Submitted:
28 April 2023
Posted:
29 April 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell line and working model
2.2. Chemically induced hypoxia
2.3. Proliferation and cell viability tests
2.4. Cell cycle measurement by BrdU flow kit (# 552598, BD)
2.5. RNA isolation and qRT-PCR
2.6. Western Blot
2.7. Metabolic assays
3. Results
3.1. Optimization of oxygen level and time points for in vitro culturing of MEC-1 cells in hypoxia chamber.
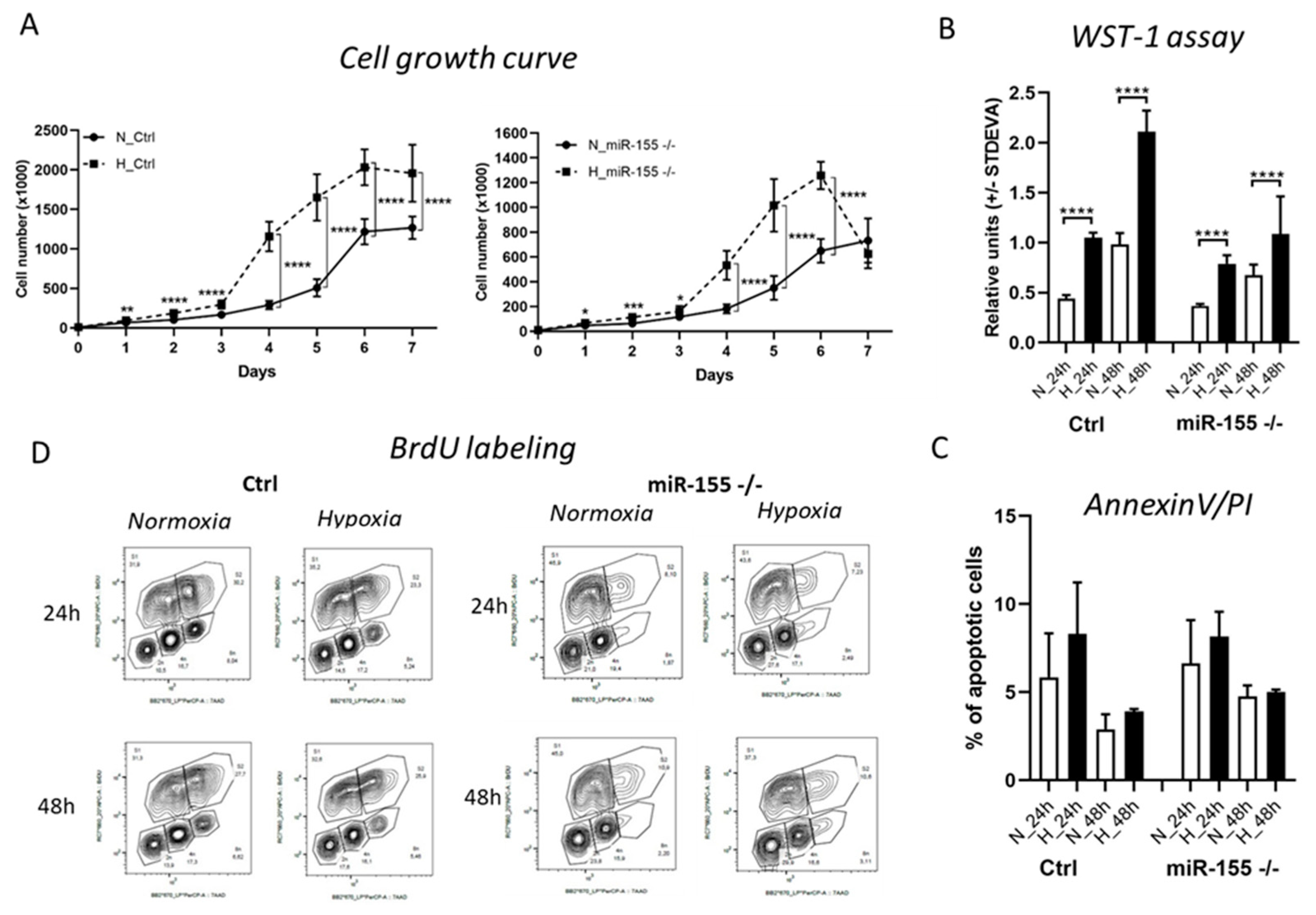
3.2. Higher proliferation rate of MEC-1 cells in hypoxia is miR-155 dependent.
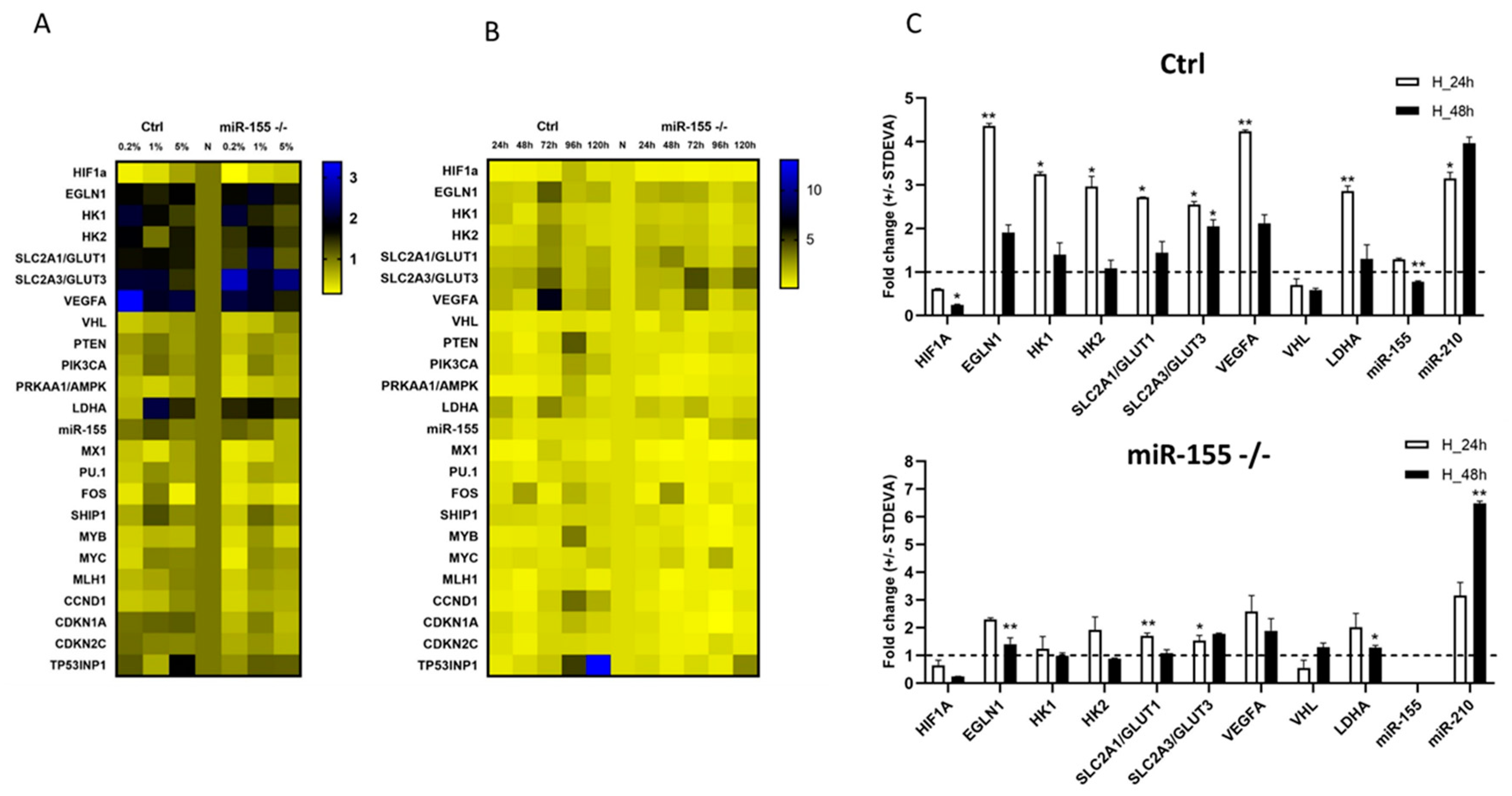
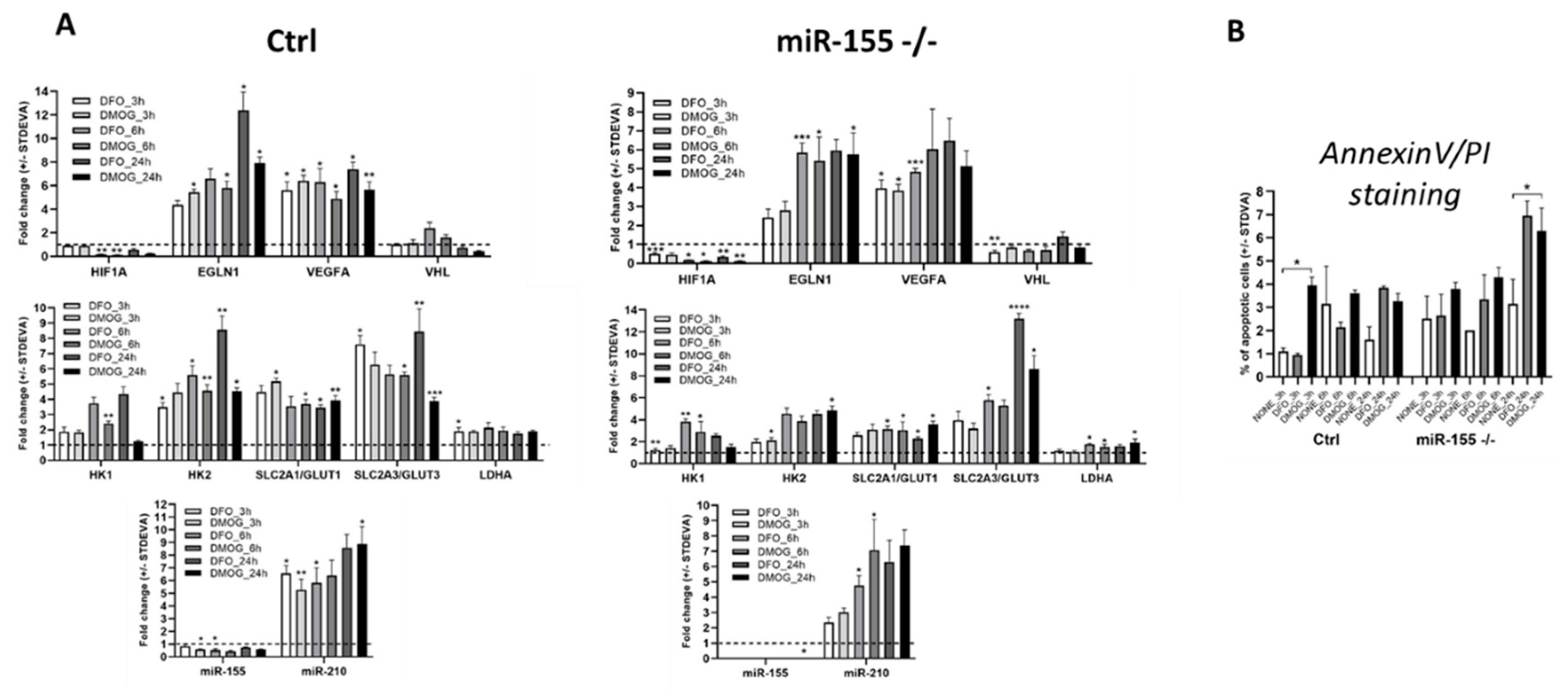
3.3. Chemically induced hypoxia stimulates hypoxia genes and hypoxamiR-210 in MEC-1 cells.
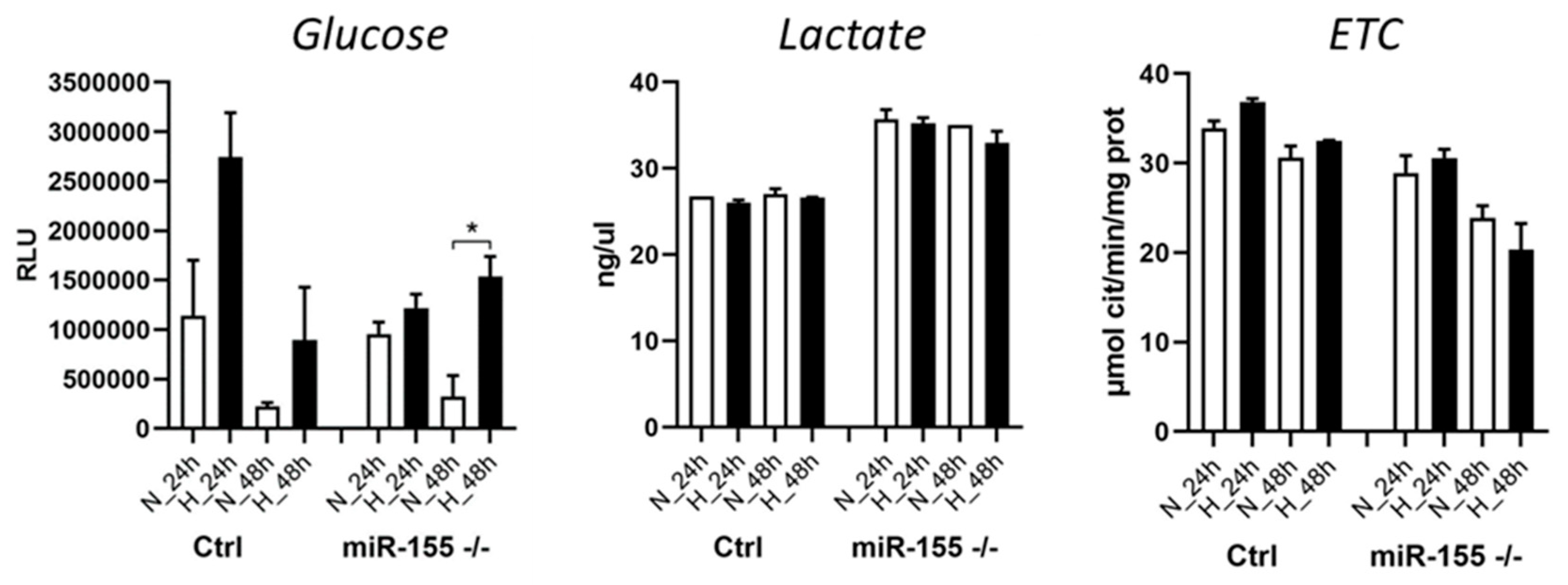
3.4. Cellular metabolism of leukemic cells during hypoxia significantly depends on the presence of miR-155.
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Infantino, V.; Santarsiero, A.; Convertini, P.; Todisco, S.; Iacobazzi, V. Cancer Cell Metabolism in Hypoxia: Role of HIF-1 as Key Regulator and Therapeutic Target. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gacche, R.N.; Assaraf, Y.G. Redundant angiogenic signaling and tumor drug resistance. Drug Resist. Updat. 2018, 36, 47–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Arora, R.; Kaur, P.; Singh, B.; Mannan, R.; Arora, S. Overexpression of hypoxia-inducible factor and metabolic pathways: possible targets of cancer. Cell Biosci. 2017, 7, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godet, I.; Shin, Y.J.; Ju, J.A.; Ye, I.C.; Wang, G.; Gilkes, D.M. Fate-mapping post-hypoxic tumor cells reveals a ROS-resistant phenotype that promotes metastasis. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koczula, K.M.; Ludwig, C.; Hayden, R.; Cronin, L.; Pratt, G.; Parry, H.; Tennant, D.; Drayson, M.; Bunce, C.M.; Khanim, F.L.; et al. Metabolic plasticity in CLL: adaptation to the hypoxic niche. Leukemia 2016, 30, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, H.; Simon, M.C. Oxygen availability and metabolic reprogramming in cancer. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 16825–16832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Lee, E.; Jung, J.; Lee, J.W.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, J.; Yoo, H.J.; Lee, H.J.; Chae, S.Y.; Jeon, S.M.; et al. microRNA-155 positively regulates glucose metabolism via PIK3R1-FOXO3a-cMYC axis in breast cancer. Oncogene 2018, 37, 2982–2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Lin, X.; Fu, X.; An, Y.; Zou, Y.; Wang, J.-X.; Wang, Z.; Yu, T. Lactate metabolism in human health and disease. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawai, S.; Wong, P.-F.; Ramasamy, T.S. Hypoxia-regulated microRNAs: the molecular drivers of tumor progression. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2022, 57, 351–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moszyńska, A.; Jaśkiewicz, M.; Serocki, M.; Cabaj, A.; Crossman, D.K.; Bartoszewska, S.; Gebert, M.; Dąbrowski, M.; Collawn, J.F.; Bartoszewski, R. The hypoxia-induced changes in miRNA-mRNA in RNA-induced silencing complexes and HIF-2 induced miRNAs in human endothelial cells. FASEB J. 2022, 