Submitted:
18 April 2023
Posted:
19 April 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Models
2.1. Classical methods
2.2. New methodology
2.2.1. Molecular models
2.2.2. Hamieh’s thermal model
2.2.3. The new Lewis’s acid base parameters
3. Materials and solvents
3. Results
3.1. Determination of the Gibbs free energy of adsorption
3.2. London dispersive surface energy of alumina particles
3.2. Surface thermodynamic of alumina particles
3.2.1. The Gibbs specific free energy of adsorption
3.2.2. Lewis’s acid base parameters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
| Polar molecule | (kJ/mol) | ||
| CCl4 | = -0.021 T + 12.489 | 12.489 | 21 |
| CH2Cl2 | = -0.135 T + 83.700 | 83.700 | 135 |
| CHCl3 | = -0.136 T + 65.871 | 65.871 | 136 |
| Diethyl ether | = -0.088 T + 68.367 | 68.367 | 88 |
| THF | = -0.071 T + 53.71 | 53.71 | 71 |
| Toluene | = -0.041 T + 21.91 | 21.91 | 41 |
Supplementary Materials
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pyda, M.; Guiochon, G. Surface properties of silica-based adsorbents measured by inverse gas–solid chromatography at finite concentration. Langmuir 1997, 13, 1020–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brendlé, E.; Papirer, E. A New Topological Index for Molecular Probes Used in Inverse Gas Chromatography for the Surface Nanorugosity Evaluation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1997, 194, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thielmann, F.; Baumgarten, E. Characterization of Microporous Aluminas by Inverse Gas Chromatography. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2000, 229, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onjia, A.E.; Milonjić, S.K.; Todorović, M.; Loos-Neskovic, C.; Fedoroff, M.; Jones, D.J. An Inverse Gas Chromatography Study of the Adsorption of Organics on Nickel- and Copper-Hexacyanoferrates at Zero Surface Coverage. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 251, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conder, J.R.; Locke, D.C.; Purnell, J.H. Concurrent solution and adsorption phenomena in chromatography. I. J. Phys. Chem. 1969, 73, 700–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conder, J.R.; Purnell, J.H. Gas chromatography at finite concentrations. Part 2.—A generalized retention theory. Trans Faraday Soc. 1968, 64, 3100–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conder, J.R.; Purnell, J.H. Gas chromatography at finite concentrations. Part 3.—Theory of frontal and elution techniques of thermodynamic measurement. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1969, 65, 824–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conder, J.R.; Purnell, J.H. Gas chromatography at finite concentrations. Part 4.—Experimental evaluation of methods for thermodynamic study of solutions. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1969, 65, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conder, J.R.; Purnell, J.H. Gas chromatography at finite concentrations. Part 1.—Effect of gas imperfection on calculation of the activity coefficient in solution from experimental data. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1968, 64, 1505–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papirer, E.; Balard, H.; Rahmani, Y.; Legrand, A.P.; Facchini, L.; Hommel, H. Characterization by inverse gas chromatography of the surface properties of silicas modified by poly(ethylene glycols) and their models (oligomers, diols). Chromatographia 1987, 23, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, A.; Papirer, E.; Jiao, W.M.; Donnet, J.B. Modification of silica surfaces by grafting of alkyl chains. I — Characterization of silica surfaces by inverse gas-solid chromatography at zero surface coverage. Chromatographia 1987, 23, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flour, C.S.; Papirer, E. Gas-solid chromatography. A method of measuring surface free energy characteristics of short glass fibers. 1. Through adsorption isotherms. Ind. Eng. Chem. Prod. Res. Dev. 1982, 21, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flour, C.S.; Papirer, E. Gas-solid chromatography: method of measuring surface free energy characteristics of short fibers. 2. Through retention volumes measured near zero surface coverage. Ind. Eng. Chem. Prod. Res. Dev. 1982, 21, 666–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papirer, E.; Balard, H.; Vidal, A. Inverse gas chromatography: A valuable method for the surface characterization of fillers for polymers (glass fibres and silicas). Eur. Polym. J. 1988, 24, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voelkel, A. Inverse Gas Chromatography: Characterization of Polymers, Fibers, Modified Silicas, and Surfactants. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 1991, 22, 411–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, R.H.; Graeter, H.; Cantow, H.J. Thermodynamic studies on polystyrene-solvent systems by gas chromatography. Macromolecules 1984, 17, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öner, M.; Dinçer, S. Thermophysical properties of polymer-probe pairs by gas chromatography. Polymer 1987, 28, 279–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillet, J. E.; Romansky, M.; Price, G.J.; Van der Mark, R. Studies of polymer structure and interactions by automated inverse gas chromatography. Inverse gas chromatography. 1989, Washington, DC: Characterization of Polymers and Other Materials, American Chemical Society 20–32. Eng. Asp. 2002, 206, 547–554. [Google Scholar]
- Katsanos, N.A.; Gavril, D.; Kapolos, J.; Karaiskakis, G. Surface energy of solid catalysts measured by inverse gas chromatography. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 270, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balard, H.; Brendlé, E.; Papirer, E. Determination of the acid–base properties of solid surfaces using inverse gas chromatography: advantages and limitations. In: Mittal, K.L., Editor. Acid–Base Interactions, Relevance to Adhesion Science and Technology. Vol. 2: CRC Press; 2000. p. 299–316.
- Kemball, C.; Rideal, E.K. The adsorption of vapours on mercury. I. Non-polar substances. Proc. R. Soc. London. Ser. A. Math. Phys. Sci. 1946, 187, 53–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onjia, A.E.; Milonjić, S.K.; Todorović, M.; Loos-Neskovic, C.; Fedoroff, M.; Jones, D.J. An Inverse Gas Chromatography Study of the Adsorption of Organics on Nickel- and Copper-Hexacyanoferrates at Zero Surface Coverage. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 251, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnet, J.-B.; Ridaoui, H.; Balard, H.; Barthel, H.; Gottschalk-Gaudig, T. Evolution of the surface polar character of pyrogenic silicas, with their grafting ratios by dimethylchlorosilane, studied by microcalorimetry. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 325, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papirer, E.; Brendlé, E.; Balard, H.; Dentzer, J. Variation of the surface properties of nickel oxide upon heat treatment evidenced by temperature programmed desorption and inverse gas chromatography studies. J. Mater. Sci. 2000, 35, 3573–3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, M.; Rubio, J.; Rubio, F.; Liso, M.; Oteo, J. Application of inverse gas chromatography to the study of the surface properties of slates. Clays Clay Miner. 1997, 45, 670–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przybyszewska, M.; Krzywania, A.; Zaborski, M.; Szynkowska, M.I. Surface properties of zinc oxide nanoparticles studied by inverse gas chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 5284–5291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Heng, J.; Nikolaev, A.; Waters, K. Introducing inverse gas chromatography as a method of determining the surface heterogeneity of minerals for flotation. Powder Technol. 2013, 249, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Bertóti, I.; Pukánszky, B.; Rosa, R.; Lazzeri, A. Structure and surface coverage of water-based stearate coatings on calcium carbonate nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 362, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi-Jam, S.; Burnett, D.; Waters, K. Surface energy of minerals – Applications to flotation. Miner. Eng. 2014, 66-68, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daoui, H.; Boutoumi, H.; Bouhamidi, Y.; Boucherit, A.; Zouikri, M. Characterization of an Algerian diatomite by inverse gas chromatography: Specific and non-specific contribution and Lewis acid–base parameters. Int. J. Polym. Anal. Charact. 2018, 23, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shui, M.; Reng, Y.; Pu, B.; Li, J. Variation of surface characteristics of silica-coated calcium carbonate. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 273, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rückriem, M.; Inayat, A.; Enke, D.; Gläser, R.; Einicke, W.-D.; Rockmann, R. Inverse gas chromatography for determining the dispersive surface energy of porous silica. Colloids Surfaces A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2010, 357, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnet, J.-B.; Balard, H.; Nedjari, N.; Hamdi, B.; Barthel, H.; Gottschalk-Gaudig, T. Influence of specific surface area of pyrogenic silicas on their heat of immersion in water and on their surface properties assessed using inverse gas chromatography. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 328, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandosz, T.J.; Putyera, K.; Jagiełło, J.; Schwarz, J.A. Application of inverse gas chromatography to the study of the surface properties of modified layered minerals. Microporous Mater. 1993, 1, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamieh, T.; Rezzaki, M.; Grohens, Y.; Schultz, J. Glass transition of adsorbed stereoregular PMMA by inverse gas chromatography at infinite dilution, J. Chim. Phys., 1998, 95, 1964–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudriche, L.; Chamayou, A.; Calvet, R.; Hamdi, B.; Balard, H. Influence of different dry milling processes on the properties of an attapulgite clay, contribution of inverse gas chromatography. Powder Technol. 2014, 254, 352–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, F.; Meyer, R.; Czihal, S.; Bertmer, M.; Decker, U.; Naumov, S.; Uhlig, H.; Steinhart, M.; Enke, D. Functionalization of porous siliceous materials, Part 2: Surface characterization by inverse gas chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1603, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Wu, D.; Heng, J.Y.; Lanceros-Méndez, S.; Hadjittofis, E.; Su, W.; Tang, J.; Zhao, H.; Wu, W. Comparative study of surface properties determination of colored pearl-oyster-shell-derived filler using inverse gas chromatography method and contact angle measurements. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2017, 78, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rueckriem, M.; Hahn, T.; Enke, D. Inverse gas chromatographic studies on porous glass, Opt. Appl. 2012, 42, 295–306. [Google Scholar]
- Batko, K.; Voelkel, A. Inverse gas chromatography as a tool for investigation of nanomaterials. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 315, 768–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, D.; Xu, P.; Wang, C.; Du, Q. Characterizing the surface properties of carbon nanotubes by inverse gas chromatography. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 7069–7075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demertzis, P.G.; Riganakos, K.A.; Kontominas, M.G. Water sorption isotherms of crystalline raffinose by inverse gas chromatography. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 1989, 24, 629–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helen, H.J.; Gilbert, S.G. Moisture Sorption of Dry Bakery Products by Inverse Gas Chromatography. J. Food Sci. 2006, 50, 454–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzel, R.; Bismarck, A.; Shaffer, M.S. Deconvolution of the structural and chemical surface properties of carbon nanotubes by inverse gas chromatography. Carbon 2012, 50, 3416–3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzel, R.; Lee, A.; Bismarck, A.; Shaffer, M.S.P. Inverse Gas Chromatography of As-Received and Modified Carbon Nanotubes. Langmuir 2009, 25, 8340–8348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, Y.-H.; Li, M.-S. Adsorption of selected volatile organic vapors on multiwall carbon nanotubes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 154, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamble, J.F.; Davé, R.N.; Kiang, S.; Leane, M.M.; Tobyn, M.; Wang, S.S. Investigating the applicability of inverse gas chromatography to binary powdered systems: An application of surface heterogeneity profiles to understanding preferential probe-surface interactions. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 445, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.D.; Young, P.; Traini, D. The use of inverse gas chromatography for the study of lactose and pharmaceutical materials used in dry powder inhalers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimsey, I.M.; Feeley, J.C.; York, P. Analysis of the surface energy of pharmaceutical powders by inverse gas chromatography. J. Pharm. Sci. 2002, 91, 571–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Shalaev, E.; Smith, S. Solid-state analysis and amorphous dispersions in assessing the physical stability of pharmaceutical formulations, Trends Anal. Chem., 2013, 49, 137–144. [Google Scholar]
- Chamarthy, S.P. The different roles of surface and bulk effects on the functionality of pharmaceutical materials, Thesis, 2007, Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana. Available online: https://www.proquest.com/docview/304841067.
