Submitted:
28 April 2023
Posted:
03 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Research Background
1.2. Literature Review
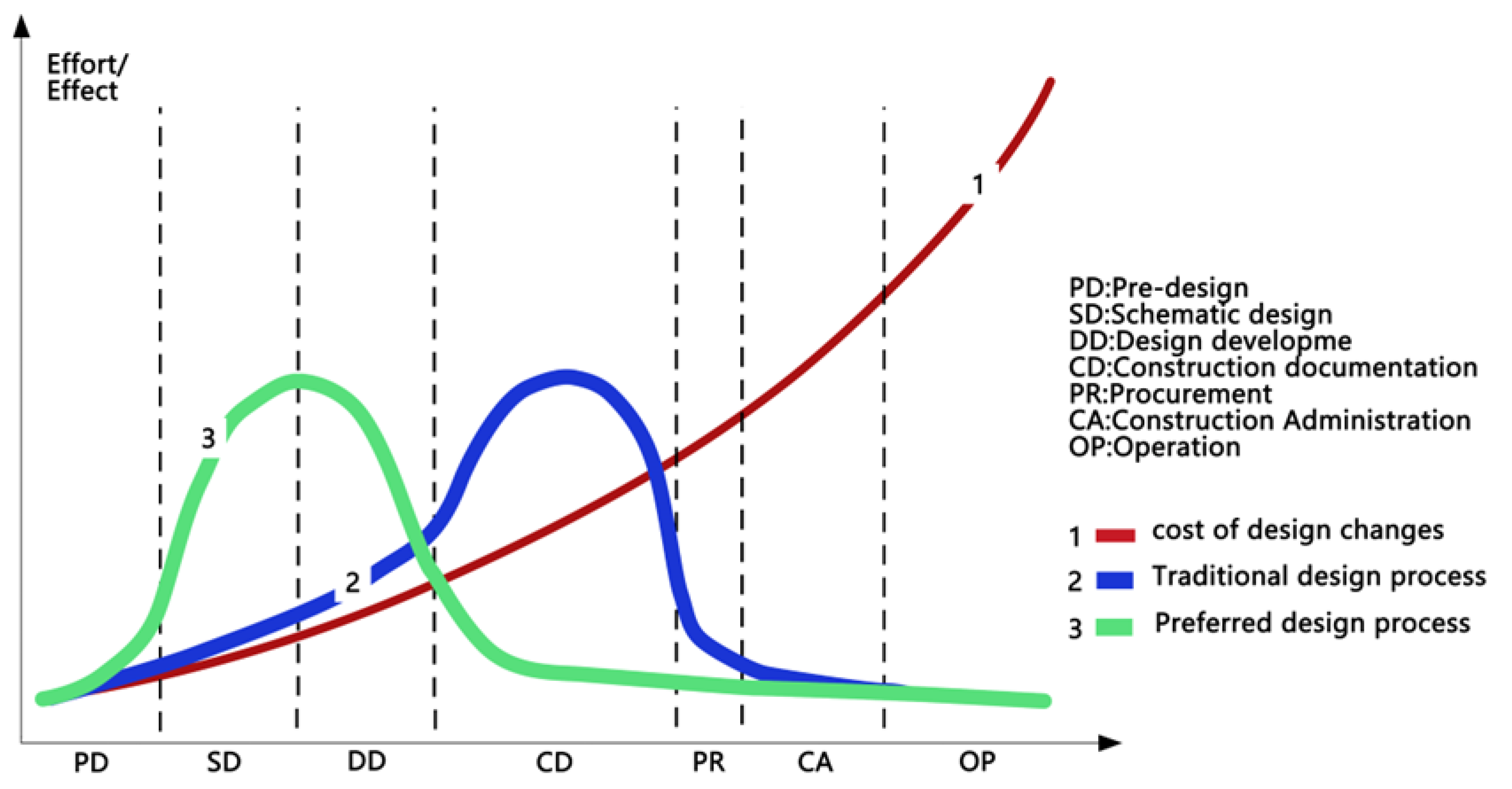
