Submitted:
08 May 2023
Posted:
09 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. What Are Entomopathogenic Fungi?
3. Effect of Different Entomopathogenic Fungi against Pest
3.1. Secondary Metabolites of Entomopathogenic Fungi and Their Role in Pest Infection
3.2. Mode of Action of Entomopathogenic Fungi against Insect Pest
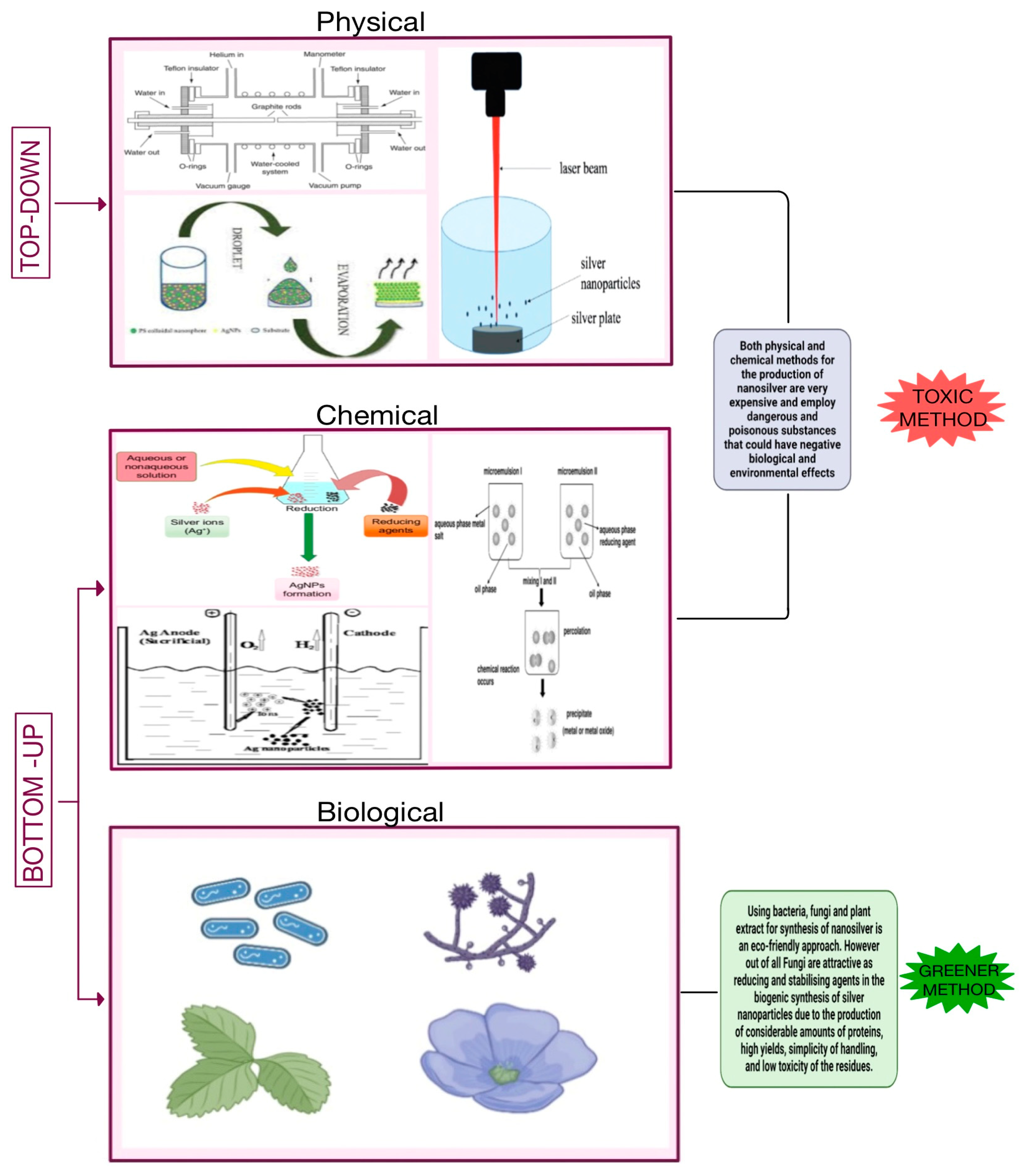
4. Different Routes of Synthesis of Nanoparticles
4.1. The Greener Synthesis of Metal Nanoparticles
5. Synthesis of Metal Nanoparticles by Entomopathogenic Fungi
5.1. Selenium Nanoparticles
5.3. Zinc Nanoparticles
5.4. Biogenic Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Mediated by Fungi
6. Effects of Mycosynthesized Silver Nanoparticles: A Greener Approach in Controlling Pest Species
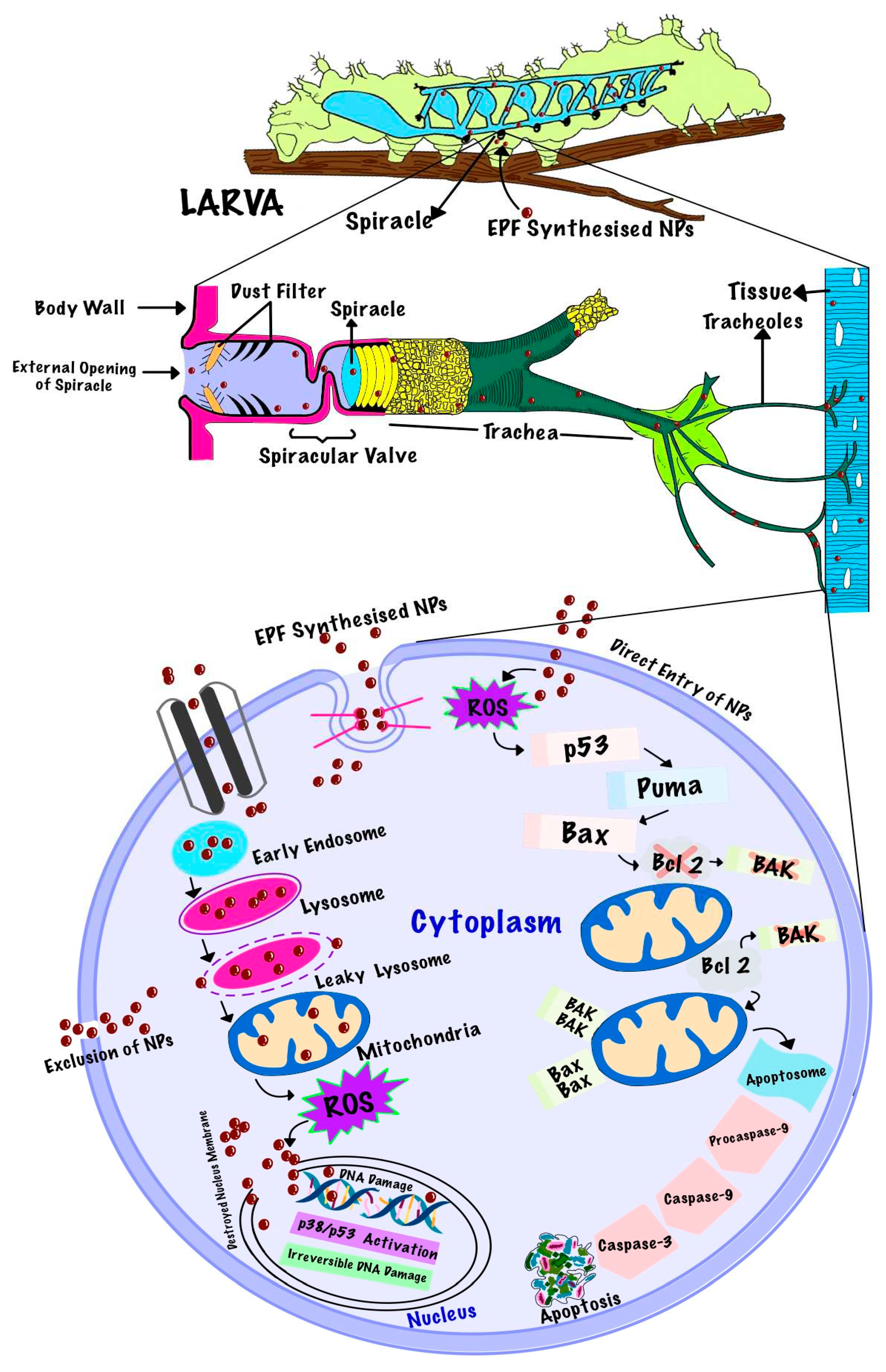
6.1. Mode of Action of Mycosynthesized Nanoparticles
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
References
- Dhaliwal, G.S.; Jindal, V; Dhawan, A. K. Insect pest problems and crop losses: changing trends. Indian J Ecol. 2007, 37, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, S.; Kooner, R.; Arora, R. Insect pests and crop losses. In Breed Insect Resistant Crops Sustain Agri, 2017, 45-66.
- Lawler, S. P. Environmental safety review of methoprene and bacterially-derived pesticides commonly used for sustained mosquito control. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 139, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rust, M.K. ., Lance, W.; Hemsarth, H. Synergism of the IGRs methoprene and pyriproxyfen against larval cat fleas (Siphonaptera: Pulicidae). J. Med. Entomol. 2016, 53, 629–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tunaz, H.; Uygun, N. Insect growth regulators for insect pest control. Turk J Agric For. 2004, 28, 377–387. [Google Scholar]
