Submitted:
03 May 2023
Posted:
05 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Technical aspects of IUS performing and reporting
- -
- Bowel wall thickness (BWT), measured in two planes from the superficial mucosal layer to the serosal layer, has a pathological finding of > 3mm for both the ileal and colonic walls;
- -
- Colour Doppler signal (CDS), measured at the most thickened bowel segment and reported at least with the intramural and/or extramural signal presence;
- -
- Bowel wall stratification (BWS), considered normal, focally or extensively lost.
- -
- Presence or absence of haustrations, ulcers, peristaltic movements and significant/persistent stenoses.
3.2. IUS in the diagnosis of CD
3.3. IUS in defining CD localisation and extension
3.4. IUS in defining complicated CD
3.4.1. Strictures
3.4.2. Abscesses
3.4.3. Intrabdominal fistula
3.5. IUS in post-operative recurrence detection
3.6. IUS in UC diagnosis
3.7. IUS in UC extension
3.8. IUS in UC disease activity
3.9. Reproducibility and scoring
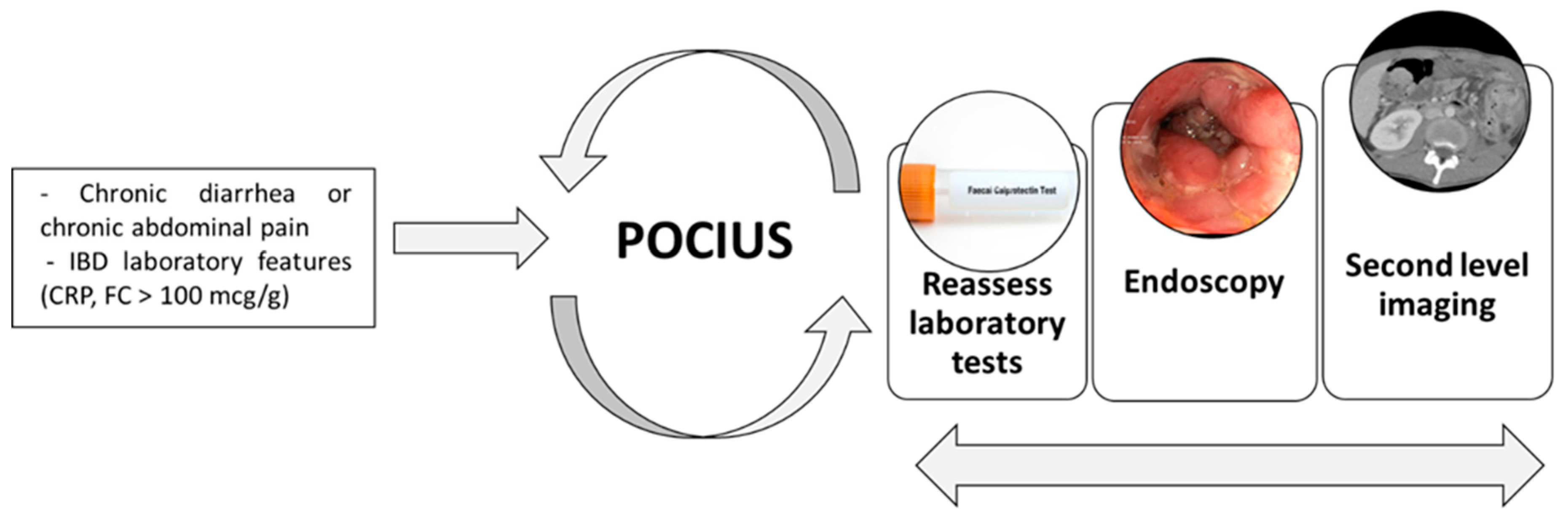
3.10. Point-of-care Intestinal Ultrasound (POCIUS)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kaplan GG, Windsor JW. The four epidemiological stages in the global evolution of inflammatory bowel disease. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021, 18, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner D, Ricciuto A, Lewis A, D’Amico F, Dhaliwal J, Griffiths AM, et al. STRIDE-II: An Update on the Selecting Therapeutic Targets in Inflammatory Bowel Disease (STRIDE) Initiative of the International Organization for the Study of IBD (IOIBD): Determining Therapeutic Goals for Treat-to-Target strategies in IBD. Gastroenterology. 2021, 160, 1570–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maaser C, Sturm A, Vavricka SR, Kucharzik T, Fiorino G, Annese V, et al. ECCO-ESGAR Guideline for Diagnostic Assessment in IBD Part 1: Initial diagnosis, monitoring of known IBD, detection of complications. Journal of Crohn's and Colitis. 2019, 13, 144–164K. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magro F, Gionchetti P, Eliakim R, Ardizzone S, Armuzzi A, Barreiro-de Acosta M, et al. Third European Evidence-based Consensus on Diagnosis and Management of Ulcerative Colitis. Part 1: Definitions, Diagnosis, Extra-intestinal Manifestations, Pregnancy, Cancer Surveillance, Surgery, and Ileo-anal Pouch Disorders. Journal of Crohn's and Colitis. 2017, 11, 649–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimola J, Torres J, Kumar S, Taylor SA, Kucharzik T. Recent advances in clinical practice: advances in cross-sectional imaging in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut. 2022, gutjnl-2021-326562.
