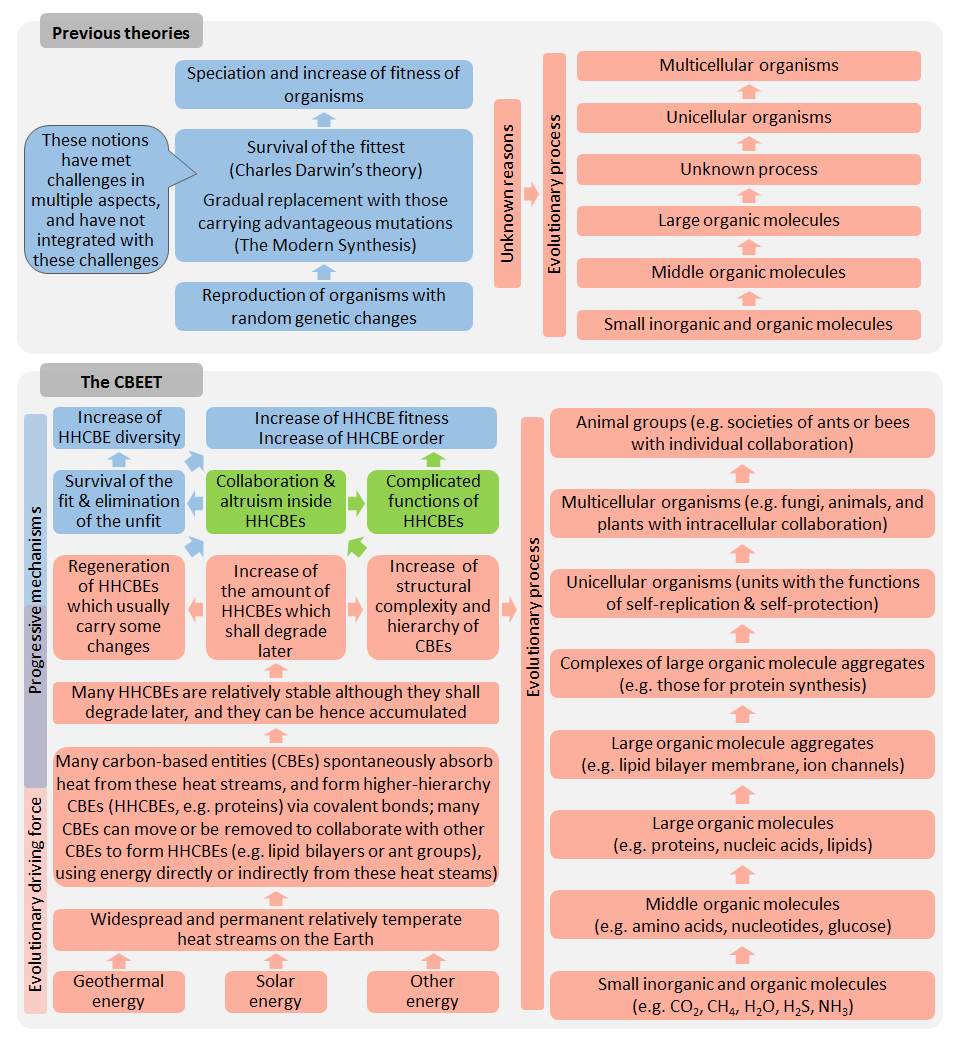
Studies on evolution have made significant progress in multiple disciplines, but evolutionary theories remain scattered and controversial. Here we deduce that, thermodynamically, many carbon-based entities (CBEs) on the Earth tend to absorb energy from widespread relatively temperate heat streams on the Earth flowing from the solar, geothermal, and other energy sources, to form higher-hierarchy CBEs (HHCBEs). This has been the driving force of evolution leading to accumulation of HHCBEs for billions of years. We further deduce three progressive mechanisms of evolution including natural selection from the driving force. We hence establish the CBE evolutionary theory (CBEET) which reinterprets the major aspects of evolution in a comprehensive and comprehensible way. The CBEET provides novel explanations for natural selection, origin of life (abiogenesis), macroevolution, sympatric speciation, and evolutionary tempos. It suggests that evolution is driven hierarchy-wise by thermodynamics and favors fitness and diversity. It elucidates that altruism, collaboration, and obeying rules with balanced freedom are important throughout the CBE evolution which includes chemical evolution, biological evolution, and animal group evolution. The CBEET refutes several erroneous views including negative entropy and survival of the fittest. It integrates with research advances in multiple disciplines and links up laws of physics, evolution in biology, and harmonious development of human society.