Submitted:
01 February 2023
Posted:
02 February 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Underlying Physics
2.1. Magnetostatic fields
2.1.1. Magnetic forces and torques
2.1.2. Fixed dipole model
2.1.3. Mutual dipole model
2.2. Incompressible fluid flow
2.3. Particle transient motion
3. Numerical Methodology
| Algorithm 1:Fully-resolved FVM-IBM-DEM-MAG algorithm to model magnetorheological fluids |
|
step 1: at time
step 2: at time
|
4. Results and discussion
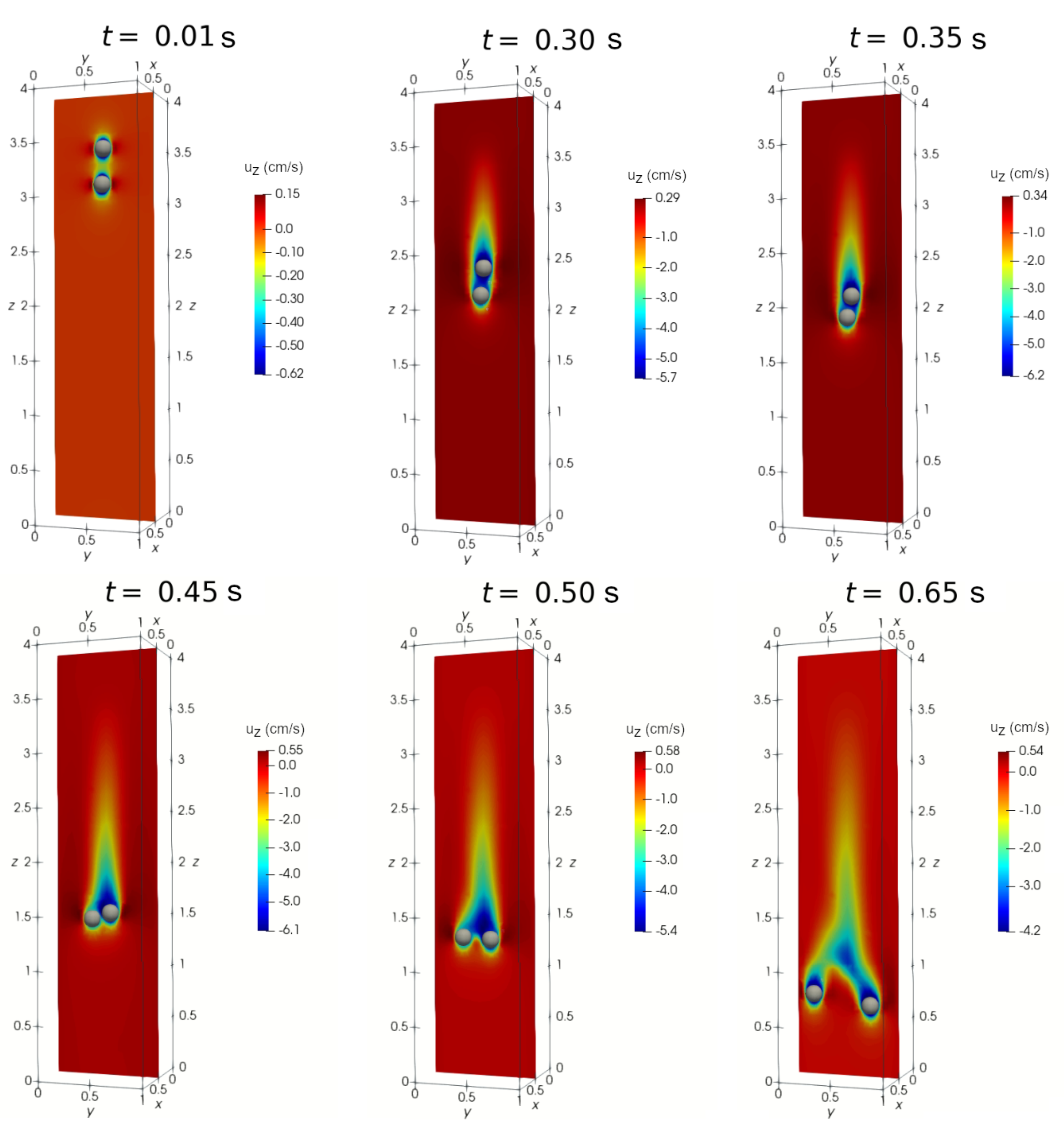
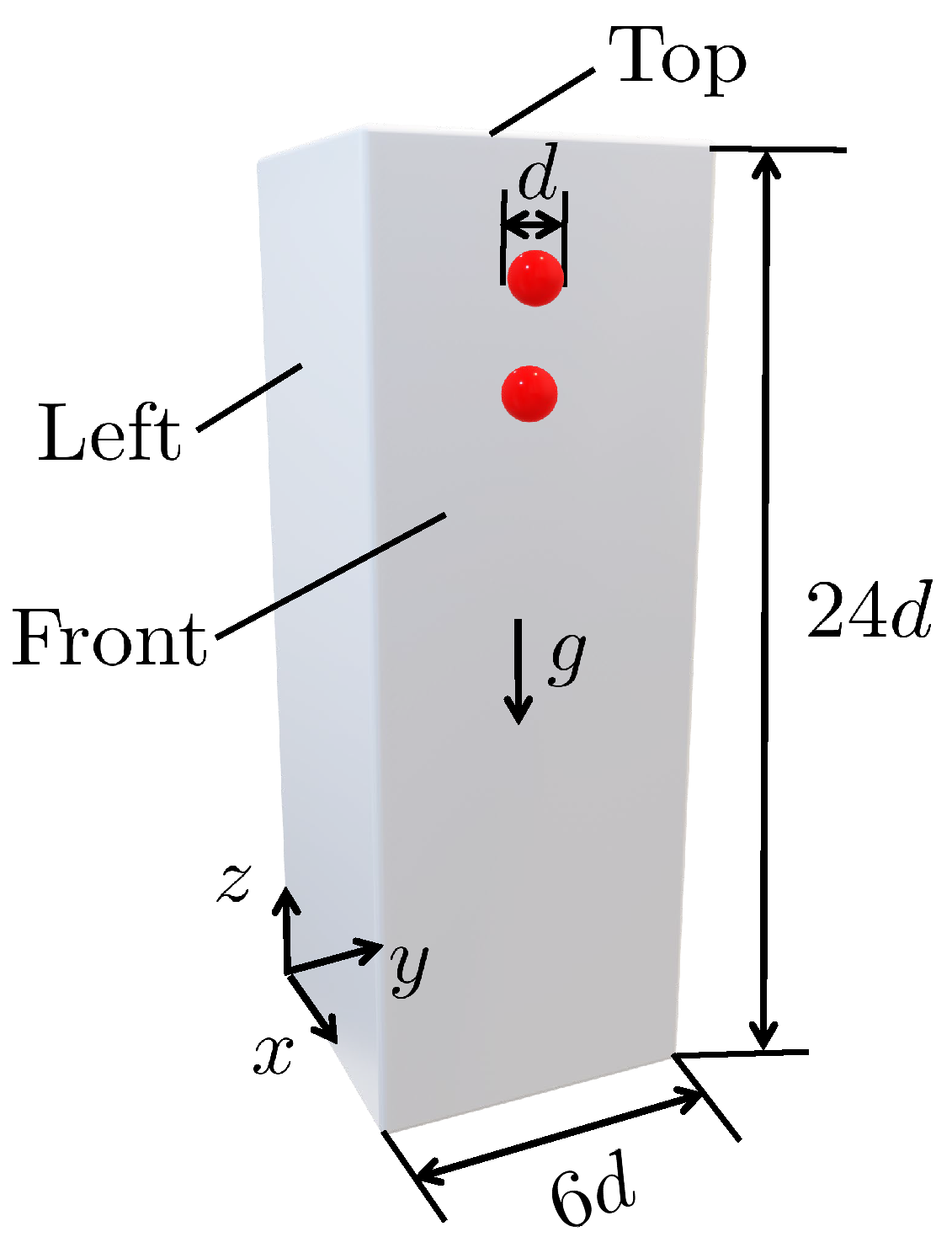
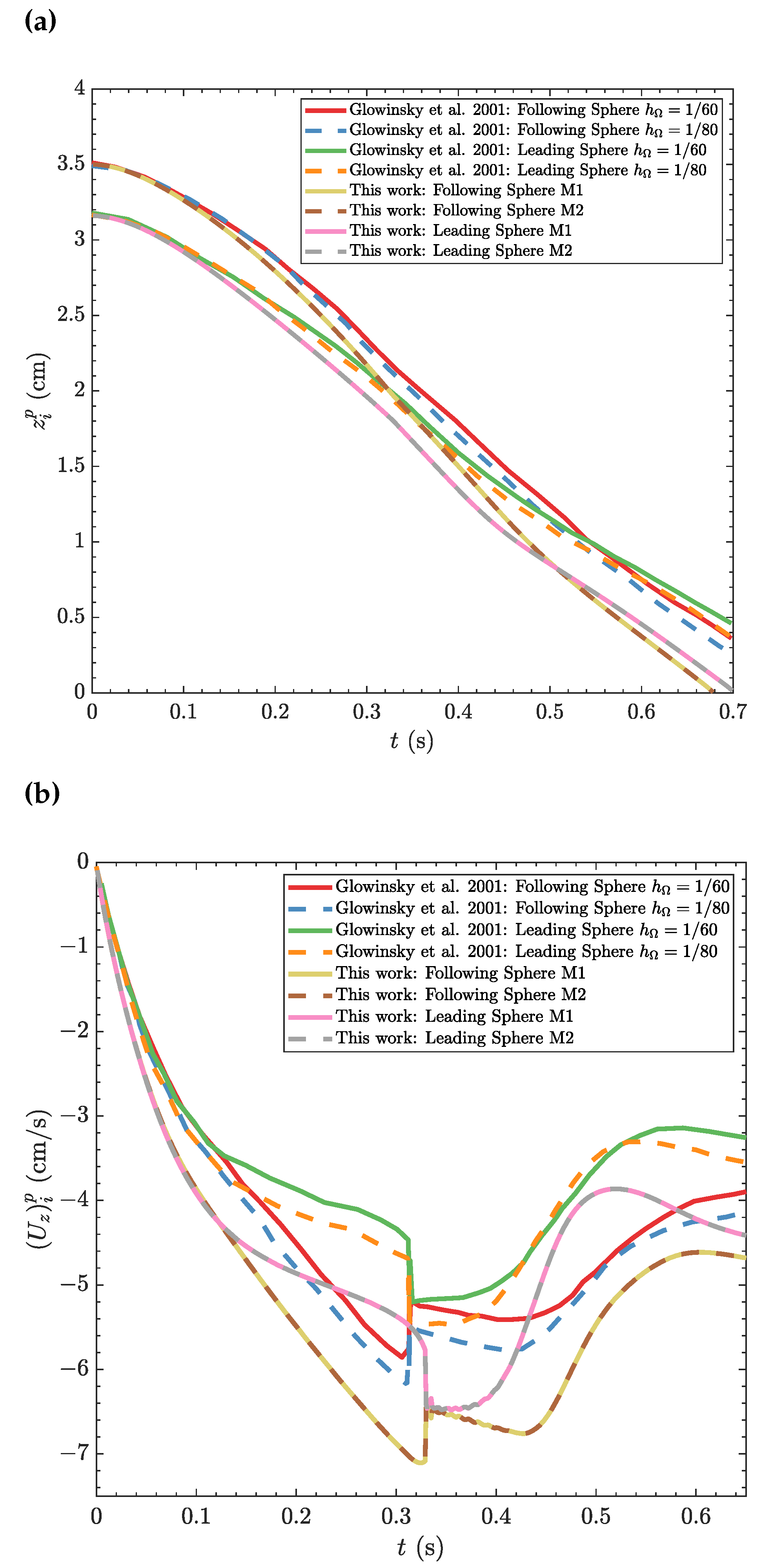
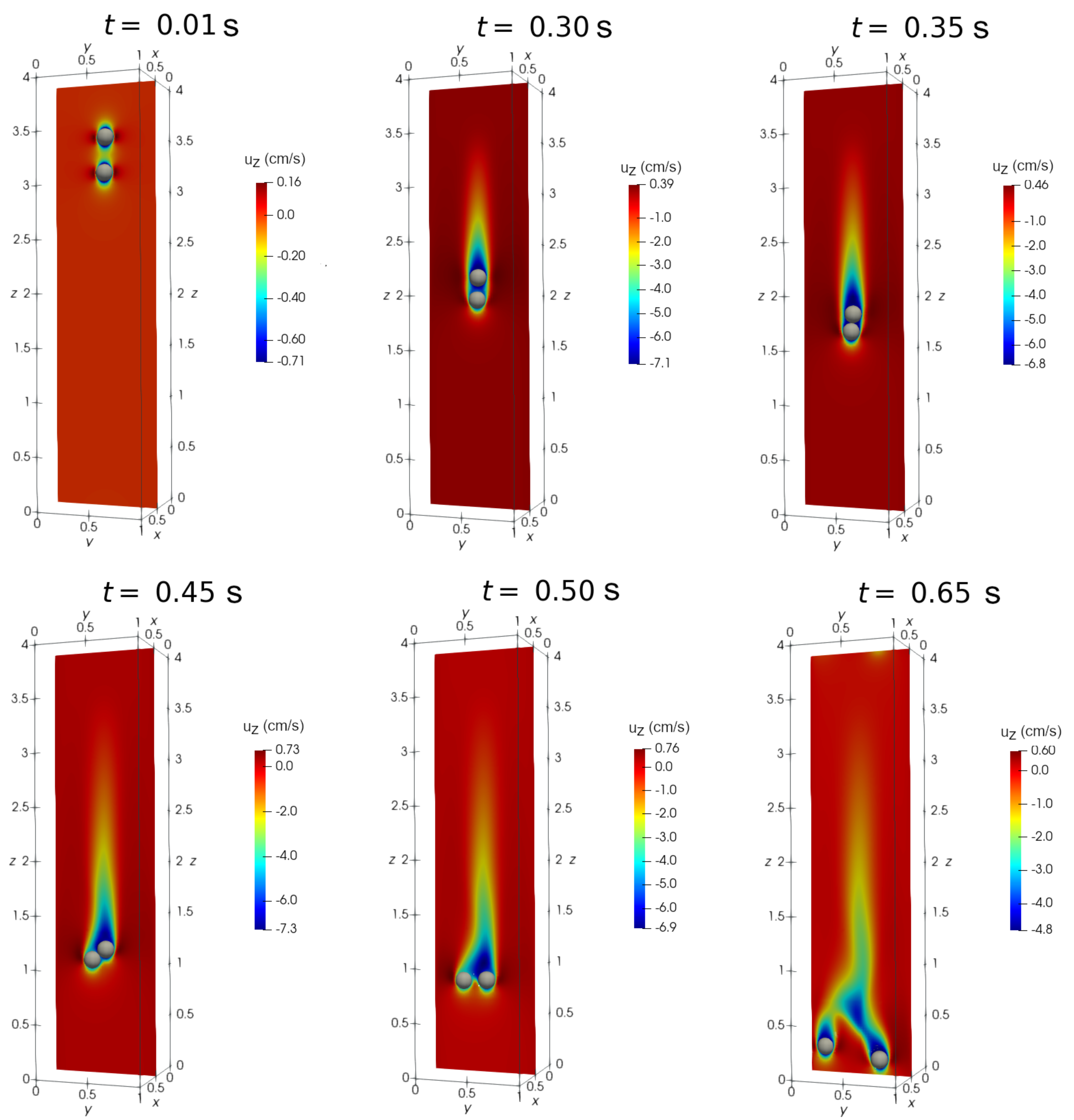
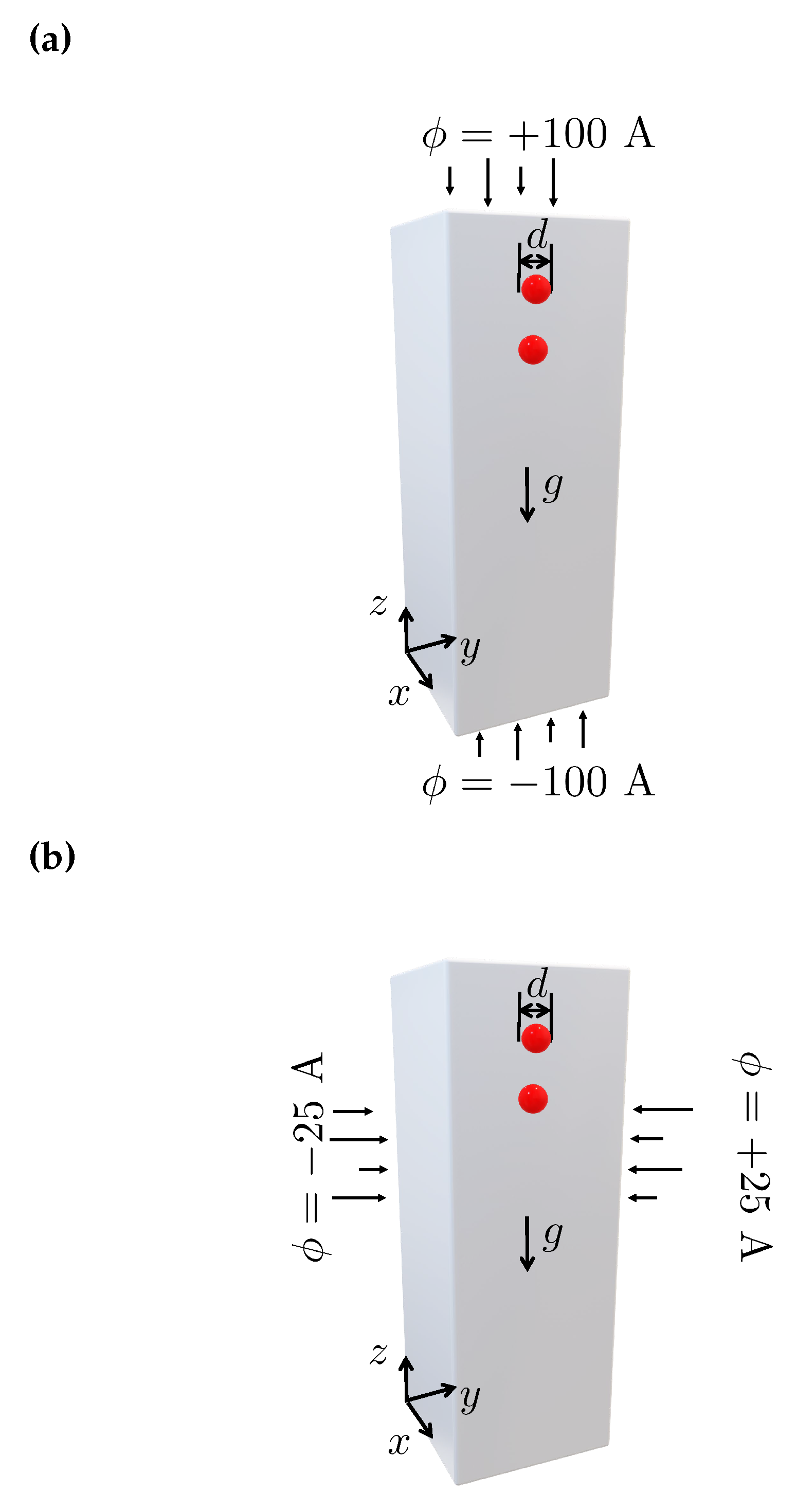
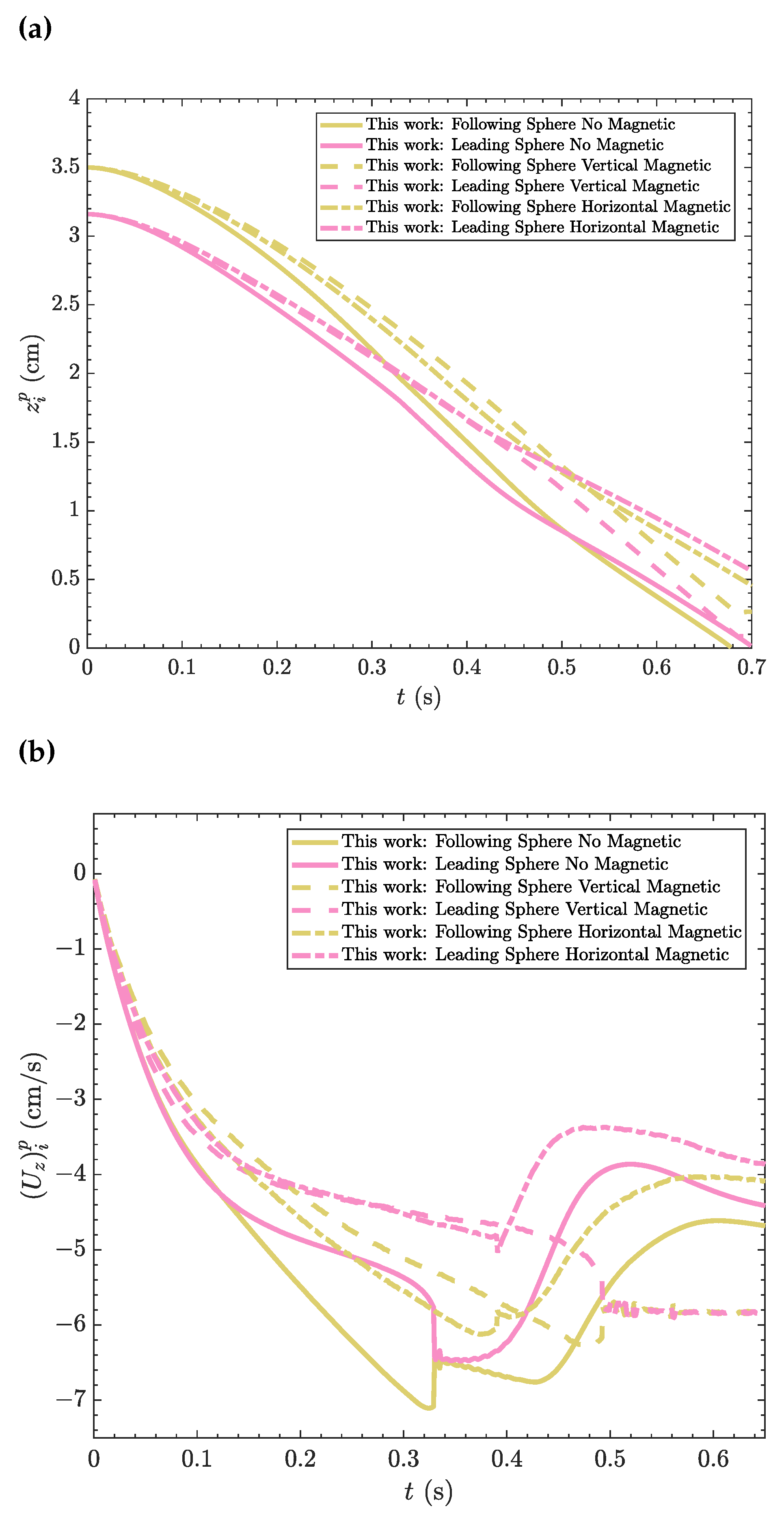
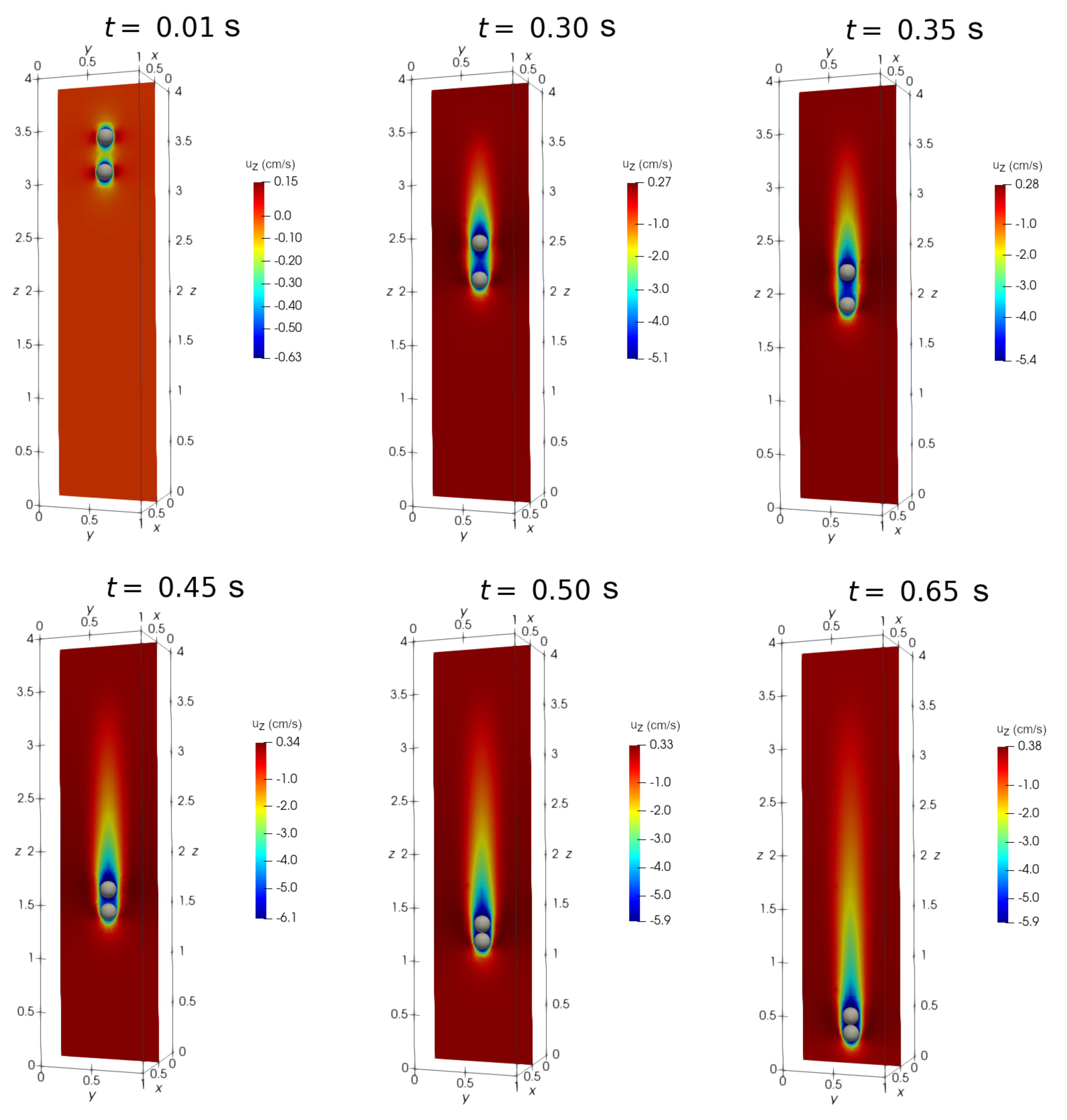
4.1. DKT phenomenon under zero magnetic field
4.2. DKT phenomenon under magnetic field
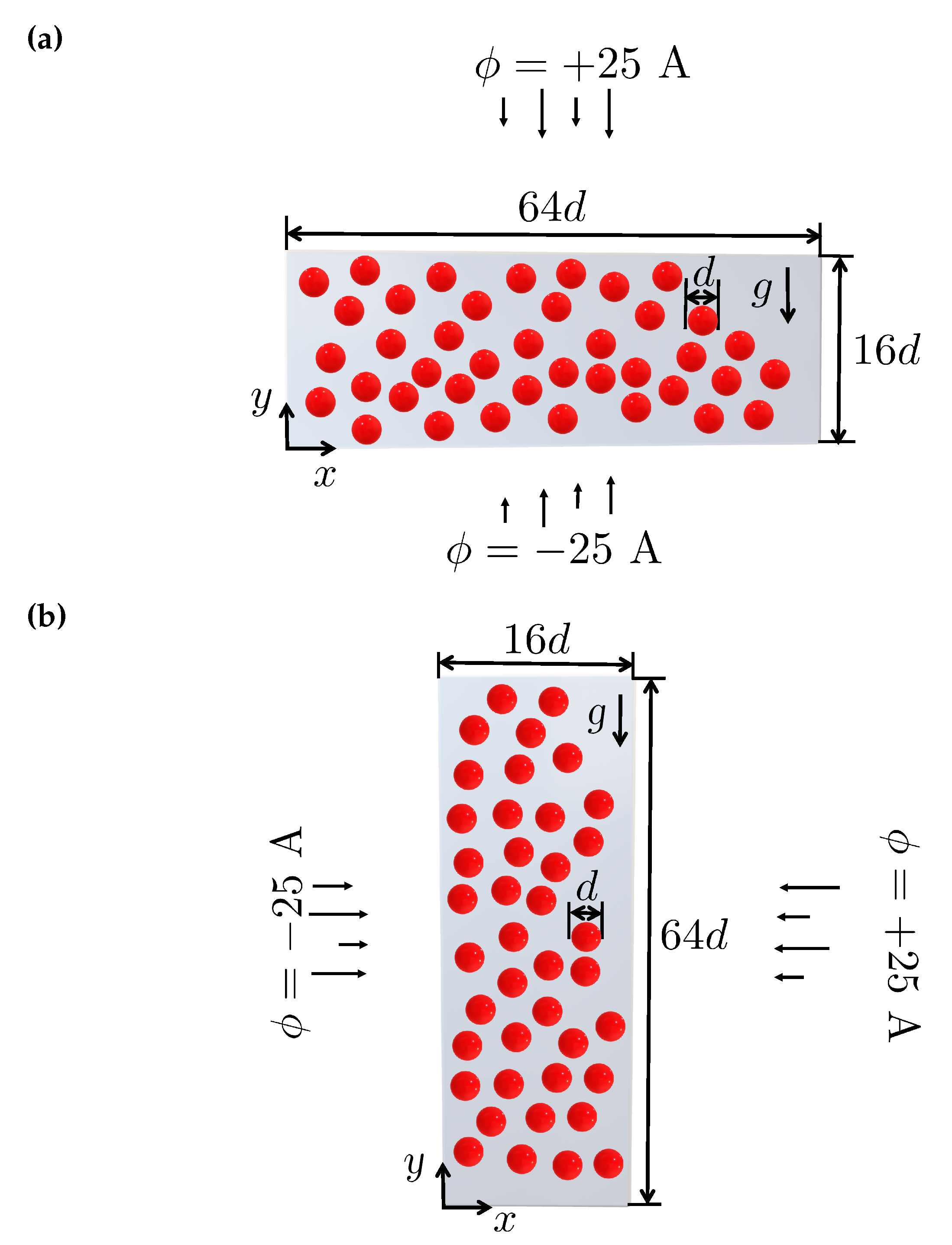