1.3. Problem Statement and Objectives
2. Materials and Research Strategy
2.1. Study Area
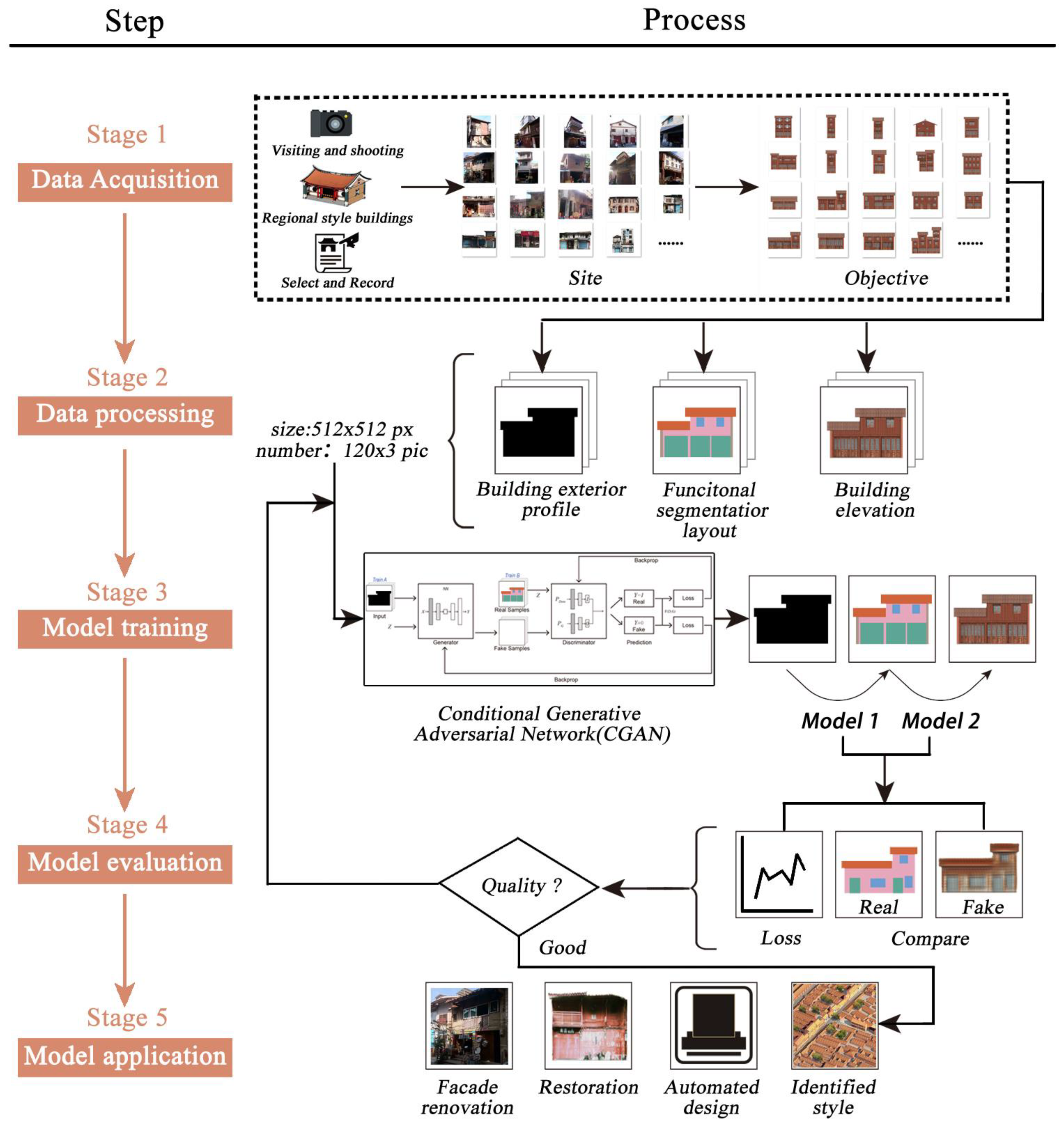
2.2. Methodology
2.3. Material Handling