- Bots S, De Voogd F, De Jong M, Ligtvoet V, Löwenberg M, Duijvestein M, et al. Point-of-care Intestinal Ultrasound in IBD Patients: Disease Management and Diagnostic Yield in a Real-world Cohort and Proposal of a Point-of-care Algorithm. Journal of Crohn's and Colitis. 2022, 16, 606–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Voogd FAE, Verstockt B, Maaser C, Gecse KB. Point-of-care intestinal ultrasonography in inflammatory bowel disease. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021, 18, 209–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardone OM, Calabrese G, Testa A, Caiazzo A, Fierro G, Rispo A, et al. The Impact of Intestinal Ultrasound on the Management of Inflammatory Bowel Disease: From Established Facts Toward New Horizons. Front Med. 2022, 9, 898092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allocca M, Furfaro F, Fiorino G, Peyrin-Biroulet L, Danese S. Point-of-Care Ultrasound in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Journal of Crohn's and Colitis. 2021, 15, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allocca M, Kucharzik T, Rubin DT. Intestinal Ultrasound in the Assessment and Management of Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Is It Ready for Standard Practice? Gastroenterology. 2023, 164, 851–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucharzik T, Tielbeek J, Carter D, Taylor SA, Tolan D, Wilkens R, et al. ECCO-ESGAR Topical Review on Optimizing Reporting for Cross-Sectional Imaging in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Journal of Crohn’s and Colitis. 2022, 16, 523–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maconi G, Parente F, Bollani S, Cesana B, Bianchi Porro G. Abdominal ultrasound in the assessment of extent and activity of Crohn's disease: clinical significance and implication of bowel wall thickening. Am J Gastroenterol. 1996, 91, 1604–1609. [Google Scholar]
- Astegiano M, Bresso F, Cammarota T, Sarno A, Robotti D, Demarchi B, et al. Abdominal pain and bowel dysfunction: diagnostic role of intestinal ultrasound. European Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology. 2001, 13, 927–931. [Google Scholar]
- Parente, F. Bowel ultrasound in assessment of Crohn's disease and detection of related small bowel strictures: a prospective comparative study versus x ray and intraoperative findings. Gut. 2002, 50, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascu M, Roznowski AB, Müller HP, Adler A, Wiedenmann B, Dignass AU. Clinical Relevance of Transabdominal Ultrasonography and Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease of the Terminal Ileum and Large Bowel. Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. 2004, 10, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallotta N, Tomei E, Viscido A, Calabrese E, Marcheggiano A, Caprilli R, et al. Small Intestine Contrast Ultrasonography: An Alternative to Radiology in the Assessment of Small Bowel Disease. Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. 2005, 11, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rispo A, Imbriaco M, Celentano L, Cozzolino A, Camera L, Mainenti PP, et al. Noninvasive Diagnosis of Small Bowel Crohnʼs Disease: Combined Use of Bowel Sonography and Tc-99M-Hmpao Leukocyte Scintigraphy. Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. 2005, 11, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castiglione F, Mainenti PP, De Palma GD, Testa A, Bucci L, Pesce G, et al. Noninvasive Diagnosis of Small Bowel Crohn’s Disease: Direct Comparison of Bowel Sonography and Magnetic Resonance Enterography. Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. 2013, 19, 991–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallotta N, Civitelli F, Di Nardo G, Vincoli G, Aloi M, Viola F, et al. Small Intestine Contrast Ultrasonography in Pediatric Crohn's Disease. The Journal of Pediatrics. 2013, 163, 778–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rispo A, de Sire R, Mainenti PP, Imperatore N, Testa A, Maurea S, et al. David Against Goliath: Direct Comparison of Handheld Bowel Sonography and Magnetic Resonance Enterography for Diagnosis of Crohn’s Disease. Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. 2022, izac116.
