Submitted:
03 March 2025
Posted:
04 March 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methods
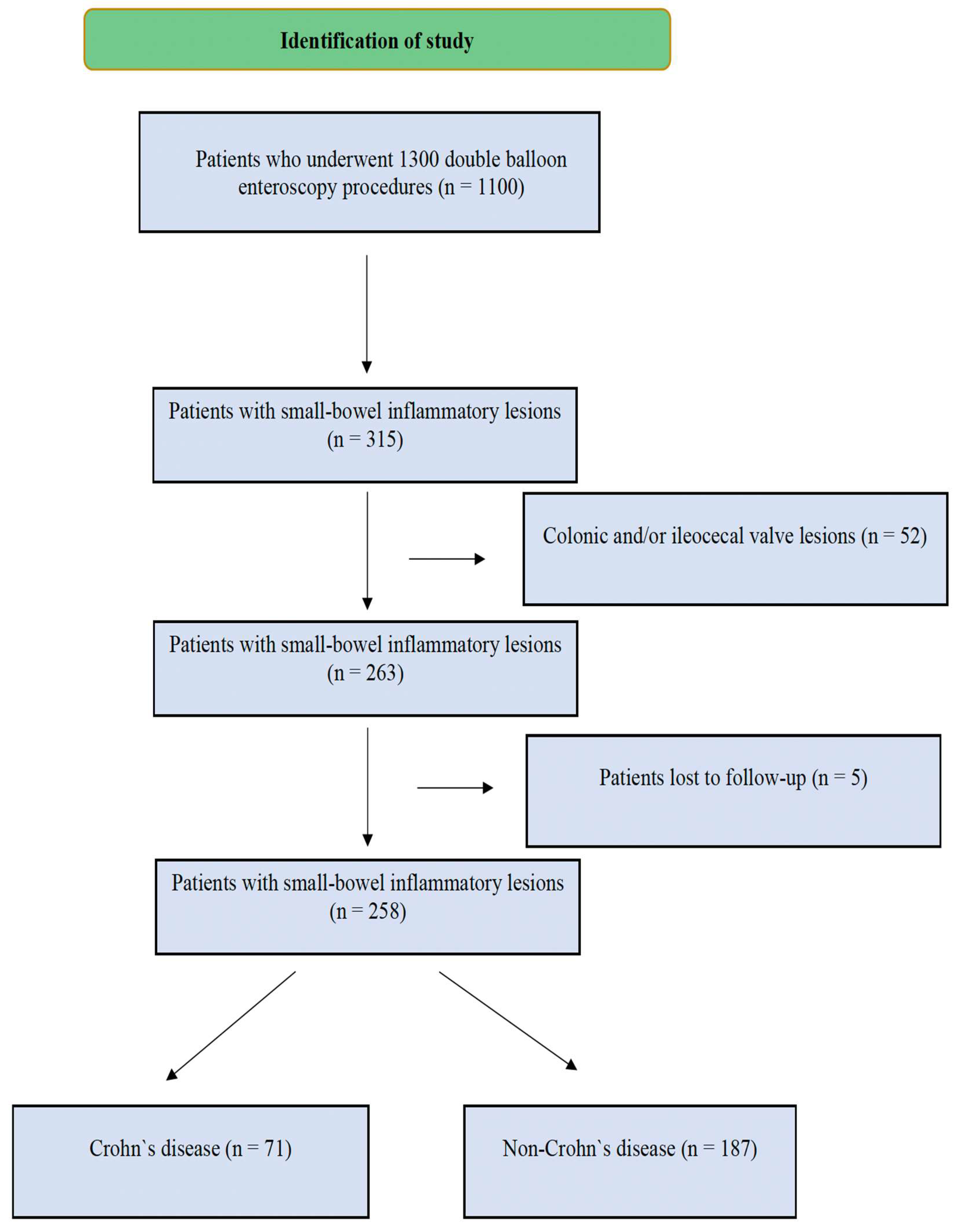
2.1. Data Collection and Study Design
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Demographics and Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Clinical Presentations and Symptoms
3.3. Comorbidities and Medication Use
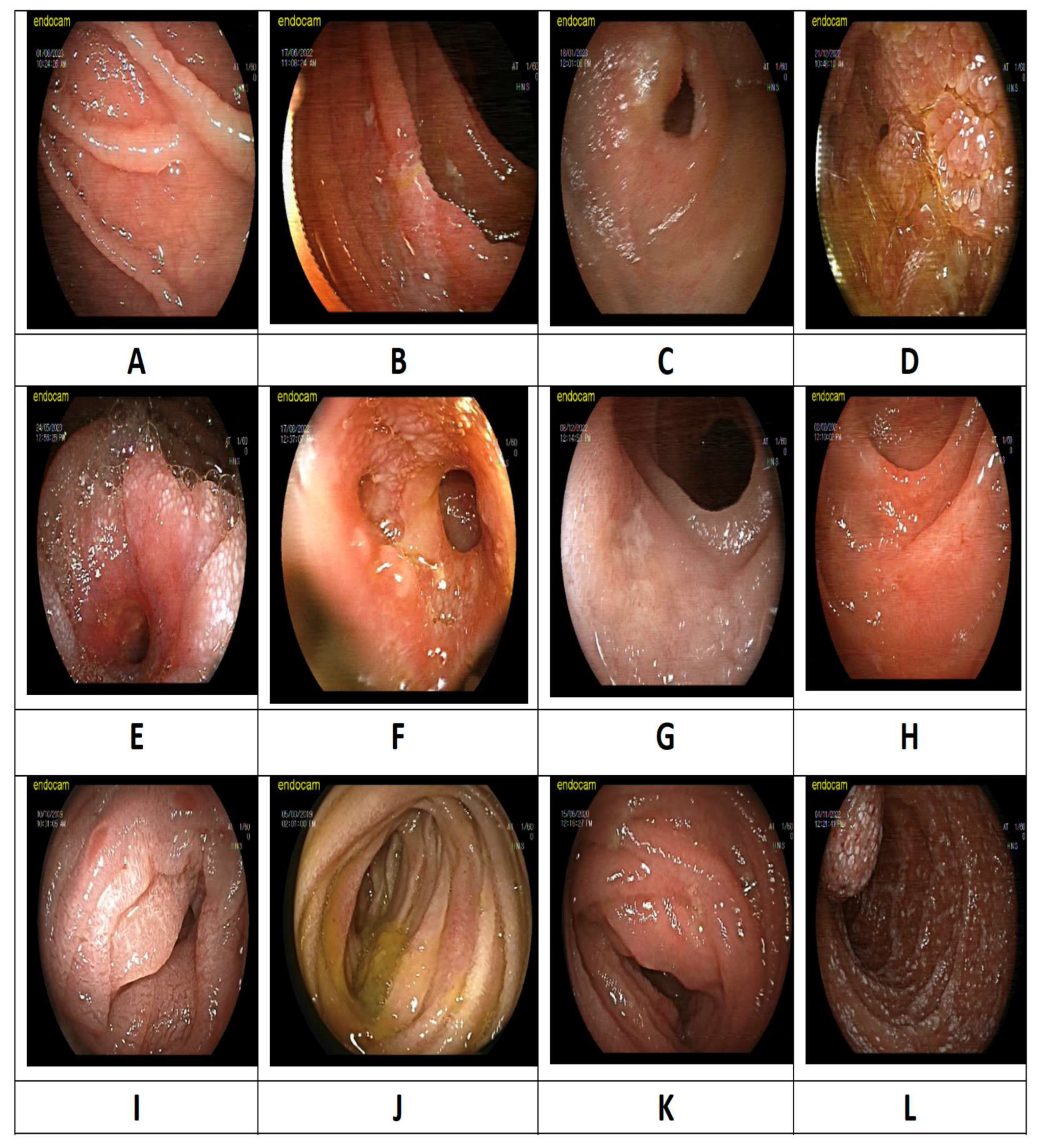
3.4. Radiological and Endoscopic Findings
3.5. Comparison of Crohn’s Disease and Other Diagnoses
3.6. Histopathological and Final Diagnoses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Ethical approval
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu F-F, Xie Q, Huang X-S, Wang W-D, Liao Y, Shi J, et al. Endoscopic Features and Clinical Characteristics of Ulcerations With Isolated Involvement of the Small Bowel. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2021;32:401–11. [CrossRef]
- Goenka MK, Majumder S, Kumar S, Sethy PK, Goenka U. Single center experience of capsule endoscopy in patients with obscure gastrointestinal bleeding. World J Gastroenterol. 2011;17:774–8.