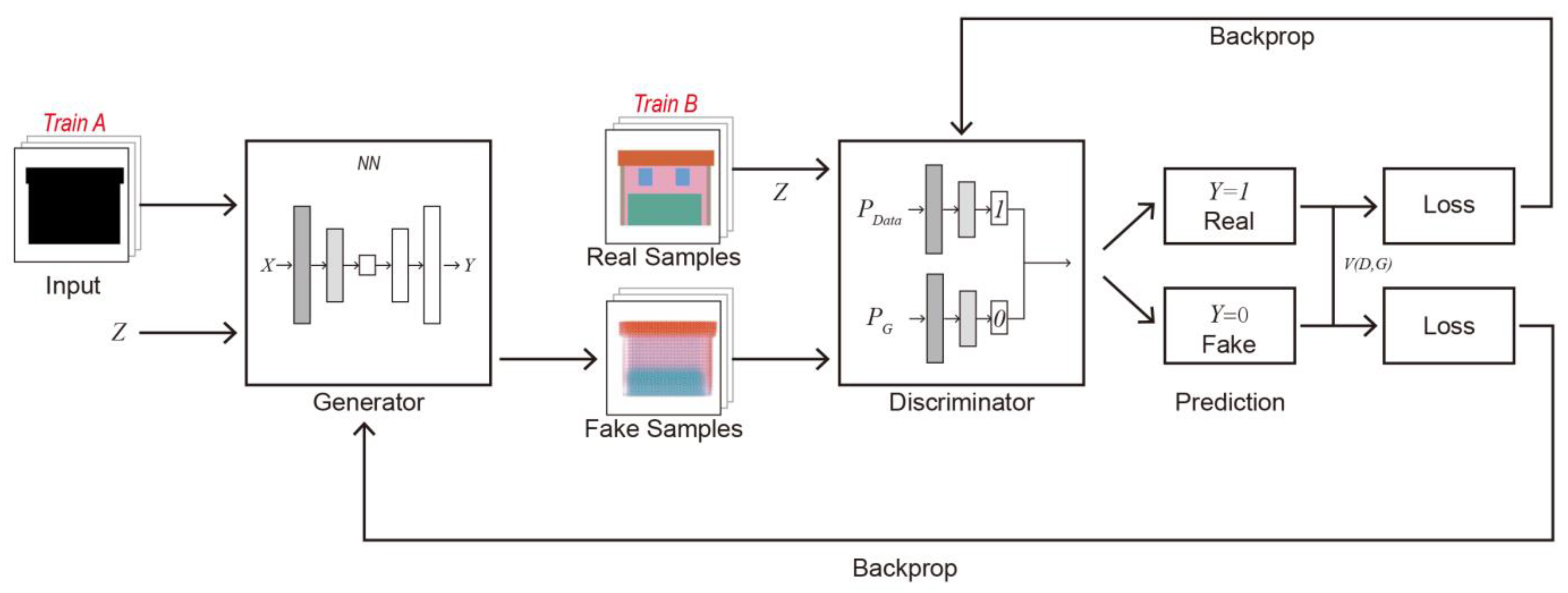
2.4 CGAN Model
3. Results
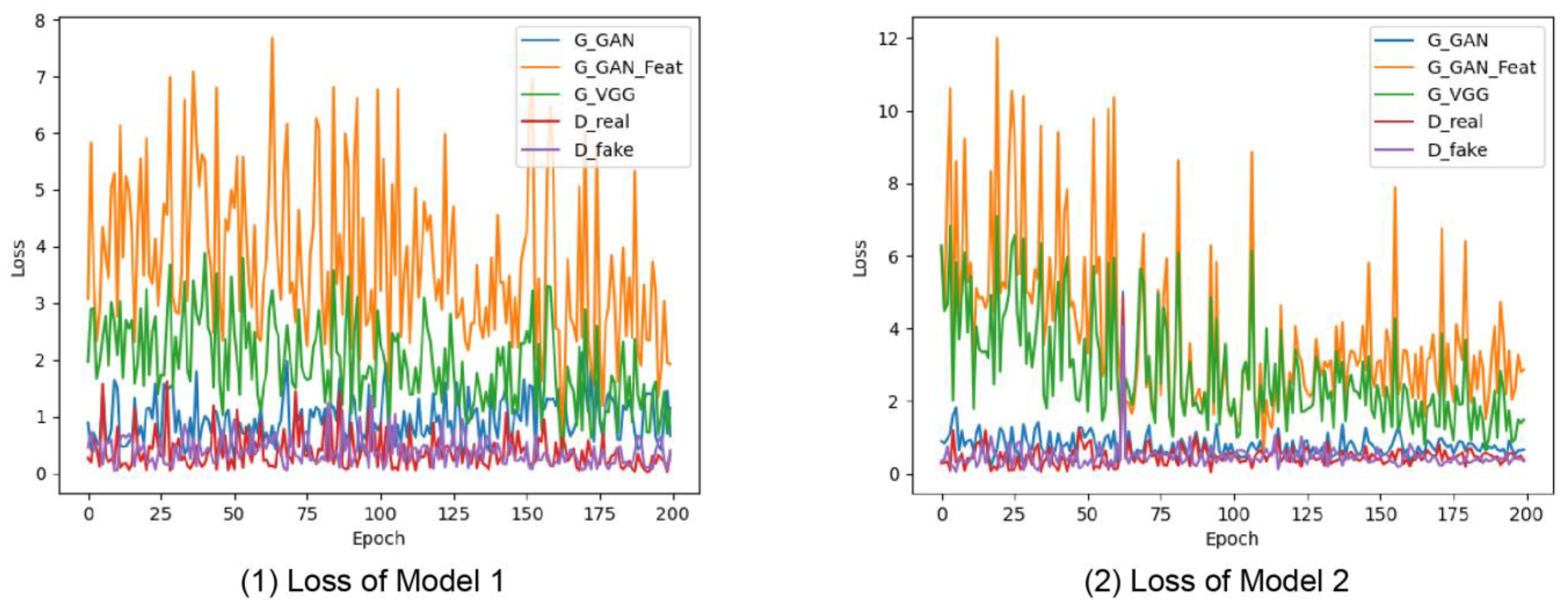
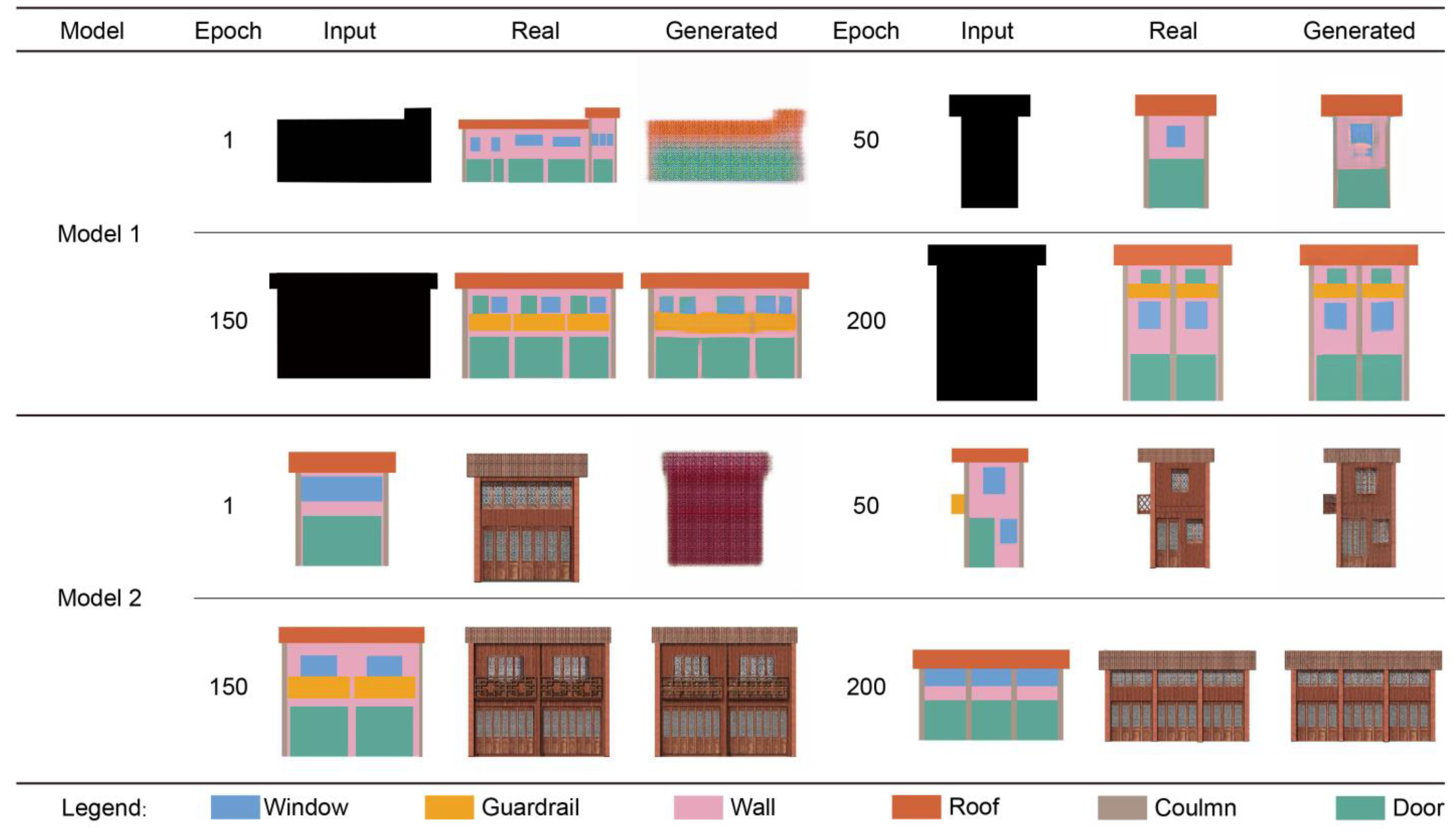
3.1. Model Evaluation