- Madhu, S. K.; Shaukath, A. K.; Vijayan, V. A. Efficacy of bioactive compounds from Curcuma aromatica against mosquito larvae. Acta tropica. 2010, 113, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.; Guo, L.; Maimaiti, Y.; et al. Entomopathogenic fungi as microbial biocontrol agent. Mol Plant Breed. 2012. [CrossRef]
- Jaihan, P.; Sangdee, K.; Sangdee, A. Selection of entomopathogenic fungus for biological control of chili anthracnose disease caused by Colletotrichum spp. Eur J Plant Pathol. 2016, 146, 551–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, J.P.; Hughes, D. P. Diversity of entomopathogenic fungi: which groups conquered the insect body? Adv Genet. 2016, 94, 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Castro, T.; Mayerhofer, J.; Enkerli, J. Persistence of Brazilian isolates of the entomopathogenic fungi Metarhiziumanisopliae and M. robertsii in strawberry crop soil after soil drench application. Agric Ecosyst Environ. 2016, 233, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rı’os-Moreno, A.; Garrido-Jurado, I.; Resquı´n-Romero, G et al. Destruxin A production by Metarhiziumbrunneum strains during transient endophytic colonisation of Solanum tuberosum. Biocontrol Sci Technol. 2016, 26, 1574–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascarin, GM.; Jaronski, ST. The production and uses of Beauveriabassiana as a microbial insecticide. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016, 32, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovett, B. ; Leger, RJS (2017) The insect pathogens. Microbiol Spectr. 2017, 5, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litwin, A.; Nowak, M.; Różalska, S. Entomopathogenic fungi: unconventional applications. Rev Environ Sci Bio/Technol. 2020, 19, 23–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skinner, M., Parker, BL.; Kim, JS. Role of entomopathogenic fungi. In: Abrol DP (ed) Integrated pest management, 2014, Academic Press, Cambridge, pp 169–191.