36, e22412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elton, T.S.; Selemon, H.; Elton, S.M.; Parinandi, N.L. Regulation of the MIR155 host gene in physiological and pathological processes. Gene 2013, 532, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faraoni, I.; Antonetti, F.R.; Cardone, J.; Bonmassar, E. miR-155 gene: a typical multifunctional microRNA. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1792, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, L.; Peng, Y.-Z.; Li, C.-G.; Jiang, H.-W.; Mei, H.; Hu, Y. Prognostic and Clinicopathological Significance of MiR-155 in Hematologic Malignancies: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 654–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargova, K.; Pesta, M.; Obrtlikova, P.; Dusilkova, N.; Minarik, L.; Vargova, J.; Berkova, A.; Zemanova, Z.; Michalova, K.; Spacek, M.; et al. MiR-155/miR-150 network regulates progression through the disease phases of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood Cancer J. 2017, 7, e585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrajoli, A.; Shanafelt, T.D.; Ivan, C.; Shimizu, M.; Rabe, K.G.; Nouraee, N.; Ikuo, M.; Ghosh, A.K.; Lerner, S.; Rassenti, L.Z.; et al. Prognostic value of miR-155 in individuals with monoclonal B-cell lymphocytosis and patients with B chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2013, 122, 1891–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, A.K.; Shanafelt, T.D.; Cimmino, A.; Taccioli, C.; Volinia, S.; Liu, C.; Calin, G.A.; Croce, C.M.; Chan, D.A.; Giaccia, A.J.; et al. Aberrant regulation of pVHL levels by microRNA promotes the HIF/VEGF axis in CLL B