1. Introduction
Kidney transplantation is the best therapy for patients with end-stage renal disease. While in liver transplantation a significant number of patients can be withdrawn immunosuppressive drugs due to the development of variable grades of tolerance, most of the other solid organ transplants need to maintain the immunosuppressive drugs while the graft is functioning to avoid alloimmune response [
1,
2]. Routine follow-up of kidney grafts for transplant physicians implies maintaining appropriate combinations of drugs and drug doses that are known that reduce the appearance of rejection. On the other hand, this immunosuppressive therapy is also associated with undesirable side effects such as infections, cancer, metabolic diseases, and cardiovascular events that increase mortality risk after solid organ transplantation [
3,
4,
5]. Traditionally, it has been thought that transplant physicians should establish an adequate balance between over- and under-immunosuppression to avoid at the same time these side effects and the alloimmune response. Unfortunately, infection and rejection can appear at the same time [
6]. Common practice is to monitor calcineurin-inhibitor (CNI) trough blood levels trying to keep them inside a narrow therapeutic range, although different studies have highlighted that these levels correlate more closely with the risk of side effects than with the rejection risk [
7,
8].
To improve the results of kidney transplantation, it would be important to have new, minimally invasive monitoring methods that would make it possible to assess the risk of both infection and rejection. Some of these methods, such as the ability to activate T helper lymphocytes, have already been used in clinical trials for monitoring liver transplantation, although their value has not been sufficiently proven [
9]. Recently, a new promising method that allows estimating the net immunosuppressive state by measuring the Torque Teno Virus (TTV) load has been developed. TTV is a member of the Anelloviridae family that are ubiquitous and non-pathogenic for humans [
10]. Previous studies in kidney transplant recipients have shown that a high TTV load relates to a higher risk of infection and other immunosuppressive-related side effects [
11,
12,
13,
14,
15,
16,
17,
18], whereas low TTV loads are associated with a higher risk of acute rejection [
14,
16,
17,
18,
19,
20,
21,
22,
23]. In this sense, by measuring TTV in blood we can assess if a kidney transplant recipient is over- or under-immunosuppressed and guide the immunosuppressive therapy.
So far, it is not known precisely which immunosuppressive-related variables influence TTV levels. Some studies have linked higher doses of antimetabolite or CNI drugs or higher CNI blood levels to higher blood TTV loads, but this has not been demonstrated in all studies [
13,
19,
24,
25,
26]. Van Rijn et al. reported that patients treated with tacrolimus showed higher TTV loads than those under cyclosporine [
21]. On the other hand, it has not been previously analyzed whether mycophenolic acid exposure measured by calculating the area under the curve (AUC-MPA) or whether continuous tacrolimus exposure influences TTV burden. The area under the curve is the gold standard to know the appropriate exposure to mycophenolic and relates better to rejection risk and side effects development than mycophenolic trough levels [
27]. Related to CNI, some studies support that continuous exposure measured as coefficient of variability (CV), time in therapeutic range (TTR), or concentration/dose ratio (C/D) relates better than the simple trough CNI blood level measurement to rejection and side effect risk [
28,
29,
30,
31]. We hypothesized that TTV load is associated with the exposure to mycophenolate mofetil and CNI.
2. Materials and Methods
This prospective study was conducted following the guidelines of Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Regional Ethics Committee in our Institution (reference number: PI20/01710; 22 December 2020). A total of 54 consecutive kidney transplants from deceased donors performed in our center from January 2021 to April 2022 were recruited after given written consent prior to kidney transplant. Recipients from non-controlled cardiac death donation, with preformed donor specific antibodies and highly hypersensitized with a panel reactive antibody over 98% were excluded.
Relevant information about recipient, donor, and transplant characteristics was collected. All acute rejection episodes were biopsy proven. Indication biopsies were performed when the level of creatinine increased by 25% or more over its previous value or when there was persistence of proteinuria >1 g per day. We considered opportunistic infections those related to cellular and humoral immunosuppression, which included viral (CMV, EBV, HSV, VZV, BK polyomavirus associated nephropathy and relapsed hepatitis HBV, HCV), bacterial (typical and atypical mycobacterium, others as Nocardia, Listeria…), and fungal (Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia, Candida and invasive fungal infections such as Aspergillus) infections. Standard microbiology techniques were used for detection of viral, bacterial and fungal infections.
Maintenance immunosuppressive therapy consisted of twice daily tacrolimus, mycophenolate mofetil, and prednisone. Recipients of organs from expanded criteria donors and at risk of delayed graft function received induction therapy with basiliximab. Thymoglobulin was used as induction therapy when patients had higher risk of rejection due to hypersensitization or previous graft loss due to acute rejection. All patients received prophylaxis with trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole for 6 months after transplantation and with valganciclovir for 3 months in CMV IgG-negative recipients of a CMV IgG-positive organ and in patients receiving Thymoglobulin induction,
Whole blood concentrations (µg/L) of tacrolimus were determined by chemiluminescent microparticle immunoassay (CMIA; Abbott Laboratories, Abbott Park, IL, USA) on the Architect iSystem. This immunoassay is designed to have a precision of ≤10% total coefficient of variation (CV), a mean recovery of 100 ± 10% of the expected value, a limit of detection of ≤1.5 µg/L, and a functional sensitivity of ≤ 2 µg/L. All levels of tacrolimus up to day 90 were collected. The tacrolimus target trough blood levels up to month 3 were 8 to 12 ng/mL. The variability of tacrolimus blood levels was estimated by means of the coefficient of variation (CV) calculated according to the following equation:
where σ is the standard deviation, and μ is the mean tacrolimus concentration of all available samples [
28]. The percent of time in therapeutic range (8 to 12 ng/mL) and above 12 ng/mL were calculated using the Rosendaal method [
30]. Tacrolimus C/D ratios were calculated at months 1 and 3. Fast metabolizers were defined by a tacrolimus level-dose ratio < 1.05 [
31].
Trough blood concentrations of mycophenolic acid (MPA) in human plasma (mg/l), were quantified by homogenous enzyme immunoassay (Emit 2000 Mycophenolic Acid Assay; Siemens) at months 1 and 3. This immunoassay is designed to have a precision of ≤10% total CV, and a limit of detection of ≤0.1 mg/l. The dynamic range of this immunoassay is from 0.1 mg/l to 15 mg/l based on the analytical sensitivity of the assay. If the analysis of a patient sample is outside the calibration range, it is diluted, allowing to determine the concentration. No cross-reactivity with MPAG (Mycophenolic Acid Glucuronide), the main metabolite of MPA, or with Cyclosporine or Tacrolimus has been observed.