- Zhang, D.; Flory, J.H.; Panmai, S.; Batra, U.; Kaufman, M.J. Wettability of pharmaceutical solids: its measurement and influence on wet granulation. Colloids Surfaces A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2002, 206, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.C.; Stewart, P.J. Characterising surface energy of pharmaceutical powders by inverse gas chromatography at finite dilution. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2012, 64, 1337–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Telko, M.J.; Hickey, A.J. Critical Assessment of Inverse Gas Chromatography as Means of Assessing Surface Free Energy and Acid–Base Interaction of Pharmaceutical Powders. J. Pharm. Sci. 2007, 96, 2647–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Autie-Pérez, M.; Infantes-Molina, A.; Cecilia, J.A.; Labadie-Suarez, J.M.; Fernández-Echevarría, H.; Santamaría-González, J.; Rodríguez-Castellón, E. LIGHT N-PARAFFINS SEPARATION BY INVERSE GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY WITH CUBAN VOLCANIC GLASS. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 36, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras-Larios, J.L.; Infantes-Molina, A.; Negrete-Melo, L.A.; Labadie-Suárez, J.M.; Yee-Madeira, H.T.; Autie-Pérez, M.A.; Rodríguez-Castellón, E. Separation of N–C5H12–C9H20 Paraffins Using Boehmite by Inverse Gas Chromatography. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conder, J.R.; Young, C.L. Physical measurements by gas chromatography. 1979, Eds: Wiley J and Sons, New York.
- Donnet, J.-B.; Qin, R.-Y. Empirical estimation of surface energies of polymers and their temperature dependence. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1992, 154, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chehimi, M.M.; Pigois-Landureau, E. Determination of acid–base properties of solid materials by inverse gas chromatography at infinite dilution. A novel empirical method based on the dispersive contribution to the heat of vaporization of probes, J. Mater. Chem. 1994, 4, 741–745. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, B. Problem in the molecular area of polar probe molecules used in inverse gas chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1601, 385–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Berg, J.C. The effective surface energy of heterogeneous solids measured by inverse gas chromatography at infinite dilution. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 260, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutmann, V. The Donor-Acceptor Approach to Molecular Interactions; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: Dordrecht, GX, Netherlands, 1978; ISBN 9781461588252. [Google Scholar]
