Submitted:
25 February 2023
Posted:
27 February 2023
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Tobacco
1.2. HIV and Tobacco
2. Alcohol
3. Diet as a risk factor for cancer.
4. Physical Inactivity and Exercise
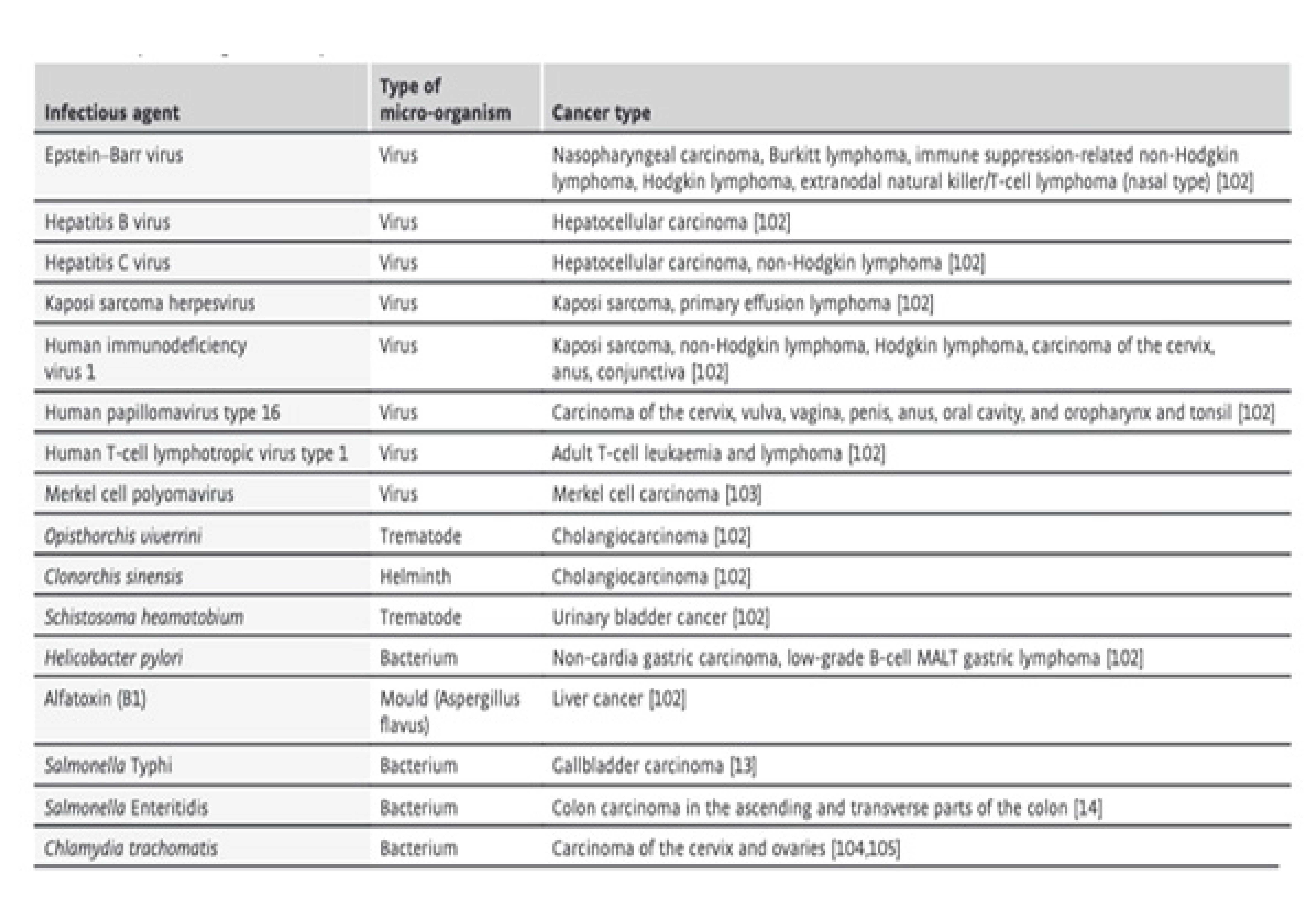
5. Infectious agents
References
- Ranjan, A.; Sharavan, R.; Nehal, G.; Itishree, K.; Stephen, W.; Suyash, S.; Hiranmoy, D.; Sangeeta, S.; Sahdeo, P.; Sanjay, S. Role of Phytochemicals in Cancer Prevention. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, P.; Kunnumakkara, A.B.; Sundaram, C.; Harikumar, K.B.; Tharakan, S.T.; Lai, O.S.; Sung, B.; Aggarwal, B.B. Cancer is a preventable disease that requires major lifestyle changes. Pharm. Res. 2008, 25, 2097–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrieu, N.; Easton, D.F.; Chang-Claude, J.; Rookus, M.A.; Brohet, R.; Cardis, E.; Antoniou, A.C.; Wagner, T.; Simard, J.; Evans, G.; et al. Effect of Chest X-Rays on the Risk of Breast Cancer Among BRCA1/2 Mutation Carriers in the International BRCA1/2 Carrier Cohort Study: A Report from the EMBRACE, GENEPSO, GEO-HEBON, and IBCCS Collaborators’ Group. J. Clin. Orthod. 2006, 24, 3361–3366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arafa, A.; Mostafa, A.; Navarini, A.A.; Dong, J.Y. The association between smoking and risk of skin cancer: A meta-analysis of cohort studies. Cancer Causes Control. 2020, 31, 787–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baecker, A.; Liu, X.; La Vecchia, C.; Zhang, Z.F. Worldwide incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma cases attributable to major risk factors. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 2018, 27, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, I.; Giordano, C. Leptin and Beyond: Actors in Cancer. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belfiore, A.; Malaguarnera, R.; Nicolosi, M.L.; Lappano, R.; Ragusa, M.; Morrione, A.; Vella, V. A Novel Functional Crosstalk between DDR1 and the IGF Axis and Its Relevance for Breast Cancer. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2018, 12, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernatsky, S.; Ramsey-Goldman, R.; Petri, M.; Urowitz, M.B.; Gladman, D.D.; Fortin, P.R.; Yelin, E.H.; Ginzler, E.; Hanly, J.G.; Peschken, C.; et al. Smoking Is the Most Significant Modifiable Lung Cancer Risk Factor in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. J. Rheumatol. 2018, 45, 393–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielecka, J.; Markiewicz-Żukowska, R. TheInfluenceof Nutritional and Lifestyle Factors on Glioma Incidence. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingham, S.A.; Hughes, R.; Cross, A.J. Effect of White versus Red Meat on Endogenous N-Nitrosation in the Human Colon and Further Evidence of a Dose Response. J. Nutr. 2002, 132 (Suppl. 11), 3522S–3525S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boffetta, P.; Hashibe, M.; La Vecchia, C.; Zatonski, W.; Rehm, J. The Burden of Cancer Attributable to Alcohol Drinking. Int. J. Cancer. J. Int. Du Cancer 2006, 119, 884–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.C.; Winters-Stone, K.; Lee, A.; Schmitz, K.H. Cancer, Physical Activity, and Exercise. Compr. Physiol. 2012, 2, 2775–2809. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Z.-Z.; Ao, Y.-J.; Zhou, S.-H. The Role of Cancer Stromal Fibroblasts in Mediating the Effects of Tobacco-Induced Cancer Cell Growth. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chazelas, E.; Pierre, F.; Druesne-Pecollo, N.; Gigandet, S.; Srour, B.; Huybrechts, I.; Julia, C.; Kesse-Guyot, E.; Deschasaux-Tanguy, M.; Touvier, M. Nitrites and Nitrates from Food Additives and Cancer Risk: Results from the NutriNet-Santé Cohort. Eur. J. Public Health 2021, 31 (Suppl. 3). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooley, T.P. Non-AIDS-defining cancer in HIV-infected people. Hematol./Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2003, 17, 889–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandawate, P.R.; Subramaniam, D.; Jensen, R.A.; Anant, S. Targeting Cancer Stem Cells and Signaling Pathways by Phytochemicals: Novel Approach for Breast Cancer Therapy. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2016, 40–41, 192–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Tu, Z.; Chen, H.; Liu, Z. Identifying modifiable risk factors of lung cancer: Indications from Mendelian randomization. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0258498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosil-Díaz, O.; Ruano-Ravina, A.; Gestal-Otero, J.J.; Barros-Dios, J.M. Meat and Fish Consumption and Risk of Lung Cancer: A Case–control Study in Galicia, Spain. Cancer Lett. 2007, 252, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Elsland, D.; Neefjes, J. Bacterial Infections and Cancer. EMBO Reports 2018, 19, e46632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippini, G.; Maisonneuve, P.; McCredie, M.; Peris-Bonet, R.; Modan, B.; Preston-Martin, S.; Mueller, B.A.; Holly, E.A.; Cordier, S.; Choi, N.W.; et al. Relation of childhood brain tumors to exposure of parents and children to tobacco smoke: The SEARCH international case-control study. Surveillance of Environmental Aspects Related to Cancer in Humans. Int. J. Cancer 2002, 100, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiolet, T.; Srour, B.; Sellem, L.; Kesse-Guyot, E.; Allès, B.; Méjean, C.; Deschasaux, M.; Fassier, P.; Latino-Martel, P.; Beslay, M.; et al. Consumption of Ultra-Processed Foods and Cancer Risk: Results from NutriNet-Santé Prospective Cohort. BMJ 2018, 360, k322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedenreich, C.M.; Ryder-Burbidge, C.; McNeil, J. Physical Activity, Obesity and Sedentary Behavior in Cancer Etiology: Epidemiologic Evidence and Biologic Mechanisms. Mol. Oncol. 2021, 15, 790–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Breitling, L.P.; Brenner, H. Tobacco Smoking and Methylation of Genes Related to Lung Cancer Development. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 59017–59028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianni, T.; Silvia, L.; Paolo, B. Alcohol and Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Review and a Point of View. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 15943–15954. [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert, E.S. Ionising Radiation and Cancer Risks: What Have We Learned from Epidemiology? Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2009, 85, 467–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, C.A.; Pera, G.; Agudo, A.; Bueno-de-Mesquita, H.B.; Ceroti, M.; Boeing, H.; Schulz, M.; Del Giudice, G.; Plebani, M.; Carneiro, F.; et al. Fruit and vegetable intake and the risk of stomach and oesophagus adenocarcinoma in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC-EURGAST). Int. J. Cancer 2006, 118, 2559–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hausen, H.z. The Search for Infectious Causes of Human Cancers: Where and Why. Virology 2009, 392, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, M.A.; Ullrich, R.L. Ionizing Radiation. In Tumour Site Concordance and Mechanisms of Carcinogenesis; Baan, R.A., Stewart, B.W., Straif, K., Eds.; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins, B.D.; Goncalves, M.D.; Cantley, L.C. Obesity and Cancer Mechanisms: Cancer Metabolism. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 4277–4283. [Google Scholar]