Full mycophenolic acid area under the curve (AUC-MPA) was calculated at month 3 using an abbreviated procedure drawing blood samples at time 0, at 30 minutes and 2 hours after having taken the drug, according to the procedure previously reported by Pawinski et al. The regression equation for AUC
0-12h estimation that gave the best performance for this model was: 7.75 + 6.49.C
0h + 0.76.C
0.5h + 2.43.C
2h [
32].
Samples for measuring TTV load were drawn before transplantation and at day 30 and 90 post-transplantation. Briefly, the blood obtained by venipuncture (BD Vacutainer K2E 5.4mg tube, cat #368856) was centrifuged at 1.300 rpm and the plasma was frozen at -80ºC until processing. Free viral DNA was purified from 400 µL of plasma from all specimens using the QIAamp MinElute Virus Spin Kit Cat. # 57704 as specified by the manufacturer. The presence and viral load of TTV in the samples were determined in duplicate using a previously described TaqMan (TM)-PCR assay human TTV APP2XDMP (ThermoFisher) in a StepOnePlus Real-Time PCR System (AB Applied Biosystems). This assay is based on the specific amplification of a highly conserved viral segment in the untranslated region of TTV, which has the potential for sensitive and specific detection of all TTV genotypes present in GenBank [
33]. The procedures used for copy number quantification and assessment of specificity, sensitivity, intra- and inter-assay precision, and reproducibility have been previously described [
34,
35]. The lower limit of sensitivity was 1.0 x 10
3 viral genomes per ml of plasma sample. This protocol has recently been compared and validated against the commercial TTV R-GENE
® kit (bioMérieux) [
18].
As a positive control, a 143 bp PCR fragment from the same untranslated region of TTV genome (NC_015783.1) was amplified using the primers TTV Sen (5’ GTGCCGTAGGTGAGTTTA 3’) and TTV AntisL (5’ ATGGACCGGCGGTCTCCACGG 3’) and cloned into the pCR™2.1 cloning vector (TA Cloning™ Kit, # K202040 ThermoFisher). The resulting plasmid was then purified with QIAprep Spin Miniprep Kit, # 2710 (Qiagen) and quantified using Nanodrop 2000C spectrophotometer (ThermoFisher Scientific # ND-2000C). The standard curve was established with the points A=1.0 x 1012 copies, B=1.0 x 1010 copies, C=1.0 x 108 copies, D= 1.0 x 106 copies, E= 1.0 x 104 copies, F=1.0 x 102 copies, G=1.0 copies, H=0 copies.
Continuous variables were expressed as mean ± standard deviation if normally distributed or as median and interquartile range (IQR) if non-normally distributed. Categorical variables were described as relative frequencies. The Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient was used to explore the relationship between TTV load and continuous variables. Wilcoxon rank test was used for comparing TTV loads at different time points. Mann-Whitney U test was used to compare TTV load differences among dichotomous variables. The ability of TTV load to discriminate infection and rejection was analyzed by constructing receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves. Univariate and multivariate logistic regression analysis were used to analyze the relationship between TTV load and infection and rejection. A p value less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Statistical analyses were performed with SPSS, version 15.0 (SPSS, Inc, Chicago, IL, USA).
3. Results
Main patient characteristics are shown in
Table 1. Fifty-four kidney transplant patients were included and followed throughout the first year. 1 patient dead due to respiratory sepsis at month 10. Biopsy proven acute rejection was diagnosed in 8 patients during the first posttransplant month, in 4 patients between first and third posttransplant and only 1 between month 3 and 6). 10 (18.5%) and 6 (11.1%) patients suffered at least one opportunistic infection between months 1 and 3 and between months 3 and 6, respectively.
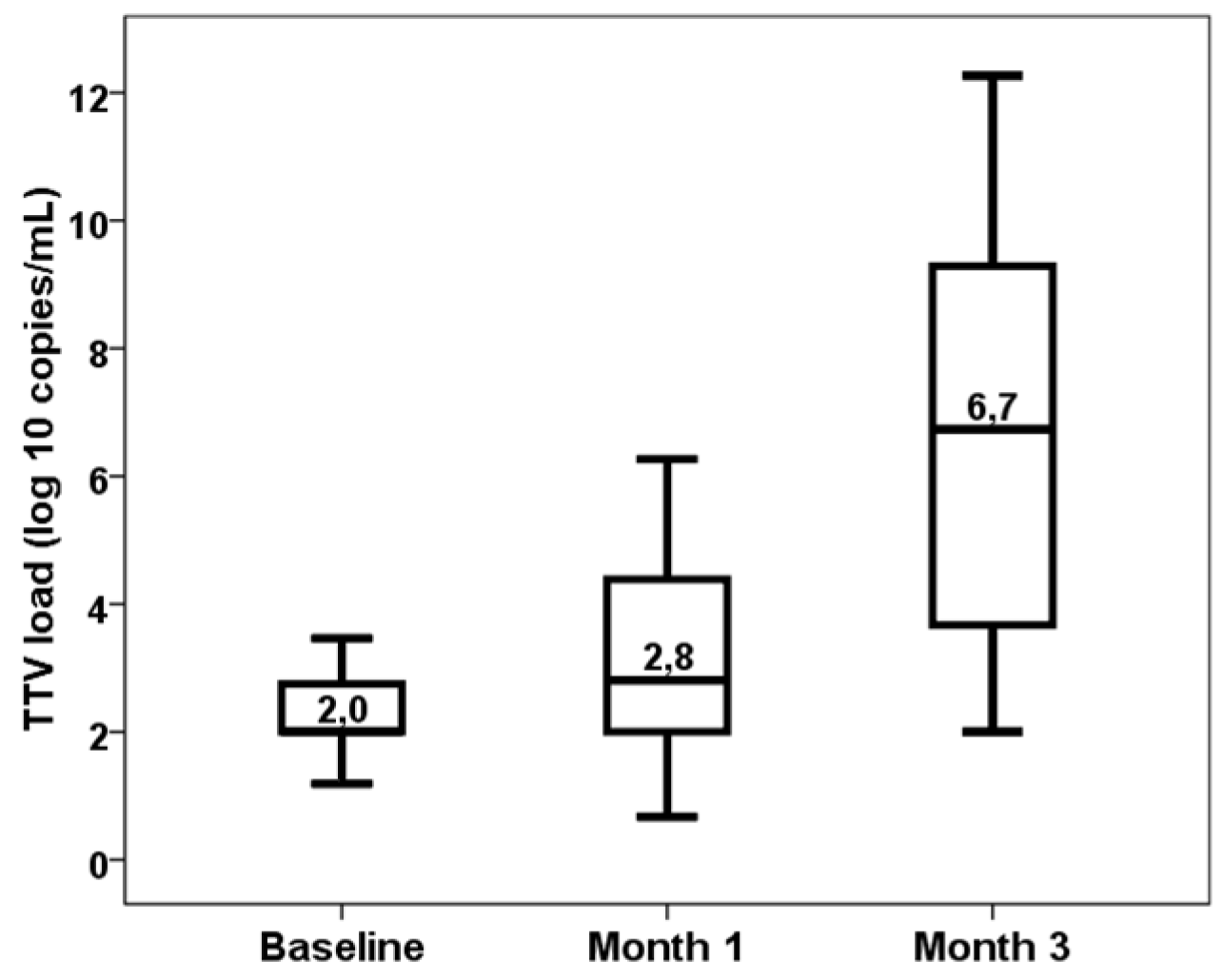
Median TTV load values increased from pretransplant (2.00, IQR 0.76) to month 1 (2.81, IQR 2.41, p < 0.001) and month 3 (6.73, IQR 5.74, p < 0.001) (
Figure 1). Baseline TTV load did not relate to recipient age (rho = 0.177, p = 0.200), to donor age (rho = 0.108, p = 0.435) and to time in renal replacement therapy (rho = 0.091, p = 0.513) according to Spearman correlation analysis. Baseline TTV load was significantly higher in male recipients (median 2.00, IQR 0 vs. median 2.47, IQR 0.98, Mann-Whitney p = 0.019). Neither CMV serostatus (median 2.00, IQR 0.87 vs. median 2.00, IQR 0.75, Mann-Whitney p = 0.453) nor preeemptive transplant (median 2.19, IQR 0.75 vs. median 2.00, IQR 0.77, Mann-Whitney p = 0.171) showed significantly different baseline TTV loads.
