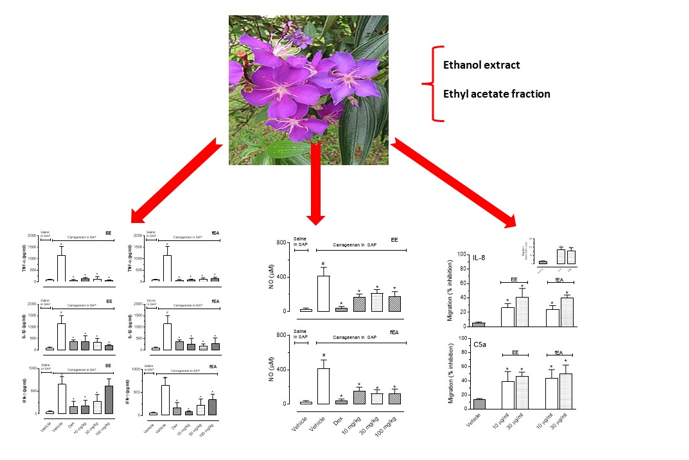
The ethanol extract (EE) prepared from the leaves of Tibouchina granulosa, and its fraction in ethyl acetate (fEA) were evaluated concerning their capacity to reduce inflammation in different experimental models. fEA was also studied concerning its chemical constituents. EE and fEA were assayed for their anti-inflammatory potential, using formalin-induced licking behaviour and carrageenan-induced inflammation into the subcutaneous air pouch (SAP) models. Reduction in polymorphonuclear cells (PMN) activation was performed in freshly isolated PMN. Chromatographic analysis of fEA was done by HPLC. Hispiduloside was isolated as the main constituent in fEA and its quantity was estimated to be 11.75% in fEA, 3.05% in EE, and 0.2% (w/w) in the plant. EE (30 mg/kg) significantly reduced the second phase of formalin-induced licking. fEA demonstrated a reduction in leukocyte migration into the SAP. EE and fEA drastically reduced cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1β, and IFN-γ), nitric oxide (NO) production, in vitro PMN migration induced by C5a and IL-8, and TNF-α and IL-1β gene expression. Taken together our data indicate that either ethanol extract or its fEA fraction from leaves of T. granulosa present an anti-inflammatory effect contributing to the pharmacological and chemical knowledge of this species and confirming the rationale behind its traditional use.