Submitted:
14 April 2023
Posted:
17 April 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Horses
2.2. Water treadmill (WT) exercise
2.3. Back Profile Dimension Measurements
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
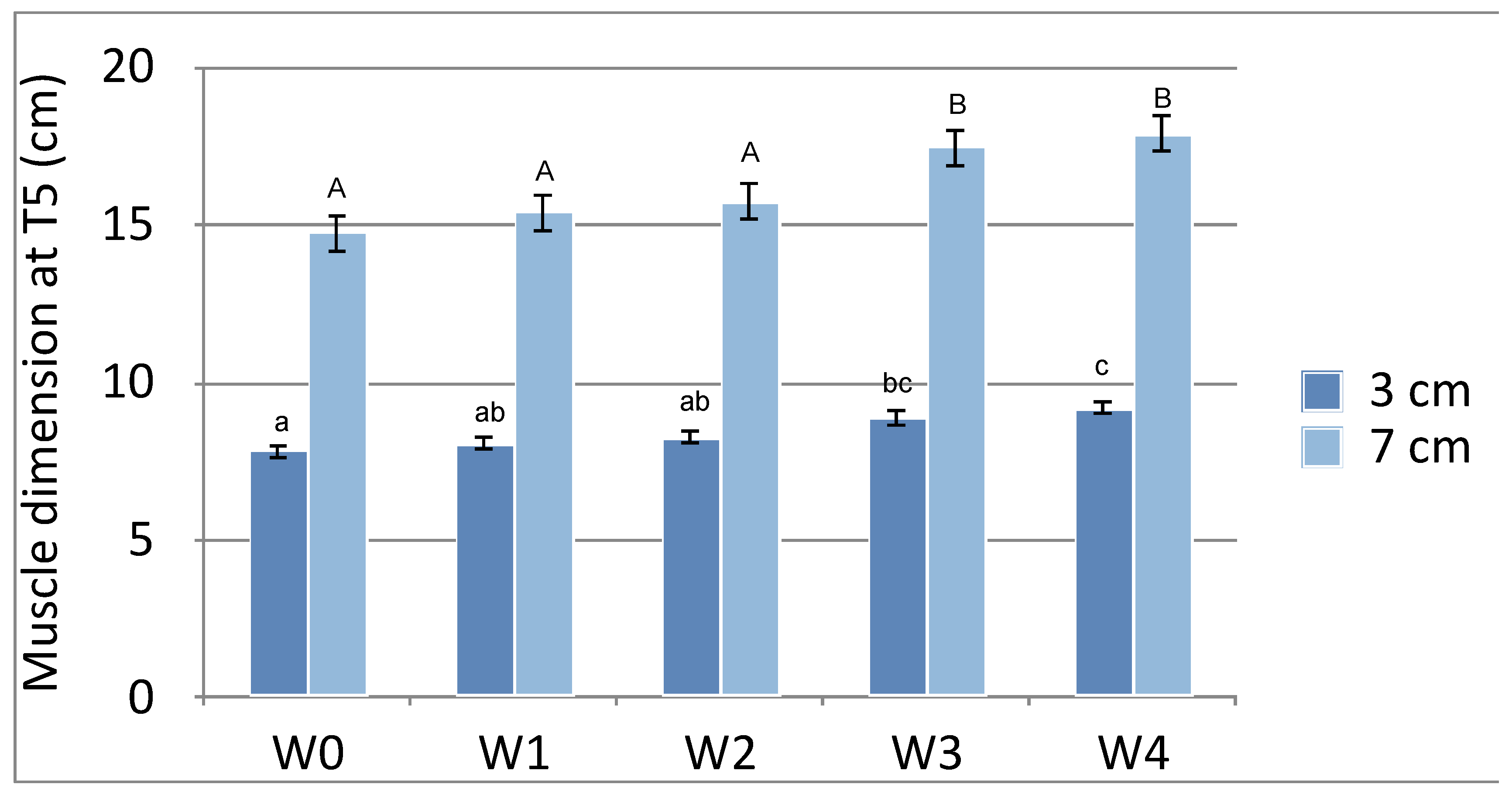
3.1. T5
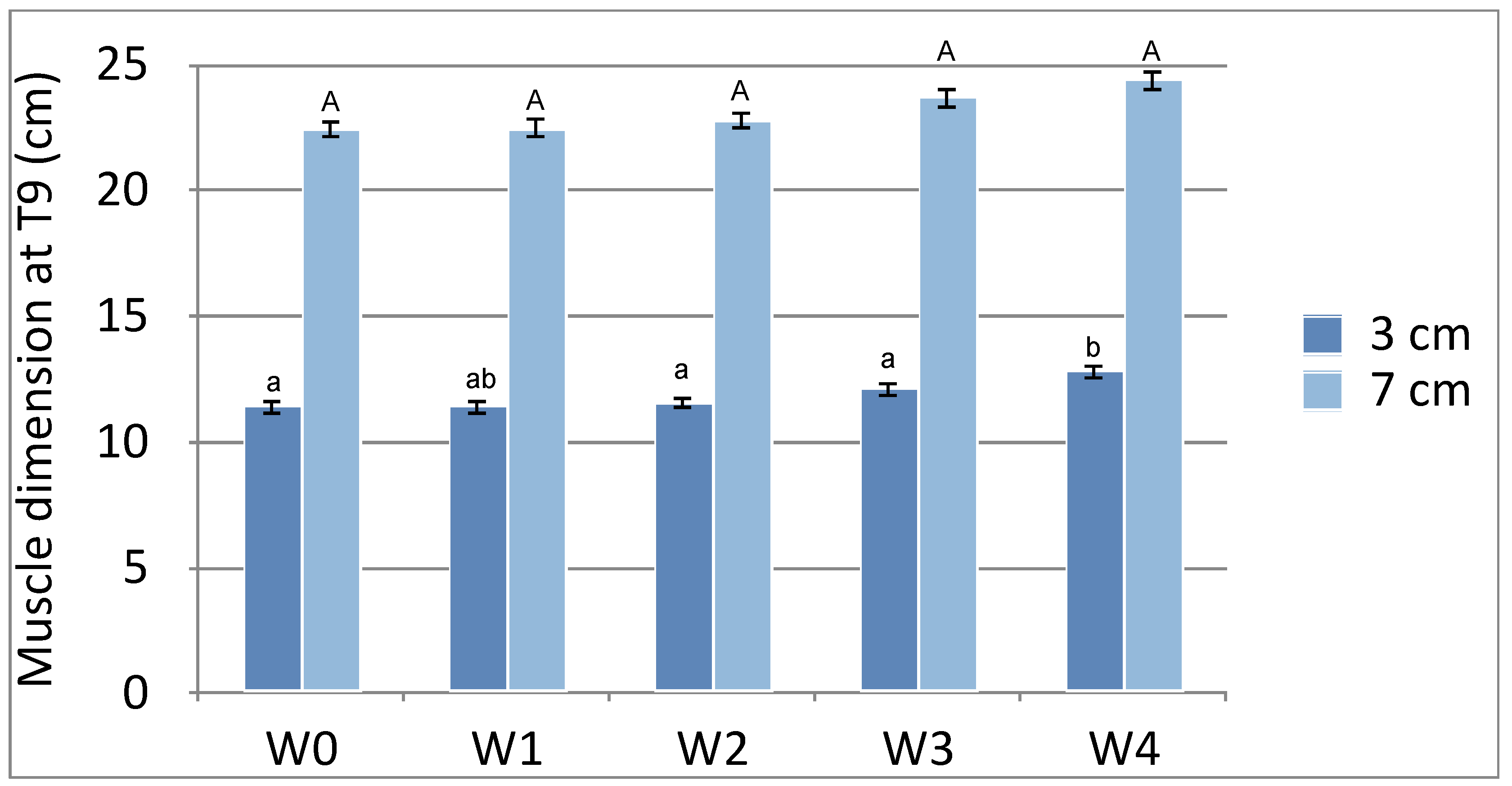
3.2. T9
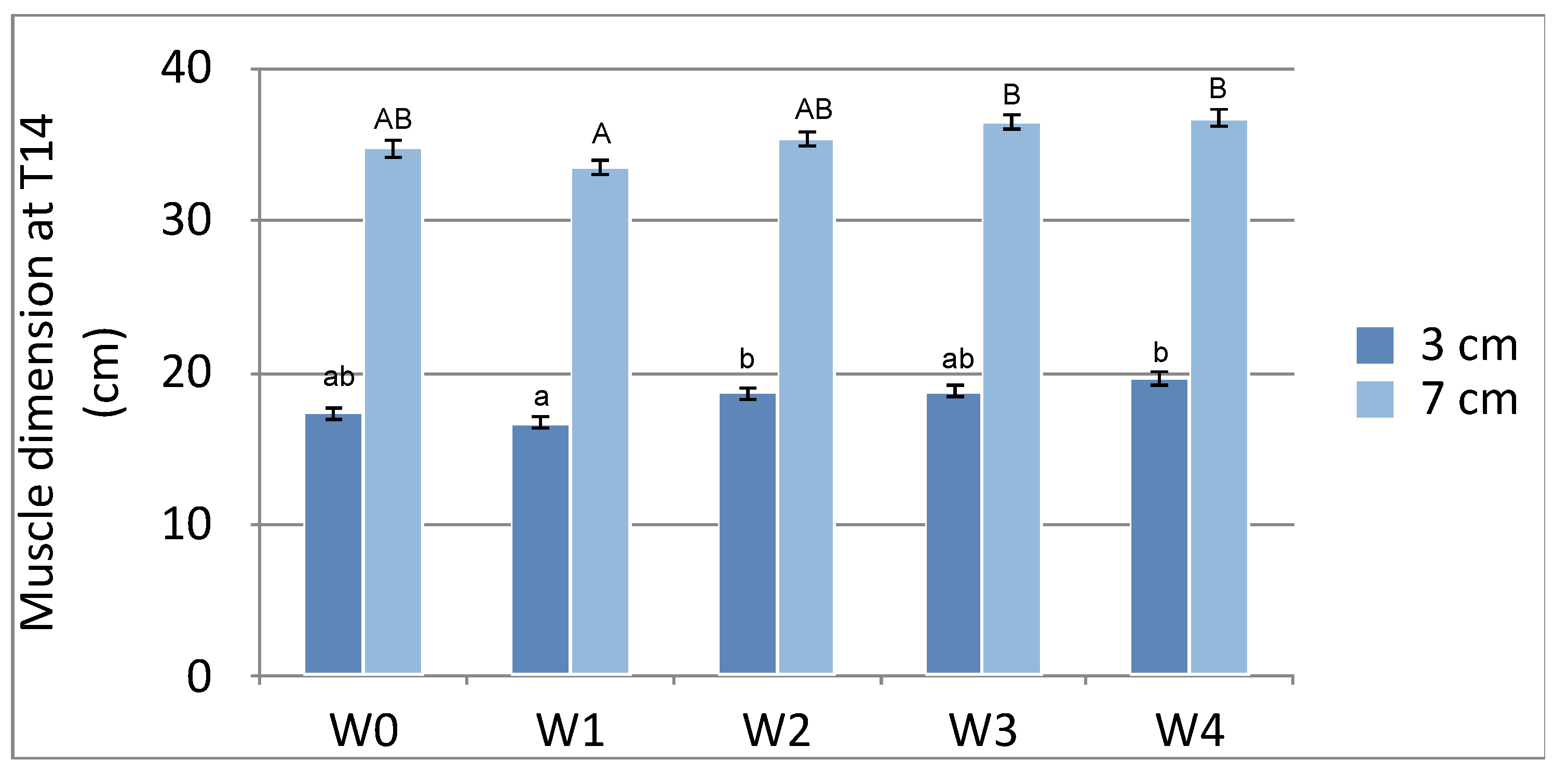
3.3. T14
