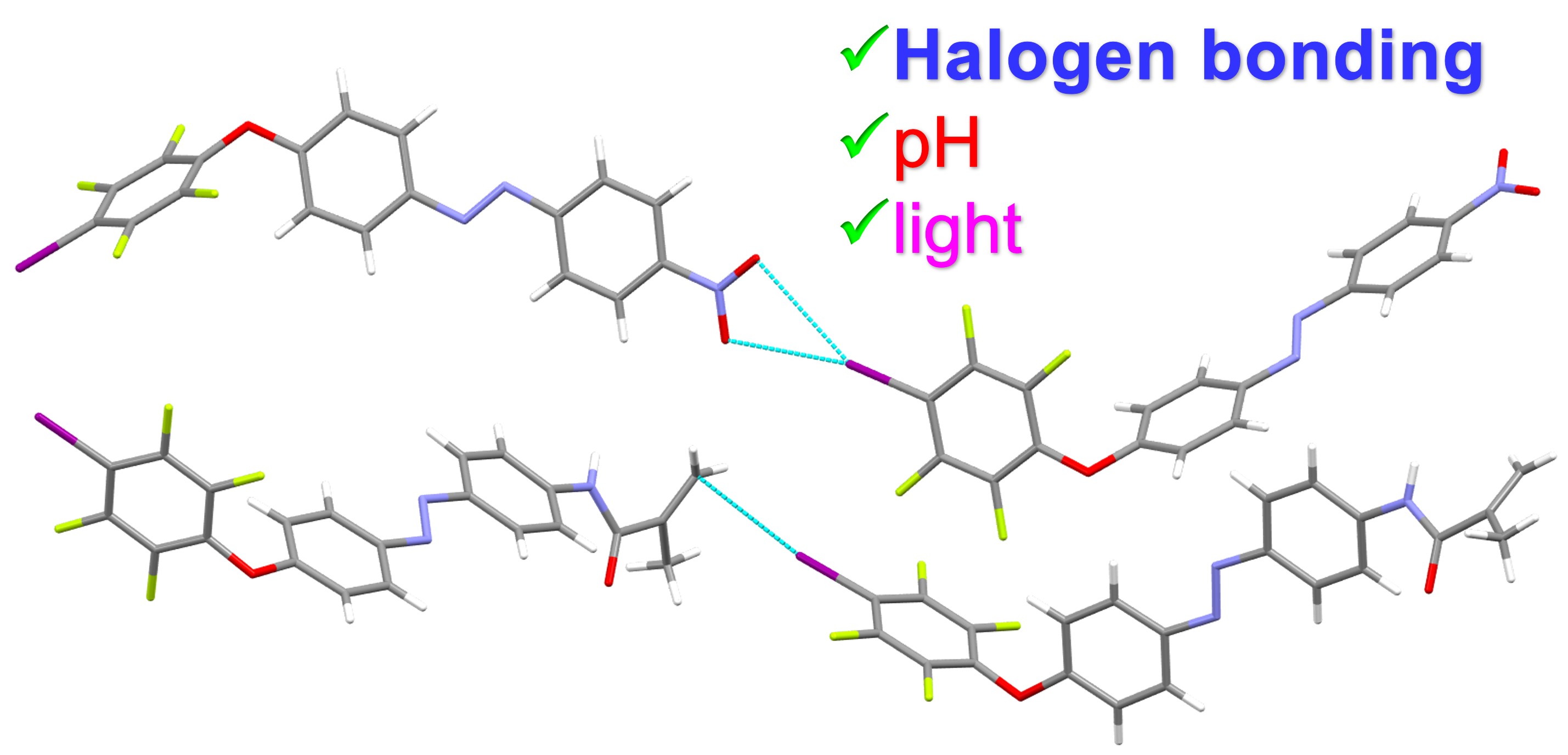
Smart materials represent an elegant class of (macro)-molecules endowed with the ability to react to chemical/physical changes in the environment. Herein, we prepared new photo responsive azobenzenes possessing halogen bond donor groups. The X-ray structures of two molecules highlight supramolecular organizations governed by unusual noncovalent bonds. In azo dye I-azo-NO2, the nitro group is engaged in orthogonal H···O···I halogen and hydrogen bonding, linking the units in parallel undulating chains. As concern parent I-azo-NH-MMA, a non-centrosymmetric pattern is formed due to a very rare I···π interaction involving the alkene group supplemented by hydrogen bonds. The Cambridge Structural Database contains only four structures with the same I···CH2=C contact. For all compounds, a 19F NMR spectroscopic analysis confirms the formation of halogen bonds in solution through a recognition process with chloride anion, and the reversible photo-responsiveness is demonstrated upon exposing a solution to UV light irradiation. Finally, intermediate I-azo-NO2 also shows a pronounced color change due to pH variation. These azobenzenes are thereby attractive building blocks to design multi-stimuli responsive materials for highly functional devices.