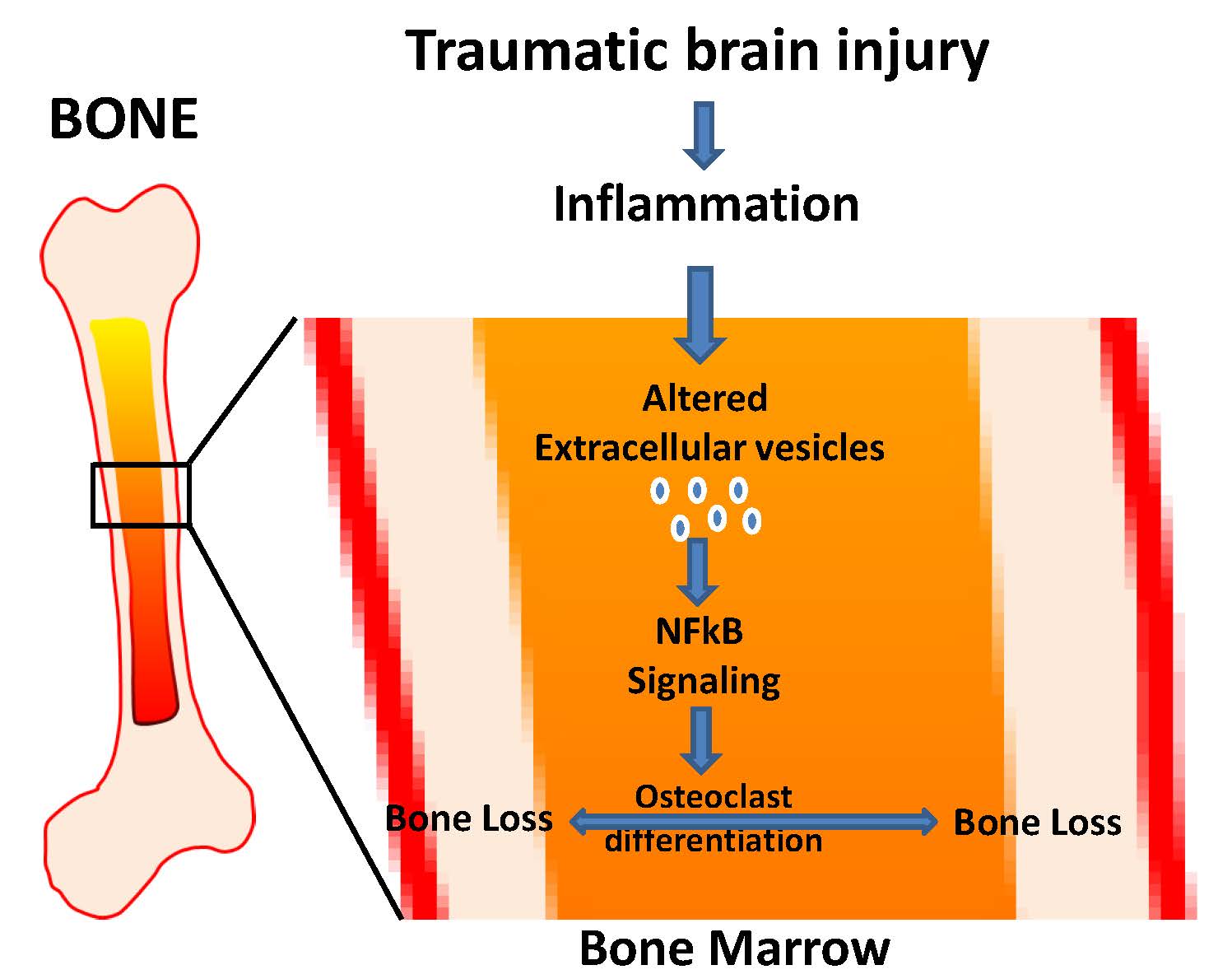
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a major source of worldwide morbidity and mortality. Patients suffering from TBI exhibit a higher susceptibility to bone loss and an increased rate of bone fractures; however, the underlying mechanisms remain poorly defined. Herein, we observed significantly lower bone quality and elevated levels of inflammation in bone and bone marrow niche after controlled cortical impact-induced TBI in in-vivo CD-1 mice. Further, we identified dysregulated NFB signaling, an established mediator of osteoclast differentiation and bone loss, within the bone marrow niche of TBI mice. Ex vivo studies revealed increased osteoclast differentiation in bone marrow-derived cells from TBI mice, as compared to sham injured mice. Finally, we found bone marrow derived extracellular vesicles (EVs) from TBI mice enhanced the colony forming ability and osteoclast differentiation efficacy of bone marrow cells and activated NFB signaling genes in bone marrow-derived cells. Taken together, we provide evidence that TBI-induced inflammatory stress on bone and the bone marrow niche may activate NFB leading to accelerated bone loss. Targeted inhibition of these signaling pathways may reverse TBI-induced bone loss and reduce fracture rates.