Spearman correlations between TTV load at months 1 and 3 and continuous variables are shown in
Table 2 and
Table 3, respectively. In patients who received Thymoglobulin induction, TTV load at month 1 (rho -0.041, p = 0.890) and at month 3 (rho -0.326, p = 0.256) was not associated with the accumulated thymoglobulin dose. Mann-Witney U test did not find significant differences in TTV load at month 1 comparing recipient gender (male) (2.10, IQR 2.66 vs. 2.92, IQR 2.30, p = 0.872), diabetic nephropathy (2.94, IQ 2.54 vs. 2.23, IQR 2.25, p = 0.401), retransplant (2.81, IQR 2.41 vs. 2.87, IQR 3.09, p = 0.896), preemptive transplantation (2.91, IQR 2.54 vs. 2.00, IQR 2.39, p = 0.362), induction use (2.57, IQR 2.66 vs. 2.96, IQR 2.37, p = 0.936), thymoglobulin (2.57, IQR 2.30 vs. 3.35, IQR 2.64, p = 0.258), any tacrolimus level < 5 at month 1 (2.66, IQR 2.45 vs. 3.15, IQR 2.45, p = 0.883), any tacrolimus level < 6 at month 1 (2.57, IQR 2.33 vs. 3.79, IQR 3.40, p = 0.205) and fast tacrolimus metabolizers (4.39, IQR 2.56 vs. 2.57, IQR 2.17, p = 0.197).
By U Mann-Witney analysis, we did not find significant differences in TTV load at month 3 comparing recipient gender (5.98, IQR 6.12 vs. 6.73, IQR 5.31, p = 0.333), diabetic nephropathy (6.95, IQR 6.74 vs. 6.34, IQR 4.11, p = 0.839), retransplant (6.74, IQR 