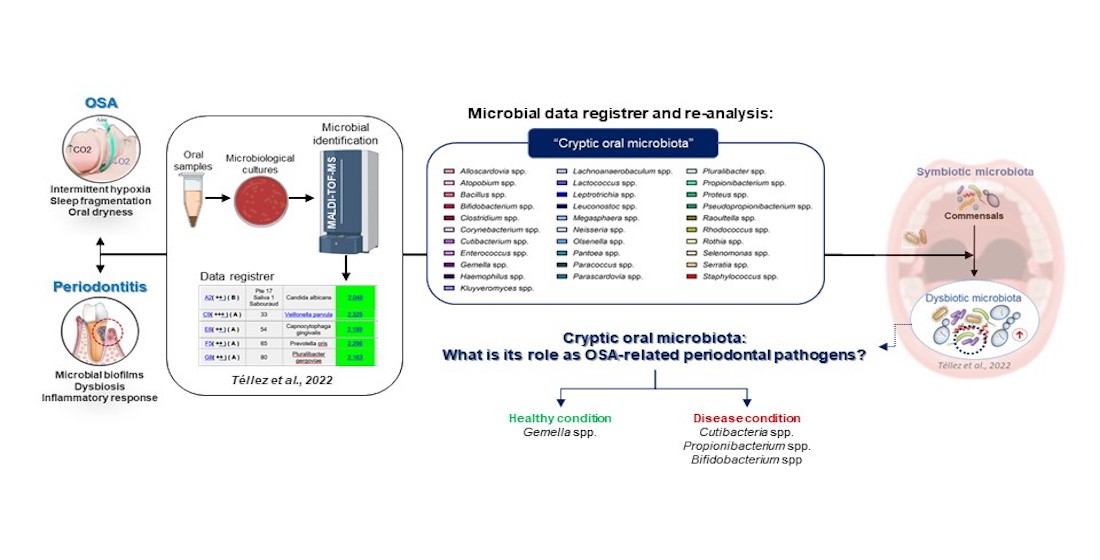
Commonly the periodontitis has been linked to periodontopathogens categorized in Socransky's microbial complexes, however, there is a lack of knowledge regarding “other microorganisms” or "cryptic microorganisms", which are rarely thought of as significant oral pathogens and are neither previously categorized nor connected to illnesses in the oral cavity. This study hypothesized that these cryptic microorganisms could contribute to the modulation of oral microbiota present in health or disease (periodontitis and/or OSA patients). For this purpose, the presence and the correlation among these cultivable cryptic oral microorganisms were identified and their possible role in both conditions was determined. Data from oral samples of individuals with or without periodontitis and with or without OSA were obtained from a previous study. Demographic data, clinical oral characteristics, and genera and species of cultivable cryptic oral microorganisms identified by MALDI-TOF were recorded. The data of 75 participants were analyzed to determine the relative frequencies of cultivable cryptic microorganisms’ genus and species, microbial clusters and correlations tests were performed. According to periodontal condition, Gingivitis - dental biofilm-induced in reduced periodontium and stage III periodontitis were found to have the highest diversity of cryptic microorganism species. Based on the experimental condition these findings showed that there are genera related to disease conditions and others related to healthy conditions, with species that could be related to different chronic diseases being highlighted as comorbidities periodontitis and OSA. The cryptic microorganisms within the oral microbiota of patients with periodontitis and OSA are present as potential pathogens, promoting the development of dysbiotic microbiota, and the occurrence of chronic diseases, which have been previously proposed to be common risk factors for periodontitis and OSA. Understanding the function of possible pathogens in the oral microbiota will take more research.