- Calabrese E, Maaser C, Zorzi F, Kannengiesser K, Hanauer SB, Bruining DH, et al. Bowel Ultrasonography in the Management of Crohnʼs Disease. A Review with Recommendations of an International Panel of Experts. Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. 2016, 22, 1168–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor SA, Mallett S, Bhatnagar G, Baldwin-Cleland R, Bloom S, Gupta A, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of magnetic resonance enterography and small bowel ultrasound for the extent and activity of newly diagnosed and relapsed Crohn's disease (METRIC): a multicentre trial. The Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology. 2018, 3, 548–558. [Google Scholar]
- Reimund JM, Jung-Chaigneau E, Chamouard P, Wittersheim C, Duclos B, Baumann R. [Diagnostic value of high resolution sonography in Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis]. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 1999, 23, 740–746. [Google Scholar]
- Bru C, Sans M, Defelitto MM, Gilabert R, Fuster D, Llach J, et al. Hydrocolonic Sonography for Evaluating Inflammatory Bowel Disease. American Journal of Roentgenology. 2001, 177, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parente F, Greco S, Molteni M, Cucino C, Maconi G, Sampietro GM, et al. Role of early ultrasound in detecting inflammatory intestinal disorders and identifying their anatomical location within the bowel: BOWEL ULTRASOUND FOR DETECTION OF INFLAMMATORY DISEASE. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics. 2003, 18, 1009–1016. [Google Scholar]
- Parente, F. Oral contrast enhanced bowel ultrasonography in the assessment of small intestine Crohn's disease. A prospective comparison with conventional ultrasound, x ray studies, and ileocolonoscopy. Gut. 2004, 53, 1652–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez MJ, Ripollés T, Paredes JM, Blanc E, Martí-Bonmatí L. Assessment of the extension and the inflammatory activity in Crohn's disease: comparison of ultrasound and MRI. Abdom Imaging. 2009, 34, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rispo A, Imperatore N, Testa A, Mainenti P, De Palma GD, Luglio G, et al. Bowel Damage in Crohnʼs Disease: Direct Comparison of Ultrasonography-based and Magnetic Resonance-based Lemann Index. Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. 2017, 23, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allocca M, Fiorino G, Bonifacio C, Furfaro F, Gilardi D, Argollo M, et al. Comparative Accuracy of Bowel Ultrasound Versus Magnetic Resonance Enterography in Combination With Colonoscopy in Assessing Crohn’s Disease and Guiding Clinical Decision-making. Journal of Crohn’s and Colitis. 2018, 12, 1280–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panés J, Bouzas R, Chaparro M, García-Sánchez V, Gisbert JP, Martínez de Guereñu B, et al. Systematic review: the use of ultrasonography, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging for the diagnosis, assessment of activity and abdominal complications of Crohn's disease: Systematic review: cross-sectional imaging in Crohn's disease. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics. 2011, 34, 125–145. [Google Scholar]
- Calabrese E, La Seta F, Buccellato A, Virdone R, Pallotta N, Corazziari E, et al. Crohnʼs Disease: A Comparative Prospective Study of Transabdominal Ultrasonography, Small Intestine Contrast Ultrasonography, and Small Bowel Enema. Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. 2005, 11, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail MS, Charabaty A. Management of Crohn's stricture: medical, endoscopic and surgical therapies. Frontline Gastroenterol. 2022, 13, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasche C, Moser G, Turetschek K, Schober E, Moeschl P, Oberhuber G. Transabdominal bowel sonography for the detection of intestinal complications in Crohn's disease. Gut. 1999, 44, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohn A, Cerro P, Milite G, De Angelis E, Prantera C. Prospective Evaluation of Transabdominal Bowel Sonography in the Diagnosis of Intestinal Obstruction in Crohnʼs Disease: Comparison with Plain Abdominal Film and Small Bowel Enteroclysis. Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. 1999, 5, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallotta N, Vincoli G, Montesani C, Chirletti P, Pronio A, Caronna R, et al. Small intestine contrast ultrasonography (SICUS) for the detection of small bowel complications in crohnʼs disease: A prospective comparative study versus intraoperative findings. Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. 2012, 18, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onali, S. Small intestine contrast ultrasonography vs computed tomography enteroclysis for assessing ileal Crohn's disease. WJG. 2012, 18, 6088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar S, Hakim A, Alexakis C, Chhaya V, Tzias D, Pilcher J, et al. Small intestinal contrast ultrasonography for the detection of small bowel complications in Crohn's disease: Correlation with intraoperative findings and magnetic resonance enterography: Small intestinal contrast ultrasonography in Crohn's disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015, 30, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maconi G, Sampietro GM, Parente F, Pompili G, Russo A, Cristaldi M, et al. Contrast Radiology, Computed Tomography and Ultrasonography in Detecting Internal Fistulas and Intra-Abdominal Abscesses in Crohn's Disease: A Prospective Comparative Study. American Journal of Gastroenterology. 2003, 98, 1545–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grażyńska A, Kufel J, Dudek A, Cebula M. Shear Wave and Strain Elastography in Crohn's Disease—A Systematic Review. Diagnostics. 2021, 11, 1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres J, Mehandru S, Colombel JF, Peyrin-Biroulet L. Crohn's disease. The Lancet. 2017, 389, 1741–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamina M, Bonovas S, Raine T, Spinelli A, Warusavitarne J, Armuzzi A, et al. ECCO Guidelines on Therapeutics in Crohn’s Disease: Surgical Treatment. Journal of Crohn’s and Colitis. 2020, 14, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rispo A, Imperatore N, Testa A, Nardone OM, Luglio G, Caporaso N, et al. Diagnostic Accuracy of Ultrasonography in the Detection of Postsurgical Recurrence in Crohn's Disease: A Systematic Review with Meta-analysis. Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. 2018, 24, 977–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreoli A, Prantera C. Role of Ultrasonography in the Diagnosis of Postsurgical Recurrence of Crohn's Disease. 1998, 93.
- Rispo A, Bucci L, Pesce G, Sabbatini F, de Palma GD, Grassia R, et al. Bowel sonography for the diagnosis and grading of postsurgical recurrence of Crohnʼs disease. Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. 2006, 12, 486–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castiglione F, Bucci L, Pesce G, De Palma GD, Camera L, Cipolletta F, et al. Oral contrast-enhanced sonography for the diagnosis and grading of postsurgical recurrence of Crohnʼs disease. Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. 2008, 14, 1240–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese E, Petruzziello C, Onali S, Condino G, Zorzi F, Pallone F, et al. Severity of postoperative recurrence in crohnʼs disease: Correlation between endoscopic and sonographic findings. Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. 2009, 15, 1635–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onali S, Calabrese E, Petruzziello C, Lolli E, Ascolani M, Ruffa A, et al. Post-operative recurrence of Crohn's disease: A prospective study at 5 years. Digestive and Liver Disease. 2016, 48, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Piaz G, Mendolaro M, Mineccia M, Randazzo C, Massucco P, Cosimato M, et al. Predictivity of early and late assessment for post-surgical recurrence of Crohn's disease: Data from a single-center retrospective series. Digestive and Liver Disease. 2021, 53, 987–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- S. Hollerbach, A. Geissler, H. Schi. The Accuracy of Abdominal Ultrasound in the Assessment of Bowel Disorders. Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology. 1998, 33, 1201–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong M, Atri M, Bret PM, Reinhold C, Kintzen G, Thibodeau M, et al. Sonographic appearance of benign and malignant conditions of the colon. American Journal of Roentgenology. 1998, 170, 1451–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim JH, Ko YT, Lee DH, Lim JW, Kim TH. Sonography of inflammatory bowel disease: findings and value in differential diagnosis. American Journal of Roentgenology. 1994, 163, 343–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwerck W, Beckh K, Raith M. A prospective evaluation of high resolution sonography in the diagnosis of inflammatory bowel disease.