cells. Blood 2009, 113, 5568–5574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griggio, V.; Vitale, C.; Todaro, M.; Riganti, C.; Kopecka, J.; Salvetti, C.; Bomben, R.; Bo, M.D.; Magliulo, D.; Rossi, D.; et al. HIF-1α is over-expressed in leukemic cells from TP53-disrupted patients and is a promising therapeutic target in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Haematologica 2020, 105, 1042–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontos, C.K.; Papageorgiou, S.G.; Diamantopoulos, M.A.; Scorilas, A.; Bazani, E.; Vasilatou, D.; Gkontopoulos, K.; Glezou, E.; Stavroulaki, G.; Dimitriadis, G.; et al. mRNA overexpression of the hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha subunit gene (HIF1A): An independent predictor of poor overall survival in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leuk. Res. 2017, 53, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wibom, R.; Hagenfeldt, L.; Döbeln, U. von. Measurement of ATP production and respiratory chain enzyme activities in mitochondria isolated from small muscle biopsy samples. Anal. Biochem. 2002, 311, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.; Chandel, N.S.; Simon, M.C. Cellular adaptation to hypoxia through hypoxia inducible factors and beyond. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 268–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebestyén, A.; Kopper, L.; Dankó, T.; Tímár, J. Hypoxia Signaling in Cancer: From Basics to Clinical Practice. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2021, 27, 1609802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burrows, N.; Maxwell, P.H. Hypoxia and B cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2017, 356, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, B.S.; Öztürk, S.; Seiffert, M. Beyond bystanders: Myeloid cells in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 110, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiffert, M. HIF-1α: a potential treatment target in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Haematologica 2020, 105, 856–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhi Pangarsa, E.; Rizky, D.; Setiawan, B.; Santosa, D.; Mubarika Haryana, S.; Suharti, C. Crosstalk between hypoxia and inflammation in non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Bali Med J. 2022, 11, 1063–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinderknecht, H.; Ehnert, S.; Braun, B.; Histing, T.; Nussler, A.K.; Linnemann, C. The Art of Inducing Hypoxia. Oxygen 2021, 1, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Song, L.-P.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, W.; Yu, Y.; Chen, G.-Q. Hypoxia-mimetic agents desferrioxamine and cobalt chloride induce leukemic cell apoptosis through different hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha independent mechanisms. Apoptosis 2006, 11, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbi, M.E.; Gilkes, D.M.; Hu, H.; Kshitiz; Ahmed, I. ; Semenza, G.L. Cyclin-dependent kinases regulate lysosomal degradation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α to promote cell-cycle progression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2014, 111, E3325–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