- Papirer, E.; Brendlé, E.; Balard, H.; Ozil, F. IGC determination of surface properties of fullerenes: comparison with other carbon materials. Carbon 1999, 37, 1265–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamieh, T.; Fadlallah, M.-B.; Schultz, J. New approach to characterise physicochemical properties of solid substrates by inverse gas chromatography at infinite dilution. III. Determination of the acid-base properties of some solid substrates (polymers, oxides and carbon fibres): a new model. J. Chromatogr. A. 2002, 969, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoss, D.J.; Knepper, R.; Hotchkiss, P.J.; Tappan, A.S.; Boudouris, B.W.; Beaudoin, S.P. An evaluation of complementary approaches to elucidate fundamental interfacial phenomena driving adhesion of energetic materials. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 473, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Berg, J.C. The effective surface energy of heterogeneous solids measured by inverse gas chromatography at infinite dilution. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 260, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margariti, S.; Bassiotis, I.; Roubani-Kalantzopoulou, F. Physicochemical characterization of interfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 274, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fekete, E.; Móczó, J.; Pukánszky, B. Determination of the surface characteristics of particulate fillers by inverse gas chromatography at infinite dilution: a critical approach. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 269, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamieh, T. Study of the temperature effect on the surface area of model organic molecules, the dispersive surface energy and the surface properties of solids by inverse gas chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1627, 461372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawyer, D.T.; Brookman, D.J. Thermodynamically based gas chromatographic retention index for organic molecules using salt-modified aluminas and porous silica beads. Anal. Chem. 1968, 40, 1847–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorris, G.M.; Gray, D.G. Adsorption of normal-alkanes at zero surface coverage on cellulose paper and wood fibers. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science. 1980, 77, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowkes, F.M. in: Surface and interfacial aspects of biomedical polymers, 1985, Vol. I, pp. 337-372, Ed: Andrade, J. D., Plenum Press, New York.