- Hua, H.; Kong, Q.; Yin, J.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, Y. Insulin-like Growth Factor Receptor Signaling in Tumorigenesis and Drug Resistance: A Challenge for Cancer Therapy. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hursting, S.D.; Digiovanni, J.; Dannenberg, A.J.; Azrad, M.; Leroith, D.; Demark-Wahnefried, W.; Kakarala, M.; Brodie, A.; Berger, N.A. Obesity, Energy Balance, and Cancer: New Opportunities for Prevention. Cancer Prev. Res. 2012, 5, 1260–1272. [Google Scholar]
- Idorn, M.; thor Straten, P. Exercise and Cancer: From ‘healthy’ to ‘therapeutic’? Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2017, 66, 667–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingraham, B.A.; Bragdon, B.; Nohe, A. Molecular Basis of the Potential of Vitamin D to Prevent Cancer. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2008, 24, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islami, F.; Goding Sauer, A.; Miller, K.D.; Siegel, R.L.; Fedewa, S.A.; Jacobs, E.J.; McCullough, M.L.; Patel, A.V.; Ma, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; et al. Proportion and number of cancer cases and deaths attributable to potentially modifiable risk factors in the United States. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 31–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalia, S.; Kwong, Y. Relationship between sun safety behaviours and modifiable lifestyle cancer risk factors and vitamin D levels. Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 2019, 35, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, Y.H.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, W.S.; Park, C.K.; Park, C.K.; Suh, Y.G.; Eom, J.S.; Cho, S.; Hur, J.Y.; Hwang, S.H.; et al. Risk factors forprimarylung canceramong never-smoking women in South Korea: A retrospective nationwide population-based cohort study. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2020, 35, 692–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolonel, L.N.; Altshuler, D.; Henderson, B.E. The multiethnic cohort study: Exploring genes, lifestyle and cancer risk. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotnis, A.; Namkung, J.; Kannan, S.; Jayakrupakar, N.; Park, T.; Sarin, R.; Mulherkar, R. MultiplePathway-Based GeneticVariations Associated with Tobacco Related Multiple Primary Neoplasms. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, R.; Matulla-Nolte, B.; Essers, M.; Brown, A.; Hopfenmüller, W. UV Radiation and Cancer Prevention: What Is the Evidence? Anticancer. Res. 2006, 26, 2723–2727. [Google Scholar]
