Submitted:
03 May 2023
Posted:
04 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Real sample
2.2. Chemicals and standards
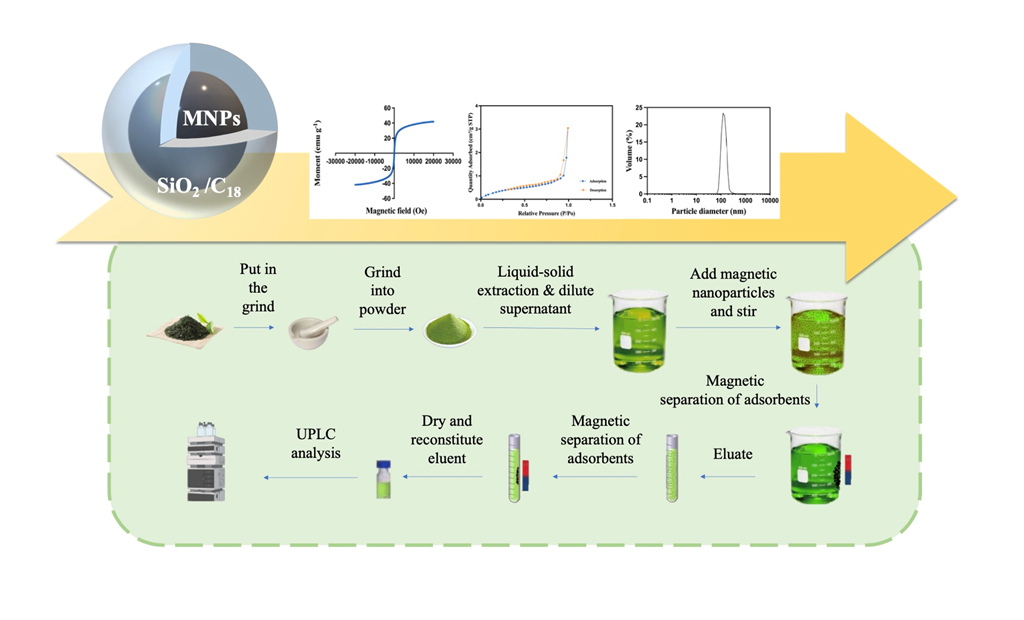
2.3. Preparation and characterization of C18/MNPs
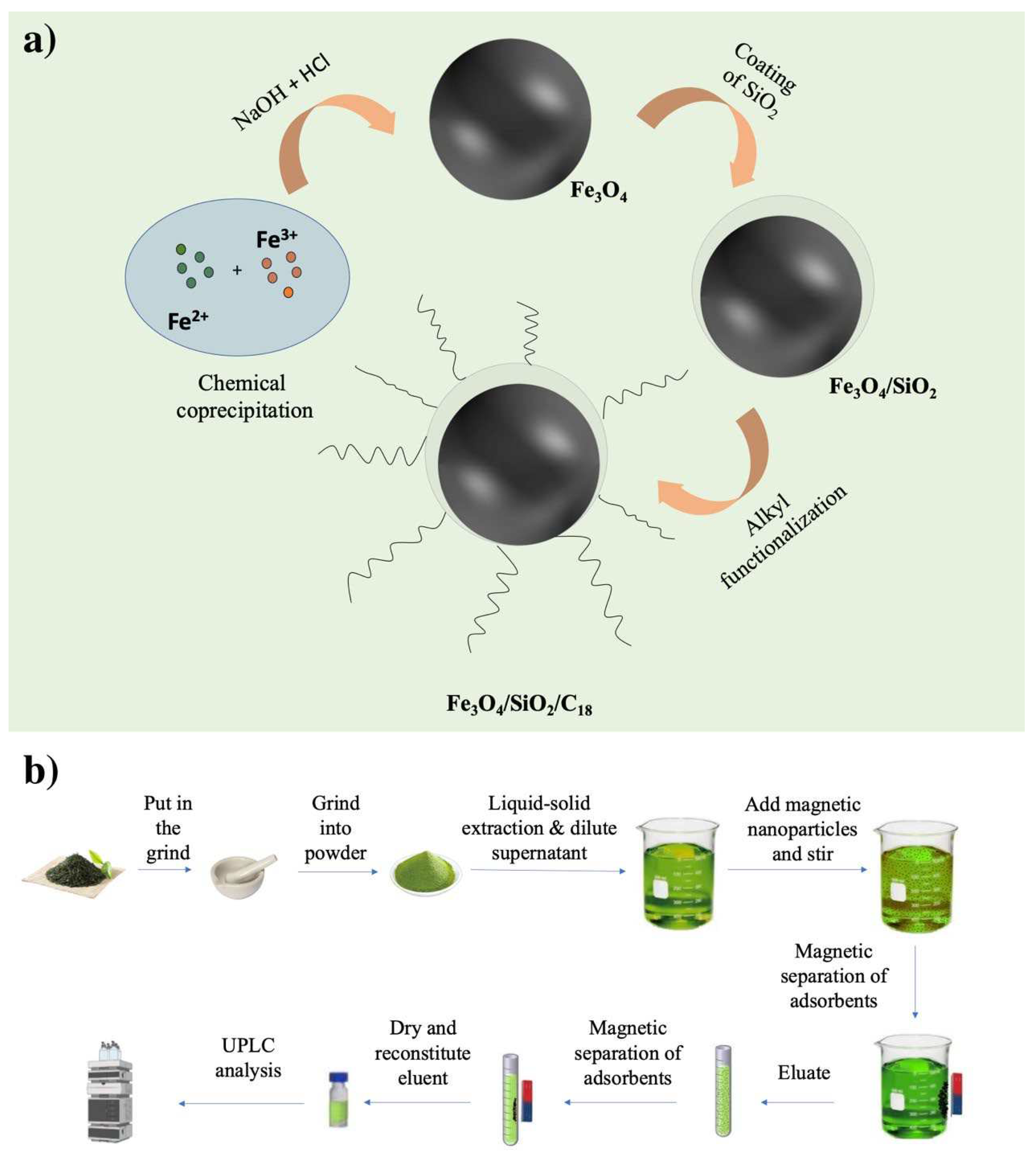
2.3.1. Synthesis of C18/MNPs
2.3.2. Characterization of C18/MNPs
2.4. C18/MNPs-based extraction procedure for the preconcentration and detection of five kinds of PAHs in Tea
2.4.1. Configuration of standard solution and preparation of spike samples
2.4.2. Preconcentration procedures
2.5. Recycling of C18/MNPs
2.6. UPLC analysis
2.7. Statistical analysis
3. Results and discussion
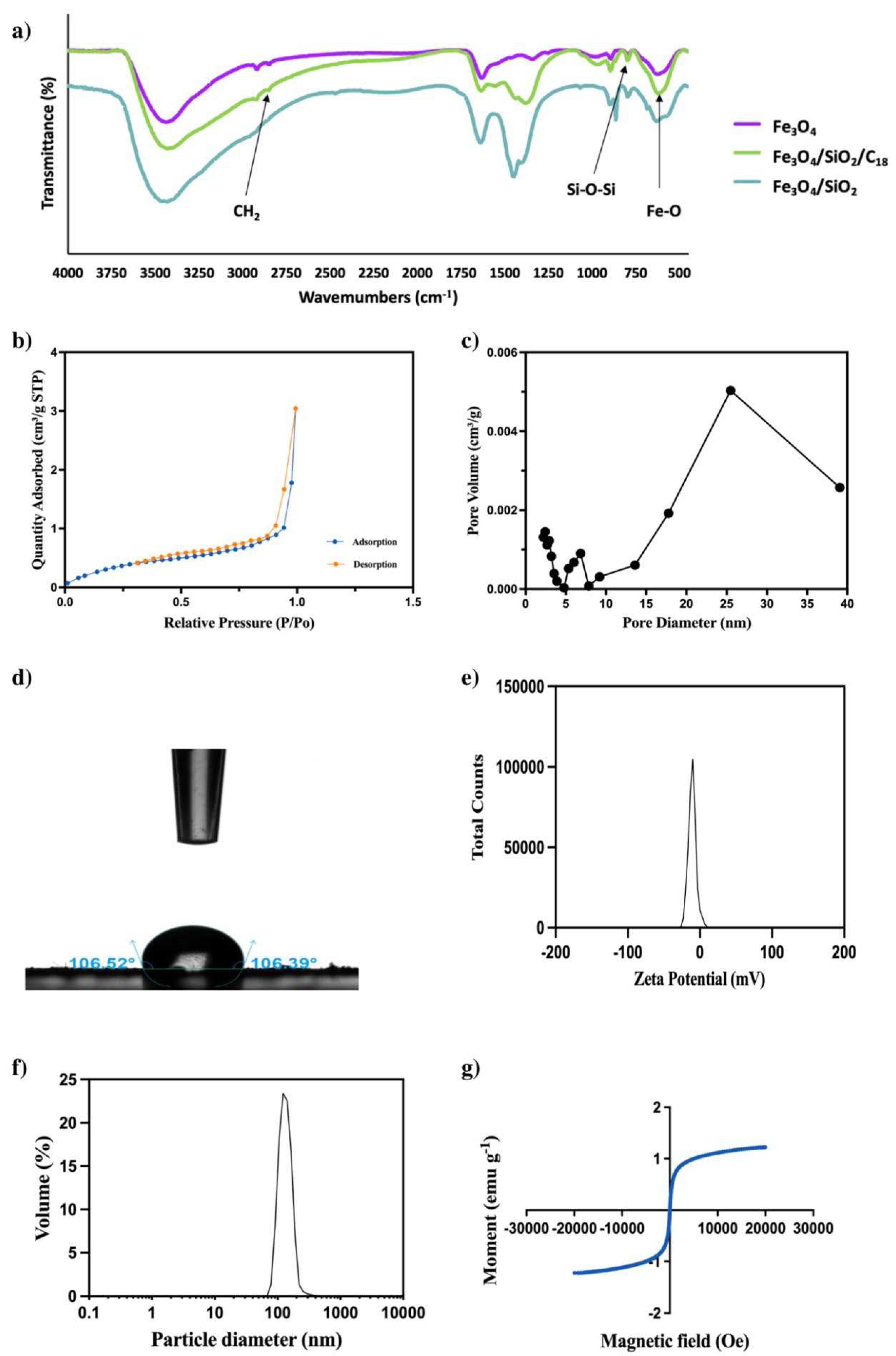
3.1. Characterizing of C18/MNPs
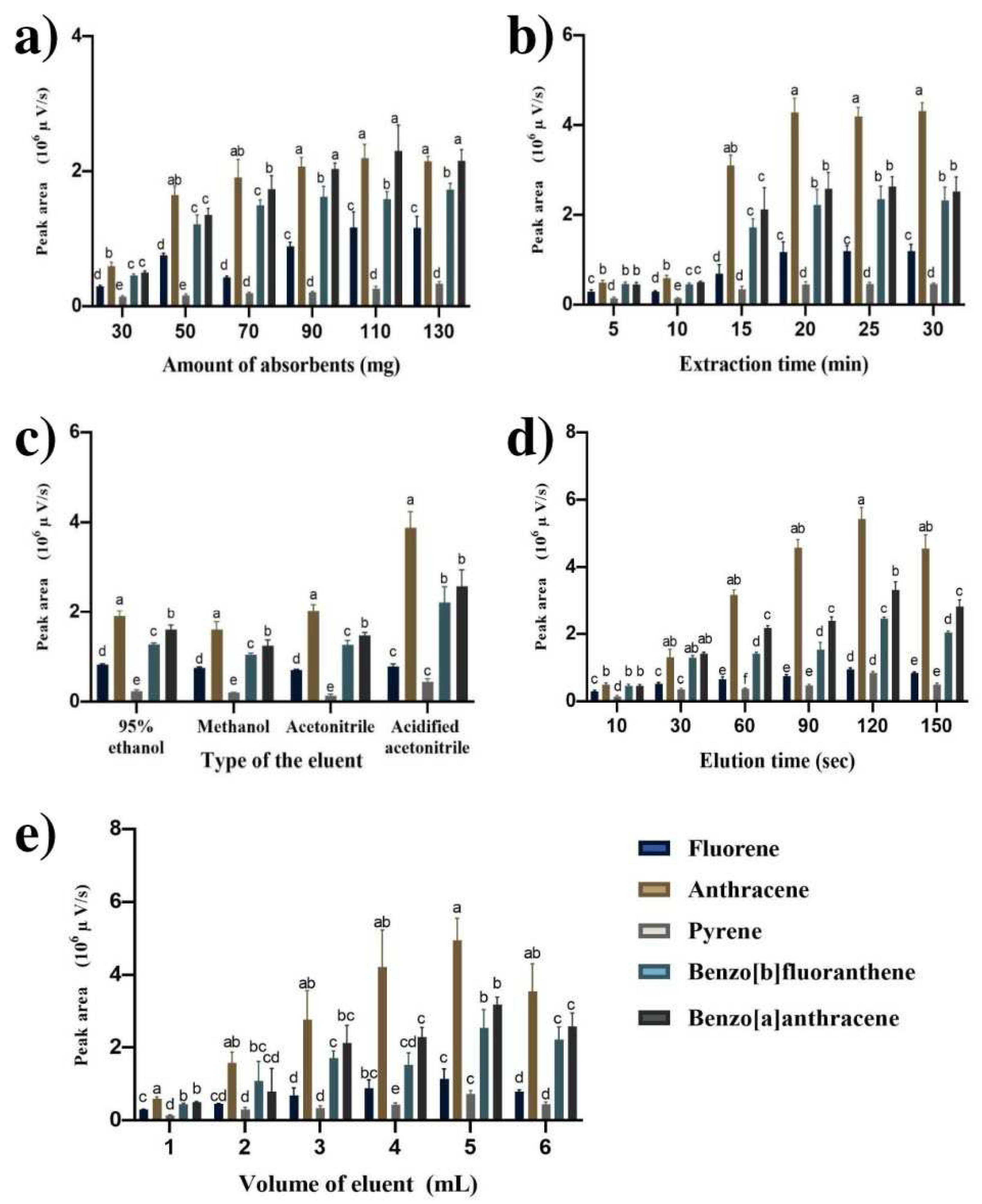
3.2. Optimizing MSPE conditions
3.2.1. Amount of absorbents
3.2.2. Extraction time
3.2.3. Type of the eluent
3.2.4. Elution time
3.2.5. Volume of eluent
3.3. Evaluation of the detection method performance
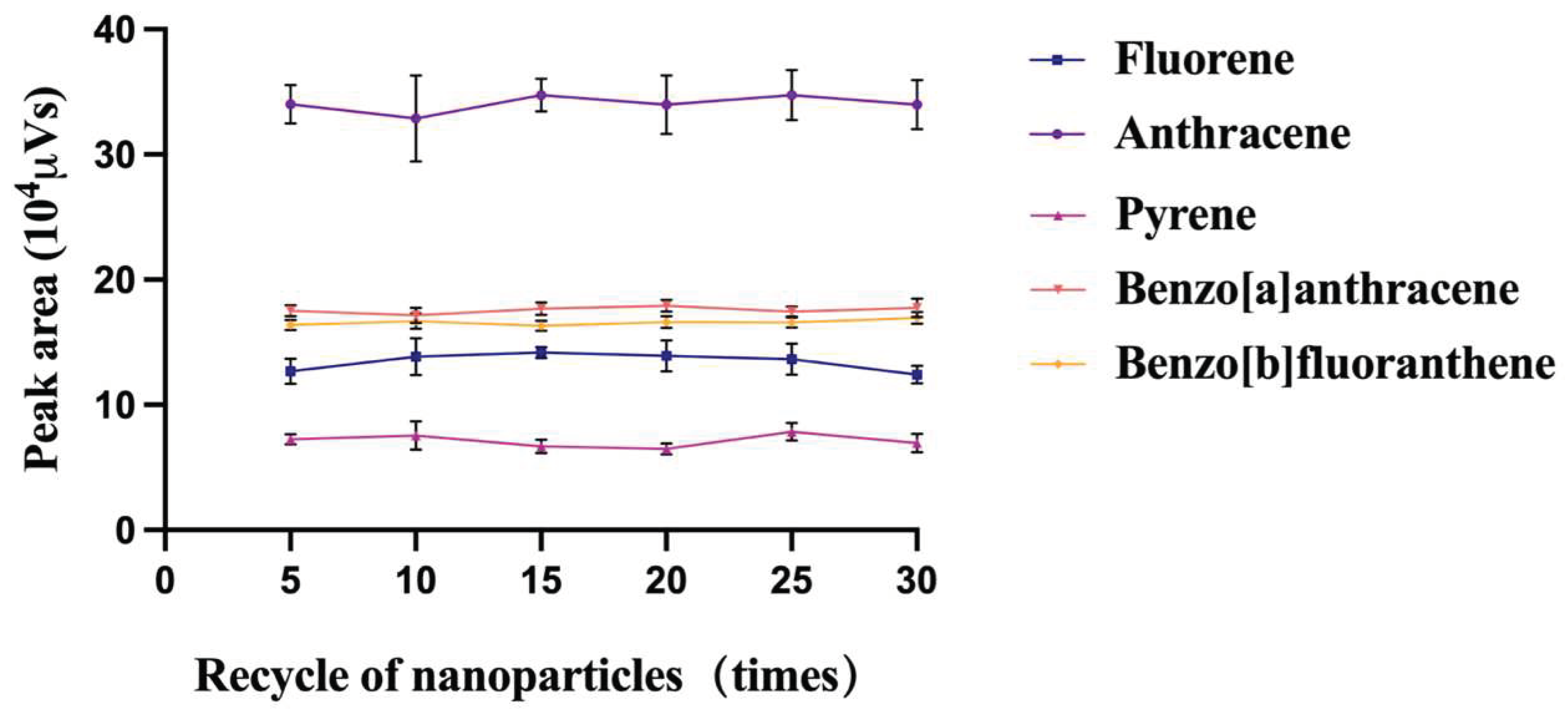
3.4. Reproducibility and Reusability of the C18/MNPs
3.5. Method comparison
3.6. Real sample analysis
4. Conclusion
Acknowledgments
References
- Sagar, B., et al. Tea and its phytochemicals: Hidden health benefits & modulation of signaling cascade by phytochemicals. Food Chemistry 2022, 371, 131098. [CrossRef]
- Li, X., et al. Determination for major chemical contaminants in tea (Camellia sinensis) matrices: A review. Food Research International 2013, 53, 649-658. [CrossRef]