- Schultz, J.; Lavielle, L.; Martin, C. The Role of the Interface in Carbon Fibre-Epoxy Composites. J. Adhes. 1987, 23, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamieh, T.; Schultz, J. Étude par chromatographie gazeuse inverse de l’influence de la température sur l’aire de molécules adsorbées. J. de Chim. Phys. et de Physico-Chimie Biol. 1996, 93, 1292–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamieh, T.; Schultz, J. Study of the adsorption of n-alkanes on polyethylene surface - State equations, molecule areas and covered surface fraction, Comptes Rendus de l’Académie des Sciences. Série IIb 1996, 323, 281–289. [Google Scholar]
- Hamieh, T.; Schultz, J. A new method of calculation of polar molecule area adsorbed on MgO and ZnO by inverse gas chromatography, Comptes Rendus de l’Académie des Sciences. Série IIb 1996, 322, 627–633. [Google Scholar]
- Hamieh, T.; Rezzaki, M.; Schultz, J. Study of the Second Order Transitions and Acid–Base Properties of Polymers Adsorbed on Oxides by Using Inverse Gas Chromatography at Infinite Dilution. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2001, 233, 339–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamieh, T.; Rezzaki, M.; Schultz, J. Study of the transition temperatures and acid-base properties of poly (methyl methacrylate) adsorbed on alumina and silica, by using inverse gas chromatography technique. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects 2001, 189, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamieh, T.; Schultz, J. New approach to characterise physicochemical properties of solid substrates by inverse gas chromatography at infinite dilution. Journal of Chromatography A 2002, 969, 17–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnet, J.B.; Park, S.J.; Balard, H. Evaluation of specific interactions of solid surfaces by inverse gas chromatography. Chromatographia 1991, 31, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamieh, T.; Rezzaki, M.; Schultz, J. Study of the Second Order Transitions and Acid–Base Properties of Polymers Adsorbed on Oxides by Using Inverse Gas Chromatography at Infinite Dilution: II. Experimental Results. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2001, 233, 343–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riddle, F.L.; Fowkes, F.M. Spectral shifts in acid-base chemistry. 1. van der Waals contributions to acceptor numbers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1990, 112, 3259–3264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamieh, T. New Methodology to Study the Dispersive Component of the Surface Energy and Acid–Base Properties of Silica Particles by Inverse Gas Chromatography at Infinite Dilution. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2021, 60, 126–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
