Submitted:
14 February 2025
Posted:
17 February 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Chronic pain significantly impacts quality of life and is often accompanied by inflammation, a natural bodily response that can become harmful when excessive. The orofacial region is commonly affected, making effective treatment crucial. However, current drugs often cause undesirable side effects, highlighting the need for new pharmacological alternatives. 4-hydroxycoumarin (4-HC), a natural compound, has shown promising antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory effects, but studies confirming its specific properties are limited. In silico analyses suggest that 4-HC exhibits favorable pharmacokinetic characteristics, not interacting with P-glycoprotein and successfully crossing the blood-brain barrier. Molecular docking studies indicate that its effects may be mediated through NMDAR or by inhibiting iNOS. Our study assessed the antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory effects of 4-HC in animal models at doses of 25, 50, and 75 mg/kg. 4-HC significantly reduced abdominal contortions induced by acetic acid and decreased nociceptive rubbing in orofacial pain models induced by formalin, glutamate, and capsaicin. Interactions with opioid receptors were not observed, suggesting that 4-HC’s antinociceptive effect does not involve this pathway. Additionally, 4-HC reduced paw edema induced by carrageenan and significantly decreased leukocyte migration and TNF-α levels. These findings highlight the therapeutic potential of 4-HC and warrant further investigation into its mechanisms.
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. In Silico Tests
2.2. In Vivo Tests
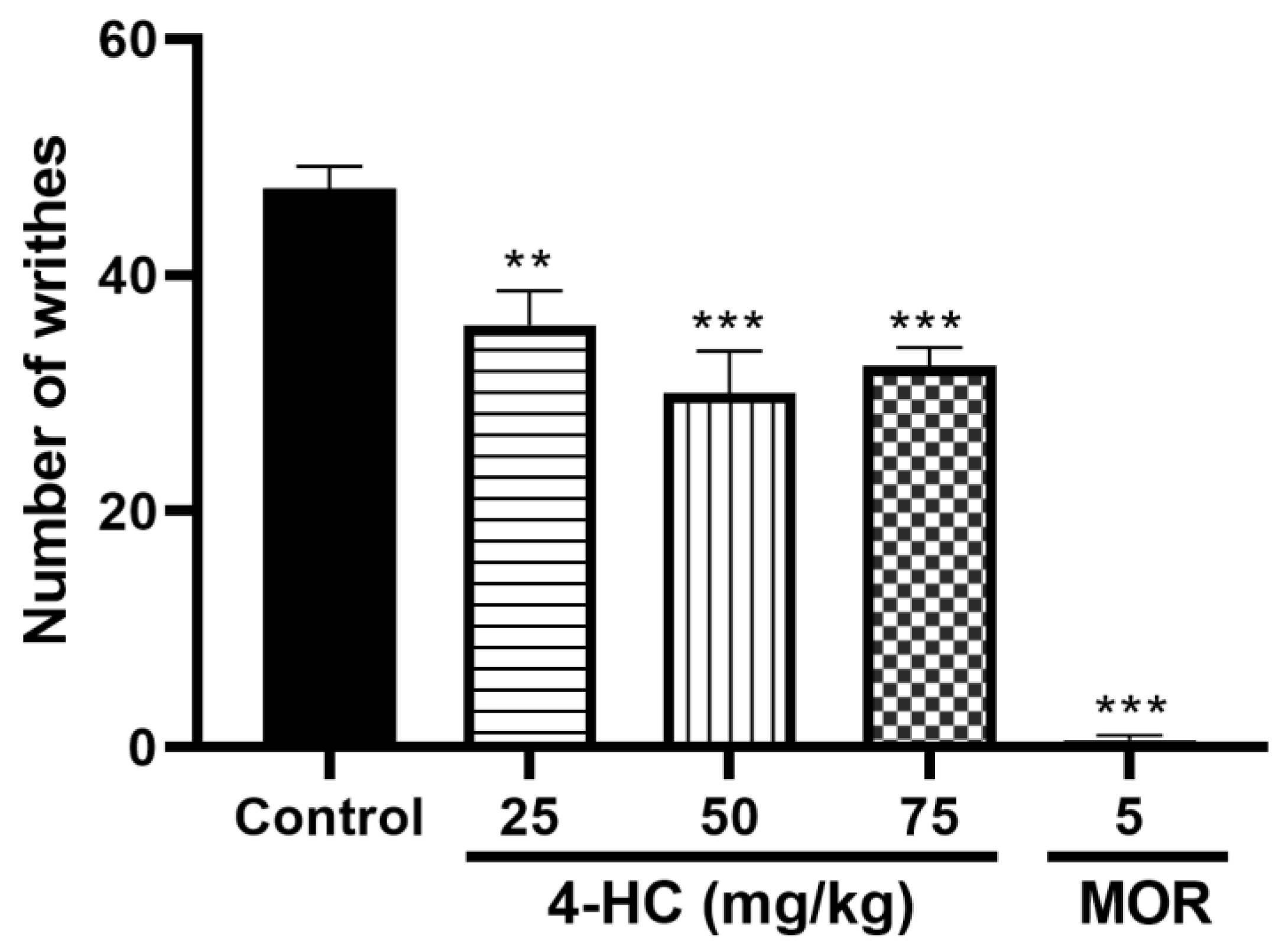
2.2.1. Effect of 4-HC on the Acetic Acid-Induced Writhing Protocol
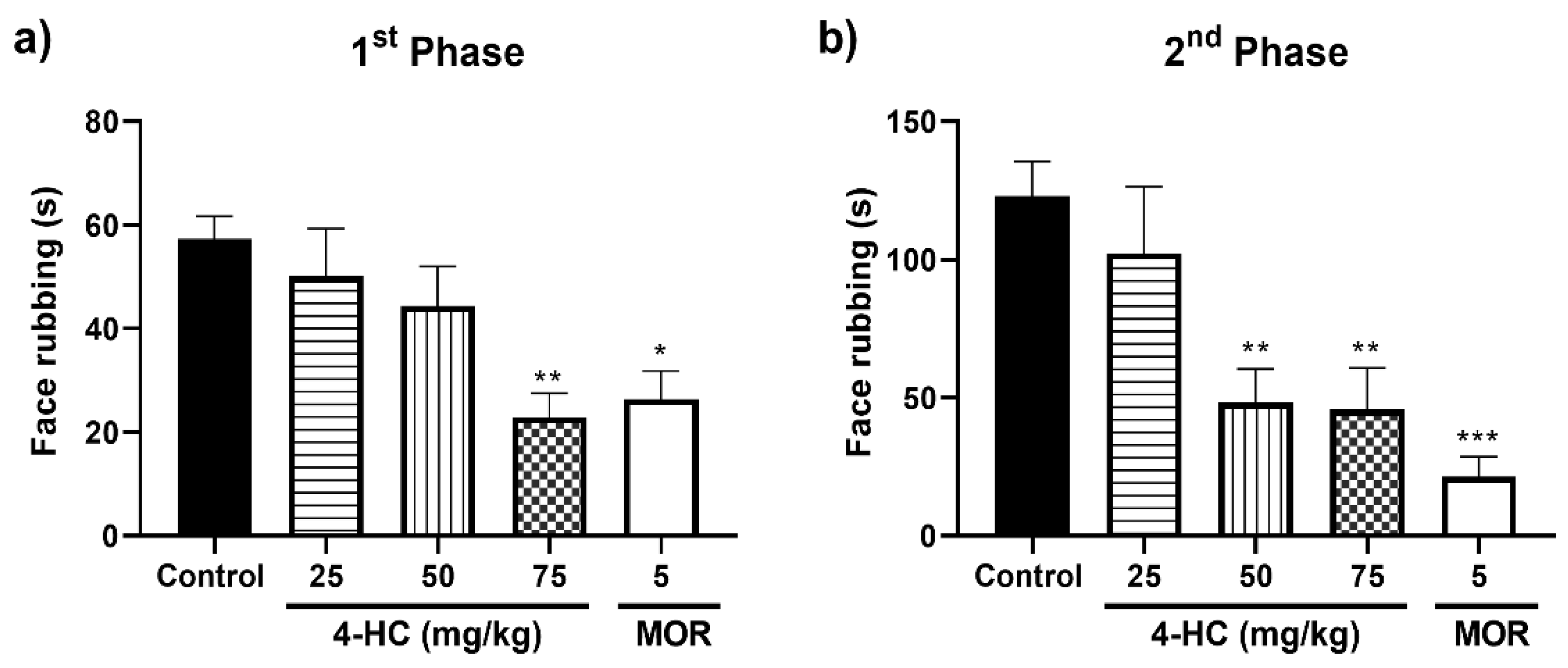
2.3. Effect of 4-HC in the Formalin-Induced Orofacial Nociception Protocol
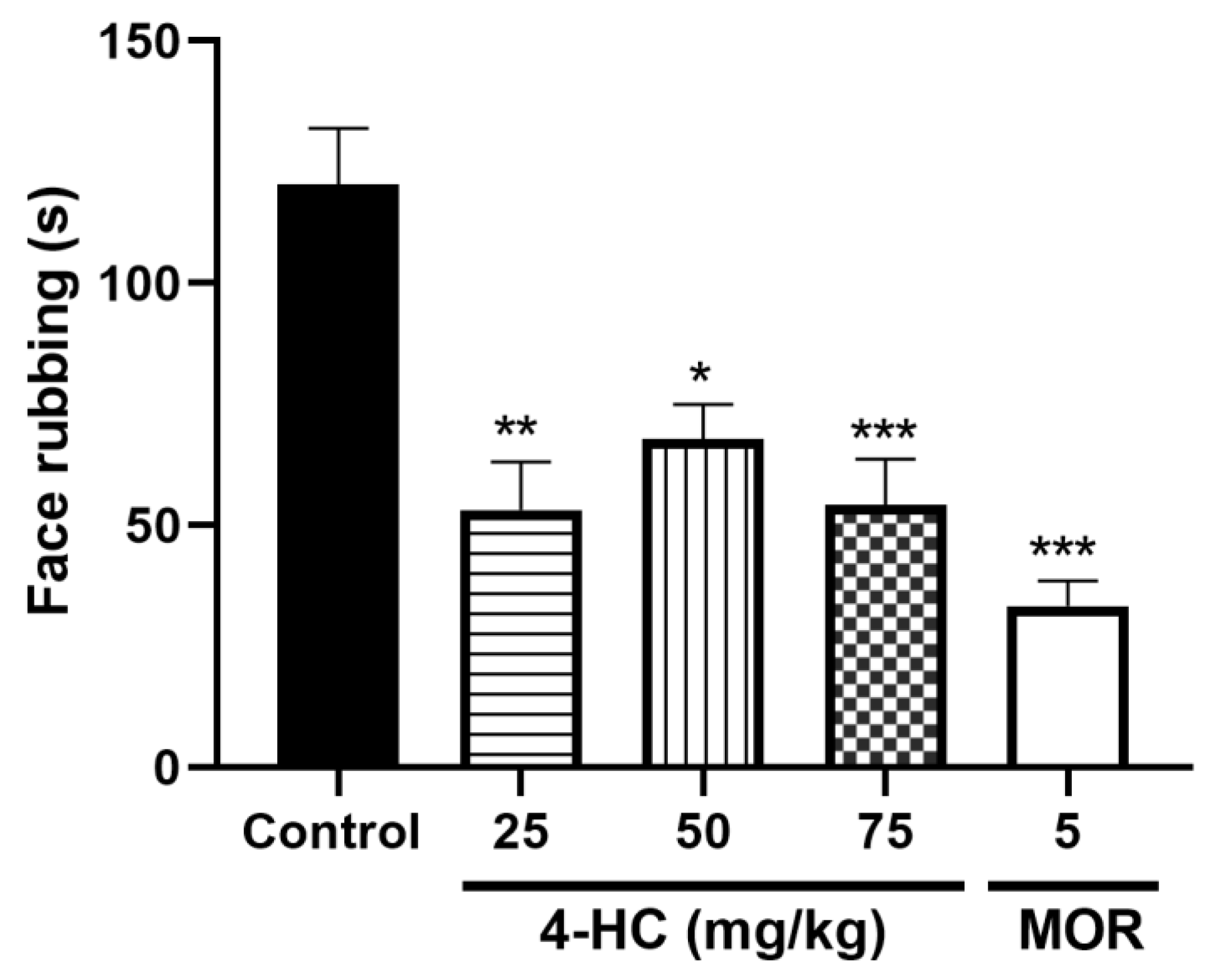
2.4. Effect of 4-HC in the Glutamate-Induced Orofacial Nociception Protocol
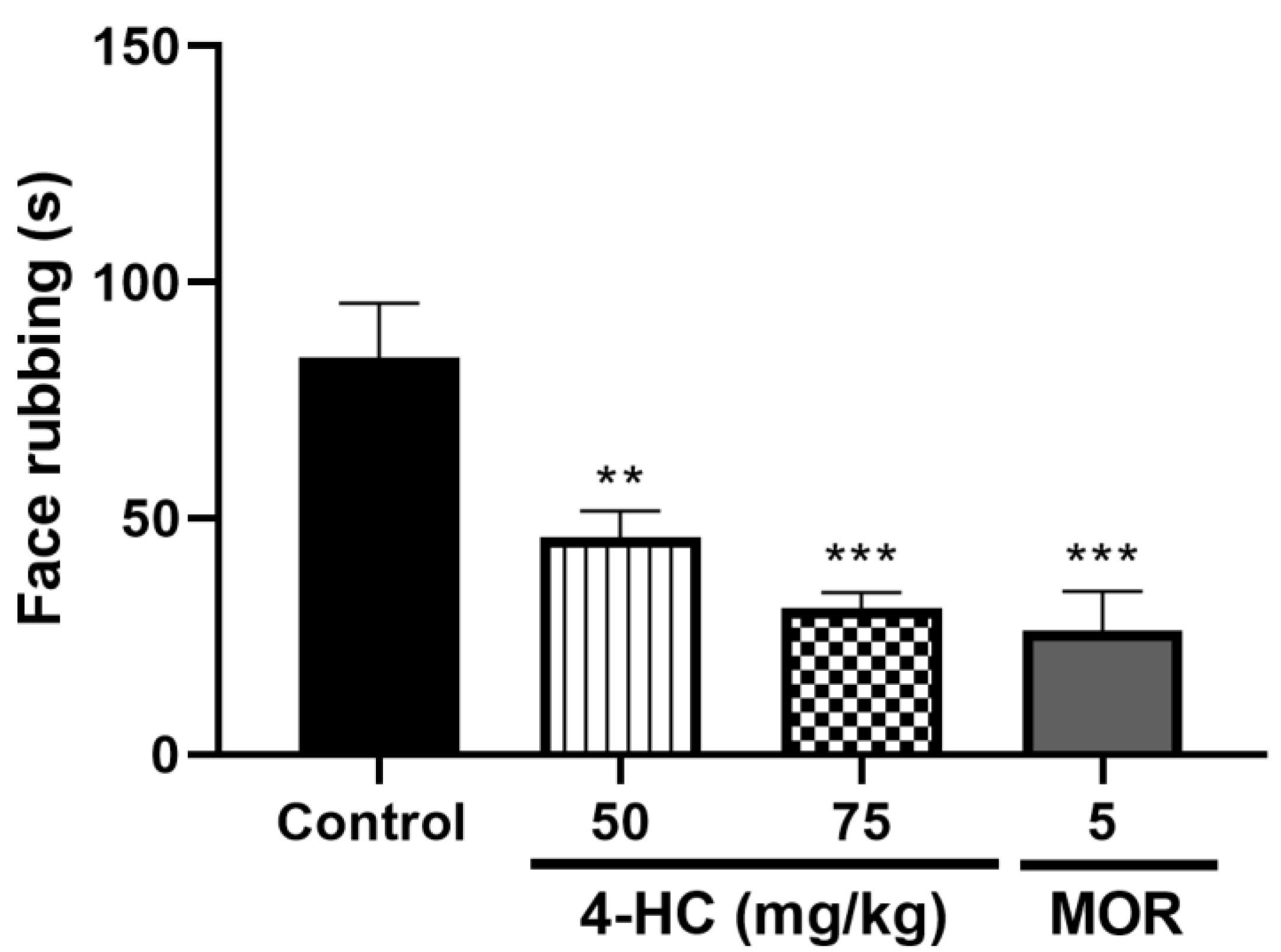
2.5. Effect of 4-HC on the Capsaicin-Induced Orofacial Nociception Protocol
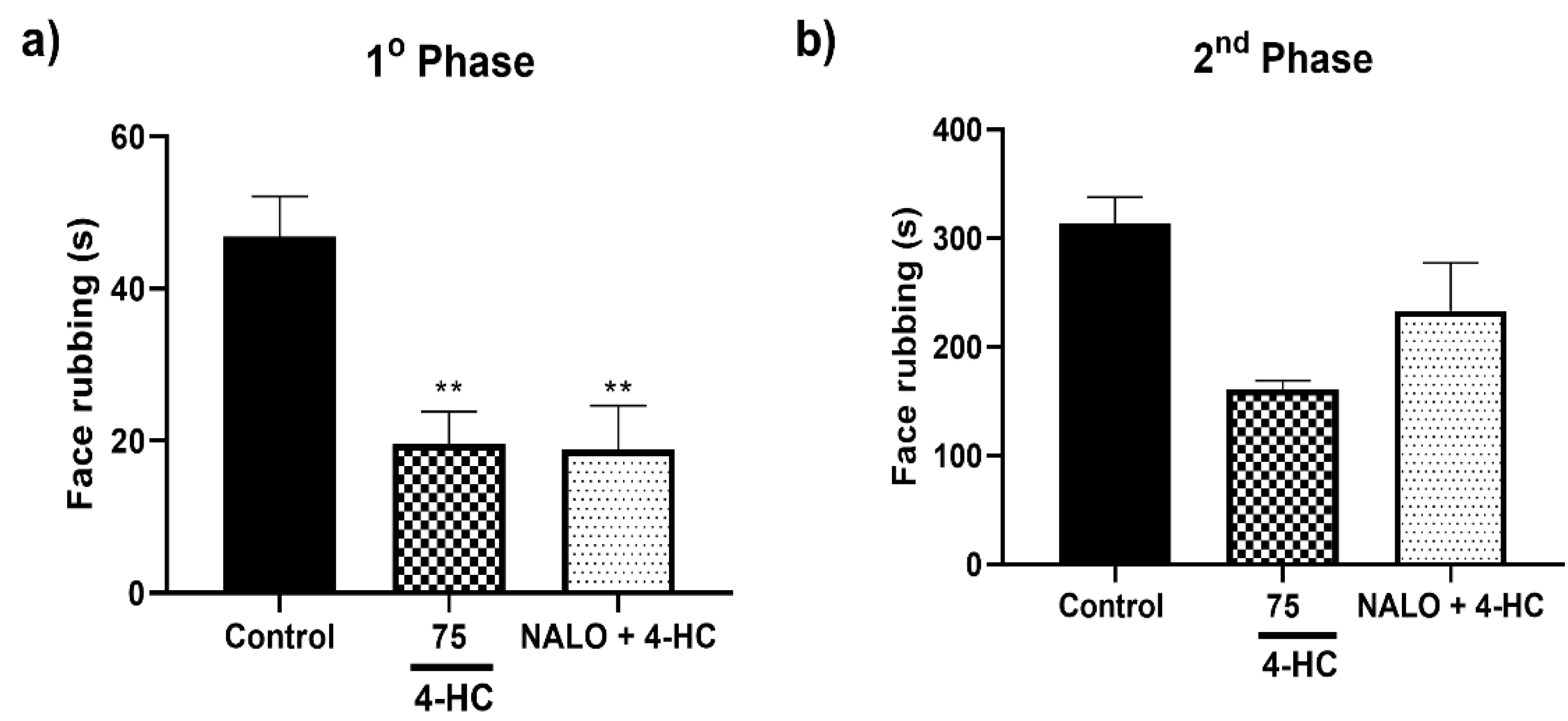
