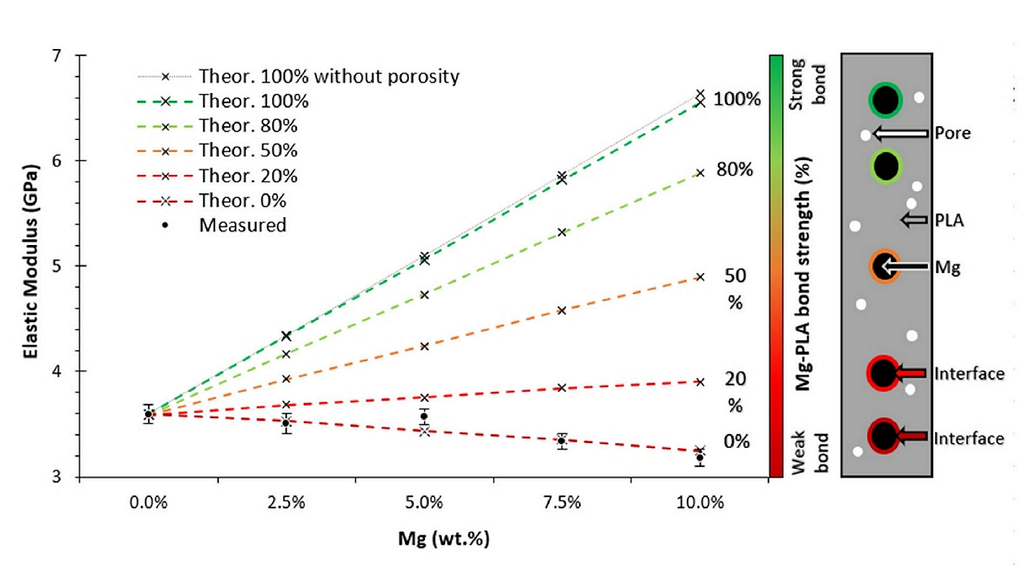
The effect of Mg particles on PLA's thermal, chemical, physical, and mechanical properties has been studied. The thermal and physical properties have been studied by differential scanning calorimetry, analysing the stability of the α and α’-crystals of the PLA. A colloidal route was used to introduce Mg particles inside the PLA matrix, ensuring a good dispersion of the particles. Materials with Mg contents from 0 to 10 wt.% have been prepared, with additions of polyethyleneimine (PEI) and polyethylene glycol (PEG). Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy has been used to confirm the influence of Mg, PEI, and PEG on PLA properties. The mechanical properties have been measured with a universal tensile test machine on printed filaments via Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF), which were naturally aged to stable conditions. Filaments with and without a notch were studied to obtain the materials' tensile strength, elastic modulus, and fracture toughness. Different analytical models to explain the results of the PLA-Mg were studied, in which the interface strength of the PLA-Mg composites was calculated.