1. Introduction
As a result of pollution and environmental deterioration, man needed to finesse alternatives as energy sources; among them is biomass, in this case, that which comes from lignocellulosic residues such as agricultural sugarcane residues. (SAR), since they have a high energy potential which comes from the solar energy they store, thanks to photosynthesis, it is for this reason that it is considered optimal to be used as a source of renewable energy, and thus prevent it from increasing the level of the ecological crisis since its CO2 content is shallow, even zero.
Sugarcane agricultural residues (SAR), which include dry leaves, roots, stems, and shoots, are among the most suitable biomasses for sustainable energy production. SAR is a low-cost material and is readily available; for example, there is a production of 50 million metric tons in Ecuador annually. Some Latin American countries with the highest sugar production are Brazil, Guatemala, Argentina, and Colombia. The SARs produced by these countries are related to their cultivation capacity and the type of sugar cane, so the amount of residue produced is between 11-15% of the harvested 1.
In Argentina, the amount of sugarcane waste produced is between 13,000 kg and 24,000 kg of SAR per hectare 2, and in Ecuador, the amount of SAR grew between 0.5 and 1 million tons of waste 3. The use of renewable energy generated from the combustion of organic matter or biomass has focused on developing high-value products that supply great ecological, economic, and social benefits. Since there is a large quantity of these residues without being used, what is sought in this research work is to evaluate the sugarcane cut residues through a proximal analysis based on the ASTM D 3172-89 Standard to determine its calorific value and establish if it is optimal to be used as solid biofuel, in this case, pellets, which will also be subjected to the same analysis.
2. Materials and Methods
Sugarcane cutting residues (SCR) is called the residues from sugarcane crops. These residues are composed of dry leaves and green leaves, buds, remaining stems during the cutting of the cane, and even roots of the same; these residues have been left behind, depriving themselves of the option of giving it some energy use even though there are more and more cane crops of sugar which in turn, generate exuberant amounts of biomass, after the harvest of the cane the residues usually remain in the crop fields serving as soil fertilizers for the following plantations, others are collected as animal feed however most of what remains within the farmland become burned. Hence, they need help with their collection, transport, and storage. Because these processes need high costs to be carried out4, it would be necessary to implement collection methods that go hand in hand with the economy and sustainable practices so that biomass can be used.
Characterization of SCRs for Use as Biofuel.
To be used as a biofuel, it is necessary to take into account the composition and its physical and chemical properties themselves, which will depend on different factors such as the harvest method applied, the conditions in which the soil is located, and therefore the state of the cane at the time of harvest
5. Thus, different studies on the chemical composition of RACs have been conducted. According to Duque (2021), it is composed of carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur, and chlorine; the different proportions can be seen in
Table 1 6.
Other data that are necessary to be taken into account to recognize whether the residues of sugarcane cuts would be suitable for use in the production of biofuel are based on the properties that they have, among which are their percentage of moisture, percentage of ash, percentage of volatile matter, fixed carbon, superior calorific value, and its lower calorific value being one of the most relevant properties for SCR to be used as biofuels. And according to the literature, these are among the ranges specified in
Table 2 below.
Pellets
The pellets, as well as the briquettes, are characterized by their cylindrical shape. However, they differ in their dimensions since the shells can be between 6 and 8 millimeters in diameter while their length can vary between 3.15 mm and 40 mm. Shots are the most used due to their variety and quality standards suitable for different types of equipment as they can be used at home in stoves and at an industrial level in boilers 7.
Pellet Specifications.
