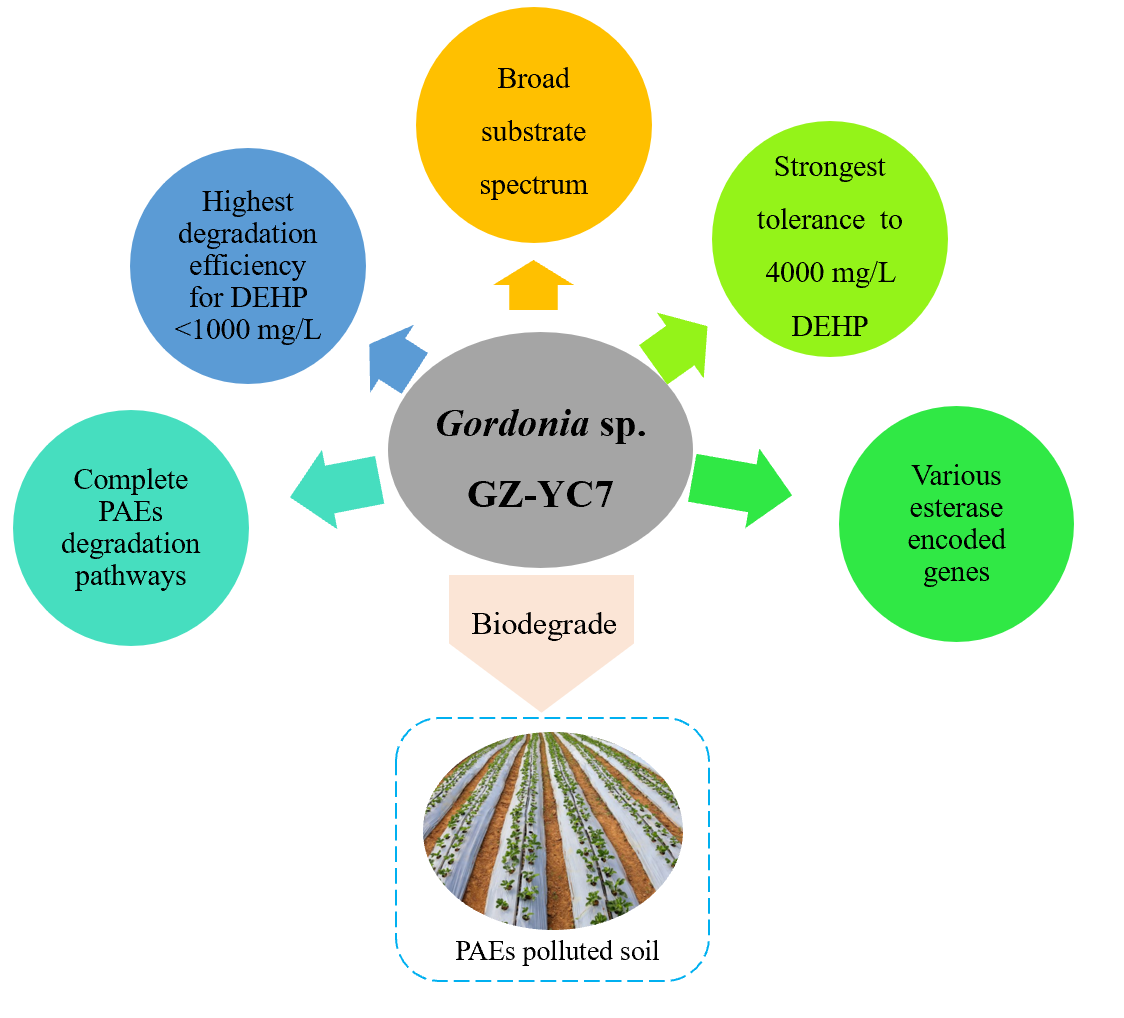
As commonly used chemical plasticizers in plastic products, phthalate esters had become a serious ubiquitous environmental pollutant, such as in soil of plastic film mulch culture. Microbial degradation or transformation was regarded as a suitable strategy to solve the phthalate esters pollution. Thus, a new phthalate esters degrading strain Gordonia sp. GZ-YC7 was isolated in this study, which exhibited the highest di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate degradation efficiency under 1000 mg/L and the strongest tolerance to 4000 mg/L. The comparative genomic analysis showed that there exist diverse degradation pathways for various phthalate esters such as di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate and dibutyl phthalate in Gordonia sp. GZ-YC7, which possibly contributes to its broad substrate spectrum, high degrading efficiency and high tolerance to phthalate esters. Gordonia sp. GZ-YC7 is potential for bioremediation of phthalate esters in polluted soil environments.