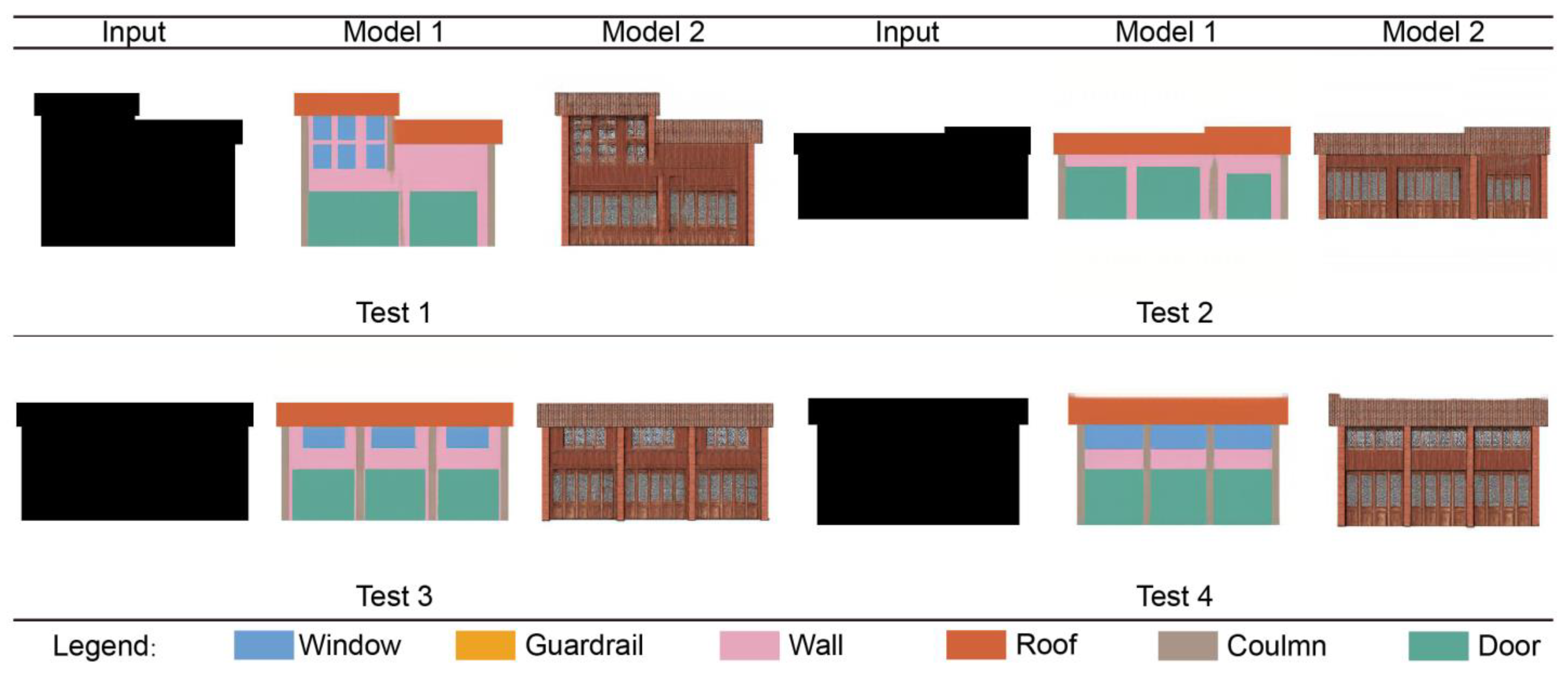
3.2. Model Testing
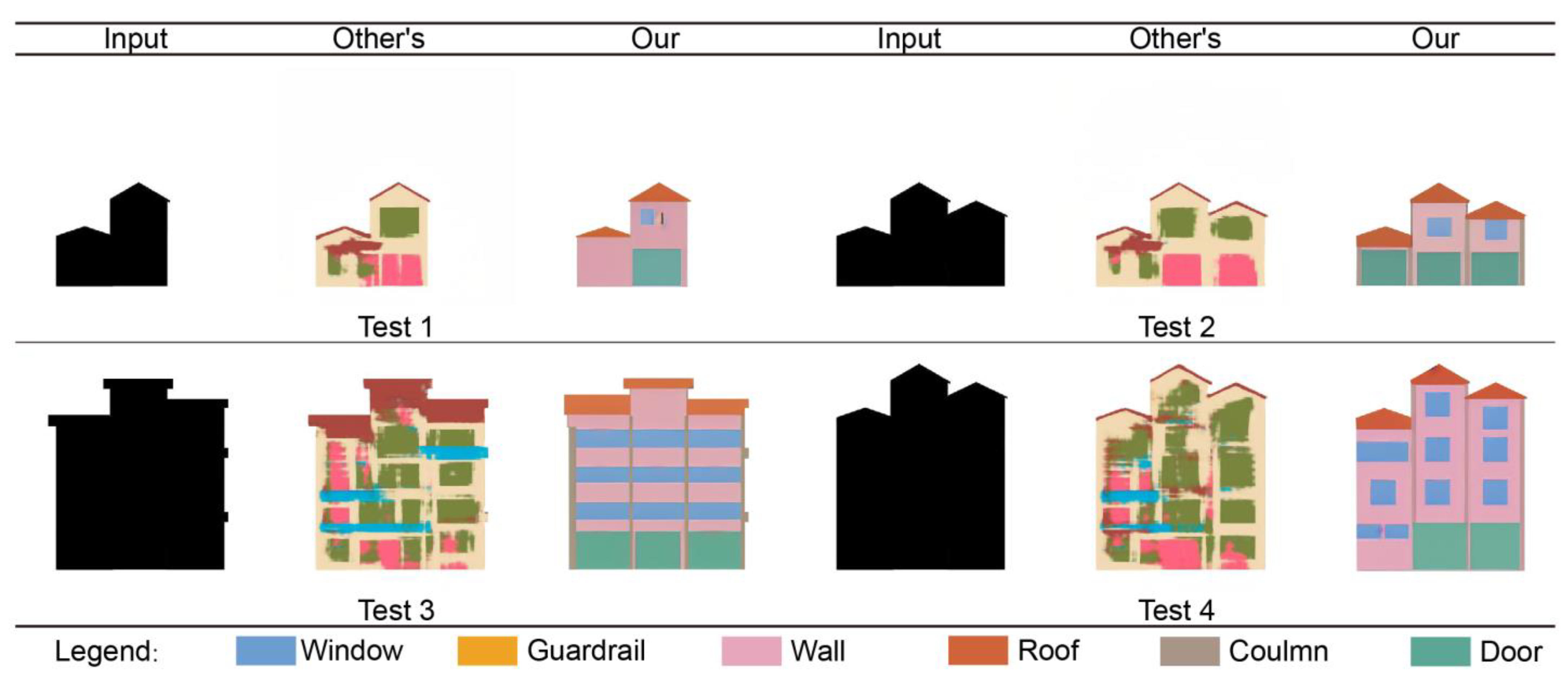
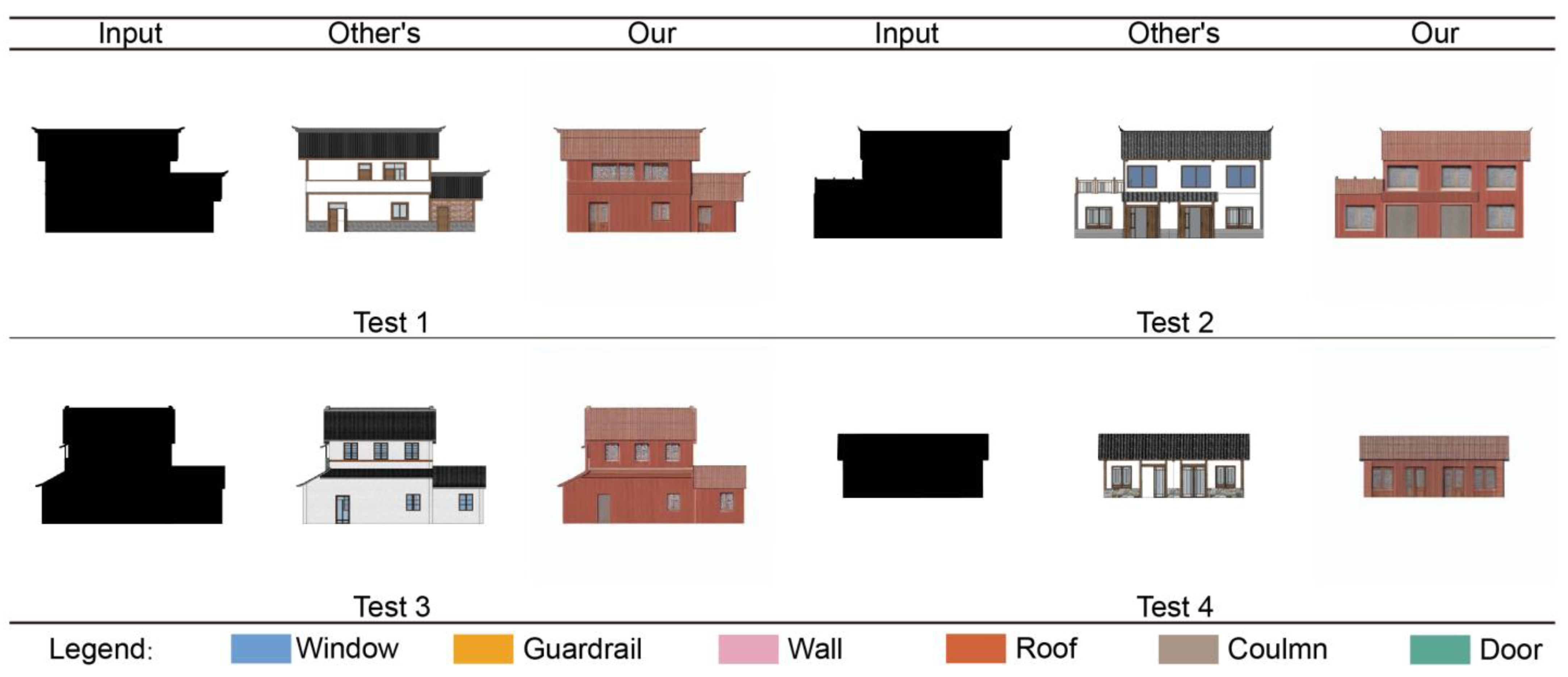
