Submitted:
06 November 2024
Posted:
07 November 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. HEXA Failed in Inducing Central Nervous System Effects in Mice
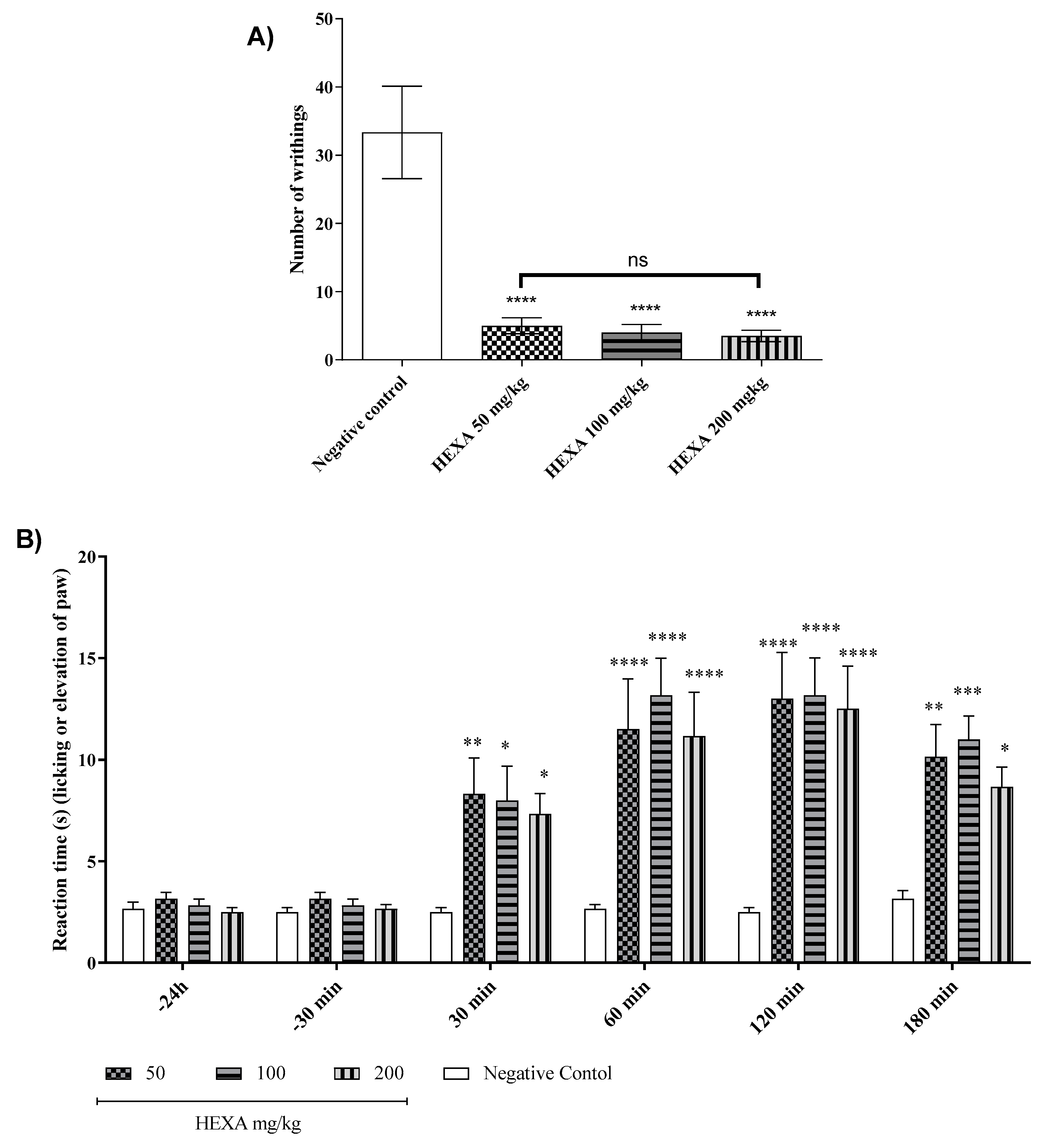
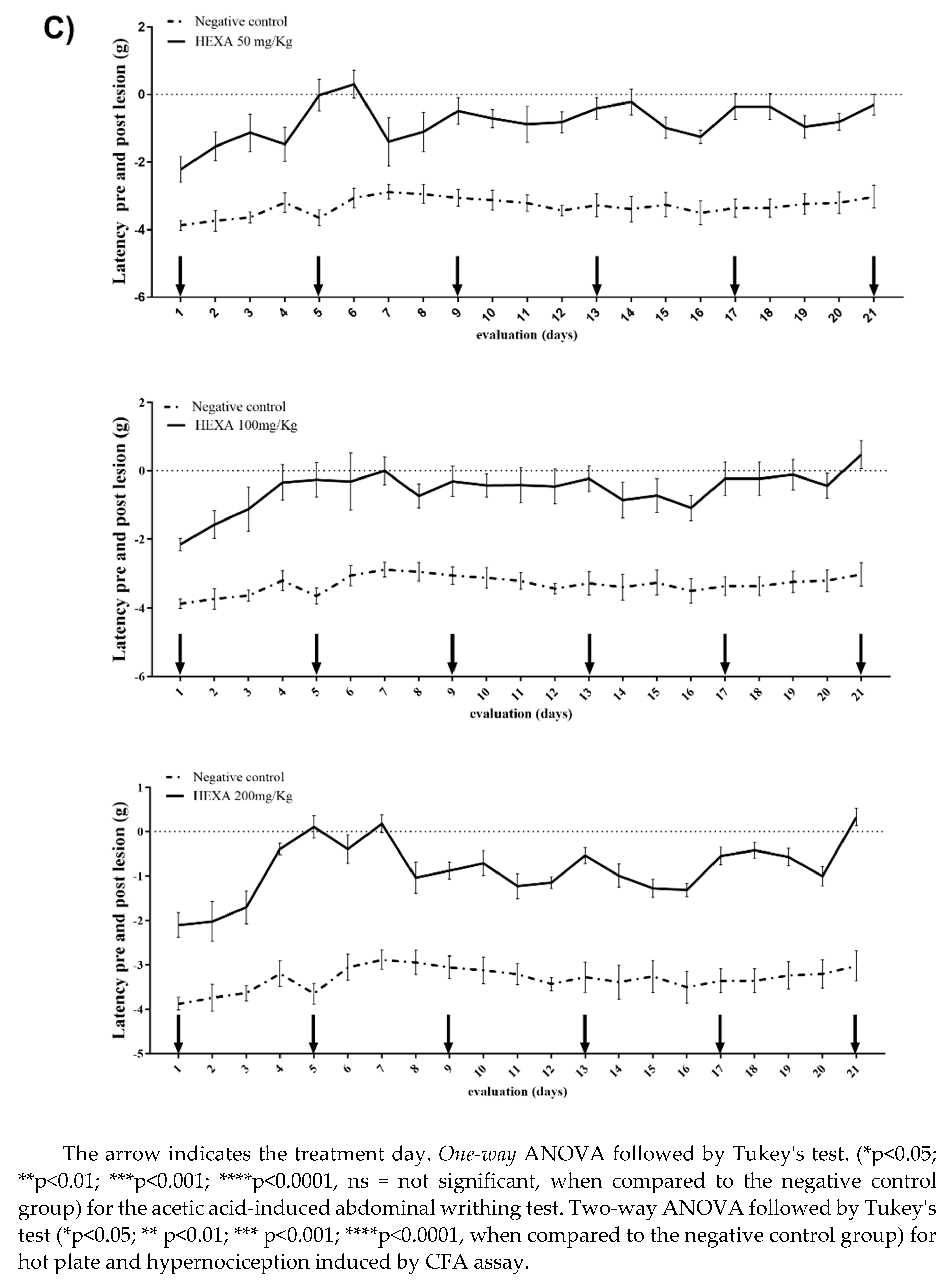
2.2. HEXA Has Antinociceptive Activity In Vivo: Central and Peripheral Effects
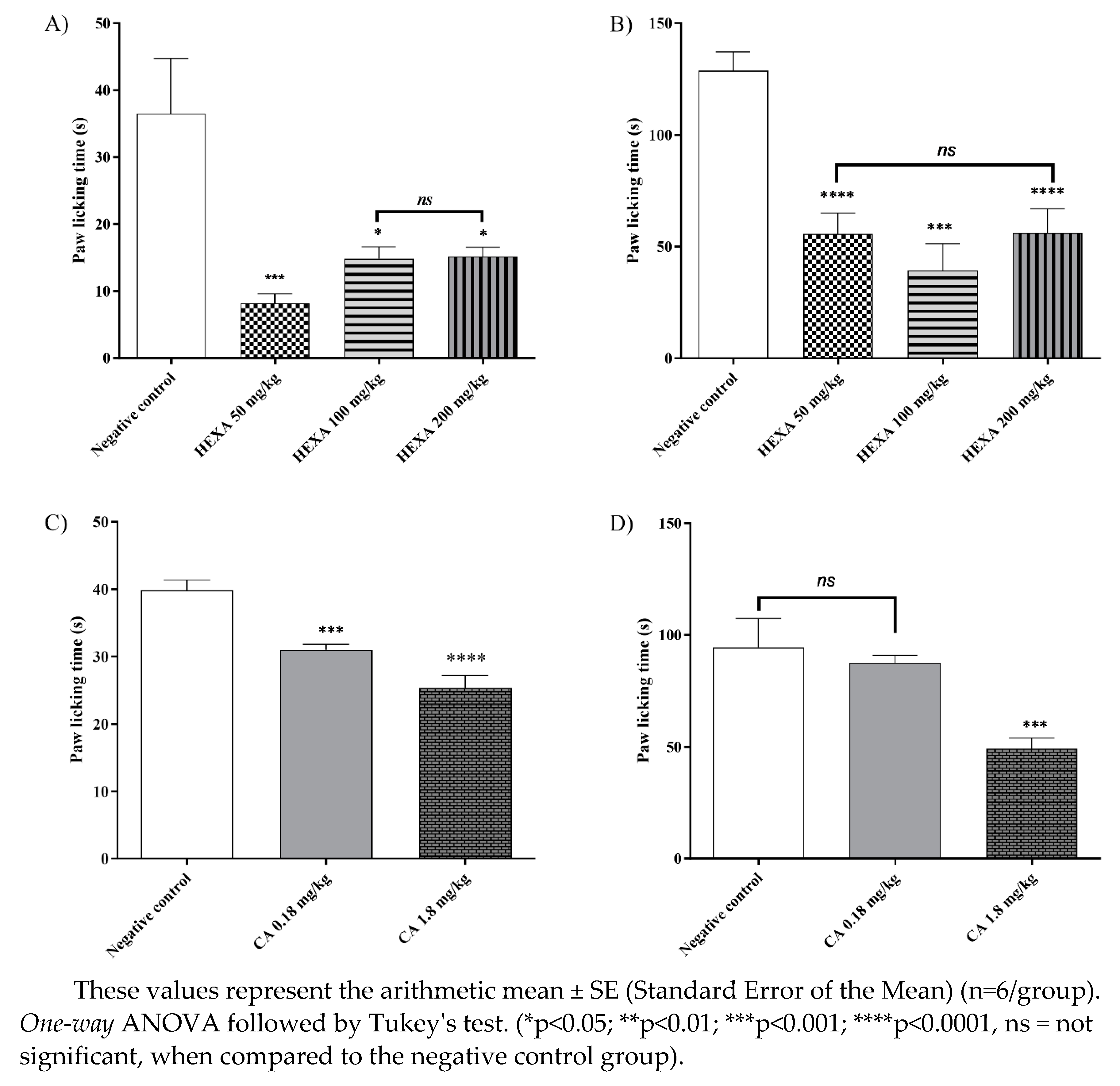
2.3. Formalin-Induced Nociception Test of HEXA and CA
2.4. Analysis of Signaling Pathways Underlying the Analgesic Effect of HEXA and CA
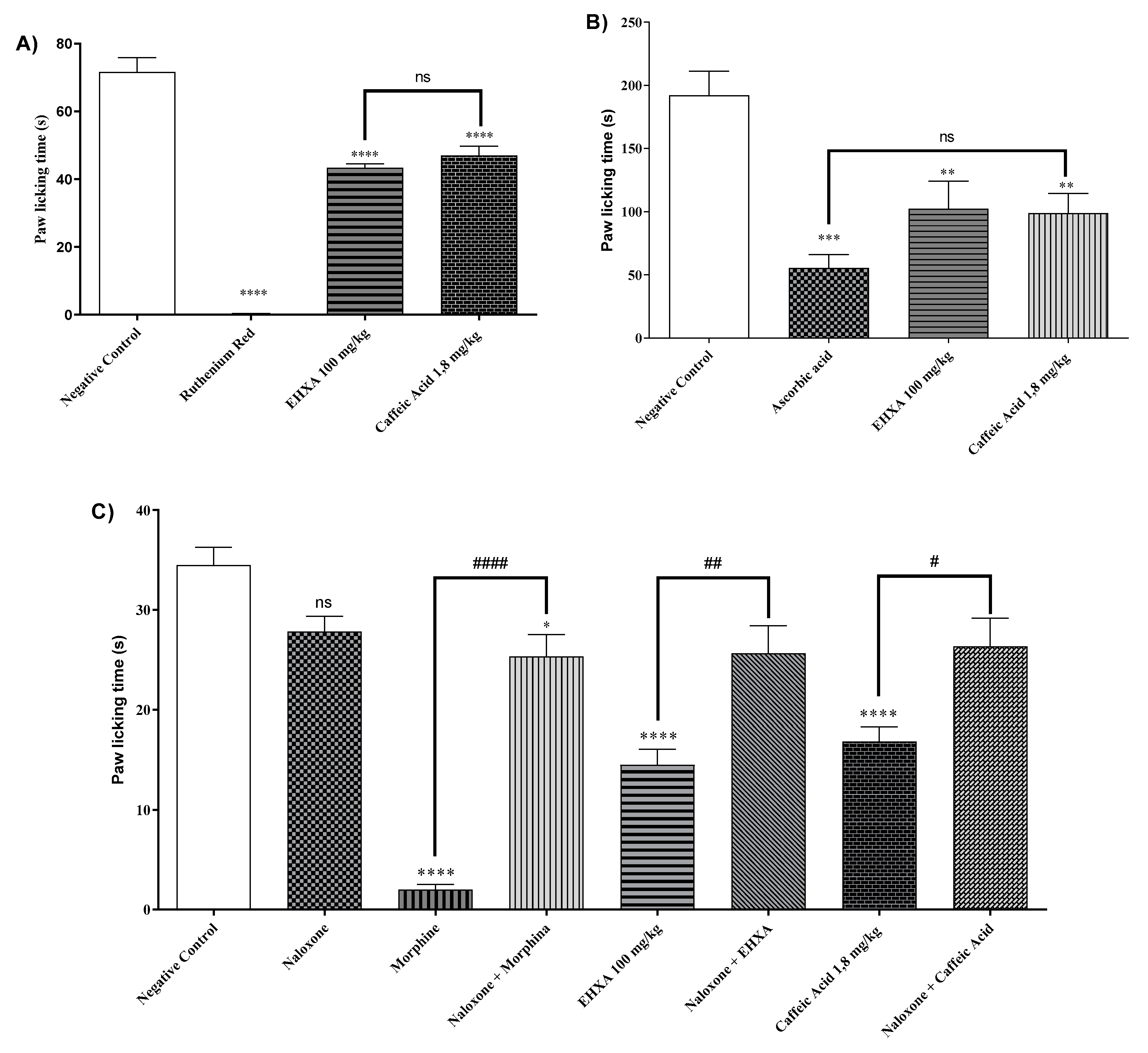
2.4.1. Vanilloid System
2.4.2. Glutamatergic Pathway
2.4.3. Opioid Pathway
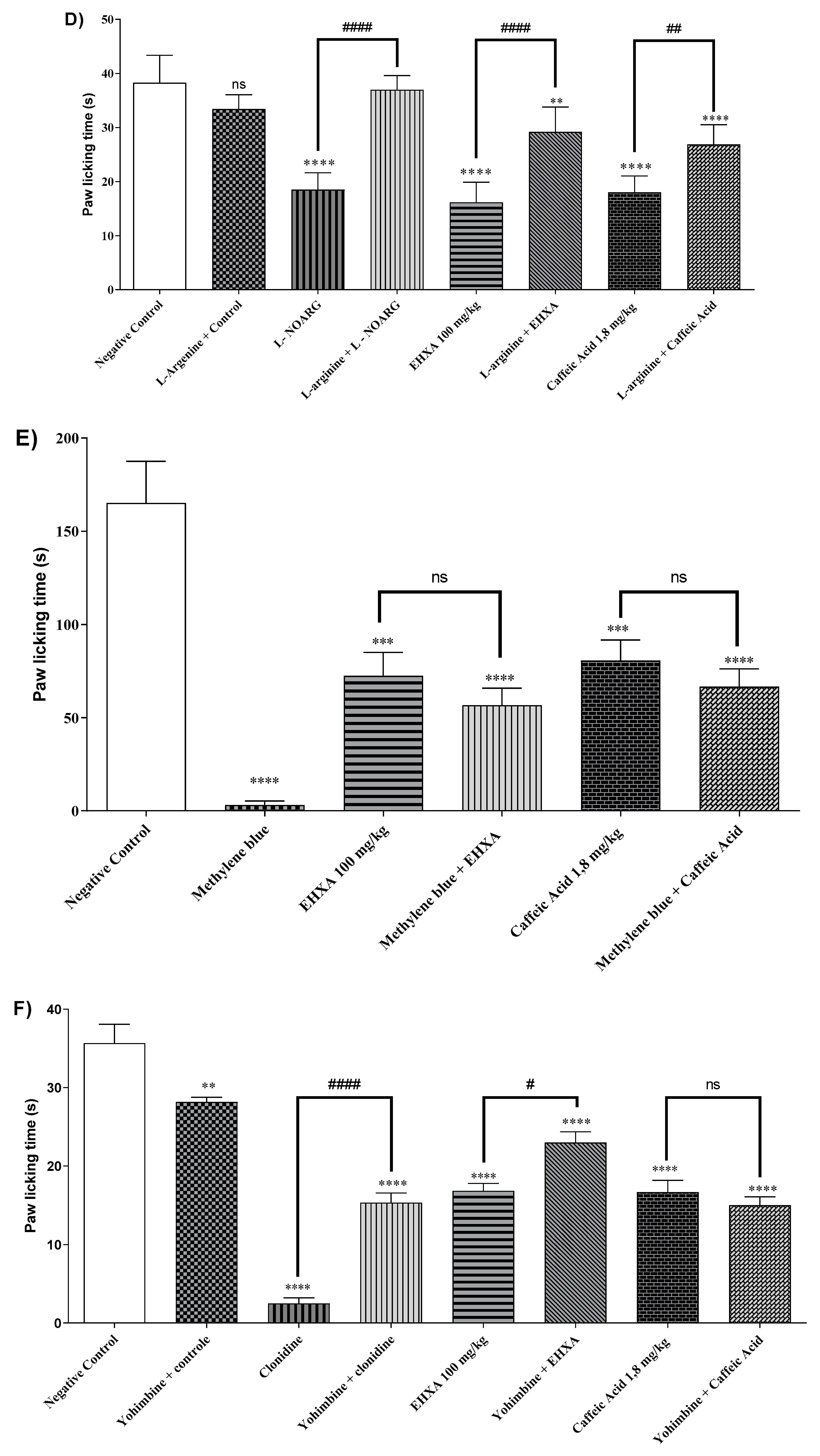
2.4.4. L-arginine/Nitric Oxide/cGMP Pathway
2.4.5. Cyclic Guanosine Monophosphate (cGMP) Pathway
2.4.6. Involvement of the α2-Adrenergic Receptor
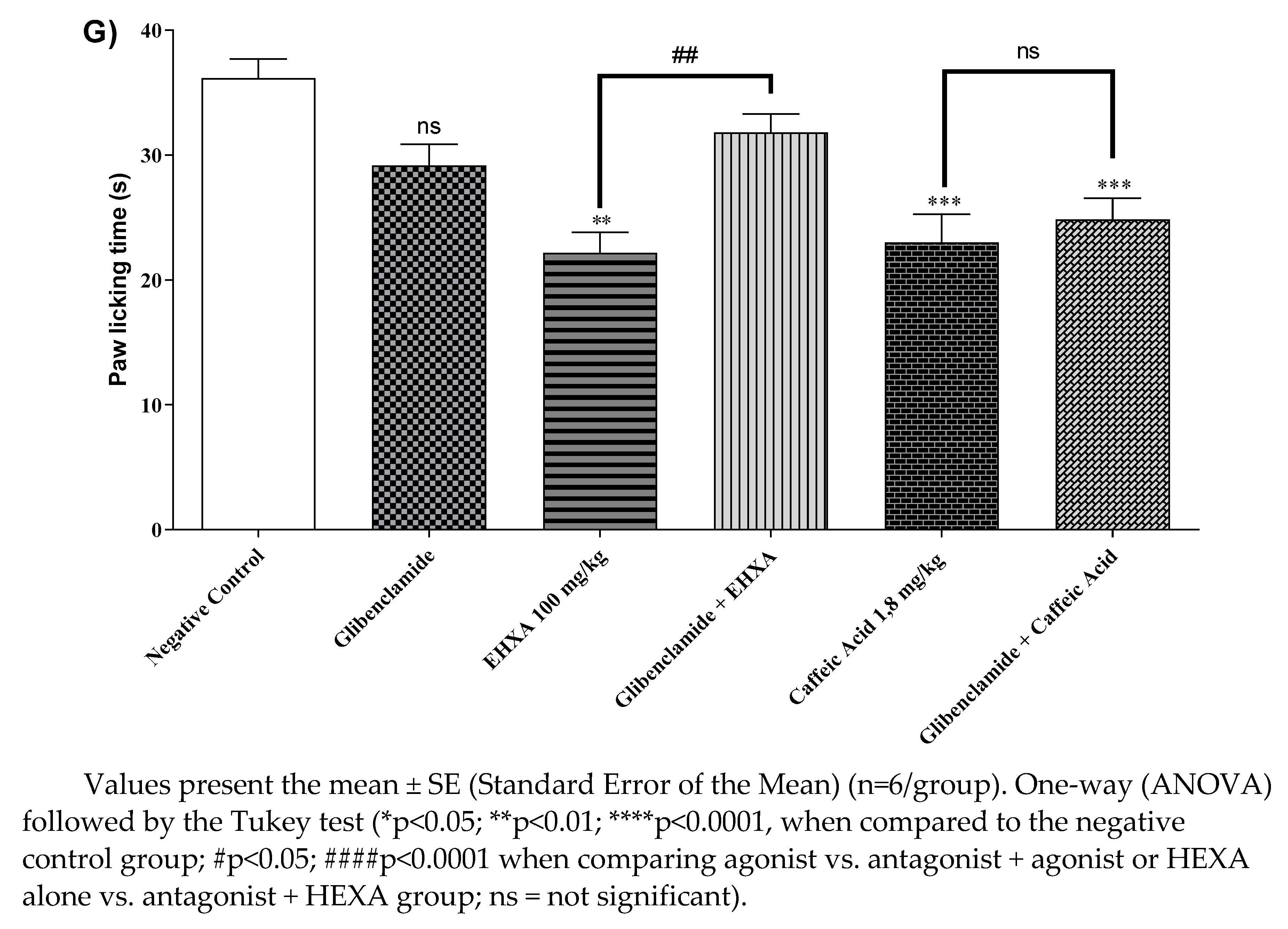
2.4.7. K+ATP Channel-Dependent Signaling
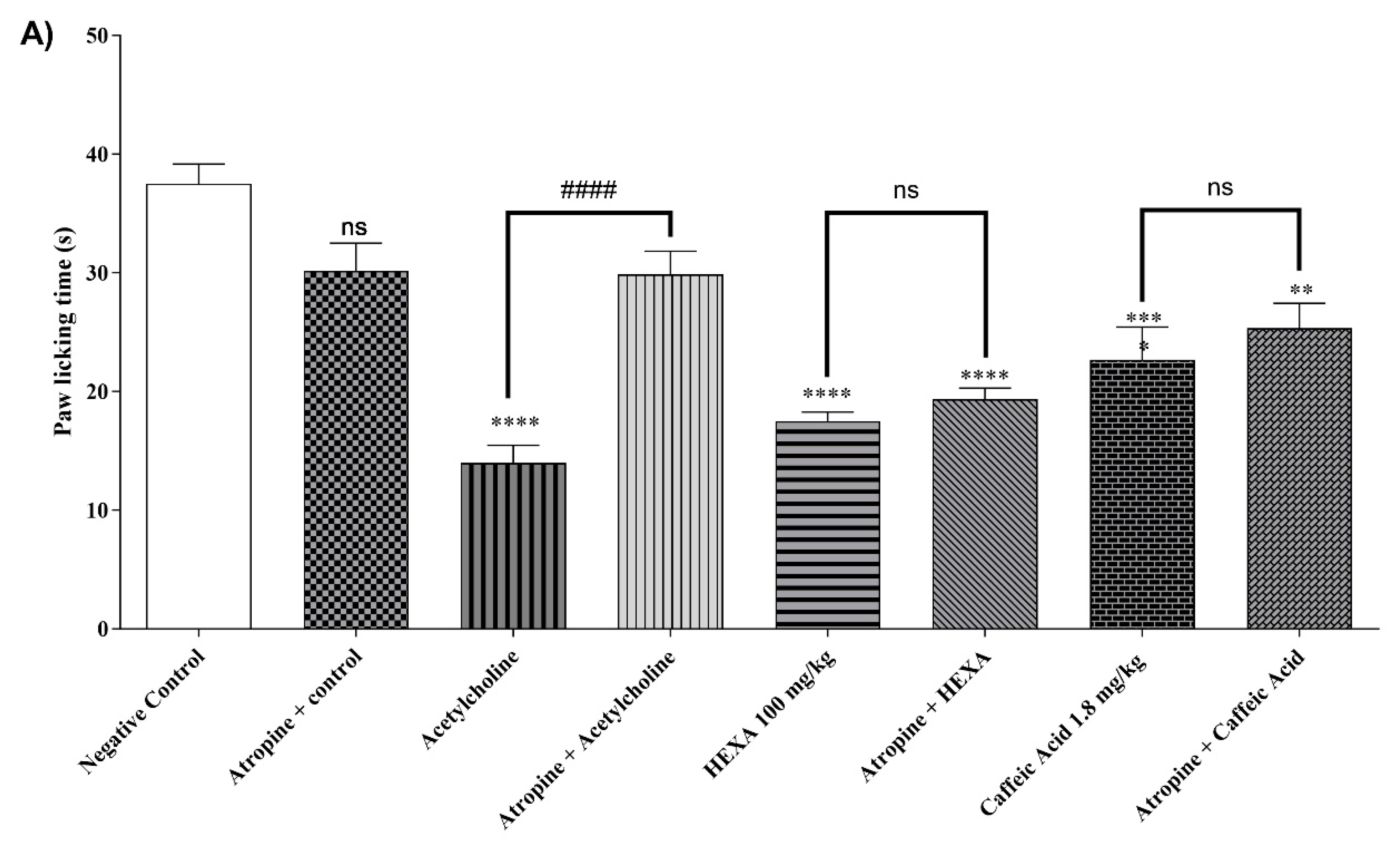
2.4.8. Cholinergic Pathway
2.4.9. Adenosinergic Pathway
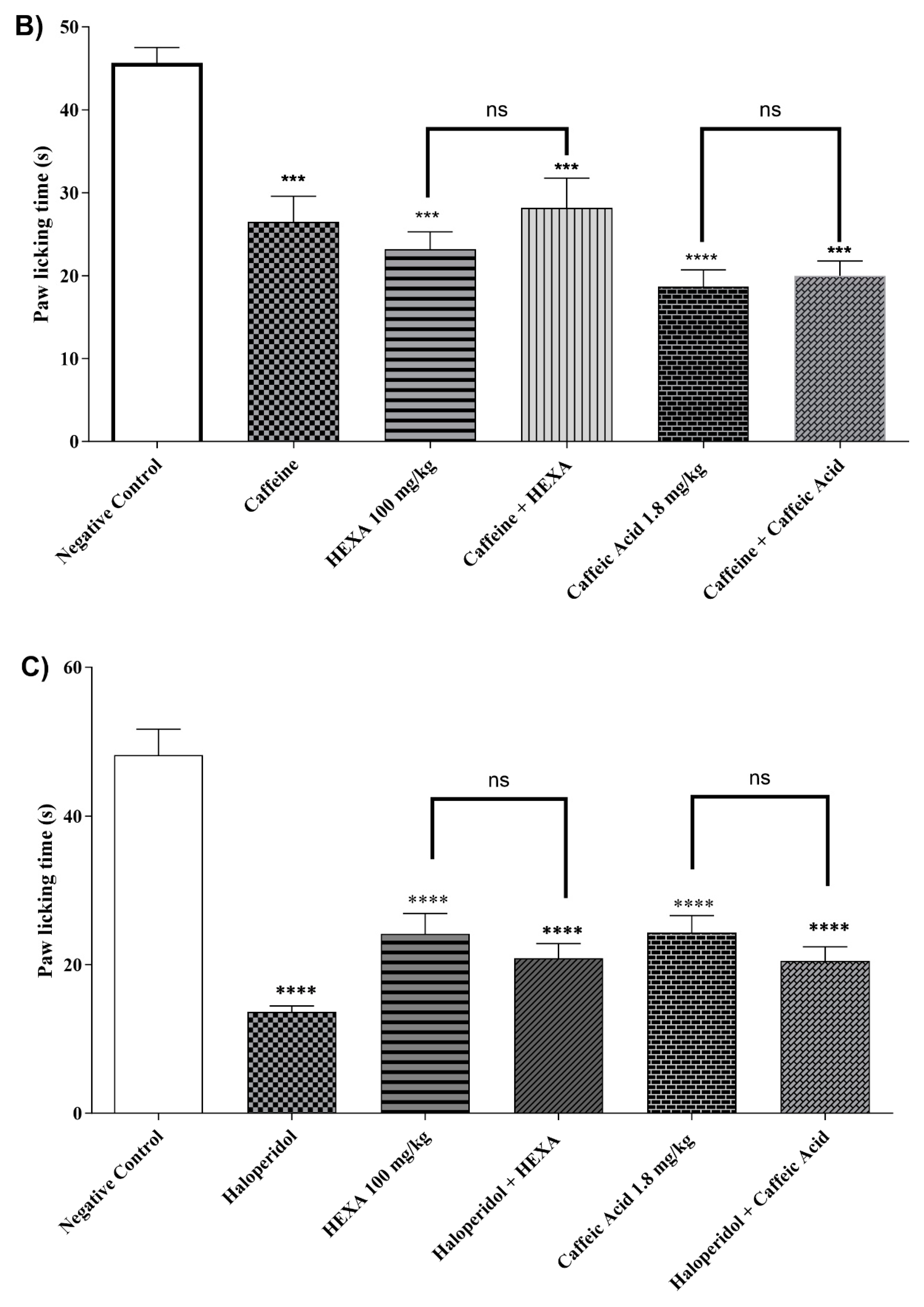
2.4.10. Dopaminergic System
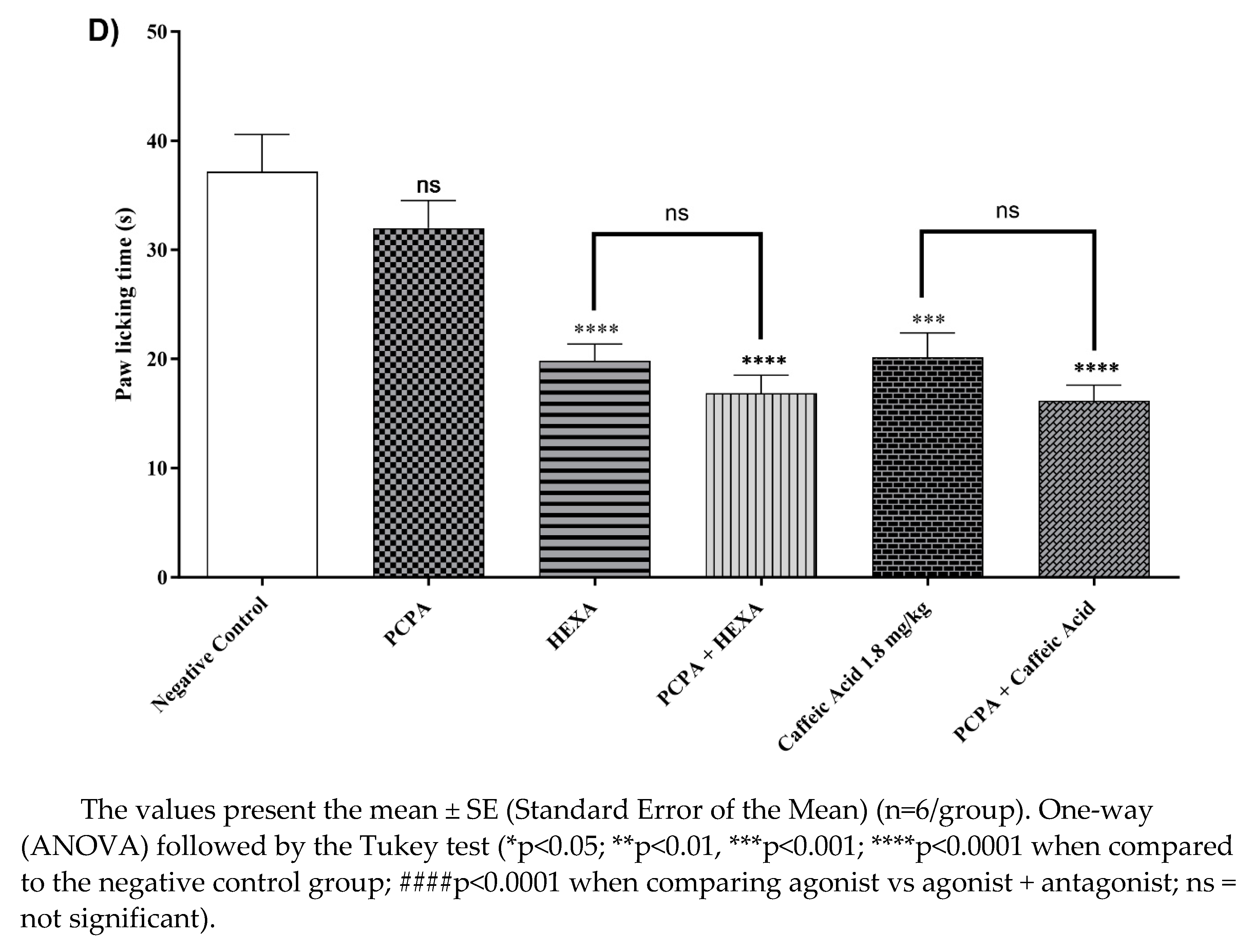
2.4.11. Involvement of the Serotonergic System
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Drugs, Reagents, and Doses
4.2. Chemical Profile by Electrospray Ionization-Mass Spectrometry (ESI-MS) Analysis
4.2.1. Compound Annotation
4.3. Animals
4.4. Ethical Information
4.5. Evaluation of the effects of HEXA on the Central Nervous System
4.5.1. Rota Rod Performance Test
4.5.2. Open Field Test
4.6. Screening for the Antinociceptive Effect
4.6.1. Acetic Acid-Induced Abdominal Contortions
4.6.2. The Formalin Test
4.7. Evaluation of Central and Peripheral Antinociceptive Responses