There are quality standards for pellets where the parameters that must be based on international standards are specified, among which are European standards such as EN14961, which refers to shots with biomass as their raw material. According to the functions, there are more European standards for industrial use, such as ISO 17225-1 and 17225-2 and biomass from pellets and for pellets from herbaceous and fruit biomass, which is the ISO 2014D standard detailed below
8,9. Some of these specifications are shown in
Table 3,
Table 4 and
Table 5,
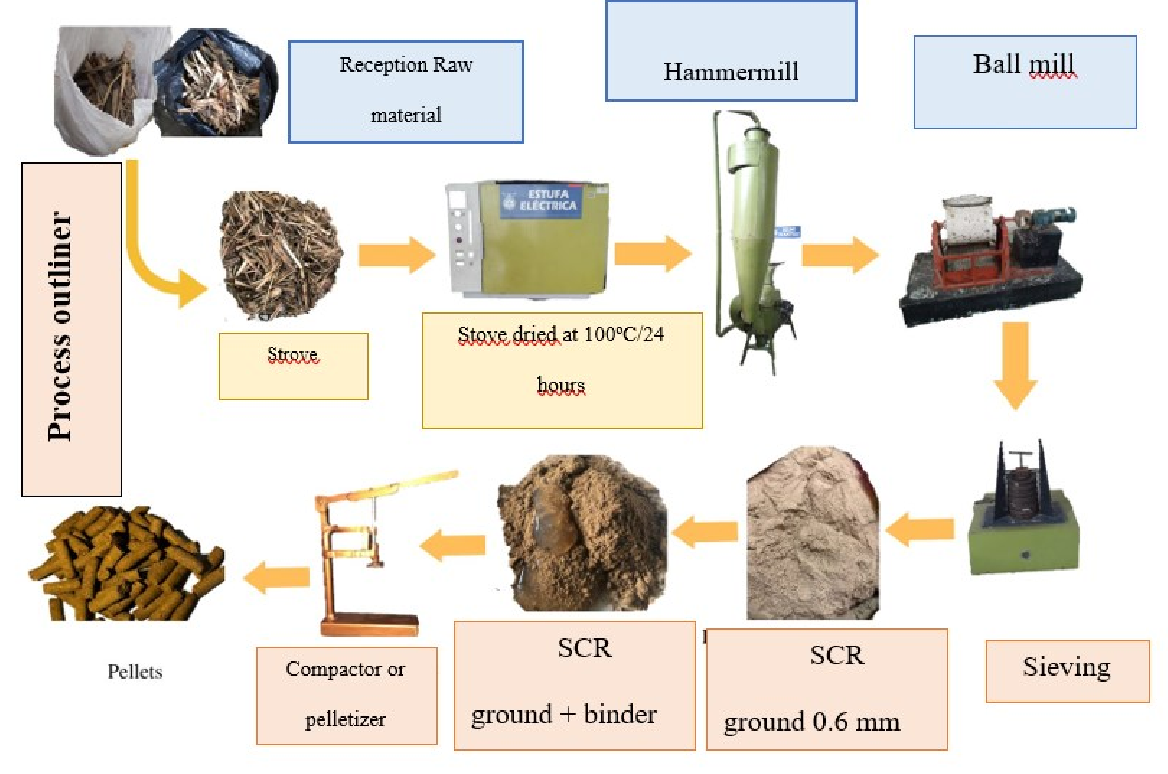
The experimental development was divided into four processes: first, obtaining the raw material and its physical treatment; second, the characterization of the raw material; third, the pelletizing; and finally, the description of the pellets produced. First, the raw material was obtained from the Valdez Sugar Mill. Then, to continue with its physical treatment, the RAC was cleaned by drying in the sun for seven days to take the waste to the unit operations laboratory and grind it in the ball mill to reduce its size. Then, the sugarcane harvest residues were passed through a sieve and taken to the stove at 180°C for one hour to reduce humidity. Once the sample with a smaller particle size was born, it was sent to the Polytechnic University of Guayaquil (Espol) laboratories for characterization. The tests conducted were moisture content, ash content, volatile matter, carbon content, and calorific value.
Then, we went ahead with the elaboration of the pellets. A mixture of 53% SCR and 47% binder was made. Finally, samples of different shots were sent to analyze where it was considered: calorific value, moisture content, ash content, % volatile, and % of coal.
Stage characterization of the raw material.
A proximal analysis of the biomass sample from the cutting residues of already ground sugarcane was conducted in the Polytechnic University of the Littoral laboratories, where they used the ASTM D-3189 method, which is detailed below. This analysis described the content of moisture, ash, volatile material, and fixed carbon, in addition to analyzing the content of lignin, cellulose, and Hemicellulose contained in the SCR.
