1. Introduction
Optimal management of prostate cancer (PCa) requires accurate assessment of potential disease aggressiveness and possible metastatic spread [
1,
2,
3]. Conventionally [
4], prostate serum antigen (PSA) detection monitors and alerts the physician for possible presence for the disease. If indicated, needle biopsy, often guided by imaging devices such as ultrasound and MRI, extract tissue samples that are processed and then evaluated by a histopathologist to determine the tumor’s aggressiveness. Unfortunately, each step in the conventional approach is fraught with problems. PSA detection suffers [
5] from excessive number of false positive and also false negatives of clinically significant cancers. Needle biopsies [
6] are invasive, may cause hemorrhaging, infection, and discomfort, and they may miss sampling the most aggressive components of the tumors. Histopathological assessment [
7] of tissue samples by pathologists determines the Gleason score that depends on the qualitative assessment of potentially misprocessed tissue samples.
To correct some of the deficiencies in conventional evaluations, imaging, such as MRI, non-invasively displays the entire prostate (and possibly tumors) without suffering from under sampling the tumor. Trained radiologists, guided by the PI-RADS protocol [
8], visually inspect and assess multi-parametric MRI (MP-MRI) for tumor aggressiveness. However, due to the qualitative nature and need for training, agreement among trained radiologists regarding tumor evaluation can vary significantly [
9].
In addition, quantitative assessments through digital processing of the MRI are a way to reduce variations in patient assessments. Artificial Intelligence (AI) [
10] tools, such as those using deep learning, neural networks, random forests, machine learning, etc., have been used to quantitatively assess prostate MRI. Currently, AI principally [
11] examines the spatial components in an image. AI finds large number of spatial features, filters out the large number of features, and combines them together through custom built connected networks. Determination of which features, how many, and the parameters in the connecting networks is determined through training on large number of samples. AI requires a large number of training samples to form the predictive model. In contrast, spectral analysis uses analytic equations and minimal features (intensity in this study) and requires minimal training.
MP-MRI [
12] is often composed of Dynamic Contrast Enhancement (DCE) [
13,
14], along with structural (T1, T2, proton density), and Diffusion weighted images (DWI) that include ADC. DCE contributes invaluable information regarding contrast flow and, therefore, to the existence and location of the vasculature that feeds the tumor. However, injecting contrast material can be burdensome [
15] for the patient and clinician, time consuming, and can result in side effects for the patient. To simplify and aid clinical implementation, it is important to investigate whether high performance can be achieved with bi-parametric MRI that does not require the inclusion of DCE [
16].
Recently, spectral algorithms for examining targets from images gathered by hyperspectral cameras mounted in airborne platforms have been adapted to the medical arena [
17,
18,
19,
20]. Unlike airborne imagers that employ dispersive optics and push-broom configuration to collect registered data, each MRI component is resized, translated, and cropped so that each voxel is spatially registered and is a vector with three components, namely Apparent Diffusion Coefficient (ADC), High-B value (HBV), T2 for this study. These algorithms are applied to spatially registered MRI segments to the voxel level. The algorithms primarily operate in the spectral regime, rather than spatial regime as is commonly employed with AI. Instead of using training to find fitting parameters that must be adjusted for each clinical situation, the spectral approach is analytic, requires minimal training, and is suited for a variety of environments.