4.7.1. Hot Plate Test
4.7.2. Mechanical Pressure Hypernociception (Von Frey Test)
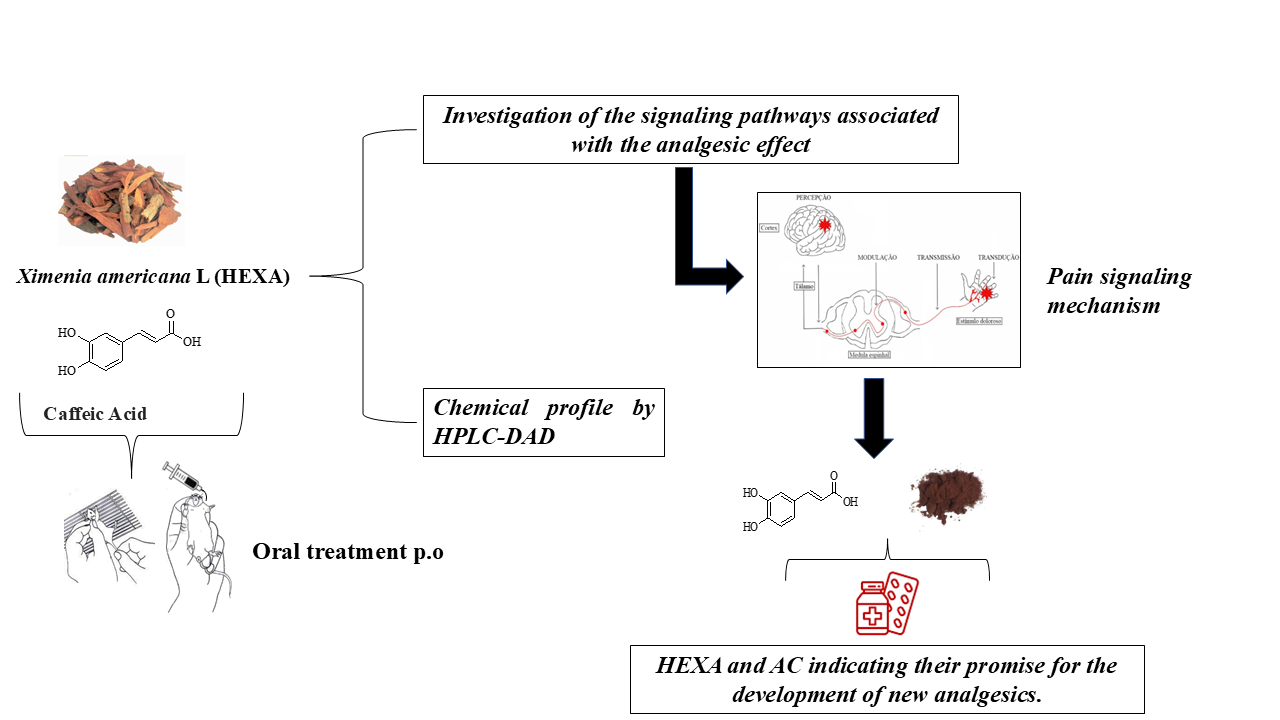
4.8. Investigation of the Signaling Pathways Associated with the Analgesic Effect of HEXA and AC
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baral, P.; Udit, S.; Chiu, I.M. Pain and Immunity: Implications for Host Defence. Nat Rev Immunol 2019, 19, 433–447. [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, M.; Huh, Y.; Ji, R.R. Roles of Inflammation, Neurogenic Inflammation, and Neuroinflammation in Pain. J Anesth 2019, 33, 131–139. [CrossRef]
- Arthur, J.; Bruera, E. Balancing Opioid Analgesia with the Risk of Nonmedical Opioid Use in Patients with Cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2019, 16, 213–226. [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.P.; Vase, L.; Hooten, W.M. Chronic Pain: An Update on Burden, Best Practices, and New Advances. The Lancet 2021, 397, 2082–2097. [CrossRef]
- Day, R.O.; Graham, G.G. Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs). BMJ 2013, 346, 1396.2-1396. [CrossRef]
- Lima, C.P.; Silva, H.R.D.O.; Pogian, V.B.; Santos, V.G. Pharmaceutical Evaluation of the Risks of the Use of Non-Steroid Anti-Inflammatories. Unisanta Health Science 2020, 4, 1–20.
- Silva, L.A.; Gerica, O, Al, H. Review on Non-Steroid Antiinflammatory: Acetylsalicylic Acid. Rev Inic Cient e Ext 2018, 1, 169–174.
- Mohammad, F.; Hasan, E.; Wedad, A.; Mohamed, E.G. Natural Antioxidant Flavonoids in Formalin-Induced Mice Paw Inflammation; Inhibition of Mitochondrial Sorbitol Dehydrogenase Activity. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 2017, 31, 1–8. [CrossRef]
