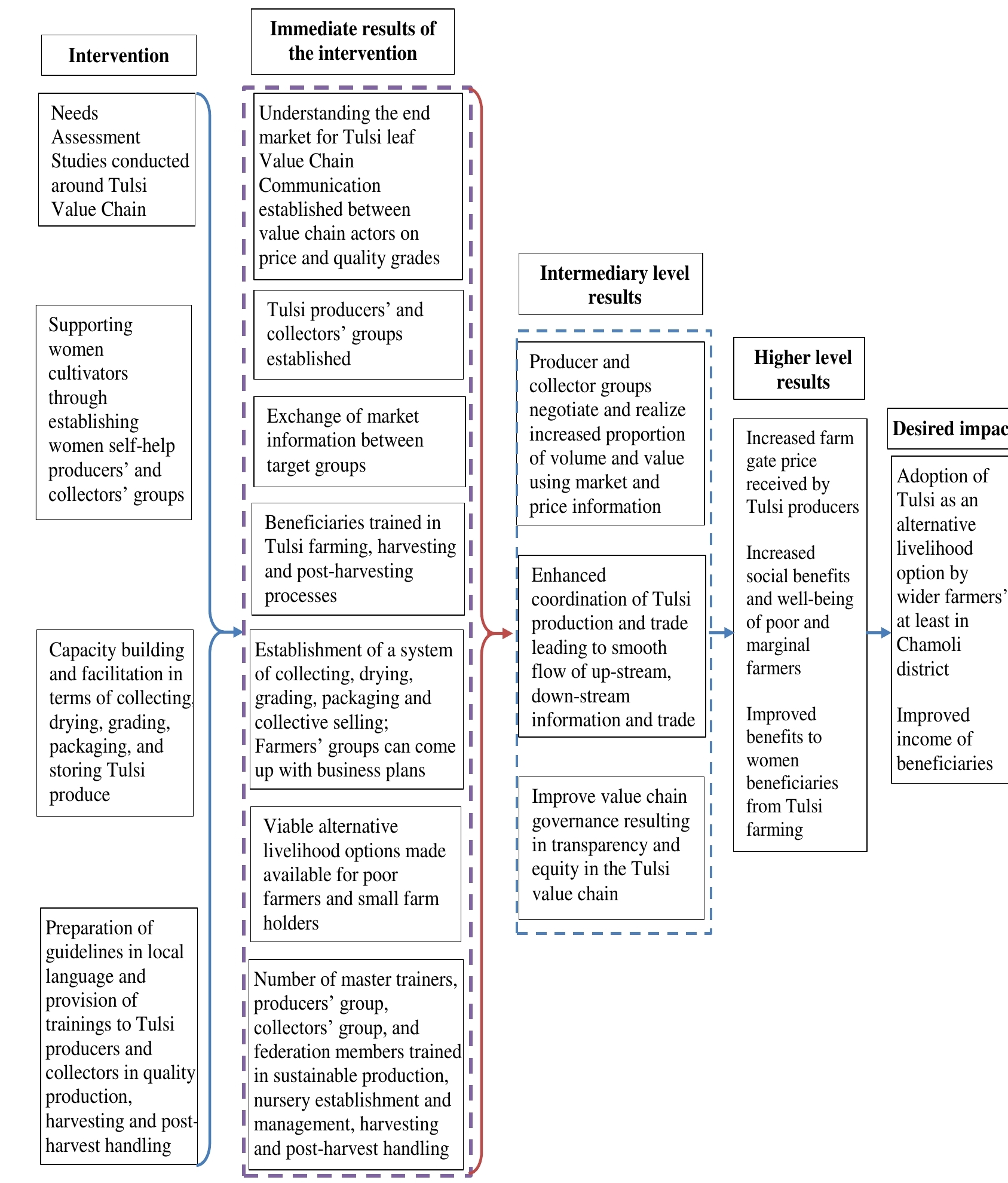
This study assesses the pursued impacts of Tulsi value chain development intervention on the livelihoods of rural poor in Uttarakhand state of India. Tulsi as an alternative livelihood, particularly for the rural poor, is less explored. With increased crop depredation of major cereal crops grown in the district by wild animals and pests, and decreasing availability of water agriculture, attempts were made to improve earnings from Tulsi as an alternative livelihood. Findings suggest that the average households’ gross profit from Tulsi farming increases by more than double within a span of two years. Total crop income of beneficiary farmers’ increases by 0.8 percent for every 1 percent increase in Tulsi income. Intervention helped enhance productivity of Tulsi, thereby enhancing earnings from Tulsi farming. Most importantly, intervention has shown a tremendous adoption rate. Towards the end of the intervention, the value chain work was out-scaled to another 19 villages in Chamoli district, thereby reaching out to more than 400 households.