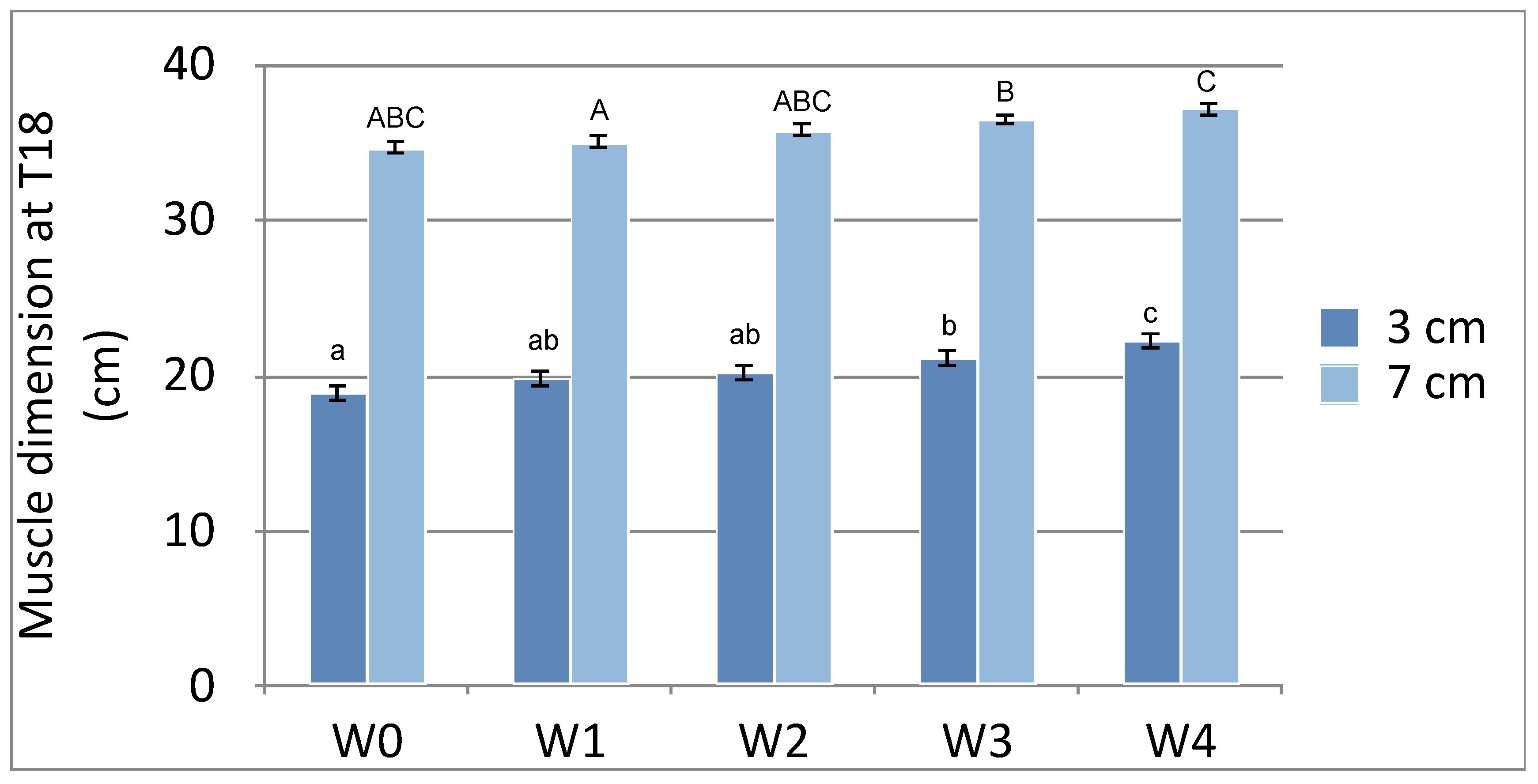
3.4. T18
4. Discussion
Funding
Data Availability
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mooij MJW, Jans W, den Heijer GJL, de Pater M, Back W Biomechanical responses of the back of riding horses to water treadmill exercise. Vet J. 2013; 198:e120–e123. [CrossRef]
- Nankervis KJ, Finney P, Launder L, Water depth modifies back kinematics of horses during water treadmill exercise. Equine Vet J. 2016; 48: 732–736. [CrossRef]
- Nankervis KJ, Launder EJ, Murray RC, The Use of Treadmills Within the Rehabilitation of Horses. J Equine Vet Sci. 2017; 53: 108–115. [CrossRef]
- Álvarez CBG, Rhodin M, Byström A, Back W, Weeren PR van, Back kinematics of healthy trotting horses during treadmill versus over ground locomotion. Equine Vet J. 2009; 41:297–300. [CrossRef]
- Tabor G, Williams J, Equine Rehabilitation: A Review of Trunk and Hind Limb Muscle Activity and Exercise Selection. J Equine Vet Sci. 2018a; 60:97-103.e3. [CrossRef]
- Robert C, Valette J, Pourcelot P, Audigié F, Denoix J, Effects of trotting speed on muscle activity and kinematics in saddlehorses. Equine Vet J. 2002; 34:295-301.