- Mussin, J.; Giusiano, G. Ethno–Phytopharmacology: Product Validation Process Based on Traditional Knowledge of Medicinal Plants. In Agricultural, Forestry and Bioindustry Biotechnology and Biodiscovery; Springer, 2020; pp. 331–353.
- Ribeiro, D.A.; Oliveira, L.G.S. de; Macêdo, D.G. de; Menezes, I.R.A. de; Costa, J.G.M. da; Silva, M.A.P. da; Lacerda, S.R.; Souza, M.M. de A. Promising Medicinal Plants for Bioprospection in a Cerrado Area of Chapada Do Araripe, Northeastern Brazil. J Ethnopharmacol 2014, 155, 1522–1533. [CrossRef]
- Sreekeesoon, D.P.; Mahomoodally, M.F. Ethnopharmacological Analysis of Medicinal Plants and Animals Used in the Treatment and Management of Pain in Mauritius. J Ethnopharmacol 2014, 157, 181–200. [CrossRef]
- Da Silva-Leite, K.E.S.; Assreuy, A.M.S.; Mendonça, L.F.; Damasceno, L.E.A.; De Queiroz, M.G.R.; Mourão, P.A.S.; Pires, A.F.; Pereira, M.G. Polysaccharide Rich Fractions from Barks of Ximenia Americana Inhibit Peripheral Inflammatory Nociception in Mice Antinociceptive Effect of Ximenia Americana Polysaccharide Rich Fractions. Revista Brasileira de Farmacognosia 2017, 27, 339–345. [CrossRef]
- Jahromi, B.; Pirvulescu, I.; Candido, K.D.; Knezevic, N.N. Herbal Medicine for Pain Management: Efficacy and Drug Interactions. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 251. [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, G.G.; De Souza, P.A.; De Morais, P.L.D.; Dos Santos, E.C.; Moura, R.D.; Menezes, J.B. Caracterização Do Fruto de Ameixa Silvestre (Ximenia Americana L.). Rev Bras Frutic 2008, 30, 311–314. [CrossRef]