- Tallei, T.E., et al. A comprehensive review of the potential use of green tea polyphenols in the management of COVID-19. Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine 2021, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Bansal, V. and K.-H. Kim. Review of PAH contamination in food products and their health hazards. Environment international 2015, 84, 26-38. [CrossRef]
- Tran-Lam, T.-T., et al. Simultaneous Determination of 18 Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Daily Foods (Hanoi Metropolitan Area) by Gas Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Foods 2018, 7, 201. [CrossRef]
- Roudbari, A., et al. Concentration and health risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in commercial tea and coffee samples marketed in Iran. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 2021, 28, 4827-4839. [CrossRef]
- Plaza-Bolaños, P., A.G. Frenich, and J.L.M. Vidal. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in food and beverages. Analytical methods and trends. Journal of Chromatography A 2010, 1217, 6303-6326. [CrossRef]
- Atirah Mohd Nazir, N., M. Raoov, and S. Mohamad. Spent tea leaves as an adsorbent for micro-solid-phase extraction of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) from water and food samples prior to GC-FID analysis. Microchemical Journal 2020, 159, 105581. [CrossRef]
- Zelinkova, Z. and T. Wenzl. The Occurrence of 16 EPA PAHs in Food – A Review. Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds 2015, 35, 248-284. [CrossRef]
