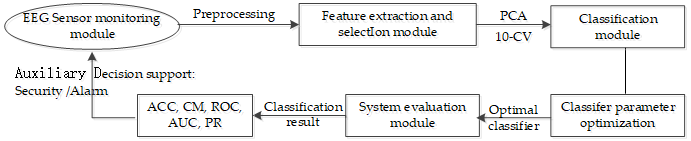
Automatic recognition methods for non-stationary EEG data collected from EEG sensors play an essential role in neurological detection. The integrative approaches proposed in this study consists of Symlet wavelet processing, a gradient boosting machine, and a grid search optimizer for a three-level classification scheme for normal subjects, intermittent epilepsy, and continuous epilepsy. Fourth-order Symlet wavelets were adopted to decompose the EEG data into five time-frequency sub-bands, whose statistical features were computed and used as classification features. The grid search optimizer was used to automatically find the optimal parameters for training the classifier. The classification accuracy of the gradient boosting machine was compared with that of a support vector machine and a random forest classifier constructed according to previous descriptions. Multiple-index were used to evaluate the Symlet wavelet transform-gradient boosting machine-grid search optimizer classification scheme, which provided better classification accuracy and detection effectiveness than has recently reported in other work on three-level classification of EEG data.