- Robert, C, Valette JP, Denoix JM, The effects of treadmill inclination and speed on the activity of two hindlimb muscles in the trotting horse. Equine Vet J. 2001; 32: 312–317. [CrossRef]
- Tabor G, Williams J, 2018b. The use of outcome measures in equine rehabilitation. Vet Nurs. 2018b; 9:497–500. [CrossRef]
- Greve L, Dyson S, Saddle fit and management: An investigation of the association with equine thoracolumbar asymmetries, horse and rider health. Equine Vet J. 2105a; 47:415–421. [CrossRef]
- Peinen KV, Wiestner T, Rechenberg B.V, Weishaupt MA, Relationship between saddle pressure measurements and clinical signs of saddle soreness at the withers. Equine Vet J. 2010; 42:650–653. [CrossRef]
- Denoix JMD, Spinal Biomechanics and Functional Anatomy. Vet Clin N Am-Equine.2015; 15:27–60. [CrossRef]
- van Weeren PR, Structure and biomechanical concept of the equine back. Pferdeheilkunde.2004; 20:341–348. [CrossRef]
- Muñoz A, Saitua, A, Becero, M, Riber C, Satué K, Medina AS, Argüelles D, Castejón-Riber C, The use of the water treadmill for the rehabilitation of musculoskeletal injuries in the sport horse. J Vet Res.2019; 63:439–445. [CrossRef]
- Paulekas R, Haussler KK, Principles and Practice of Therapeutic Exercise for Horses. J Equine Vet Sci. 2009; 298:70–893. [CrossRef]
- Murray R, Hopkins E, Jack B, Nankervis K, Deckers I, Tranquile CA, Change in muscle development of horses undergoing 20 weeks of water treadmill exercise compared with control horses, Equine Vet J. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Faber M, Schamhardt H, Weeren R, Johnston C, Roepstorff L, Barneveld A, Basic three-dimensional kinematics of the vertebral column of horses walking on a treadmill. Am J Vet Res. 2000; 61: 399–406. [CrossRef]
- Zaneb H, Peham C, Stanek C, Functional anatomy and biomechanics of the equine thoracolumbar spine: a review. Turk J Vet Anim Sci. 2013; 37: 380–389.
- Townsend HGG, Leach DH, Fretz PB, Kinematics of the equine thoracolumbar spine. Equine Vet J. 1983;15:117–122. [CrossRef]
- Faber M, Johnston C, Schamhardt H, Weeren R, Roepstorff L, Barneveld A, Basic three-dimensional kinematics of the vertebral column of horses trotting on a treadmill. Am J Vet Res. 2001; 62:57–764. [CrossRef]
- Ridgway K, Harman J, Equine Back Rehabilitation. Vet Clin N Am-Equine. 1999; 15:263–280. [CrossRef]
- Holloway TM, Snijders T, Van Kranenburg J, Van Loon LJC, Verdij LB, Temporal Response of Angiogenesis and Hypertrophy to Resistance Training in Young Men. Med Sci Sport Exer. 2018: 50: 36–45. [CrossRef]
- Baxter GM, 2011. Manual of Equine Lameness. John Wiley & Sons.
- Zsoldos RR, Kotschwar, A, Kotschwar B, Rodriguez, CP, Peham C, Licka T, Activity of the equine rectus abdominis and oblique external abdominal muscles measured by surface EMG during walk and trot on the treadmill. Equine Vet J. 2010; 42: 523–529. [CrossRef]
- Budras KD, Sack WO, Röck S, 2012. Anatomy of the Horse: with Aaron Horowitz and Rolf Berg. Schlütersche.