5.73 vs. 5.98, IQR 7.80, p = 0.802), preemptive transplantation (6.78, IQR 6.00 vs. 5.43, IQR 4.64, p = 0.420), thymoglobulin (6.63, IQR 5.61 vs. 7.77, IQR 5.94, p = 0.286), any tacrolimus level < 5 at month 3 (6.51, IQR 5.95 vs. 6.87, IQR 5.60, p = 0.157), any tacrolimus level < 6 at month 3 (7.49, IQR 5.89 vs. 6.59, IQR 6.87, p = 0.961) and fast tacrolimus metabolizers (7.78, IQR 3.84 vs. 6.63, IQR 6.20, p = 0.381). Induction use (3.47, IQR 4.10 vs. 7.53, IQR 4.98, p = 0.008) was the only immunosuppression-related variable associated with the TTV load at month 3.
Patient who developed opportunistic infection between months 1 and 3 showed higher levels of TTV load at first month (2.51, IQR 2.22 vs. 4.08, IQR 5.57, p = 0.020) (
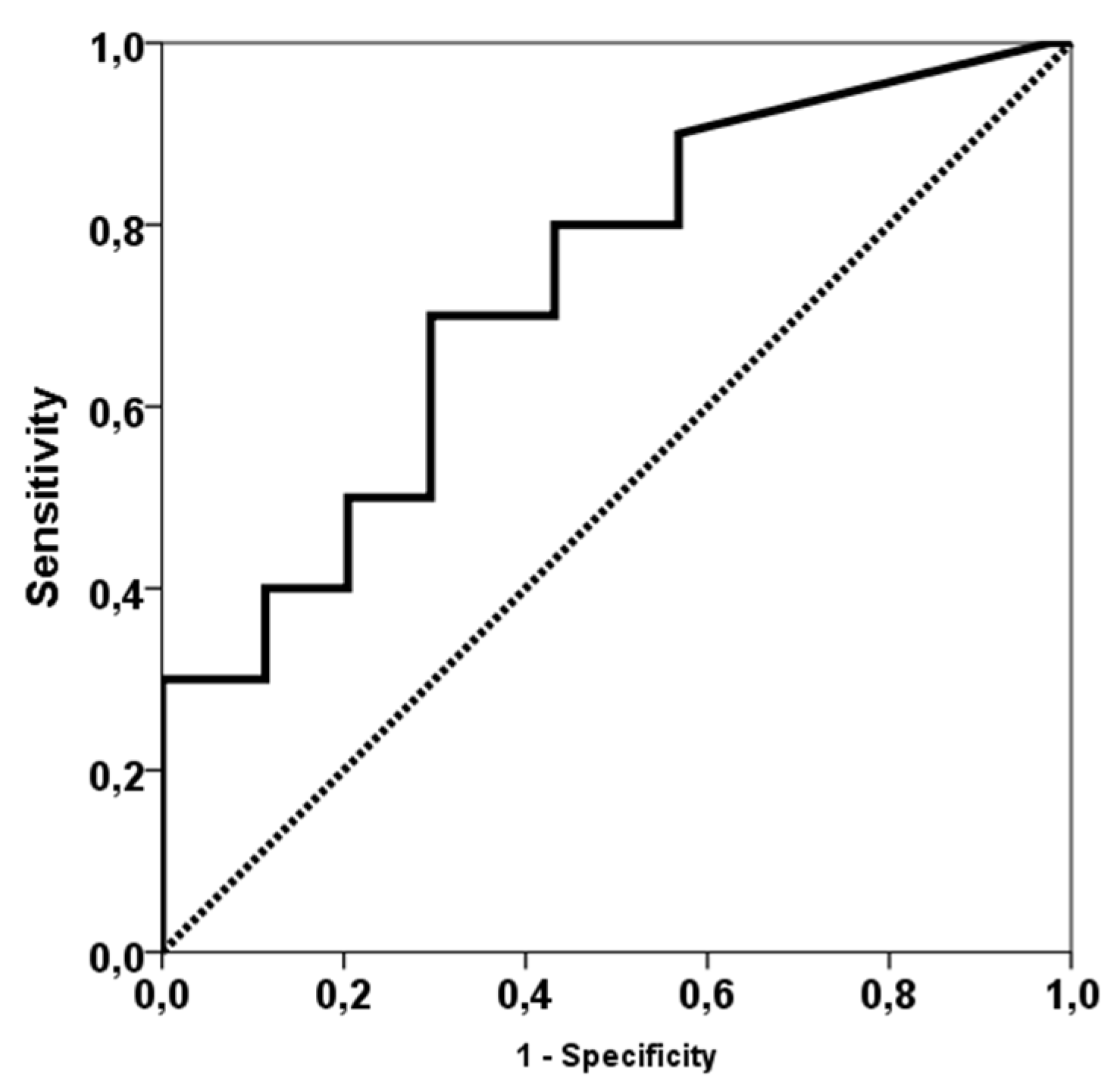
Figure 2). TTV load at first month was able to discriminate those patients at risk of developing opportunistic infections between months 1 and 3 (AUC-ROC 0.723, 95%CI 0.559-0.905, p = 0.023) (
Figure 3). By univariate logistic regression, TTV load at month 1 related to a higher risk of opportunistic infection from months 1 to 3 (OR 1.682, 95%CI 1.134-2.495, p = 0.010). After multivariate logistic regression analysis adjusting for other variables related to TTV load (recipient age, donor age, estimated GFR, diabetes mellitus and recipient female), TTV load at month 1 remained independently associated with a higher risk of opportunistic infection from months 1 to 3 (OR 1.682, 95%CI 1.134-2.495, p = 0.010).