- La Vecchia, C.; Tavani, A.; Franceschi, S.; Levi, F.; Corrao, G.; Negri, E. Epidemiology and Prevention of Oral Cancer. Oral Oncol. 1997, 33, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauber, S.N.; Nigel, J. Gooderham. The Cooked Meat Derived Genotoxic Carcinogen 2-Amino-3-methylimidazo[4,5-B] pyridine Has Potent Hormone-like Activity: Mechanistic Support for a Role in Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 9597–9602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.W.; Lee, H.J.; Surh, Y.-J.; Lee, C.Y. Vitamin C and Cancer Chemoprevention: Reappraisal. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 78, 1074–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, W.; Wang, R.; Xing, B.; Yao, Y. Fish intake and the risk of brain tumour: A meta-analysis with systematic review. Nutr. J. 2017, 16, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ligibel, J.A.; Basen-Engquist, K.; Bea, J.W. Weight Management and Physical Activity for Breast Cancer Prevention and Control. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncology. Annu. Meet. 2019, 39, e22–e33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longo, V.D.; Finch, C.E. Evolutionary Medicine: From Dwarf Model Systems to Healthy Centenarians? Science 2003, 299, 1342–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massarweh, N.N.; El-Serag, H.B. Epidemiology of Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. Cancer Control. 2017, 24, 1073274817729245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, H.; Takaki, A. Alcohol and Hepatocellular Carcinoma. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2019, 6, e000260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mentella, M.C.; Scaldaferri, F.; Ricci, C.; Gasbarrini, A.; Miggiano, G.A.D. Cancer and Mediterranean Diet: A Review. Nutrients 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muncke, J. Tackling the Toxics in Plastics Packaging. PLoS Biol. 2021, 19, e3000961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayanan, D.L.; Saladi, R.N.; Fox, J.L. Ultraviolet Radiation and Skin Cancer. Int. J. Dermatol. 2010, 49, 978–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimptsch, K.; Pischon, T. Obesity Biomarkers, Metabolism and Risk of Cancer: An Epidemiological Perspective. In Obesity and Cancer; Recent Results in Cancer Research. Fortschritte Der Krebsforschung. Progres Dans Les Recherches Sur Le Cancer; Springer: Cham, The Switzerland, 2016; Volume 208, pp. 199–217. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, D.; McNally, R.; Birch, J.M. Parental smoking and childhood cancer: Results from the United Kingdom Childhood Cancer Study. Br. J. Cancer 2003, 88, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappas, G. Infectious Causes of Cancer: An Evolving Educational Saga. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2009, 15, 961–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsonnet, J. Bacterial Infection as a Cause of Cancer. Environ. Health Perspect. 1995, 103, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peltzer, K.; Phaswana-Mafuya, N. Fruit and vegetable intake and associated factors in older adults in South Africa. Glob. Health Action 2012, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petros, W.P.; Younis, I.R.; Ford, J.N.; Weed, S.A. Effects of Tobacco Smoking and Nicotine on Cancer Treatment. Pharmacotherapy 2012, 32, 920–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisani, P.; Parkin, D.M.; Muñoz, N.; Ferlay, J. Cancer and Infection: Estimates of the Attributable Fraction in 1990. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 1997, 6, 387–400. [Google Scholar]