Methodology for obtaining lignin, cellulose, and Hemicellulose.
To obtain lignin, we worked with the TAPPI 222 Standard, which consists of a quantitative acid hydrolysis procedure that is divided into two parts: the first with sulfuric acid of concentration 72 % that allows hydrolyzing the polysaccharides in oligosaccharides and, therefore, the acid at 4% where the oligomers are transformed into monosaccharides, It is necessary to take 1 gram free of extractable, and then be placed inside a beaker, where additional 72% H2SO4 is added, during constant stirring, where this sample began to change from a light color to a dark one when this characteristic is observed, the contents of the 1L precipitate vessel are emptied, and a 4% solution of H2SO4 is made with boiling distilled water at low flame for 4 hours. Once this process is finished, it is expected to precipitate the sample to decant and filter. Finally, be taken to the stove at 105 ° C for a day and proceed with the final weighing of sample 10. Next, the TAPPI 203 Standard was used to obtain cellulose and Hemicellulose, which consists of treating the sample, in this case, the SCR, with an aqueous solution of 17.5% sodium hydroxide for approximately 45 min, and thus be able to reduce the concentration of this to 8.3%, To obtain as precipitate the alpha-cellulose, remaining in solution the beta-cellulose and gamma-cellulose. First, a tiny amount of the filtrate is taken and titrated with the acetic acid solution until it reaches a pH between 6 and 7 to precipitate the beta-cellulose. Next, the precipitate is separated, washed with distilled water, and dried at 105 °C until a constant weight is obtained. Finally, Hemicellulose is determined by subtracting the total values of (alpha-cellulose and the total beta-cellulose 11,12.
3. Results
Biomass
Biomass is considered bioenergy because its source is renewable, and alternates are one of today’s most vital energies. It is understood that the type of organisms, such as the remains of crops in which leaves, straw, shells, etc., from agriculture, agribusiness, and forest residues are found 13. The way of obtaining biomass can be made in diverse ways, either naturally or made in crops destined for a specific need. The residual form produced by industries or people in their homes is also called, in another way, the garbage of humans. The purpose of biomass is the contribution as a raw material for producing so-called biofuels or green energy to reduce the environmental impact due to its low amount of carbon, making it a minor producer of greenhouse gas emissions.
Composition of biomass.
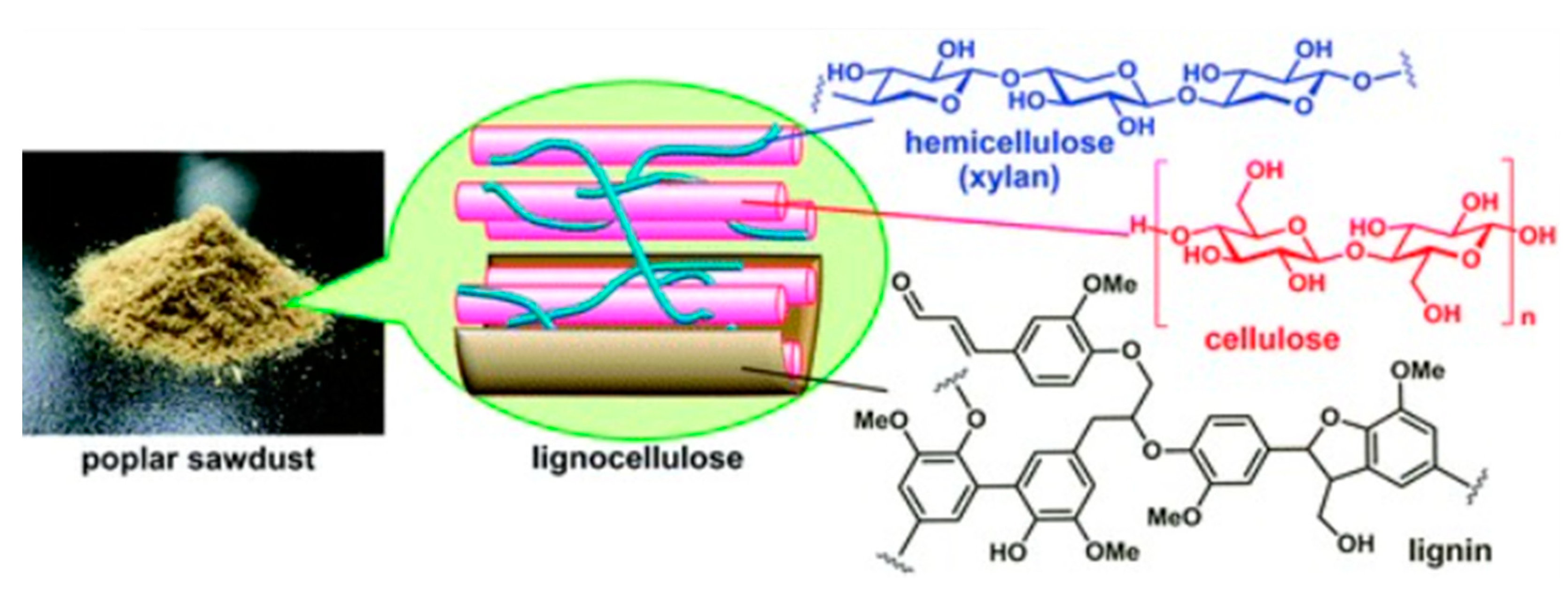