- Donzelli, BGG. ; Krasnoff, SB.; Churchill, ACL. Identification of a hybrid PKS–NRPS required for the biosynthesis of NG-391 in Metarhiziumrobertsii. Curr Genet. 2010, 56, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maina, U. M.; Galadima, I. B.; Gambo, F. M.; Zakaria, D. A review on the use of entomopathogenic fungi in the management of insect pests of field crops. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2018, 6, 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, A. M.; Duan, H.; Rhyner, M. N.; Ruan, G.; Nie, S. A systematic examination of surface coatings on the optical and chemical properties of semiconductor quantum dots. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2006, 8, 3895–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, A.; Roy, I.; Sengupta, S.; Debnath, N. Novel applications of solid and liquid formulations of nanoparticles against insect pests and pathogens. Thin Solid Films. 2010, 519, 1252–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya A, Duraisamy P, Govindarajan M, Buhroo AA, and Prasad R, Nano biofungicides: emerging trend in insect pest control. In Advances and applications through fungal nanobiotechnology, ed. by Prasad R. Springer International Publishing, Switzerland, 2016, 307–319.
- Cantu, A.A. Nanoparticles in forensic science. In Optics and Photonics for Counterterrorism and Crime Fighting IV, 2008, 7119, 71190F. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Li, F.; Wang, L.; Sheng, J.; Xin, Z.; Zhao, L. . & Hu, Q. Effect of nano-packing on preservation quality of Chinese jujube (Ziziphus jujuba Mill. var. inermis (Bunge) Rehd). Food Chem. 2009, 114, 547–552. [Google Scholar]
- Yokesh Babu, M.; Janaki Devi, V.; Ramakritinan, C.M.; Umarani, R.; Taredahalli, N.; Kumaraguru, A.K. Application of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles in agricultural and marine pest control. Curr Nanosci. 2014, 10, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilger-Casagrande, M.; Lima, R.D. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles mediated by fungi: a review. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazaa, M.; Alm-Eldin, M.; Ibrahim, A.E.; Elbarky, N.; Salama, M.; Sayed, R.; Sayed, W. Biosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles using Borago officinslis leaf extract, characterization and larvicidal activity against cotton leaf worm, Spodoptera littoralis (Bosid). Int J Trop Insect Sci. 2021, 41, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, K.K.; Choudhary, A.K.; Kumari, P. Entomopathogenic fungi. In Ecofriendly pest management for food security, 2016, 475–505.
- Lin, B.X. ‘Use of Beauveria bassiana against the Sweet Potato Weevil’, ActaEntomologicaSinica. 1956, 6, 539540 (in Chinese).
- Xu, Q.F. ‘Study on Soybean Moth Control by Beauveria bassiana’, ActaEntomologicaSinica. 1959, 9, 203215 (in Chinese).