- Ziegenhals, K., W. Jira, and K. Speer. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) in various types of tea. European Food Research and Technology 2008, 228, 83-91. [CrossRef]
- Duedahl-Olesen, L., et al. PAH in Some Brands of Tea and Coffee. Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds 2015, 35, 74-90. [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-Y., et al. A Novel Synchronous Fluorescence Spectroscopic Approach for the Rapid Determination of Three Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Tea with Simple Microwave-Assisted Pretreatment of Sample. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 2011, 59, 5899-5905. [CrossRef]
- Adisa, A., et al. Determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in dry tea. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, Part B 2015, 50, 552-559. [CrossRef]
- Khiadani , M., et al. Determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons concentration in eight brands of black tea which are used more in Iran. International Journal of Environmental Health Engineering 2013, 2, 40-40. [CrossRef]
- Sadowska-Rociek, A., M. Surma, and E. Cieślik. Comparison of different modifications on QuEChERS sample preparation method for PAHs determination in black, green, red and white tea. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 2014, 21, 1326-1338. [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z., et al. Effect of heat-treated tea water-insoluble protein nanoparticles on the characteristics of Pickering emulsions. LWT 2021, 149, 111999. [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z., et al. Characteristics and application of fish oil-in-water pickering emulsions structured with tea water-insoluble proteins/κ-carrageenan complexes. Food Hydrocolloids 2021, 114, 106562. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.-B., et al. Magnetic solid-phase extraction based on [60]fullerene functionalization of magnetic nanoparticles for the determination of sixteen polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in tea samples. Journal of Chromatography A 2018, 1578, 53-60. [CrossRef]
- Yu, X., et al. Design, Preparation, and Application of Magnetic Nanoparticles for Food Safety Analysis: A Review of Recent Advances. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 2022, 70, 46-62. [CrossRef]
- Baber, O., et al. Amorphous silica coatings on magnetic nanoparticles enhance stability and reduce toxicity to in vitro BEAS-2B cells. Inhalation Toxicology 2011, 23, 532-543. [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y., et al. Determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in coffee and tea samples by magnetic solid-phase extraction coupled with HPLC–FLD. Food Chemistry 2016, 199, 75-80. [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, F., et al. Magnetic solid-phase extraction based on diphenyl functionalization of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles for the determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in urine samples. Journal of Chromatography A 2012, 1231, 8-15. [CrossRef]