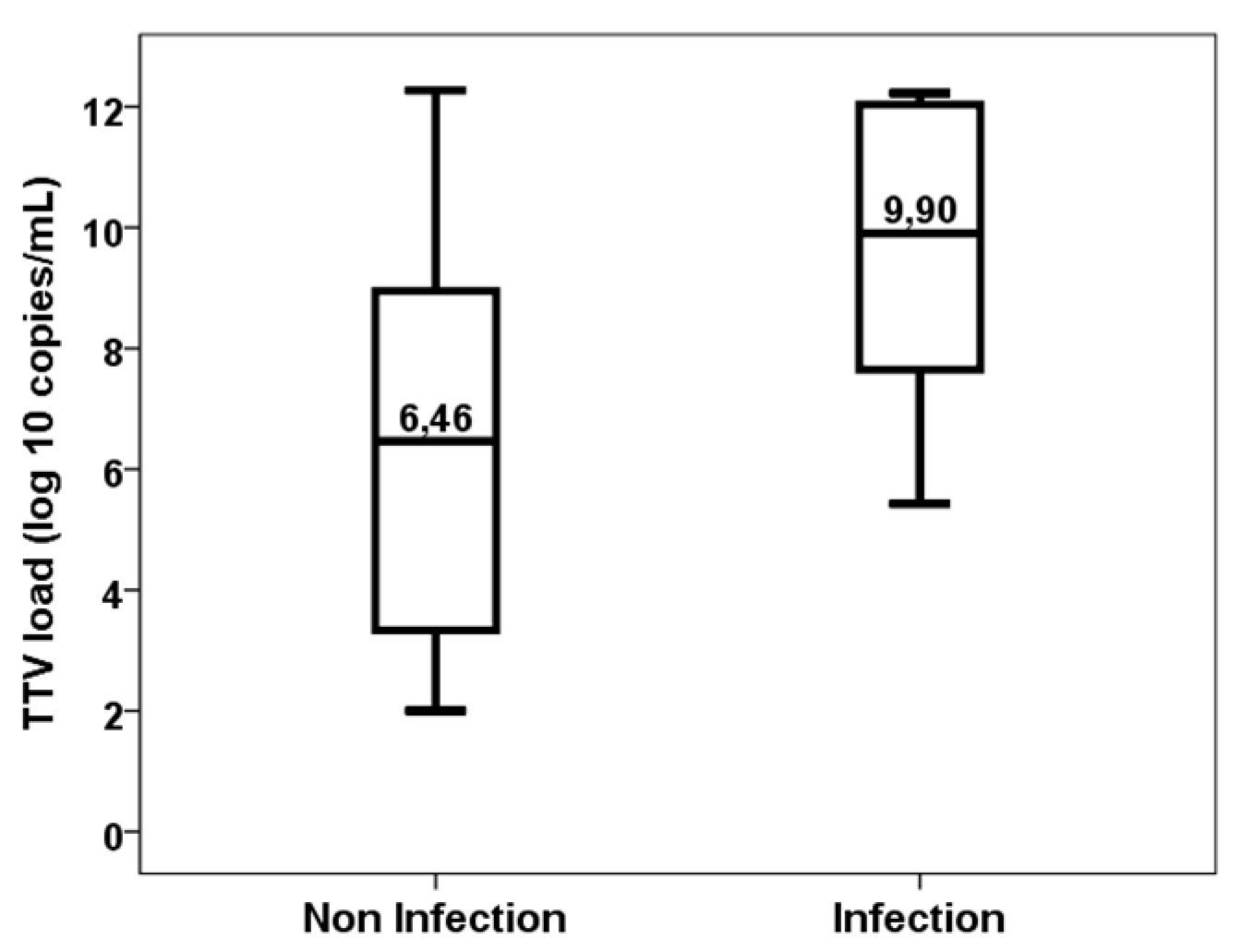
Similarly, patients who developed opportunistic infection between months 3 and 6 showed higher levels of TTV load at third month (6.46, IQR 5.74 vs. 9.90, IQR 4.99, p = 0.026) (
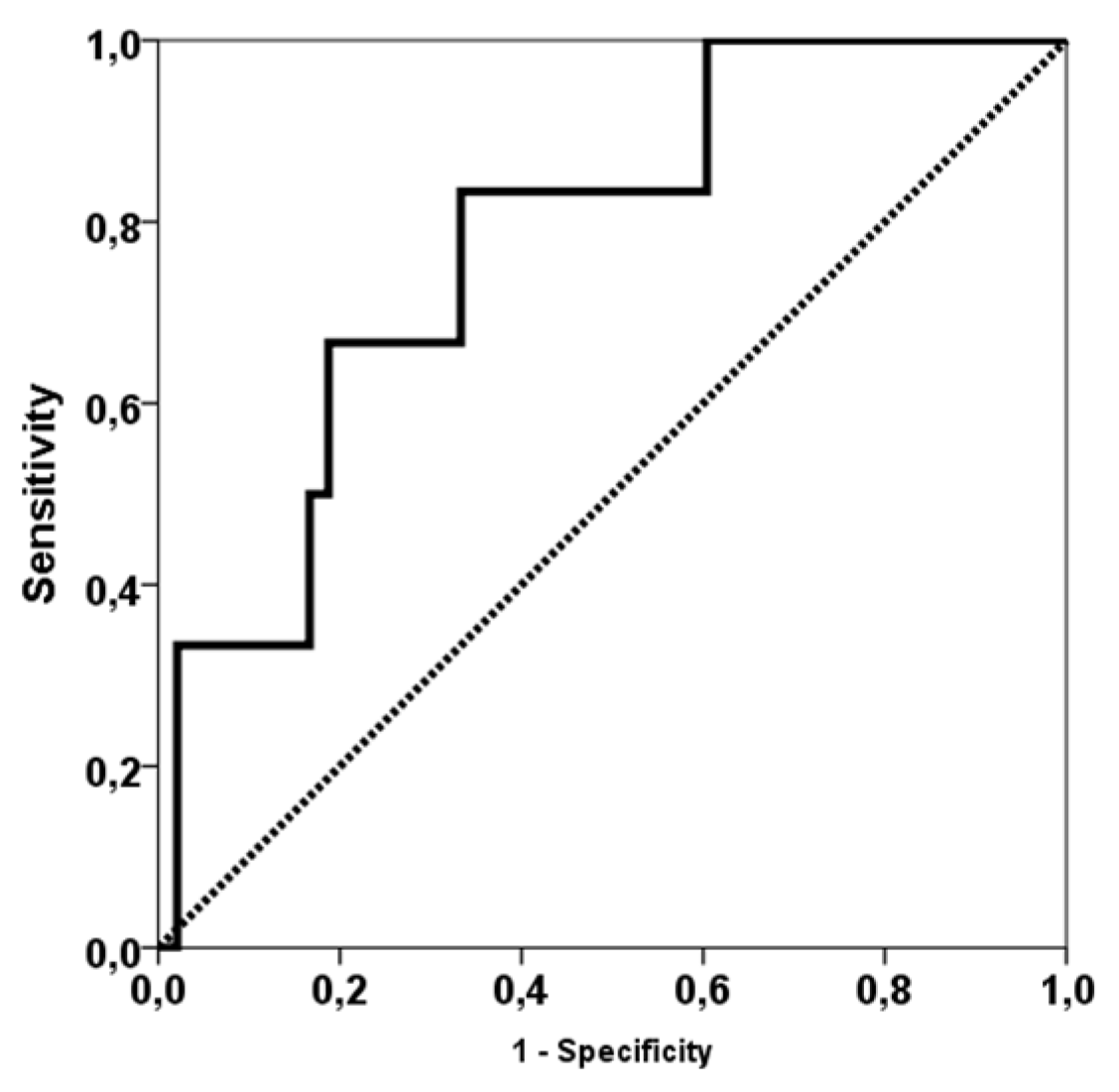
Figure 4). TTV load at third month discriminated those patients at risk of developing opportunistic infections from months 3 to 6 (AUC-ROC 0.778, 95%CI 0.599-0.957, p = 0.028) (
Figure 5). TTV load at month 3 related to a higher risk of opportunistic infection from months 3 to 6 (OR 1.444, 95%CI 1.017-2.050, p = 0.040) and this relationship remained significant (OR 1.444, 95%CI 1.017-2.050, p = 0.040) after adjusting by confounders variables such as recipient age, donor age, female recipient gender, estimated GFR and diabetes mellitus.
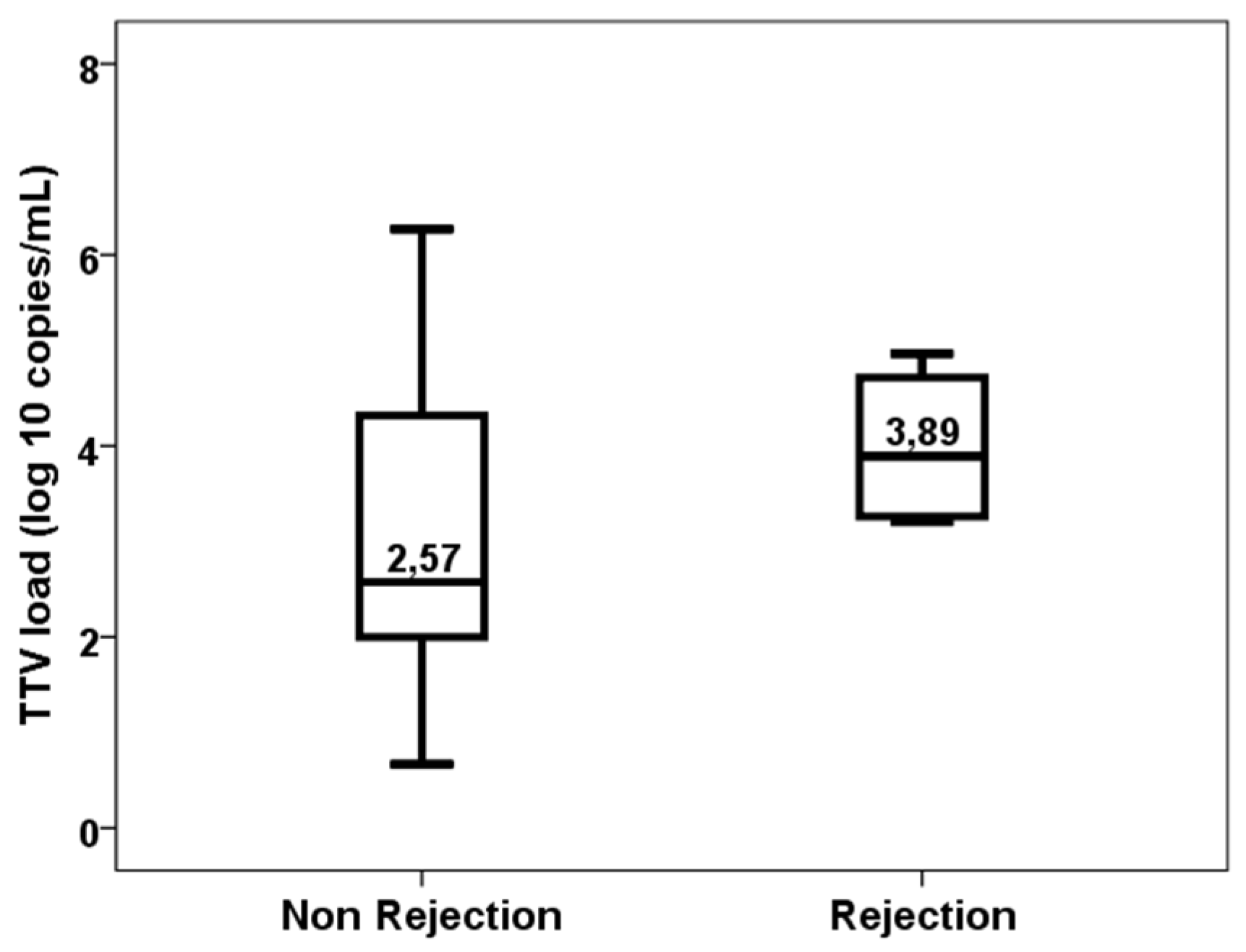
By contrast, TTV load at first month was not significantly higher in patients who developed acute rejection between month 1 and 3 (2.57, IQR 2.33 vs. 3.89, IQR 1.61, p = 0.177) (
Figure 6) and was not useful to discriminate these patients (AUC-ROC 0.710, 95%CI 0.565-0.855, p = 0.165).
