Submitted:
25 April 2023
Posted:
26 April 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
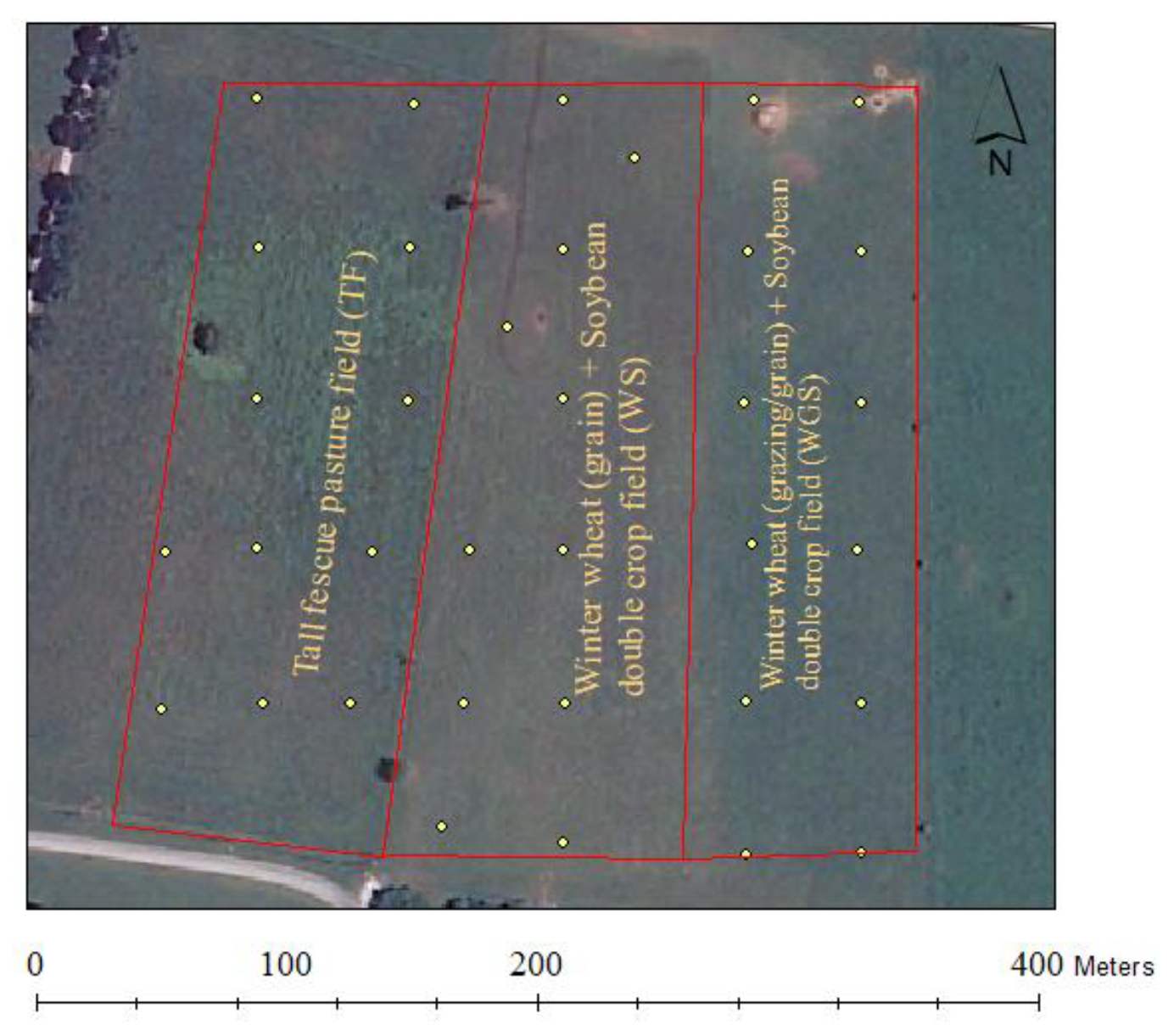
2.1. Site management and experimental setup
2.2. Soil physicochemical analysis
2.3. Quantification of total bacteria and N Cycling bacteria genes in soil samples
2.4. Statistical analysis, geostatistical modeling, and spatial mapping
3. Results
3.1. The initial soil physicochemical properties
3.2. Effect of cropping systems on soil physicochemical properties
| n | Spring 2017 | Fall 2017 | Spring 2018 | Fall 2018 | Mean | |
| pH | ||||||
| TF | 12 | 6.33 ± 0.14 a | 6.37 ± 0.14a | 6.28± 0.13a | 6.51 ± 0.15a | |
| WS | 11 | 6.06 ± 0.13a | 5.80 ± 0.14b | 5.75 ± 0.13b | 5.66 ± 0.16b | |
| WGS | 12 | 6.05 ± 0.14a | 5.83 ± 0.14b | 5.83 ± 0.13b | 5.77 ± 0.15b | |
| ------------------------------------ g kg-1------------------------------------ | ||||||
| OM | ||||||
| TF | 12 | 26.40 ± 1.00a | 24.78 ± 1.02a | 32.13 ± 1.14a | 33.47 ± 1.06a | |
| WS | 11 | 27.65 ± 1.03a | 23.32 ± 1.07ab | 31.54 ± 1.19a | 30.30 ± 1.10ab | |