- Shettar, A.K.; Sateesh, M.K.; Kaliwal, B.B.; Vedamurthy, A.B. In Vitro Antidiabetic Activities and GC-MS Phytochemical Analysis of Ximenia Americana Extracts. South African Journal of Botany 2017, 111, 202–211. [CrossRef]
- Almeida, M.L.B.; Freitas, W.E.D.S.; Morais, P.L.D. De; Sarmento, J.D.A.; Alves, R.E. Bioactive Compounds and Antioxidant Potential Fruit of Ximenia Americana L. Food Chem 2016, 192, 1078–1082. [CrossRef]
- Aragão, T.P.; dos Prazeres, L.D.K.T.; Brito, S.A.; Neto, P.J.R.; Rolim, L.A.; da Silva Almeida, J.R.G.; Caldas, G.F.R.; Wanderley, A.G. alves Contribution of Secondary Metabolites to the Gastroprotective Effect of Aqueous Extract of Ximenia Americana L. (Olacaceae) Stem Bark in Rats. Molecules 2018, 23, 1–18. [CrossRef]
- de Menezes, I.R.A.; da Costa, R.H.S.; Augusti Boligon, A.; Rolón, M.; Coronel, C.; Vega, C.; Melo Coutinho, H.D.; da Costa, M.S.; Tintino, S.R.; Silva Pereira, R.L.; et al. Ximenia Americana L. Enhances the Antibiotic Activity and Inhibit the Development of Kinetoplastid Parasites. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis 2019, 64, 40–46. [CrossRef]
- Da Palma, A.F.M.; Marques, L.K.M.; Carneiro, R.D.S.; Carvalho, G.F.S.; Ferreira, D.C.L.; Sant’Ana, A.E.G.; Maia Filho, A.L.M.; Marques, R.B.; Alves, W.D.S.; Uchôa, V.T.; et al. Evaluation of Hydroalcoholic Extracts of Stem and Leaves of Ximenia Americana L. In the Healing of Excisional Acute Wounds in Mice. Revista Virtual de Quimica 2020, 12, 37–50. [CrossRef]
- da Silva, B.A.F.; da Costa, R.H.S.; Fernandes, C.N.; Leite, L.H.I.; Ribeiro-Filho, J.; Garcia, T.R.; Coutinho, H.D.M.; Wanderley, A.G.; de Menezes, I.R.A. HPLC Profile and Antiedematogenic Activity of Ximenia Americana L. (Olacaceae) in Mice Models of Skin Inflammation. Food and Chemical Toxicology 2018, 119, 199–205. [CrossRef]
