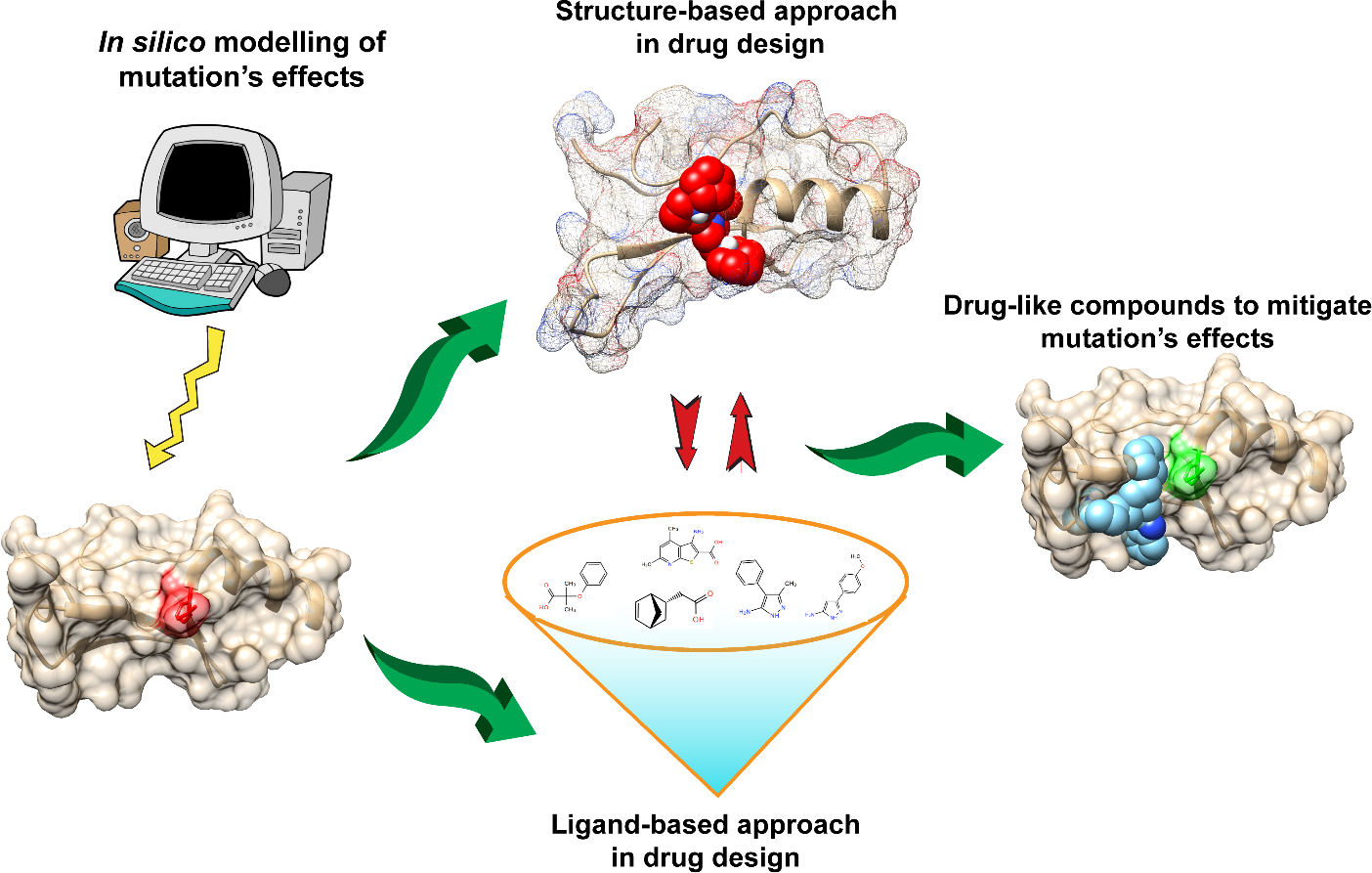
Structural information of biological macromolecules is crucial and necessary to deliver predictions about the effects of mutations—whether polymorphic or deleterious (i.e., disease causing), wherein, thermodynamic parameters, namely, folding and binding free energies potentially serve as effective biomarkers. It is to be emphasized that the effect of a mutation depends on various factors, including the type of protein (globular, membrane or intrinsically disordered protein) and the structural context to which it occurs. Furthermore, due to the intrinsic plasticity of proteins, even mutations involving radical change of the structural and physico-chemical properties of the amino acids (native vs. mutant) can still have minimal effects of protein thermodynamics. However, if a mutation causes significant perturbation of either folding or binding free energies, it is quite likely to be deleterious. Mitigating such effects is a promising alternative to the traditional approaches of designing inhibitors. This can be done by structure-based in silico screening of small molecules for which binding to the dysfunctional protein restores its wild type thermodynamics. In this review we emphasize on the effects of mutations on two important biophysical characteristics, stability and binding affinity and how structures can be used for structure-based drug design to mitigate the effects of disease-causing variants on the above biophysical characteristics.