| WGS | 12 | 23.15 ± 0.99b | 20.30 ± 1.03b | 26.66 ± 1.14b | 27.12 ± 1.06b | |
| TC | ||||||
| TF | 12 | 20.50 ± 0.98a | 36.50 ± 1.63a | 33.80 ± 1.4a | 28.68 ± 1.07a | |
| WS | 11 | 22.09 ± 1.02a | 30.96 ± 1.70ab | 31.99 ± 1.02a | 27.17 ± 1.12a | |
| WGS | 12 | 17.60 ± 0.98b | 28.32 ± 0.95b | 29.95 ± 1.83a | 25.24 ± 1.07a | |
| TN | ||||||
| TF | 12 | 2.36 ± 0.09a | 3.45 ± 0.14a | 3.67 ± 0.19b | 2.59 ± 0.07a | |
| WS | 11 | 2.34 ± 0.09a | 2.92 ± 0.15ab | 4.46 ± 0.20a | 2.59 ± 0.07a | |
| WGS | 12 | 1.92 ± 0.09b | 2.82 ± 0.15b | 4.19 ± 0.19ab | 2.22 ± 0.07b | |
| ------------------------------------ mg kg-1------------------------------------ | ||||||
| NH4-N | ||||||
| TF | 48 | - | - | - | - | 9.56 ± 0.94a |
| WS | 44 | - | - | - | - | 10.1 ± 1.05a |
| WGS | 48 | - | - | - | - | 9.54 ± 1.0a |
| NO3-N | ||||||
| TF | 12 | 5.79 ± 1.13a | 8.49 ± 1.1a | 5.77 ± 0.94b | 6.56 ± 0.45a | |
| WS | 11 | 3.33 ± 1.18a | 9.47 ± 1.14a | 11.51 ± 0.94a | 4.72 ± 0.45b | |
| WGS | 12 | 4.06 ± 1.13a | 8.74 ± 1.10a | 10.35 ± 0.9a | 4.17 ± 0.47b | |
3.3. Effect of cropping systems on the abundance of total and soil nitrogen cycling bacterial marker genes.