- Allocca M, Fiorino G, Bonovas S, Furfaro F, Gilardi D, Argollo M, et al. Accuracy of Humanitas Ultrasound Criteria in Assessing Disease Activity and Severity in Ulcerative Colitis: A Prospective Study. Journal of Crohn’s and Colitis. 2018, 12, 1385–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita K, Katsurada T, Nishida M, Omotehara S, Onishi R, Mabe K, et al. Usefulness of transabdominal ultrasonography for assessing ulcerative colitis: a prospective, multicenter study. J Gastroenterol. 2019, 54, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagami S, Kobayashi T, Miyatani Y, Okabayashi S, Yamazaki H, Takada T, et al. Accuracy of Ultrasound for Evaluation of Colorectal Segments in Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology. 2021, 19, 908–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozkurt T, Rommel T, Stabenow-Lohbauer U, Langer M, Schmiegelow P, Lux G. Sonographic bowel wall morphology correlates with clinical and endoscopic activity in crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. European Journal of Ultrasound. 1996, 4, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonelli E, Giuliano V, Casella G, Villanacci V, Baldini V, Baldoni M, et al. Ultrasonographic assessment of colonic wall in moderate–severe ulcerative colitis: Comparison with endoscopic findings. Digestive and Liver Disease. 2011, 43, 703–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allocca M, Filippi E, Costantino A, Bonovas S, Fiorino G, Furfaro F, et al. Milan ultrasound criteria are accurate in assessing disease activity in ulcerative colitis: external validation. United European Gastroenterol j. 2021, 9, 438–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bots S, Nylund K, Löwenberg M, Gecse K, D'Haens G. Intestinal Ultrasound to Assess Disease Activity in Ulcerative Colitis: Development of a novel UC-Ultrasound Index. Journal of Crohn's and Colitis. 2021, 15, 1264–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraquelli M, Sarno A, Girelli C, Laudi C, Buscarini E, Villa C, et al. Reproducibility of bowel ultrasonography in the evaluation of Crohn's disease. Digestive and Liver Disease. 2008, 40, 860–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Voogd F, Wilkens R, Gecse K, Allocca M, Novak K, Lu C, et al. A Reliability Study: Strong Inter-Observer Agreement of an Expert Panel for Intestinal Ultrasound in Ulcerative Colitis. Journal of Crohn's and Colitis. 2021, 15, 1284–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novak KL, Nylund K, Maaser C, Petersen F, Kucharzik T, Lu C, et al. Expert Consensus on Optimal Acquisition and Development of the International Bowel Ultrasound Segmental Activity Score [IBUS-SAS]: A Reliability and Inter-rater Variability Study on Intestinal Ultrasonography in Crohn's Disease. Journal of Crohn's and Colitis. 2021, 15, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allocca M, Craviotto V, Dell’Avalle C, Furfaro F, Zilli A, D’Amico F, et al. Bowel ultrasound score is accurate in assessing response to therapy in patients with Crohn's disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2022, 55, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allocca M, Dell’Avalle C, Craviotto V, Furfaro F, Zilli A, D’Amico F, et al. Predictive value of Milan ultrasound criteria in ulcerative colitis: A prospective observational cohort study. UEG Journal. 2022, 10, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mjolstad OC, Dalen H, Graven T, Kleinau JO, Salvesen O, Haugen BO. Routinely adding ultrasound examinations by pocket-sized ultrasound devices improves inpatient diagnostics in a medical department. European Journal of Internal Medicine. 2012, 23, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wastl D, Löwe A, Dietrich CF. Echoscopy in scanning abdominal diseases in a critical care setting. Med Klin Intensivmed Notfmed [Internet]. 2022 Jun 2. Available online: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s00063-022-00926-4 (accessed on 31 October 2022).