2.6. Opioid Receptors
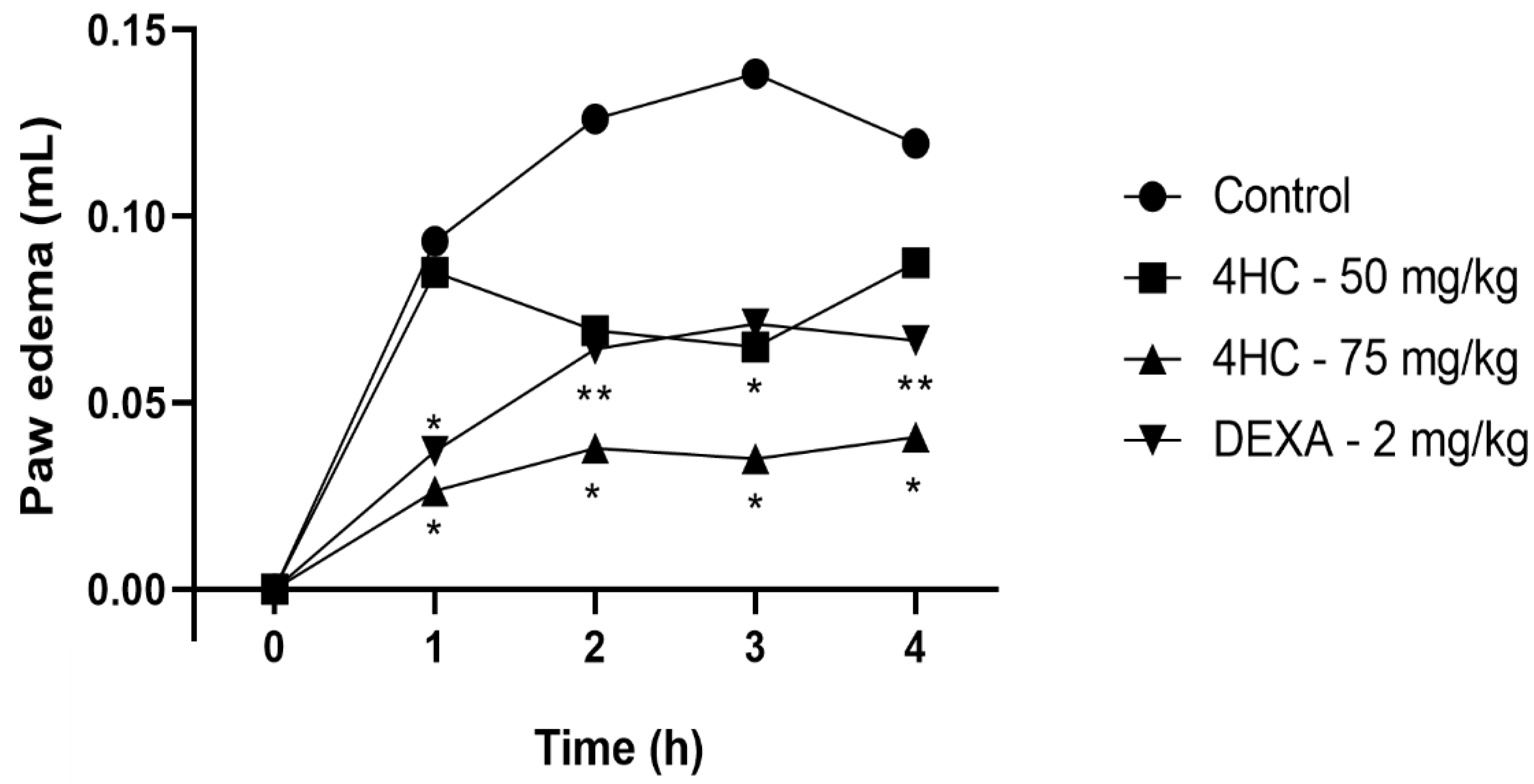
2.7. Carrageenan-Induced Paw Edema Test
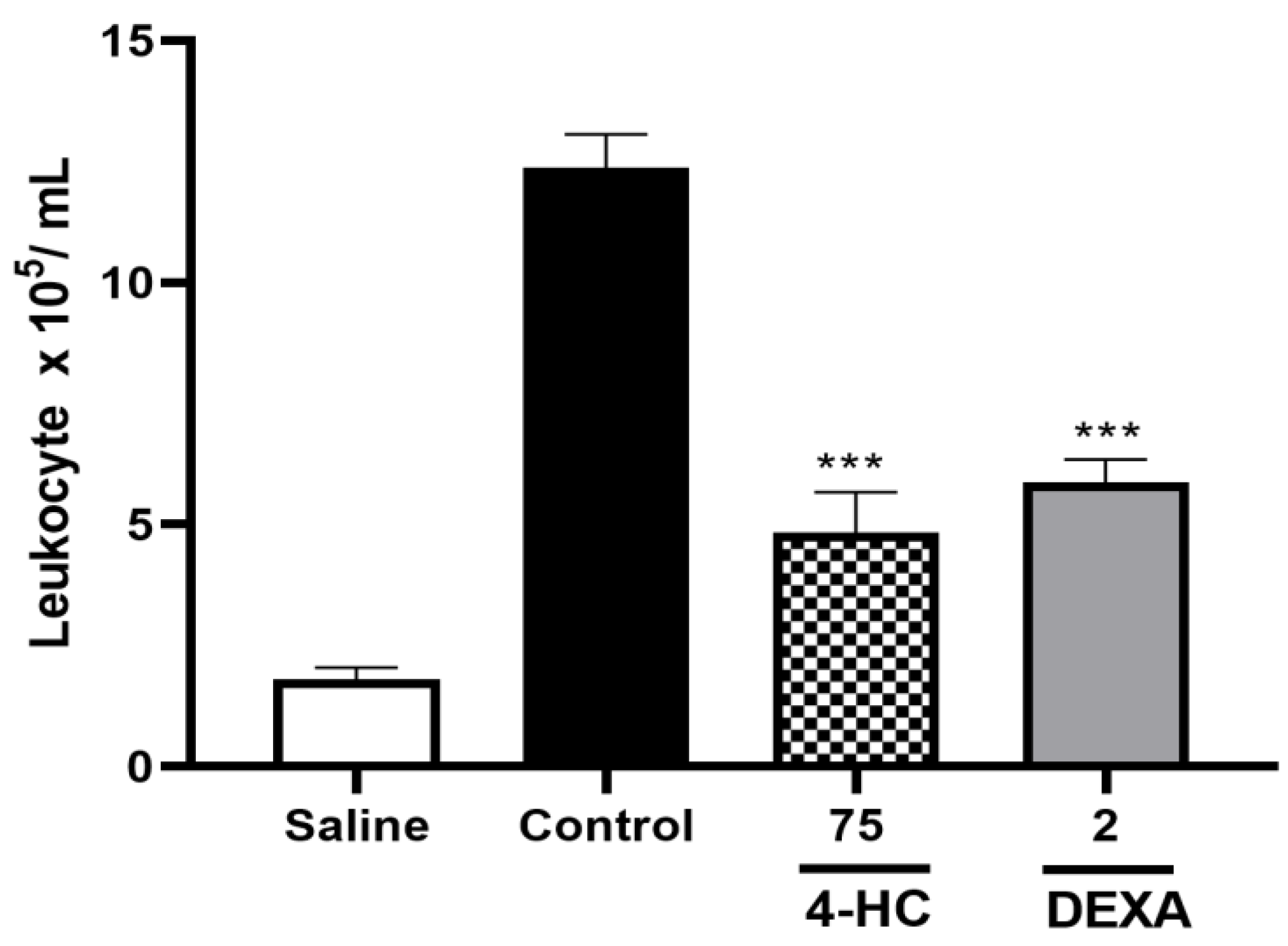
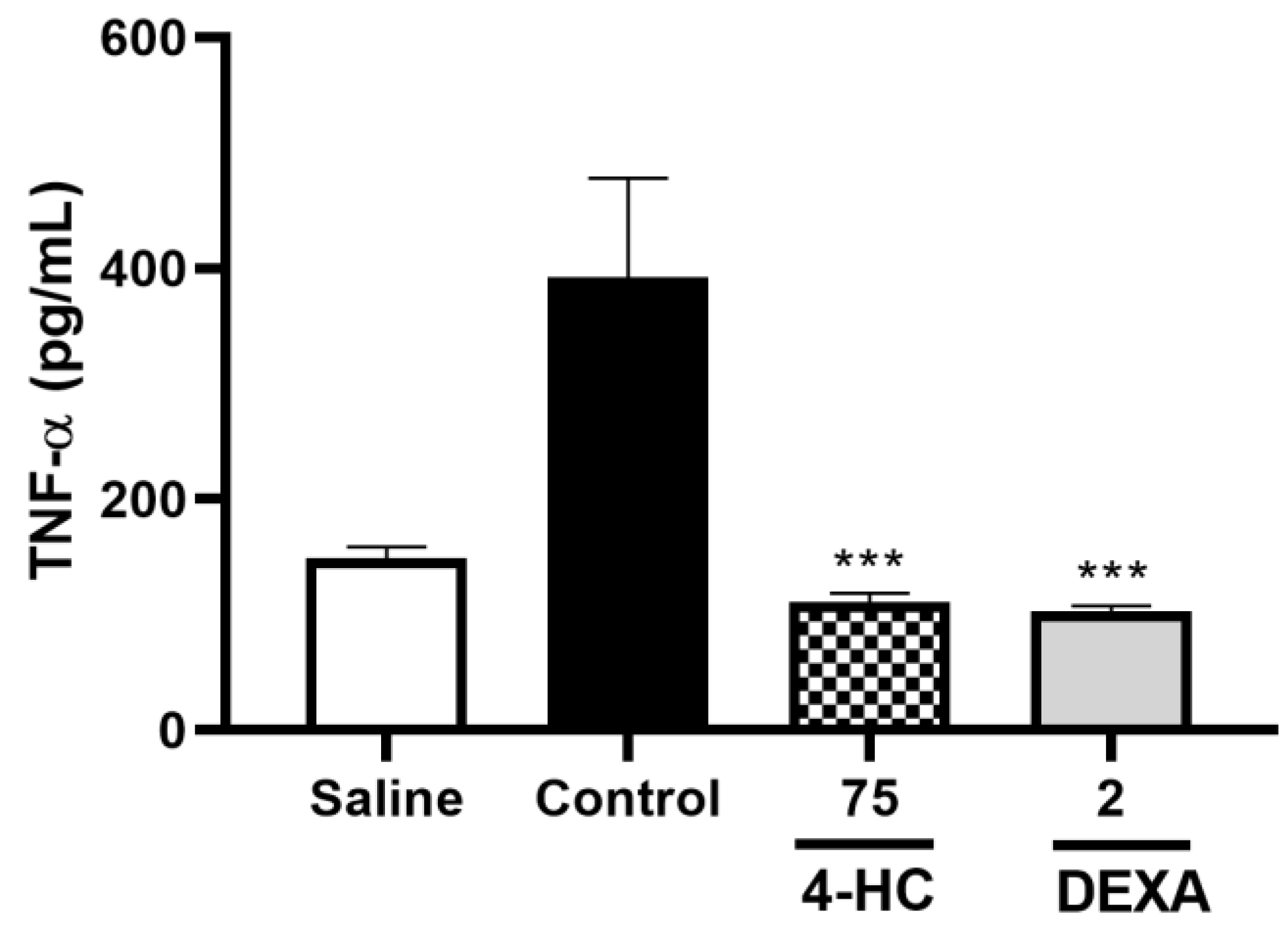
2.8. Leukocyte Count Test and Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine TNF-α Dosage
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Computational Studies
4.2. In Vivo Tests
4.2.1. Animals
4.2.2. Materials Preparation
4.2.3. Acetic Acid-Induced Abdominal Contortions Test
4.2.4. Formalin-Induced Orofacial Nociception Test
4.2.5. Glutamate-Induced Orofacial Nociception Test
4.2.6. Capsaicin-Induced Orofacial Nociception Test
4.2.7. Investigation of the Opioid System in the Orofacial Antinociceptive Activity of 4-Hydroxycoumarin
4.2.8. Evaluation of Anti-Inflammatory Activity Using the Carrageenan-Induced Paw Edema Protocol
4.2.9. Leukocyte Count Test and TNF-α Cytokine Dosage
4.3. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- DeSantana, J.M.; Perissinotti, D.M.N.; Oliveira Junior, J.O.D.; Correia, L.M.F.; Oliveira, C.M.D.; Fonseca, P.R.B.D. Definition of Pain Revised after Four Decades. Brazilian Journal Of Pain 2020, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Câmara-Gomes, L.F.; Dibai Filho, A.V.; Diniz, R.R.; Alvares, P.D.; Veneroso, C.E.; Cabido, C.E.T. Mechanisms of muscle stretching exercises for reduction of low back pain: narrative review. Brazilian Journal Of Pain 2022, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcante, S.R.P.; Fernandes, H.B.; Santos, J.S. Uma análise sobre o potencial da cumarina e a sua utilização como fármaco natural. RSD 2022, 11, e269111637850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamontain, V.; Schmid, T.; Weber-Steffens, D.; Zeller, D.; Jenei-Lanzl, Z.; Wajant, H.; Straub, R.H.; Männel, D.N. Stimulation of TNF Receptor Type 2 Expands Regulatory T Cells and Ameliorates Established Collagen-Induced Arthritis in Mice. Cell Mol Immunol 2019, 16, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cioce, A.; Cavani, A.; Cattani, C.; Scopelliti, F. Role of the Skin Immune System in Wound Healing. Cells 2024, 13, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, D.J.G.; Cardoso, I.P.; Oliveira, I.S.; Chaves, M.D.G.A.M.; Fabri, G.M.C. The