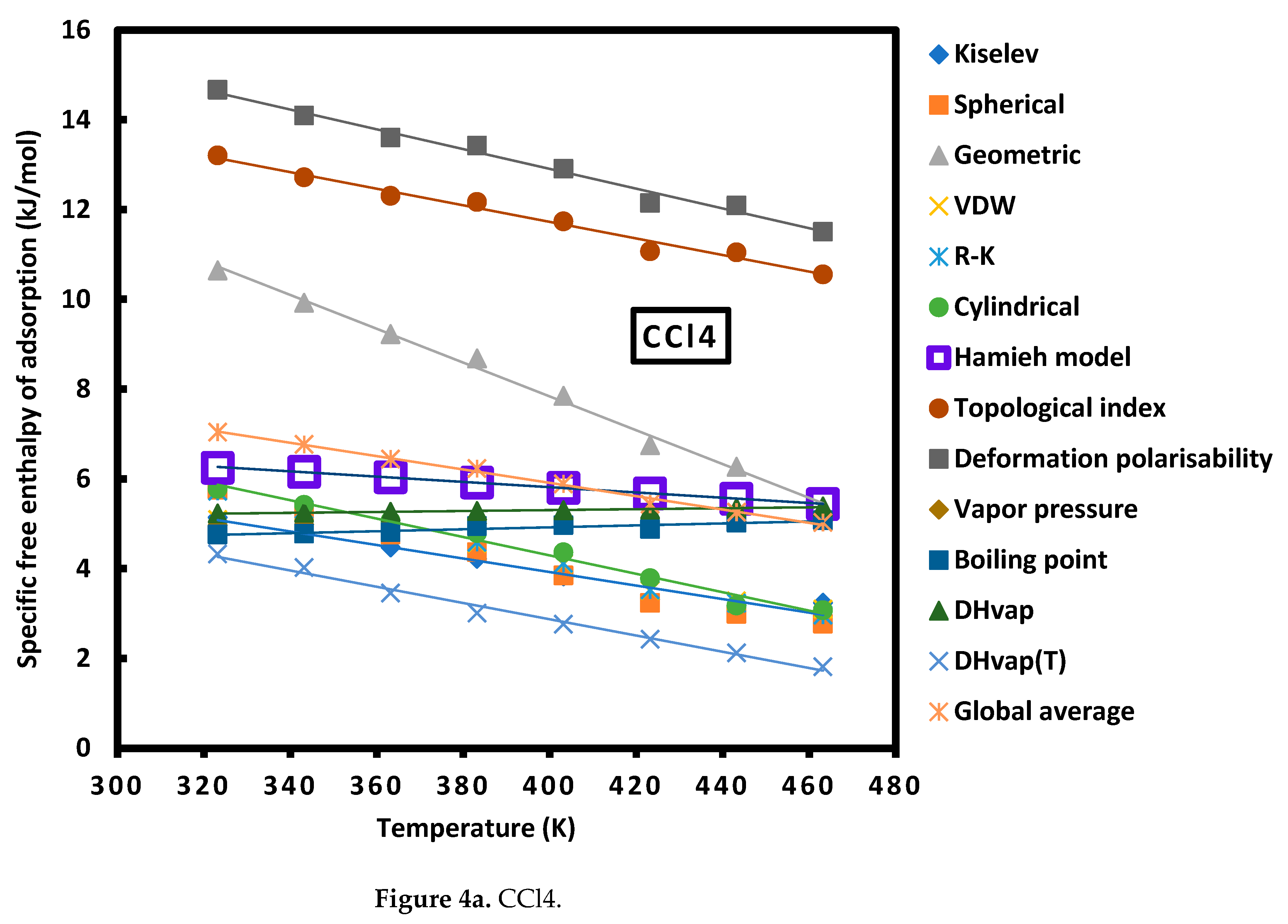
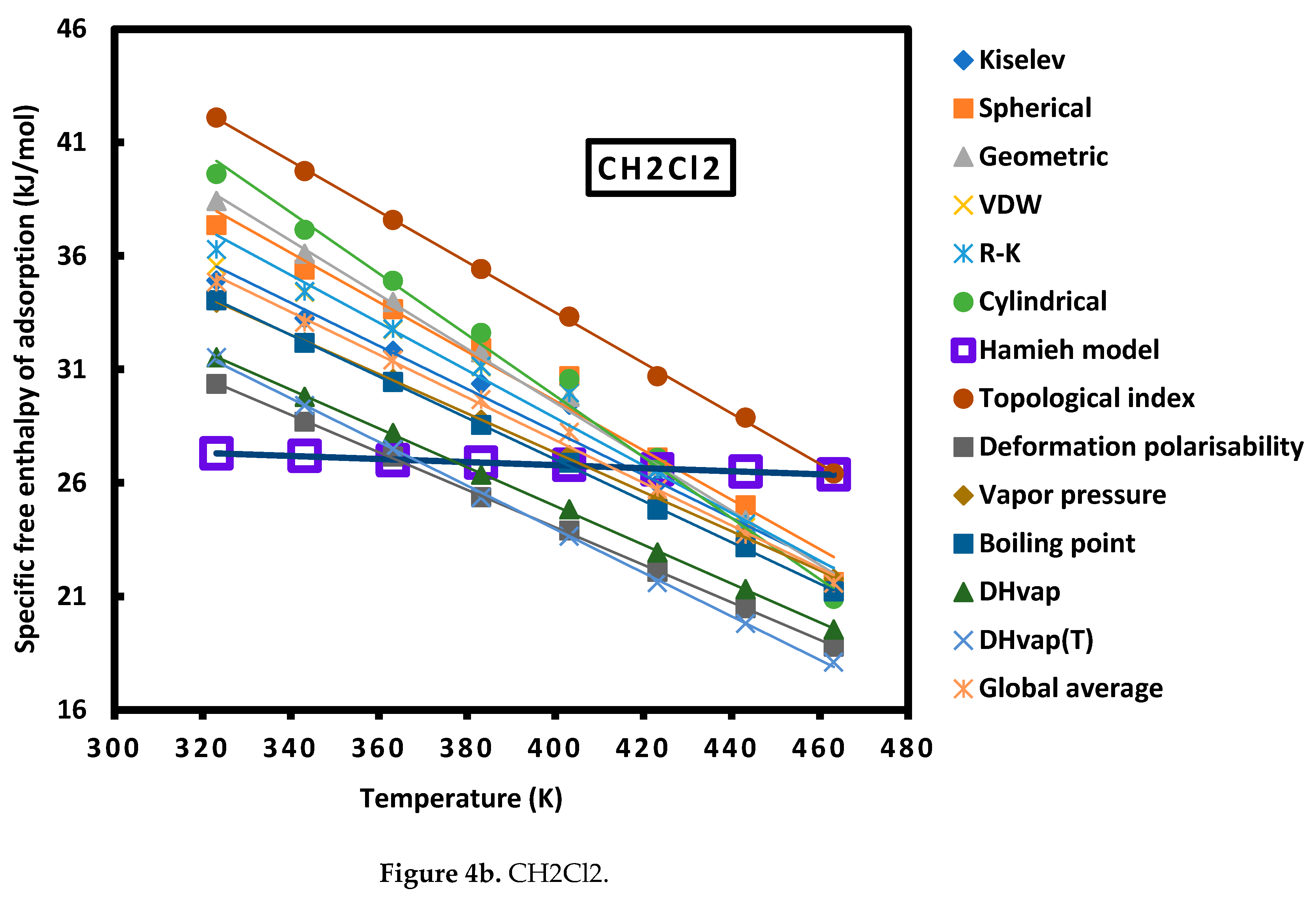
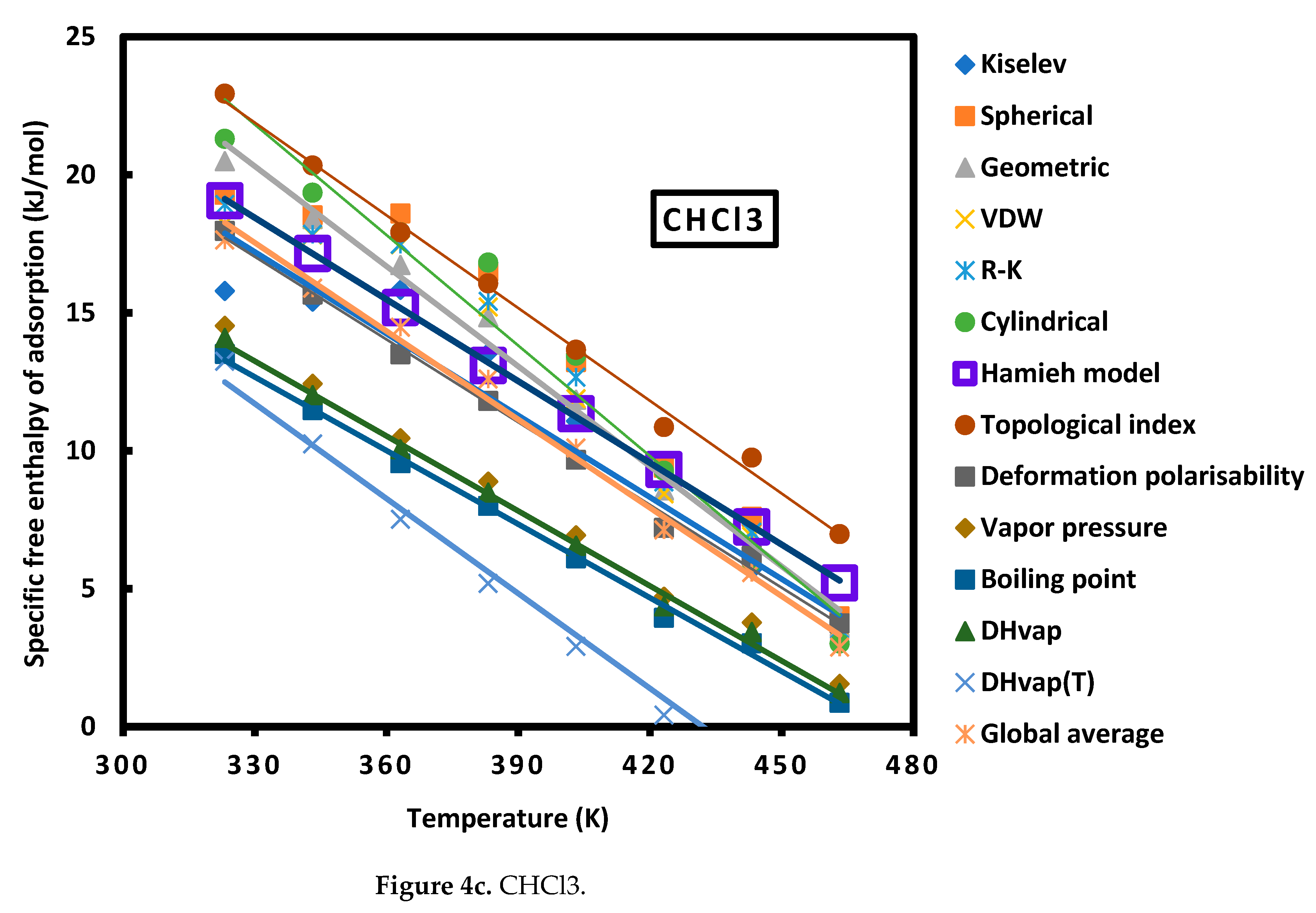
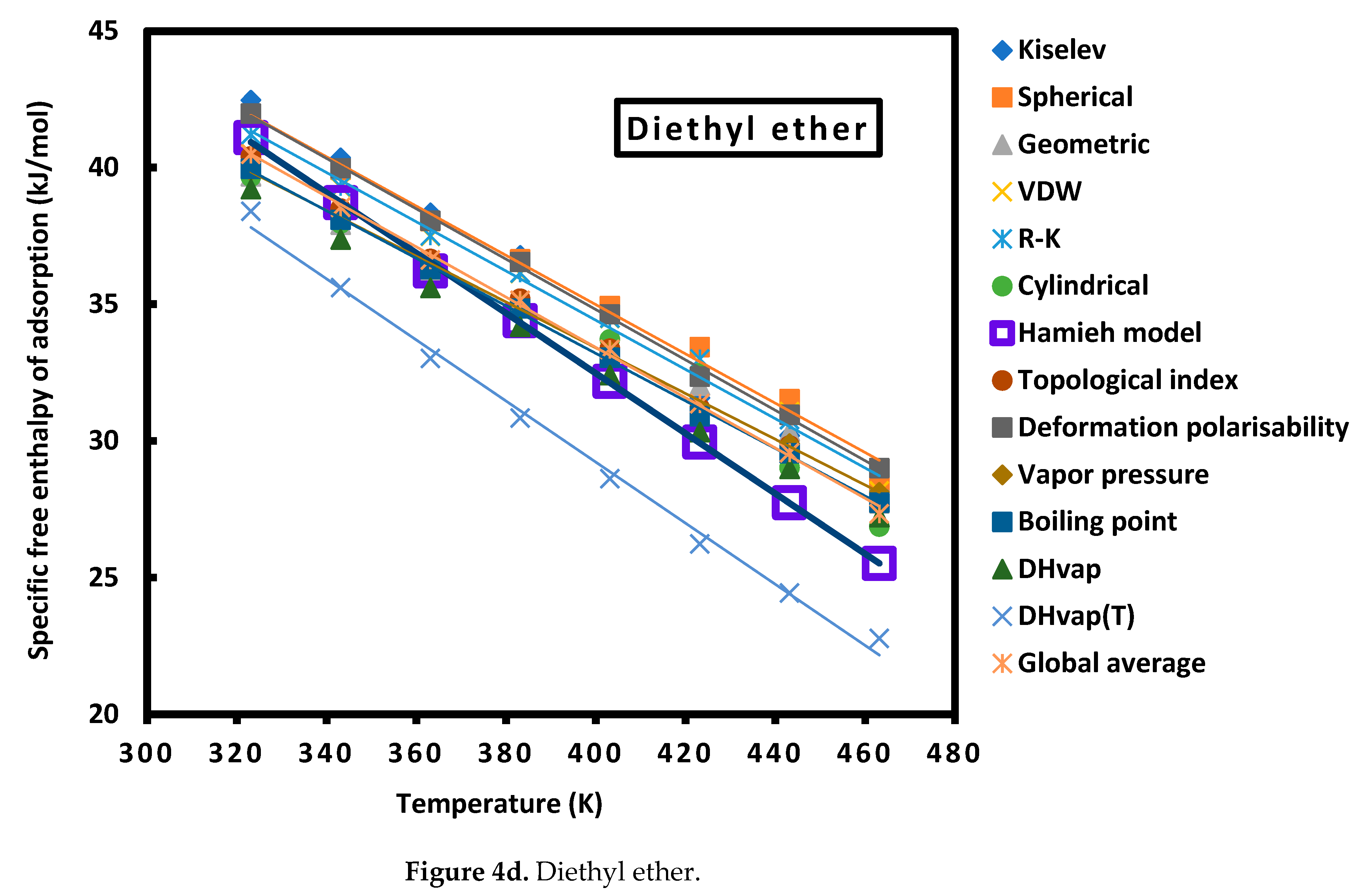
| Cn | Sph. | Geom. | R-K | Cyl. | Kiselev | VDW |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C5 | 36.4 | 32.9 | 36.8 | 39.3 | 45 | 47 |
| C6 | 39.6 | 40.7 | 41.3 | 45.5 | 51.5 | 52.7 |
| C7 | 42.7 | 48.5 | 46.4 | 51.8 | 57 | 59.2 |
| C8 | 45.7 | 56.2 | 50.8 | 58.1 | 63 | 64.9 |
| C9 | 48.7 | 64 | 54.5 | 64.4 | 69 | 69.6 |
| C10 | 51.7 | 71.8 | 58.2 | 70.7 | 75 | 74.4 |
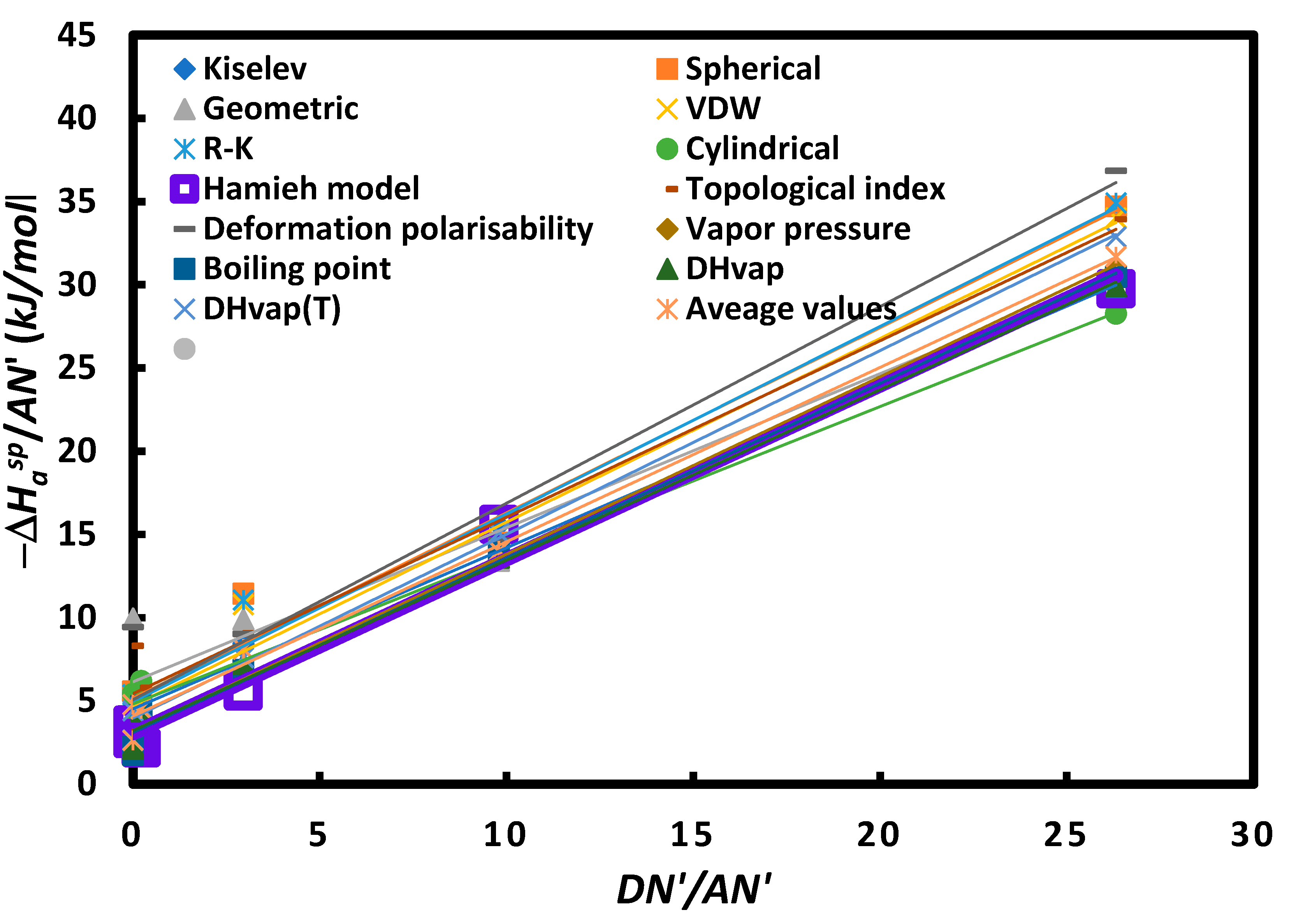
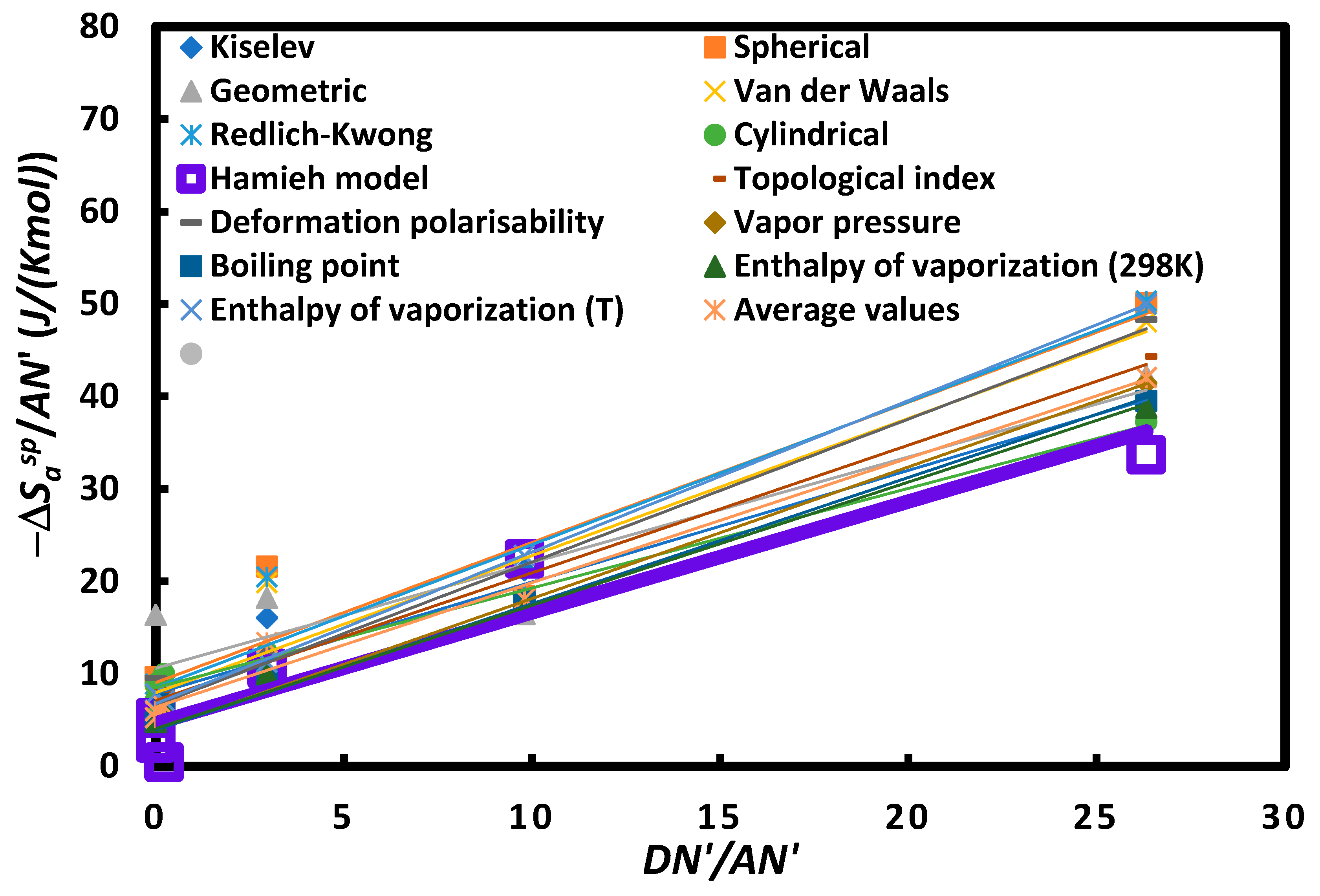
| Probes | DN’ | AN’ | DN’/AN’ | Acid base force |
| CCl4 | 0 | 2.3 | 0 | acid |
| CHCl3 | 0 | 18.7 | 0 | Stronger acidity |
| CH2Cl2 | 3 | 13.5 | 0.2 | weaker amphoteric |
| Toluene | 9.75 | 3.3 | 3.0 | Amphoteric |
| Diethyl ether | 48 | 4.9 | 9.8 | Amphoteric |
| THF | 50 | 1.9 | 26.3 | Stronger Basicity |
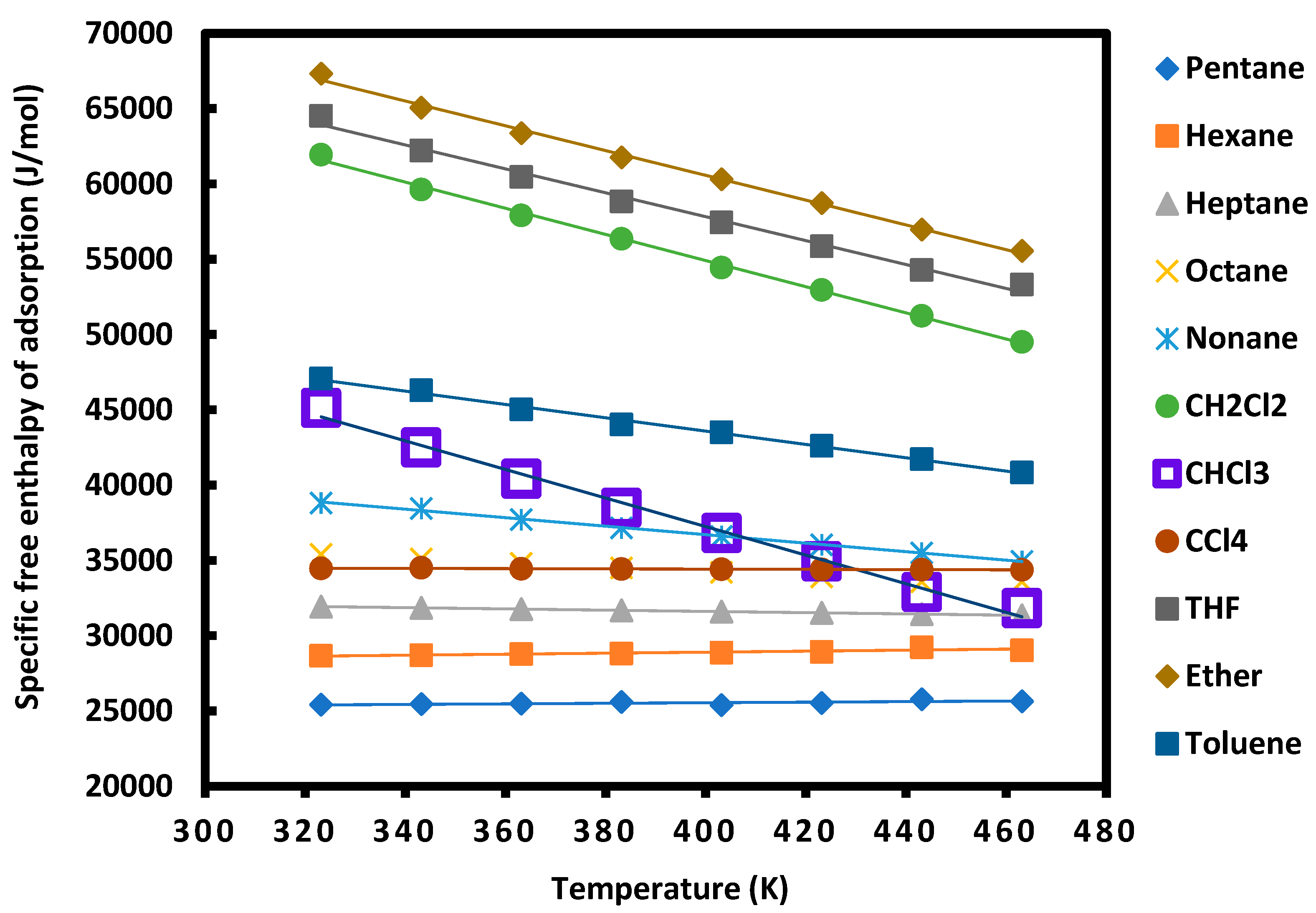
| T(K) | 303.15 | 323.15 | 343.15 | 363.15 | 383.15 | 403.15 | 423.15 | 443.15 | 463.15 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pentane | 25430 | 25461 | 25493 | 25609 | 25397 | 25538 | 25784 | 25651 | 25682 |
| Hexane | 28674 | 28716 | 28776 | 28827 | 28878 | 28929 | 29241 | 29032 | 29349 |
| Heptane | 31940 | 31857 | 31774 | 31692 | 31609 | 31527 | 31444 | 31361 | 31123 |
| Octane | 35420 | 35117 | 34813 | 34510 | 34207 | 33904 | 33601 | 33604 | 32995 |
| Nonane | 38821 | 38467 | 37716 | 37163 | 36611 | 36058 | 35506 | 34953 | 34401 |
| CH2Cl2 | 61952 | 59637 | 57919 | 56367 | 54442 | 52966 | 51248 | 49509 | 47769 |
| CHCl3 | 45147 | 42524 | 40448 | 38512 | 36838 | 34950 | 32911 | 31850 | 29664 |
| CCl4 | 34479 | 34514 | 34449 | 34435 | 34420 | 34405 | 34391 | 34376 | 34361 |
| THF | 64519 | 62228 | 60464 | 58838 | 57449 | 55865 | 54281 | 53324 | 51507 |
| Ether | 67319 | 65062 | 63377 | 61763 | 60317 | 58729 | 56976 | 55555 | 53967 |
| Toluene | 47084 | 46302 | 45020 | 44028 | 43511 | 42617 | 41724 | 40831 | 39937 |
| Probes | R² | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pentane | 26284 | 2.2 | = -2.2T + 26284 | 0.9967 |
| Hexane | 30423 | 4.5 | = -4.5T + 30423 | 0.9967 |
| Heptane | 33192 | 4.1 | = -4.1T + 33192 | 1.0000 |
| Octane | 40094 | 15.4 | = -15.4T + 40094 | 0.9989 |
| Nonane | 47409 | 28.1 | = -28.1T + 47409 | 0.9985 |
| CCl4 | 34696 | 0.7 | = -0.7T + 34696 | 0.9991 |
| CHCl3 | 72931 | 93.8 | = -93.8T + 72931 | 0.9949 |
| CH2Cl2 | 87807 | 86.6 | = -86.6T + 87807 | 0.9985 |
| Toluene | 60493 | 44.4 | = -44.4T + 60493 | 0.9978 |
| THF | 86959 | 76.8 | = -76.8T + 86959 | 0.9970 |