The biomass, in general, is composed of Hemicellulose, lignin, and cellulose; these can change according to the type of plant that comes from the biomass 14. Lignocellulose residues reside in three primary chemical compounds or precursors of Hemicellulose and polyose, a pentose sugar in more significant quantities; cellulose, a glucose polymer; and lignin, a polymer of phenols lignin cannot be split in natural enzymes making it suitable for ethanol production processes and in the hydrolysis of cellulose to glucose, The type of biomass and its properties establish the amount of energy that is accumulated in it. The composition of sugars (pentoses and hexoses) requires the theoretical performance of biofuel.
Lignin.
It is considered a phenolic polymer that goes hand in hand with cellulose and Hemicellulose; through covalent bonds, these polymers in sets constitute part of the cellular tissues of plants; it is thanks to these components that it is considered essential in the biomass destined for the production of Biofuels 15 16; 17.
Cellulose.
It is considered a linear homopolymer and is composed of Glucopyranose and glycosidic; on the other hand, cellulose is a fundamental part of the cell walls of plants in the same way as Hemicellulose and lignin, the amount of cellulose present in these varies according to the type of plant, additional there are elements such as carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen that are part of cellulose so its chemical formula is written as C6H10O5 18.
Hemicellulose.
Hemicellulose with the chemical formulae (C
5H
8O
4) like cellulose and Hemicellulose is also part of the cell wall of plants. Therefore, it is considered a Heteropolysaccharide composed of pentoses and hexose. Below is shown in
Figure 1, the structures of the lignocellulosic compositions of the biomass mentioned above
18–20.
Solid Biofuels
Chips consist of pieces from solid wood or mass that have been reduced into smaller particles of irregular shape 21.
Briquettes.
Briquettes are those characterized by having a cylindrical shape where their dimensions can be from 50 to 130 millimeters, and their diameters can be from 5 to 30 millimeters in length. Briquettes can be made with the help of presses that run at high pressures and temperatures. In addition, binders are added to the briquettes to improve their compaction 22.
A proximal analysis determined the characteristics that biomass must have to be an energy source; a 300g sample was sent for research, and this characterization of the SCR resulted in the calorific value being 15,702 MJ / Kg, a moisture percentage of 3.54%, the volatile material of 86.53% and an ash content of 2.987%, these results fall into the ranges of sugarcane residue properties, according to research conducted by Golato Marcos et al., (2019) and Duque Jonathan, (2021). As shown in Table 2, What makes the raw material (SCR), according to its characteristics obtained, suitable for production in pellets?