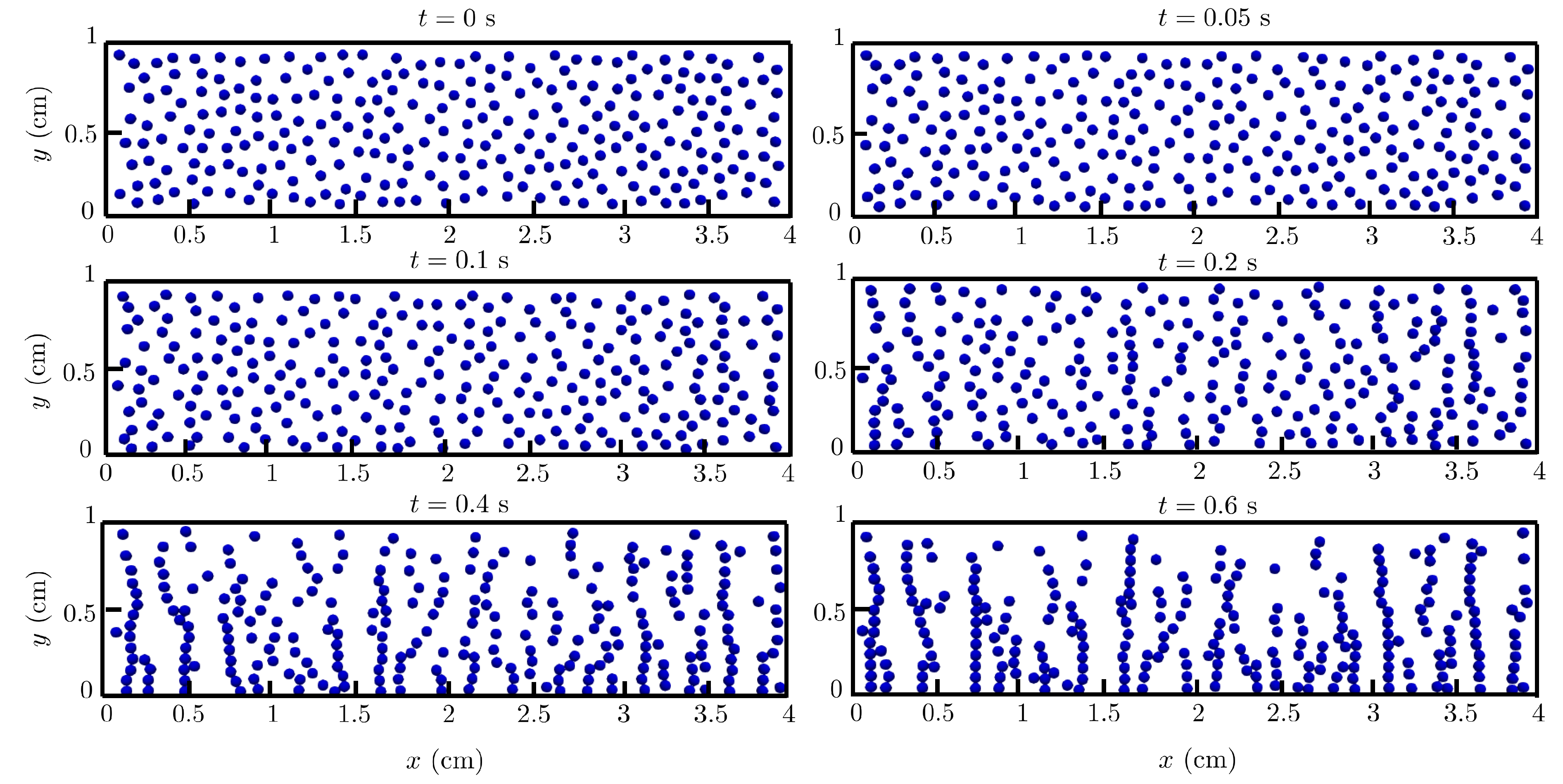
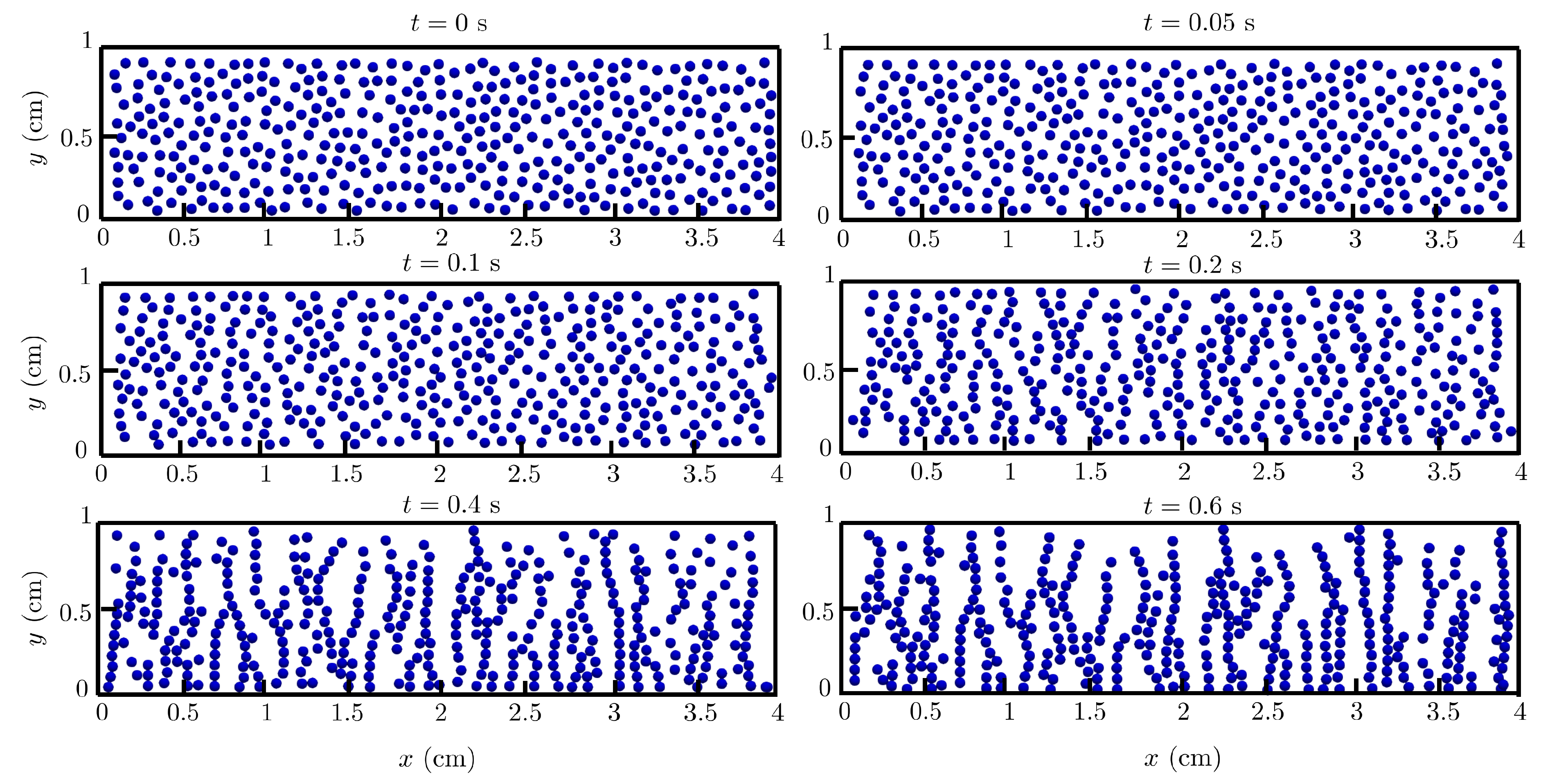
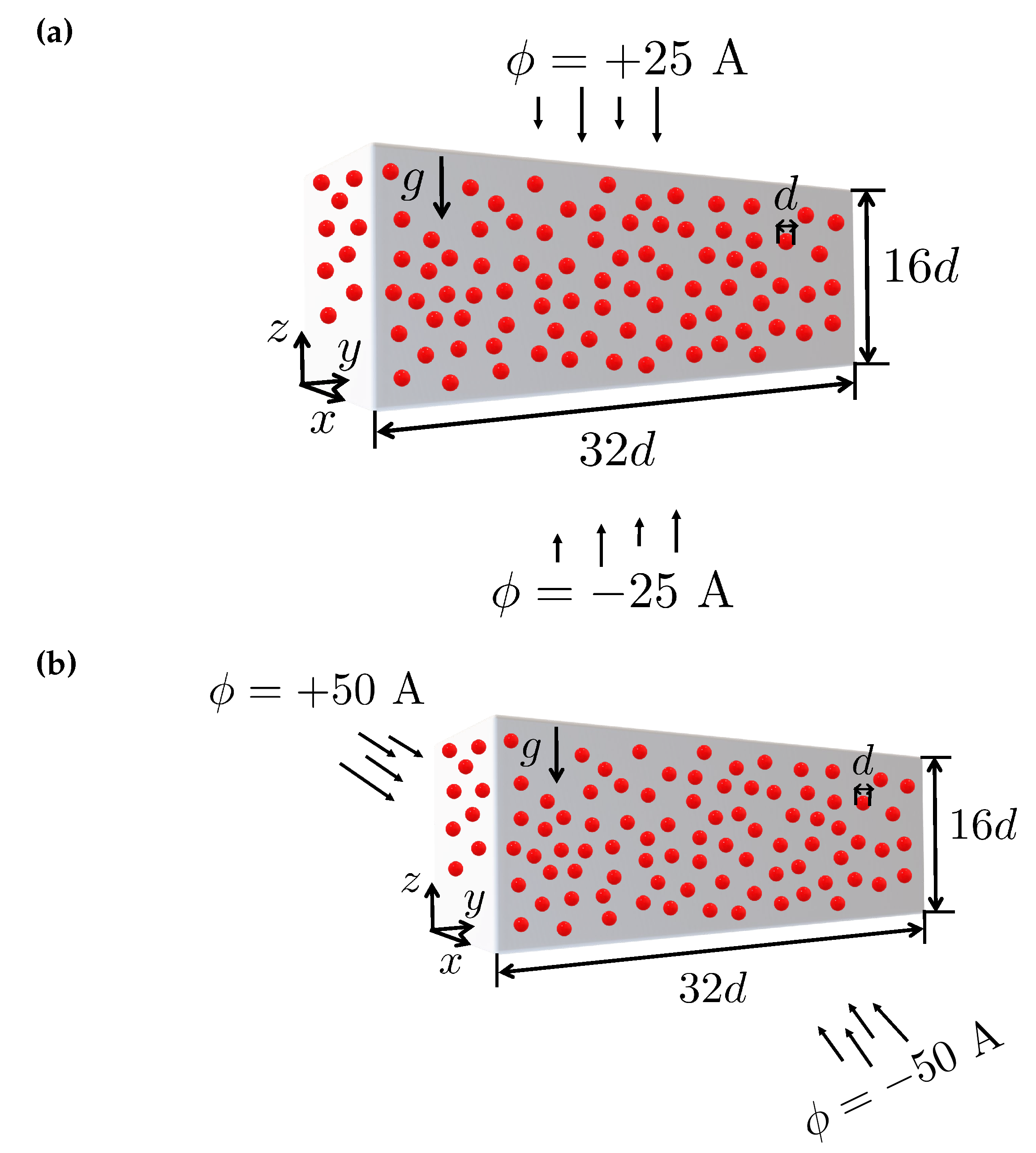
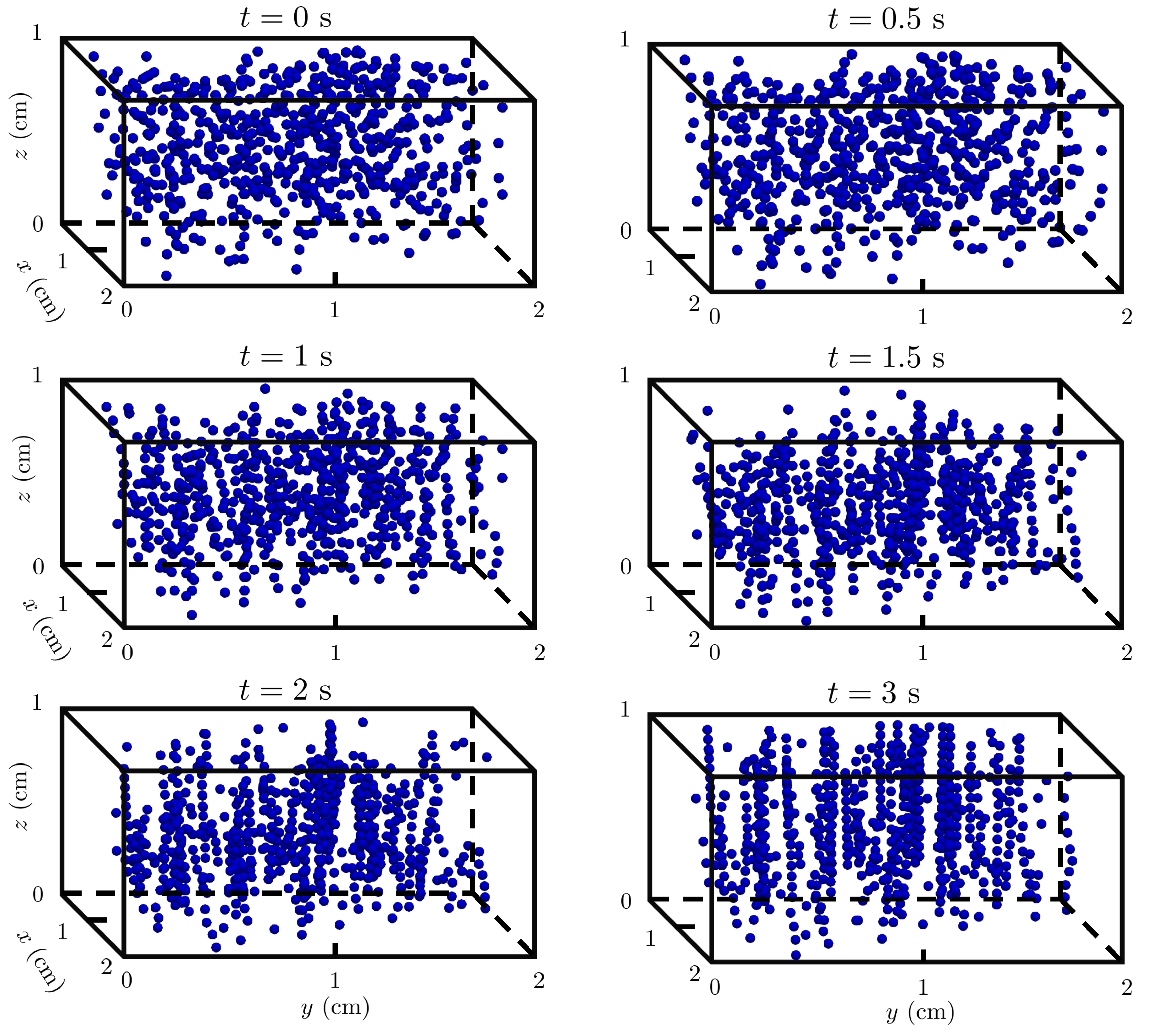
4.3. Multi-particle chaining under magnetic field: 2D
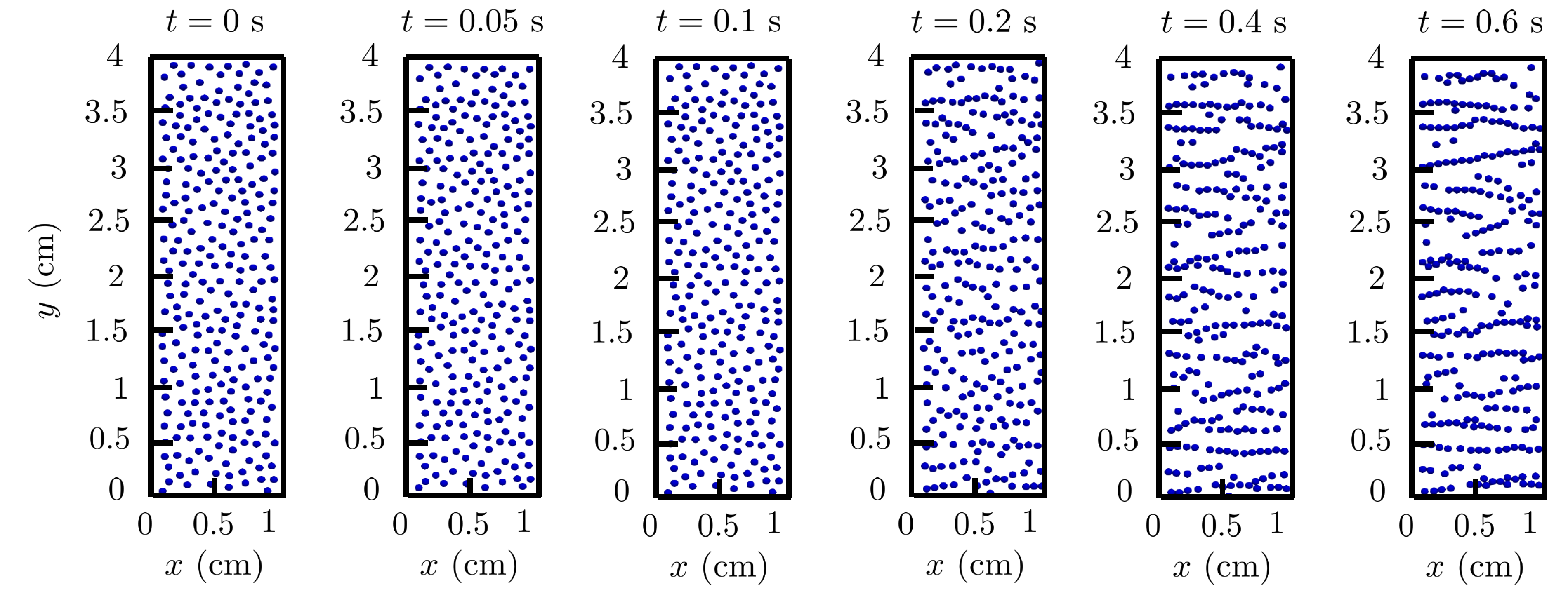
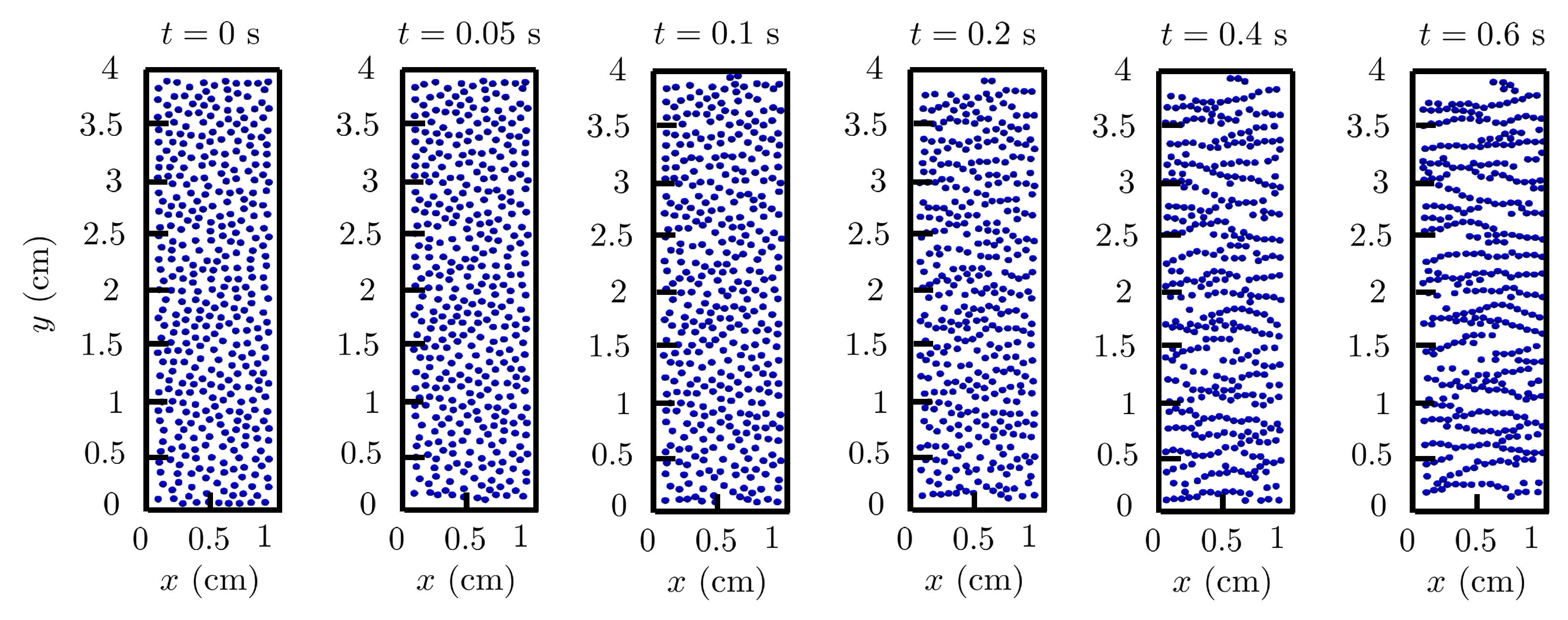
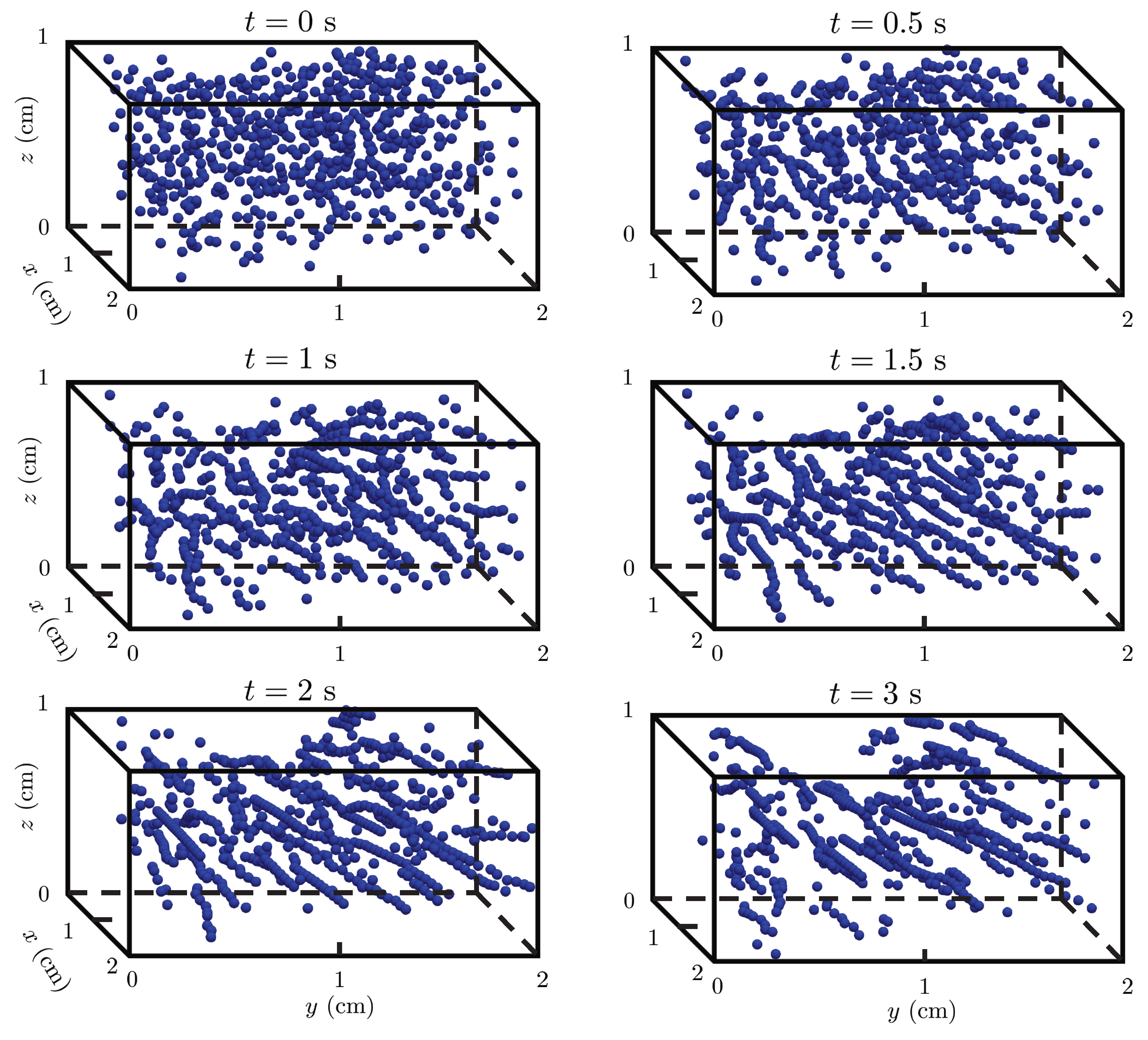
4.4. Multi-particle chaining under magnetic field: 3D
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References