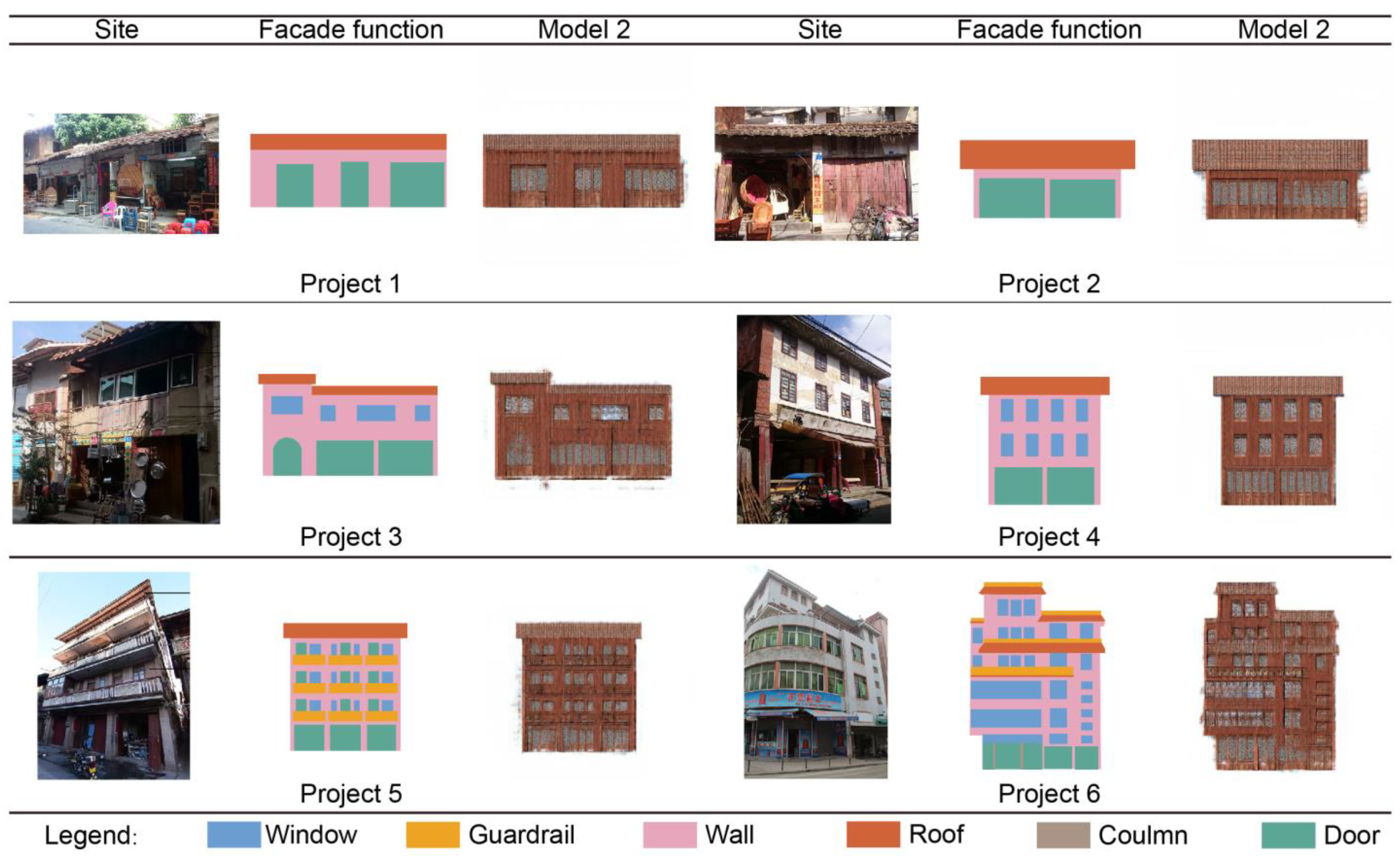
3.3. Model Comparison
4. Discussion:Application of Model and Design of Historic District Scheme
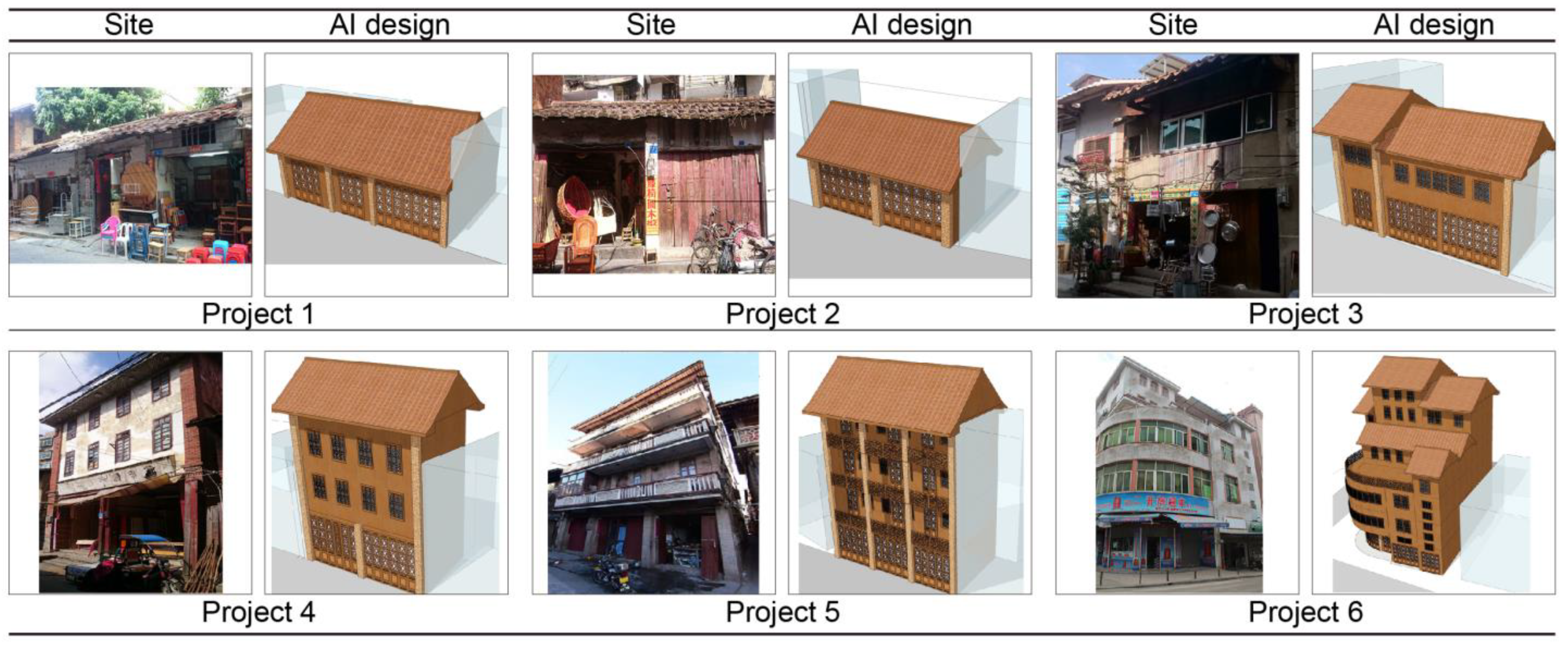