- Ma, J., et al. C18-Functionalized Magnetic Silica Nanoparticles for Solid Phase Extraction of Microcystin-LR in Reservoir Water Samples Followed by HPLC-DAD Determination. Journal of Liquid Chromatography & Related Technologies 2015, 38, 655-661. [CrossRef]
- Guo, B., et al. Preparation of C18-functionalized Fe3O4@SiO2 core–shell magnetic nanoparticles for extraction and determination of phthalic acid esters in Chinese herb preparations. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis 2014, 100, 365-368. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C., et al. Removal of sudan dyes from water with C18-functional ultrafine magnetic silica nanoparticles. Talanta 2012, 89, 38-46. [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X., et al. Magnetic solid-phase extraction modified Quick, Easy, Cheap, Effective, Rugged and Safe method combined with pre-column derivatization and ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry for determination of estrogens and estrogen mimics in pork and chicken samples. J Chromatogr A 2020, 1622, 461137. [CrossRef]
- Venkateswarlu, S., et al. Biogenic synthesis of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles using plantain peel extract. Materials Letters 2013, 100, 241-244. [CrossRef]
- Yu, X., et al. Quantification of aflatoxin B1 in vegetable oils using low temperature clean-up followed by immuno-magnetic solid phase extraction. Food Chemistry 2019, 275, 390-396. [CrossRef]