- A. Satoh. Modeling of magnetic particle suspensions for simulations, CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group: Florida, 2017.
- J.S. Kumar, P.S. Paul, G. Raghunathan, and D.G. Alex. A review of challenges and solutions in the preparation and use of magnetorheological fluids. International Journal of Mechanical and Materials Engineering, 14:13, 2019. [CrossRef]
- W.A. Bullough. Electro-Rheological Fluids, Magneto-Rheological Suspensions and Associated Technology. World Scientific, Singapore, 1996.
- N.M. Wereley. Magnetorheology: Advances and Applications. Royal Society of Chemistry, London, 2013.
- A.A. Kuznetsov, V.I. Filippov, O.A. Kuznetsov, V.G. Gerlivanov, E.K. Dobrinsky, and S.I. Malashin. New ferro-carbon adsorbents for magnetically guided transport of anti-cancer drugs. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 194:22–30, 1999. [CrossRef]
- J. Weingart, P. Vabbilisetty, and X. Sun. Membrane mimetic surface functionalization of nanoparticles: Methods and applications. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 197–198:68–84, 2013. [CrossRef]
- P.I. Girginova, A.L. Daniel da Silva, C.B. Lopes, P. Figueira, M. Otero, V.S. Amaral, E. Pereira, and T. Trindade. Silica coated magnetite particles for magnetic removal of Hg2+ from water. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 345:234–240, 2010. [CrossRef]
- S. Lan, X. Wu, L. Li, M. Li, F. Guo, and S. Gan. Synthesis and characterization of hyaluronic acid-supported magnetic microspheres for copper ions removal. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 425:42–50, 2013. [CrossRef]
- T.L. Chow. Introduction to electromagnetic theory: a modern perspective. Jones & Bartlett Learning, Massachusetts, 2006.