3.4. Relationship between total and soil nitrogen cycling bacterial gene abundances and soil chemical properties.
| Cropping system/ bacterial gene | n | pH | OM | NO3-N | NH4-N |
| TF | 48 | ||||
| 16S rRNA | 0.20 | 0.34** | 0.18 | 0.31* | |
| amoA | 0.37** | 0.32* | 0.39** | 0.14 | |
| narG | 0.46** | 0.46** | 0.30* | 0.17 | |
| nirK | 0.18 | 0.37** | 0.18 | 0.53** | |
| nosZ | 0.20 | 0.35* | 0.13 | 0.52** | |
| WS/WGS | 92 | ||||
| 16S rRNA | 0.25* | 0.30** | 0.13 | 0.17 | |
| amoA | 0.59* | 0.25* | 0.16 | 0.12 | |
| narG | 0.46** | 0.32** | 0.14 | 0.18 | |
| nirK | 0.50** | 0.12 | 0.03 | 0.42** | |
| nosZ | 0.59** | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.35** |
3.5. Spatial distribution of total and N cycling bacterial genes and soil chemical properties
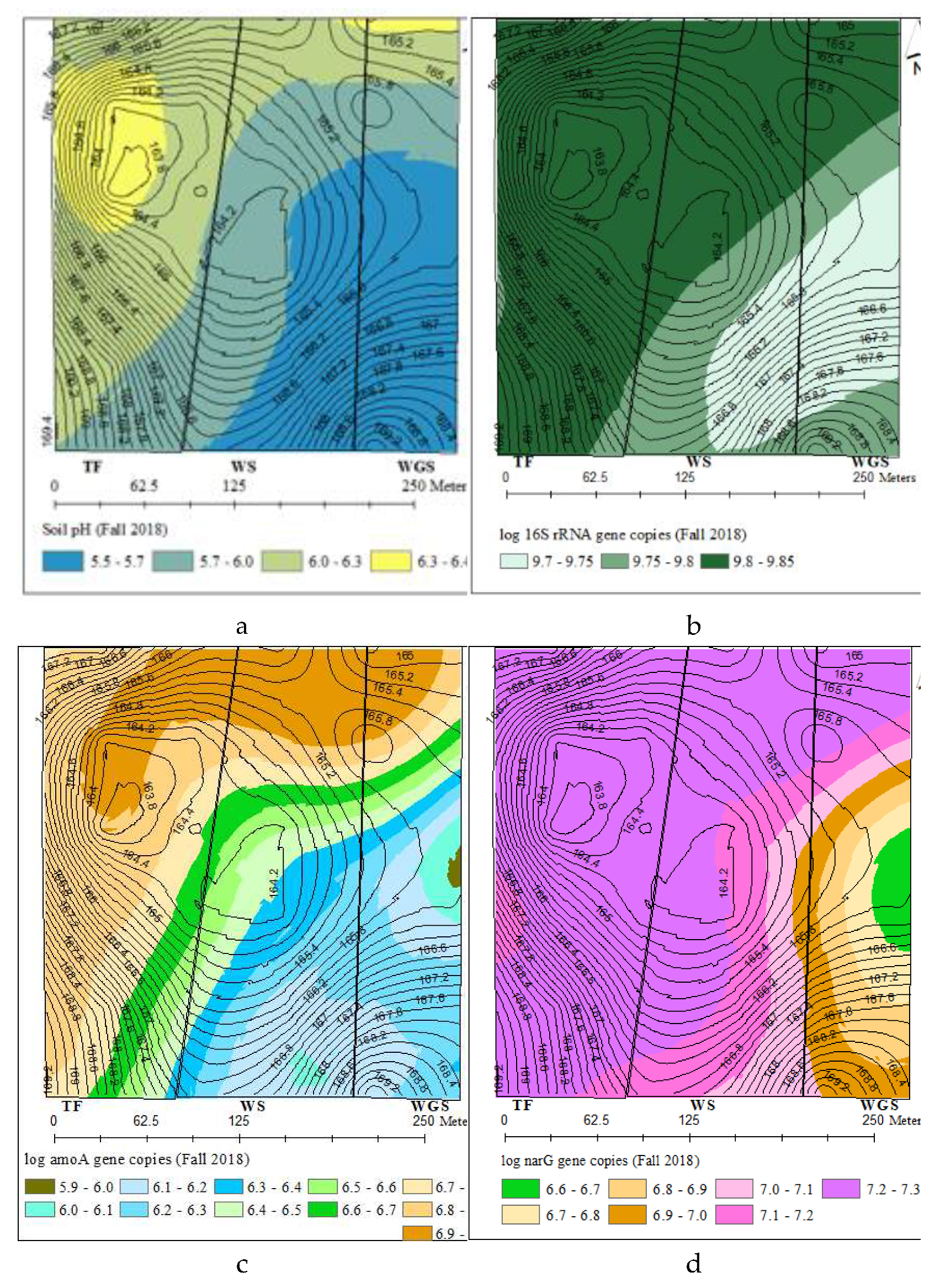
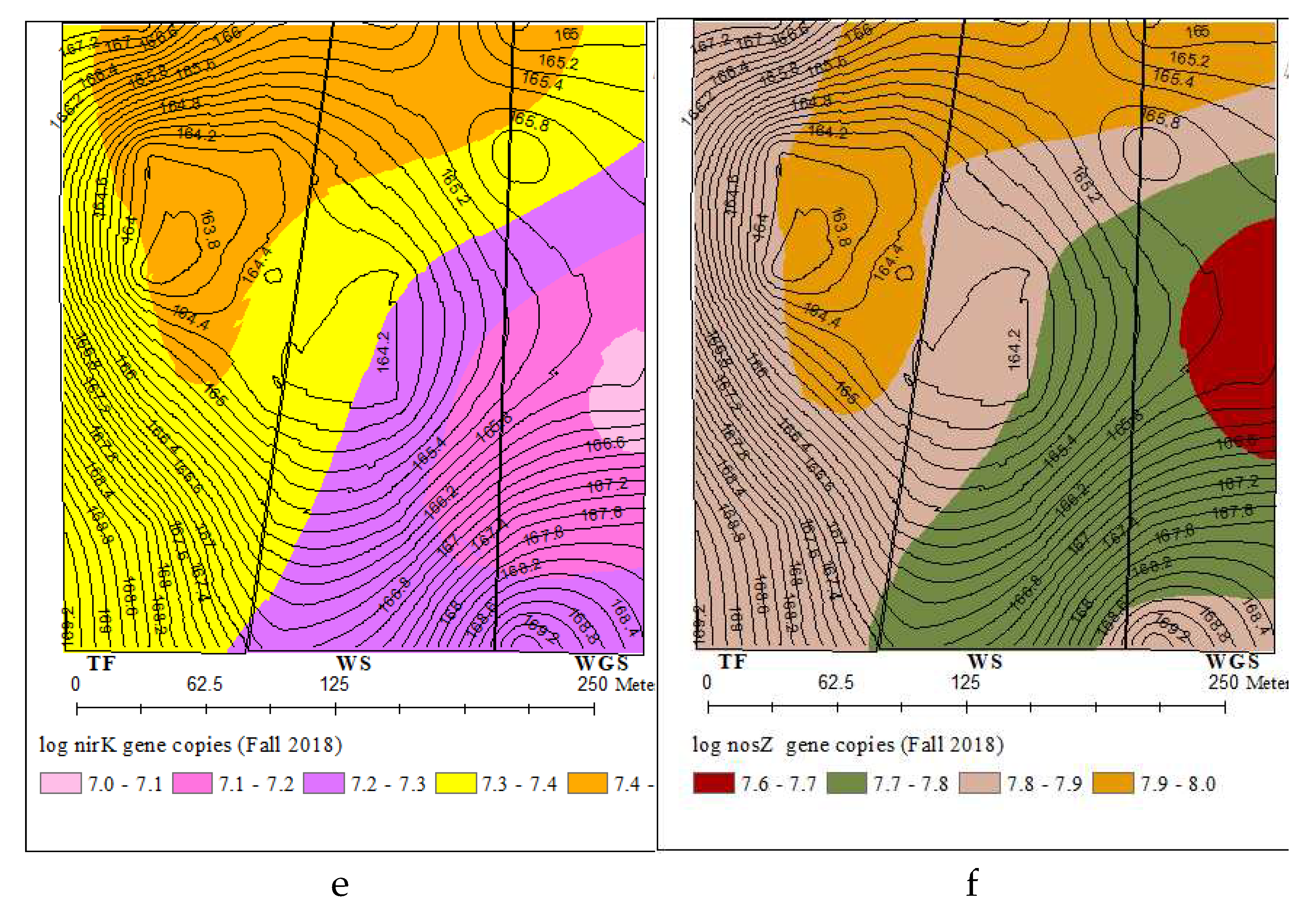
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
References
- Sanford: G., R.; Jackson, R. D.; Booth, E. G.; Hedtcke, J. L.; Picasso, V. , Perenniality and diversity drive output stability and resilience in a 26-year cropping systems experiment. Field Crops Research 2021, 263, 108071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P. , Delivering food security without increasing pressure on land. Global food security 2013, 2(1), 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemaire, G.; Franzluebbers, A.; de Faccio Carvalho, P. C.; Dedieu, B., Integrated crop–livestock systems: Strategies to achieve synergy between agricultural production and environmental quality. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment 2014, 190, 4-8.
- Planisich, A.; Utsumi, S.; Larripa, M.; Galli, J. , Grazing of cover crops in integrated crop-livestock systems. Animal 2021, 15(1), 100054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moomaw, R. S.; Powell, T. A. , Multiple cropping systems in small grains in Northeast Nebraska. Journal of production agriculture 1990, 3(4), 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, F. In Chemical composition of wheat pasture, Natl. Wheat Pasture Symp. Proc. GW Horn, ed. Oklahoma Agric. Exp. Stn., Stillwater, 1984; pp 47-54.