4.1. Model Application
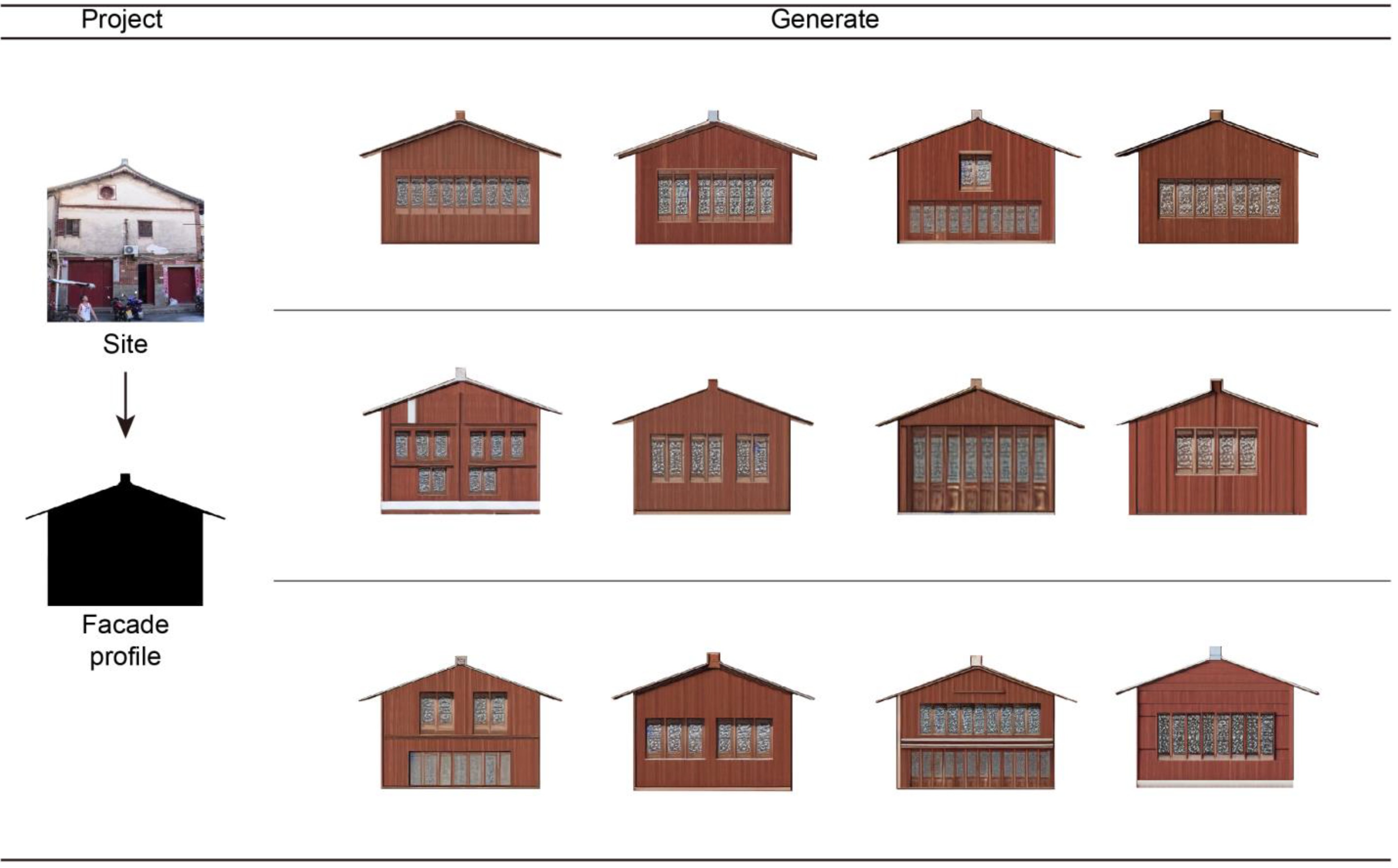
4.2 Application of Multi-scheme Generation
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Editorial Team of the Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development: Beautiful Urban and Rural Housing in China. Beijing: China Urban Publishing House, 2022:303.