- Shahidi NC, Ou G, Svarta S, Law JK, Kwok R, Tong J, et al. Factors associated with positive findings from capsule endoscopy in patients with obscure gastrointestinal bleeding. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012;10:1381–5. [CrossRef]
- Gay G, Delvaux M, Frederic M. Capsule endoscopy in non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs-enteropathy and miscellaneous, rare intestinal diseases. World J Gastroenterol. 2008;14:5237–44. [CrossRef]
- Niu M, Chen Z-H, Li M, Zhang X, Chen C-X. Differentiation of Isolated Small Bowel Crohn’s Disease from Other Small Bowel Ulcerative Diseases: Clinical Features and Double-Balloon Enteroscopy Characteristics. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2022;2022:5374780. [CrossRef]
- Esaki M, Matsumoto T, Ohmiya N, Washio E, Morishita T, Sakamoto K, et al. Capsule endoscopy findings for the diagnosis of Crohn’s disease: a nationwide case-control study. J Gastroenterol. 2019;54:249–60. [CrossRef]
- Belhassine M, Dragean C, Dano H, Moreels TG. Cryptogenic multifocal ulcerative stenosing enteritis (CMUSE) diagnosed by retrograde motorized spiral enteroscopy. Acta Gastroenterol Belg. 2022;85:527–30. [CrossRef]
- Orjollet-Lecoanet C, Ménard Y, Martins A, Crombé-Ternamian A, Cotton F, Valette PJ. [CT enteroclysis for detection of small bowel tumors]. J Radiol. 2000;81:618–27.
- Huang Z, Liu X, Yang F, Wang G, Ge N, Wang S, et al. Diagnostic efficacy of double-balloon enteroscopy in patients with suspected isolated small bowel Crohn’s disease. BMC Gastroenterol. 2020;20:42. [CrossRef]
- Dolu S, Onem S, Htway Z, Hajıyev F, Bilgen A, Binicier HC, et al. Endoscopic and histological characteristics of small bowel tumors diagnosed by double-balloon enteroscopy. Clin Endosc. 2023;56:83–91. [CrossRef]
- Dolu S, Arayici ME, Onem S, Buyuktorun I, Dongelli H, Bengi G, et al. Evaluation of double-balloon enteroscopy in the management of type 1 small bowel vascular lesions (angioectasia): a retrospective cohort study. BMC Gastroenterol. 2025;25:15. [CrossRef]
- Yalçın E, Döngelli H, Dolu S, Akarsu M. Eosinophilic jejunitis presenting as acute abdomen with eosinophilic ascites. BMJ Case Rep. 2024;17:e261123. [CrossRef]
- Tang L, Huang L-Y, Cui J, Wu C-R. Effect of Double-Balloon Enteroscopy on Diagnosis and Treatment of Small-Bowel Diseases. Chinese Medical Journal. 2018;131:1321–6. [CrossRef]
- Dolu S, Arayici ME, Onem S, Buyuktorun I, Dongelli H, Bengi G, et al. Effectiveness of Double Balloon Enteroscopy in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Small Bowel Varices. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025;15:336. [CrossRef]
- Ma J-J, Wang Y, Xu X-M, Su J-W, Jiang W-Y, Jiang J-X, et al. Capsule endoscopy and single-balloon enteroscopy in small bowel diseases: Competing or complementary? World J Gastroenterol. 2016;22:10625–30.
- Catassi G, Marmo C, Gasbarrini A, Riccioni ME. Role of Device-Assisted Enteroscopy in Crohn’s Disease. J Clin Med. 2024;13:3919. [CrossRef]
- Arulanandan A, Dulai PS, Singh S, Sandborn WJ, Kalmaz D. Systematic review: Safety of balloon assisted enteroscopy in Crohn’s disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2016;22:8999–9011. [CrossRef]
- Jeon SR, Kim J-O, Byeon J-S, Yang D-H, Ko BM, Goong HJ, et al. Enteroscopy in Crohn’s Disease: Are There Any Changes in Role or Outcomes Over Time? A KASID Multicenter Study. Gut Liver. 2021;15:375–82.