- Soro, T.Y.; Zahoui, O.S.; Nene-bi, A.S. Analgesic Activity of the Fractions of the Aqueous Extract of Ximenia Americana (Linné) (Olacaceae). International Journal of Pharmacology and Toxicology 2016, 4, 1. [CrossRef]
- da Silva, B.A.F.; da Costa, R.H.S.; Fernandes, C.N.; Leite, L.H.I.; Ribeiro-Filho, J.; Garcia, T.R.; Coutinho, H.D.M.; Wanderley, A.G.; de Menezes, I.R.A. HPLC Profile and Antiedematogenic Activity of Ximenia Americana L. (Olacaceae) in Mice Models of Skin Inflammation. Food and Chemical Toxicology 2018, 119, 199–205. [CrossRef]
- da Costa, R.H.S.; Martins, A.O.B.P.B.; de Oliveira, M.R.C.; Alcântara, I.S.; Ferreira, F.F.; dos Santos, F.F.C.; de Araújo Delmondes, G.; da Cunha, F.A.B.; Coutinho, H.D.M.; de Menezes, I.R.A. Acaricide Activity of the Ximenia Americana L. (Olacaceae) Stem Bark Hydroethanolic Extract against Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) Microplus. Biologia (Bratisl) 2022, 77, 1667–1674. [CrossRef]
- Cizmarova, B.; Hubkova, B.; Bolerazska, B.; Marekova, M.; Birkova, A. Caffeic Acid: A Brief Overview of Its Presence, Metabolism, and Bioactivity. Bioact Compd Health Dis 2020, 3, 74–81. [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.; Ahmed, S.; Elasbali, A.M.; Adnan, M.; Alam, S.; Hassan, M.I.; Pasupuleti, V.R. Therapeutic Implications of Caffeic Acid in Cancer and Neurological Diseases. Front Oncol 2022, 12. [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.; Bamunuarachchi, N.I.; Tabassum, N.; Kim, Y.M. Caffeic Acid and Its Derivatives: Antimicrobial Drugs toward Microbial Pathogens. J Agric Food Chem 2021, 69, 2979–3004.