Lignocellulosic biomass is composed of 35-55% cellulose, 20-40% hemicellulose, and 10-25% lignin. The type of biomass and its properties prove the amount of energy accumulated in it. The composition of sugars (pentoses and hexoses) requires the theoretical performance of biofuel. That is why it was figured out by an analysis that an amount of these biomass components is present in the SCR, obtaining that the most significant amount current is cellulose with 28.9%, followed by Hemicellulose with 23.4%, and finally lignin with 18%. It can be shown that the lignocellulosic percentages described above are within the ranges except for cellulose which is below the field; however, as lignin and Hemicellulose are within the contents, the raw material (SCR) is still suitable for use in the production of biofuel because it would supply a satisfactory performance of it.
Table 7 shows that the moisture percentage obtained for the pellets was lower, with a moisture content of 5.768%. By French standards, these values are within the range for producing pellets, between 11-15%.
Table 7.
Results of proximal analysis of the pellets.
Table 7.
Results of proximal analysis of the pellets.
| Parameters |
Unit |
Pellets
(53 %-47 %) |
| Humidity |
% |
5.768 |
| Ash |
% |
6.376 |
| Caloric Value |
% |
82.313 |
| Fixed Carbon |
% |
5.543 |
| Caloric Value |
KJ/Kg |
15.635 |
Ash content
The ash content is the number of inorganic compounds present in the pellets. It is inversely proportional to the calorific value since the higher the percentage of ash generated by the shots, the lower the calorific value will be. Therefore, the elaborated pellets had a lower value of ash content of 6.376%, which was suitable according to the standards.
Volatile material content: The combustible material influences the combustion speed; if the volatile material content is higher, the biofuel is more flammable 23.
Physical Characterization
Friability test: Ten pellets were taken for each proportion to find friability, thrown from 1 meter above the ground. The value obtained for this parameter stands for a higher content of volatile matter, 82.313%. This value is acceptable since it allows the pellets to ignite while keeping high combustion temperatures easily.
Fixed carbon content: The fixed carbon is inversely proportional to the calorific value since, if the selected carbon content is lower, the energy content of the pellet will be higher and vice versa. Then it was obtained that the pellet sample has a carbon content of 5.543%, within international parameters. Therefore, it is equivalent to a high energy content.