This is the first study to apply and test hyperspectral approaches for assessing tumor aggressiveness on spatially registered bi-parametric MRI.
2. Methods
2.1. Overview
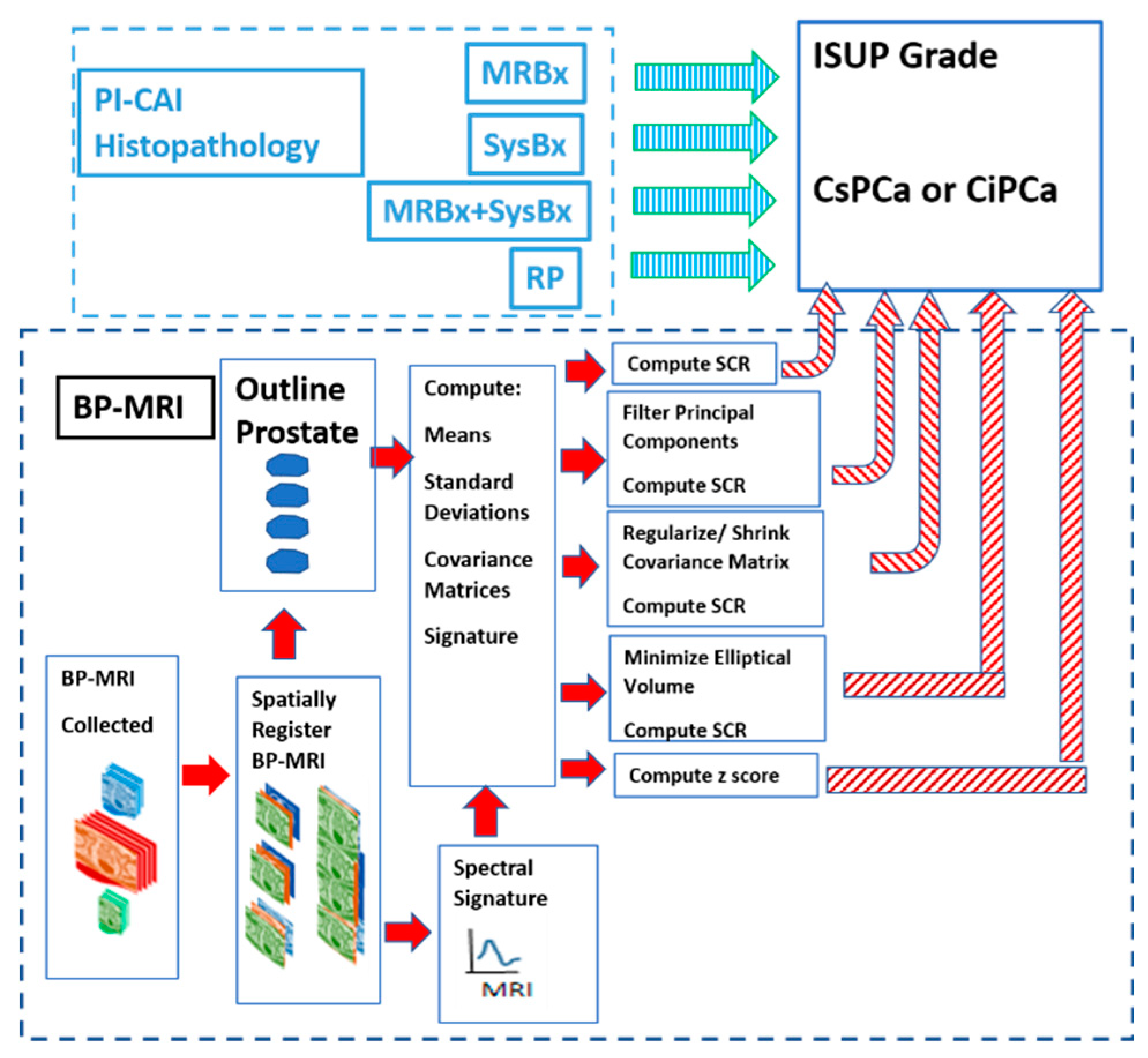
Figure 1 shows the overall scheme to compare a metric related to Gleason score, namely International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) grade [
21] and Clinically Significant (Insignificant) Prostate Cancer or CSci (CiPCa) with metrics generated from spatially registered MRI, namely z-score and processed Signal to Clutter Ratio (SCR) [
18]. For this study, patient MRI data and its assessment were gathered as part of the PI-CAI Grand Challenge [
22]. ISUP grade is determined from PI-CAI pathology analysis [
23] of the histopathology slides from MRI directed biopsy (MRBx), Systematic Biopsy (SysBx), the combination of MRBx and SysBx, and radical prostatectomy (RP). In the BP-MRI arm [
17,
18,
19,
20] of the study, spatially registered hypercubes are assembled from the individual MRI sequences, specifically the Apparent Diffusion Coefficient (ADC), High B-value (HBV) from the diffusion weighted images, and T2. The prostate is outlined and in scene signatures are derived from the hypercube and provide input for the z-score and SCR computation [
17,
18,
19,
20]. Noise in the SCR [
18,
19,
20] is reduced through principal component filtering, regularizing the covariance matrix, or elliptical volume minimization. The processed SCR, z-score are linear (logistical probability) fitted to the ISUP grade (CsPCa/CiPCa), respectively. Metrics describing the linear and logistic fits are given by the correlation coefficients (R) and the Area Under the Curve (AUC) from Receiver Operator Characteristic (ROC) [
18,
19,
20].
The spatial registration of the bi-parametric data, processing and calculations of SCR, ROC curve and AUC computations were executed using the python 3 programming language.
2.2. Study Design and Population
Patient data from prostate tumor MRI and assessments were collected and stored through PI-CAI [
22]. The PI-CAI challenge provides an annotated multi-center, multi-vendor dataset of 1,500 bpMRI exams (including their basic clinical and acquisition variables) that is made publicly available for the research community at large. The histopathology techniques range from MRBx, SysBx, MRBx+SysBx, and RP [
23], and only a subset of the 1,500-patient cohort underwent or had available biopsy results. Patients were scanned in a variety of centers and with a variety of scanners from Siemens and Philips. The PI-CAI data collection [
22] only contains bi-parametric MRI, namely ADC, HBV, and T2 sequences.
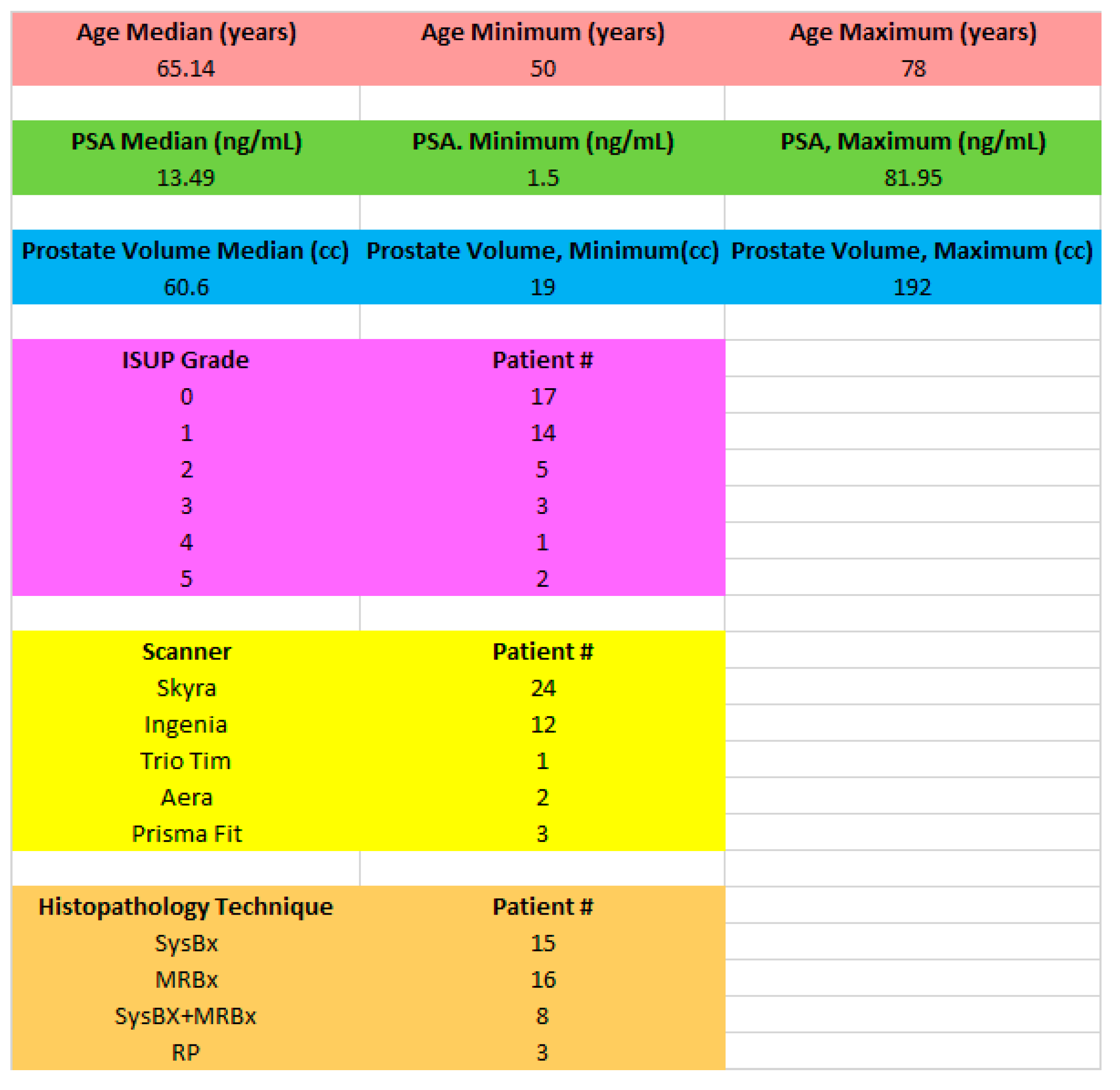
For this study (
Table 1), 42 consecutive patients that had been biopsied in the PI-CAI database were assessed. All patients had biopsy proven adenocarcinoma of the prostate, with mean patient age of 65.1 years (range, 50 to 78 years), with a mean PSA of 13.49 ng/mL (range, 1.5 to 81.95 ng/mL), mean prostate volume mean of 60.6 cm
3 (range 19 to 192 cm
3), and mean ISUP grade of 1.12 (range, 0 to 5) are shown in
Table 1. The distribution of histopathology techniques and scanners is listed in
Table 1. This study did not place restrictions on tumor location within the prostate. All cases were anonymized for subsequent analysis.
2.3. Spatial Registered Hypercube Assembly: Magnetic Resonance Imaging
The MRI collection [
22] was composed of structural (T2) images, diffusion weighted images (DWIs), specifically the ADC, High B Value (HBV). Dynamic Contrast Enhancement (DCE) images were excluded from this data collection, unlike some MP-MRI.