- May A, Nachbar L, Schneider M, Neumann M, Ell C. Push-and-pull enteroscopy using the double-balloon technique: method of assessing depth of insertion and training of the enteroscopy technique using the Erlangen Endo-Trainer. Endoscopy. 2005;37:66–70. [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto H, Kita H, Sunada K, Hayashi Y, Sato H, Yano T, et al. Clinical outcomes of double-balloon endoscopy for the diagnosis and treatment of small-intestinal diseases. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2004;2:1010–6. [CrossRef]
- Van Assche G, Dignass A, Panes J, Beaugerie L, Karagiannis J, Allez M, et al. The second European evidence-based Consensus on the diagnosis and management of Crohn’s disease: Definitions and diagnosis. Journal of Crohn’s and Colitis. 2010;4:7–27. [CrossRef]
- Lee SP, Jang HJ, Kae SH, Lee JG, Kwon JH. Indication, Location of the Lesion, Diagnostic Yield, and Therapeutic Yield of Double-Balloon Enteroscopy: Seventeen Years of Experience. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022;12:2224. [CrossRef]
- Xin L, Liao Z, Jiang Y-P, Li Z-S. Indications, detectability, positive findings, total enteroscopy, and complications of diagnostic double-balloon endoscopy: a systematic review of data over the first decade of use. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011;74:563–70. [CrossRef]
- Heine GD, Hadithi M, Groenen MJ, Kuipers EJ, Jacobs MA, Mulder CJ. Double-balloon enteroscopy: indications, diagnostic yield, and complications in a series of 275 patients with suspected small-bowel disease. Endoscopy. 2006;38:42–8. [CrossRef]
- Tun GSZ, Rattehalli D, Sanders DS, McAlindon ME, Drew K, Sidhu R. Clinical utility of double-balloon enteroscopy in suspected Crohn’s disease: a single-centre experience. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;28:820–5. [CrossRef]
- Ge Z-Z, Hu Y-B, Xiao S-D. Capsule endoscopy in diagnosis of small bowel Crohn’s disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2004;10:1349–52. [CrossRef]
- Wang J, Guo Q, Zhao J, Liu M, Liao G, Chen N, et al. Multidetector CT Enterography versus Double-Balloon Enteroscopy: Comparison of the Diagnostic Value for Patients with Suspected Small Bowel Diseases. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2016;2016:5172873. [CrossRef]
- Manes G, Imbesi V, Ardizzone S, Cassinotti A, Pallotta S, Porro GB. Use of double-balloon enteroscopy in the management of patients with Crohn’s disease: feasibility and diagnostic yield in a high-volume centre for inflammatory bowel disease. Surg Endosc. 2009;23:2790–5. [CrossRef]
- Lei II, Thorndal C, Manzoor MS, Parsons N, Noble C, Huhulea C, et al. The Diagnostic Accuracy of Colon Capsule Endoscopy in Inflammatory Bowel Disease-A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024;14:2056.
