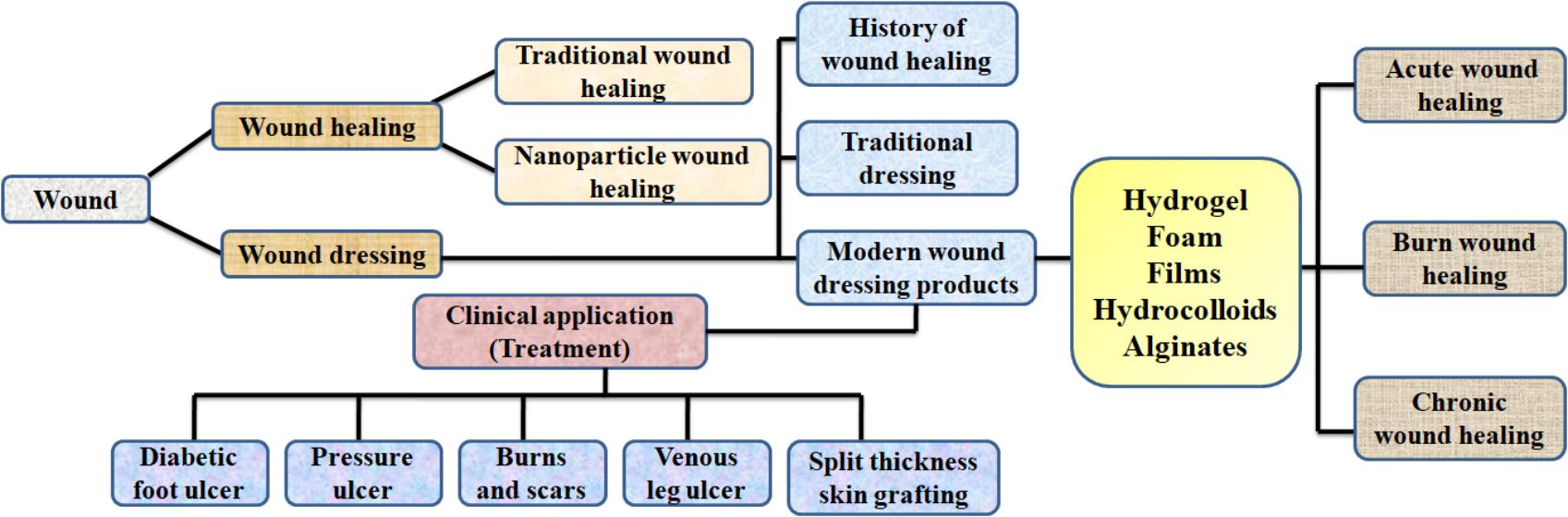
Wounds are structural and functional disruptions of the skin that occur because of an accident. Chronic wounds are caused by a breakdown in the finely coordinated cascade of events that occurs during wound healing. Wound healing is a long process that split into at least three continuous and overlapping processes: an inflammatory response, a proliferative phase that leads to tissue repair, and third one is tissue remodeling. Therefore, wound healing studies are extensively studied to develop techniques that can achieve maximum recovery with minimum scar. Several growth hormones and cytokines secreted at the wound site tightly regulate wound healing processes. The traditional approach for wound management has been represented by topical treatments. Metal nanoparticles (e.g., silver, gold, zinc) are increasingly being employed in dermatology due to their favorable effects on wound healing, as well as in treating and preventing bacterial infections. The development of wound dressings materials has now been used to overcome the issues of external environments. The impregnated nanomaterials have provided moist environment that removes the exudates and avoid maceration. This review highlights the mechanism and focus on the current advancement of various nanoparticles impregnation material for wound healing process that can protect wound from infection and maintain the optimum exchange of gases.