2.4. Spatial Registered Hypercube Assembly: Image Processing, Pre-Analysis
Prior to registration, spatial resolution and spatial offsets for the scanning setup of a given patient was read from image header files for MRI sequences (ADC, HBV, T2). All MRI images were digitally resized [
17,
18,
19,
20] to the sequence with the lowest spatial resolution in the transverse direction. Based on the offsets denoted in the image header files, the images were translated a few pixels to the reference image (ADC, HBV)). Using the known location of the axial offsets, the slices were selected to match the offsets. Based on visual inspection, small rigid adjustments (minor transverse translation) were applied to the T2 image to match the ADC, HBV. A “cube” is composed of stacked individual slices that were scaled, translated and cropped so as to be spatially registered at the voxel level. Following cropping, all images shared the common field of view (FOV). These “three dimensional” (two transverse directions plus spectral dimension composed of BP-MRI sequences) cubes were “stitched” together into a narrow three-dimensional hypercube to depict the entire prostate and other tissues in the field of view of the MRI scan. This stitching or mosaicking follows the approach used in remote sensing in which large areas are stitched together. Mosaicking or stitching cubes greatly increases the processing speed for handling high dimensional data.
Figure 2 shows an example of a stitched spatially registered image. The three sequences (ADC, HBV, T2) plus a color composite derived from the three spatially registered images are shown. Slices in the axial direction are “stitched” together, placed side by side in the horizontal display. Color composite is shown with red, green, and blue assigned ADC, HBV, and T2, respectively. Common zoomed in portion of the image is shown for ADC, HBV, T2 and the composite color image. The tumor in such a color scheme appears as green (low ADC, high HBV, low T2).
2.5. Overall Quantitative Metrics Description: SCR, Z-Score
Instead of relying on trained radiologists to visually inspect multiple MRI images, the Signal to Clutter Ratio and z-score quantitatively assesses tumors departure from normal prostate tissue. The z-score and SCR formulation combines information from all MRI sequences. Both compute the difference between the mean tumor signature value and the mean normal prostate value and scaled by the normal prostate standard deviation for each MRI sequence (ADC, HBV, T2). z-score does not account for correlation among the i sequences (ADC, HBV, T2). In contrast, the SCR decorrelates the sequences through whitening but adds noise. The SCR formulation uses the covariance matrix to correct and account for correlations among the different components (for example, the correlation between ADC and DWI) to get a true measure of the aggregate contribution of each sequence. The Appendix summarizes some of the mathematics behind the SCR algorithm. For more details see References [
18,
19,
20].
2.6. SCR: Filtering Noise
Computing the covariance matrix for the SCR generates principal components [
24]. Principal components are linear combinations of all MRI components but are orthogonal or totally decorrelated from each other. The principal components are ordered based on their eigenvalue or statistical variation. Well resolved images have high eigenvalue and high variation within the image. In contrast, the noisy principal components have small eigenvalues. Noise is reduced by filtering and eliminating the noisy (low eigenvalue) principal components resulting in a more accurate SCR calculation. The Appendix summarizes some of the mathematics behind the filtering of principal components. For more details see References [
18,
25,
26].