- Winterholler, S.; Lalman, D.; Hudson, M.; Ward, C.; Krehbiel, C.; Horn, G. , Performance, carcass characteristics, and economic analysis of calf-fed and wheat pasture yearling systems in the southern Great Plains. The Professional Animal Scientist 2008, 24(3), 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netthisinghe, A.; Galloway, H.; DeGraves, F.; Agga, G. E.; Sistani, K. , Grain yield and beef cow–calf growth performance in dual-purpose and conventional grain wheat production systems and stockpiled tall fescue pasturing. Agronomy 2020, 10(10), 1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourtev, P.; Ehrenfeld, J.; Häggblom, M. , Experimental analysis of the effect of exotic and native plant species on the structure and function of soil microbial communities. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 2003, 35(7), 895–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuedemann, J. A.; Hoveland, C. S. , Fescue endophyte: History and impact on animal agriculture. Journal of Production Agriculture 1988, 1(1), 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoveland, C. S., Origin and history. Tall fescue for the twenty-first century 2009, 53, 1-10.
- Leuchtmann, A.; Clay, K. , Isozyme variation in the Acremonium/Epichloë fungal endophyte complex. Phytopathology 1990, 80(10), 1133–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvatic, J.; Peršić, V.; Kočić, A.; Čačić, L.; Has-Schoen, E. , Water quality and nutrient limitation in an area of the Danube River and an adjoining oxbow lake (1299 r. km): algal bioassay. Fresenius Environmental Bulletin 2009, 18 (1), 12-20.
- Tripathi, N.; Singh, R. S. , Influence of different land uses on soil nitrogen transformations after conversion from an Indian dry tropical forest. Catena 2009, 77(3), 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orwin, K. H.; Wardle, D. A. , New indices for quantifying the resistance and resilience of soil biota to exogenous disturbances. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 2004, 36(11), 1907–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, M.; Cai, Z.-C.; Mary, B.; Hao, X.; Chang, S. X. , Land-use type and temperature affect gross nitrogen transformation rates in Chinese and Canadian soils. Plant and soil 2010, 334, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakelin, S. A.; Gregg, A. L.; Simpson, R. J.; Li, G. D.; Riley, I. T.; McKay, A. C. , Pasture management clearly affects soil microbial community structure and N-cycling bacteria. Pedobiologia 2009, 52(4), 237–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayatsu, M.; Tago, K.; Saito, M. , Various players in the nitrogen cycle: diversity and functions of the microorganisms involved in nitrification and denitrification. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition 2008, 54(1), 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.; Patrick, W.; Broadbent, F. , Nitrogen transformations and loss in flooded soils and sediments. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology 1984, 13(4), 273–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolan, N. S.; Saggar, S.; Luo, J.; Bhandral, R.; Singh, J. , Gaseous emissions of nitrogen from grazed pastures: processes, measurements and modeling, environmental implications, and mitigation. Advances in agronomy 2004, 84(37), 120. [Google Scholar]
- Lashof, D. A.; Ahuja, D. R. , Relative contributions of greenhouse gas emissions to global warming. Nature 1990, 344(6266), 529–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotthauwe, J.-H.; Witzel, K.-P.; Liesack, W. , The ammonia monooxygenase structural gene amoA as a functional marker: molecular fine-scale analysis of natural ammonia-oxidizing populations. Applied and environmental microbiology 1997, 63(12), 4704–4712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Boer, W.; Kowalchuk, G. A. , Nitrification in acid soils: micro-organisms and mechanisms. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 2001, 33 (7-8), 853-866.