- Nasr Bouzaiene, N.; Kilani Jaziri, S.; Kovacic, H.; Chekir-Ghedira, L.; Ghedira, K.; Luis, J. The Effects of Caffeic, Coumaric and Ferulic Acids on Proliferation, Superoxide Production, Adhesion and Migration of Human Tumor Cells in Vitro. Eur J Pharmacol 2015, 766, 99–105. [CrossRef]
- Zielińska, D.; Zieliński, H.; Laparra-Llopis, J.M.; Szawara-Nowak, D.; Honke, J.; Giménez-Bastida, J.A. Caffeic Acid Modulates Processes Associated with Intestinal Inflammation. Nutrients 2021, Vol. 13, Page 554 2021, 13, 554. [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Sim, Y.B.; Kim, S.M.; Lee, J.K.; Jung, J.S.; Suh, H.W. The Effect of Caffeic Acid on the Antinociception and Mechanisms in Mouse. J Appl Biol Chem 2011, 54, 177–182. [CrossRef]
- Crevar-Sakač, M.; Vujić, Z.; Kotur-Stevuljević, J.; Ivanišević, J.; Jelić-Ivanović, Z.; Milenković, M.; Markelić, M.; Vujčić, Z. Uticaj Atorvastatina i Tinkture Lista Artičoke Na Oksidativni Stres Kod Pacova Sa Hiperholesterolemijom. Vojnosanit Pregl 2016, 73, 178–187. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.-J.; Ma, X.-L.; Fang, D.-M.; Qi, H.-Y.; Ren, W.-J.; Zhang, G.-L. Analysis of Caffeic Acid Derivatives from Osmanthus Yunnanensis Using Electrospray Ionization Quadrupole Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry. European Journal of Mass Spectrometry 2009, 15, 415–429. [CrossRef]
- Brandão, D.O.; Fernandes, F.H.A.; Júnior, F.J.L.R.; Silva, P.C.D.; Santana, C.P.; De Medeiros, F.D.; Véras, G.; Medeiros, A.C.D. Validation of UPLC Method for Determination of Gallic Acid from Ximenia Americana L. Planta Med 2014, 80, P2O60.
- de Araújo, M.R.S.; da Costa Assunção, J.C.; Dantas, I.N.F.; Costa-Lotufo, L.V.; Monte, F.J.Q. Chemical Constituents of Ximenia Americana. Nat Prod Commun 2008, 3, 1934578X0800300605.
- Le, N.H.T.; Malterud, K.E.; Diallo, D.; Paulsen, B.S.; Nergård, C.S.; Wangensteen, H. Bioactive Polyphenols in Ximenia Americana and the Traditional Use among Malian Healers. J Ethnopharmacol 2012, 139, 858–862. [CrossRef]
- Queiroz Monte, F.J.; de Lemos, T.L.G.; de Arajo, M.R.S.; Sousa Gomes, E. de Ximenia Americana: Chemistry, Pharmacology and Biological Properties, a Review. Phytochemicals - A Global Perspective of Their Role in Nutrition and Health 2012. [CrossRef]
- Siddaiah, M.; Jayavcera, K.N.; Mallikarjuna, R.P.; Ravindra, R.K.; Yasodha, K.Y.; Narender, R.G. Phytochemical Screening and Analgesic Activity of Methanolic Extract of Ximenia Americana. Journal of Pharmacy and Chemistry 2009, 3, 23–25.
- Hemamalini, K.; Srikanth, A.; Sunny, G.; Praneethkumar, H. Phytochemical Screening and Analgesic Activity of Methanolic Extract of Ximenia Americana. Journal of Current Pharma Research 2011, 1, 153.
- Coutinho, M.A.S.; Muzitano, M.F.; Costa, S.S. Flavonoids: Potential Therapeutic Agents for the Inflammatory Process. Revista Virtual de Química 2009, 1, 241–256. [CrossRef]
- Dias, T.L.M.F.; Melo, G.M.A.; Da Silva, Y.K.C.; Queiroz, A.C.; Goulart, H.F.; Alexandre-Moreira, M.S.; Santana, A.E.G.; Uchôa, V.T. Antinociceptive and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of the Ethanolic Extract, of Fractions and of Epicatechin Isolated from the Stem Bark of Ximenia Americana L. (Oleacaceae). Revista Virtual de Quimica 2018, 10, 86–101. [CrossRef]
- Kiessoun, K.; Ouattara, N.; Arsène, M.; Souza, A.; Sytar, O.; Brestic, M.; Mamoudou, D.H. Anti-Nociceptive and Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Polyphenol-Rich Fractions of Roots from Ximenia Americana L ., ( Olacaceae ), in Experimental Mice. Int J Pharm Pharm Res 2018, 12, 281–297.
- Matejczyk, M.; Świsłocka, R.; Golonko, A.; Lewandowski, W.; Hawrylik, E. Cytotoxic, Genotoxic and Antimicrobial Activity of Caffeic and Rosmarinic Acids and Their Lithium, Sodium and Potassium Salts as Potential Anticancer Compounds. Adv Med Sci 2018, 63, 14–21. [CrossRef]
- de Alencar Silva, A.; Pereira-de-Morais, L.; Rodrigues da Silva, R.E.; de Menezes Dantas, D.; Brito Milfont, C.G.; Gomes, M.F.; Araújo, I.M.; Kerntopf, M.R.; Alencar de Menezes, I.R.; Barbosa, R. Pharmacological Screening of the Phenolic Compound Caffeic Acid Using Rat Aorta, Uterus and Ileum Smooth Muscle. Chem Biol Interact 2020, 332. [CrossRef]
- Amorati, R.; Pedulli, G.F.; Cabrini, L.; Zambonin, L.; Landi, L. Solvent and PH Effects on the Antioxidant Activity of Caffeic and Other Phenolic Acids. J Agric Food Chem 2006, 54, 2932–2937. [CrossRef]
- Kolgazi, M.; Cilingir, S.; Yilmaz, O.; Gemici, M.; Yazar, H.; Ozer, S.; Acikel-Elmas, M.; Arbak, S.; Suyen, G.G. Caffeic Acid Attenuates Gastric Mucosal Damage Induced by Ethanol in Rats via Nitric Oxide Modulation. Chem Biol Interact 2021, 334, 109351. [CrossRef]
- Quintans-Júnior, L.J.; De Almeida, R.N.; Falcão, A.C.G.M.; Agra, M. de F.; De Sousa, M. de F.V.; Barbosa-Filho, J.M. Avaliação Da Atividade Anticonvulsivante de Plantas Do Nordeste Brasileiro. Acta Farmaceutica Bonaerense 2002, 21, 179–184.