2.7. Regularization and Shrinkage
Regularization is another way to correct for the imperfections of the computed covariance matrix. The statistics describing the background (normal prostate) should follow a normal distribution. However, the analytic formula for the covariance matrix results in only an approximation. The goal of shrinkage regularization [
18,
27] is to perturb the original covariance matrix CM(γ) by mixing in a diagonal matrix with a mixing parameter γ to generate a regularized or modified regularized covariance matrix. The appropriate γ is chosen to maximize the normal distribution. Regularized or modified regularized covariance matrix generation follow the same procedure but differ in the mixing diagonal matrix. The Appendix summarizes some of the mathematics behind regularization. For more details see References [
18,
27].
2.8. Elliptical Volume Minimization
Elliptical volume minimization (EVM) [
28] provides another approach for reducing the effects of noise in the covariance matrix calculation. EVM does not use an analytic solution. Instead EVM sequentially removes 10% of randomly chosen pixels searches and computes and records the hypervolume elliptical volume for the remaining 90% of the prostate pixels. The minimum elliptical volume after the search is chosen, presumably reducing the effects of the 10% aberrant voxels
2.9. Logistic Regression
A logistic regression fit [
29] is obtained by fitting processed SCR, or z-score, or patient data to the dependent categorial variable CsPCa. The ISUP grade is derived from the pathological assessment MRBx, SysBx, MRBx+SysBX, or RP. The clinically significant PCa (CsPCa) was assigned to ISUP grade >=2, and the clinically insignificant PCa (CiPCa) was assigned to <2. The training/test sets were randomly assigned among the 42 patients but maintained 70%/30% for the patient sets. New randomized sets were generated 1,000 times forming configurations of patients within the training/test sets but also multiple ROC [
30] curves and resulting in a distribution of AUC. The distribution of AUC scores was recorded, and the 2.5% and 97.5% largest AUC delineated the 95% confidence interval. The quality of the fit was assessed through the AUC and the 95% confidence interval from the ROC curves.
3. Results
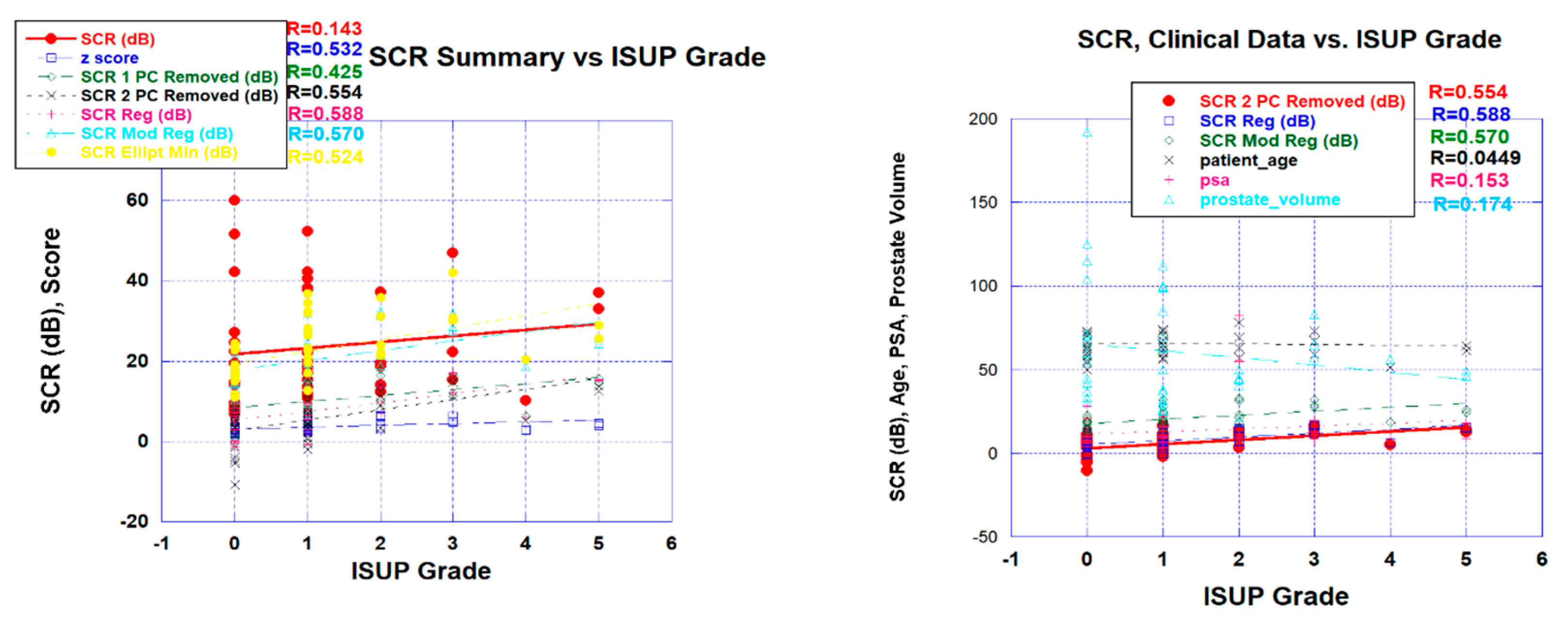
Figure 3a displays a scatterplot linear fit of bi-parametric spatially registered metrics against the ISUP grade determined by the PI-CAI radiologists, and the associated correlation coefficient R (also shown in
Table 2 in column R(ALL)). The bi-parametric metrics include unprocessed SCR, z-score, filtered SCR with one and two principal components removed, regularized and modified regularized SCR, and SCR after the elliptical volume has been minimized. Unprocessed SCR yields the smallest correlation coefficient (R=0.143) relative to the processed SCR and z score (R>0.55) (see
Table 2 in the column R(ALL)).
Figure 3b displays a scatter plot of patient related metrics such psa, prostate volume, and age against ISUP grade as well as the correlation coefficients. For reference, processed SCR, specifically 2 principal components removed, regularized SCR, modified regularized SCR are also shown as reference. The patient related metrics yielded much lower correlation coefficients (R ~.115).