- Ma, L., et al. Rapid detection of clenbuterol in milk using microfluidic paper-based ELISA. Food Chemistry 2018, 246, 437-441. [CrossRef]
- Ciemniak, A., et al. Assessing the contamination levels of dried teas and their infusions by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Journal of Consumer Protection and Food Safety 2019, 14, 263-274. [CrossRef]
- Pissinatti, R., et al. Simultaneous analysis of 10 polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in roasted coffee by isotope dilution gas chromatography-mass spectrometry: Optimization, in-house method validation and application to an exploratory study. Food Control 2015, 51, 140-148. [CrossRef]
- Drabova, L., et al. Rapid determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in tea using two-dimensional gas chromatography coupled with time of flight mass spectrometry. Talanta 2012, 100, 207-216. [CrossRef]
- Benson, N.U., et al. Concentrations, sources and risk characterisation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in green, herbal and black tea products in Nigeria. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis 2018, 66, 13-22. [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.-B., et al. Fast microextraction of phthalate acid esters from beverage, environmental water and perfume samples by magnetic multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Talanta 2012, 90, 123-131. [CrossRef]
- Tran-Lam, T.-T., et al. Simultaneous Determination of 18 Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Daily Foods (Hanoi Metropolitan Area) by Gas Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Foods, 2018. 7. [CrossRef]