| Ether | 91555 | 81.5 | = -81.5T + 91555 | 0.9976 |
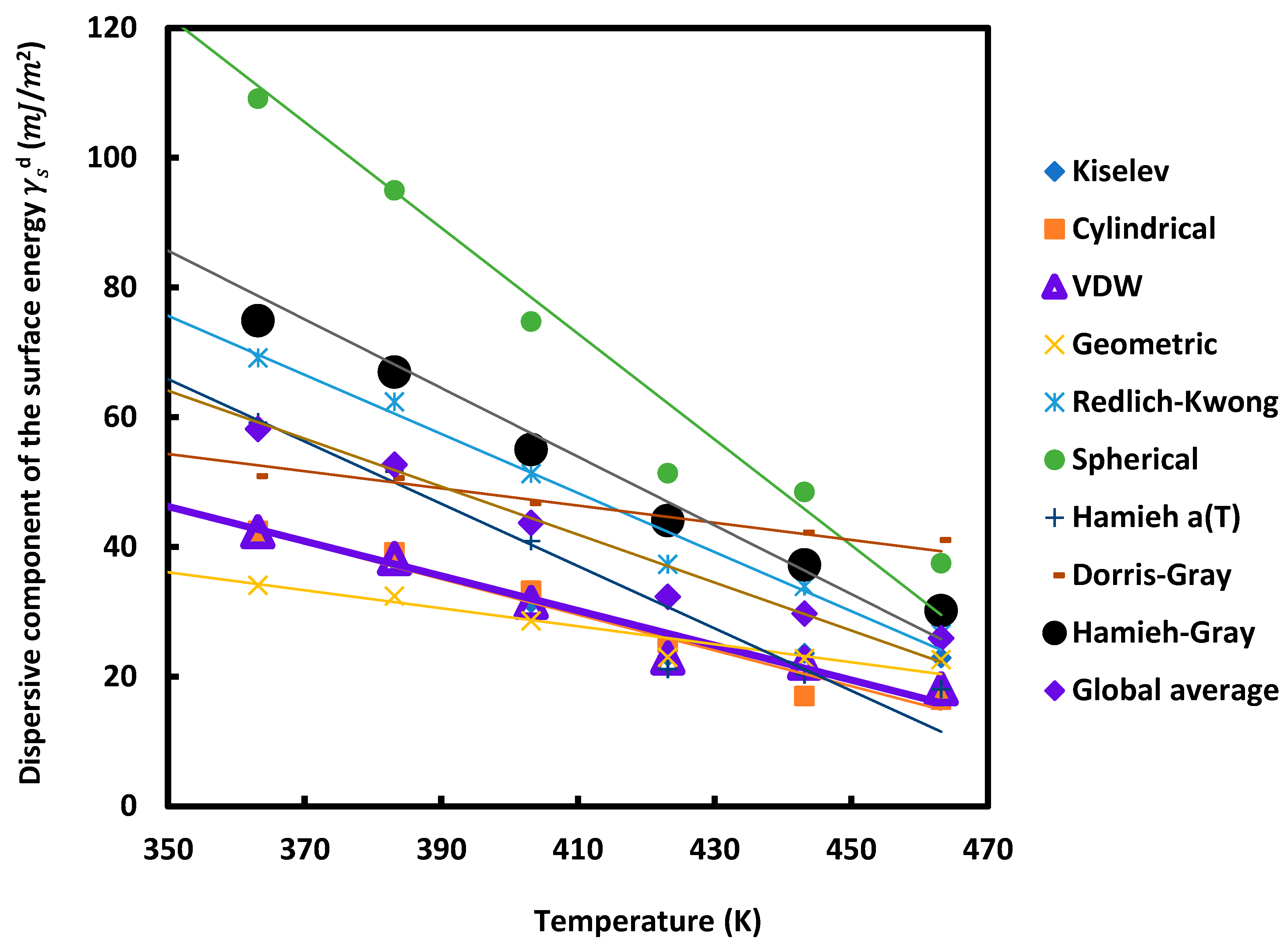
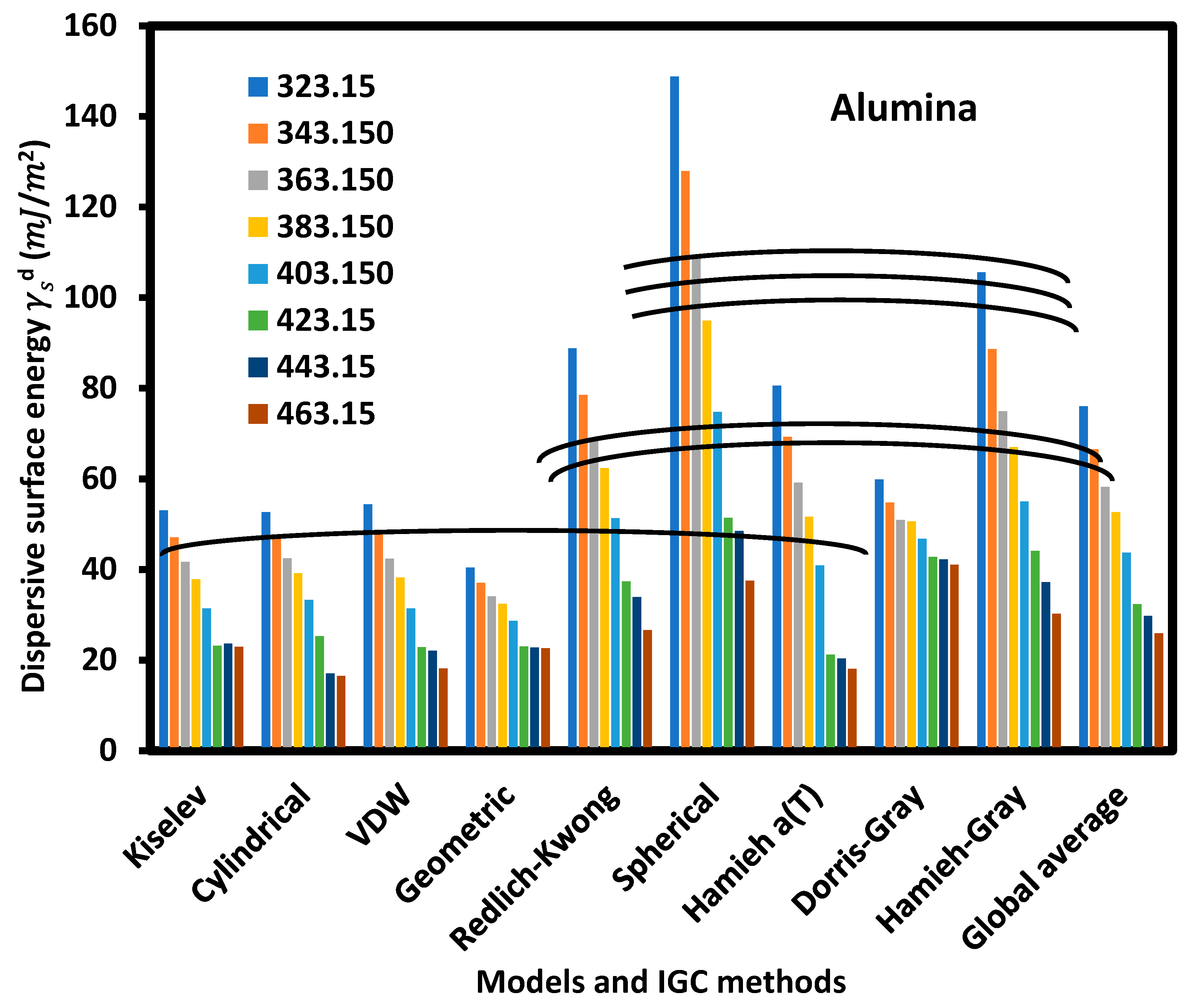
| (alumina) | ||||||||
| T (K) | 323.15 | 343.15 | 363.15 | 383.15 | 403.15 | 423.15 | 443.15 | 463.15 |
| Kiselev | 53.0 | 47.1 | 41.7 | 37.8 | 31.4 | 23.2 | 23.6 | 22.9 |
| Cylindrical | 52.6 | 47.3 | 42.4 | 39.2 | 33.2 | 25.2 | 17.0 | 16.4 |
| VDW | 54.4 | 48.1 | 42.3 | 38.2 | 31.4 | 22.9 | 22.1 | 18.1 |
| Geometric | 40.4 | 37.0 | 34.1 | 32.4 | 28.6 | 23.0 | 22.8 | 22.6 |
| Redlich-Kwong | 88.8 | 78.5 | 69.1 | 62.3 | 51.3 | 37.3 | 33.9 | 26.6 |
| Spherical | 148.8 | 127.9 | 109.1 | 95.0 | 74.7 | 51.4 | 48.5 | 37.5 |
| Hamieh a(T) | 80.6 | 69.3 | 59.2 | 51.6 | 40.9 | 21.2 | 20.4 | 18.1 |
| Dorris-Gray | 59.8 | 54.8 | 50.9 | 50.6 | 46.8 | 42.8 | 42.2 | 41.1 |
| Hamieh-Gray | 105.6 | 88.7 | 74.9 | 67.0 | 55.0 | 44.1 | 37.2 | 30.2 |
| Global average | 76.0 | 66.5 | 58.2 | 52.7 | 43.7 | 32.3 | 29.7 | 25.9 |
| Molecular model | (mJ/m2) | (mJ m-2 K-1) | (mJ/m2) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kiselev | = -0.232T + 126.4 | -0.232 | 126.4 | 544.36 |
| Cylindrical | = -0.275T + 142.3 | -0.275 | 142.3 | 517.41 |
| VDW | = -0.2674T + 139.8 | -0.267 | 139.8 | 522.89 |
| Geometric | = -0.138T + 84.6 | -0.139 | 84.6 | 610.58 |
| Redlich-Kwong | = -0.455T + 235.1 | -0.456 | 235.1 | 516.05 |
| Spherical | = -0.815T + 407.2 | -0.815 | 407.2 | 499.39 |
| Hamieh model | = 0.480T + 233.9 | -0.480 | 233.9 | 487.21 |
| Dorris-Gray | = -0.132T + 100.7 | -0.133 | 100.7 | 760.08 |
| Hamieh-Gray | = -0.500T + 271.0 | -0.530 | 271.0 | 511.78 |
| Global average | = -0.370T + 141.2 | -0.370 | 193.4 | 523.42 |
| Model or method | Polar solvent | Equation(kJ/mol) |
| Kiselev | CCl4 | = -0.015 T + 9.951 |
| CHCl3 | = -0.0950 T + 66.196 | |
| CH2Cl2 | = -0.099 T + 49.816 | |
| Diethyl ether | = -0.104 T + 76.237 | |
| THF | = -0.073 T + 55.663 | |
| Toluene | = -0.053 T + 27.836 | |
| Spherical | CCl4 | = -0.022 T + 12.846 |
| CHCl3 | = -0.109 T + 73.138 | |
| CH2Cl2 | = -0.115 T + 58.418 | |
| Diethyl ether | D= -0.090 T + 71.08 | |
| THF | = -0.095 T + 65.952 | |
| Toluene | = -0.071 T + 37.748 | |
| Geometric | CCl4 | = -0.038 T + 22.904 |
| CHCl3 | = -0.119 T + 77.161 | |
| CH2Cl2 | = -0.121 T + 60.18 | |
| Diethyl ether | = -0.081 T + 65.801 | |
| THF | = -0.080 T + 59.029 | |
| Toluene | = -0.060 T + 32.654 | |
| Vand der Waals (VDW) | CCl4 | = -0.017 T + 10.919 |
| CHCl3 | = -0.101 T + 69.275 | |
| CH2Cl2 | = -0.111 T + 56.128 | |
| Diethyl ether | = -0.085 T + 68.404 | |
| THF | = -0.091 T + 64.627 | |
| Toluene | = -0.066 T + 35.609 | |
| Redlich-Kwong (R-K) | CCl4 | = -0.021 T + 12.349 |
| CHCl3 | = -0.105 T + 70.824 | |