- Nankervis KJ, Lefrancois K, A Comparison of Protraction-Retraction of the Distal Limb During Treadmill and Water Treadmill Walking in Horses. J Equine Vet Sci. 2018; 70:57–62. [CrossRef]
- Tranquille CA, Tacey JB, Walker VA, Nankervis KJ, Murray RC, International Survey of Equine Water Treadmills, Why, When, and How? J Equine Vet Sci. 2018: 69:34–42. [CrossRef]
- Greve L, Murray R, Dyson S, Subjective analysis of exercise-induced changes in back dimensions of the horse: The influence of saddle-fit, rider skill and work quality. Veterinary J. 2105b; 206:39–46. [CrossRef]
- Lamb, GD. Understanding “within” versus “between” ANOVA Designs: Benefits and Requirements of Repeated Measures. 2003. Annual meeting of the southwest educational research association, San Antonio, Feb, 2003.37p.
- Caruana EJ, Roman M, Hernández-Sánchez J, Solli P, Longitudinal studies. J Thorac Dis. 2105; 7:e537–e540. [CrossRef]
- Arifin WN, Zahiruddin WM. Sample Size Calculation in Animal Studies Using Resource Equation Approach. Malays J Med Sci. 2017;24(5):101-105. [CrossRef]
- Robert C, Valette JP, Denoix JM. The effects of treadmill inclination and speed on the activity of three trunk muscles in the trotting horse. Equine Vet J. 2001 Sep;33(5):466-72. [CrossRef]
- Takahashi T, Matsui A, Mukai K, Ohmura H, Hiraga A, Aida H. The Effects of Inclination (Up and Down) of the Treadmill on the Electromyogram Activities of the Forelimb and Hind limb Muscles at a Walk and a Trot in Thoroughbred Horses. J Equine Sci. 2014;25(4):73-7. Epub 2014 Dec 15. [CrossRef]