- da Silva-Leite, K.E.S.; Girão, D.K.F.B.; de Freitas Pires, A.; Assreuy, A.M.S.; de Moraes, P.A.F.; Cunha, A.P.; Ricardo, N.M.P.S.; Criddle, D.N.; de Souza, M.H.L.P.; Pereira, M.G.; et al. Ximenia Americana Heteropolysaccharides Ameliorate Inflammation and Visceral Hypernociception in Murine Caerulein-Induced Acute Pancreatitis: Involvement of CB2 Receptors. Biomedicine and Pharmacotherapy 2018, 106, 1317–1324. [CrossRef]
- Zhen, J.; Guo, Y.; Villani, T.; Carr, S.; Brendler, T.; Mumbengegwi, D.R.; Kong, A.N.T.; Simon, J.E.; Wu, Q. Phytochemical Analysis and Anti-Inflammatory Activity of the Extracts of the African Medicinal Plant Ximenia Caffra. J Anal Methods Chem 2015, 2015. [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, J.; Campos, M.M.; Pesquero, J.B.; Araújo, R.C.; Bader, M.; Calixto, J.B. Evidence for the Participation of Kinins in Freund’s Adjuvant-Induced Inflammatory and Nociceptive Responses in Kinin B1 and B2 Receptor Knockout Mice. Neuropharmacology 2001, 41, 1006–1012. [CrossRef]
- Billiau, A.; Matthys, P. Modes of Action of Freund’s Adjuvants in Experimental Models of Autoimmune Diseases. J Leukoc Biol 2001, 70, 849–860. [CrossRef]
- Dutra, R.C.; Campos, M.M.; Santos, A.R.S.; Calixto, J.B. Medicinal Plants in Brazil: Pharmacological Studies, Drug Discovery, Challenges and Perspectives. Pharmacol Res 2016, 112, 4–29. [CrossRef]
- Sandkühler, J. Models and Mechanisms of Hyperalgesia and Allodynia. Physiol Rev 2009, 89, 707–758. [CrossRef]
- Gamaro, G.D.; Suyenaga, E.; Borsoi, M.; Lermen, J.; Pereira, P.; Ardenghi, P. Effect of Rosmarinic and Caffeic Acids on Inflammatory and Nociception Process in Rats. ISRN Pharmacol 2011, 2011, 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Leal, S.S.; Uchôa, V.T.; Figuerêdo-Silva, J.; Soares, R.B.; Mota, D.M.; De Alencar, R.C.; Filho, A.L.M.M.; Sant’Ana, A.E.G.; Beltrame Junior, M. Eficácia Da Fonoforese Com Ximenia Americana L. Na Inflamação de Tendão de Ratos. Revista Brasileira de Medicina do Esporte 2016, 22, 355–360. [CrossRef]
- Dhawan, B.N.; Cesselin, F.; Raghubir, R.; Reisine, T.; Bradley, P.B.; Portoghese, P.S.; Hamon, M. International Union of Pharmacology. XII. Classification of Opioid Receptors. Pharmacol Rev 1996, 48, 567–592.
- Stein, C.; Hassan, A.H.S.; Lehrberger, K.; Stein, C.; Giefing, J.; Yassouridis, A. Local Analgesic Effect of Endogenous Opioid Peptides. The Lancet 1993, 342, 321–324. [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, D.; Yu, L.C. Antinociceptive Effects of Galanin in the Central Nucleus of Amygdala of Rats, an Involvement of Opioid Receptors. Brain Res 2010, 1320, 16–21. [CrossRef]
- Shih, C.C.; Hwang, H.R.; Chang, C.I.; Su, H.M.; Chen, P.C.; Kuo, H.M.; Li, P.J.; Wang, H.M.D.; Tsui, K.H.; Lin, Y.C.; et al. Anti-Inflammatory and Antinociceptive Effects of Ethyl Acetate Fraction of an Edible Red Macroalgae Sarcodia Ceylanica. Int J Mol Sci 2017, 18, 1–15. [CrossRef]
- Iacopucci, A.P.; Mello, R.O.; Barbosa-Silva, R.; Melo-Thomas, L. L-NOARG-Induced Catalepsy Can Be Influenced by Glutamatergic Neurotransmission Mediated by NMDA Receptors in the Inferior Colliculus. Behavioural Brain Research 2012, 234, 149–154. [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.R.; Jung, Y.R.; Kim, D.H.; An, H.J.; Kim, M.K.; Kim, N.D.; Chung, H.Y. Caffeic Acid Regulates LPS-Induced NF-ΚB Activation through NIK/IKK and c-Src/ERK Signaling Pathways in Endothelial Cells. Arch Pharm Res 2014, 37, 539–547.
- Tominaga, M.; Caterina, M.J.; Malmberg, A.B.; Rosen, T.A.; Gilbert, H.; Skinner, K.; Raumann, B.E.; Basbaum, A.I.; Julius, D. The Cloned Capsaicin Receptor Integrates Multiple Pain-Producing Stimuli. Neuron 1998, 21, 531–543. [CrossRef]
- Devesa, I.; Planells-Cases, R.; Fernández-Ballester, G.; González-Ros, J.M.; Ferrer-Montiel, A.; Fernández-Carvajal, A. Role of the Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid 1 in Inflammation and Sepsis. J Inflamm Res 2011, 4, 67–81. [CrossRef]
- Gamse, R.; Holzer, P.; Lembeck, F. Indirect Evidence for Presynaptic Location of Opiate Receptors on Chemosensitive Primary Sensory Neurones. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 1979, 308, 281–285. [CrossRef]
- Maia, J.L.; Lima-Júnior, R.C.P.; Melo, C.M.; David, J.P.; David, J.M.; Campos, A.R.; Santos, F.A.; Rao, V.S.N. Oleanolic Acid, a Pentacyclic Triterpene Attenuates Capsaicin-Induced Nociception in Mice: Possible Mechanisms. Pharmacol Res 2006, 54, 282–286. [CrossRef]
- Beirith, A.; Santos, A.R.S.; Calixto, J.B. Mechanisms Underlying the Nociception and Paw Oedema Caused by Injection of Glutamate into the Mouse Paw. Brain Res 2002, 924, 219–228. [CrossRef]
- Vorobeychik, Y.; Willoughby, C.D.; Mao, J. NMDA Receptor Antagonists in the Treatment of Pain. In Comprehensive Treatment of Chronic Pain by Medical, Interventional, and Integrative Approaches; Springer New York: New York, NY, 2013; pp. 61–67.
- Soares, A.C.; Leite, R.; Tatsuo, M.A.K.F.; Duarte, I.D.G. Activation of ATP-Sensitive K+ Channels: Mechanism of Peripheral Antinociceptive Action of the Nitric Oxide Donor, Sodium Nitroprusside. Eur J Pharmacol 2000, 400, 67–71. [CrossRef]
- Garthwaite, J. Glutamate, Nitric Oxide and Cell-Cell Signalling in the Nervous System. Trends Neurosci 1991, 14, 60–67. [CrossRef]
- Kimura, M.; Saito, S.; Obata, H. Dexmedetomidine Decreases Hyperalgesia in Neuropathic Pain by Increasing Acetylcholine in the Spinal Cord. Neurosci Lett 2012, 529, 70–74. [CrossRef]
- Obata, H. Analgesic Mechanisms of Antidepressants for Neuropathic Pain. Int J Mol Sci 2017, 18. [CrossRef]
- Chan, A.K.M.; Cheung, C.W.; Chong, Y.K. Alpha-2 Agonists in Acute Pain Management. Expert Opin Pharmacother 2010, 11, 2849–2868. [CrossRef]
- Lopes, L.D.S.; Marques, R.B.; Fernandes, H.B.; Pereira, S.D.S.; Ayres, M.C.C.; Chaves, M.H.; Almeida, F.R.C. Mechanisms of the Antinociceptive Action of (-) Epicatechin Obtained from the Hydroalcoholic Fraction of Combretum Leprosum Mart & Eic in Rodents. J Biomed Sci 2012, 19, 2–7. [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Carver, J.J.; Phelan, V. V.; Sanchez, L.M.; Garg, N.; Peng, Y.; Nguyen, D.D.; Watrous, J.; Kapono, C.A.; Luzzatto-Knaan, T.; et al. Sharing and Community Curation of Mass Spectrometry Data with GNPS. Nat Biotechnol 2016, 34, 828. [CrossRef]
- Dunham, N.W.; Miya, T.S. A Note on a Simple Apparatus for Detecting Neurological Deficit in Rats and Mice. J Am Pharm Assoc 1957, 46, 208–209.
- Lapa, A.J.J.; Souccar, C.; Lima-Landman, M.T.R.; Castro, M.S. de A.; Lima, T.C.M. Pharmacological Activity Evaluation Methods of Medicinal Plants; Sociedade Brasileira de Plantas Medicinais, 2008;
- Pessoa, R.T.; Alcântara, I.S.; da Silva, L.Y.S.; da Costa, R.H.S.; Silva, T.M.; de Morais Oliveira-Tintino, C.D.; Ramos, A.G.B.; de Oliveira, M.R.C.; Martins, A.O.B.P.B.; de Lacerda, B.C.G.V.; et al. Ximenia Americana L.: Chemical Characterization and Gastroprotective Effect. Analytica 2023, 4, 141–158. [CrossRef]
- Koster, R. Acetic Acid for Analgesic Screening. In Proceedings of the Fed proc; 1959; Vol. 18, p. 412.
- Tjølsen, A.; Berge, O.-G.; Hunskaar, S.; Rosland, J.H.; Hole, K. The Formalin Test: An Evaluation of the Method. Pain 1992, 51, 5–17. [CrossRef]
- Bannon, A.; Malmberg, A. Models of Nociception: Hot-Plate, Tail-Flick, and Formalin Tests in Rodents; 2007; Vol. Chapter 8;
- Martinov, T.; Mack, M.; Sykes, A.; Chatterjea, D. Measuring Changes in Tactile Sensitivity in the Hind Paw of Mice Using an Electronic von Frey Apparatus. Journal of Visualized Experiments 2013. [CrossRef]
- Tena, B.; Escobar, B.; Arguis, M.J.; Cantero, C.; Rios, J.; Gomar, C. Reproducibility of Electronic von Frey and von Frey Monofilaments Testing. Clin J Pain 2012, 28, 318–323. [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, G.W.; Bilsky, E.J.; Negus, S.S. Targeting Pain-Suppressed Behaviors in Preclinical Assays of Pain and Analgesia: Effects of Morphine on Acetic Acid-Suppressed Feeding in C57BL/6J Mice. J Pain 2006, 7, 408–416. [CrossRef]
- Miller, E.C.; Swanson, A.B.; Phillips, D.H.; Fletcher, T.L.; Liem, A.; Miller, J.A. Structure-Activity Studies of the Carcinogenicities in the Mouse and Rat of Some Naturally Occurring and Synthetic Alkenylbenzene Derivatives Related to Safrole and Estragole. Cancer Res 1983, 43, 1124–1134.
