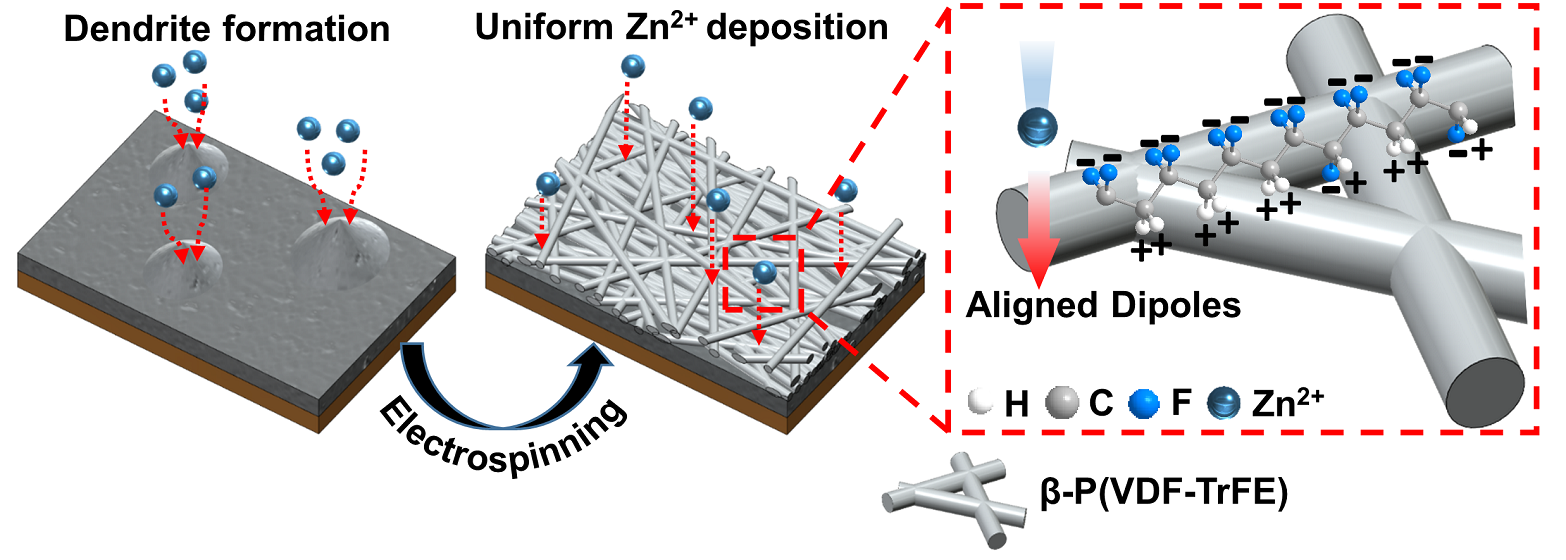
Uncontrollable Zn dendrite formations and parasitic side reactions on Zn electrodes induce poor cycling stability and safety issues, preventing the large-scale commercialization of Zn-ion batteries. Herein, to achieve uniform Zn deposition and suppress side reactions, an electrospun ferroelectric poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-trifluoroethylene) copolymer, a [P(VDF-TrFE)] nanofiber layer, is introduced as an artificial solid-electrolyte interface on a Cu substrate acting as a current collector. The aligned molecular structure of β-P(VDF-TrFE) can effectively suppress localized current density on the Cu surface, lead to uniform Zn deposition, and suppress side reactions by preventing direct contact between electrodes and aqueous electrolytes. The half-cell configuration formed by the newly fabricated electrode can achieve an average coulombic efficiency of 99.2% over 300 cycles without short circuiting at a current density of 1 mA cm-2 and areal capacity of 1 mAh cm-2. Stable cycling stability is also maintained for 200 cycles at a current density of 0.5 A g-1 in a full-cell test using MnO2 as a cathode.