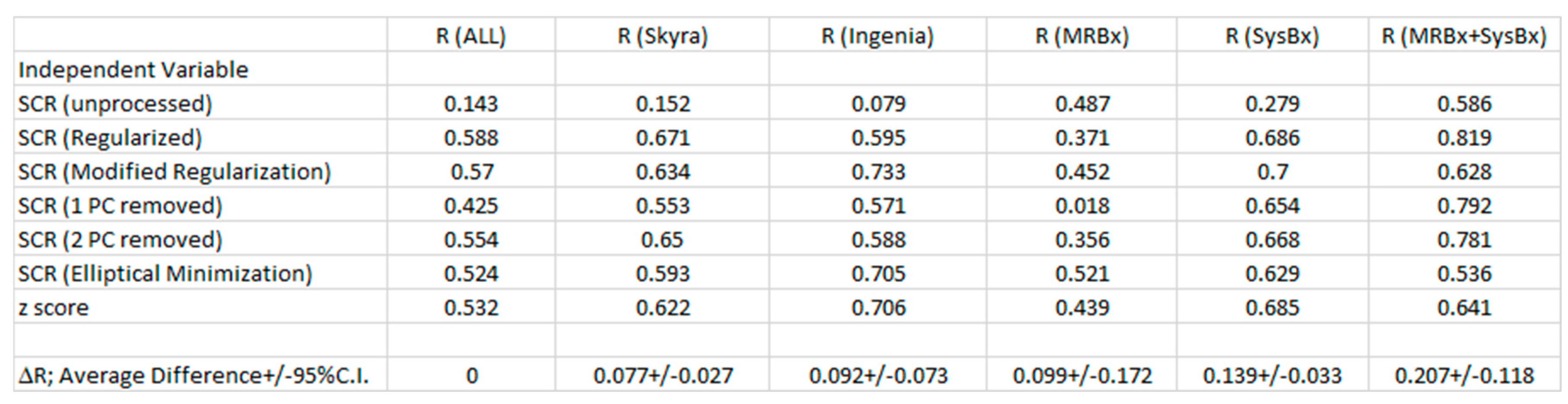
Table 2 shows correlation coefficients for all patients included in the fit (R(ALL)).
Table 2 also shows the correlation coefficients for selected groups of patients based on the type of scanner (R(Skyra), R(Ingenia)) and histological technique (MRBx, SysBx, MRB+SysBx). The correlation coefficients for the fits restricted to individual scanners exceeded the correlation coefficients obtained from including all patients. Combining MRBX and SysBx to determine the ISUP grade achieved the highest correlation coefficients, although only slightly higher than from SysBx alone. Also shown are the average differences in R (ΔR) relative fitting ALL patients, ΔR+/-95% C.I. (95% confidence interval). ΔR (Skyra), ΔR(Ingenia), ΔR(SysBx), and ΔR (MRBx+SysBx) slightly exceeds fits using all patients.
The SCR metric depends on the tumor signature. In this study, candidate signatures were chosen based on their color (green in this study) from the spatially registered color composite image. For a given patient, a number of candidate tumor may be displayed. This study examined a number of tumor signatures and found that the signatures that occupied the largest area and was most prominent generated the highest correlation with ISUP grade. Even the signatures that were less prominent generated R>0.35, exceeding the patient related metrics (PSA, age, prostate volume) R~0.15.
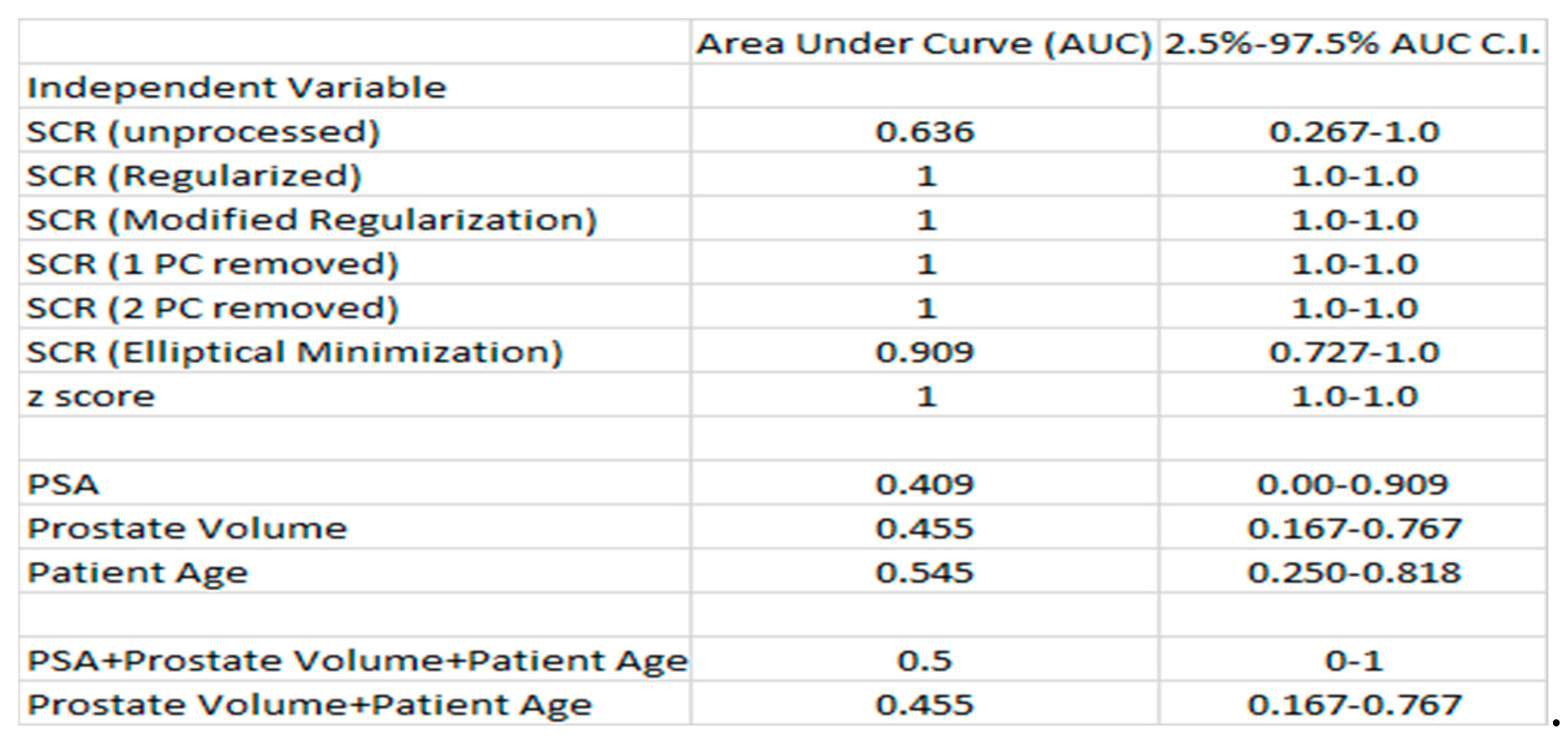
Table 3 displays the average and 95% confidence interval values for the AUC for ROC curves resulting from logistical probability fits of bp-MRI and patient-based metrics the CsPCa/CiPCa)). The bi-parametric metrics include unprocessed SCR, z-score, filtered SCR with one and two principal components removed, regularized and modified regularized SCR, and SCR after the elliptical volume has been minimized. Patient-related metrics include patient PSA, prostate volume, and age. Processed SCR (Regularized, modified regularized, filtered principal components, z-score AUC (=1.0) with narrow 95% confidence intervals. The patient-related metrics yielded much lower AUC relative to bp-MRI-based metrics. Multi-variable fits by combining patient metrics results in small AUC increases.
4. Discussion
This is the first study to apply and test hyperspectral approaches for assessing tumor aggressiveness on spatially registered bi-parametric MRI. This study examined 42 consecutive patients and found high correlation coefficients for linear fits between certain processed SCR, z-score and the ISUP grade. In addition, this study also demonstrated high AUC values with narrow 95% confidence intervals from ROC curve analysis characterizing logistic probability fitting for the categorical variable CsPCa/CiPCa. The AUC from this study compares favorably with those from AI applied to bi-parametric MRI that generally achieved AUC=0.85 up to the highest AUC=0.95. Previously high correlation coefficients were achieved using processed SCR fits to Gleason score were achieved in a MP-MRI studies with seven components that included DCE images. The high AUC fits to the ISUP grade from processed SCR were much higher than those generated by conventional metrics such as PSA, prostate volume, and patient age.