Expression of the Nitric Oxide Synthase Enzyme in Periodontal Disease and Orofacial Pain: Systematic Review. Brazilian Journal Of Pain 2021, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, J.M.T.; Vidoti, V.A.; Simm, W.; Lopes, K.C. O IMPACTO DA DISFUNÇÃO TEMPOROMANDIBULAR E DA DOR OROFACIAL NA QUALIDADE DE VIDA. 2019.
- Franco, D.; Pereira, T.; Vitorio, F.; Nadur, N.; Lacerda, R.; Kümmerle, A. A IMPORTÂNCIA DAS CUMARINAS PARA A QUÍMICA MEDICINAL E O DESENVOLVIMENTO DE COMPOSTOS BIOATIVOS NOS ÚLTIMOS ANOS. Quím. Nova. [CrossRef]
- Gouda, M.A.; Hussein, B.H.M.; El-Demerdash, A.; Ibrahim, M.E.; Salem, M.A.; Helal, M.H.; Hamama, W.S. A Review: Synthesis and Medicinal Importance of Coumarins and Their Analogues (Part II). CBC 2020, 16, 993–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, J.A.; Saidachary, G.; Mallesham, G.; Sridhar, B.; Jain, N.; Kalivendi, S.V.; Rao, V.J.; Raju, B.C. Synthesis, Anticancer Activity and Photophysical Properties of Novel Substituted 2-Oxo-2H-Chromenylpyrazolecarboxylates. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2013, 65, 389–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdou, M.M.; El-Saeed, R.A.; Bondock, S. Recent Advances in 4-Hydroxycoumarin Chemistry. Part 1: Synthesis and Reactions. Arabian Journal of Chemistry 2019, 12, 88–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanda, C.; Aluru, R.R. Anticuagulants: An Overview of Natural and Synthetic Therapeutic Anticoagulants. J Biochem Technol 2021, 12, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, N.C.; Mondal, P.; Roy, S. A Mild Efficient Iodine-Catalyzed Synthesis of Novel Anticoagulants with 2,8-Dioxabicyclo [3.3.1]Nonane Core. Tetrahedron Letters 2013, 54, 2386–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, Mohd. Z.; Osman, H.; Ali, M.A.; Ahsan, M.J. Therapeutic Potential of Coumarins as Antiviral Agents. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2016, 123, 236–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, S.S.; Gupta, J.; Sharma, S.; Sahu, D. An Insight into the Therapeutic Applications of Coumarin Compounds and Their Mechanisms of Action. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 2020, 152, 105424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrianjafy, T.M.; Ramanandraibe, V.V.; Andrianarijaona, E.T.; Ramarosandratana, N.H.; Ravaomanarivo, L.H.; Mavingui, P.; Lemaire, M. Field Assessment of 4-Hydroxycoumarin as an Attractant for Anthropophilic Anopheles Spp. Vectors of Malaria in Madagascar. Sci Rep 2020, 10, 3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumorek-Wiadro, J.; Zając, A.; Maciejczyk, A.; Jakubowicz-Gil, J. Furanocoumarins in Anticancer Therapy – For and Against. Fitoterapia 2020, 142, 104492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, A.; Wang, Y.; Tong, L.; Liu, G.; Feng, J.; Li, Y.; Shen, C.; Wu, W. Coumarins and Flavones from Ficus Erecta and Their Anti-Inflammatory Activity. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 2024, 333, 118472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Kini, S.G.; Rathi, E. A Recent Appraisal of Artificial Intelligence and In Silico ADMET Prediction in the Early Stages of Drug Discovery. MRMC 2021, 21, 2788–2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto-Martínez, F.D.; Arciniega, M.; Medina-Franco, J.L. Acoplamiento Molecular: Avances Recientes y Retos. TIP RECQB 2018, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammed, M.T.; Aki-Yalcin, E. Molecular Docking: Principles, Advances, and Its Applications in DrugDiscovery. LDDD 2024, 21, 480–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, J.V.; Rosa, J.M.C.; Kimani, N.M.; Giuliatti, S.; Dos Santos, C.B.R. The Role of Celecoxib as a Potential Inhibitor in the Treatment ofInflammatory Diseases - A Review. CMC 2022, 29, 3028–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamal-Eltrabily, M.; Martínez-Lorenzana, G.; González-Hernández, A.; Condés-Lara, M. Cortical Modulation of Nociception. Neuroscience 2021, 458, 256–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velzen, M.V.; Dahan, J.D.C.; Van Dorp, E.L.A.; Mogil, J.S.; Hooijmans, C.R.; Dahan, A. Efficacy of Ketamine in Relieving Neuropathic Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Animal Studies. Pain 2021, 162, 2320–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husain, A.; Makadia, V.; Valicherla, G.R.; Riyazuddin, M.; Gayen, J.R. Approaches