- Tokuriki M, Ohtsuki R, Kai M, Hiraga A, Oki H, Miyahara Y, Aoki O. EMG activity of the muscles of the neck and forelimbs during different forms of locomotion. Equine Vet J Suppl. 1999 Jul;(30):231-4. [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira K, Soutello RVG, da Fonseca R, Costa C, Paulo PR, Fachiolli DF, et al. Gymnastic Training and Dynamic Mobilization Exercises Improve Stride Quality and Increase Epaxial Muscle Size in Therapy Horses. J Equine Vet Sci 2015;35:888–93. [CrossRef]
- Stubbs NC, Kaiser LJ, Hauptman J, Clayton HM. Dynamic mobilisation exercises increase cross sectional area of musculus multifidus. Equine Vet J 2011;43:522–9. [CrossRef]
- Lucas RG, Rodríguez-Hurtado I, Álvarez CT, Ortiz G. Effectiveness of Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation and Dynamic Mobilization Exercises on Equine Multifidus Muscle Cross-Sectional Area. J Equine Vet Sci. 2022 Jun;113:103934. [CrossRef]
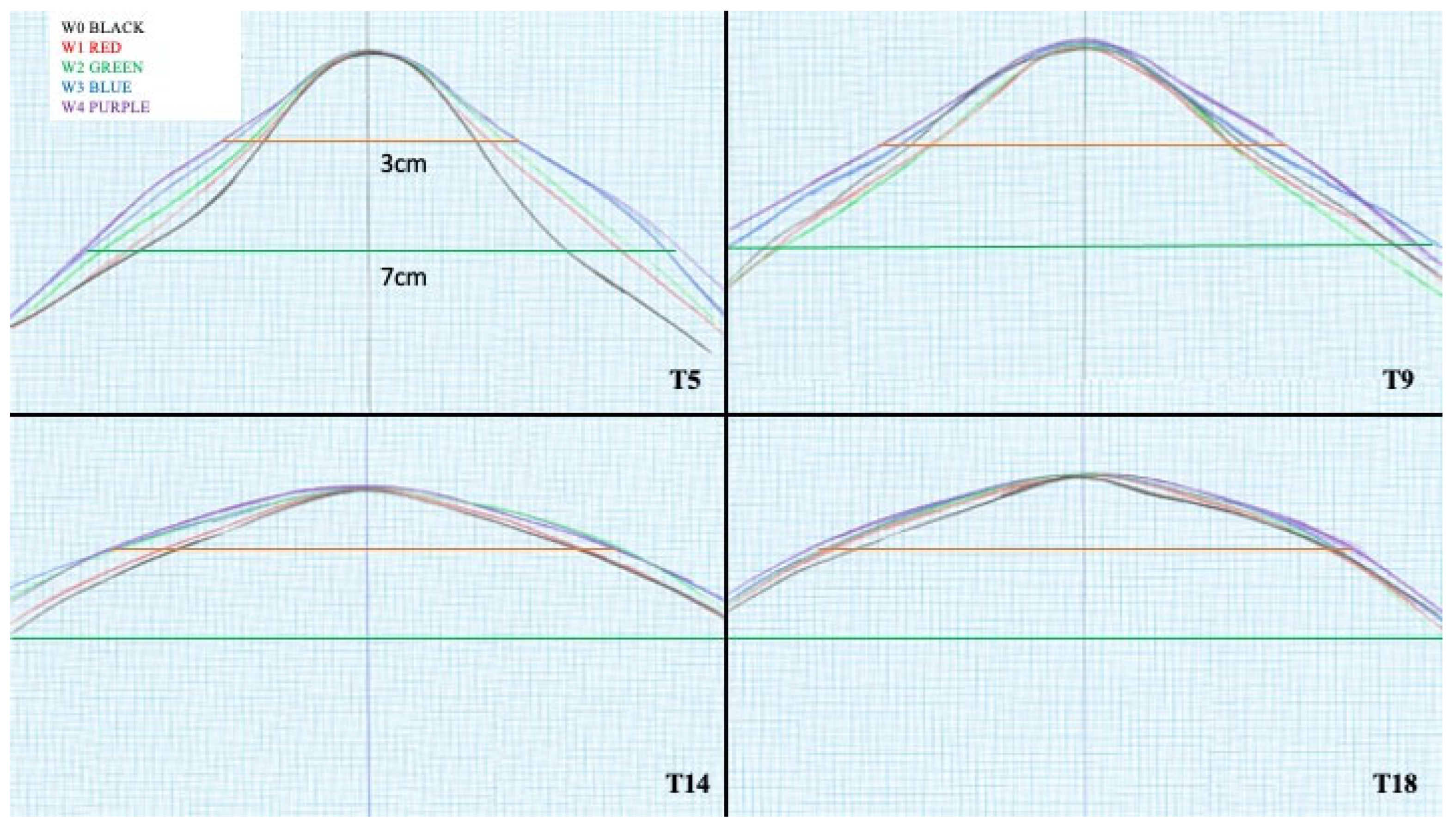
| Vertebra (location of measurement) |
Start measure (W0) | End week 1 (W1) | End week 2 (W2) | End week 3 (W3) |
End week 4 (W4) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T5 (3cm) | 7.817±0.8010a | 8.067±0.5354ab | 8.267±0.6121ab | 8.883±1.1232bc | 9.200±0.6753c |
| T5 (7cm) | 14.733±2.8591a | 15.400±2.0552a | 15.733±1.6513a | 17.450±2.8981b | 17.883±2.4879b |
| T9 (3cm) | 11.417±2.3086a | 11.417±1.9631ab | 11.567±2.0285a | 12.100±2.5962a | 12.817±2.7044b |
| T9 (7cm) | 22.417±4.8938a | 22.483±4.2874a | 22.767±4.1611a | 23.667±5.1798a | 24.383±4.8688a |
| T14 (3cm) | 17.317±3.1543ab | 16.717±2.7110a | 18.617±3.6880b | 18.750±3.5155ab | 19.583±3.5578b |
| T14 (7cm) | 34.700±3.8137ab | 33.500±2.6199a | 35.367±2.6726ab | 36.433±2.9743b | 36.733±2.5375b |
| T18 (3cm) | 18.867±4.4898a | 19.883±3.9842ab | 20.150±3.0755ab | 21.150±2.9084b | 22.167±3.3224c |
| T18 (7cm) | 34.683±3.4336abc | 35.050±1.8971a | 35.733±2.0906abc | 36.467±1.8316b | 37.150±1.5643c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





