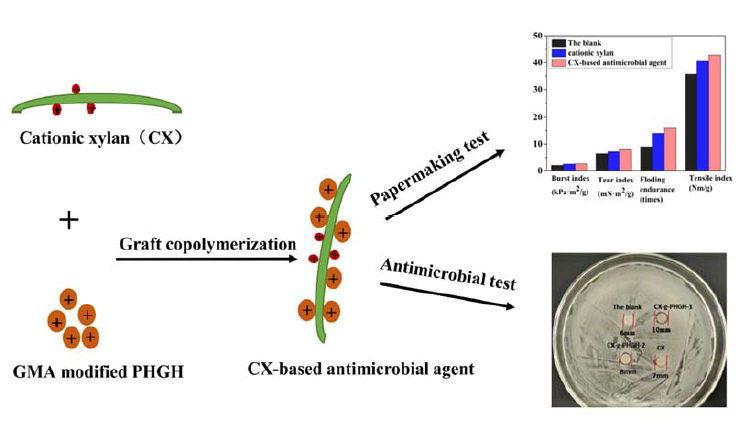
In this work, a xylan-based antimicrobial additive agent was prepared and aimed for uses in paper products against Escherichia coli bacteria. The derived Cationic-Xylan-grafted-PHGH (CX-g-PHGH) was successfully synthesized by graft copolymerization of cationic-xylan with guanidine polymer (PHGH) using ceric ammonium nitrate as initiator. The obtained CX-g-PHGH had maximum PHGH grafting ratio of 18.45% and efficiency of 58.45%, and showed good viscosity and thermal stability. Furthermore, the paper samples prepared in this work were reinforced obviously with the addition of CX-g-PHGH by improved mechanical properties. Compared to the reference paper without any of the xylan-derivatives, the index of tensile, tear, burst and folding endurance of the paper had increases up to 20.07%, 25.31%, 30.20% and 77.78%, respectively. Moreover, the prepared CX-g-PHGH paper exhibited an efficient antimicrobial activity against E. coli bacterial, by which a lot of applications based on the new xylan-derived additive agent obtained in this work could be found, especially in field of antimicrobial paper products against E. Coli bacteria from contaminated food.