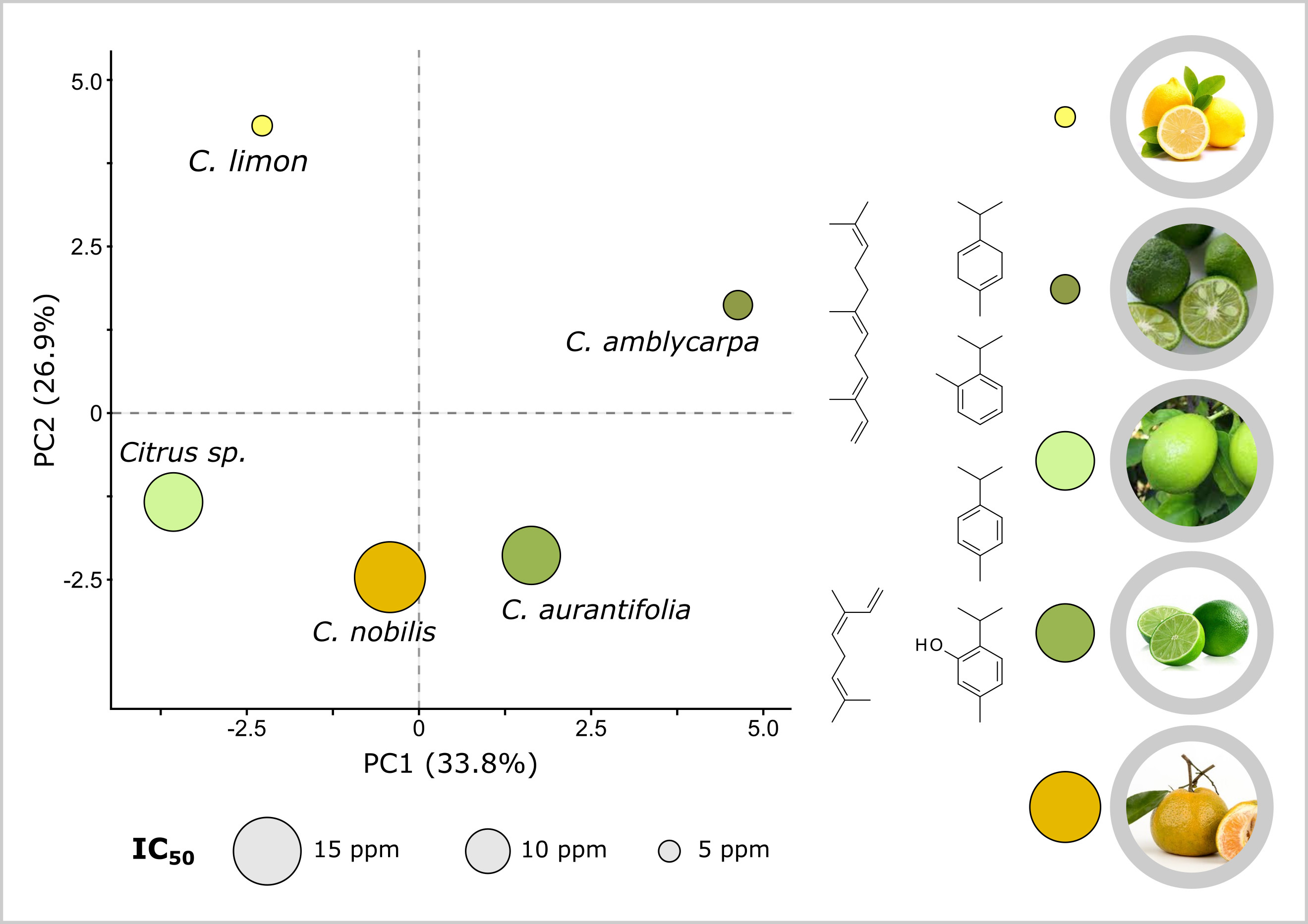
Citrus essential oils (EOs) have various bioactivities like antioxidants, with many applications. Antioxidant activities depend on the chemical compositions of the EOs, which are affected by climate, soil, and geographical region. Thus, investigations on chemical compositions and antioxidant activities of Citrus EOs in different countries are valuable. In this study, we distilled EOs from peels of Indonesian-grown Citrus, including C. nobilis, C. limon, C. aurantifolia, C. amblycarpa, and Citrus spp.Chemical compositions of EOs were analyzed using Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometer (GC-MS), whereas the antioxidant activities were determined by employing 2,2-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) method. Furthermore, principal component analysis (PCA) was applied to elucidate the main contributing compounds for antioxidant activity. The results show that all EOs possess unique chemical characteristics, with limonene as the majority constituent. For antioxidant activities, C. limon and C. amblycarpa EOs are the two strongest, IC50 values below 7.00 μL/mL. PCA approach suggests that -terpinene mainly contributes to the high antioxidant activities of C. limon and C. amblycarpa. Moreover, o-cymene, thymol, p-cymene, and α-pharnesene may also be responsible for the antioxidant activity of C. limon EO. These results are valuable information for the applications of Citrus EOs as antioxidant sources.