Calorific value measurement: The results obtained for the calorific value, according to Table 3, have a higher energy content with a weight of 15,635 KJ/kg. Therefore, it is best for the quality of the pellets. In addition, the friability of the shots at the proportion of 53% ground SCR and 47% binder presented greater friability; this is because they have a more incredibly adequate amount of binder that allows better adherence of the ground SCR to each other and therefore makes the pellets have more excellent resistance to falls or blows.
Percentage of pellet yields
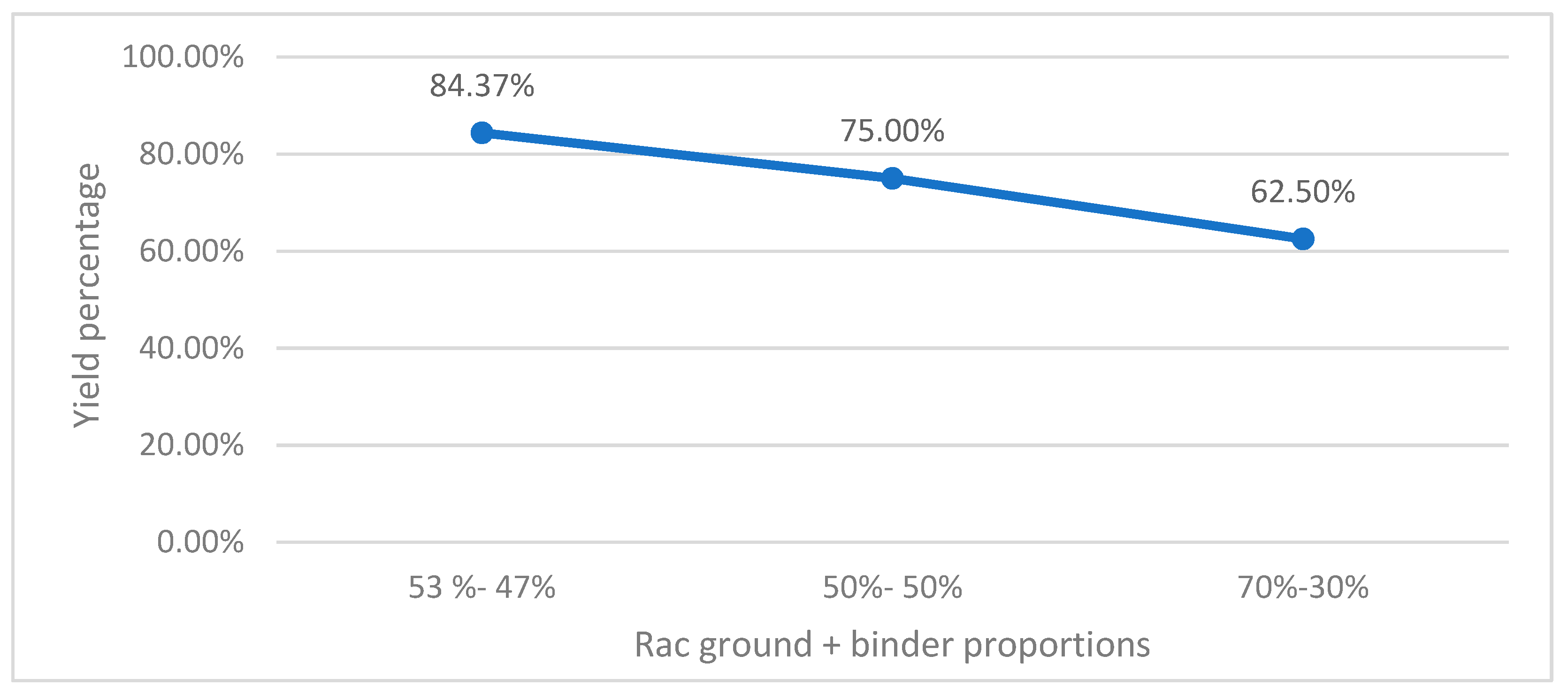
A calculation was made to obtain the yield percentage for each pelleting process according to its proportion. Then, calculate the performance with the accurate and theoretical performance data, according to the proportions made from 47-53; 50-50; 70-30, from the sugar cane, cutting residue, and binder.
To determine the quality of the pellets, the moisture content, ash, volatile material, and fixed carbon were characterized for each of the samples made with different mixtures of SCR and binder, being M1 (53% SCR-47% binder), M2(50% SCR-50% binder) and M3 (70% SCR-30% binder). The data of the proximal analysis of the mixtures made with different proportions are presented in
Table 8.
This total cost is shown in
Table 9, what was required to produce 300 g of pellets during this investigation. The quantity produced is due to the efficiency of the equipment (manual pelletizer) and the amount of raw material used. If you want to reduce costs, a market study must be carried out, since an investment must be made in more efficient machinery, physical location if necessary, and have a source of suppliers to produce x quantity of a final marketable product and thus achieve a reasonable cost. And in the same way, to obtain the final price of the pellets.
4. Discussion
The proximal analysis of the sugarcane cut residue was conducted. As a result, its functionality as a raw material is suitable for producing biofuels since they have adequate parameters representative of biomass and, in turn, are related to the physicochemical parameters of the pellets. On the other hand, the lignocellulosic component supports the excellent performance that solid biofuel could have. As shown in
Figure 2, based on the results obtained from the yield calculation, the highest yield in pellet processing can be observed in a ratio of 53% ground SCR and 47% binder since the amount of binder added gives more excellent adhesion, so there is not much loss of product, unlike the granules with a ratio of 50-50%, because this significant difference in the binder keeps the mass more humid. Therefore, there is a loss because when it's the wettest material, some of it still sticks to the container the mix was made in, so mixes with a 70-30% ratio have the lowest yield because the binder ratio is lower the ground does not stick very well to each other, Plus the residues cannot enter the manual pelletizer.