- Barreiros A, Cui X, Ignee A, De Molo C, Pirri C, Dietrich C. EchoScopy in Scanning Abdominal Diseases: Initial Clinical Experience. Z Gastroenterol. 2014, 52, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testuz A, Muller H, Keller PF, Meyer P, Stampfli T, Sekoranja L, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of pocket-size handheld echocardiographs used by cardiologists in the acute care setting. European Heart Journal - Cardiovascular Imaging. 2013, 14, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rispo A, Calabrese G, Testa A, Imperatore N, Patturelli M, Allocca M, et al. Hocus Pocus: the Role of Handheld Ultrasonography in Predicting Disease Extension and Endoscopic Activity in Ulcerative Colitis. Journal of Crohn's and Colitis. 2023, jjad024.
| STUDY | YEAR | COMPARISON | SEGMENT | SENSITIVITY (%) | SPECIFICITY (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MACONI[12] ET AL. | 1996 | IC, radiology, histology | Ileum, colon | 89.1 | 94 |
| ASTEGIANO[13] ET AL. | 2001 | IC, radiology, clinical evaluation | Ileum, colon | 74 | 98 |
| PARENTE[14] ET AL. | 2002 | IC, radiology, surgery | Ileum, colon | 93.4 | 97.3 |
| PASCU[15] ET AL. | 2004 | IC | Ileum, colon | 82 | 97 |
| PALLOTTA[16] ET AL. | 2005 | IC, radiology, surgery, clinical evaluation | Jejunum, ileum | 57; 94.3 | 100; 98 |
| RISPO[17] ET AL. | 2005 | IC, radiology | Ileum | 92 | 97 |
| CASTIGLIONE[18] ET AL. | 2013 | IC | Ileum, colon | 94 | 97 |
| PALLOTTA[19] ET AL.^ | 2013 | IC, radiology, clinical evaluation | Jejunum, ileum | 75 | 100 |
| RISPO[20] ET AL.* | 2022 | IC, radiology | Ileum, colon | 87.5 | 91.9 |
| IUS: INTESTINAL ULTRASOUND; CD: CROHN’S DISEASE; IC: ILEOCOLONOSCOPY . ^STUDY CONDUCTED ON CHILDREN*IUS HAS BEEN PERFORMED WITH HANDHELD DEVICE | |||||
| STUDY | YEAR | COMPARISON | SEGMENT | SENSITIVITY (%) | SPECIFICITY (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MACONI[12] ET AL. | 1996 | IC, enteroclysis | Ileum and colon | 89 | 94 |
| REIMUND[23] ET AL. | 1999 | IC, enteroclysis | Ileum and colon | 83 | 67 |
| BRU[24] ET AL. | 2001 | IC | Ileum and colon | 83 | 87 |
| PARENTE[14] ET AL. | 2002 | IC, enteroclysis | Ileum and colon | 93 | 97 |
| PARENTE[25] ET AL. | 2003 | IC, enteroclysis, CT, surgery | Ileum and colon | 77 | 95 |
| PASCU[15] ET AL. | 2004 | IC | Ileum and colon | 74 | 97 |
| PARENTE[26] ET AL. | 2004 | IC, enteroclysis | Small bowel | 96 | 98 |
| MARTINEZ[27] ET AL. | 2009 | IC, enteroclysis, CT | Small bowel and colon | 91 | 98 |
| CASTIGLIONE[18] ET AL. | 2013 | IC, MRE, surgery | Small bowel and colon | 73 | 92 |
| RISPO[28] ET AL. | 2017 | IC, MRE | Small bowel and colon | 78 | 94 |
| ALLOCCA[29] ET AL. | 2018 | IC, MRE | Ileum and colon | 88 | 96 |