- Quesada-Moraga, E.; Carrasco-Diaz, J.A.; Santiago-Á, lvarez C. Insecticidal and antifeedant activities of proteins secreted by entomopathogenic fungi against Spodoptera littoralis (Lep., Noctuidae). J Appl Entomol. 2006, 130, 442–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, F.E.; Infante, F.; Castillo, A.; Jaramillo, J. The coffee berry borer, Hypothenemushampei (Ferrari)(Coleoptera: Curculionidae): a short review, with recent findings and future research directions. 2009. [Google Scholar]
- BADII, M.H.; ABREU, J.L. Control biológicouna forma sustentable de control de plagas. Int J Good Consci. 2006, 1, 82–89. [Google Scholar]
- Behie, SW.; Bidochka, MJ. Ubiquity of insect-derived nitrogen transfer to plants by endophytic insect-pathogenic fungi: an additional branch of the soil nitrogen cycle. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2014, 80, 1553–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DELGADO, P.A.M.; MURCIA, O.P. Hongosentomopatógenos: umaalternativa para la obtención de Biopesticidas. Ambi-Agua. 2011, 6, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanzini, M.; Alves, S.; Setten, A.; Augusto, N. Compatibilidad de agent estensoactivos com Beauveria bassiana y Metarhizium anisopliae. ManejoIntegrado De Plagas. 2001, 59, 15–18. [Google Scholar]
- Mantzoukas, S.; Eliopoulos, P.A. Endophytic entomopathogenic fungi: A valuable biological control tool against plant pests. Appl Sci. 2020, 10, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Sood, K.; Kaur, J.; Khatri, M. Agrochemical loaded biocompatible chitosan nanoparticles for insect pest management. Biocatal Agri Biotechnol. 2019, 18, 101079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deka, B.; Baruah, C.; Babu, A. Entomopathogenic microorganisms: their role in insect pest management. Egypt J Biol Pest Control. 2021, 31, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umaru, F.F.; Simarani, K. Efficacy of Entomopathogenic Fungal Formulations against Elasmolomuspallens (Dallas) (Hemiptera: Rhyparochromidae) and Their Extracellular Enzymatic Activities. Toxins. 2022, 14, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tennant, P.F.; Fermin, G.A.; Roye, M.E. Viruses infecting papaya (Carica papaya L.): etiology, pathogenesis, and molecular biology. Plant Viruses. 2007, 1, 178–188. [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti, S.; Raychaudhuri, D.N. New and little known aphids (Homoptera: Aphididae) from Kumaon Himalaya, India. Entomon. 1978, 3, 95–103. [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee, A. , Debnath, P., Ghosh, S.K.; Medda, P.K. Biological control of papaya aphid (Aphis gossypii Glover) using entomopathogenic fungi. Vegetos. 2020, 33, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sani, I.; Ismail, S.I.; Abdullah, S.; Jalinas, J.; Jamian, S.; Saad, N. A review of the biology and control of whitefly, Bemisiatabaci (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae), with special reference to biological control using entomopathogenic fungi. Insects. 2020, 11, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filgueiras, C.C.; Willett, D.S. The Lesser Chestnut Weevil (Curculio sayi): Damage and Management with Biological Control Using Entomopathogenic Fungi and Entomopathogenic Nematodes. Insects. 2022, 13, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donzelli, BGG.; Krasnoff, SB. Molecular genetics of secondary chemistry in Metarhizium Fungi. In Lovett B, Leger RJS (eds) Advances in genetics. 2016, 94, 365–436.
- Gibson, D.M.; Donzelli, B.G.; Krasnoff, S.B.; Keyhani, N.O. Discovering the secondary metabolite potential encoded within entomopathogenic fungi. Nat Prod Rep. 2014, 31, 1287–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrini, N. The entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana shows its toxic side within insects: expression of genes encoding secondary metabolites during pathogenesis. J Fungi. 2022, 8, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zibaee, A.; Bandani, A.R.; Talaei-Hassanlouei, R.; Malagoli, D. Cellular immune reactions of the sunn pest, Eurygasterintegriceps, to the entomopathogenic fungus, Beauveria bassiana and its secondary metabolites. J Insect Sci. 2011, 11, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freed, S.; Feng-Liang, J.; Naeem, M.; Shun-Xiang, R.; Hussian, M. Toxicity of proteins secreted by entomopathogenic fungi against Plutellaxylostella (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae). Int J Agri Biol. 2012, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Vinayaga Moorthi, P.; Balasubramanian, C.; Selvarani, S.; Radha, A. Efficacy of sub lethal concentration of entomopathogenic fungi on the feeding and reproduction of Spodoptera litura. Springerplus. 2015, 4, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sawy, M.; Mostafa, E.H.; Ismail, N.A.E.R. Secondary metabolites of the entomopathogenic fungus, Cladosporium cladosporioides and its relation to toxicity of cotton aphid, Aphis gossypii (Glov. ). Int J. 2019, 5, 115–120. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, R.M.; Park, M.G.; Choi, J.Y.; Park, D.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Wang, M.; Kim, H.J.; Woo, S.D.; Kim, J.S.; Je, Y.H. Insecticidal and insect growth regulatory activities of secondary metabolites from entomopathogenic fungi, Lecanicilliumattenuatum. J Appl Entomol. 2020, 144, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunthirumeni, M.; Vinitha, G.; Shivakumar, M.S. Antifeedant and larvicidal activity of bioactive compounds isolated from entomopathogenic fungi Penicillium sp. for the control of agricultural and medically important insect pest (Spodoptera litura and Culex quinquefasciatus). Parasitol Int. 2023, 92, 102688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevim, A.; Sevim, E.; Demirbağ, Z. General biology of entomopathogenic fungi and their potential to control pest species in Turkey (EntomopatojenikfunguslarıngenelbiyolojileriveTürkiye’dezararlıböceklerinmücadelesindekullanılmapotansiyelleri). Erzincan Üniversitesi Fen BilimleriEnstitüsüDergisi. 2015, 8, 115–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- S. O. Andersen, Biochemistry of insect cuticle. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1979, 29–59. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, H. H. A textbook of entomology. A Textbook of Entomology. 1948. [Google Scholar]
- Glare, T. 11 Entomopathogenic Fungi and their Role in Regulation of Insect Populations. Insect Control. 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Hajek, A. E. ; St. Leger, R. J. Interactions between fungal pathogens and insect hosts. AnnRev Entomol. 1994, 39, 293–322. [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz-Urquiza, A. and Keyhani, N.O. Action on the surface: entomopathogenic fungi versus the insect cuticle. Insects. 2013, 4, 357–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, W.; Adnan, M.; Shabbir, A.; Naveed, H.; Abubakar, Y.S.; Qasim, M.; Tayyab, M.; Noman, A.; Nisar, M.S.; Khan, K.A.; Ali, H. Insect-fungal-interactions: A detailed review on entomopathogenic fungi pathogenicity to combat insect pests. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 159, 105122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zacharuk, R. Y. Electron-microscope studies of the histopathology of fungal infections by Metarrhizium anisopliae. Misc. Publ. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1973, 9, 112–119. [Google Scholar]
- J. Moty ´ an, ´ F. Toth, ´ J. Tozs ˝ ´er, Research applications of proteolytic enzymes in molecular biology. Biomolecules 2013, 3, 923–942. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- St Leger, R.J. The role of cuticle-degrading proteases in fungal pathogenesis of insects, Can. J. Bot. 1995, 73, 1119–1125. [Google Scholar]
- Pedrini, N.; Ortiz-Urquiza, A.; Huarte-Bonnet, C.; Zhang, S.; Keyhani, N.O. Targeting of insect epicuticular lipids by the entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana: hydrocarbon oxidation within the context of a host-pathogen interaction. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrini, N.; Zhang, S.; Ju´ arez, M.P.; Keyhani, N.O. Molecular characterization and expression analysis of a suite of cytochrome P450 enzymes implicated in insect hydrocarbon degradation in the entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana, Microbiol. 2010, 156, 2549–2557.