to Minimize the Effects of P-glycoprotein in Drug Transport: A Review. Drug Development Research 2022, 83, 825–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanni, D.; Pinna, F.; Gerosa, C.; Paribello, P.; Carpiniello, B.; Faa, G.; Manchia, M. Anatomical Distribution and Expression of CYP in Humans: Neuropharmacological Implications. Drug Development Research 2021, 82, 628–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Ma, J.; Li, M.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, B.; Zhao, X.; Huai, C.; Shen, L.; Zhang, N.; He, L.; et al. Cytochrome P450 Enzymes and Drug Metabolism in Humans. IJMS 2021, 22, 12808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olonode, E.T.; Aderibigbe, A.O.; Bakre, A.G. Anti-Nociceptive Activity of the Crude Extract of Myrianthus Arboreus P. Beauv (Cecropiaceae) in Mice. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 2015, 171, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Kaur, A.; Kaur, J.; Bhatti, M.S.; Singh, P.; Bhatti, R. Bergapten Inhibits Chemically Induced Nociceptive Behavior and Inflammation in Mice by Decreasing the Expression of Spinal PARP, iNOS, COX-2 and Inflammatory Cytokines. Inflammopharmacol 2019, 27, 749–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bars, D.; Gozariu, M.; Cadden, S.W. Animal Models of Nociception. Pharmacological Reviews 2001, 53, 597–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gripp, E.L.O.; Carneiro, L.U.; Pereira, I.D.S.P.; Vega, M.R.G.; Marinho, B.G. Avaliação das propriedades analgésicas de Anaxagorea dolichocarpa Sprague and Sandwith LC. BJHR 2020, 3, 382–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sr, B.V.C.; Sr, P.K.; Jr, J.N.; Shanmugasundaram, J.; Sr, S.; Sr, V.S. Anti-nociceptive Effect of 7-methoxy Coumarin from Eupatorium Triplinerve Vahl (Asteraceae).
- Xu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Li, W.; Zhang, S.; Liao, X.; Liu, Y.; Su, Y.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, J. Active Components of Bupleurum Chinense and Angelica Biserrata Showed Analgesic Effects in Formalin Induced Pain by Acting on Nav1.7. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 2021, 269, 113736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beirith, A.; Santos, A.R.S.; Calixto, J.B. Mechanisms Underlying the Nociception and Paw Oedema Caused by Injection of Glutamate into the Mouse Paw. Brain Research 2002, 924, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelissier, T.; Pajot, J.; Dallel, R. The Orofacial Capsaicin Test in Rats: Effects of Different Capsaicin Concentrations and Morphine. Pain 2002, 96, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, R.T.; Almeida, D.B.D.; Monteiro, F.M.D.R.; Kowacs, P.A.; Ramina, R. Receptores opioides até o contexto atual. Rev. dor 2012, 13, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, A.P.D.; Fujii, Y.W.H.; Rangel, M.P.; Nishida, F.S. RETIRADA DE OPIOIDES: UMA REVISÃO BIBLIOGRÁFICA / OPIOID WITHDRAWAL: A LITERATURE REVIEW. BJD 2020, 6, 67098–67112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-H.; Sim, Y.-B.; Kang, Y.-J.; Kim, S.-S.; Kim, C.-H.; Kim, S.-J.; Lim, S.-M.; Suh, H.-W. Antinociceptive Profiles and Mechanisms of Orally Administered Coumarin in Mice. Biological & Pharmaceutical Bulletin 2013, 36, 925–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farsam, H.; Amanlou, M.; Reza Dehpour, A.; Jahaniani, F. Anti-Inflammatory and Analgesic Activity of Biebersteinia Multifida DC. Root Extract. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 2000, 71, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guay, J.; Bateman, K.; Gordon, R.; Mancini, J.; Riendeau, D. Carrageenan-Induced Paw Edema in Rat Elicits a Predominant Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) Response in the Central Nervous System Associated with the Induction of Microsomal PGE2 Synthase-1. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2004, 279, 24866–24872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Chen, Z.-H.; Huang, Z.-Y.; Zu, F.-Q. Optimizing Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of Hypereutectic Al-18%Si Alloy via Manipulating Its Parent Liquid State. Materials Science and Engineering: A 2017, 690, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, S.; Tan, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, L.; Wang, K.; Wen, C.; Wang, M. Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Effects of Esculin and Esculetin (Review). Exp Ther Med 2024, 27, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antika, L.D.; Tasfiyati, A.N.; Hikmat, H.; Septama, A.W. Scopoletin: A Review of Its Source, Biosynthesis, Methods of Extraction, and Pharmacological Activities. Zeitschrift für Naturforschung C 2022, 77, 303–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myung, Y.; de Sá, A.G.C.; Ascher, D.B. Deep-PK: Deep Learning for Small Molecule Pharmacokinetic and Toxicity Prediction. Nucleic Acids Research 2024, 52, W469–W475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccagli, L.; Fabbri, E.; Borgatti, M.; Bezzerri, V.; Mancini, I.; Nicolis, E.; Dechecchi, M.C.; Lampronti, I.; Cabrini, G.; Gambari, R. Docking of Molecules Identified in Bioactive Medicinal Plants Extracts into the P50 NF-kappaB Transcription Factor: Correlation with Inhibition of NF-kappaB/DNA Interactions and Inhibitory Effects on IL-8 Gene Expression. BMC Struct Biol 2008, 8, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.L.; Limburg, D.; Graneto, M.J.; Springer, J.; Hamper, J.R.B.; Liao, S.; Pawlitz, J.L.; Kurumbail, R.G.; Maziasz, T.; Talley, J.J.; et al. The Novel Benzopyran Class of Selective Cyclooxygenase-2 Inhibitors. Part 2: The Second Clinical Candidate Having a Shorter and Favorable Human Half-Life. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 2010, 20, 7159–7163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.J.; Gharpure, A.; Teng, J.; Zhuang, Y.; Howard, R.J.; Zhu, S.; Noviello, C.M.; Walsh, R.M.; Lindahl, E.; Hibbs, R.E. Shared Structural Mechanisms of General Anaesthetics and Benzodiazepines. Nature 2020, 585, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeld, R.J.; Garcin, E.D.; Panda, K.; Andersson, G.; Åberg, A.; Wallace, A.V.; Morris, G.M.; Olson, A.J.; Stuehr, D.J.; Tainer, J.A.; et al. Conformational Changes in Nitric Oxide Synthases Induced by Chlorzoxazone and Nitroindazoles: Crystallographic and Computational Analyses of Inhibitor Potency. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 13915–13925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, G.; Duyne, G.V.; Ghosh, S. Structure of NF-KB P50 Homodimer Bound to a KB Site. 1995, 373. 373.