| IUS: INTESTINAL ULTRASOUND; CD: CROHN’S DISEASE; IC: ILEOCOLONOSCOPY; MRE: MAGNETIC RESONANCE ENTEROGRAPHY | |||||
| STUDY | YEAR | COMPARISON | US TECHNIQUES | SENSITIVITY (%) | SPECIFICITY (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GASCHE[33] ET AL. | 1999 | Surgery | US | 100 | 91 | |
| KOHN[34] ET AL. | 1999 | Surgery | US | 75 | 89 | |
| PALLOTTA[35] ET AL. | 2012 | Surgery | US/SICUS | 80 | 75 | |
| ONALI[36] ET AL. | 2012 | Surgery | SICUS | 92 | 0 | |
| KUMAR[37] ET AL. | 2015 | Surgery | SICUS | 88 | 88 | |
| IUS: INTESTINAL ULTRASOUND; CD: CROHN’S DISEASE; SICUS: SMALL INTESTINE CONTRAST ULTRASONOGRAPHY | ||||||
| STUDY | YEAR | COMPARISON | US TECHNIQUES | SENSITIVITY (%) | SPECIFICITY (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MACONI[12] ET AL. | 1996 | Endoscopy, CT, enteroclysis | US | 83 | 94 |
| GASCHE[33] ET AL. | 1999 | Surgery | US | 100 | 92 |
| MACONI[38] ET AL. | 2003 | Surgery | US | 80 | 93 |
| ONALI[36] ET AL. | 2012 | Surgery | SICUS | 100 | 80 |
| ALLOCCA[29] ET AL. | 2018 | IC, MRI | IUS | 100 | 96 |
| IUS: INTESTINAL ULTRASOUND; CD: CROHN’S DISEASE; CT: COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY; MRI: MAGNETIC RESONANTE IMAGING | |||||
| STUDY | YEAR | COMPARISON | US TECHNIQUES | SENSITIVITY (%) | SPECIFICITY (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MACONI[12] ET AL. | 1996 | Endoscopy, CT, enteroclysis | US | 66 | 96 |
| GASCHE[33] ET AL. | 1999 | Surgery | US | 87 | 90 |
| PALLOTTA[35] ET AL. | 2012 | Surgery | SICUS | 96 | 90.5 |
| ONALI[36] ET AL. | 2012 | Surgery | SICUS | 60 | 88 |
| ALLOCCA[29] ET AL. | 2018 | IC, MRI | IUS | 100 | 98 |
| IUS: INTESTINAL ULTRASOUND; CD: CROHN’S DISEASE; CT: COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY; IC: ILEOCOLONOSCOPY; MRI: MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING | |||||
| STUDY | YEAR | COMPARISON | RESULTS |
|---|---|---|---|
| BOZKURT[56] ET AL. | 1996 | IC, CRP | Three grades based upon BWT > 4 mm, BWS and haustration |
| PASCU[15] ET AL. | 2004 | IC, CRP | Four levels based upon BWT > 3 mm, CD and BWS |
| ANTONELLI[57] ET AL. | 2011 | IC, CRP | BWT > 4 mm |
| ALLOCCA[29] ET AL. | 2018 | IC | BWT > 3 mm, CD, BWS, lymph nodes mesentery inflammation |
| KINOSHITA[54] ET AL. | 2019 | IC, barium studies, clinics | Four grades based upon BWT and BWS |
| ALLOCCA[58] ET AL. | 2021 | IC | MUC ( MUC = 1.4 x BWT +2.0 x CD) > 6.2 |
| BOTS[59] ET AL. | 2021 | IC | UC-IUS (0-7) = BWT >2 mm + CD + haustration + fat wrapping |
| UC: ULCERATIVE COLITIS; IC: ILEO-COLONOSCOPY; CRP: C-REACTIVE PROTEIN; BWT: BOWEL WALL THICKNESS; BWS:BOWEL WALL STRATIFICATION; MUC: MILAN ULTRASOUND CRITERIA; UC-IUS: ULCERATIVE COLITIS INTESTINAL ULTRASOUND | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