- I.S. Grant and W.R. Phillips. Electromagnetism. John Wiley & Sons, New York, 2008.
- T.G. Kang, M.A. Hulsen, J.M.J. den Toonder, P.D. Anderson, and H.E.H. Meijer. A direct simulation method for flows with suspended paramagnetic particles. Journal of Computational Physics, 227:4441–4458, 2008. [CrossRef]
- M.A. Hayes, N.P. Polson, and A.A. Garcia. Active control of dynamic supraparticle structures in microchannels. Langmuir, 17:2866–2871, 2001. [CrossRef]
- S. Melle and J.E. Martin. Chain model of a magnetorheological suspension in a rotating field. Journal of Chemical Physics, 118:9875–9881, 2003. [CrossRef]
- E.E. Keaveny and M.R. Maxey. Modeling the magnetic interactions between paramagnetic beads in magnetorheological fluids. Journal of Computational Physics, 227:9554–9571, 2008. [CrossRef]
- K. Han, Y.T. Feng, and D.R.J. Owen. Three-dimensional modelling and simulation of magnetorheological fluids. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 84:1273–1302, 2010. [CrossRef]
- G.G. Stokes. On the effect of internal friction of fluids on the motion of pendulums. In G.G. Stokes, editor, Mathematical and Physical Papers. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1901. [CrossRef]
- C.-H. Ke, S. Shu, H. Zhang, and H.-Z. Yuan. LBM-IBM-DEM modelling of magnetic particles in a fluid. Powder Technology, 314:264–280, 2017. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J. Zhou, and C. Shao. Numerical investigation on yielding phenomena of magnetorheological fluid flowing through microchannel governed by transverse magnetic field. Physics of Fluids, 31:022005, 2019. [CrossRef]
- J.-Feng Zhou, S. Zhang, F. Tian, and C.-Lei Shao. Simulation of oscillation of magnetic particles in 3D microchannel flow subjected to alternating gradient magnetic field. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 473:32–41, 2019. [CrossRef]
- T. Leps and C. Hartzell. High fidelity, discrete element method simulation of magnetorheological fluids using accurate particle size distributions in LIGGGHTS extended with mutual dipole method. Materials Research Express, 8:085701, 2021. [CrossRef]
- DCS Computing GmbH. LIGGGHTS public documentation, 2015. Available online: https://www.cfdem.com/media/DEM/docu/gran_model_hertz.html.
- Tajfirooz, J.G. Meijer, R.A. Dellaert, A.M. Meulenbroek, J.C.H. Zeegers, and J.G.M. Kuerten. Direct numerical simulation of magneto-Archimedes separation of spherical particles. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 910:A52, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Z. Zhou, S. Kuang, K. Chu, and A. Yu. Discrete particle simulation of particle-fluid flow: Model formulations and their applicability. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 661:482–510, 2010. [CrossRef]
- C. Fernandes, D. Semyonov, L.L. Ferrás, and J.M. Nóbrega. Validation of the CFD–DPM solver DPMFoam in OpenFOAM through analytical, numerical and experimental comparisons. Granular Matter, 20:64, 2018. [CrossRef]
- S. Osher and S. Fedkiw. Level Set Methods and Dynamic Implicit Surfaces. Springer-Verlag, New York, 2003.
- J.D. Jackson. Classical Electrodynamics. John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1999.
- R.G. Gontijo and F.R. Cunha. Numerical simulations of magnetic suspensions with hydrodynamic and dipole-dipole magnetic interactions and dipole-dipole magnetic interactions. Physics of Fluids, Physics of Fluids 29(6):062004, 2017 . [CrossRef]
- V.C.A. Ferraro. Electromagnetic Theory. The Athlone Press, London, 1961.
- Large-scale Atomic/Molecular Massively Parallel Simulator. Dipole-dipole, 2022. Available online: https://docs.lammps.org/pair_dipole.html.
- R. Glowinski, T.W. Pan, T.I. Hesla, D.D. Joseph, and J. Périaux. A fictitious domain approach to the direct numerical simulation of incompressible viscous flow past moving rigid bodies: Application to particulate flow. Journal of Computational Physics, 169:363–426, 2001. [CrossRef]
- C. Fernandes, S.A. Faroughi, O.S. Carneiro, J.M. Nóbrega, and G.H. McKinley. Fully-resolved simulations of particle-laden viscoelastic fluids using an immersed boundary method. Journal of Non-Newtonian Fluid Mechanics, 266:80–94, 2019. [CrossRef]
- A. Di Renzo and F.P. Di Maio. Comparison of contact-force models for the simulation of collisions in DEM-based granular flow codes. Chemical Engineering Science, 59:525–541, 2004. [CrossRef]
- C. Kloss, C. Goniva, A. Hager, S. Amberger, and S. Pirker. Models, algorithms and validation for opensource DEM and CFD-DEM. Progress in Computational Fluid Dynamics, 12:140–152, 2012. [CrossRef]
- P.A. Cundall and O.D.L. Strack. A discrete numerical model for granular assemblies. Géotechnique, 29:47–65, 1979. [CrossRef]
- E.G. Nezami, Y.M.A. Hashash, D. Zhao, and J. Ghaboussi. A fast contact detection algorithm for 3-D discrete element method. Computers and Geotechnics, 31(7):575–587, 2004. [CrossRef]
- L. Lu, X. Gao, J.-F. Dietiker, M. Shahnam, and W.A. Rogers. Machine learning accelerated discrete element modeling of granular flows. Chemical Engineering Science, 245:116832, 2021. [CrossRef]
- A. Hager, C. Kloss, S. Pirker, and C. Goniva. Parallel resolved open source CFD-DEM: method, validation and application. The Journal of Computational Multiphase Flows, 6:13–27, 2014. [CrossRef]
- K.I. Aycock, R.L. Campbell, K.B. Manning, and B.A. Craven. A resolved two-way coupled CFD/6-DOF approach for predicting embolus transport and the embolus-trapping efficiency of IVC filters. Biomechanics and Modeling in Mechanobiology, 16:851–869, 2017. [CrossRef]
- L. Verlet. Computer experiments on classical fluids I. Thermodynamical properties of Lennard-Jones molecules. Physical Review, 159:98–103, 1967. [CrossRef]
- R.I. Issa. Solution of the implicitly discretized fluid flow equations by operator-splitting. Journal of Computational Physics, 62:40–65, 1986. [CrossRef]
- CFDEMcoupling. CFDEM project, 2011. Available online: https://www.cfdem.com/cfdemcoupling.
- F. Fortes, D.D. Joseph, and T.S. Lundgren. Non-linear mechanics of fluidization of beds of spherical particles. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 177:467–483, 1987. [CrossRef]
- H.H. Hu, D.D. Joseph, and M.J. Crochet. Direct simulation of fluid particle motions. Theoretical and Computational Fluid Dynamics, 3:285–306, 1992. [CrossRef]
- A.A. Johnson and T.E. Tezduyar. Simulation of multiple spheres falling in a liquid-filled tube. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 134:351–373, 1996. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering. [CrossRef]
- J. Feng, H.H. Hu, and D.D. Joseph. Direct simulation of initial value problems for the motion of solid bodies in a Newtonian fluid. Part 1. Sedimentation. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 261:95–134, 1994. [CrossRef]
- H. Jasak. Dynamic mesh handling in OpenFOAM. In 47th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting, Orlando, Florida, 2009.
- P.Y. Huang, J. Feng, and D.D. Joseph. The turning couples on an elliptic particle settling in a vertical channel. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 271:1–16, 1994. [CrossRef]
- J.B. Ritz and J.P. Caltagirone. A numerical continuous model for the hydrodynamics of fluid particle systems. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Fluids, 30:1067–1090, 1999. [CrossRef]
- H.V. Ly, F. Reitich, M.R. Jolly, H.T. Banks, and K. Ito. Simulations of particle dynamics in magnetorheological fluids. Journal of Computational Physics, 155:160–177, 1999. [CrossRef]
- M. Mohebi, N. Jamasbi, and J. Liu. Simulation of the formation of nonequilibrium structures in magnetorheological fluids subject to an external magnetic field. Physical Review E, 54:5407–5413, 1996. [CrossRef]
- M. Fermigier and A.P. Gast. Structure evolution in a paramagnetic latex suspension. Journal of Colloid Interface Sciences, 154:522–539, 1992. [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