- Roszko, M., et al. Dietary risk evaluation for 28 polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in tea preparations made of teas available on the Polish retail market. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, Part B 2018, 53, 25-34. [CrossRef]
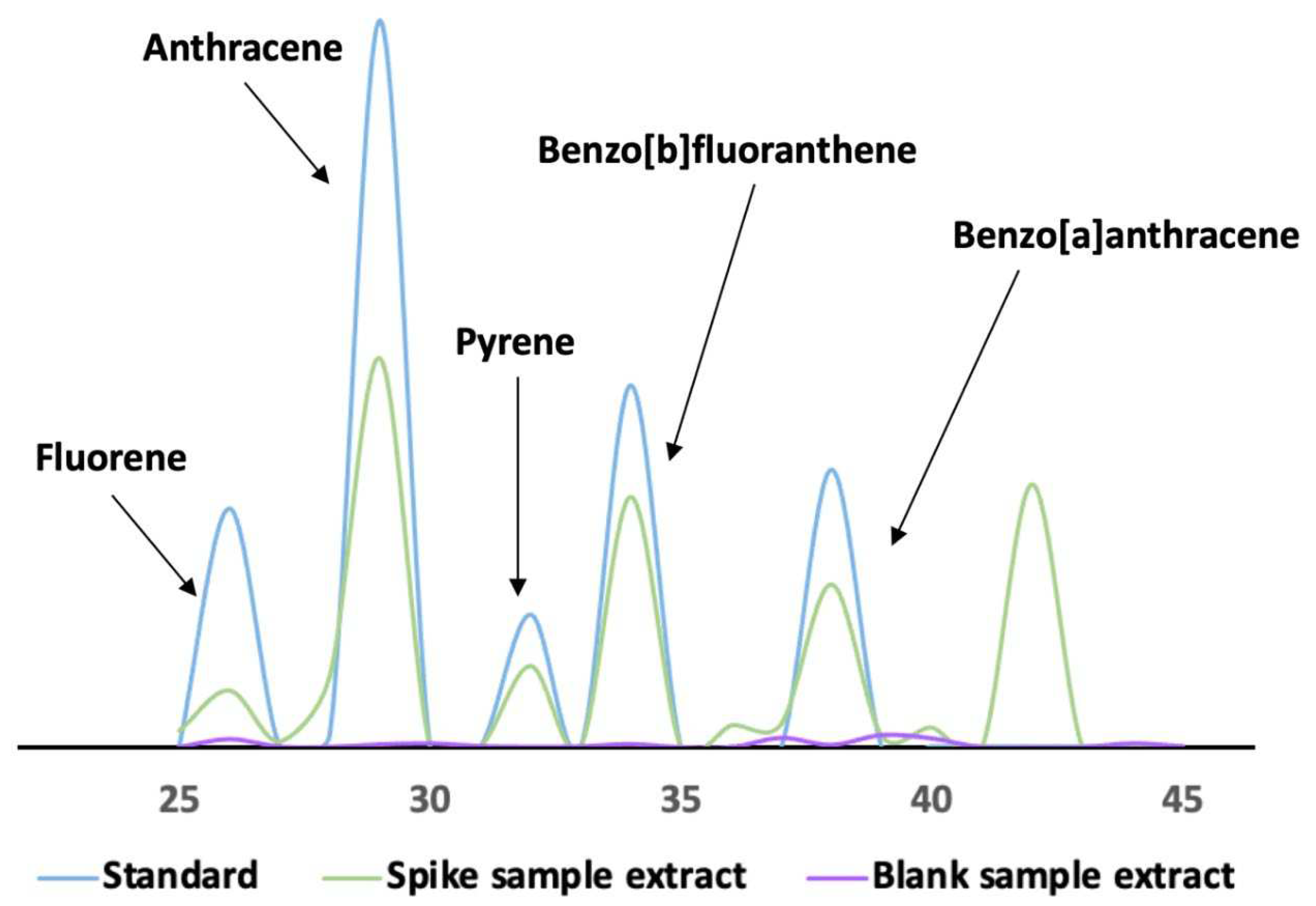
| Analyte | Equation of calibration curve | R2 | LOD (ng g-1) | LOQ (ng g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fluorene | 48627x+71642 | 0.998 | 7.93 | 24.03 |
| Anthracene | 106034x+4318855 | 0.999 | 5.32 | 16.12 |
| Pyrene | 22396x+216848 | 0.997 | 9.97 | 30.21 |
| Benzo[a]anthracene | 56517x+357848 | 0.998 | 1.69 | 5.12 |
| Benzo[b]fluoranthene | 51622x+661315 | 0.998 | 5.43 | 16.45 |
| Analyte | Concentration (ng g−1) | Intra-day precision | Inter-day precision | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recovery±SD (%) | RSD (%) | Recovery±SD (%) | RSD (%) | ||
| Fluorene | 0.5 | 94.8±2.8 | 3.4 | 84.8±2.9 | 6.8 |
| 1 | 95.2±0.7 | 1.3 | 91.6±0.3 | 3.1 | |
| 10 | 98.1±1.7 | 1.7 | 93.6±1.5 | 4.3 | |
| Anthracene | 0.5 | 91.7±0.8 | 2.9 | 88.1±0.9 | 5.9 |
| 1 | 100.2±1.6 | 1.3 | 94.6±0.7 | 3.7 | |
| 10 | 94.9±1.2 | 3.2 | 93.7±2.3 | 11.3 | |
| Pyrene | 0.5 | 89.9±1.2 | 5.9 | 99.3±0.7 | 2.8 |
| 1 | 95.8±1.4 | 2.3 | 100.5±1.7 | 4.7 | |
| 10 | 103.7±0.2 | 0.6 | 98.4±1.6 | 3.9 | |
| Benzo[a] anthracene |
0.5 | 99.1±1.1 | 2.1 | 93.2±1.8 | 5.1 |
| 1 | 97.4±0.9 | 2.4 | 96.7±0.6 | 6.2 | |