The high AUC for the logistical fits to the CsPCa/CiPCa and high correlation coefficients fits to the ISUP grade compares favorably with those from AI. AI is currently heavily studied. AI requires a substantial amount of training to generate a model. Ep. Normal prostate tissue is currently manually identified but each new clinical situation requires new training. The spectral technology may require a radiologist to identify potential tumor signatures, which is relatively easy with the color applied to the spatially registered images. Spatial registration can be automated based on offsets and careful patient setup and minor translation shifts. Currently, normal prostate masking is currently a manually input but can be automated through k-means segmentation for the spatially registered set of with AI segmentation techniques.
Spectral algorithms and approaches had previously been applied for MP-MRI that was composed of seven sequences, including multiple sequences derived from DCE. For an individual data set and correct spatial registration, reduction in the number of sequences means reduced SCR. This analysis described in this manuscript suggests that sufficient fitting to the ISUP grade with fewer sequences has little deleterious effect. The images in the PI-CAI collection are more recent than the previously used NIH and possibly of better quality. Using scanner offsets to spatially register the images simplifies and improves the registration.
One impetus for quantitative analysis of medical imaging is to guide, support or reduce the need for a radiologist’s input. AI offers the promise of voiding the need for any radiologist intervention. The spectral analysis likely requires a radiologist to identify tumor signatures. However, the need for a radiologist may be an advantage by requiring some human supervision. Tumors are heterogenous, and each patient presents a unique case that requires some monitoring.
Although the number of patients is relatively small, this study examined linear fits to ISUP grade based on biopsy methods. The highest correlation coefficients were achieved by combining MRBx with SysBx, followed closely by SysBx. Others have found fits to the combination of MRBx with SysBX closely resembles the fits to radical prostatectomy, which is the “gold standard.” The current examined data set only includes biopsies from three radical prostatectomy patients, precluding comparison to the “gold standard.”
In addition, this study examined linear fits of processed SCR to ISUP grade based on scanner. Individually fitting the SCR from images scanned with the Siemens Skyra and Philips Ingenia scanners generated larger correlation coefficients than lumping all patient data files into the fit. Such results suggest that ADC, HBV, T2 images from the scanners are meaningfully but consistently different. Scanners use different pulse sequences to generate T2 images and different b-values to form HBV images. Therefore, lumping all scanners together in the fits degrades the fit. Higher number of patient samples will enable exclusive fits from the Siemens Trio Tim, Aera, and Prisma Fit Scanners.
Only a limited number of patients in this current effort were analyzed and, therefore, this work must be regarded as a pilot study. However, the excellent results demonstrated in this study warrant future investigation with a greater number of patients. Future work should assess fitting of processed SCR to patients that were biopsied through radical prostatectomy, the gold standard for determining tumor aggressiveness.