| CH2Cl2 | = -0.113 T + 57.257 | |
| Diethyl ether | = -0.090 T + 70.46 | |
| THF | = -0.096 T + 66.356 | |
| Toluene | = -0.068 T + 36.511 | |
| Cylindrical | CCl4 | = -0.021 T + 12.489 |
| CHCl3 | = -0.135 T + 83.700 | |
| CH2Cl2 | = -0.136 T + 65.871 | |
| Diethyl ether | = -0.088 T + 68.367 | |
| THF | = -0.071 T + 53.71 | |
| Toluene | = -0.041 T + 21.91 | |
| Hamieh model | CCl4 | = -0.006 T + 8.164 |
| CH2Cl2 | = -0.007 T + 29.475 | |
| CHCl3 | = -0.099 T + 51.024 | |
| Diethyl ether | = -0.110 T + 76.509 | |
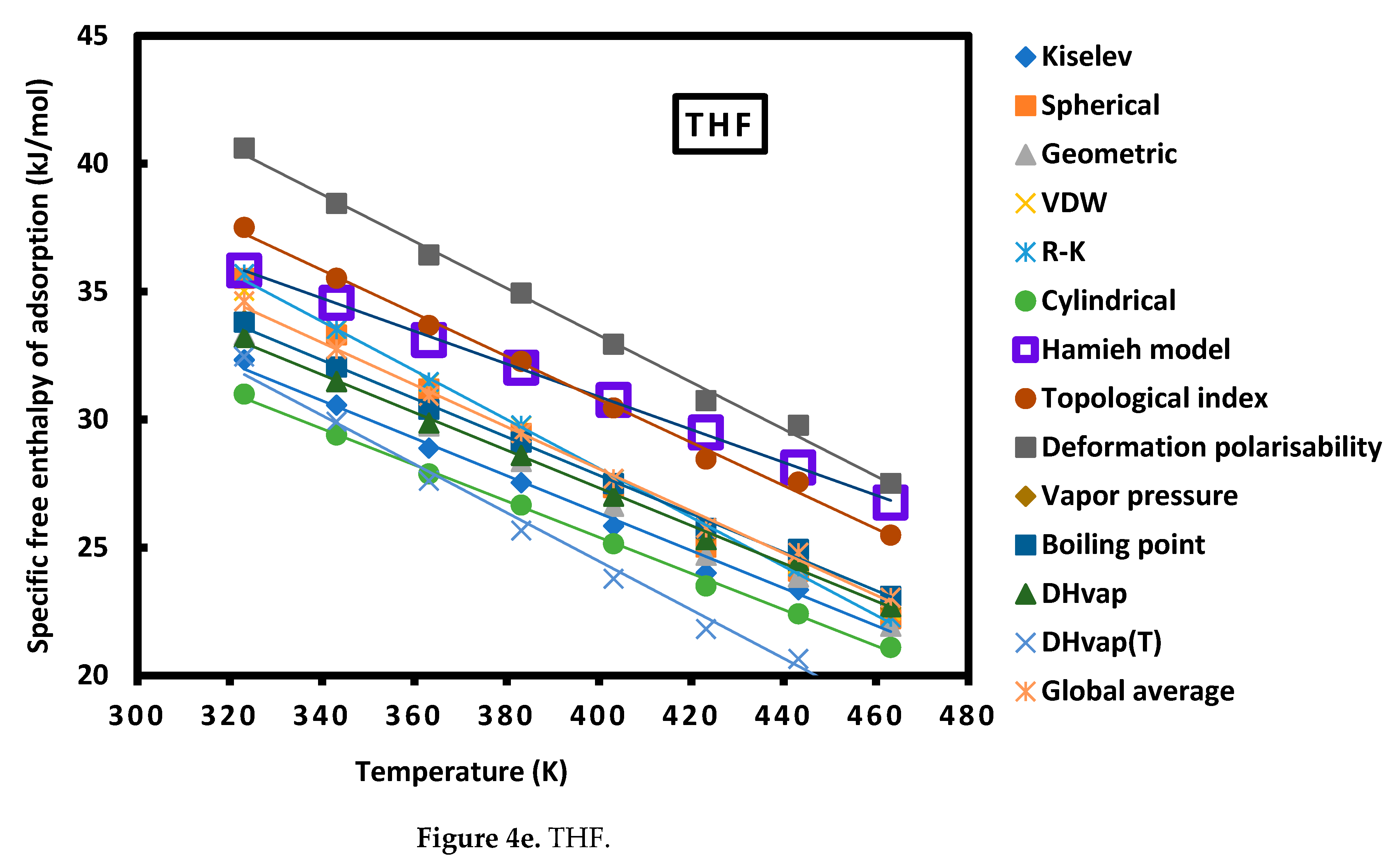
| THF | = -0.064 T + 56.551 | |
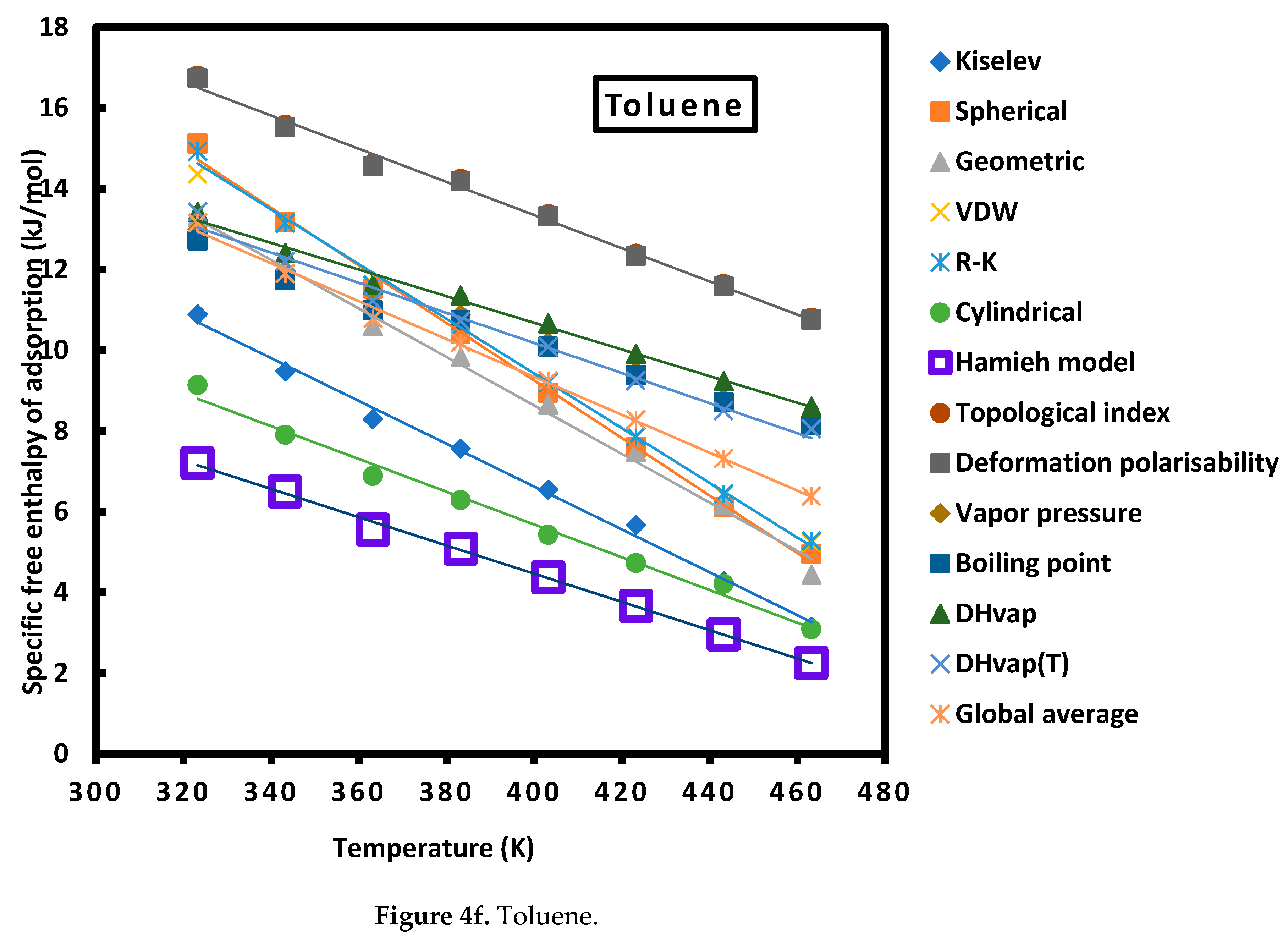
| Toluene | = -0.035 T + 18.456 | |
| Topological index | CCl4 | = -0.019 T + 19.115 |
| CH2Cl2 | = -0.111 T + 77.995 | |
| CHCl3 | = -0.112 T + 58.858 | |
| Diethyl ether | = -0.088 T + 68.894 | |
| THF | = -0.084 T + 64.482 | |
| Toluene | = -0.041 T + 29.895 | |
| Deformation polarizability | CCl4 | = -0.022 T + 21.723 |
| CH2Cl2 | = -0.083 T + 57.101 | |
| CHCl3 | = -0.100 T + 50.004 | |
| Diethyl ether | = -0.0922 T + 71.692 | |
| THF | = -0.092 T + 70.019 | |
| Toluene | = -0.041 T + 29.774 | |
| Vapor pressure | CCl4 | = 0.001 T + 4.7609 |
| CH2Cl2 | = -0.087 T + 61.958 | |
| CHCl3 | = -0.091 T + 43.784 | |
| Diethyl ether | = -0.084 T + 66.903 | |
| THF | = -0.079 T + 59.071 | |
| Toluene | = -0.033 T + 23.369 | |
| Boiling point | CCl4 | = 0.002 T + 4.0546 |
| CH2Cl2 | = -0.091 T + 63.571 | |
| CHCl3 | = -0.089 T + 42.024 | |
| Diethyl ether | = -0.087 T + 68.002 | |
| THF | = -0.075 T + 57.849 | |
| Toluene | = -0.031 T + 22.645 | |
| Enthalpy of vaporization DHvap(298K) | CCl4 | = 0.001 T + 4.8875 |
| CH2Cl2 | = -0.086 T + 59.17 | |
| CHCl3 | = -0.091 T + 43.106 | |
| Diethyl ether | = -0.086 T + 66.757 | |
| THF | = -0.074 T + 56.843 | |
| Toluene | = -0.033 T + 23.885 | |
| Thermic enthalpy of vaporization DHvap(T) | CCl4 | = -0.018 T + 10.116 |
| CH2Cl2 | = -0.096 T + 62.393 | |
| CHCl3 | = -0.115 T + 49.546 | |
| Diethyl ether | = -0.112 T + 73.958 | |
| THF | = -0.095 T + 62.454 | |
| Toluene | = -0.037 T + 25.095 |
| Probes | CCl4 | CHCl3 | CH2Cl2 | Diethyl ether | THF | Toluene |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kiselev | 9.95 | 49.82 | 66.20 | 76.24 | 55.66 | 27.84 |
| Spherical | 12.85 | 58.42 | 73.14 | 71.08 | 65.95 | 37.75 |
| Geometric | 22.90 | 60.18 | 77.16 | 65.80 | 59.03 | 32.65 |
| VDW | 10.92 | 56.13 | 69.28 | 68.40 | 64.63 | 35.61 |
| R-K | 12.35 | 57.26 | 70.82 | 70.46 | 66.36 | 36.51 |
| Cylindrical | 12.49 | 65.87 | 83.70 | 68.37 | 53.71 | 21.91 |
| Hamieh model | 8.16 | 51.02 | 29.48 | 76.51 | 56.55 | 18.46 |
| Topological index | 19.12 | 58.86 | 78.00 | 68.89 | 64.48 | 29.90 |