- Zumft, W. G. , Cell biology and molecular basis of denitrification. Microbiology and molecular biology reviews 1997, 61(4), 533–616. [Google Scholar]
- Chèneby, D.; Hallet, S.; Mondon, M.; Martin-Laurent, F.; Germon, J.; Philippot, L. , Genetic characterization of the nitrate reducing community based on narG nucleotide sequence analysis. Microbial ecology 2003, 46(1), 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, S.; Bru, D.; Stres, B.; Hallet, S.; Philippot, L. , Quantitative detection of the nosZ gene, encoding nitrous oxide reductase, and comparison of the abundances of 16S rRNA, narG, nirK, and nosZ genes in soils. Applied and environmental microbiology 2006, 72(8), 5181–5189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Gutiérrez, J. C.; Henry, S.; Hallet, S.; Martin-Laurent, F.; Catroux, G.; Philippot, L. , Quantification of a novel group of nitrate-reducing bacteria in the environment by real-time PCR. Journal of microbiological methods 2004, 57(3), 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colloff, M.; Wakelin, S.; Gomez, D.; Rogers, S. , Detection of nitrogen cycle genes in soils for measuring the effects of changes in land use and management. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 2008, 40(7), 1637–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicol, G. W.; Leininger, S.; Schleper, C.; Prosser, J. I. , The influence of soil pH on the diversity, abundance and transcriptional activity of ammonia oxidizing archaea and bacteria. Environmental microbiology 2008, 10(11), 2966–2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, H. L.; Packer, A.; Bever, J. D.; Clay, K. , Grassroots ecology: plant–microbe–soil interactions as drivers of plant community structure and dynamics. Ecology 2003, 84(9), 2281–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girvan, M. S.; Bullimore, J.; Pretty, J. N.; Osborn, A. M.; Ball, A. S. , Soil type is the primary determinant of the composition of the total and active bacterial communities in arable soils. Applied and environmental microbiology 2003, 69(3), 1800–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fierer, N.; Jackson, R. B. , The diversity and biogeography of soil bacterial communities. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2006, 103(3), 626–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, S. D.; Knorr, M.; Parrent, J. L.; Simpson, R. T. , Chronic nitrogen enrichment affects the structure and function of the soil microbial community in temperate hardwood and pine forests. Forest Ecology and Management 2004, 196(1), 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, H. L.; Drake, J.; Imhof, M.; Oxley, A. P.; Norng, S.; Mele, P. M. , The abundance of nitrogen cycle genes amoA and nifH depends on land-uses and soil types in South-Eastern Australia. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 2010, 42(10), 1774–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallenstein, M. D.; Myrold, D. D.; Firestone, M.; Voytek, M. , Environmental controls on denitrifying communities and denitrification rates: insights from molecular methods. Ecological applications 2006, 16(6), 2143–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bissett, A.; Brown, M. V.; Siciliano, S. D.; Thrall, P. H. , Microbial community responses to anthropogenically induced environmental change: towards a systems approach. Ecology letters 2013, 16, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauber, C. L.; Strickland, M. S.; Bradford, M. A.; Fierer, N. , The influence of soil properties on the structure of bacterial and fungal communities across land-use types. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 2008, 40(9), 2407–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborne, C. A.; Zwart, A. B.; Broadhurst, L. M.; Young, A. G.; Richardson, A. E. , The influence of sampling strategies and spatial variation on the detected soil bacterial communities under three different land-use types. FEMS Microbiology Ecology 2011, 78(1), 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franklin, R. B.; Mills, A. L. , Multi-scale variation in spatial heterogeneity for microbial community structure in an eastern Virginia agricultural field. FEMS microbiology ecology 2003, 44(3), 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunan, N.; Wu, K.; Young, I. M.; Crawford, J. W.; Ritz, K. , In situ spatial patterns of soil bacterial populations, mapped at multiple scales, in an arable soil. Microbial Ecology 2002, 44, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritz, K.; McNicol, J.; Nunan, N.; Grayston, S.; Millard, P.; Atkinson, D.; Gollotte, A.; Habeshaw, D.; Boag, B.; Clegg, C. , Spatial structure in soil chemical and microbiological properties in an upland grassland. FEMS Microbiology Ecology 2004, 49(2), 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, V. , Soil Biology in Pasture Systems: Knowledge and Opportunity Audit. Meat and Livestock Australia: 2003.
- Hurlbert, S. H. , Pseudoreplication and the design of ecological field experiments. Ecological monographs 1984, 54(2), 187–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wester, D. B., replication, randomization, and statistics in range research. Rangeland Ecology & Management/Journal of Range Management Archives 1992, 45 (3), 285-290.
- Rowell, D., Laboratory methods for studying mineralization. Soil science: Methods and Applications. Longman Scientific and Technical, Longman Group UK Ltd., Longman House, London, England 1994.
- Nelson, D. a.; Sommers, L. E., Total carbon, organic carbon, and organic matter. Methods of soil analysis: Part 2 chemical and microbiological properties 1983, 9, 539-579.
- Mulvaney, R. L., Nitrogen—inorganic forms. Methods of soil analysis: Part 3 Chemical methods 1996, 5, 1123-1184. 1123.
- Blake, G. ꎬ.; Hartge, K., Bulk density. Methods of soil analysis: Part 1 Physical and mineralogical methods 1986, 5, 363-375.
- Cook, K.; Ritchey, E.; Loughrin, J.; Haley, M.; Sistani, K.; Bolster, C. H. , Effect of turning frequency and season on composting materials from swine high-rise facilities. Waste Management 2015, 39, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, P. A., Notes on continuous stochastic phenomena. Biometrika 1950, 37 (1/2), 17-23.