- Poorolajal, J.; Moradi, L.; Mohammadi, Y.; Cheraghi, Z.; Gohari-Ensaf, F. Risk factors for stomach cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Epidemiol. Health 2020, 42, e2020004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preston-Martin, S.; Yu, M.C.; Benton, B.; Henderson, B.E. N-Nitroso compounds and childhood brain tumors: A case-control study. Cancer Res. 1982, 42, 5240–5245. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rajalakshmi, T.R.; Babu, N.A.; Shanmugam, K.T.; Masthan, K.M.K. DNA Adducts-Chemical Addons. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2015, 7 (Suppl. 1), S197–S199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranjan, A.; Ramachandran, S.; Gupta, N.; Kaushik, I.; Wright, S.; Srivastava, S.; Das, H.; Srivastava, S.; Prasad, S.; Srivastava, S.K. Role of Phytochemicals in Cancer Prevention. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratna, A.; Mandrekar, P. Alcohol and Cancer: Mechanisms and Therapies. Biomolecules 2017, 7, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renehan, A.G.; Roberts, D.L.; Dive, C. Obesity and Cancer: Pathophysiological and Biological Mechanisms. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2008, 114, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumgay, H.; Murphy, N.; Ferrari, P.; Soerjomataram, I. Alcohol and Cancer: Epidemiology and Biological Mechanisms. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, G.L. Ins and Outs of Dietary Phytochemicals in Cancer Chemoprevention. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2007, 74, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, Y.F.; Kawaguchi, S.; Kamaya, A.; Ohshita, M.; Kabasawa, K.; Iwama, K.; Taniguchi, K.; Tsuda, S. The Comet Assay with 8 Mouse Organs: Results with 39 Currently Used Food Additives. Mutat. Res. 2002, 519, 103–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Zhou, H.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, T.; Yang, Y.; Fang, W.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, L. A modifiable risk factors atlas of lung cancer: A Mendelian randomization study. Cancer Med. 2021, 10, 4587–4603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigel, K.; Makinson, A.; Thaler, J. Lung cancer in persons with HIV. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2017, 12, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stickel, F.; Lutz, P.; Buch, S.; Nischalke, H.D.; Silva, I.; Rausch, V.; Fischer, J.; Weiss, K.H.; Gotthardt, D.; Rosendahl, J.; et al. Genetic Variation in HSD17B13 Reduces the Risk of Developing Cirrhosis and Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Alcohol Misusers. Hepatology 2020, 72, 88–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.-H.; Chiu, Y.-C.; Tan, T.-W.; Yang, R.-S.; Fu, W.-M. Adiponectin Enhances IL-6 Production in Human Synovial Fibroblast via an AdipoR1 Receptor, AMPK, p38, and NF-Kappa B Pathway. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 5483–5492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viarisio, D.; Gissmann, L.; Tommasino, M. Human papillomaviruses and carcinogenesis: Well-established and novel models. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2017, 26, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, M.; Holman, D.M.; Maguire-Eisen, M. Ultraviolet Radiation Exposure and Its Impact on Skin Cancer Risk. Semin. Oncol. Nurs. 2016, 32, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, D.D.; Aminzadeh-Gohari, S.; Tulipan, J.; Catalano, L.; Feichtinger, R.G.; Kofler, B. Ketogenic Diet in the Treatment of Cancer—Where Do We Stand? Mol. Metab. 