6. Conclusion
High values of R and AUC to fit the ISUP grade and CsPCa/CiPCA based on non-invasive SRBP-MRI in this pilot study were comparable or better than those from artificial intelligence from other studies. Additional studies involving a higher number of patients and those assessed with radical prostatectomy are required to possibly confirm, strengthen, and validate this study. Not using DCE simplifies the scanning for clinician and patients, making implementation of spectral analysis of bi-parametric MRI attractive.
Author Contributions
(I) Conception and design: R Mayer; (II) Administrative support: R Mayer, CB Simone 2nd, P Choyke; (III) Provision of study materials or patients: R Mayer; (IV) Collection and assembly of data: R Mayer; (V) Data analysis and interpretation: R Mayer; (VI) Manuscript writing: All authors; (VII) Final approval of manuscript: All authors.
Funding
No external funding for this research
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable, Followed the PI-CAI Challenge. See Reference 22
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable. Followed the PI-CAI Challenge. See Reference 22
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. Overall Quantitative Metrics Description: SCR, Z-Score
The z-score [
18,
19,
20] is a sum of the total of M differences (M=3) of each sequence i (ADC, HBV, T2) between the difference between tumor signature S
i for component i that is an average over W target voxels and the mean normal prostate μ
i for component i that is the average over N normal prostate voxels, scaled by the normal prostate standard deviation σ
i and is given by
and
The target voxels q and the normal prostate voxels p were identified from the composite color image by inspection. z-score does not account for correlation among the i sequences (ADC, HBV, T2). Similarly, the signal to Clutter Ratio SCR [
18,
19,
20] is given by
that is a matrix multiplication over MP-MRI modalities. The superscript T denotes a vector transpose operation, CM is the covariance matrix, and the superscript -1 denotes a matrix inverse operation, where S is the vector tumor signature or mean over the identified tumor voxels (Equation (2)). Vector μ is the mean value for normal prostate or background (Equation (2)).
Appendix A.2. SCR: Filtering Noise
The filtered SCR
Filtered is given by
where the inverse covariance matrix CM
Filtered-1 is a square symmetrical matrix and decomposes into three parts [
26],
with the eigenmatrix Λ, transpose of the eigenmatrix Λ
T, and diagonal matrix with eigenvalues λ
21, λ
22, λ
23…λ
2M populating the diagonal [
26]
The eigenvalues are ordered according to size ranging from the largest λ
1 to the smallest λ
M. For unfiltered processing, the images corresponding to the eigenvalues and eigenvectors range from high signal and variation (1,2) to low variation and very noisy (M-1, M. Filtering out the noisy eigenvectors [
18,
19,
20] means removing or deleting the lowest valued eigenvalues (1 or 2 in this study) for Equations (4) and (5).
Appendix A.3. Regularization and Shrinkage
The goal of shrinkage regularization [
18,
20,
27] is to perturb the covariance matrix CM(γ) to maximize the normal distribution, or equivalently minimize the discriminant function d(γ) [=-ln(normal distribution)] by adding a diagonal component that is controlled by the parameter γ and thereby perturbing the covariance matrix CM into the regularized CM
mod_
Reg(γ)
V is a diagonal matrix filled up with the square of the standard deviations from M modalities is given by
The goal of regularization is to perturb the covariance matrix CM(g) so as to maximize the normal distribution, or equivalently minimize the discriminant function d(g) (=-ln(normal distribution)) i.e. Using Equations (7) and (8) the modified discriminant function d
mod_Reg (γ)
is computed for 0<γ<1 and a minimum d
mod(γ
min) is found at γ
min. resulting in a CM
Mod_Reg and SCR
Mod_Reg using a modified regularization procedure (using Equations (7)–(9)).
And Equations (7)–(10) to get
Another approach for reducing noise is through a more standard form of regularization and shrinkage [
18,
19,
20,
27]). That is shrinking the difference in the highest and lowest eigenvalues by adding a diagonal component that is controlled by the parameter γ and thereby perturbing the covariance matrix CM into the regularized CM
Reg(γ)
where Tra denotes the trace operator and I is the identity matrix and γ ranges from γ=0.0 or no CM modification to γ=1.0 or CM is proportional to the identity matrix. The goal of regularization is to perturb the covariance matrix CM(γ) so as to maximize the normal distribution, or equivalently minimize the discriminant function d(γ) (=-ln(normal distribution)) i.e.
where the sum is over all N samples in the prostate ensemble and det denotes the determinant operation. A search is conducted among the γ’s (range 0<γ<1) for the lowest discriminant function that can be achieved with γ
min and results in a regularized SCR
Reg
It should be noted that γ=0 results in the standard SCR (Equation (3)).
References
- Sobin L, Wittekind C. TNM classification of malignant tumors. 5th ed John Wiley and Sons, Inc, New York; 1997.