- Isaaks, E. H.; Srivastava, R. M. , Applied geostatistics. Oxford university press New York: 1989; Vol. 561.
- Bhandral, R.; Saggar, S.; Bolan, N.; Hedley, M. , Transformation of nitrogen and nitrous oxide emission from grassland soils as affected by compaction. Soil and Tillage Research 2007, 94(2), 482–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Neve, S.; Hofman, G. , Influence of soil compaction on carbon and nitrogen mineralization of soil organic matter and crop residues. Biology and fertility of soils 2000, 30, 544–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greacen, E. L.; Sands, R. , Compaction of forest soils. A review. Soil Research 1980, 18(2), 163–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murty, D.; Kirschbaum, M. U.; Mcmurtrie, R. E.; Mcgilvray, H. , Does conversion of forest to agricultural land change soil carbon and nitrogen? A review of the literature. Global change biology 2002, 8(2), 105–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, W. M.; Mann, L. Changes in soil organic carbon and nitrogen as a result of cultivation; Environmental System Science Data Infrastructure for a Virtual Ecosystem …: 2005.
- Sun, R.; Guo, X.; Wang, D.; Chu, H. , Effects of long-term application of chemical and organic fertilizers on the abundance of microbial communities involved in the nitrogen cycle. Applied Soil Ecology 2015, 95, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyaert, R.; Paul Voroney, R. , Estimation of decay constants for crop residues measured over 15 years in conventional and reduced tillage systems in a coarse-textured soil in southern Ontario. Canadian journal of soil science 2011, 91(6), 985–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broder, M.; Wagner, G. , Microbial colonization and decomposition of corn, wheat, and soybean residue. Soil Science Society of America Journal 1988, 52(1), 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDaniel, M.; Grandy, A.; Tiemann, L.; Weintraub, M. , Crop rotation complexity regulates the decomposition of high and low quality residues. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 2014, 78, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D. L.; Ineson, P.; Coward, P. , Temporal variations in nitrous oxide fluxes from urine-affected grassland. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 1999, 31(5), 779–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasiah, V.; Kay, B. , Legume N mineralization: effect of aeration and size distribution of water-filled pores. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 1998, 30(1), 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frijlink, M. J.; Abee, T.; Laanbroek, H. J.; de Boer, W.; Konings, W. N. , The bioenergetics of ammonia and hydroxylamine oxidation in Nitrosomonas europaea at acid and alkaline pH. Archives of Microbiology 1992, 157, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashworth, A.; DeBruyn, J.; Allen, F.; Radosevich, M.; Owens, P. , Microbial community structure is affected by cropping sequences and poultry litter under long-term no-tillage. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 2017, 114, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauber, C. L.; Ramirez, K. S.; Aanderud, Z.; Lennon, J.; Fierer, N. , Temporal variability in soil microbial communities across land-use types. The ISME journal 2013, 7(8), 1641–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardgett, R.; Leemans, D.; Cook, R.; Hobbs, P. J. , Seasonality of the soil biota of grazed and ungrazed hill grasslands. Soil biology and Biochemistry 1997, 29(8), 1285–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruns, M. A.; Stephen, J. R.; Kowalchuk, G. A.; Prosser, J. I.; Paul, E. A. , Comparative diversity of ammonia oxidizer 16S rRNA gene sequences in native, tilled, and successional soils. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 1999, 65(7), 2994–3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Martínez, K.; Suttle, K. B.; Brodie, E. L.; Power, M. E.; Andersen, G. L.; Banfield, J. F. , Despite strong seasonal responses, soil microbial consortia are more resilient to long-term changes in rainfall than overlying grassland. The ISME journal 2009, 3(6), 738–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philippot, L.; Hallin, S.; Schloter, M. , Ecology of denitrifying prokaryotes in agricultural soil. Advances in agronomy 2007, 96, 249–305. [Google Scholar]