- Oshitani N, Yukawa T, Yamagami H, Inagawa M, Kamata N, Watanabe K, et al. Evaluation of deep small bowel involvement by double-balloon enteroscopy in Crohn’s disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006;101:1484–9. [CrossRef]
|
Duodenum (n=31) |
Jejunum (n=63) |
Ileum (n=82) |
Panenteritis (n=82) |
Total (n=258) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, mean ± SD | 57.1±16.8 | 52.7±17.2 | 46.6±17.5 | 42.0±15.6 | 48.2±17.3 |
| Female sex, n (%) | 12 (38.7) | 27 (42.9) | 30 (36.6) | 31 (37.8) | 100 (38.8) |
| Complaint at admission, n (%) Abdominal pain Diarrhea Nausea Bleeding Steatorrhea Weight loss Anemia Ileus/subileus Fever |
10 (32.3) 5 (16.1) 5 (16.1) 8 (25.8) 2 (6.5) 6 (19.4) 5 (16.1) 0 (0) 1 (3.2) |
35 (55.6) 12 (19.0) 2 (3.2) 10 (15.9) 3 (4.8) 10 (19.4) 10 (15.9) 3 (4.8) 1 (1.6) |
36 (43.9) 31 (37.8) 1 (1.2) 16 (19.5) 3 (3.7) 8 (9.8) 9 (11.0) 15 (18.3) 0 (0) |
42 (51.2) 34 (41.5) 6 (7.3) 10 (12.2) 9 (11.0) 13 (15.9) 7 (8.5) 9 (11.0) 3 (3.7) |
123 (47.7) 82 (31.8) 14 (5.4) 44 (17.1) 17 (6.6) 37 (14.3) 31 (12.0) 27 (10.5) 5 (1.9) |
| Comorbidity, n (%) Hypertension DM Dyslipidemia CAD Heart failure Afib COPD CKD Immunodeficiency Hypothyroidism Malignancy Liver cirrhosis CTD |
10 (32.3) 4 (12.9) 2 (6.5) 5 (16.1) 0 (0) 2 (6.5) 1 (3.2) 1 (3.2) 0 (0) 3 (9.7) 6 (19.4) 0 (0) 0 (0) |
25 (39.7) 12 (19) 4 (6.3) 5 (7.9) 2 (3.2) 4 (6.3) 3 (4.8) 1 (1.6) 0 (0) 2 (3.2) 11 (17.5) 1 (1.6) 3 (4.8) |
17 (20.7) 11 (13.4) 6 (7.3) 6 (7.3) 3 (3.7) 1 (1.2) 5 (6.1) 2 (2.4) 1 (1.2) 2 (2.4) 7 (8.5) 2 (2.4) 5 (6.1) |
14 (17.1) 7 (8.5) 1 (1.2) 3 (3.7) 0 (0) 2 (2.4) 1 (1.2) 0 (0) 4 (4.9) 1 (1.2) 6 (7.3) 1 (1.2) 7 (8.5) |
66 (25.6) 34 (13.2) 13 (5.0) 19 (7.4) 5 (1.9) 9 (3.5) 10 (3.9) 4 (1.6) 5 (1.9) 8 (3.1) 30 (11.6) 4 (1.6) 15 (5.8) |
| Medication, n (%) NSAIDs ASA SSRIs NOACs Warfarin Glucocorticosteroid Metformin |
5 (16.1) 6 (19.4) 1 (3.2) 1 (3.2) 0 (0) 0 (0) 1 (3.2) |
13 (20.6) 9 (14.3) 2 (3.2) 3 (4.8) 1 (1.6) 1 (1.6) 6 (9.5) |
25 (28.0) 11 (13.4) 3 (3.3) 1 (1.2) 1 (1.2) 3 (3.7) 0 (0) |
24 (29.3) 4 (4.9) 1 (1.2) 0 (0) 2 (2.4) 2 (2.4) 3 (3.7) |
65 (25.2) 30 (11.6) 7 (2.7) 5 (1.9) 4 (1.6) 6 (2.3) 10 (3.9) |
| History of GIS surgery, n (%) | 2 (6.5) | 1 (1.6) | 8 (9.8) | 1 (1.2) | 12 (4.6) |
| CT findings, n (%) Not performed Normal Wall thickness Mass appearance Bleeding Lymphadenopathy Ileus/subileus |
7 (22.6) 9 (29.0) 6 (19.4) 5 (16.1) 0 (0) 0 (0) 4 (12.9) |
7 (11.1) 14 (22.2) 22 (34.9) 17 (27.0) 0 (0) 2 (3.2) 1 (1.6) |
15 (18.3) 27 (32.9) 23 (28.0) 7 (8.5) 0 (0) 2 (2.4) 8 (9.8) |
16 (19.5) 28 (34.1) 30 (36.6) 2 (2.4) 1 (1.2) 2 (2.4) 3 (3.7) |
45 (17.4) 78 (30.2) 81 (31.4) 31 (12.0) 1 (0.4) 6 (2.3) 16 (6.2) |
| Double-balloon enteroscopy findings, n (%) Superficial changes Edema Ulcer Stenosis |
4 (12.9) 7 (22.6) 17 (54.8) 3 (9.7) |
14 (22.2) 16 (25.4) 25 (39.7) 8 (12.7) |
21 (25.6) 7 (8.5) 47 (57.3) 7 (8.5) |