4. Discussion
After transplantation, TTV load increased in month 1 and to higher levels in month 3. Similar to us, most authors analyzing kinetic changes of TTV load have reported that TTV load increases after transplantation reaching its maximal value at months 3 to 6 [
13,
14,
17,
36,
37]. In this sense, an optimal point to measure TTV load would be at month 3 post-transplantation, although we detected that both TTV loads at months 1 and 3 related to a higher risk of opportunistic infection. This relationship between TTV load and later infection has been clearly demonstrated by most but not all authors [
11,
12,
13,
14,
15,
16,
17,
18,
21,
37]. The AUC-ROC of TTV for predicting infection ranged between 0.580 and 0.650 [
11,
12,
13,
14,
16,
17,
18]. We also reported that for each log 10 increase of TTV load at month 1 the risk of opportunistic infection increased by 68% and at month 3 increased by 44%. This result is concordant with other studies in which the increase in infection risk ranged from 6% to 188% per 1 log of TTV load, depending on the infection definition [
13,
14,
17,
18]. Pooled data from 16 studies have shown that the risk of infection increased by 16% per 1 log of TTV load increase [
23]. Being opportunistic infection more specifically related to over-immunosuppression, it would be expected that the relationship between TTV load and opportunistic infection were stronger than with global infection, as previously reported by Doberer et al. [
17]. Of note, TTV load is associated with higher infection-related death even beyond the first-year post-transplantation [
38].
Due to the low number of rejection episodes in our study, we did not find a relationship with TTV load, although the median differences between patients with (3.89 log) and without rejection (2.57 log) were striking. Most previous studies have found that patients with lower TTV loads are at a higher risk of acute rejection [
14,
16,
17,
18,
19,
20,
21,
23], antibody-mediated rejection [
19] and subclinical rejection [
22]. TTV load has a discriminative ability for predicting acute rejection with AUC-ROC ranging from 0.73 to 0.82 [
17,
18,
20]. Collecting data from 15 studies, the meta-analysis by Van Rijn et al. concluded that the risk of rejection decreased by 10% per 1 log of TTV load [
23]. The fact that rejection can be diagnosed in a more homogeneous way thanks to the Banff consensus among the different centers could facilitate more concordant results in the different studies.
The only immunosuppressive-drug variable related to TTV load was induction use. Those patients who have received induction showed higher TTV loads. Although the use of thymoglobulin did not relate statistically to TTV load, there was a trend in the median TTV load between those treated and non-treated with lymphocyte-depleting antibodies as induction. Antibody and/or Thymoglobulin induction is the most consistently immunosuppressive drug related to higher TTV loads, as related to a higher degree of immunosuppression, although this relationship has not been confirmed by all authors [
13,
14,
19,
36].
The main finding of our study was that higher exposure to maintenance immunosuppressive drugs such as tacrolimus, mycophenolate mofetil, or prednisone was not associated with a higher TTV load. We conducted a detailed study of global tacrolimus exposure. To this end, we collected variables related to sustained exposure to tacrolimus that had not previously been studied in relation to TTV burden. The tacrolimus CV has been related to a worse outcome in solid organ transplantation, not only in relation to under-immunosuppression and increased risk of rejection, but also in relation to over-immunosuppression and increased risk of infections [
28,
29]. A shorter TTR has also been related to a worse evolution of renal transplantation, with more rejection, renal graft loss, and infections [
30]. A lower tacrolimus level-value dose ratio is related to rapid metabolizers who have more difficulty in maintaining stable levels, which puts them at risk of changes in the level of immunosuppression [
31]. We found no relationship between any of these tacrolimus exposure variables and TTV burden. We also did not find that the mean tacrolimus levels were related to TTV load as in other studies in kidney transplantation [
13,
19,
25], unlike Gorzer et al. in lung transplants [
24].
Moreover, different from previous studies, we analyzed the relationship between TTV load and exposure to mycophenolic acid by measuring the gold standard AUC-MPA. Previous authors reported that MMF dose related to TTV load, but neither of them analyzed AUC-MPA [
13]. There is strong evidence in favor of using AUC-MPA, rather than trough levels or no monitoring, to accurately assess the level of mycophenolic acid exposure to monitor kidney transplant recipients [
27]. Difficulties in measuring AUC-MPA, which requires multiple blood samples over several hours, have made it not the standard practice in most centers. Unexpectedly, we found no relationship between mycophenolic exposure and TTV levels. In the same way, the prednisone dose was not related to TTV. This lack of relationship leads us to suspect that the overall levels of immunosuppression in patients depend to a large extent on factors not exclusively related to immunosuppressive treatment, such as nutritional status or frailty. The relationship of TTV with the infection, and, in previous studies, with the rejection, confirms that it is a biomarker of the state of immunosuppression and that it is not fully dependent on the maintenance immunosuppression.
In our study, male recipients showed higher baseline TTV loads. Previous studies reported a similar finding [
13,
19,
36]. By contrast, we did not find any relationship between pretransplant TTV load and recipient age and CMV serostatus, having been these relationships previously reported [
13,
14,
19,
36]. Some variables that could be related to a certain degree of immunosuppression such as the time in renal replacement therapy and if the recipient was receiving preemptive transplantation were not related to pretransplant TTV load in our study [
21]. At month 3 posttransplantation, we found that a higher donor age was associated with a higher TTV load. The relationship between donor age and TTV load has been reported by XXX and XXX [
13]. Since TTV viral load increases with age, grafts from older donors would transmit a higher TTV load with the graft itself, which could increase the long-term recipient blood TTV load.