- Bardgett, R. D.; Wardle, D. A. , Herbivore-mediated linkages between aboveground and belowground communities. Ecology 2003, 84(9), 2258–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaillard, V.; Chenu, C.; Recous, S.; Richard, G. , Carbon, nitrogen and microbial gradients induced by plant residues decomposing in soil. European Journal of Soil Science 1999, 50(4), 567–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermansson, A.; Lindgren, P.-E. , Quantification of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria in arable soil by real-time PCR. Applied and environmental microbiology 2001, 67(2), 972–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.; Yang, Q.; Li, Z.; Wei, D.; Cui, X. a.; Liang, Y. , Impacts of organic and inorganic fertilizers on nitrification in a cold climate soil are linked to the bacterial ammonia oxidizer community. Microbial ecology 2011, 62, 982–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J. z.; Shen, J. p.; Zhang, L. m.; Zhu, Y. g.; Zheng, Y. m.; Xu, M. g.; Di, H. , Quantitative analyses of the abundance and composition of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and ammonia-oxidizing archaea of a Chinese upland red soil under long-term fertilization practices. Environmental microbiology 2007, 9(9), 2364–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAndrew, D.; Malhi, S. , Long-term N fertilization of a solonetzic soil: effects on chemical and biological properties. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 1992, 24(7), 619–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.; Zebarth, B.; Dandie, C.; Burton, D.; Goyer, C.; Trevors, J. , Crop residue influence on denitrification, N2O emissions and denitrifier community abundance in soil. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 2008, 40(10), 2553–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C. M.; Stres, B.; Rosenquist, M.; Hallin, S. , Phylogenetic analysis of nitrite, nitric oxide, and nitrous oxide respiratory enzymes reveal a complex evolutionary history for denitrification. Molecular biology and evolution 2008, 25(9), 1955–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philippot, L., Denitrifying genes in bacterial and archaeal genomes. Biochimica et biophysica acta (BBA)-Gene structure and expression 2002, 1577 (3), 355-376.
- Bru, D.; Ramette, A.; Saby, N.; Dequiedt, S.; Ranjard, L.; Jolivet, C.; Arrouays, D.; Philippot, L. , Determinants of the distribution of nitrogen-cycling microbial communities at the landscape scale. The ISME journal 2011, 5(3), 532–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessén, E.; Söderström, M.; Stenberg, M.; Bru, D.; Hellman, M.; Welsh, A.; Thomsen, F.; Klemedtson, L.; Philippot, L.; Hallin, S. , Spatial distribution of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea across a 44-hectare farm related to ecosystem functioning. The ISME journal 2011, 5(7), 1213–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| TF | WS | WGS | |
| n | 12 | 11 | 12 |
| Soil properties | |||
| Bulk density (g cm-3) | 1.29 ± 0.03a | 1.38 ± 0.04ab | 1.42 ± 0.02b |
| pH | 6.62± 0.16a | 5.76 ± 0.29a | 5.81 ± 0.25a |
| ------------------------------- g kg-1------------------------------- | |||
| OM | 27.4 ± 1.62a | 24.9 ± 1.38a | 24.55 ± 0.86a |
| TN | 2.85 ± 0.09a | 2.96 ± 0.09a | 2.72 ± 0.08a |
| ------------------------------ mg kg-1------------------------------ | |||
| NO3-N | 4.19 ± 0.51a | 1.77 ± 0.24b | 1.82 ± 0.29b |
| NH4-N | 27.35 ± 1.77a | 22.6 ± 0.77b | 21.78 ± 1.01b |
| Bacterial genes | ----------------------- log10 gene copies ----------------------- | ||
| 16S rRNA | 10.07 ± 0.04a | 9.95 ± 0.04a | 9.94 ± 0.04a |
| amoA | 7.13 ± 0.10a | 6.64 ± 0.18a | 6.64 ± 0.11a |
| narG | 7.57 ± 0.12a | 7.13 ± 0.17a | 7.23 ± 0.06a |
| nirk | 7.74 ± 0.05a | 7.60 ± 0.08a | 7.52 ± 0.02a |
| nosZ | 8.21 ± 0.05a | 8.09 ± 0.09a | 7.94 ± 0.05a |
| TF | WS | WGS | |
| n | 24 | 22 | 24 |
| -------------------------------- g cm-3 -------------------------------- | |||
| Bulk Density | 1.22± 0.02a | 1.34± 0.02b | 1.39± 0.02b |
| TF | WS | WGS | |
| n | 12 | 11 | 12 |
| 16S rRNA | 9.87 ± 0.06a | 9.78 ± 0.06ab | 9.63 ± 0.06b |
| amoA | 7.01 ± 0.1a | 6.49 ± 0.1b | 6.42 ± 0.1b |
| narG | 7.25 ± 0.06a | 7.17 ± 0.06a | 6.88 ± 0.06b |
| nirK | 7.52 ± 0.04a | 7.35 ± 0.04b | 7.25 ± 0.04b |
| nosZ | 7.98 ± 0.05a | 7.89 ± 0.05a | 7.82 ± 0.05a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