| Deformation polarizability | 21.72 | 50.00 | 57.10 | 71.69 | 70.02 | 29.77 |
| Vapor pressure | 4.76 | 43.78 | 61.96 | 66.90 | 59.07 | 23.37 |
| Boiling point | 4.05 | 42.02 | 63.57 | 68.00 | 57.85 | 22.65 |
| DHvap(298K) | 4.89 | 43.11 | 59.17 | 66.76 | 56.84 | 23.89 |
| DHvap(T) | 10.12 | 49.55 | 62.39 | 73.96 | 62.45 | 25.10 |
| Average values | 11.87 | 52.77 | 65.54 | 70.24 | 60.97 | 28.11 |
| Standard deviation | 6.16 | 7.34 | 13.41 | 3.52 | 4.99 | 6.17 |
| Error percentage | 51.86 | 13.91 | 20.47 | 5.01 | 8.18 | 21.96 |
| Probes | CCl4 | CHCl3 | CH2Cl2 | Diethyl ether | THF | Toluene |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kiselev | 15.1 | 98.8 | 94.9 | 104.1 | 73.3 | 53 |
| Spherical | 22.2 | 114.5 | 108.8 | 90.2 | 95.2 | 71.3 |
| Geometric | 37.7 | 120.8 | 119.1 | 80.8 | 80.2 | 60.1 |
| VDW | 17 | 111.1 | 101.1 | 84.9 | 91.4 | 65.6 |
| R-K | 20.5 | 113.3 | 104.9 | 90.1 | 95.7 | 67.7 |
| Cylindrical | 20.5 | 133.5 | 134.7 | 87.7 | 70.8 | 40.6 |
| Hamieh model | 5.9 | 98.7 | 6.7 | 110.1 | 64.1 | 35 |
| Topological index | 18.5 | 112 | 111.2 | 88.4 | 84.2 | 41.2 |
| Deformation polarizability | 22 | 99.9 | 82.7 | 92.2 | 91.8 | 41.1 |
| Vapor pressure | -0.6 | 91.2 | 86.6 | 83.7 | 78.8 | 32.8 |
| Boiling point | -2.2 | 88.9 | 91.3 | 87 | 75.1 | 31.4 |
| DHvap(298K) | -1 | 90.5 | 85.5 | 85.5 | 73.8 | 33 |
| DHvap(T) | 18.1 | 114.7 | 96.1 | 111.8 | 95 | 37.3 |
| Average values | 14.9 | 106.8 | 94.1 | 92.0 | 82.3 | 46.9 |
| Standard deviation | 11.48 | 13.31 | 30.08 | 10.07 | 10.68 | 14.61 |
| Error percentage | 77.02 | 12.46 | 31.97 | 10.94 | 12.98 | 31.15 |
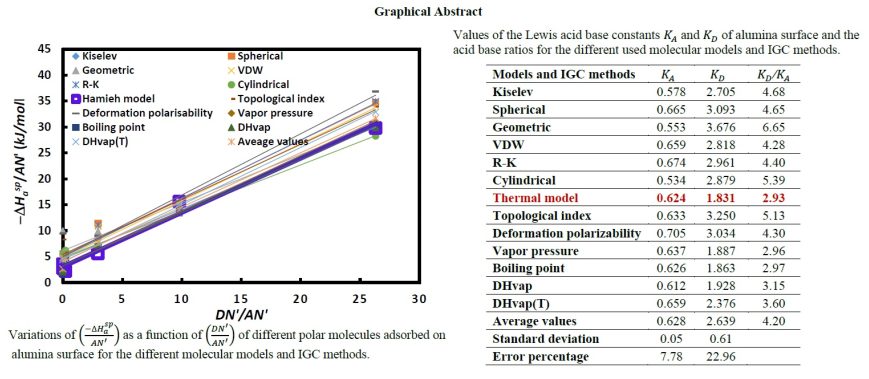
| Models and IGC methods | / | 103. | 103. | / | ||
| Kiselev | 0.578 | 2.705 | 4.68 | 0.72 | 4.71 | 6.5 |
| Spherical | 0.665 | 3.093 | 4.65 | 0.91 | 5.42 | 6.0 |
| Geometric | 0.553 | 3.676 | 6.65 | 0.68 | 6.34 | 9.3 |
| VDW | 0.659 | 2.818 | 4.28 | 0.89 | 4.76 | 5.4 |
| R-K | 0.674 | 2.961 | 4.40 | 0.92 | 5.11 | 5.5 |
| Cylindrical | 0.534 | 2.879 | 5.39 | 0.64 | 5.09 | 7.9 |
| Hamieh model | 0.624 | 1.831 | 2.93 | 0.72 | 2.79 | 3.9 |
| Topological index | 0.633 | 3.250 | 5.13 | 0.82 | 4.27 | 5.2 |
| Deformation polarizability | 0.705 | 3.034 | 4.30 | 0.92 | 3.97 | 4.3 |
| Vapor pressure | 0.637 | 1.887 | 2.96 | 0.85 | 2.35 | 2.8 |
| Boiling point | 0.626 | 1.863 | 2.97 | 0.82 | 2.36 | 2.9 |
| DHvap | 0.612 | 1.928 | 3.15 | 0.80 | 2.46 | 3.1 |
| DHvap(T) | 0.659 | 2.376 | 3.60 | 0.98 | 4.07 | 4.2 |
| Average values | 0.628 | 2.639 | 4.20 | 0.82 | 4.13 | 5.0 |
| Standard deviation | 0.05 | 0.61 | 0.10 | 1.29 | ||
| Error percentage | 7.78 | 22.96 | 12.79 | 31.34 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