2020, 33, 102–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willett, W.C.; MacMahon, B. Diet and Cancer--an Overview. New Engl. J. Med. 1984, 310, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willett, W.C.; Stampfer, M.J.; Colditz, G.A.; Rosner, B.A.; Hennekens, C.H.; Speizer, F.E. Moderate alcohol consumption and the risk of breast cancer. New Engl. J. Med. 1987, 316, 1174–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wie, G.A.; Cho, Y.A.; Kang, H.H.; Ryu, K.A.; Yoo, M.K.; Kim, Y.A.; Jung, K.W.; Kim, J.; Lee, J.H.; Joung, H. Red meat consumption is associated with an increased overall cancer risk: A prospective cohort study in Korea. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 112, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, R.R.; Horm, J.W. Association of Cancer Sites with Tobacco and Alcohol Consumption and Socioeconomic Status of Patients: Interview Study from the Third National Cancer Survey. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1977, 58, 525–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Shen, S.; Verma, I.M. NF-κB, an Active Player in Human Cancers. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2014, 2, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Luo, J. Alcohol and Cancer Stem Cells. Cancers 2017, 9, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamura, Y.; Oum, R.; Gbito, K.Y.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Strom, S.S. Dietary intake of vegetables, fruits, and meats/beans as potential risk factors of acute myeloid leukemia: A Texas case-control study. Nutr. Cancer 2013, 65, 1132–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.D.; Hainaut, P.; Gores, G.J.; Amadou, A.; Plymoth, A.; Roberts, L.R. A global view of hepatocellular carcinoma: Trends, risk, prevention and management. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 589–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu Mimi, C.; Yuan, J.-M.; Lu, S.C. Alcohol, Cofactors and the Genetics of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 23 (Suppl. 1), S92–S97. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Chen, Y.; Heiman, M.; Dimarchi, R. Leptin: Structure, Function and Biology. Vitamins and Hormones 2005, 71, 345–372. [Google Scholar]
- Zumel-Marne, A.; Castano-Vinyals, G.; Kundi, M.; Alguacil, J.; Cardis, E. Environmental Factors and the Risk of Brain Tumours in Young People: A Systematic Review. Neuroepidemiology 2019, 53, 121–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Luo, J. Alcohol and Cancer Stem Cells. Cancers 2017, 9, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamura, Y.; Oum, R.; Gbito, K.Y.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Strom, S.S. Dietary intake of vegetables, fruits, and meats/beans as potential risk factors of acute myeloid leukemia: A Texas case-control study. Nutr. Cancer 2013, 65, 1132–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.D.; Hainaut, P.; Gores, G.J.; Amadou, A.; Plymoth, A.; Roberts, L.R. A global view of hepatocellular carcinoma: Trends, risk, prevention and management. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 589–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.C.; Yuan, J.-M.; Lu, S.C. Alcohol, Cofactors and the Genetics of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 23 (Suppl. 1), S92–S97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Chen, Y.; Heiman, M.; Dimarchi, R. Leptin: Structure, Function and Biology. Vitam. Horm. 2005, 71, 345–372. [Google Scholar]
- Zumel-Marne, A.; Castano-Vinyals, G.; Kundi, M.; Alguacil, J.; Cardis, E. Environmental Factors and the Risk of Brain Tumours in Young People: A Systematic Review. Neuroepidemiology 2019, 53, 121–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