The main limitation of our single-center study was the sample size. We demonstrated a relationship between the burden of TTV and opportunistic infections, but not with rejection, mainly due to its low incidence. Another limitation was that we used a non-standardized in-house PCR technique to measure the TTV burden. A recent publication has highlighted the agreement between in-house and standardized techniques and that both methods are useful for measuring TTV [
39]. As an advantage, we performed a detailed prospective study on the global exposure of each patient to global immunosuppression. Being a prospective study allowed us to collect the incidence of infection and rejection in defined periods (1 to 3 months, 3 to 6 months) to determine the predictive capacity of each TTV value. Until now, each study has defined infection in a variable way and the times in which the risk of infection and rejection were analyzed in relation to the TTV have not been homogeneous. There is an ongoing randomized controlled trial comparing standard versus TTV-guided immunosuppression that will allow us to know in more detail the relationship between TTV and kidney transplant complications more accurately [
40].
5. Conclusions
To conclude, we carried out a prospective study in which it was shown that the TTV load at one month and the third month after transplantation were independently related to the subsequent risk of infection in renal transplantation. A trend was also detected that patients who were going to suffer an acute rejection had lower levels of TTV. TTV viral load was related to induction use but was not related to overall exposure to maintenance immunosuppression. It is necessary to analyze in greater depth which variables determine the blood values of TTV to use it as a non-invasive biomarker useful to assess the global level of immunosuppression in kidney transplants and other solid organ transplants.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.R. and A.B.H.; methodology, E.R., M.G.S and A.B-H.; software, L.C. and E.G.; validation, J.C.R., M.A.C, R.V. and L.B.; formal analysis, E.R. and A.B.H.; investigation, L.C. and E.G.; resources, E.R. and A.B.H.; data curation, L.C., C.E., M.R.V. and E.G. writing—original draft preparation, E.R.; writing—review and editing, E.R., M.G.S and A.B-H.; funding acquisition, E.R. and A.B.H.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by grants for Fondo de Investigaciones Sanitarias-ISCIII (PI20/01710) and RICORS (ISCIII RD21/0005/0010, “Financiado por la Unión Europea −NextGenerationEU,” Mecanismo para la Recuperación y la Resiliencia [MRR])
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Regional Ethics Committee of Cantabria (reference number: PI20/01710; 22 December 2020).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors are indebted to Consuelo Agüeros (Nephrology Research Laboratory, Hospital Marqués de Valdecilla-IDIVAL) for technician support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Levitsky, J. Operational tolerance: Past lessons and future prospects. Liver Transpl 2011; 17: 222-32. [CrossRef]
- Dugast E, Soulillou JP, Foucher Y, Papuchon E, Guerif, P., Paul, C.; et al. Failure of Calcineurin Inhibitor (Tacrolimus) Weaning Randomized Trial in Long-Term Stable Kidney Transplant Recipients. Am J Transplant 2016; 16: 3255-3261. [CrossRef]
- Briggs JD. Causes of death after renal transplantation. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2001; 16: 1545-1549. [CrossRef]
- Buell JF, Gross TG, Woodle ES. Malignancy after transplantation. Transplantation 2005; 80(2 Suppl): S254-S264. [CrossRef]
- Woodward RS, Flore MC, Machnicki, G., Brennan DC. The long-term outcomes and costs of diabetes mellitus among renal transplant recipients: Tacrolimus versus cyclosporine. Value Health 2011; 14: 443-449. [CrossRef]
- Mafune A, Tanno Y, Yamamoto H, Kobayashi A, Saigawa H, Yokoo T; et al. A case of BK virus nephropathy and cytomegalovirus infection concurrent with plasma cell-rich acute rejection. Clin Transplant 2012; 26 Suppl 24: 49-53. [CrossRef]
- Bouamar R, Shuker N, Hesselink DA, Weimar W, Ekberg H, Kaplan B; et al. Tacrolimus predose concentrations do not predict the risk of acute rejection after renal transplantation: A pooled analysis from three randomized controlled clinical trials. Am J Transplant 2013; 13: 1253–1261. [CrossRef]
- Percy C, Hassoun Z, Mourad M; et al. Impact of Acute Infection Requiring Hospitalization on Tacrolimus Blood Levels in Kidney Transplant Recipients. Transplant Proc 2017; 49: 2065–2069. [CrossRef]
- Ravaioli M, Neri F, Lazzarotto T, Bertuzzo VR, Di Gioia, P., Stacchini, G.; et al. Immunosuppression Modifications Based on an Immune Response Assay: Results of a Randomized, Controlled Trial. Transplantation 2015; 99: 1625-1632. [CrossRef]
- Jaksch P, Görzer I, Puchhammer-Stöckl, E., Bond, G. Integrated Immunologic Monitoring in Solid Organ Transplantation: The Road Toward Torque Teno Virus-guided Immunosuppression. Transplantation 2022; 106: 1940-1951. [CrossRef]
- Maggi F, Focosi D, Statzu M; et al. Early post-transplant torquetenovirus viremia predicts cytomegalovirus reactivations in solid organ transplant recipients. Sci Rep 2018; 8: 15490. [CrossRef]
- Herrmann A, Sandmann L, Adams O; et al. Role of BK polyomavirus (BKV) and Torque teno virus (TTV) in liver transplant recipients with renal impairment. J Med Microbiol 2018; 67: 1496-1508. [CrossRef]
- Strassl R, Schiemann M, Doberer K, Gorzer I, Puchhammer-Stockl, E., Eskandary, F.; et al. Quantification of torque Teno virus viremia as a prospective biomarker for infectious disease in kidney allograft recipients. J Infect Dis 2018; 218: 1191–1199. [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Ruiz M, Albert E, Gimenez E; et al. Monitoring of alphatorquevirus DNA levels for the prediction of immunosuppression related complications after kidney transplantation. Am J Transpl 2019; 19: 1139-1149. [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Ruiz M, Albert E, Gimenez E; et al. Early kinetics of Torque Teno virus DNA load and BK polyomavirus viremia after kidney transplantation. Transpl Infect Dis 2020; 22: e13240. [CrossRef]
- Solis M, Velay A, Gantner P; et al. Torquetenovirus viremia for early prediction of graft rejection after kidney transplantation. J Infect 2019; 79: 56-60. [CrossRef]
- Doberer K, Schiemann M, Strassl, R.; et al. Torque teno virus for risk stratification of graft rejection and infection in kidney transplant recipients—A prospective observational trial. Am J Transpl 2020; 20: 2081-2090. [CrossRef]
- Görzer I, Haupenthal F, Maggi F, Gelas F, Kulifaj D, Brossault, L.; et al. Validation of plasma Torque Teno viral load applying a CE-certified PCR for risk stratification of rejection and infection post kidney transplantation. J Clin Virol 2023; 158: 105348. [CrossRef]
- Schiemann M, Puchhammer-Stockl E, Eskandary F, Kohlbeck P, Rasoul-Rockenschaub, S., Heilos, A.; et al. Torque Teno virus load-inverse association with antibody-mediated rejection after kidney transplantation. Transplantation 2017;101: 360–7. [CrossRef]
- Strassl R, Doberer K, Rasoul-Rockenschaub, S.; et al. Torque teno virus for risk stratification of acute biopsy-proven alloreactivity in kidney transplant recipients. J Infect Dis 2019; 219: 1934-1939. [CrossRef]
- van Rijn AL, Wunderink HF, Sidorov IA; et al. Torque teno virus loads after kidney transplantation predict allograft rejection but not viral infection. J Clin Virol 2021; 140: 104871. [CrossRef]
- Doberer K, Haupenthal F, Nackenhorst M, Bauernfeind F, Dermuth F, Eigenschink.