| 10 | 88.2±1.2 | 3.2 | 89.3±1.3 | 7.1 | |
| Benzo[b] fluoranthene |
0.5 | 102.1±3.1 | 7.1 | 96.2±2.1 | 4.9 |
| 1 | 98.2±1.7 | 2.9 | 98.5±5.2 | 5.2 | |
| 10 | 99.2±1.5 | 6.0 | 91.7±1.2 | 2.7 | |
| Method | Detection technique | Sample | Linear range (ng g-1) | LOD (ng g-1) |
Recovery (%) | RSD (%) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPE |
GC-MS |
Dry tea Tea |
- |
0.09-0.32 |
37.0-96.10 |
- |
Ciemniak (2019) [30] |
| LLE |
GC–MS |
Roasted coffee | 0.25-4 | 0.04-0.18 | 87.08-111.28 | 3.26-23.75 | Pissinatti et al(2015) [31] |
| SPE UAE UAE |
GC×GC–TOFMS HPLC-FLD GC-FID |
Tea Tea infusions Dry tea |
0.05-100 0.2-200 - |
50-200 0.03-0.24 0.3 |
81-103 64.1-99.4 90.24-108.92 |
2.0-9.0 1-10 77.02-100.60 |
Drabova et al. (2012) [32] Iwegbue et al. (2016) [13] Benson et al. (2018) [33] |
| SPME |
GC-MS | Green Tea beverage | 0.1-100 | 0.1-50 | 91.1-101.2 | 0.8-4.5 | Loh et al. (2013) [34] |
| MSPE | UPLC–FLD | Tea | 0.5-300 | 1.69-9.97 | 84.8-100.5 | 2.7-11.3 | This work |
| Tea type | Fluorene (ng g-1) |
Anthracene (ng g-1) | Pyrene (ng g-1) | Benzo[b]fluoranthene (ng g-1) | Benzo[a]anthracene (ng g-1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Green (10 tea brands) |
Mean | 132.3 | 41.9 | 109.5 | 8.2 | 3.7 |
| Min | 31.2 | 5.4 | 27.3 | N.D. | N.D. | |
| Max | 364.2 | 196.5 | 284.1 | 16.2 | 8.4 | |
| Black (3 tea brands) |
Mean | 109.8 | 21.7 | 94.6 | 5.7 | 2.6 |
| Min | 81.9 | 15.1 | 70.3 | N.D. | N.D. | |
| Max | 141.5 | 31.2 | 113.4 | 7.2 | 5.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