- Suzuki, A.; Kawakami, K.; Tamura, S. Detection of destruxins in silkworm larvae infected with Metarrhizium anisopliae. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1971, 35, 1641–1643. [Google Scholar]
- Eyal, J.; Mabud, M.A.; Fischbein, K.L.; Walter, J.F.; Osborne, L.S.; Landa, Z. Assessment of Beauveria bassiana Nov. EO-1 strain, which produces a red pigment for microbial control, Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 1994, 44, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweet, M.J.; Chessher, A.; Singleton, I. Metal-based nanoparticles; size, function, and areas for advancement in applied microbiology. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 80, 113–142. [Google Scholar]
- Beltrán Pineda, M.E.; Lizarazo Forero, L.M.; Sierra, Y.C.A. Mycosynthesis of silver nanoparticles: a review. BioMetals. 2022, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iravani, S.; Korbekandi, H.; Mirmohammadi, SV.; Zolfaghari, B. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles: chemical, physical and biological methods. Res. Pharma. Sci. 2014, 9, 385. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Bhushan, P.; Bhattacharya, S. Fabrication of nanostructures with bottom-up approach and their utility in diagnostics, therapeutics, and others. In: Environmental Chemical and Medical Sensors, Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp 167-198.
- Prabhu, S.; Poulose, E.K. Silver nanoparticles: mechanism of antimicrobial action, synthesis, medical applications, and toxicity effects. Int. nano lett. 2012, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, D.; Gupta, R. Nanotechnology and potential of microorganisms. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2005, 25, 25,199–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakkar, K.N.; Mhatre, S.S.; Parikh, R.Y. Biological synthesis of metallic nanoparticles. Nanomed: NanotechnolBiol Med. 2010, 6, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, E.; Milani, M.; Fekri, S.; Kouhi, M.; Akbarzadeh, A.; Nasrabadi, H.; Nikasa, P.; Joo, S.; Hanifehpour, Y.; Nejati-Koshki, K.; Samiei, M. International nano letters Silver nanoparticles: synthesis methods, bioapplications and properties. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2014, 42, 173–180. [Google Scholar]
- Keat, C.; Aziz, A. Eid A, Elmarzugi A Biosynthesis of nanoparticles and silver nanoparticle. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhainsa, K.C.; D’Souza, S.F. Extracellular biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using the fungus Aspergillus fumigatus. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2006, 47, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X. , Yan, S., Tyagi, R.D., Surampalli, R.Y. Synthesis of nanoparticles by microorganisms and their application in enhancing microbiological reaction rates. Chemosphere. 2011, 82, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudesia, N. , Najitha Banu, A., Raut, A.M. and Wahengbam, J., Biofabricated Nanoparticles: A Greener Approach Towards Insect Control. In Advances in Integrated Pest Management Technology: Innovative and Applied Aspects; Cham: Springer International Publishing. 2019, 391–419.
