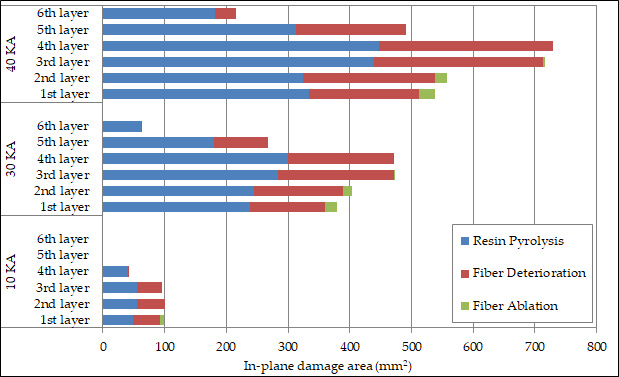
Lightning strike can cause a considerable damage in aircraft parts made from semiconducting materials such as Carbon Fiber Reinforced Plastics (CFRPs). Therefore, in recent years, the lightning strike phenomenon has attracted the interest of the academic community and the aircraft industry. Until now, the problem has been addressed mainly experimentally, while the reported numerical works are very limited. In the present work, a coupled electro-thermal FE model has been developed using the ANSYS commercial FE code to simulate the lightning strike damage in unidirectional CFRP laminates due to the Joule heat flux phenomenon. The model is based on the SOLID69 thermoelectric element and applies a non-linear, time-transient analysis. The main input to the model is the thermal-electrical properties of the composite material which vary with temperature. Using the model, a parametric study on the effect of mesh density and peak intensity on the thermal damage has been performed. Three electrical lightning strikes of low (10 kA), medium (30 kA) and high peak intensity (40 kA) have been applied according to the SAE ARP 5412 standard. The electro-thermal model has been validated against a numerical model from the literature. The numerical results reveal that the increase of peak intensity leads to the increase of the area and penetration depth of matrix thermal damage (pyrolysis) as well as to the increase of the area of fiber damage (deterioration and ablation). Through progressive damage modeling, the residual tensile strength of the CFRP plate after being subjected to lightning strike of different peak intensity has been predicted. Lightning strike initial damage has been simulated by translating the thermal field into degradation of elastic properties of the lamina. The results show an increase in the accumulated matrix damage and a decrease of tensile strength due to the initial lightning strike damage. For the maximum peak intensity of 40 kA, a decrease in tensile strength of 4.8% has been predicted