- Shariat, SF, Karakiewicz PI, Roehrborn CG, Kattan MW. An Updated Catalog of Prostate Cancer Predictive Tools. Cancer 2008; 113: 3075-3099. [CrossRef]
- Martin NE, Mucci LA, Loda M, DePinho RA. Prognostic Determinants in Prostate Cancer. Cancer J. 2011; 17(6): 429–437. [CrossRef]
- Parker C, Castro E, Fizazi K, Heidenreich A, Ost P, Procopio G, Tombal B, Gillessen S Prostate cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up Ann Oncol2020 Sep;31(9):1119-1134. [CrossRef]
- Bernal-Soriano MC, Parker LA, López-Garrigos M, Hernández-Aguado I, Caballero-Romeu JP, Gómez-Pérez L, Alfayate-Guerra R, Pastor-Valero M, García N, Lumbreras B. Factors associated with false negative and false positive results of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) and the impact on patient health: Cohort study protocol. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Oct;98(40):e17451. PMID: 31577771; PMCID: PMC6783167. [CrossRef]
- Madej A, Wilkosz J, Różański W, Lipinski M, Complication rates after prostate biopsy according to the number of sampled cores Cent European J Urol. 2012; 65(3): 116–118. 2012 Sep 4. PMCID: PMC3921797PMID: 2457894. [CrossRef]
- Humphrey PA, Histopathology of Prostate Cancer Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2017 Oct; 7(10):a030411. PMCID: PMC5629988PMID: 28389514. [CrossRef]
- Weinreb JC, Barentsz JO, Choyke PI, et al. PI-RADS Prostate Imaging-Reporting and Data System:2015,Version 2. Eur Urol 2016;69:16-40. [CrossRef]
- Rosenkrantz A.B., Ginocchio L.A., Cornfeld, D. , Froemming A.T., Gupta R., Turkbey B, Westphalen A.C., Babb, J.S., Margolis D.J., Interobserver Reproducibility of the PI-RADS Version 2 Lexicon: A Multicenter Study of Six Experienced Prostate Radiologists Radiology 2016, 280:793–80. [CrossRef]
- Twilt, J.J.; van Leeuwen, K.G.; Huisman, H.J.; Fütterer, J.J.; de Rooij, M. Artificial Intelligence Based Algorithms for Prostate Cancer Classification and Detection on Magnetic Resonance Imaging: A Narrative Review. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 959. [CrossRef]
- Barragán-Montero A, Javaid U, Valdés G, Nguyen D, Desbordes P, Macq B, Willems S, Vandewinckele L, Holmström M, Löfman F, Michiels S, Souris K, Sterpin E, Lee JA. Artificial intelligence and machine learning for medical imaging: A technology review. Phys Med. 2021 Mar;83:242-256. Epub 2021 May 9. PMID: 33979715; PMCID: PMC8184621. [CrossRef]
- Stabile, A., Giganti, F., Rosenkrantz, A.B. et al. Multiparametric MRI for prostate cancer diagnosis: current status and future directions. Nat Rev Urol 17, 41–61 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Tofts PS, Brix G, Buckley DL, Evelhoch JL, Henderson E, Knopp MV, Larsson HB, Lee TY, Mayr NA, Parker GJ, Port RE, Taylor J, Weisskoff RM Estimating Kinetic Parameters from Dynamic Contrast-EnhancedT1-Weighted MRI of a Diffusable Tracer: Standardized Quantities and Symbols. J Magn Res Imag. 1999; 10:223–232. [CrossRef]
- Tofts PS, T1-weighted DCE Imaging Concepts: Modelling, Acquisition and Analysis. Magnetom Flash 2010; 3: 31-39.
- Padhani AR, Schoots I, Villeirs G. Contrast Medium or No Contrast Medium for Prostate Cancer Diagnosis. That Is the Question. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2021 Jan;53(1):13-22. Epub 2020 May 3. PMID: 32363651. [CrossRef]
- Tamada T, Kido A, Yamamoto A, Takeuchi M, Miyaji Y, Moriya T, Sone T. Comparison of Biparametric and Multiparametric MRI for Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer Detection With PI-RADS Version 2.1. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2021 Jan;53(1):283-291. Epub 2020 Jul 2. PMID: 32614123. [CrossRef]
- Mayer R, Simone CB 2nd, Skinner W, Turkbey B, Choyke P, Pilot study for supervised target detection applied to spatially registered multiparametric MRI in order to non-invasively score prostate cancer. Computers in Biology and Medicine 2018; 94: 65-73. [CrossRef]
- Mayer R, Simone CB 2nd, Turkbey B, Choyke P. Development and testing quantitative metrics from multi-parametric magnetic resonance imaging that predict Gleason score for prostate tumors. Quant Imaging Med Surg 12 (3) 1859-1870 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Mayer R, Turkbey B, Choyke P, Simone CB 2nd. Combining and Analyzing Novel Multi-parametric MRI Metrics for Predicting Gleason Score, Quant Imaging Med Surg,. 12, No 7 (July 2022). [CrossRef]
- Mayer R, Turkbey B, Choyke P, Simone CB 2nd. (2023) Pilot Study for Generating and Assessing Nomograms and Decision Curves Analysis to Predict Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer Using Only Spatially Registered Multi-Parametric MRI Front. Oncol. Sec. Genitourinary Oncology 13 – 202. [CrossRef]
- Egevad L, Delahunt B, Srigley JR, Samaratunga H. International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) grading of prostate cancer - An ISUP consensus on contemporary grading. APMIS. 2016 Jun;124(6):433-5. PMID: 27150257. [CrossRef]
-
https://pi-cai.garnd-challenge.org/TAM/.
- Ahdoot M, Wilbur AR, Reese, SE, Lebastchi AH, Mehralivand S, Gomella PT, Bloom J, Gurram S, Siddiqui M, Pinsky P, Parnes H, Linehan WM, Merino M, Choyke PL, Shih JH, Turkbey B, Wood BJ, Pinto PA MRI-Targeted, Systematic, and Combined Biopsy for Prostate Cancer Diagnosis N Engl J Med 2020;382:917-28. [CrossRef]
- Strang G. Linear algebra and its applications (Fourth ed). Belmont, CA, Thomson, Brooks/Cole, 2006.
- Manolakis D, Shaw G. Detection algorithms for hyperspectral imaging applications. IEEE Sign. Processing Magazine 2002;19:29-43.
- Chen G, Qian S. Denoising of Hyperspectral Imagery Using Principal Component Analysis and Wavelet Shrinkage. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 2011;49:973-80. [CrossRef]
- Friedman JH. Regularized Discriminant Analysis. J Amer Stat Assoc 1989; 84:165-75. [CrossRef]
- Rousseeuw, P.J., Van Driessen, K.. A fast algorithm for the minimum covariance determinant estimator. Technometrics 1999: 41(3):212-223. [CrossRef]
- Hosmer, David W.; Lemeshow, Stanley (2000). Applied Logistic Regression (2nd ed.). Wiley. ISBN 978-0-471-35632-5.
- Fawcett, T. An Introduction to ROC Analysis. Pattern Recognition Letters. 2006: 27 (8): 861–874. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).