- Yu, Q.; Malaeb, J.; Ma, W. Architectural facade recognition and generation through generative adversarial networks. 2020 International Conference on Big Data & Artificial Intelligence & Software Engineering (ICBASE). [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Zhou, Y.; Han, Y. Automatic generation of architecture facade for historical urban renovation using generative adversarial network. Building and Environment 2022, 212, 108781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang Yang. Discussion on the implementation mode of protection and renovation of historical and cultural blocks. World Architecture 2022, 12, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu Zixuan. Protection and Improvement Planning of Tunxi Old Street. Architectural Journal, 1996, 9, 10–14. [Google Scholar]
- 6. Zhang Yang, He Yi. “Between Poli and Li”: A Study on the Openness of Streets and Alleys in Historic Urban Areas——Taking Pingyao Ancient City’s Shuyuan Block as an Example. Modern Urban Studies.
- 7. Ruan Yisan, Shao Yong. The Characteristics and Protection of Ancient Towns in the South of the Yangtze River. Journal of Tongji University: Social Science Edition.
- Lin Zhaoxia. The Evolution of Space, Imagery and Inner Spirit of China’s Coastal Cities——Reflections on the Changes of “Three Lanes and Seven Alleys” in Historic Districts. Southeast Academic 2020, 6, 58–65. [Google Scholar]
- 9. Yuan Ying, Lu Yin. A Syntactic Study on the Spatial Pattern Evolution of Historic Commercial Blocks—A Case Study of Zhongshan Road in Xiamen. Planner.
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative adversarial networks. Communications of the ACM 2020, 63, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L. Deep learning: methods and applications. Foundations and Trends® in Signal Processing 2014, 7, 197–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isola, P.; Zhu, J.-Y.; Zhou, T.; Efros, A.A. Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye Chen, Guan Wei. Application Review of Generative Adversarial Networks. Journal of Tongji University: Natural Science Edition, 2020, 48, 591–601. [Google Scholar]
- Duan Yaru, Zhao Jiayu, He Liming. Text-to-image generation algorithm based on generative adversarial networks. Computer System Applications 2023, 32, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karras, T.; Laine, S.; Aila, T. A style-based generator architecture for generative adversarial networks. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 2021, 43, 4217–4228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Mateu, D.; Carrasco, O.; Cortes Nieves, P. Color-patterns to architecture conversion through conditional generative adversarial networks. Biomimetics 2021, 6, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Ahmed, F. PaDGAN: learning to generate high-quality novel designs. Journal of Mechanical Design 2020, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Guo, S.; Chen, J.; Deng, X.; Sun, L.; Zheng, X.; Xu, W. Improved srgan for remote sensing image super-resolution across locations and sensors. Remote Sensing 2020, 12, 1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.; Guo, J.; Li, Y. Multi-head mutual-attention cyclegan for unpaired image-to-image translation. IET Image Processing 2020, 14, 2395–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafavi, F.; Tahsildoost, M.; Zomorodian, Z.S.; Shahrestani, S.S. An interactive assessment framework for residential space layouts using pix2pix predictive model at the early-stage building design. Smart and Sustainable Built Environment 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 21. Lin Jinru, Dong Zhiyong. Application Research of Image-to-Image Generative Adversarial Network in Urban Texture Generation. Digital Intelligence Empowerment: Proceedings of the 2022 National Symposium on Teaching and Research of Architectural Digital Technology in Schools of Architecture. [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Park, S.; Kim, H.; Yu, K. Deep floor plan analysis for complicated drawings based on style transfer. Journal of Computing in Civil Engineering 2021, 35, 04020066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karadag, I. , Güzelci, O. Z., & Alaçam, S. EDU-ai: a twofold machine learning model to support classroom layout generation. Construction Innovation 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng Shengyu, Xu Xinhui. Building Plane Image Generation and Latent Space Exploration Based on Generative Adversarial Network. Chinese Building Decoration 2022, 12, 87–92. [Google Scholar]
- Newton, D. Deep generative learning for the generation and analysis of architectural plans with small datasets. Blucher Design Proceedings 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen Kai, Lei Shaohua, Dai Wen, Wang Chun, Liu Aili, Li Min. Terrain reconstruction method based on open source data and conditional generative adversarial network. Journal of Geoinformation Science 2023, 25, 252–264. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, Y.; Ji, Y.; Jiang, S.; Liu, X.; Feng, Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y. Integrating aesthetic and emotional preferences in social robot design: an affective design approach with kansei engineering and deep convolutional generative adversarial network. International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics 2021, 83, 103128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin Yuanxue, Zhu Fengting, Shi Pengfei, et al. Image super-resolution reconstruction algorithm based on improved enhanced super-resolution generative adversarial network. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress 2022, 59, 0420002–0420002. [Google Scholar]
- Garozzo, R.; Santagati, C.; Spampinato, C.; Vecchio, G. Knowledge-based generative adversarial networks for scene understanding in cultural heritage. Journal of Archaeological Science: Reports 2021, 35, 102736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L. , Zheng, L., Chen, Y., Huang, L., & Zhou, S. CGAN-assisted renovation of the styles and features of street facades—a case study of the wuyi area in fujian, china. Sustainability 2022, 14, 16575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang Haoyi, Yang Junran, Wu Ziyue, Zhang Ye. Research on street style generation method based on residents’ preference from the perspective of machine learning. New Architecture 2022, 06, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- As, I.; Pal, S.; Basu, P. Artificial intelligence in architecture: generating conceptual design via deep learning. International Journal of Architectural Computing 2018, 16, 306–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