- Wang, H.; Lv, S.; Stroebel, D.; Zhang, J.; Pan, Y.; Huang, X.; Zhang, X.; Paoletti, P.; Zhu, S. Gating Mechanism and a Modulatory Niche of Human GluN1-GluN2A NMDA Receptors. Neuron 2021, 109, 2443–2456.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Wang, Y.; He, B.; He, X.; Zhou, X.E.; Guo, S.; Rao, Q.; Yang, J.; Liu, J.; Zhou, Q.; et al. Molecular Recognition of Morphine and Fentanyl by the Human μ-Opioid Receptor. Cell 2022, 185, 4361–4375.e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Cao, E.; Julius, D.; Cheng, Y. TRPV1 Structures in Nanodiscs Reveal Mechanisms of Ligand and Lipid Action. Nature 2016, 534, 347–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastos, G.N.T.; Santos, A.R.S.; Ferreira, V.M.M.; Costa, A.M.R.; Bispo, C.I.; Silveira, A.J.A.; Do Nascimento, J.L.M. Antinociceptive Effect of the Aqueous Extract Obtained from Roots of Physalis Angulata L. on Mice. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 2006, 103, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perla, A.D.S. universidade federal do rio grande do sul instituto de ciências básicas da saúde programa de pós-graduação em ciências biológicas: neurocincias.
- Siqueira-Lima, P.S.; Araújo, A.A.S.; Lucchese, A.M.; Quintans, J.S.S.; Menezes, P.P.; Alves, P.B.; De Lucca Júnior, W.; Santos, M.R.V.; Bonjardim, L.R.; Quintans-Júnior, L.J. β-Cyclodextrin Complex Containing Lippia Grata Leaf Essential Oil Reduces Orofacial Nociception in Mice - Evidence of Possible Involvement of Descending Inhibitory Pain Modulation Pathway. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 2014, 114, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazerani, P.; Wang, K.; Cairns, B.E.; Svensson, P.; Arendt-Nielsen, L. Effects of Subcutaneous Administration of Glutamate on Pain, Sensitization and Vasomotor Responses in Healthy Men and Women. Pain 2006, 124, 338–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, P.R.; Do Espírito Santo, R.F.; Melo, C.D.O.; Pachú Cavalcante, F.E.; Costa, T.B.; Barbosa, Y.V.; E Silva, Y.M.S.D.M.; De Sousa, N.F.; Villarreal, C.F.; De Moura, R.O.; et al. The Compound (E)-2-Cyano-N,3-Diphenylacrylamide (JMPR-01): A Potential Drug for Treatment of Inflammatory Diseases. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, L.C.C.; Meyer, T.N.; Pereira, J.B.B.; Silva, G.R.D. avaliação da atividade anti-inflamatória do extrato hidroalcoólico do caroço de abacate sobre a peritonite induzida pela carragenina em ratos. RUVRV 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Absorption | |
| P-Glycoprotein Inhibitor | Non-Inhibitor |
| P-Glycoprotein Substrate | Non-Substrate |
| Human Intestinal Absorption | Absorbed |
| Distribution | |
| BBB | Penetrable |
| Excretion | |
| Clearance | 5.76 |
| Half-Life of Drug | Half-Life < 3hs |
| Metabolism | |
| CYP 1A2 Inhibitor / Substrate | Non-Inhibitor / Substrate |
| CYP 2C19 Inhibitor / Substrate | Non-Inhibitor / Non-Substrate |
| CYP 2C9 Inhibitor / Substrate | Non-Inhibitor / Non-Substrate |
| CYP 2D6 Inhibitor / Substrate | Non-Inhibitor / Substrate |
| CYP 3A4 Inhibitor / Substrate | Non-Inhibitor / Non-Substrate |
| Toxicity | |
| Biodegradation | Safe |
| Carcinogenesis | Safe |
| Ames Mutagenesis | Safe |
| Target | Ligands | Escore MolDock | RMSD |
|---|---|---|---|
| COX-2 | 4-HC | -54.84 | 0.27 |
| Celecoxib | -158.60 | ||
| GABAA | 4-HC | -50.64 | 0.08 |
| Bicuculline | -146.56 | ||
| iNOS | 4-HC | -106.52 | 0.19 |
| 7-Nitroindazole | -103.34 | ||
| NFκB | 4-HC | -58.71 | - |
| Dexamethasone | -91.38 | ||
| NMDAR | 4-HC | -56.12 | - |
| Sketamine | -51.11 | ||
| µ-opioid receptor | 4-HC | -28.36 | 0.11 |
| Morphine | -78.23 | ||
| TRPV1 | 4-HC | -62.20 | 0.66 |
| Capsazepine | -87.79 |
| Target | PDB (ID) | Resolution | Ligand |
|---|---|---|---|
| COX-2 | 3LN1 [46] | 2.40 Å | Celecoxib |
| GABAA | 6X3S [47] | 3.12 Å | Bicuculline |
| iNOS | 1M8E [48] | 2.90 Å | 7-Nitroindazole |
| NFκB | 1NFK [49] | 2.30 Å | Dexamethasone |
| NMDAR | 7EOQ [50] | 3.50 Å | Sketamine |
| µ-opioid receptor | 8EF6 [51] | 3.20 Å | Morphine |
| TRPV1 | 5IS0 [52] | 3.43 Å | Capsazepine |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