- Guilger-Casagrande, M.; Lima, R.D. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles mediated by fungi: a review. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gade, A. K.; Bonde, P.; Ingle, A. P.; Marcato, P. D.; Durán, N.; Rai, M. K. Exploitation of Aspergillus niger for synthesis of silver nanoparticles. J. Biobased Mater. Bioenergy. 2008, 2, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velusamy, P.; Kumar, G.V.; Jeyanthi, V.; Das, J.; Pachaiappan, R. Bio-inspired green nanoparticles: synthesis, mechanism, and antibacterial application. Toxicol. Res. 2016, 32, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Hong, Y.N.; Weyers, A.; Kim, Y.S.; Linhardt, R. J. Polysaccharides and phytochemicals: a natural reservoir for the green synthesis of gold and silver nanoparticles. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2011, 5, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vela´zquez-Robledo, R.; Contreras-Cornejo, H.A.; Macı´asRodrı´guez, L.; Herna´ndez-Morales, A.; Aguirre, J.; Casas-Flores, S.; Herrera-Estrella, A. Role of the 4-phosphopantetheinyl transferase of Trichoderma virens in secondary metabolism and induction of plant defense responses. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2011, 24, 1459–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iranifam, M.; Fathinia, M.; Rad, T. S.; Hanifehpour, Y.; Khataee, A. R.; Joo, S. W. Talanta. A novel selenium nanoparticles-enhanced chemiluminescence system for determination of dinitrobutylphenol. Talanta 2013, 107, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras-Cornejo, H. A.; Macı´as-Rodrı´guez, L.; HerreraEstrella, A.; Lo´pez-Bucio, J. The 4-phosphopantetheinyl transferase of Trichoderma virens plays a role in plant protection against Botrytis cinerea through volatile organic compound emission. Plant Soil. 2014, 379, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berini, F.; Caccia, S.; Franzetti, E.; Congiu, T.; Marinelli, F.; Casartelli, M.; Tettamanti, G. Effects of Trichoderma viride chitinases on the peritrophic matrix of Lepidoptera. Pest Manag. Sci. 2016, 72, 980–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadhwani, S.A.; Shedbalkar, U.U.; Singh, R.; Chopade, B. A. Biogenic selenium nanoparticles: current status and future prospects. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 2555–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanakumar, K.; Li, Y.; Yu, C.; Wang, Q.Q.C.; Wang, M.; Sun, J.; Chen. Effect of Trichoderma harzianum on maize rhizosphere microbiome and biocontrol of Fusarium Stalk rot. J. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martı´nez-Medina, Appels, F. V.; van Wees, S. C. Impact of salicylic acid-and jasmonic acid-regulated defences on root colonization by Trichoderma harzianum T-78. Plant Signal. Behav. 2017, 12, e1345404. [Google Scholar]
- Arunthirumeni, M. , Veerammal, V., & Shivakumar, M. S. Biocontrol efficacy of mycosynthesized selenium nanoparticle using Trichoderma sp. on insect pest Spodoptera litura. J. Clust. Sci. 2022, 33, 1645–1653. [Google Scholar]
- Pimentel, D. J. Amounts of Pesticides Reaching Target Pests: Environmental Impacts and Ethics. Agric. Environ. Ethics 1995, 8, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengottayan, S. N. [HTML] Physiological and biochemical effect of neem and other Meliaceae plants secondary metabolites against Lepidopteran insects. Front. Physiol. 2013, 4, 359. [Google Scholar]
- Senthil-Nathan. A Review of Biopesticides and Their Mode of Action Against Insect Pests. A Review of Biopesticides and Their Mode of Action Against Insect Pests. Environ. Sustain. 2015, 49–63. [Google Scholar]
- Dhivya, K.; Vengateswari, G.; Arunthirumeni, M.; Karthi, S.; Senthil-Nathan, S.; Shivakumar, M. S. Bioprospecting of Prosopis juliflora (Sw.) DC seed pod extract effect on antioxidant and immune system of Spodoptera litura (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2018, 101, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamayo, L.; Azócar, M.; Kogan, M.; Riveros, A.; Páez, M. Copper-polymer nanocomposites: An excellent and cost-effective biocide for use on antibacterial surfaces. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 69, 1391–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kora, A.J. Copper-based nanopesticides. Copper Nanostructures: Next-Generation of Agrochemicals for Sustainable Agroecosystems. 2022, 133–153. [Google Scholar]
- Vivekanandhan, P.; Swathy, K.; Thomas, A.; Kweka, E. J.; Rahman, A.; Pittarate, S.; Krutmuang, P. Insecticidal efficacy of microbial-mediated synthesized copper nano-pesticide against insect pests and non-target organisms. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021, 18, 10536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafeeq, C. M.; Paul, E.; Saagar, E. V.; Ali, P. M. Mycosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Pleurotus floridanus and optimization of process parameters. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 12375–12380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, A.; Saba, M.; Ullah, K.; Almutairi, S. M.; AlMunqedhi, B. M.; Ragab abdelGawwad, M. Mycosynthesis, Characterization of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles, and Its Assessment in Various Biological Activities. Crystals. 2023, 13, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shobha, B.; Lakshmeesha, T. R.; Ansari, M. A.; Almatroudi, A.; Alzohairy, M. A.; Basavaraju, S.; Chowdappa, S. Mycosynthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using Trichoderma spp. isolated from rhizosphere soils and its synergistic antibacterial effect against Xanthomonas oryzaepv. oryzae. J. Fungi. 