The results obtained for the calorific value according to
Table 8, sample 1 has a higher energy content with a weight of 15,635 KJ/kg and sample 3 with a value of 15,017 KJ/kg. Hence, these two samples are optimal for the pellet quality; however, sample 2 with 14,897 KJ/kg is the lowest value obtained. Among the three samples, it can be seen that sample 1 is the one with the highest calorific value. Hence, producing pellets with the proportion of 53% SCR and 47% binder is the best option regarding the calorific value, being within the parameters established in international standards.
5. Conclusions
A sample of pellets in different proportions was prepared, being the proportion of 53% SCR and 47% binder the one that had the best performance at the time of its production, followed by the pellets in the same proportion sent for their respective proximal analysis. The physical and chemical characteristics of the shells were evaluated; where as a result, shots of 8 mm in diameter and 30 mm in length were obtained; it as evidence that the highest density, 1000 kg/m3, was for the pellets with a proportion of 53-47%, being the most suitable since it allows more significant storage space and ease of transport, however, in the same way, the friability is more important pellets with a proportion of 53-47%, this is because this amount of binder is ideal since that allows better compaction and resistance to blows. On the other hand, the humidity, % ash, and volatility, or the 53-47 ratio, are suitable and give veracity of the quality of the pellets produced, according to international regulations,
To conclude, the sample with a 53% Rac-47% binder ratio is the best since it had a higher calorific value, which shows the effectiveness of the pellets for their proper combustion, adding that the value results were remarkably similar to international standards.
6. Patents
There is no patent in this research.
Author Contributions
The Conceptualization and methodology, Denisse Bermeo and Flor Reyes; to the validation Eduardo Arango; investigation, resources, Sandra Peña, and Carmen Forero; writing—original draft preparation, Sandra Peña; review Francisco Velasco and editing, Sandra Peña; visualization, supervision, project administration, Carmen Forero.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support provided by the Colombia Scientific Program within the framework of the call Ecosistema Científico (Contract No. FP44842- 218-2018); and Coal Science and Technology Laboratory of the Universidad del Valle, Cali- Colombia. The gratitude for the support received by the Petroleum Laboratory of the Faculty and Career of Chemical Engineering of the University of Guayaquil, Guayaquil-Ecuador
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Gutierrez. Combustión y Gasificación de la Biomasa. in Seminario biomasa (ed. Facultad de Ciencias Forestales, D. I. de la M.) (Universidad de Chile, 2003).
- Moreno, S. Estudio de sistemas de captura de CO2 y métodos de concentración de CO2 en corrientes gaseosas aplicados a ciclos combinados. (Universidad de Sevilla, 2019).
- Peña, S., Forero, C. & Velasco, F. BIBLIOMETRIC STUDY OF THE COMBUSTION OF RAC IN THE CAPTURE OF CARBON DIOXIDE. International Journal of Mechanical and Production Engineering 9, 24–30 (2021).
- Azucarera, I. Z. Instituto azucarero dominicano -inazucar-. 2009, 1–5 (2018).
- Velasco-Sarria, F.J.; Forero, C.R.; Adánez-Rubio, I.; Abad, A.; Adánez, J. Assessment of low-cost oxygen carrier in South-western Colombia, and its use in the in-situ gasification chemical looping combustion technology. Fuel 2018, 218, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña, S., Forero, C. & Velasco, F. Bibliometric study of the combustion of cane cutting waste (RAC) in carbon dioxide capture. SN Appl Sci 4, (2022).
- Santos-Lema, J. J. & Silva-Arroyo, C. A. Obtención de nanocelulosa a partir de la cascarilla de arroz mediante hidrólisis ácida. (2019).
- Perez, S., Silva, I., Penueña, G. & Cardona, S. Evaluación De Biocombustibles E Hidrocarburos Del Petróleo (Gasolina Y Diesel) En Un Suelo: Proceso De Transporte Y Biorremediación. Revista EIA 12, 21–46 (2015).