- M; et al. Torque Teno Virus Load Is Associated With Subclinical Alloreactivity in Kidney Transplant Recipients: A Prospective Observational Trial. Transplantation 2021; 105: 2112-2118. [CrossRef]
- van Rijn AL, Roos R, Dekker FW, Rotmans JI, Feltkamp, M. Torque teno virus load as marker of rejection and infection in solid organ transplantation—A systematic review and meta-analysis. Rev Med Virol 2023; 33: e2393. [CrossRef]
- Görzer I, Haloschan M, Jaksch P, Klepetko W, Puchhammer-Stöckl, E. Plasma DNA levels of Torque teno virus and immunosuppression after lung transplantation. J Heart Lung Transplant 2014; 33: 320-323. [CrossRef]
- Focosi D, Macera L, Boggi U, Nelli LC, Maggi, F. Short-term kinetics of torque Teno virus viraemia after induction immunosuppression confirm T lymphocytes as the main replication-competent cells. J Gen Virol 2015; 96: 115–117. [CrossRef]
- Görzer I, Jaksch P, Kundi M, Seitz T, Klepetko W, Puchhammer-Stöckl, E. Pre-transplant plasma Torque Teno virus load and increase dynamics after lung transplantation. PLoS One 2015; 10: e0122975. [CrossRef]
- Metz DK, Holford N, Kausman JY, Walker A, Cranswick N, Staatz CE, Barraclough KA, Ierino, F. Optimizing Mycophenolic Acid Exposure in Kidney Transplant Recipients: Time for Target Concentration Intervention. Transplantation 2019; 103: 2012-2030. [CrossRef]
- Sharma A, Cherukuri A, Mehta RB, Sood, P., Hariharan, S. High Calcineurin Inhibitor Intrapatient Variability Is Associated With Renal Allograft Inflammation, Chronicity, and Graft Loss. Transplant Direct 2019; 5: e424. [CrossRef]
- Rayar M, Tron C, Jézéquel C, Beaurepaire JM, Petitcollin A, Houssel-Debry P; et al. High Intrapatient Variability of Tacrolimus Exposure in the Early Period After Liver Transplantation Is Associated with Poorer Outcomes. Transplantation 2018; 102: e108-e114. [CrossRef]
- Song T, Yin S, Jiang Y, Huang Z, Liu J, Wang Z; et al. Increasing Time in Therapeutic Range of Tacrolimus in the First Year Predicts Better Outcomes in Living-Donor Kidney Transplantation. Front Immunol 2019; 10: 2912. [CrossRef]
- Jouve T, Fonrose X, Noble J, Janbon B, Fiard G, Malvezzi P; et al. The TOMATO Study (Tacrolimus Metabolization in Kidney Transplantation): Impact of the Concentration-Dose Ratio on Death-censored Graft Survival. Transplantation 2020; 104: 1263-1271. [CrossRef]
- Pawinski T, Luszczynska P, Durlik M, Majchrzak J, Baczkowska T, Chrzanowska M; et al. Development and validation of limited sampling strategies for the estimation of mycophenolic acid area under the curve in adult kidney and liver transplant recipients receiving concomitant enteric-coated mycophenolate sodium and tacrolimus. Ther Drug Monit 2013; 35: 760-769. [CrossRef]
- Maggi F, Pifferi M, Fornai C, Andreoli E, Tempestini E, Vatteroni, M.; et al. TT virus in the nasal secretions of children with acute respiratory diseases: Relations to viremia and disease severity. J Virol 2003; 77: 2418-2425. [CrossRef]
- Maggi F, Fornai C, Vatteroni ML, Siciliano G, Menichetti F, Tascini, C.; et al. Low prevalence of TT virus in the cerebrospinal fluid of viremic patients with central nervous system disorders. J Med Virol 2001; 65: 418–422. [CrossRef]
- Pistello M, Morrica A, Maggi F, Vatteroni ML, Freer, G., Fornai, C.; et al. TT virus levels in the plasma of infected individuals with different hepatic and extrahepatic pathology. J Med Virol 2001; 63: 189-195.
- Forqué L, Fernández-Ruiz M, Albert E, Giménez E, Monzó C, Chaves, J.; et al. Dynamics of Human Anelloviruses in Plasma and Clinical Outcomes Following Kidney Transplantation. Transplantation 2023; 107: 511-520. [CrossRef]
- Handala L, Descamps V, Morel V, Castelain S, François C, Duverlie, G.; et al. No correlation between Torque Teno virus viral load and BK virus replication after kidney transplantation. J Clin Virol 2019; 116: 4-6. [CrossRef]
- Gore EJ, Gomes-Neto AW, Wang L, Bakker SJL, Niesters HGM, de Joode AAE; et al. Torquetenovirus Serum Load and Long-Term Outcomes in Renal Transplant Recipients. J Clin Med 2020; 9: 440. [CrossRef]
- Kulifaj D, Durgueil-Lariviere B, Meynier F, Munteanu E, Pichon N, Dubé M; et al. Development of a standardized real time PCR for Torque teno viruses (TTV) viral load detection and quantification: A new tool for immune monitoring. J Clin Virol 2018; 105: 118-127. [CrossRef]
- Haupenthal F, Rahn J, Maggi F, Gelas F, Bourgeois P, Hugo C, et al.; TTVguideTX consortium partners. A multicentre, patient- and assessor-blinded, non-inferiority, randomised and controlled phase II trial to compare standard and torque teno virus-guided immunosuppression in kidney transplant recipients in the first year after transplantation: TTVguideIT. Trials 2023; 24: 213. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).