21 (25.6) 27 (32.9) 27 (32.9) 7 (8.5) |
60 (23.3) 57 (22.1) 116 (45.0) 25 (9.7) |
|
Crohn’s Disease (n=71) |
Non-Crohn’s Disease (n=187) | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, mean ± SD | 40.9±14.7 | 50.9±17.5 | <0.001 |
| Female sex, n (%) | 26 (36.6) | 74 (39.6) | 0.664 |
| Complaint at admission, n (%) Abdominal pain Diarrhea Nausea Bleeding Steatorrhea Weight loss Anemia Ileus/subileus Fever |
49 (69.0) 37 (52.1) 2 (2.8) 2 (2.8) 4 (5.6) 11 (15.5) 3 (4.2) 13 (18.3) 0 (0) |
74 (39.6) 45 (24.1) 12 (6.4) 42 (22.5) 13 (7.0) 26 (13.9) 28 (15.0) 14 (7.5) 5 (2.7) |
<0.001 <0.001 0.362 <0.001 0.703 0.745 0.018 0.011 0.327* |
| Comorbidities, n (%) Hypertension DM Dyslipidemia CAD Heart failure Afib COPD CKD Immunodeficiency Hypothyroidism Malignancy Liver cirrhosis CTD |
9 (12.7) 4 (5.6) 2 (2.8) 2 (2.8) 0 (0) 0 (0) 2 (2.8) 0 (0) 0 (0) 1 (1.4) 4 (5.6) 1 (1.4) 8 (11.3) |
57 (30.5) 30 (16.0) 11 (5.9) 17 (9.1) 5 (2.7) 9 (4.8) 8 (4.3) 4 (2.1) 5 (2.7) 7 (3.7) 26 (13.9) 3 (1.6) 7 (3.7) |
0.003 0.027 0.524 0.085 0.327* 0.067* 0.732 0.578* 0.327* 0.452* 0.064 0.909* 0.021 |
| Medications, n (%) NSAIDs ASA SSRIs NOACs Coumadine Glucocorticosteroid Metformin |
14 (19.7) 8 (11.3) 1 (1.4) 0 (0) 0 (0) 1 (1.4) 2 (2.8) |
51 (27.3) 22 (11.8) 6 (3.2) 5 (2.7) 4 (2.1) 5 (2.7) 8 (4.3) |
0.212 0.911 0.677* 0.327* 0.578* 0.889* 0.732 |
| History of GIS surgery, n (%) | 3 (4.2) | 9 (4.8) | 0.841 |
| Intestinal involvement, n (%) Duodenum (only) Jejunum (only) Ileum (only) Duodenum and jejunum Duodenum and ileum Jejunum and ileum Panenteritis |
3 (4.2) 5 (7.0) 39 (54.9) 2 (2.8) 2 (2.8) 13 (18.3) 7 (9.9) |
28 (15.0) 58 (31.0) 43 (23.0) 26 (13.9) 6 (3.2) 18 (9.6) 8 (4.3) |
N/A |
| CT findings, n (%) Not performed Normal Wall thickness Mass appearance Bleeding Lymphadenopathy Ileus/subileus |
9 (12.7) 19 (26.8) 29 (40.8) 3 (4.2) 0 (0) 3 (4.2) 8 (11.4) |
36 (19.3) 59 (31.6) 52 (27.8) 28 (15.0) 1 (0.5) 3 (1.6) 8 (4.3) |
N/A |
| Double-balloon enteroscopy findings, n (%) Superficial changes Edema Ulcer Stenosis |
10 (14.1) 11 (15.5) 43 (60.3) 7 (9.9) |
50 (26.7) 46 (24.6) 73 (39.0) 18 (9.6) |
0.032 0.115 0.002 0.955 |
| Final Diagnosis | N = 258 | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Crohn’s disease | 71 | 27,5% |
| Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs enteropathy | 31 | 12,0% |
| Celiac | 24 | 9,3% |
| Radiation enteritis | 4 | 1,6% |
| Infection | 6 | 2,3% |
| Ischemia | 3 | 1,2% |
| Autoimmune enteropathy | 5 | 1,9% |
| Behcet's disease | 1 | 0,4% |
| Lymphoproliferative disease | 8 | 3,1% |
| Malignancy | 41 | 15,9% |
| Eosinophilic enteritis | 8 | 3,1% |
| Vasculitis | 5 | 1,9% |
| Graft-versus-host disease | 1 | 0,4% |
| Lymphangectasia | 9 | 3,5% |
| Amyloidosis | 3 | 1,2% |
| Non-specific | 38 | 14,7% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