- Schechtmann, G.; Song, Z.; Ultenius, C.; Meyerson, B.A.; Linderoth, B. Cholinergic Mechanisms Involved in the Pain Relieving Effect of Spinal Cord Stimulation in a Model of Neuropathy. Pain 2008, 139, 136–145. [CrossRef]
- Lam, D.K.; Sessle, B.J.; Cairns, B.E.; Hu, J.W. Neural Mechanisms of Temporomandibular Joint and Masticatory Muscle Pain: A Possible Role for Peripheral Glutamate Receptor Mechanisms. Pain Res Manag 2005, 10, 145–152. [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhuo, M. Silent Glutamatergic Synapses and Nociception in Mammalian Spinal Cord. Nature 1998, 393, 695–698. [CrossRef]
- Majewska, M.D.; Bell, J.A.; London, E.D. Regulation of the NMDA Receptor by Redox Phenomena: Inhibitory Role of Ascorbate. Brain Res 1990, 537, 328–332. [CrossRef]
- Zeraati, F.; Araghchian, M.; Farjoo, M.H. Ascorbic Acid Interaction With Analgesic Effect of Morphine and Tramadol in Mice. Anesth Pain Med 2014, 4. [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.R.S.; Gadotti, V.M.; Oliveira, G.L.; Tibola, D.; Paszcuk, A.F.; Neto, A.; Spindola, H.M.; Souza, M.M.; Rodrigues, A.L.S.; Calixto, J.B. Mechanisms Involved in the Antinociception Caused by Agmatine in Mice. Neuropharmacology 2005, 48, 1021–1034. [CrossRef]
- Ocaña, M.; Cendán, C.M.; Cobos, E.J.; Entrena, J.M.; Baeyens, J.M. Potassium Channels and Pain: Present Realities and Future Opportunities. Eur J Pharmacol 2004, 500, 203–219. [CrossRef]
- Ferré, S.; Diamond, I.; Goldberg, S.R.; Yao, L.; Hourani, S.M.O.; Huang, Z.L.; Urade, Y.; Kitchen, I. Adenosine A2A Receptors in Ventral Striatum, Hypothalamus and Nociceptive Circuitry. Prog Neurobiol 2007, 83, 332–347. [CrossRef]
- Finan, P.H.; Smith, M.T. The Comorbidity of Insomnia, Chronic Pain, and Depression: Dopamine as a Putative Mechanism. Sleep Med Rev 2013, 17, 173–183. [CrossRef]
- Wood, P.B. Mesolimbic Dopaminergic Mechanisms and Pain Control. Pain 2006, 120, 230–234. [CrossRef]
- Maleki, N.; Nayebi, A.M.; Garjani, A. Effects of Central and Peripheral Depletion of Serotonergic System on Carrageenan-Induced Paw Oedema. Int Immunopharmacol 2005, 5, 1723–1730. [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, R.; Rygh, L.J.; Dickenson, A.H. Bad News from the Brain: Descending 5-HT Pathways That Control Spinal Pain Processing. Trends Pharmacol Sci 2004, 25, 613–617. [CrossRef]
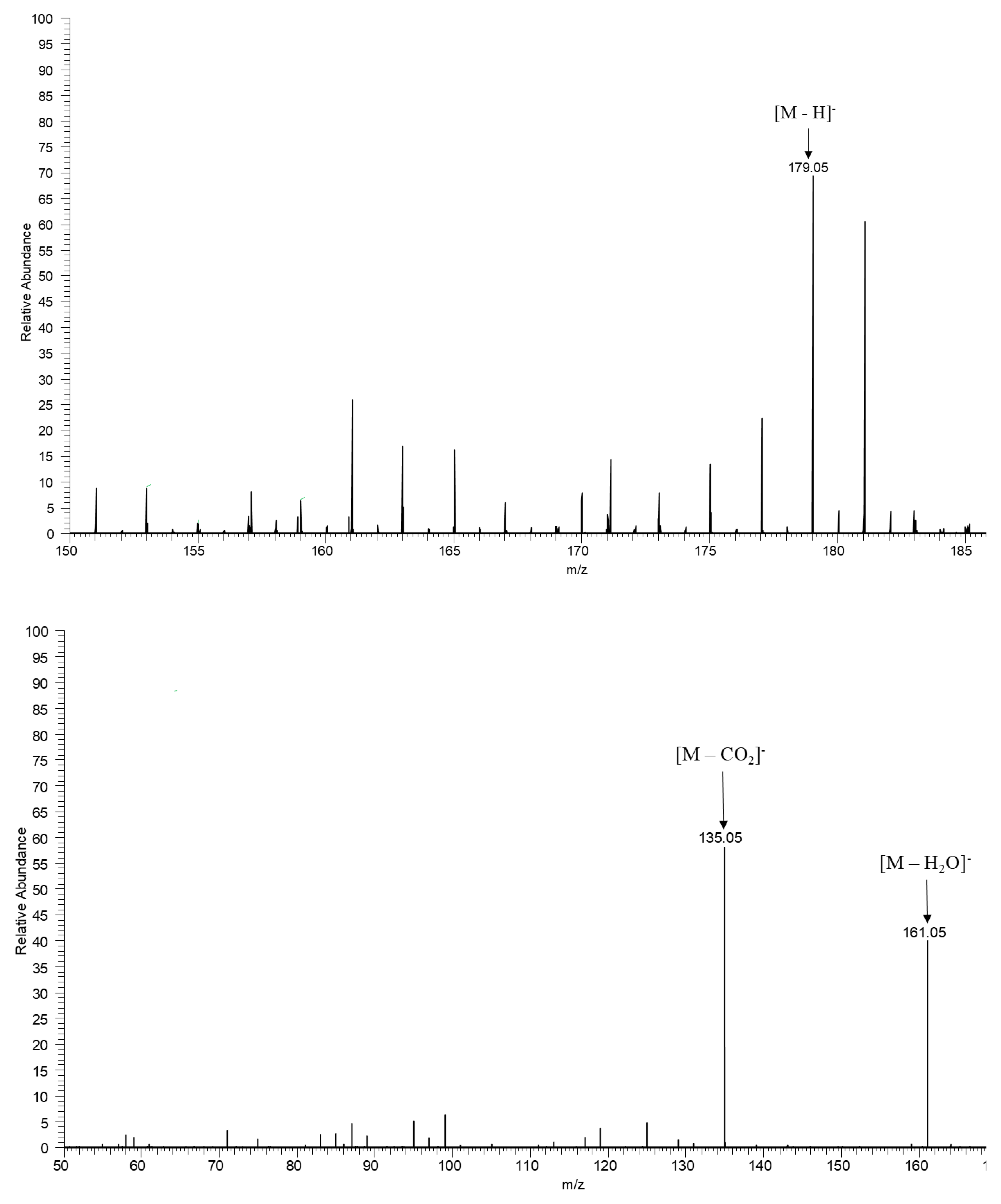
| Parent Mass | Adduct | Molecular Formula | Metabolite Name | Chemical Structure | Chemical Class |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 169.014 | [M-H] - | C7H6O5 | Gallic acid | 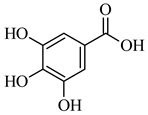 |
Organic acid |
| 179.034 | [M-H] - | C9H8O4 | Caffeic acid | 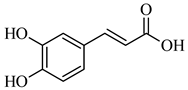 |
Organic acid |
| 195.050 | [M-H] - | C6H12O7 | Gluconic acid | 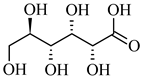 |
Organic acid |
| 193.034 | [M-H] - | C6H10O7 | D-Glucuronic acid | 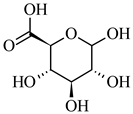 |
Organic acid |
| 285.039 | [M-H] - | C15H10O6 | Kaempferol | 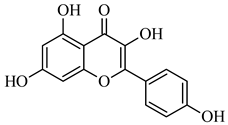 |
Flavonoid |
| 289.071 | [M-H] - | C15H14O6 | (-)-Catechin | 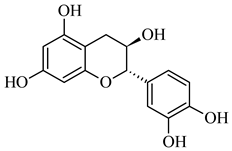 |
Flavonoid |
| 301.035 | [M-H] - | C15H10O7 | Quercetin |
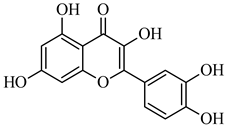 |
Flavonoid |
| 609.147 | [M-H] - | C27H30O16 | Rutin | 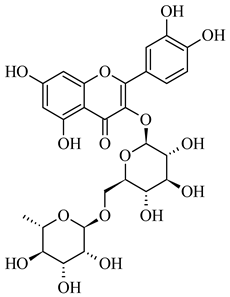 |
Flavonoid |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