2020, 6, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, A.G.; Ping, L.Y.; Marcato, P.D.; Alves, O.L.; Silva, M.C.; Ruiz, R.C.; Melo, I.S.; Tasic, L.; De Souza, A.O. ; Biogenic antimicrobial silver nanoparticles produced by fungi. Appl.Microbial. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 775–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honary, S.; Barabadi, H.; Gharaei-Fathabad, E.; Naghibi, F. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles induced by the fungus Penicillium citrinum. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2013, 12, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Mukherjee, T.; Chakraborty, S.; Das, T.K. Biosynthesis, characterisation & antifungal activity of silver nanoparticles synthesized by the fungus Aspergillus foetidus MTCC8876. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostruct. 2013, 8, 197–205. [Google Scholar]
- Banu, A.N.; Balasubramanian, C. Optimization and synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Isaria fumosorosea against human vector mosquitoes. Parasitol. Res. 2014, 113, 3843–3851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amerasan, D.; Nataraj, T.; Murugan, K.; Panneerselvam, C.; Madhiyazhagan, P.; Nicoletti, M.; Benelli, G. Myco-synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Metarhizium anisopliae against the rural malaria vector Anopheles culicifacies Giles (Diptera: Culicidae). J. pest sci. 2016, 89, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamil, D.; Prameeladevi, T.; Ganesh, S.; Prabhakaran, N.; Nareshkumar, R.; Thomas, S. P. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles by entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana and their bioefficacy against mustard aphid (Lipaphiserysimi Kalt. ). 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Elamawi, R.M.; Al-Harbi, R.E.; Hendi, A.A. Biosynthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using Trichoderma longibrachiatum and their effect on phytopathogenic fungi. Egypt. j. biological pest control, 2018, 28, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, P.; Khan, I.; Rehman, A.; Jamil, T.; Hayat, A.; Rehman, M.U.; Ullah, N.; Sarwar, A.; Alharbi, A.A.; Dablool, A.S.; Daudzai, Z. ; Myogenesis and Analysis of Antimicrobial Potential of Silver Nanoparticles (AgNPs) against Pathogenic Bacteria. Molecules, 2023, 28, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bérdy, J. Bioactive Microbial Metabolites. J Antibiot. 2005, 58, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banu, A.N.; Kudesia, N.; Raut, A.M.; Pakrudheen, I.; Wahengbam, J. Toxicity, bioaccumulation, and transformation of silver nanoparticles in aqua biota: A review. Environ. Chem. Letters. 2021, 19, 4275–4296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banu, A.N.; Balasubramanian, C. Myco-synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Beauveria bassiana against dengue vector, Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae). Parasitol. Res. 2014, 113, 2869–2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omran, B.A.; Nassar, H.N.; Younis, S.A.; Fatthallah, N.A.; Hamdy, A.; El-Shatoury, E.H.; El-Gendy, N.S. ; Physiochemical properties of Trichoderma longibrachiatum DSMZ 16517-synthesized silver nanoparticles for the mitigation of halotolerant sulphate-reducing bacteria. J. appl.microbio. 2019, 126, 138–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Rai, N.; Verma, A.; Saikia, D.; Singh, S.P.; Kumar, R.; Singh, S.K.; Kumar, D.; Gautam, V. Green-Based Approach to Synthesize Silver Nanoparticles Using the Fungal Endophyte Penicillium oxalicum and Their Antimicrobial, Antioxidant, and In Vitro Anticancer Potential. ACS omega. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaravadivelan, C.; Padmanabhan, M. N. Effect of mycosynthesized silver nanoparticles from filtrate of Trichoderma harzianum against larvae and pupa of dengue vector Aedes aegypti L. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 4624–4633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnaperumal, K.; Govindasamy, B.; Paramasivam, D.; Dilipkumar, A.; Dhayalan, A.; Vadivel, A. , Pachiappan, P. Bio-pesticidal effects of Trichoderma viride formulated titanium dioxide nanoparticle and their physiological and biochemical changes on Helicoverpa armigera (Hub. ). Pestic. Biochem. physiol. 2018, 149, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthick Raja Namasivayam, S. , Arvind Bharani, R. S. Biocompatible silver nanoparticles-loaded fungal metabolites nanoconjugate (agnp–fm) preparation for the noteworthy pesticidal activity. Natl. Acad. Sci. Lett. 2021, 44, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yosri, M.; Abdel-Aziz, M.M.; Sayed, R.M. Larvicidal potential of irradiated myco-insecticide from Metarhizium anisopliae and larvicidal synergistic effect with its mycosynthesized titanium nanoparticles (TiNPs). J Radiat Res Appl Sci. 2018, 11, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, T.S.; Passos, E.M.D.; Seabra, M.G.D.J.; Souto, E.B.; Severino, P.; Mendonça, M.D.C. Entomopathogenic fungi biomass production and extracellular biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles for bioinsecticide action. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, G.; Gaurav, S.S.; Singh, A.; Rani, P. Synthesis of mycogenic silver nanoparticles by Fusarium pallidoroseum and evaluation of its larvicidal effect against white grubs (Holotrichia sp. ). Mater. Today: Proc. 2022, 49, 3517–3527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamalakannan, S.; Gobinath, C.; Ananth, S. Synthesis and characterization of fungus mediated silver nanoparticle for toxicity on filarial vector, Culex quinquefasciatus. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res. 2014, 24, 124–132. [Google Scholar]
