nguyen, N.T. Stretching induces overexpression of RhoA and Rac1 GTPases in breast cancer cells. Advanced Biosystems 2020, 4, 1900222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Kashaninejad, N.; Nguyen, N.-T. RhoA and Rac1 in liver cancer cells: Induction of overexpression using mechanical stimulation. Micromachines 2020, 11, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