- Philippini, R.R.; Martiniano, S.E.; Chandel, A.K.; de Carvalho, W.; da Silva, S.S. Pretreatment of Sugarcane Bagasse from Cane Hybrids: Effects on Chemical Composition and 2G Sugars Recovery. Waste Biomass- Valorization 2017, 10, 1561–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, H. P., Mendoza, D. A. & Caballero, M. P. Análisis de las propiedades fisicoquímicas de gasolina y diesel mexicanos reformulados con Etanol Analysis of Physicochemical Properties of Mexican Gasoline and Diesel Reformulated with Ethanol. Ingeniería Investigación y Tecnología XIII, 293–306 (2017).
- Lesme-Jaén, René; Garcia-Faure, Luis; Oliva-Ruiz, Luis; Pajarín-Rodríguez, Juan; Revilla -Suarez, D. Gasificación de biomasa para la generación de electricidad con motores de combustión interna. Eficiencia del proceso. Tecnologí a Química 36, 161–172 (2016).
- Cornejo, A.; Alegria-Dallo, I.; García-Yoldi, Í.; Sarobe, Í.; Sánchez, D.; Otazu, E.; Funcia, I.; Gil, M.J.; Martínez-Merino, V. Pretreatment and enzymatic hydrolysis for the efficient production of glucose and furfural from wheat straw, pine and poplar chips. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 288, 121583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanerva, U. Characteristics of various new oxygen carriers for CLC. 2009–2011 (2010).
- Golato, M., Feijóo, E., Franck Colombres, F., Paz, D. & Cárdenas, G. Estudio preliminar del aprovechamiento de los residuos agrícolas de cosecha de la caña de azúcar como combustible adicional para calderas bagaceras de Tucumán (Argentina). Revista Industrial y Agrícola de Tucumán 94, 21–31 (2017).
- Peña, S. & Zambrano, E. Bioremediación de suelos contaminados con hidrocarburos derivados del petróleo. Colloquium vol. 1 (2022).
- Guilherme, A.A.; Dantas, P.V.F.; Santos, E.S.; Fernandes, F.A.N.; Macedo, G.R. EVALUATION OF COMPOSITION, CHARACTERIZATION AND ENZYMATIC HYDROLYSIS OF PRETREATED SUGAR CANE BAGASSE. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2015, 32, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Services, W. B. and T. Furfural Chemicals and Biofuels from Agriculture. Development 39 (2006).
- Faba, L., Díaz, E. & Ordóñez, S. Transformación de biomasa en biocombustibles. Madera y Bosques 20, 11–24 (2014).
- Jesús, I., Artigas, D., Concepción, A. D., Piñero, A. J. R. & Álvarez, A. A. Briquetas energeticas con aserrín y corteza de pino. Ingeniería Energética XLI, 1–6 (2020).
- Faba, L., Díaz, E. & Ordóñez, S. TRANSFORMACIÓN DE BIOMASA EN BIOCOMBUSTIBLES DE SEGUNDA GENERACIÓN. Madera Bosques 20, 11–24 (2014).
- Chandler, C. et al. HIDRÓLISIS ÁCIDA DILUIDA EN DOS ETAPAS DE BAGAZO DE CAÑA DE AZÚCAR PARA LA PRODUCCIÓN DE AZÚCARES FERMENTABLES. Multiciencias 12, 245–253 (2012).
- Jesús, I., Artigas, D., Concepción, A. D., Piñero, A. J. R. & Álvarez, A. A. Briquetas energeticas con aserrín y corteza de pino. Ingeniería Energética XLI, 1–6 (2020).
- Meléndez Hernández, P. A., Hernández Beltrán, J. U., Hernandez Escoto, H. & Morales Rodriguez, R. ANÁLISIS DEL PRETRATAMIENTO DE RESIDUOS LIGNOCELULÓSICOS PARA LA PRODUCCIÓN DE BIOCOMBUSTIBLES Y BIOPRODUCTOS DE ALTO VALOR AGREGADO. JÓVENES EN LA CIENCIA 1, 534–538 (2015).
- Velázquez, F. Cambio climático y protocolo de Kioto. Ciencia y estrategias: Compromisos para España. Rev Esp Salud Publica 79, 191–201 (2015).
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).