- Salunkhe, R.B.; Patil, S.V.; Patil, C.D.; et al. Larvicidal potential of silver nanoparticles synthesized using fungus Cochliobolus lunatus against Aedes aegypti (Linnaeus, 1762) and Anopheles stephensi Liston (Diptera; Culicidae). Parasitol. Res. 2011, 109, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salunkhe, R.B.; Patil, S.V.; Patil, C.D.; Salunke, B.K. ; Larvicidal potential of silver nanoparticles synthesized using fungus Cochliobolus lunatus against Aedes aegypti (Linnaeus, 1762) and Anopheles stephensi Liston (Diptera; Culicidae). Parasitol. Res. 2011, 109, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KHOOSHE-BAST, Z.; Sahebzadeh, N.; GHAFFARI-MOGHADDAM, M.; MIRSHEKAR, A. Insecticidal effects of zinc oxide nanoparticles and Beauveria bassiana TS11 on Trialeurodes vaporariorum (Westwood, 1856)(Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae). Acta AgriculturaeSlovenica. 2016, 107, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, J.; Wang, X.; Qiu, B.; Cuthbertson, A.G.; Du, C.; Wu, J.; Ali, S.; Isaria fumosorosea-based zero-valent iron nanoparticles affect the growth and survival of sweet potato whitefly, Bemisia tabaci (Gennadius). Pest manag. Sci. 2019, 75, 2174–2181. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, K.; Cuthbertson, A. G.; Du, C.; Ali, S. Toxicity and biological effects of Beauveria brongniartii Fe0 nanoparticles against Spodoptera litura (Fabricius). Insects. 2020, 11, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahayaraj, K.; Madasamy, M.; Radhika, S.A. Insecticidal activity of bio-silver and gold nanoparticles against PericalliariciniFab.(Lepidaptera: Archidae). J. Biopestic. 2016, 9, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foldbjerg, R.; Jiang, X; Miclăus, T. ; Chunying, C.; Autrup, H.; Beer, C. Silver nanoparticles—wolves in sheep’s clothing? Toxicol. Res. 2015, 4, 563–575. [Google Scholar]
- Shahzad, K.; Manzoor, F. Nanoformulations and their mode of action in insects: a review of biological interactions. Drug chem. toxicol. 2021, 44, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lade, B.D.; Gogle, D.P. Nano-biopesticides: Synthesis and applications in plant safety. Nanobiotechnol. Application Plant Prot. 2019, 2, 169–189. [Google Scholar]
- Stadler, T. et al., Nanostructured alumina: biocidal properties and mechanism of action of a novel insecticide powder. Bull. Insectology. 2017, 70, 17–25. [Google Scholar]
- Hashem, A.S.; et al. Pimpinella anisum essential oil nanoemulsions against Tribolium castaneum-insecticidal activity and mode of action. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, N.; Ramamoorthy, M.; Lyon, D.; Jones, K.; Duttaroy, A. Mechanism of silver nanoparticles action on insect pigmentation reveals intervention of copper homeostasis. PLoS One 2013, 8, e53186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sultana, N.; et al. Nanoweapon: control of mosquito breeding using carbon-dot-silver nanohybrid as a biolarvicide. Environmental Chemistry Letters. 2018. [CrossRef]
- Nair, P.M.G.; Choi, J. Identification, characterization and expression profiles of Chironomus riparius glutathione S-transferase (GST) genes in response to cadmium and silver nanoparticles exposure. AquatToxicol. 2011, 101, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, A.; Shah, P.; Agrawal, N. ; Sedentary behavior and altered metabolic activity by AgNPs ingestion in Drosophila melanogaster. Scientific Reports. 2017, 7, 15617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.; et al. Cellular internalization and stress response of ingested amorphous silica nanoparticles in the midgut of Drosophila melanogaster. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 2013, 1830, 2256–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Entomopathogenic fungi used | Particle size | Time is taken for synthesis | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aspergillus tubingensis | 35nm | 96hrs | [101] |
| Penicillium citrinum | 109nm | 24hrs | [102] |
| Aspergillus foetidus | 20-40 nm | 24hrs | [103] |
| Isariafumosorosea | 51.31 -111.02 nm | 72hrs | [104] |
| Metarhizium anisopliae | 28–38 nm | 72hrs | [105] |
| Beauveria bassaina | 20–30 nm | 5 days | [106] |
| Trichoderma longibrachiatum | 24.43 nm | 72hrs | [107] |
| Penicillium oxalicum | 150nm | 96hs | [108] |
| Entomopathogenic based Nanoparticles | Targeted Pest | Mortality value | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Penecillium verucosum based silver nanoparticles | Culex quinquefasciatus | LC50-4.91, 5.16, 5.95 7.83; LC90-8.13, 8.44,7.76,12.63 | [120] |
| Cochliobolus lunatus based silver nanoparticles | Aedes aegypti | LC50- 1.29, 1.48, 1.58 ppm ; LC90 3.08, 3.33, 3.41 ppm. | [121] |
| Cochliobo luslunatus based silver nanoparticles | Anopheles stephensiListon | LC50- 1.17, 1.30, 1.41 ppm; LC90 2.99, 3.13, 3.29 ppm | [122] |
| Beauveria bassiana TS11 based zinc oxide nanoparticles | Trialeurodesvaporariorum | LC50-7.35 ppm | [123] |
| Isaria fumosorosea based iron nanoparticles | Bemisiatabaci | LC50- 19.17, 26.10,37.71 ppm | [124] |
|
Beauveria brongniartii based iron nanoparticles |
Spodoptera litura | LC50-59 ppm | [125] |
| Trichoderma based selenium nanoparticles | Spodoptera litura | LC50-39.739; LC90-142.839 ppm | [52] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





